Effect(s) of assisted hatching on assisted conception (IVF & ICSI)
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. | |
| Participants | Women from Italy with repeated implantation failure and zona thickness >12 um undergoing IVF. Mean age control 34.8 (5.1), AH 34.6 (5.2). | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; partial zona breach; 48 hours egg retrieval to AH; 0 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Italy (first IVF treatment) with zona thickness >12 um undergoing IVF. Mean age control 34.6 (5.2), AH 34.4 (5.1). | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; partial zona breach; 48 hours egg retrieval to AH; 0 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Italy with repeated (2‐4 previous) implantation failure and zona thickness >12 um undergoing IVF. Mean age control 37.8 (1.5), AH 38.2 (1.3). | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH; 0 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. | |
| Participants | Women from Italy without previous IVF experience undergoing IVF. Mean age control 27.0, AH 27.5. | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH;? hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Italy with >6 previous IVF failures undergoing IVF. Mean age control 36.0, AH 37.5. | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH;? hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Brazil aged 37 years or less, undergoing ICSI for the first time (mean zona thickness control 17.1 um (sd 1.7), AH 16.6 um (sd 2.2). Mean age control 31.4 (3.6), AH 31.8 (3.6). | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; partial zona breach; 48 hours egg retrieval to AH; 0 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, miscarriage | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Taiwan with repeated IVF failure, undergoing IVF. (Mean basal FSH levels control 6.9 (2.9), AH 6.7 (2.4) IU/L). Mean age control 34.0 (3.9), AH 36.5 (5.2). | |
| Interventions | AH (mechanical; complete zona breach; 48 hours egg retrieval to AH; 4‐6 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment inadequate. | |
| Participants | Women from North America undergoing IVF, normal 3 day FSH levels (15IU/L or less). Mean age control 36.7 (3.7), AH 36.5 (3.3). | |
| Interventions | AH by acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 68‐72 hours egg retrieval to AH; 4‐8 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, live births, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study. Reply received, but no additional information was offered. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment inadequate. | |
| Participants | Women from North America undergoing IVF, high basal FSH ( >15IU/L). Mean age not stated. | |
| Interventions | AH by acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 68‐72 hours egg retrieval to AH; 4‐8 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study. Reply received, but no additional information was offered. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment inadequate. | |
| Participants | Women from Belgium undergoing IVF or ICSI. Mean age control 30.8 (3.9), AH 30.9 (4.3). | |
| Interventions | AH (mechanical; complete zona breach; 48 hours egg retrieval to AH; 0.2 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, live births, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study. A reply including much useful additional information was received. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from North America undergoing IVF either with no prior IVF (30 years or less, FSH<10IU/L, normal endometrium and sperm) or prior IVF (35 years or less, 6 embryos, 50% fertilisation, normal endometrium). Mean age control 30 (2.1), AH 30 (3.2). | |
| Interventions | AH by acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH; ? hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implatation, clinical pregnancy, live births | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study. A reply including much useful additional information was received. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Turkey with >5 day‐3 cleavage stage embryos (FSH at day‐3 control 6.1 (3.0), AH 5.5 (1.4) IU/L, mean duration of infertility 6.7 years) undergoing ICSI. Mean age control 29.1 (3.6), AH 30.5 (5.2). | |
| Interventions | AH enzymatic (chemical; complete zona breach; 120‐144 hours egg retrieval to AH; 0.5‐1 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Turkey undergoing IVF. Mean age not stated. | |
| Interventions | AH (mechanical; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH;? hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from North America aged less than 40 years undergoing IVF. Mean age not stated. | |
| Interventions | AH (mechanical; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH;? hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from North America aged at least 36 years (mean basal FSH control 7.6 IU/l (sd 2.0), AH 7.9 IU/l (sd 2.5)), undergoing IVF (some with ICSI), half had been previously treated with IVF. Mean age control 38.5 (1.8), AH 38.3 (2.0). | |
| Interventions | AH by acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 55 hours egg retrieval to AH;? hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy, multiple pregnancy, live births | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study. A reply including much useful additional information was received. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment inadequate. | |
| Participants | Women from Egypt less than 40 years old and undergoing their first ICSI treatment. Mean age control 33.2 (1.4), AH 32.1 (2.5). | |
| Interventions | AH with acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 72 hours egg retrieval to AH; 2 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy, live births, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment inadequate. | |
| Participants | Women from Egypt with poor prognosis (at least 40 years old and/or with 2 previous IVF or ICSI failures) undergoing ICSI treatment. Mean age control 36.3 (5.2), AH 37.3 (5.6). | |
| Interventions | AH with acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 72 hours egg retrieval to AH; 2 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy, live births, miscarriage, multiple pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Italy with cryopreserved embryos undergoing IVF and ICSI. Mean age control 31.4 (3.7), AH 32.0 (4.0). | |
| Interventions | AH (laser; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retreival to AH;? hours AH to transfer) with concomitant removal of damaged blastomeres versus no AH and no damaged blastomere removal | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy | |
| Notes | No attempt to contact author about this study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised, method stated. | |
| Participants | Women from France undergoing IVF with high basal FSH (>8iU/L). Mean ages not stated. | |
| Interventions | AH with acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 72 hours egg retrieval to AH; <1 hour AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study. Useful additional information received. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Australia undergoing IVF with or without ICSI, with cryopreserved or fresh embryos. Mean age not stated. | |
| Interventions | AH with acide tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH; 2 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from Israel with repeated implantation failure (>3 attempts) undergoing IVF. Mean age not stated. | |
| Interventions | AH (mechanical; complete zona breach; ? hours egg retrieval to AH; 1.5 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | clinical pregnancy, miscarriage | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from North America undergoing IVF. (Mean basal FSH control 9.0 (5.3), AH 8.8 (3.7) IU/L). Mean age control 34.2 (4.1), AH 34.1 (4.8). | |
| Interventions | AH with acid tyrodes (chemical; partial zona breach; 72 hours egg retrieval to AH; 1‐3 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomisation stated, but method unclear or incorrect. Allocation concealment unclear. | |
| Participants | Women from North America undergoing ICSI. Mean age control 33.5 (4.3), AH 35.3 (4.2). | |
| Interventions | AH with acid tyrodes (chemical; complete zona breach; 72 hours egg retrieval to AH; 4 hours AH to transfer) versus no AH | |
| Outcomes | implantation, clinical pregnancy | |
| Notes | Attempted to contact author about this study, no reply received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
AH = assisted hatching
IVF = in‐vitro fertilisation, ICSI = intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Mean age given in years (standard deviation).
note: only arms where all or no embryos transfered were treated with AH were accepted for data extraction
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Not randomised. No appropriate controls. | |
| Not randomised. | |
| Not randomised. No embryo transfer occurred, so no review outcomes could be measured. | |
| Not randomised. Benefits of AH confounded by concurrent assessment of 2 different culture media. | |
| Not randomised. Benefits of assisted hatching confounded by concurrent assessment of two different culture media. | |
| Comparison of two types of assisted hatching, no 'no assisted hatching' control group was used. More than one cycle per woman. | |
| Not randomised. | |
| No appropriate outcome measure. | |
| Benefits of assisted hatching confounded by concurrent assessment of two different culture media. | |
| More than one cycle per woman. | |
| Not randomised. | |
| Not randomised. The control group were from the period 1990‐1993, while the assisted hatching group were from 1994‐1996 (historical controls). | |
| Not randomised. Benefits of AH confounded by concurrent assessment of 2 different culture media. | |
| Not randomised. | |
| More than one cycle per woman. | |
| More than one cycle per woman. | |
| More than one cycle per woman. | |
| Not randomised. No concurrent controls. | |
| Not randomised. No concurrent controls. | |
| Not randomised. No concurrent controls. | |
| No appropriate outcome measure. | |
| More than one cycle per woman. Included women had treatment during one or more cycles, and it was not possible to determine events per woman (only events per cycle) | |
| Not randomised. No concurrent controls. | |
| It was not clear how many women were included in the study, or for how many cycles (only cycles were mentioned), and a mixture of participants and donated eggs were used for the study. | |
| Not randomised. Control and intervention groups recruited at different times. | |
| Not randomised. Benefits of assisted hatching confounded by concurrent assessment of two different culture media. | |
| Not randomised. Some of the women in the assisted hatching group were randomised, but most were allocated assisted hatching routinely, with no control option. | |
| Not randomised. | |
| Study definition of clinical pregnancy was 'viewing of the gestational sac using ultrasound tomography', as distinct from the review definition 'foetal heartbeat on ultrasound scan', so outcome data could not be used. | |
| Numbers in tables do not add up correctly and the text and tables are contradictory on the age groups used in the prospective part of the study. |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
| Trial name or title | |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Group I, women who initiate their first transfer cycle of frozen‐thawed embryos. |
| Interventions | Assisted hatching with a diode laser (use of immunosuppressive and antibiotic treatment will also be tested). |
| Outcomes | Clinical pregnancy. |
| Starting date | Underway in 1998. |
| Contact information | M. Germond, Reproductive Medicine Unit, Dept. of Obstetrics‐Gynaecology, CHUV, CH‐1011 Lausanne, Switzerland. |
| Notes |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 per woman randomised, following this set of cycles Show forest plot | 23 | 523 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.82, 1.78] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 live births, Outcome 1 per woman randomised, following this set of cycles. | ||||
| 2 per clinical pregnancy, following from this set of cycles Show forest plot | 22 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 live births, Outcome 2 per clinical pregnancy, following from this set of cycles. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 rate per woman randomised Show forest plot | 19 | 2175 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.63 [1.27, 2.09] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 clinical pregnancy, Outcome 1 rate per woman randomised. | ||||
| 2 Subgrouping according to first or repeat IVF attempt Show forest plot | 8 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 clinical pregnancy, Outcome 2 Subgrouping according to first or repeat IVF attempt. | ||||
| 2.1 First attempt at IVF or ICSI | 4 | 586 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.77, 2.53] |
| 2.2 Repeat attempt at IVF or ICSI | 4 | 666 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.33 [1.63, 3.34] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 per clinical pregnancy Show forest plot | 11 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 miscarriages, Outcome 1 per clinical pregnancy. | ||||

Comparison 1 live births, Outcome 1 per woman randomised, following this set of cycles.
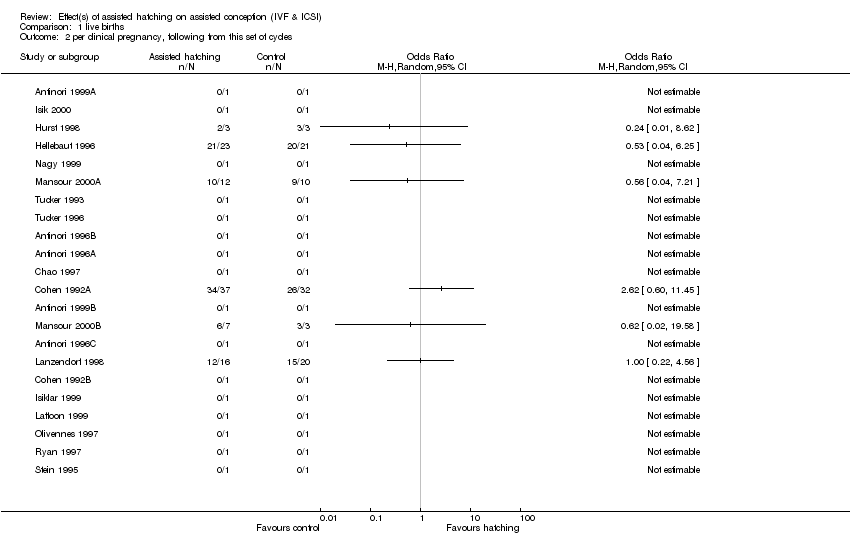
Comparison 1 live births, Outcome 2 per clinical pregnancy, following from this set of cycles.

Comparison 2 clinical pregnancy, Outcome 1 rate per woman randomised.

Comparison 2 clinical pregnancy, Outcome 2 Subgrouping according to first or repeat IVF attempt.

Comparison 3 miscarriages, Outcome 1 per clinical pregnancy.
| Study | n, mean age (sd) AH | n, mean age (sd) con | WMD (95% CI) |
| Antinori 1996A | 104, 34.60 (5.20) | 104, 34.80 (5.10) | ‐0.20 (‐1.60 to 1.20) |
| Antinori 1996B | 104, 34.40 (5.10) | 121, 34.60 (5.20) | ‐0.20 (‐1.55 to 1.15) |
| Antinori 1996C | 72, 38.2 (1.32) | 98, 37.80 (1.48) | 0.40 (‐0.02 to 0.82) |
| Baruffi 2000 | 51, 31.80 (3.60) | 52, 31.40 (3.60) | 0.40 (‐0.99 to 1.79) |
| Chao 1997 | 33, 36.50 (5.20) | 31, 34.00 (3.90) | 2.50 (0.26 TO 4.74) |
| Cohen 1992A | 39, 36.50 (3.30) | 68, 36.70 (3.70) | ‐0.20 (‐1.37 to 0.97) |
| Hellebaut 1996 | 60, 30.90 (4.30) | 60, 30.80 (3.90) | 0.10 (‐1.37 to 1.57) |
| Hurst 1998 | 13, 30.00 (0.90) | 7, 30.00 (0.80) | 0.00 (‐0.77 to 0.77) |
| Isik 2000 | 24, 30.50 (5.20) | 22, 29.10 (3.60) | 1.40 (‐1.17 to 3.97) |
| Lanzendorf 1998 | 41, 38.30 (0.31) | 48, 38.50 (0.26) | ‐0.20 (‐0.32 to ‐0.08) |
| Mansour 2000A | 27, 32.10 (2.50) | 25, 33.20 (1.40) | ‐1.10 (‐2.19 to ‐0.01) |
| Mansour 2000B | 30, 37.30 (5.60) | 41, 36.30 (5.20) | 1.00 (‐1.56 to 3.56) |
| Nagy 1999 | 20, 32.00 (4.00) | 20, 31.40 (3.70) | 0.60 (‐1.79 to 2.99) |
| Tucker 1993 | 110, 34.10 (4.80) | 108, 34.20 (4.10) | ‐0.10 (‐1.28 to 1.08) |
| Tucker 1996 | 50, 35.30 (4.20) | 50, 33.50 (4.30) | 1.80 (0.13 to 3.47) |
| Outcome | Analysis type | Description | No. of studies | OR (random effects) | 95% CI | heterogeneity p |
| Live births, per woman randomised | Overall meta‐analysis | 6 | 1.21 | 1.82 to 1.78 | 0.43 | |
| Live births, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Allocation concealment | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Live births, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Method of randomisation | 4 | 1.13 | 0.72 to 1.76 | 0.37 |
| Live births, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Unbalanced or unreported age | 4 | 1.31 | 0.71 to 2.43 | 0.23 |
| Clinical pregnancy, per woman randomised | Overall meta‐analysis | 19 | 1.63 | 1.27 to 2.09 | 0.05 | |
| Clinical pregnancy, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Allocation concealment | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clinical pregnancy, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Method of randomisation | 7 | 1.34 | 0.79 to 2.26 | 0.03 |
| Clinical pregnancy, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Unbalanced or unreported age | 10 | 1.81 | 1.23 to 2.66 | 0.02 |
| Clinical pregnancy, per woman randomised | Sub‐grouping | First IVF attempt | 4 | 1.40 | 0.77 to 2.53 | 0.05 |
| Clinical pregnancy, per woman randomised | Sub‐grouping | Repeat IVF attempt | 4 | 2.33 | 1.63 to 3.34 | 0.51 |
| Implantations, per woman randomised | Overall meta‐analysis | 15 | 1.97 (incorrect, several implantations may be counted per woman) | 1.28 to 3.03 | <0.01 | |
| Implantations, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Allocation concealment | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Implantations, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Method of randomisation | 9 | 2.10 (incorrect, several implantations may be counted per woman) | 1.12 to 3.92 | <0.01 |
| Implantations, per woman randomised | Sensitivity analysis | Unbalanced or unreported age | 10 | 2.11 (incorrect, several implantations may be counted per woman) | 1.35 to 3.28 | <0.01 |
| Implantations, per embryo transferred | Overall meta‐analysis | 15 | 1.52 (incorrect, several implantations may be counted per woman) | 1.16 to 2.00 (incorrect, real 95% CI would be wider)!! | <0.01 | |
| Miscarriage, per clinical pregnancy | Overall meta‐analysis | 11 | 0.70 | 0.41 to 1.19 (may be too wide as clinical pregnancies fewer than women randomised) | 0.91 | |
| Live births, per clinical pregnancy | Overall meta‐analysis | 6 | 1.07 | 0.46 to 2.52 (may be too wide as clinical pregnancies fewer than women randomised) | 0.74 | |
| Mean age in AH and control groups | Overall meta‐analysis | 15 | WMD = 0.09 years | ‐0.24 to 0.43 | 0.05 | |
| analysis | explanatory variable | slope coefficient | 95% CI | p‐value for slope | no. of trials |
| overall meta‐regression | mean maternal age in intervention group | 0.053 | ‐0.0004 to 0.1054 | 0.052 | 19 (some of these are subgroups from within trials) |
| sensitivity analysis removing age‐unbalanced studies | mean maternal age in intervention group | 0.097 | ‐0.0025 to 0.1970 | 0.056 | 10 (some of these are subgroups from within trials) |
| sensitivity analysis removing studies where randomisation method unclear | mean maternal age in intervention group | 0.068 | ‐0.0168 to 0.1520 | 0.116 | 7 (some of these are subgroups from within trials) |
| Study | implantations, AH | women rand., AH | embryos trans., AH | imlant., control | women rand., cont. | embryos trans., cont |
| Antinori 1996A | 46 | 96 | 376 | 28 | 104 | 381 |
| Antinori 1996B | 47 | 111 | 397 | 29 | 121 | 411 |
| Antinori 1996C | 35 | 72 | 218 | 21 | 98 | 407 |
| Baruffi 2000 | 25 | 51 | 141 | 31 | 52 | 149 |
| Chao 1997 | 17 | 33 | 155 | 5 | 31 | 1134 |
| Cohen 1992A | 67 | 69 | 239 | 49 | 68 | 229 |
| Cohen 1992B | 10 | 15 | 38 | 4 | 15 | 41 |
| Hellebaut 1996 | 30 | 60 | 168 | 28 | 60 | 162 |
| Hurst 1998 | 5 | 13 | 52 | 3 | 7 | 28 |
| Isik 2000 | 17 | 24 | 71 | 12 | 22 | 63 |
| Isiklar 1999 | 32 | 83 | 13 | 78 | ||
| Lanzendorf 1998 | 20 | 41 | 183 | 24 | 48 | 219 |
| Nagy 1999 | 11 | 20 | 65 | 2 | 20 | 52 |
| Tucker 1993 | 73 | 110 | 333 | 59 | 108 | 312 |
| Tucker 1996 | 16 | 50 | 189 | 25 | 50 | 184 |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 per woman randomised, following this set of cycles Show forest plot | 23 | 523 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.82, 1.78] |
| 2 per clinical pregnancy, following from this set of cycles Show forest plot | 22 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 rate per woman randomised Show forest plot | 19 | 2175 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.63 [1.27, 2.09] |
| 2 Subgrouping according to first or repeat IVF attempt Show forest plot | 8 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 First attempt at IVF or ICSI | 4 | 586 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.77, 2.53] |
| 2.2 Repeat attempt at IVF or ICSI | 4 | 666 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.33 [1.63, 3.34] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 per clinical pregnancy Show forest plot | 11 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |

