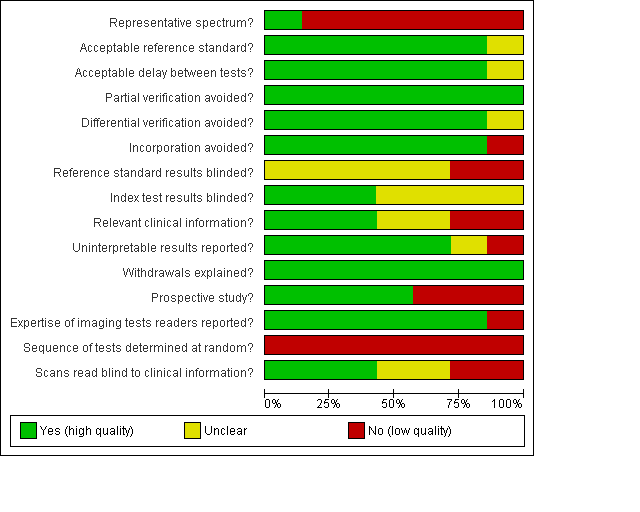
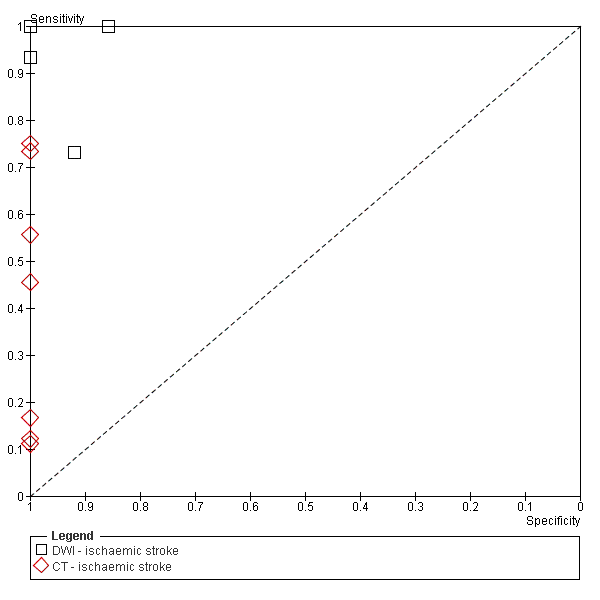
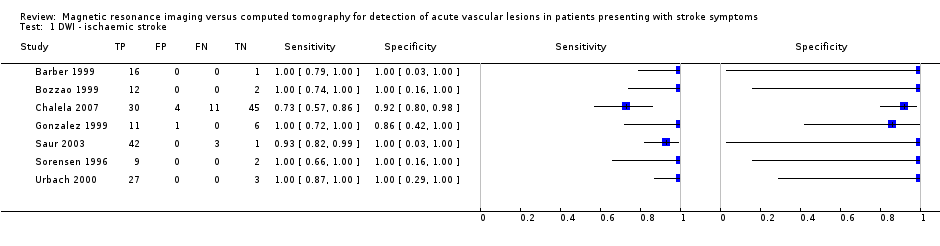
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Colin B Josephson, Philip M White, Ashma Krishan, Rustam Al‐Shahi Salman | 1 septiembre 2014
Wouter H Mallee, Junfeng Wang, Rudolf W Poolman, Peter Kloen, Mario Maas, Henrica CW de Vet, Job N Doornberg | 5 junio 2015
Nigel D'Souza, Georgina Hicks, Richard Beable, Antony Higginson, Bo Rud | 14 diciembre 2021
Joline F Roze, Jacob P Hoogendam, Fleur T van de Wetering, René Spijker, Leen Verleye, Joan Vlayen, Wouter B Veldhuis, Rob JPM Scholten, Ronald P Zweemer | 8 octubre 2018
Jacqueline Dinnes, Lavinia Ferrante di Ruffano, Yemisi Takwoingi, Seau Tak Cheung, Paul Nathan, Rubeta N Matin, Naomi Chuchu, Sue Ann Chan, Alana Durack, Susan E Bayliss, Abha Gulati, Lopa Patel, Clare Davenport, Kathie Godfrey, Manil Subesinghe, Zoe Traill, Jonathan J Deeks, Hywel C Williams, Cochrane Skin Cancer Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group | 1 julio 2019
Bo Rud, Thomas S Vejborg, Eli D Rappeport, Johannes B Reitsma, Peer Wille‐Jørgensen | 19 noviembre 2019
Bas Vaarwerk, Willemijn B Breunis, Lianne M Haveman, Bart de Keizer, Nina Jehanno, Lise Borgwardt, Rick R van Rijn, Henk van den Berg, Jérémie F Cohen, Elvira C van Dalen, Johannes HM Merks | 9 noviembre 2021
Lawrence MJ Best, Vishal Rawji, Stephen P Pereira, Brian R Davidson, Kurinchi Selvan Gurusamy | 17 abril 2017
Maria I Aguilar, Robert Hart, Lesly A Pearce | 18 julio 2007
Nicolle Cassola, Jose CC Baptista-Silva, Luis CU Nakano, Carolina DQ Flumignan, Ricardo Sesso, Vladimir Vasconcelos, Nelson Carvas Junior, Ronald LG Flumignan | 11 julio 2022