Long‐acting beta2‐agonist in addition to tiotropium versus either tiotropium or long‐acting beta2‐agonist alone for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Design: A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group trial from October 2003 to January 2006. The trial included 27 Canadian medical centres; 20 centres were academic hospital‐based pulmonary clinics, 5 were community‐based pulmonary clinics, and 2 were community‐based primary care clinics. | |
| Participants | Population: 304 adults, with a clinical history of moderate or severe COPD as defined by ATS and GOLD guidelines, were randomised to tiotropium + salmeterol (148) and tiotropium (156) Baseline Characteristics: Mean age 68 years. COPD severity moderate to severe with mean FEV1 predicted of 38%. 57% men. Inclusion Criteria: At least 1 exacerbation of COPD that required treatment with systemic steroids or antibiotics within the 12 months before randomisation; age older than 35 years; a history of 10 pack‐years or more of cigarette smoking; documented chronic airflow obstruction, with an FEV1/FVC ratio less than 0.70 and a post‐bronchodilator FEV1 less than 65% of the predicted value. Exclusion Criteria: History of physician‐diagnosed asthma before 40 years of age; history of physician‐diagnosed chronic congestive heart failure with known persistent severe left ventricular dysfunction; those receiving oral prednisone; those with a known hypersensitivity or intolerance to tiotropium, salmeterol, or fluticasone‐salmeterol; history of severe glaucoma or severe urinary tract obstruction, previous lung transplantation or lung volume reduction surgery, or diffuse bilateral bronchiectasis; and those who were pregnant or were breastfeeding. | |
| Interventions | 1. Tiotropium + salmeterol: tiotropium 18 μg once daily using a Handihaler plus salmeterol 25 μg/puff, 2 puffs twice daily using a pressurized metered‐dose inhaler using a spacer device 2. Tiotropium + placebo: tiotropium, 18 μg once daily, plus placebo inhaler, 2 puffs twice daily | |
| Outcomes | Primary: Proportion of patients with one or more exacerbation of COPD. Secondary: Mean number of COPD exacerbations per patient‐year; the total number of exacerbations that resulted in urgent visits to a health care provider or emergency department; the number of hospitalizations for COPD; the total number of hospitalizations for all causes; changes in health‐related quality of life, dyspnoea, lung function. | |
| Notes | Co‐medication: All study patients were provided with inhaled albuterol and were instructed to use it when necessary to relieve symptoms. At baseline, tiotropium + placebo group 52% on combined inhalers (ICS+LABA), 25% on ICS inhaler; tiotropium + salmeterol group 44% on combined inhalers (ICS+LABA) and 35% on ICS inhalers. Any treatment with inhaled corticosteroids, long‐acting 2‐agonists, and anticholinergics that the patient may have been using before entry was discontinued on entry into the study. Therapy with other respiratory medications, such as oxygen, antileukotrienes, and methylxanthines, was continued in all patient groups. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation was done through central allocation of a randomisation schedule that was prepared from a computer‐generated random listing of the 3 treatment allocations, blocked in variable blocks of 9 or 12 and stratified by site. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Neither research staff nor patients were aware of the treatment assignment before or after randomisation. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (LABA+TIO versus TIO) (performance bias) | Low risk | Neither research staff nor patients were aware of the treatment assignment before or after randomisation. The metered‐dose inhalers containing placebo, salmeterol, and fluticasone–salmeterol were identical in taste and appearance, and they were enclosed in identical tamper‐proof blinding devices. The medication canisters within the blinding devices were stripped of any identifying labelling. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | The assembled data from the visit for the suspected exacerbation were presented to a blinded adjudication committee for review, and the committee confirmed whether the encounter met the study definition of COPD exacerbation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | The number of people who stopped drug therapy was high in both groups. 74 patients (47%) withdrew from the tiotropium + placebo group and 64 patients (43%) on LABA + tiotropium group. However, the number of people who did not complete the trial was lower (30 patients (19%) on tiotropium + placebo and 20 patients (14%) on LABA + tiotropium). The incomplete data were however addressed by sensitivity analyses of the data comprising alternative assumptions for patients who prematurely withdrew from treatment. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Results for all listed primary and secondary outcomes were reported. |
| Methods | Design: A multi‐centre, multi‐national, randomised, double‐blind, parallel‐group study from March 2009 to March 2010. The trial included 186 study centres in 14 countries: Argentina (10), Australia (6), Colombia (5), Denmark (5), Germany (25), Greece (4), Guatemala (5), Mexico (5), Peru (6), Philippines (2), South Africa (6), Spain (13), Turkey (13), and USA (81). | |
| Participants | Population: 1134 patients with a clinical history of moderate or severe COPD as defined by GOLD guidelines, were randomised to tiotropium + indacaterol (570) and tiotropium (564). Baseline Characteristics: Mean age 64 years, 67% male, mean FEV1 1.3 L, mean FEV1 predicted 49%, 47 pack‐years smoking history. Inclusion Criteria: Men and women aged ≥40 years with moderate‐to‐severe COPD, with a smoking history ≥10 pack‐years and post‐bronchodilator FEV1 ≤ 65% and ≥ 30% predicted and FEV1/FVC < 70%. Exclusion Criteria: Patients who have received systematic corticosteroids and/or antibiotics and/or was hospitalised for a COPD exacerbation in the 6 weeks prior to screening or during the run‐in period or had a respiratory tract infection within 6 weeks prior to screening. Patients with concomitant pulmonary disease, a history of asthma, diabetes Type I or uncontrolled diabetes Type II, lung cancer or a history of lung cancer, a history of certain cardiovascular comorbid conditions. | |
| Interventions | 1. Indacaterol 150 μg through single‐dose dry powder inhaler (SDDPI), once daily + tiotropium 18 μg through SDDPI Handihaler, once daily 2. Placebo to indacaterol + tiotropium 18 μg through SDDPI Handihaler, once daily | |
| Outcomes | Primary: Standardised area under the curve (AUC) FEV1 between 5min and 8h post‐dose after 12 weeks of treatment. Secondary: Trough FEV1 on day 1 and after 12 weeks treatment, FEV1 AUC (5min‐8h) day 1, FEV1 AUC (5min‐4h) on day 1 and after 12 weeks of treatment, resting inspiratory capacity (IC), use of albuterol as rescue medication, safety (adverse events and serious adverse events). | |
| Notes | Co‐medication: Albuterol was available for rescue use. Patients (53%) receiving inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) at baseline continued treatment (or the ICS component alone if taken as a fixed combination with a bronchodilator) at equivalent dose and regimen throughout the study. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | A patient randomisation list was produced by the IVRS provider using a validated system that automates the random assignment of patient numbers to randomisation numbers. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The randomisation numbers were linked to the different treatment arms, which in turn were linked to medication numbers. A separate medication randomisation list was produced by or under the responsibility of Novartis Drug Supply Management using a validated system that automates the random assignment of medication numbers to medication packs containing each of the study drugs. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (LABA+TIO versus TIO) (performance bias) | Low risk | Patients, investigator staff, persons performing the assessments, data analysts and the Novartis trial team were all blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Persons performing the assessments were blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | The withdrawal rates were low and even (tiotropium + indacaterol 6.8%, tiotropium 6.2%). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Results for all listed primary and secondary outcomes were reported. |
| Methods | Design: A multi‐centre, multi‐national, randomised, double‐blind, parallel‐group study from April 2009 to February 2010. The trial included 182 study centres in 11 countries: Argentina (9), Canada (16), Colombia (3), Czech Republic (9), Hungary (4), India (9), Netherlands (6), Philippines (3), Slovakia (10), Spain (11), and USA (102). | |
| Participants | Population: 1142 patients with a clinical history of moderate or severe COPD as defined by GOLD guidelines, were randomised to tiotropium + indacaterol (572) and tiotropium (570). Baseline Characteristics: Mean age 63 years, 65% male, mean FEV1 1.3 L, mean FEV1 predicted 49%, 46 pack‐years smoking history. Inclusion Criteria: Men and women aged ≥40 years with moderate‐to‐severe COPD, with a smoking history ≥10 pack‐years and post‐bronchodilator FEV1 ≤ 65% and ≥ 30% predicted and FEV1/FVC < 70%. Exclusion Criteria: Patients who have received systematic corticosteroids and/or antibiotics and/or was hospitalised for a COPD exacerbation in the 6 weeks prior to screening or during the run‐in period or had a respiratory tract infection within 6 weeks prior to screening. Patients with concomitant pulmonary disease, a history of asthma, diabetes Type I or uncontrolled diabetes Type II, lung cancer or a history of lung cancer, a history of certain cardiovascular comorbid conditions. | |
| Interventions | 1. Indacaterol 150 μg through single‐dose dry powder inhaler (SDDPI), once daily + tiotropium 18 μg through SDDPI Handihaler, once daily 2. Placebo to indacaterol + tiotropium 18 μg through SDDPI Handihaler, once daily | |
| Outcomes | Primary: Standardised area under the curve (AUC) FEV1 between 5min and 8h post‐dose after 12 weeks of treatment. Secondary: Trough FEV1 on day 1 and after 12 weeks treatment, FEV1 AUC (5 min‐8 h) day 1, FEV1 AUC (5 min‐4 h) on day 1 and after 12 weeks of treatment, resting inspiratory capacity (IC), use of albuterol as rescue medication, safety (adverse events and serious adverse events). | |
| Notes | Co‐medication: Albuterol was available for rescue use. Patients (53%) receiving inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) at baseline continued treatment (or the ICS component alone if taken as a fixed combination with a bronchodilator) at equivalent dose and regimen throughout the study. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | A patient randomisation list was produced by the IVRS provider using a validated system that automates the random assignment of patient numbers to randomisation numbers. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The randomisation numbers were linked to the different treatment arms, which in turn were linked to medication numbers. A separate medication randomisation list was produced by or under the responsibility of Novartis Drug Supply Management using a validated system that automates the random assignment of medication numbers to medication packs containing each of the study drugs. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (LABA+TIO versus TIO) (performance bias) | Low risk | Patients, investigator staff, persons performing the assessments, data analysts and the Novartis trial team were all blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Persons performing the assessments were blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | The withdrawal rates were low and even (tiotropium + indacaterol 5.1%, tiotropium 6.5%). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Results for all listed primary and secondary outcomes were reported. |
| Methods | Design: A randomised, double‐blind, active‐control, parallel group trial. The trial included 35 centres across the United States, of which the majority were primary care centres. | |
| Participants | Population: 255 adults with a clinical history of COPD were randomised to tiotropium + formoterol (124) and tiotropium (131). Baseline Characteristics: Mean age 64 years. COPD severity mild to severe. 67% men. Inclusion Criteria: Male and non‐pregnant female patients aged >40 years who had a clinical history of COPD were enrolled in this study. Each patient had a post‐bronchodilator FEV1 < 70% and >30% predicted normal or >0.75 L, whichever was less, at run‐in, and a FEV1 to FVC ratio (FEV1/FVC) of < 0.70 at screening and run‐in. Daytime and/or nighttime symptoms of COPD, including dyspnoea, must have been present on ≥4 of the 7 days before the baseline visit. Exclusion Criteria: A current or previous history of asthma or other significant medical condition that may have interfered with study treatment as assessed by the investigator, smoking cessation within the previous 3 months, ventilator support for respiratory failure within the previous year, the use of oxygen (≥2 L/min or for >2 h/d), initiation of pulmonary rehabilitation within the previous 3 months, the requirement for nasal continuous positive airway pressure or bilevel positive airway pressure, clinically significant lung disease other than COPD (i.e., bronchiectasis, sarcoidosis, pulmonary fibrosis, tuberculosis), sleep apnoea, chronic narrow‐angle glaucoma, symptomatic prostatic hyperplasia or bladder neck obstruction, and the need for chronic or prophylactic antibiotic therapy. | |
| Interventions | 1. Formoterol (Foradil Aerolizer) 12 µg twice daily and tiotropium (Handihaler) 18 μg once‐daily in the morning delivered via 2 separate inhalers 2. Formoterol‐matched placebo twice‐daily and tiotropium 18 µg once‐daily delivered via 2 separate inhalers | |
| Outcomes | Primary: The normalized area under the curve (AUC) for FEV1 measured 0 to 4 hours post‐morning dose (FEV1 AUC 0‐4 h) at the last visit. Secondary: Changes from baseline in trough (average of values obtained 10 and 30 min pre‐dose) FEV1 and FVC, weekly morning and evening peak expiratory flow (PEF), symptom severity scores, transition dyspnoea index (TDI), and health related quality of life (St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire, SGRQ) scores, number and severity of exacerbations, the global therapeutic response, discontinuations because of worsening COPD, and percentages of patients achieving targeted improvements in the SGRQ and TDI scores, use of rescue albuterol, nocturnal awakenings requiring rescue albuterol, changes in study or concomitant medications, and adverse events. | |
| Notes | Co‐medication: Continued use of prior stable inhaled corticosteroid (27%) regimens and systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of exacerbations was permitted throughout the study. All patients were provided with albuterol for use as rescue medication. Run‐in: Following screening, prohibited medications (i.e., beta‐agonists, beta‐blockers, cromolyn sodium, ipratropium bromide, leukotriene antagonists, cytotoxic agent, and theophylline) were withdrawn. Patients previously using TIO or FORM discontinued the drugs at least 4 weeks or 48 hours before screening, respectively. Patients completed a 2‐week run‐in period using placebo and as‐needed rescue albuterol. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Patients were randomised sequentially as they qualified for the study according to a pre‐generated computer code labelled on the medication kit. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | A pre‐generated computer code was labelled on the medication kit. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (LABA+TIO versus TIO) (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | The number of withdrawals in the different groups was relatively low but uneven (LABA + tiotropium (14.5%), and tiotropium + placebo (6.1%)). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Results for all listed primary and secondary outcomes were reported. |
| Methods | Design: A randomised, partly‐blind , partly placebo‐controlled, parallel group trial from October 2004 to November 2005. The trial included 86 centres in Germany (30), Italy (19), Netherlands (9), Russian federation (9), Poland (7), Czech Republic (4), Spain (4) and Hungary (4). | |
| Participants | Population: 638 adults, with a clinical history of moderate to very severe COPD as defined by GOLD guidelines, were randomised to tiotropium + formoterol (207), formoterol (210), and tiotropium (221). Baseline Characteristics: Mean age 63 years. COPD severity moderate to very severe with mean FEV1 predicted of 52%. 78% men. Inclusion Criteria: Males and females with stable COPD aged ≥40 years at COPD onset and with a smoking history of ≥10 pack‐years, forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) < 70% of patient’s predicted normal value (and ≥1.00 L), and FEV1/forced vital capacity (FVC) < 70%. They were to be symptomatic on at least 4 of 7 days prior to randomisation (symptom score >0 on diary card). Exclusion Criteria: Patients who had a respiratory tract infection or had been hospitalised for an acute exacerbation of COPD within the month prior to screening. Patients with a clinically significant condition such as ischaemic heart disease that might compromise patient safety or compliance were also excluded. | |
| Interventions | 1. Formoterol 10 µg twice daily via multi‐dose dry powder inhaler (MDDPI) 2. Tiotropium 18 µg once daily via the HandiHaler + formoterol 10 µg via MDDPI | |
| Outcomes | Primary: FEV1 measured 2 hours post‐dose after 24 weeks of treatment. Secondary: FEV1 and FVC at other time points during the study (5 min, 2 and 3 hours post‐dose following the first dose of treatment, and after 12 and 24 weeks of treatment); COPD exacerbations; symptom scores, rescue medication use and PEF; quality of life, and 6‐minute walking distance. | |
| Notes | Co‐medication: Salbutamol pMDI (2 × 100 µg/puff) was permitted as rescue medication. Patients were asked not to use salbutamol in the 8 hours before a study visit. Patients (40 to 44%) could receive inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) at a stable daily dose (any patients receiving fixed combinations of ICS and beta2‐agonists were switched to receive the same dose of ICS and on demand salbutamol). Run‐in: A screening period of up to 4 weeks included 2 weeks for washout of disallowed medications and 2 weeks for eligibility assessment and baseline evaluations. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | A randomisation list was produced using a validated system that automates the random assignment of treatment groups to randomisation numbers in the specified ratio. The randomisation scheme was reviewed by a Biostatistics Quality Assurance Group and locked by them after approval. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation data were kept strictly confidential until the time of unbinding, and was not accessible by anyone else involved in the study. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (LABA+TIO versus TIO) (performance bias) | Low risk | The study was partially blinded. The study was double‐blind for treatment comparison tiotropium + formoterol vs. tiotropium + placebo (MDDPI only), but not for other comparisons as tiotropium was administered open‐label. Randomisation was not stratified. Certihaler active and placebo devices were identical in packaging, labelling, schedule of administration and appearance. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (LABA+TIO versus LABA) (performance bias) | High risk | The study was partially blinded. The study was double‐blind for treatment comparison tiotropium + formoterol vs. tiotropium + placebo (MDDPI only), but not for other comparisons as tiotropium was administered open‐label. Randomisation was not stratified. Certihaler active and placebo devices were identical in packaging, labelling, schedule of administration and appearance. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Persons performing the assessments, and data analysts were blinded to the identity of the treatment from the time of randomisation until database lock. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | The number of withdrawals in the different groups were relatively low and even (LABA + tiotropium (12.1%), formoterol (11.9%) and tiotropium + placebo (13.1%)). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Results for all listed primary and secondary outcomes were reported. |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| No tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment | |
| No tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment | |
| No tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment | |
| 8 weeks of treatment and no tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment | |
| 4 weeks of treatment, no tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment, and crossover design | |
| crossover design | |
| 2 weeks of treatment, no tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment, and crossover design | |
| 6 weeks of treatment | |
| 6 weeks of treatment, no tiotropium plus long‐acting beta2‐agonists combination treatment, and crossover design | |
| 6 weeks of treatment and crossover design | |
| 6 weeks of treatment and crossover design |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Change in quality of life Show forest plot | 2 | 732 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.61 [‐2.93, ‐0.29] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 1 Change in quality of life. | ||||
| 1.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.8 [‐3.32, ‐0.28] |
| 1.2 Formoterol | 1 | 428 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐3.70, 1.70] |
| 2 Hospital admission (all cause) Show forest plot | 2 | 732 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.63, 1.61] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 2 Hospital admission (all cause). | ||||
| 2.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.61, 1.76] |
| 2.2 Formoterol | 1 | 428 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.36, 2.50] |
| 3 Hospital admission (exacerbation) Show forest plot | 2 | 732 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.63, 1.81] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 3 Hospital admission (exacerbation). | ||||
| 3.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.16 [0.66, 2.06] |
| 3.2 Formoterol | 1 | 428 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.15, 2.69] |
| 4 Mortality (all cause) Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.56 [0.56, 4.33] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 4 Mortality (all cause). | ||||
| 4.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.59 [0.45, 5.62] |
| 4.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [0.26, 8.57] |
| 5 Exacerbation Show forest plot | 3 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 5 Exacerbation. | ||||
| 5.1 Salmeterol | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 Formoterol | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Trough FEV1 Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.05, 0.09] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 6 Trough FEV1. | ||||
| 6.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.07, 0.13] |
| 6.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.02, 0.11] |
| 6.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.05, 0.10] |
| 7 Symptom score Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 7 Symptom score. | ||||
| 7.1 Formoterol | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Serious adverse event (non‐fatal) Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.76, 1.55] |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 8 Serious adverse event (non‐fatal). | ||||
| 8.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.37, 2.40] |
| 8.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.54, 2.13] |
| 8.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.72, 1.81] |
| 9 Withdrawal Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.74, 1.37] |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 9 Withdrawal. | ||||
| 9.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.54, 1.33] |
| 9.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.46 [0.52, 4.09] |
| 9.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.65, 1.34] |
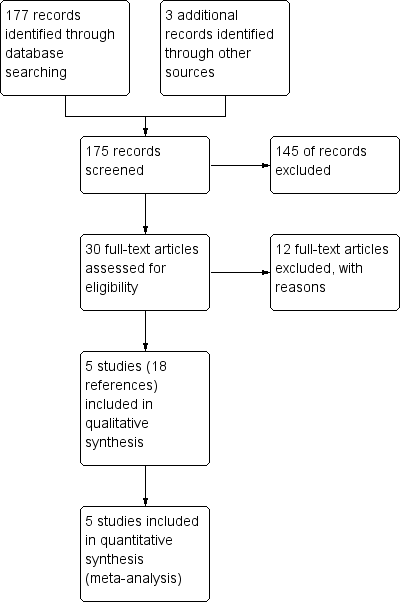
Study flow diagram.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Forest plot of comparison: 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, outcome: 1.1 Change in quality of life.
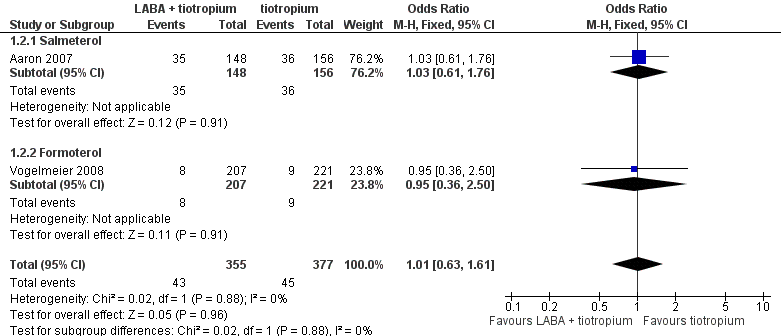
Forest plot of comparison: 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, outcome: 1.2 Hospital admission (all cause).
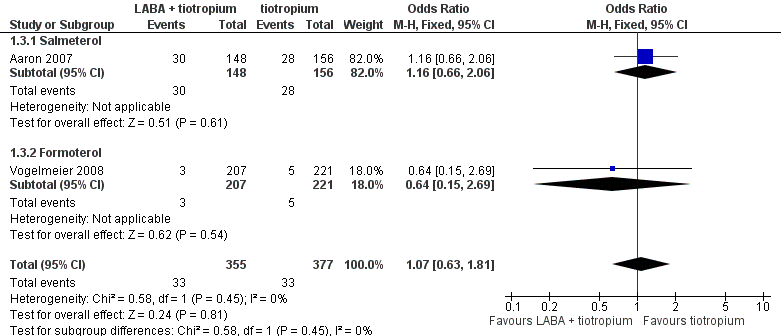
Forest plot of comparison: 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, outcome: 1.3 Hospital admission (exacerbation).

Forest plot of comparison: 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, outcome: 1.4 Mortality (all cause).

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 1 Change in quality of life.

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 2 Hospital admission (all cause).

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 3 Hospital admission (exacerbation).

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 4 Mortality (all cause).

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 5 Exacerbation.
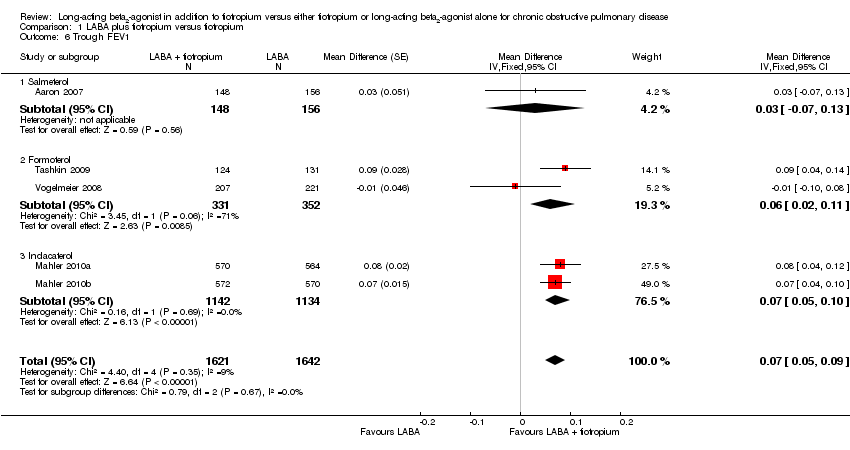
Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 6 Trough FEV1.
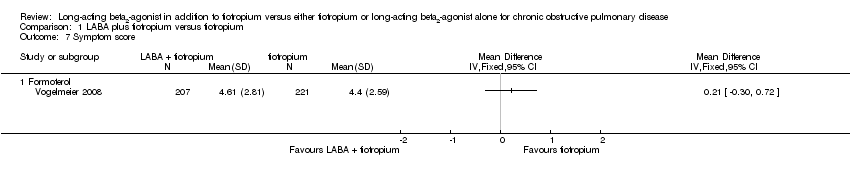
Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 7 Symptom score.

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 8 Serious adverse event (non‐fatal).

Comparison 1 LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium, Outcome 9 Withdrawal.
| LABA plus tiotropium versus tiotropium for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | ||||||
| Patient or population: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Tiotropium | LABA plus tiotropium | |||||
| Change in quality of life | The mean change in quality of life in the control group was | The mean change in quality of life in the intervention group was ‐6.3 units1 (‐7.43 to ‐4.79) | MD ‐1.61 | 732 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | The mean treatment effect was statistically significant but it was smaller than what is regarded as a clinically important difference. |
| Exacerbations leading to hospital admission | 88 per 1000 | 93 per 1000 | OR 1.07 | 732 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| Hospital admission (all cause) | 119 per 1000 | 120 per 1000 | OR 1.01 | 732 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| Mortality (all cause) | 4 per 1000 | 6 per 1000 | OR 1.56 | 3263 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 The control group risk is based on Aaron 2007. 2 One study was a year long with high and unbalanced dropouts. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Change in quality of life Show forest plot | 2 | 732 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.61 [‐2.93, ‐0.29] |
| 1.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.8 [‐3.32, ‐0.28] |
| 1.2 Formoterol | 1 | 428 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐3.70, 1.70] |
| 2 Hospital admission (all cause) Show forest plot | 2 | 732 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.63, 1.61] |
| 2.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.61, 1.76] |
| 2.2 Formoterol | 1 | 428 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.36, 2.50] |
| 3 Hospital admission (exacerbation) Show forest plot | 2 | 732 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.63, 1.81] |
| 3.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.16 [0.66, 2.06] |
| 3.2 Formoterol | 1 | 428 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.15, 2.69] |
| 4 Mortality (all cause) Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.56 [0.56, 4.33] |
| 4.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.59 [0.45, 5.62] |
| 4.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [0.26, 8.57] |
| 5 Exacerbation Show forest plot | 3 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 Salmeterol | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 Formoterol | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Trough FEV1 Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.05, 0.09] |
| 6.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.07, 0.13] |
| 6.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.02, 0.11] |
| 6.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.05, 0.10] |
| 7 Symptom score Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.1 Formoterol | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Serious adverse event (non‐fatal) Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.76, 1.55] |
| 8.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.37, 2.40] |
| 8.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.54, 2.13] |
| 8.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.72, 1.81] |
| 9 Withdrawal Show forest plot | 5 | 3263 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.74, 1.37] |
| 9.1 Salmeterol | 1 | 304 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.54, 1.33] |
| 9.2 Formoterol | 2 | 683 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.46 [0.52, 4.09] |
| 9.3 Indacaterol | 2 | 2276 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.65, 1.34] |

