Prebiotics for the prevention of hyperbilirubinaemia in neonates
Información
- DOI:
- https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012731Copiar DOI
- Base de datos:
-
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- Versión publicada:
-
- 20 julio 2017see what's new
- Tipo:
-
- Intervention
- Etapa:
-
- Protocol
- Grupo Editorial Cochrane:
-
Grupo Cochrane de Neonatología
- Copyright:
-
- Copyright © 2017 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cifras del artículo
Altmetric:
Citado por:
Autores
Contributions of authors
Dr. Armanian initiated and designed the review.
Dr. Armanian, Dr. Feizi, Dr. Sadeghi, and Dr. Salehimehr reviewed the literature and wrote the protocol.
Dr. Molaeinezhad assisted in review of the literature and in writing of the protocol.
All stages of design and writing of the protocol were performed under the guidance of Dr. Jahanfar.
Sources of support
Internal sources
-
Division of Neonatology, Child Growth and Development Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Iran.
External sources
-
Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, USA.
Editorial support of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group has been funded with Federal funds from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, USA, under Contract No. HHSN275201600005C
Declarations of interest
None to declare.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the opportunities provided by our institution (Isfahan University of Medical Sciences) to write this protocol.
Version history
| Published | Title | Stage | Authors | Version |
| 2019 Aug 13 | Prebiotics for the prevention of hyperbilirubinaemia in neonates | Review | Amir Mohammad Armanian, Shayesteh Jahanfar, Awat Feizi, Nima Salehimehr, Mitra Molaeinezhad, Erfan Sadeghi | |
| 2017 Jul 20 | Prebiotics for the prevention of hyperbilirubinaemia in neonates | Protocol | Amir Mohammad Armanian, Shayesteh Jahanfar, Awat Feizi, Mitra Molaeinezhad, Nima Salehimehr, Erfan Sadeghi | |
PICO
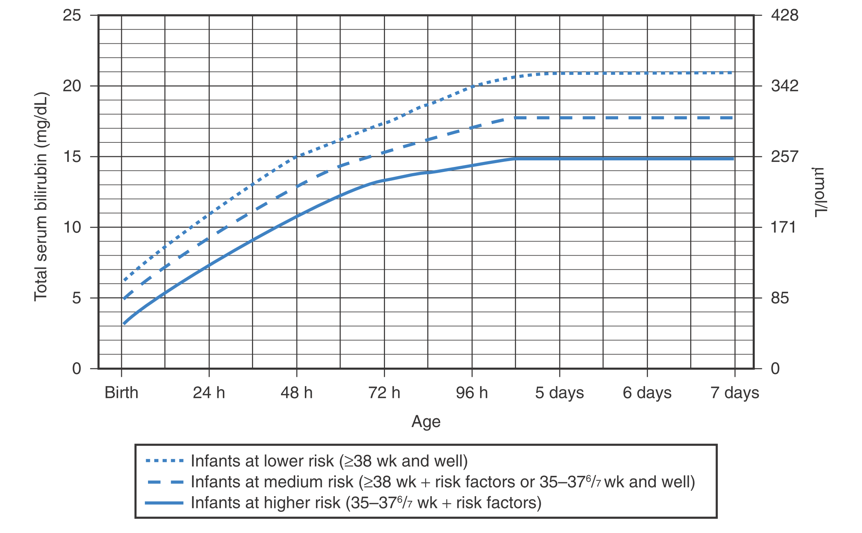
Guidelines for phototherapy in infants at ≥ 35 weeks' gestation.
(American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia. Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2004;114:297.)

Suggested guidelines for initiating phototherapy or exchange transfusion in premature infants.
(Maisels MJ, Watchko JF, Bhutani VK, et al. An approach to the management of hyperbilirubinemia in the preterm infant less than 35 weeks of gestation. Journal of Perinatology 2012;32:660‐664.)

