Diarios para la recuperación de enfermedades graves
Información
- DOI:
- https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010468.pub2Copiar DOI
- Base de datos:
-
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- Versión publicada:
-
- 09 diciembre 2014see what's new
- Tipo:
-
- Intervention
- Etapa:
-
- Review
- Grupo Editorial Cochrane:
-
Grupo Cochrane de Atención crítica y de emergencia
- Copyright:
-
- Copyright © 2019 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cifras del artículo
Altmetric:
Citado por:
Autores
Contributions of authors
Amanda J Ullman (AU), Leanne M Aitken (LA), Janice Rattray (JR), Justin Kenardy (JK) Robyne Le Brocque (RLB), Stephen MacGillivray (SM), Alastair M Hull (AH)
Conceiving the review: all authors
Co‐ordinating the review: AU
Undertaking manual searches: AU
Screening search results: AU and LA
Organizing retrieval of papers: AU
Screening retrieved papers against inclusion criteria: AU and LA
Appraising quality of papers: AU, LA and RLB
Abstracting data from papers: AU, LA and RLB
Writing to authors of papers for additional information: AU
Providing additional data about papers: AU
Obtaining and screening data on unpublished studies: AU and LA
Data management for the review: AU
Entering data into Review Manager (RevMan 5.2): AU
RevMan statistical data: AU and SM
Other statistical analysis not using RevMan: AU
Interpretation of data: all authors
Statistical inferences: SM
Writing the review: all authors
Securing funding for the review: N/A
Performing previous work that was the foundation of the present study: all authors
Guarantor for the review (one author): AU
Person responsible for reading and checking review before submission: AU
Sources of support
Internal sources
-
NH&MRC Centre of Research Excellence in Nursing Interventions, Griffith University, Australia.
-
Centre of Health Practice Innovation, Griffith University, Australia.
-
Princess Alexandra Hospital, Woolloongabba, Australia.
-
School of Nursing and Midwifery, University of Dundee, UK.
-
Department of Psychiatry, NHS Tayside, Perth, UK.
-
School of Medicine, University of Queensland, Australia.
-
Centre of National Research on Disability and Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Queensland, Australia.
-
Social Dimensions of Health Institute, University of Dundee, UK.
External sources
-
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
Amanda J Ullman: none known
Leanne M Aitken: none known
Janice Rattray: none known
Justin Kenardy: none known
Robyne Le Brocque: none known
Stephen MacGillivray: none known
Alastair M Hull: none known
Acknowledgements
We thank Jane Cracknell (Managing Editor, Cochrane Anaesthesia Review Group) and Karen Hovhannisyan (Trials Search Co‐ordinator, Cochrane Anaesthesia Review Group) for their assistance in the preparation of the protocol and review.
We would like to thank Bronagh Blackwood (content editor), Nathan Pace (statistical editor), Christina Jones, Megan Prictor, Louise Rose (peer reviewers), and Robert Wylie (consumer referee) for their help and editorial advice during the preparation of this systematic review
The National Health and Medical Research Council (NH&MRC) has provided funding for this review from its Centre of Research Excellence scheme, which funds one or more of the authors.
Version history
| Published | Title | Stage | Authors | Version |
| 2014 Dec 09 | Diaries for recovery from critical illness | Review | Amanda J Ullman, Leanne M Aitken, Janice Rattray, Justin Kenardy, Robyne Le Brocque, Stephen MacGillivray, Alastair M Hull | |
| 2013 Apr 30 | Diaries for recovery from critical illness | Protocol | Amanda J Ullman, Leanne M Aitken, Janice Rattray, Justin Kenardy, Robyne Le Brocque, Stephen MacGillivray, Alastair M Hull | |
Differences between protocol and review
Due to the small number of studies contained within the review, we were unable to undertake the meta‐analyses or provide a summary of findings table planned in the protocol (Ullman 2013).
Keywords
MeSH
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Keywords
- *Medical Records;
- Anxiety [psychology, rehabilitation];
- Caregivers [*psychology];
- Convalescence [psychology];
- Critical Care [*psychology];
- Critical Illness [*psychology, therapy];
- Depression [psychology, rehabilitation];
- Family [*psychology];
- Intensive Care Units;
- Outcome Assessment, Health Care;
- Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic;
- Stress Disorders, Post‐Traumatic [psychology];
- Stress, Psychological [psychology, *rehabilitation];
Medical Subject Headings Check Words
Humans;
PICO
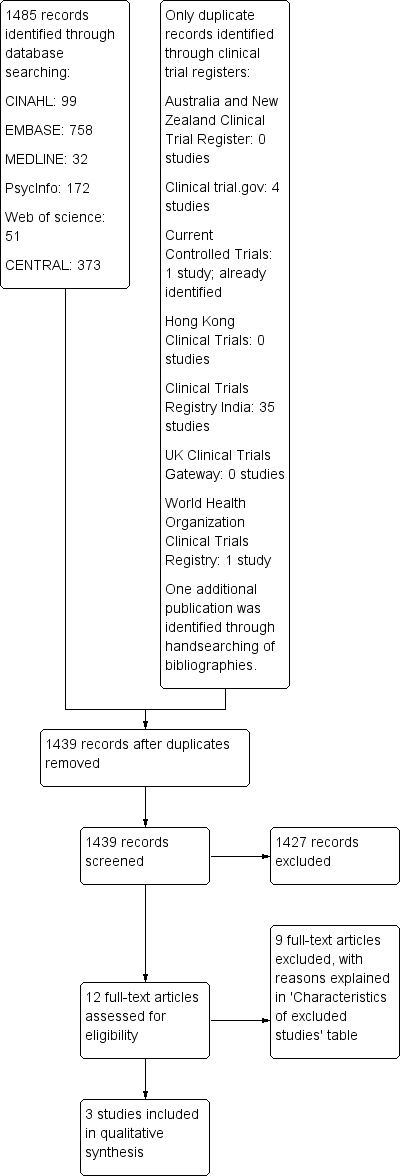
Study flow diagram.
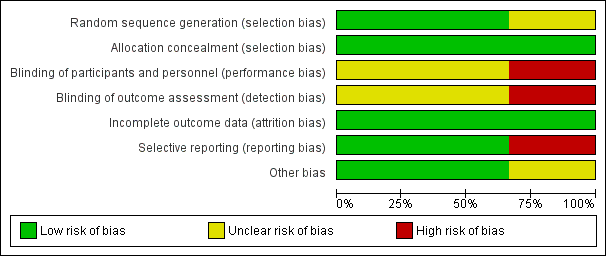
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
| Outcomes | Study | Incidence | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence: GRADE |
| Risk of anxiety in patients recovering from admission to ICU Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (Zigmond 1983) | Patient diary: 2 of 18 participants (11.1%) had the likely presence of clinically significant anxiety. No patient diary: 7 of 18 participants (38.9%) had the likely presence of clinically significant anxiety. | 36 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ very low 1,2 | |
| Risk of depression in patients recovering from admission to ICU Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (Zigmond 1983) | Patient diary: 3 of 18 participants (16.7%) had the likely presence of clinically significant depression. No patient diary: 8 of 18 participants (44.4%) had the likely presence of clinically significant depression. | 36 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ very low 1,2 | |
| Risk of memory recall of ICU in patients recovering from admission to ICU Intensive Care Unit Memory Tool (Jones 2000) | Patient diary: 85 of 162 participants (55%) had recall of delusional ICU memories. No patient diary: 81 of 160 participants (52%) had recall of delusional ICU memories. | 322 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low 2 | |
| Post‐traumatic stress symptomatology in patients recovering from admission to ICU Post‐Traumatic Stress Disorder‐Related Symptoms Screening Tool 14 (Twigg 2008) | Patient diary: The median post‐traumatic stress symptomatology in the patient diary group was 24 (SD 11.6)3 No patient diary: The median post‐traumatic stress symptomatology in the no patient diary group was 24 (SD 11.6) 3 | 322 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low 2 | |
| Post‐traumatic stress symptomatology in family members of patients recovering from admission to ICU Post‐Traumatic Stress Disorder‐Related Symptoms Screening Tool 14 (Twigg 2008) | Patient diary: The median post‐traumatic stress symptomatology in the patient diary group was 19 (range 14 to 28) 3 No patient diary: The median post‐traumatic stress symptomatology in the no diary group was 28 (range 14 to 38) 3 | 30 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low 2 | |
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||
| CI: Confidence interval | ||||
| 1 Results are from a single study at risk of bias regarding blinding of outcome assessment and participants. | ||||

