Análogos de insulina de acción rápida subcutáneos para la cetoacidosis diabética
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategies
| Cochrane Library |
| 1. [mh "Diabetic Ketoacidosis"] |
| MEDLINE (Ovid SP) |
| 1. Diabetic Ketoacidosis/ |
| PubMed |
| #1 (hyperglycemic emergenc*[tw] OR hyperglycaemic emergenc*[tw] OR diabetic emergenc*[tw] OR (diabet*[tw] AND (ketoac*[tw] OR acidos*[tw] OR coma[tw])) OR DKA[tw]) #2 (glulisine[tw] OR apidra[tw] OR humulin[tw] OR novolin[tw] OR lispro[tw] OR aspart[tw] OR novolog[tw] OR novorapid[tw] OR (insulin[tw] AND analog*[tw]) OR acting insulin*[tw]) #3 #1 AND #2 #4 #3 NOT medline[sb] NOT pmcbook |
| EMBASE (Ovid SP) |
| 1. diabetic ketoacidosis/ |
| LILACS (IAHx) |
| (MH: "Diabetic Ketoacidosis" OR MH: "Diabetic Coma" OR (diabet$ AND (keto$ OR acidos$ OR "coma"))) AND (MH: "Insulin Lispro" OR MH: "Insulin Aspart" OR MH: "Insulin, Short‐Acting" OR ("glulisine" OR "apidra") OR ("humulin" OR "novolin") OR ("lispro" OR "aspart") OR ("novolog" OR "novorapid") OR (insulin$ AND analogue$) OR (acting AND insulin$)) |
| CINAHL (Ebsco) |
| S1. MH "Diabetic Ketoacidosis" |
| ICTRP Search Portal |
| Standard search: |
| ClinicalTrials.gov |
| Advanced Search |
Appendix 2. Description of interventions
| Intervention(s) | Adequatea intervention (Yes/No) | Comparator(s) | Adequatea comparator (Yes/No) | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | Subcutaneous insulin lispro every hour: initial injection of 0.3 units/kg followed by 0.1 unit/kg/h until blood glucose levels reached 250 mg/dL; the insulin dose was then reduced to 0.05 units/kg/h, and the intravenous fluids were changed to dextrose 5% in 0.45% normal saline to keep blood glucose at a level of about 200 mg/dL until resolution of DKA | Yes | Intravenous regular insulin: initial bolus of 0.1 units/kg, followed by a continuous infusion of 0.1 units/kg/h until blood glucose levels decreased to approx. 250 mg/dL; at this time, intravenous fluids were changed to dextrose‐containing solutions, and the insulin infusion rate was decreased to 0.05 units/kg/h until resolution of DKA | Yes |
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: initial injection of 0.3 units/kg, followed by 0.1 units/kg/h until blood glucose reached 250 mg/dL; the insulin dose was then reduced to 0.05 units/kg/h, and the intravenous fluids were changed to dextrose 5%, 0.45 saline to maintain blood glucose at 200 mg/dL until resolution of DKA | Yes | Intravenous regular insulin: initial bolus of 0.1 units/kg, followed by a continuous infusion of regular insulin calculated to deliver 0.1 units/kg/h until blood glucose levels were 250 mg/dL; the insulin dose was then reduced to 0.05 units/kg/h, and the intravenous fluids were changed to dextrose 5%, 0.45 saline to maintain blood glucose at 200 mg/dL until resolution of DKA | Yes |
| I2: initial dose of 0.3 units/kg followed by 0.2 units/kg 1 h later and every 2 h until blood glucose reached 250 mg/dL; the insulin dose was then reduced to 0.1 units/kg every 2 h, and the intravenous fluids were changed to dextrose 5%, 0.45 saline to keep blood glucose at 200 mg/dL until resolution of DKA | Yes | |||
| Della Manna 2005 | 0.15 units/kg of a insulin lispro was administered subcutaneously every 2 h; when capillary blood glucose levels neared 249 mg/dL, 0.15 units/kg were administered every 4 h for the next 24 h After approx. 12 h of intensive insulin administration, intermediate human insulin was initiated at a dosage of 0.4 unit/kg every 12 h | Yes | Regular insulin was infused with a syringe pump at a rate of 0.1 unit/kg/h from an independent intravenous line through a second catheter inserted into a peripheral vein. This infusion was continued until capillary blood glucose levels decreased to ≤ 249 mg/dL; thereafter, 0.15 units/kg regular insulin were given subcutaneously 30 min before stopping the intravenous line and every 4 h for the next 24 h After approx. 12 h of intensive insulin administration, intermediate human insulin was initiated at a dosage of 0.4 unit/kg every 12 h | Yes |
| Ersöz 2006 | Following a bolus injection of 0.15 units/kg i.v. regular insulin, group L received half of this dose as hourly s.c. insulin lispro. Insulin dose was titrated according to serum glucose and pH levels; if serum glucose did not fall by 50‐70 mg/dL in the first hour, insulin dose was planned to be doubled hourly until glucose fell by 50‐70 mg/dL | Yes | Following a bolus injection of 0.15 units/kg i.v. regular insulin, group R was treated conventionally with standard i.v. regular insulin infusion. Insulin dose was titrated according to serum glucose and pH levels; if serum glucose did not fall by 50‐70 mg/dL in the first hour, insulin dose was planned to be doubled hourly until glucose fell by 50‐70 mg/dL | Yes |
| Karoli 2011 | Initial bolus of 0.3 units/kg followed by 0.2 units/kg 1 h later and then 0.2 units/kg every 2 h until blood glucose reached 250 mg/dL; the insulin dose was then reduced to 0.1 units/kg/h to keep blood glucose at approx. 200 mg/dL | Yes | Initial bolus of regular insulin 0.1 unit/kg i.v. followed by continuous infusion of regular insulin calculated to deliver 0.1 unit/kg/h until blood glucose levels decreased to approx. 250 mg/dL; the insulin infusion rate was then decreased to 0.05 units/kg/h until resolution of DKA, and intravenous fluids were changed to dextrose‐containing solutions (5% dextrose) to keep blood glucose level at approx. 200 mg/dL | Yes |
| aThe term 'adequate' refers to sufficient use of the intervention/comparator with regard to dose, dose escalation, dosing scheme, provision for contraindications, and other features necessary to establish a fair contrast between intervention and comparator. DKA: diabetic ketoacidosis; I: intervention | ||||
Appendix 3. Baseline characteristics (I)
| Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Duration of intervention | Description of participants | Trial period | Country | Setting | Ethnic groups | Duration of diabetes [mean/range years (SD), or as reported] | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | I: s.c. insulin lispro | Resolution of DKA: mean 10 h (mean hospital stay: 4 d) | Adults with "uncomplicated" DKA (not stated if type 1 or 2 diabetes) | ‐ | USA | Regional medical centre DKA established in the ED Regular medicine ward, intermediate care unit (step‐down unit) | African American: 75 | 6.7 (5) |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | Resolution of DKA: mean 11 h (mean hospital stay: 4 d) | Regional medical centre DKA established in the ED ICU | African American: 80 | 6.9 (4) | ||||
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: s.c. insulin aspart, every hour | Resolution of DKA: mean 10 h (mean hospital stay: 3.4 d) | Adults with "uncomplicated" DKA (not stated if type 1 or 2 diabetes) | ‐ | USA | Regional medical centre DKA established in the ED General medical ward or step‐down unit | ‐ | ‐ |
| I2: s.c. insulin aspart, every 2 h | Resolution of DKA: mean 10.7 h (mean hospital stay: 3.9 d) | |||||||
| C: i.v. regular insulin | Resolution of DKA: mean 11 h (mean hospital stay: 4.5 d) | Regional medical centre ICU | ||||||
| Della Manna 2005 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | Resolution of metabolic acidosis/ketosis: "in the next 6 h interval" (later than after i.v. regular insulin) Resolution of DKA: 12 h after capillary glucose < 250 mg/dL (mean hospital stay 2‐3 d) | Children and adolescents with DKA | 2001 to 2003 | Brazil | University children's hospital, 57 DKA episodes treated in ED, 3 DKA episodes treated in ICU | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | Resolution of metabolic acidosis/ketosis: 6 h after capillary glucose ≤ 250 mg/dL Resolution of DKA: 12 h after capillary glucose < 250 mg/dL (mean hospital stay 2‐3 d) | |||||||
| Ersöz 2006 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | Resolution of DKA: no data | Adults with mild or moderate DKA (not stated if type 1 or 2 diabetes) | ‐ | Turkey | ‐ | ‐ | 3.9 (4.5) |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 4.5 (4.3) | |||||||
| Karoli 2011 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | Resolution of DKA: mean 12 h (mean hospital stay 6 d) | Adults with mild to moderate DKA (> 50% of participants had type 2 diabetes) | 2009 to 2010 | India | Teaching hospital, ED | ‐ | 6.4 (5) |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | Resolution of DKA: mean 11 h (mean hospital stay 6.6 d) | Teaching hospital, ICU | 6.8 (4) | |||||
| ‐ denotes not reported C: comparator; d: days; DKA: diabetic ketoacidosis; ED: emergency department; h: hours; I: intervention; ICU: intensive care unit; i.v.: intravenous; s.c.: subcutaneous; SD: standard deviation | ||||||||
Appendix 4. Baseline characteristics (II)
| Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Sex | Glucose levels at admission | Age | HbA1c | BMI | Comedications / Cointerventions | Comorbidities | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 40 | 674 (154) | 37 (12) | ‐ | 26 (7) | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 35 | 611 (264) | 39 (14) | ‐ | 27 (9) | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: s.c. insulin aspart, every hour | 27 | 787 (378) | 36 (8) | 11.5 (1.6) | 27 (6) | ‐ | 27% had an associated comorbid condition (leg abscess, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, pancreatitis) |
| I2: s.c. insulin aspart, every 2 h | 33 | 758 (373) | 38 (12) | 11.4 (2) | 29 (7) | ‐ | 27% had an associated medical illness (cellulitis, urinary tract infection, olanzapine overdose, failure to take oral antidiabetic agent) | |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 33 | 717 (239) | 40 (13) | 11.7 (2) | 27 (7) | ‐ | 27% had an associated medical illness (pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infection, and tooth abscess) | |
| Della Manna 2005 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 68 | 434 (142) | 11 (4) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 76 | 434 (146) | 12 (3) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Ersöz 2006 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 50 | 512 (138) | 39 (20) | 13.9 (2.3) | ‐ | ‐ | Retinopathy/neuropathy/nephropathy/cardiovascular disease/cerebrovascular disease: 10%/10%/0%/10%/10% |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 60 | 556 (43) | 49 (18) | 11.6 (1.7) | ‐ | ‐ | Retinopathy/neuropathy/nephropathy/cardiovascular disease/cerebrovascular disease: 20%/20%/0%/30%/0% | |
| Karoli 2011 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 44 | 650 (113) | 34 (13) | ‐ | 25 (3) | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 36 | 679 (125) | 35 (11) | ‐ | 24 (2) | ‐ | ‐ | |
| ‐ denotes not reported BMI: body mass index; C: comparator; HbA1c: glycosylated haemoglobin A1c; I: intervention; i.v.: intravenous; s.c.: subcutaneous; SD: standard deviation | ||||||||
Appendix 5. Matrix of study endpoints (publications and trial documents)
| Endpoints quoted in trial document(s) | Study results posted in trial register, publications specified in trial register | Endpoints quoted in publication(s)b,c | Endpoints quoted in abstract of publication(s)b,c | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | N/T | Primary outcome measure(s): response to medical therapy: the time required for resolution of hyperglycaemia and ketoacidosis, and the rate of hypoglycaemia during insulin infusion | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |
| Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |||
| Other outcome measure(s): levels of blood glucose, electrolytes, phosphorus, venous pH, beta‐hydroxybutyrate, free fatty acids, insulin; medical care data (site of admission and treatment in the hospital, amount of fluid and insulin administration, length of hospitalisation); deaths | Other outcome measure(s): duration of treatment until correction of hyperglycaemia and resolution of ketoacidosis, deaths, length of hospital stay, amount of insulin until resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis, rate of hypoglycaemia, hospitalisation charges | |||
| Umpierrez 2004b | N/T | Primary outcome measure(s): time to resolve ketoacidosis | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |
| Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |||
| Other outcome measure(s): levels of glucose, electrolytes, phosphorus, venous pH, beta‐hydroxybutyrate, free fatty acids, insulin; response to medical | Other outcome measure(s): duration of treatment until resolution of hyperglycaemia and ketoacidosis, total length of hospitalisation, amount of insulin administration until resolution of hyperglycaemia and ketoacidosis, number of hypoglycaemic events | |||
| Della Manna 2005 | N/T | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |
| Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |||
| Other outcome measure(s): blood glucose, blood gas, beta‐hydroxybutyrate, electrolytes, phosphate, magnesium, urea nitrogen, creatinine, urine ketones; resolution of metabolic acidosis and ketosis, DKA recovery; (near) deaths, cerebral oedema; hypoglycaemic episodes | Other outcome measure(s): blood glucose, blood gas, beta‐hydroxybutyrate, electrolytes, metabolic acidosis and ketosis, DKA recovery | |||
| Ersöz 2006 | N/T | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |
| Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |||
| Other outcome measure(s): serum glucose, pH, beta‐hydroxybutyrate, electrolytes, urine ketone levels and urinary output, lipids; resolution of ketoacidosis, time elapsed until normalisation of the monitored parameters, total amount of insulin delivered until resolution of DKA; mortality, hypoglycaemic events | Other outcome measure(s): time needed for normalisation of serum glucose, beta‐hydroxybutyrate, blood pH and urine ketone levels; mortality, serious side effects | |||
| Karoli 2011 | N/T | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Primary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |
| Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | Secondary outcome measure(s): ‐ | |||
| Other outcome measure(s): blood glucose levels, resolution of DKA, response to therapy was assessed by time and amount of insulin required for resolution of hyperglycaemia and ketoacidosis, number of hypoglycaemic events; duration of hospital stay; deaths | Other outcome measure(s): response to therapy (duration of treatment and amount of insulin administered until resolution of hyperglycaemia and ketoacidosis, total length of hospital stay, and number of hypoglycaemic events); mortality | |||
| ‐ denotes not reported aTrial document(s) refers to all available information from published design papers and sources other than regular publications (e.g. FDA/EMA documents, manufacturers' websites, trial registers) DKA: diabetic ketoacidosis; EMA: European Medicines Agency; FDA: US Food and Drug Administration; N/T: no trial document available | ||||
Appendix 6. Examination of outcome reporting bias according to ORBIT classification
| Outcome | High risk of bias | High risk of bias | High risk of bias | High risk of bias | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Umpierrez 2004b | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Della Manna 2005 | Time to resolution of DKA | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Ersöz 2006 | Time to resolution of DKA | Yes | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Karoli 2011 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| aClear that outcome was measured and analysed; trial report states that outcome was analysed but reports only that result was not significant. DKA: diabetic ketoacidosis; N/A: not applicable; ORBIT: Outcome Reporting Bias In Trials | |||||
Appendix 7. Definition of endpoint measurement (I)
| Resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis | All‐cause mortality | Morbidity | Patient satisfaction | HbA1c | Socioeconomic effects | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | Serum bicarbonate level ≥ 18 mEq/L and venous pH > 7.30 | N/D | N/I | N/I | N/I | Hospital stay in days and cost as data on hospital charges |
| Umpierrez 2004b | Serum bicarbonate level ≥ 18 mmol/L and venous pH > 7.30 | N/D | N/I | N/I | N/I | Length of hospital stay in days |
| Della Manna 2005 | Mentally alert and able to eat, serum bicarbonate > 15 mmol/L, venous pH > 7.30, anion gap < 16 mmol/L | N/D | Cerebral oedema | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| Ersöz 2006 | Serum glucose < 200 mg/dL , serum bicarbonate level > 18 mmol/L, venous pH > 7.30, capillary hydroxybutyrate level < 0.6 mmol/L, and negative urine ketone | N/D | N/I | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| Karoli 2011 | Serum bicarbonate level > 18 mmol/L and arterial pH > 7.30 | N/D | Venous thrombosis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, hyperchloraemic acidosis | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| HbA1c: glycosylated haemoglobin A1c; N/D: not defined; N/I: not investigated | ||||||
Appendix 8. Definition of endpoint measurement (II)
| All hypoglycaemic events | Severe hypoglycaemia | Nocturnal hypoglycaemia | Severe/serious | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | ≤ 60 mg/dL | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| Umpierrez 2004b | ≤ 60 mg/dL | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| Della Manna 2005 | < 60 mg/dL, described as "mild" | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| Ersöz 2006 | N/D | N/I | N/I | N/D |
| Karoli 2011 | < 60 mg/dL, described as "mild" | N/I | N/I | N/I |
| N/D: not defined; N/I: not investigated | ||||
Appendix 9. Adverse events (I)
| Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Participants included in analysis | Deaths | Deaths | Participants with at least one adverse event | Participants with at least one adverse event | Participants with at least one severe/serious adverse event | Participants with at least one severe/serious adverse event | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 20 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 20 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: s.c. insulin aspart, every hour | 15 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| I2: s.c. insulin aspart, every 2 h | 15 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 15 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Della Manna 2005 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 25 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 21 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Ersöz 2006 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 10 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | 0 | 0 |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 10 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | 0 | 0 | |
| Karoli 2011 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 25 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 25 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| ‐ denotes not reported C: comparator; I: intervention; i.v.: intravenous; s.c.: subcutaneous | ||||||||
Appendix 10. Adverse events (II)
| Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Participants included in analysis | Participants discontinuing trial due to an adverse event | Participants discontinuing trial due to an adverse event | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 20 | 0 | 0 | |
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: s.c. insulin aspart, every hour | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| I2: s.c. insulin aspart, every 2 h | 15 | 0 | 0 | |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 15 | 0 | 0 | |
| Della Manna 2005 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 21 | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Ersöz 2006 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| Karoli 2011 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 25 | 0 | 0 | |
| ‐ denotes not reported C: comparator; I: intervention; i.v.: intravenous; s.c.: subcutaneous | ||||
Appendix 11. Adverse events (III)
| Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Participants included in analysis | Participants with hypoglycaemic episodes | Participants with hypoglycaemic episodes | Participants with nocturnal hypoglycaemic episodes | Participants with nocturnal hypoglycaemic episodes | Participants with severe/serious hypoglycaemic episodes | Participants with severe/serious hypoglycaemic episodes | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 20 | 1 | 5 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 20 | 1 | 5 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: s.c. insulin aspart, every hour | 15 | 1 | 6.6 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| I2: s.c. insulin aspart, every 2 h | 15 | 1 | 6.6 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 15 | 1 | 6.6 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Della Manna 2005 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 25 | 4 | 16 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 21 | 6 | 29 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Ersöz 2006 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 10 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 10 | 0 | 0 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Karoli 2011 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | 25 | 1 | 4 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 25 | 2 | 8 | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| ‐ denotes not reported C: comparator; I: intervention; i.v.: intravenous; s.c.: subcutaneous | ||||||||
Appendix 12. Checklist to aid consistency and reproducibility of GRADE assessments
| 'Summary of findings' tables outcome measures (for both insulin lispro and insulin aspart) | All‐cause mortality | Hypoglycaemic episodes | Morbidity | Adverse events other than hypoglycaemic episodes | Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis | Patient satisfaction | Socioeconomic effects (length of hospital stay) | |
| Trial limitations | Was random sequence generation used (i.e. no potential for selection bias)? | Unclear | Yes/unclear | N/A | N/I | Unclear | N/I | Yes/unclear |
| Was allocation concealment used (i.e. no potential for selection bias)? | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | ||||
| Was there blinding of participants and personnel (i.e. no potential for performance bias)? | No | No (↓) | No (↓) | No (↓) | ||||
| Was there blinding of outcome assessment (i.e. no potential for detection bias)? | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | No (↓) | ||||
| Was an objective outcome used? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Were more than 80% of participants enrolled in trials included in the analysis (i.e. no potential reporting bias)?e | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Were data reported consistently for the outcome of interest (i.e. no potential selective reporting)? | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | ||||
| No other biases reported (i.e. no potential for other bias)? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Did the trials end as scheduled (i.e. not stopped early)? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Inconsistencyb | Point estimates did not vary widely? | N/A | Yesf | Yesf | Yesf | |||
| To what extent did confidence intervals overlap (substantial: all confidence intervals overlap at least 1 of the included studies' point estimate; | N/A | Substantialf | Substantialf | Substantialf | ||||
| Was the direction of effect consistent? | Yes | Yesf | No (↓)f | Yesf | ||||
| What was the magnitude of statistical heterogeneity (as measured by I²): low (I² < 40%), moderate (I² 40% ‐ 60%), high (I² > 60%)? | N/A | Lowf | High (↓)f | Lowf | ||||
| Was the test for heterogeneity statistically significant (P < 0.1)? | N/A | Not statistically significantf | Not statistically significantf | Not statistically significantf | ||||
| Indirectnessa | Were the populations in the included studies applicable to the decision context? | Highly applicable | Highly applicable | Highly applicable | Highly applicable | |||
| Were the interventions in the included studies applicable to the decision context? | Highly applicable | Highly applicable | Highly applicable | Highly applicable | ||||
| Was the included outcome not a surrogate outcome? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Was the outcome time frame sufficient? | Sufficient | Sufficient | Sufficient | Sufficient | ||||
| Were the conclusions based on direct comparisons? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Imprecisionc | Was the confidence interval for the pooled estimate not consistent with benefit and harm? | N/A | No (↓)f | No (↓)f | No (↓)f | |||
| What is the magnitude of the median sample size (high: 300 participants, intermediate: 100‐300 participants, low: < 100 participants)?e | Intermediateg | Intermediateg | Low (↓) | Low (↓) | ||||
| What was the magnitude of the number of included studies (large: > 10 studies, moderate: 5‐10 studies, small: < 5 studies)?e | Small (↓) | Small (↓) | Small (↓) | Small (↓) | ||||
| Was the outcome a common event (e.g. occurs more than 1/100)? | N/A | Yes | N/A | N/A | ||||
| Publication biasd | Was a comprehensive search conducted? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Was grey literature searched? | No (↓) | No (↓) | No (↓) | No (↓) | ||||
| Were no restrictions applied to study selection on the basis of language? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| There was no industry influence on studies included in the review? | No (↓) | No (↓) | No (↓) | No (↓) | ||||
| There was no evidence of funnel plot asymmetry? | N/A | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | ||||
| There was no discrepancy in findings between published and unpublished trials? | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | ||||
| aQuestions on risk of bias are answered in relation to the majority of the aggregated evidence in the meta‐analysis rather than to individual trials cWhen judging the width of the confidence interval, it is recommended to use a clinical decision threshold to assess whether the imprecision is clinically meaningful fN/A for insulin aspart gLow for insulin aspart (↓): key item for possible downgrading the quality of the evidence (GRADE) as shown in the footnotes of the 'Summary of findings' table(s) | ||||||||
Appendix 13. Survey of authors providing information on included trials
| Date trial author contacted | Date trial author replied | Trial author asked for additional information | Trial author provided data | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| Umpierrez 2004b | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| Della Manna 2005 | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| Ersöz 2006 | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| Karoli 2011 | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| El Ebrashy 2010 | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| Baldwin 2009 | 2 April 2015 | No reply | N/A | N/A |
| N/A: not applicable | ||||
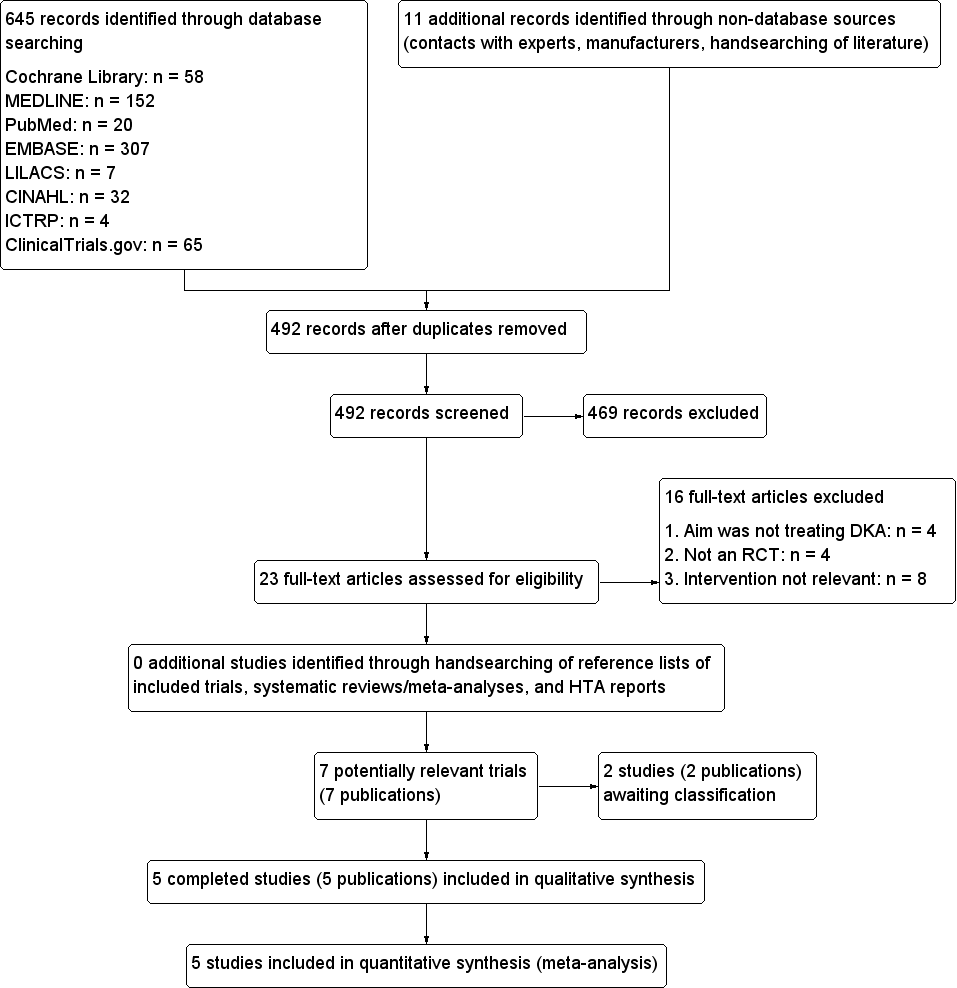
Study flow diagram.

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included trials (blank cells indicate that the particular outcome was not measured in some trials).

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included trial (blank cells indicate that the trial did not measure that particular outcome).
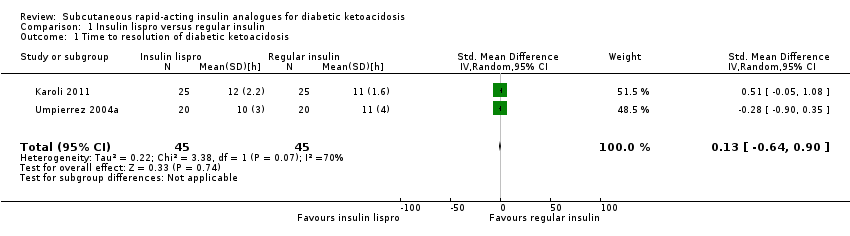
Comparison 1 Insulin lispro versus regular insulin, Outcome 1 Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis.

Comparison 1 Insulin lispro versus regular insulin, Outcome 2 All‐cause mortality.

Comparison 1 Insulin lispro versus regular insulin, Outcome 3 Hypoglycaemic episodes.
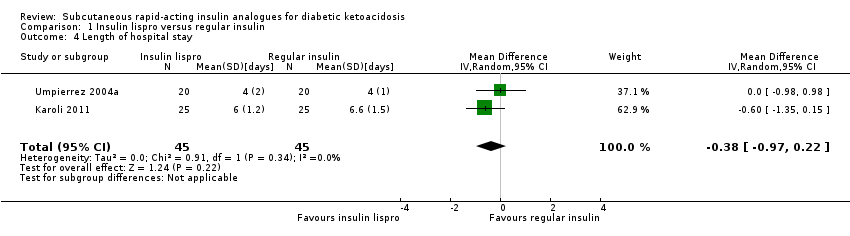
Comparison 1 Insulin lispro versus regular insulin, Outcome 4 Length of hospital stay.

Comparison 2 Insulin aspart versus regular insulin, Outcome 1 Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis.
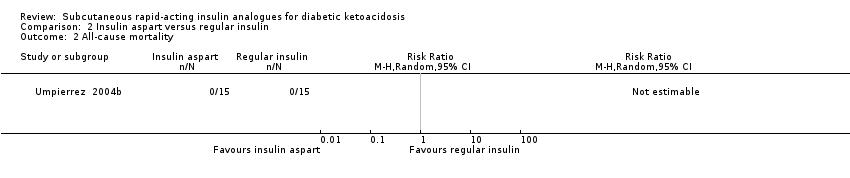
Comparison 2 Insulin aspart versus regular insulin, Outcome 2 All‐cause mortality.

Comparison 2 Insulin aspart versus regular insulin, Outcome 3 Hypoglycaemic episodes.

Comparison 2 Insulin aspart versus regular insulin, Outcome 4 Length of hospital stay.
| Subcutaneous insulin lispro versus intravenous regular insulin for diabetic ketoacidosis | ||||||
| Patient: participants with diabetic ketoacidosis | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Intravenous regular insulin | Subcutaneous insulin lispro | |||||
| All‐cause mortality (N) Mean hospital stay: 2‐7 days | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | 156 (4) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | No deaths reported |
| Hypoglycaemic episodes (N) Mean hospital stay: 2‐7 days | 118 per 1000 | 70 per 1000 | RR 0.59 | 156 (4) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Comparable risk ratios for adults (4 trials) and children (1 trial) |
| Morbidity (N) Mean hospital stay: 2‐7 days | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | 96 (2) | See comment | No cases of cerebral oedema, venous thrombosis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, hyperchloraemic acidosis |
| Adverse events other than hypoglycaemic episodes | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | See comment | See comment | Not investigated |
| Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis (h) Mean hospital stay: 2‐4 days | The mean time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis across the intravenous regular insulin groups was 11 h | The mean time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis in the subcutaneous insulin lispro groups was 0.2 h higher (1.7 h lower to 2.1 h higher) | ‐ | 90 (2) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Metabolic acidosis and ketosis took longer to resolve in the subcutaneous insulin lispro group in 1 trial (60 children); no exact data published |
| Patient satisfaction | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | See comment | See comment | Not investigated |
| Socioeconomic effects: length of hospital stay (days) Mean hospital stay: 4‐7 days | The mean length of hospital stay in the intravenous regular insulin groups ranged between 4 and 6.6 days | The mean length of hospital stay in the subcutaneous insulin lispro groups was 0.4 days shorter (1 day shorter to 0.2 days longer) | ‐ | 90 (2) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | US setting: treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis in a non–intensive care setting (step‐down unit or general medicine ward) was associated with a 39% lower hospitalisation charge than was treatment with intravenous regular insulin in the intensive care unit (USD 8801 (SD USD 5549) vs USD 14,429 (SD USD 5243); the average hospitalisation charges per day were USD 3981 (SD USD 1067) for participants treated in an intensive care unit compared with USD 2682 (SD USD 636) for those treated in a non–intensive care setting |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| *Assumed risk was derived from the event rates in the comparator groups. | ||||||
| Subcutaneous insulin aspart versus intravenous regular insulin for diabetic ketoacidosis | ||||||
| Patient: participants with diabetic ketoacidosis | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Intravenous regular insulin | Subcutaneous insulin aspart | |||||
| All‐cause mortality (N) Mean hospital stay: 3‐5 days | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | 45 (1) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | No deaths reported |
| Hypoglycaemic episodes (N) Mean hospital stay: 3‐5 days | 67 per 1000 | 67 per 1000 | RR 1.00 | 30 (1) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| Morbidity | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | See comment | See comment | Not investigated |
| Adverse events other than hypoglycaemic episodes | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | See comment | See comment | Not investigated |
| Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis (h) Mean hospital stay: 3‐5 days | The mean time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis across the intravenous regular insulin groups was 11 h | The mean time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis in the subcutaneous insulin aspart group was 1 h lower (3.2 h lower to 1.2 h higher) | ‐ | 30 (1) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| Patient satisfaction | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | See comment | See comment | Not investigated |
| Socioeconomic effects: length of hospital stay (days) Mean hospital stay: 3‐5 days | The mean length of hospital stay in the intravenous regular insulin group was 4.5 days | The mean length of hospital stay in the subcutaneous insulin aspart group was 1.1 days shorter (3.3 days shorter to 1.1 days longer) | ‐ | 30 (1) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| *Assumed risk was derived from the event rates in the comparator groups | ||||||
| Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Sample sizea | Screened/eligible | Randomised | Analysed | Finishing trial | Randomised finishing trial | Follow‐up timeb | |
| Umpierrez 2004a | I: s.c. insulin lispro | Arbitrary estimation of a difference between groups of ≥ 5 hours to determine ketoacidosis as being clinically important; a sample size of 20 participants was needed in each group to provide a power of 0.93, given an alpha level of 0.05, a SD of 4, and a 1:1 inclusion ratio | ‐ | 20 | 20 | 20 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 4 days |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 20 | 20 | 20 | 100 | ||||
| total: | 40 | 40 | 40 | 100 | ||||
| Umpierrez 2004b | I1: s.c. insulin aspart, every hour | Arbitrary estimation of a difference between groups of ≥ 4 hours to determine ketoacidosis as being clinically significant. A sample size of 15 participants was needed in each group to provide a power of 0.81, given an alpha error of 0.05 and a SD of 3 | ‐ | 15 | 15 | 15 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 3.4 days |
| I2: s.c. insulin aspart, every 2 h | 15 | 15 | 15 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 3.9 days | |||
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 15 | 15 | 15 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 4.5 days | |||
| total: | 45 | 45 | 45 | 100 | ||||
| Della Manna 2005 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | ‐ | ‐ | 25 | 25 | 25 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 2‐3 days |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 21 | 21 | 21 | 100 | ||||
| total: | 46 | 46 | 46 | 100 | ||||
| Ersöz 2006 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | ‐ | ‐ | 10 | 10 | 10 | 100 | ‐ |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 10 | 10 | 10 | 100 | ||||
| total: | 20 | 20 | 20 | 100 | ||||
| Karoli 2011 | I: s.c. insulin lispro | ‐ | ‐ | 25 | 25 | 25 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 6 days |
| C: i.v. regular insulin | 25 | 25 | 25 | 100 | Mean hospital stay: 6.6 days | |||
| total: | 50 | 50 | 50 | 100 | ||||
| Grand total | All interventions | 110 | 110 | |||||
| All comparators | 91 | 91 | ||||||
| All interventions and comparators | 201 | 201 | ||||||
| aAccording to power calculation in study publication or report ‐ denotes not reported C: comparator; I: intervention; i.v.: intravenous; s.c.: subcutaneous; SD: standard deviation | ||||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis Show forest plot | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.13 [‐0.64, 0.90] |
| 2 All‐cause mortality Show forest plot | 4 | 156 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Hypoglycaemic episodes Show forest plot | 4 | 156 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.59 [0.23, 1.52] |
| 3.1 Adults | 3 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.67 [0.11, 3.94] |
| 3.2 Children | 1 | 46 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.18, 1.72] |
| 4 Length of hospital stay Show forest plot | 2 | 90 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.38 [‐0.97, 0.22] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Time to resolution of diabetic ketoacidosis Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2 All‐cause mortality Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3 Hypoglycaemic episodes Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4 Length of hospital stay Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |

