Lamotrigina para la esquizofrenia
Referencias
Referencias de los estudios incluidos en esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en espera de evaluación
Referencias adicionales
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Allocation: randomised in 1:1 ratio, computer generated code. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM IV). | |
| Interventions | 1. Lamotrigine 150 mg/day + risperidone 6 mg. N=18. 2. Placebo + risperidone 6 mg. N=18. Biperiden, as required to both groups. | |
| Outcomes | Mental state: PANSS (data for total, negative symptoms and general psychopathology subscales approximated from graph). Unable to use ‐ | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Allocation: randomised in approximately 1:1 ratio, stratified by current therapy. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder. | |
| Interventions | 1. Lamotrigine + other atypical antipsychotic (including clozapine): dose 125 mg/day, flexible dose. N=109. 2. Placebo + other atypical antipsychotic. N=108. | |
| Outcomes | Global effect: CGI‐S (data skewed). | |
| Notes | * number randomised, numbers in text and table differ. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Allocation: random ‐ no further details. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia. | |
| Interventions | 1. Lamotrigine + other atypical antipsychotics (including clozapine): dose 200 mg/day up to week 6, flexible blind titration weeks 7‐12. N=106. 2. Placebo + other atypical antipsychotic. N=106. | |
| Outcomes | Global effect: CGI ‐I, CGI‐S, SF‐36, WHO‐5 (data skewed). | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Allocation: randomised, 2:1 ratio. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM IV). | |
| Interventions | 1. Lamotrigine + other antipsychotic (including clozapine): dose up to 400 mg/day, dose built up over 8 weeks; maximum dose held steady only in the last two weeks. N=25. 2. Placebo + other atypical antipsychotic. N=13. Both groups as required ‐ trihexyphenidyl: 2‐5 mg, chloral hydrate: 250‐750 mg. | |
| Outcomes | Mental state: PANSS, BPRS, SANS, HAM‐D21. Unable to use ‐ | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
| Methods | Allocation: block randomisation by random number generator, stratified by GAF scores, cross over after 14 weeks. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM IV), paranoid, disorganized, undifferentiated, residual. | |
| Interventions | 1. Lamotrigine + clozapine: dose up to 200 mg/day, tapered in the last week. N=16*. 2. Placebo + clozapine. N=18. | |
| Outcomes | Mental state: PANSS positive subscale (first phase before cross‐over). Unable to use ‐ | |
| Notes | *first phase of trial only, before cross‐over. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
DSM IV ‐ Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders. 4th edition
ECT ‐ Electro‐convulsive Therapy
SD ‐ standard deviation
Mental state ‐
BACS ‐ Brief Assessment of Cognition for Schizophrenia (BACS)
BPRS ‐ Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale
CDSS ‐ Calgary Depression Scale for Schizophrenia
HAM‐D21 ‐ 21‐item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression
PANSS ‐ Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale
SANS ‐ Scale for Assessment of Negative Symptoms
Global state ‐
CGI ‐ I ‐ Clinical Global Impression ‐ Improvement
CGI ‐ S ‐ Clinical Global Impression ‐ Severity
GAF ‐ Global Assessment of Functioning
SF‐36 ‐ Short Form 36
WHO‐5 ‐ World Health Organisation‐5 Well Being Index
Adverse effects ‐
ESRS ‐ Extrapyramidal Symptoms Rating Scale
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Allocation: randomised. | |
| Allocation: unclear. | |
| Allocation: unclear. | |
| Allocation: not randomised. | |
| Allocation: randomised. | |
| Allocation: randomised. | |
| Allocation: open label trial, not a randomised trial. | |
| Allocation: randomised. | |
| Allocation: randomised. |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 Global state: 1.Global improvement (CGI‐I) Show forest plot | 1 | 208 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.73, 1.54] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 1 Global state: 1.Global improvement (CGI‐I). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 Global state: 2. Average total change score ‐ short term (CGI‐S, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.2
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 2 Global state: 2. Average total change score ‐ short term (CGI‐S, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 Global state: 3. Average physical health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.3
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 3 Global state: 3. Average physical health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 Global state: 4. Average mental health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.4
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 4 Global state: 4. Average mental health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 Mental state: 1.Treatment responders (> 20% reduction in PANSS total) Show forest plot | 3 | 297 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.81, 1.97] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 5 Mental state: 1.Treatment responders (> 20% reduction in PANSS total). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 Mental state: 2a. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 67 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐16.88 [‐25.18, ‐8.57] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 6 Mental state: 2a. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 Mental state: 2b. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (BPRS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 1 | 31 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.80 [‐12.44, 6.84] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 7 Mental state: 2b. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (BPRS, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 Mental state: 2c. Average total change score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.8
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 8 Mental state: 2c. Average total change score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 Mental state: 3a. Average positive endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 65 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.10 [‐8.86, ‐1.34] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 9 Mental state: 3a. Average positive endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 Mental state: 3b. Average positive change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.10
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 10 Mental state: 3b. Average positive change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 Mental state: 4a. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 67 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.25 [‐7.07, ‐3.43] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.11  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 11 Mental state: 4a. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 Mental state: 4b. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (SANS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 1 | 31 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐8.80 [‐19.73, 2.13] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 12 Mental state: 4b. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (SANS, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 Mental state: 4c. Average negative change score ‐ short term (SANS, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.13
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 13 Mental state: 4c. Average negative change score ‐ short term (SANS, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 Mental state: 5a. Average general psychopathology endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 67 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐10.74 [‐16.53, ‐4.96] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.14  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 14 Mental state: 5a. Average general psychopathology endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 Mental state: 5c. Average general psychopathology change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.15
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 15 Mental state: 5c. Average general psychopathology change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 Mental state: 6a. Average depression endpoint score (HAM‐D 21, high=poor) Show forest plot | 1 | 31 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐3.69, 3.89] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.16  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 16 Mental state: 6a. Average depression endpoint score (HAM‐D 21, high=poor). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 Mental state: 6b. Average depression change score (CDSS, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.17
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 17 Mental state: 6b. Average depression change score (CDSS, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 Mental state: 6c. Average depression change score ‐ short term (WHO‐5, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.18
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 18 Mental state: 6c. Average depression change score ‐ short term (WHO‐5, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 Cognitive state: 1. Treatment response (BACS) Show forest plot | 2 | 329 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.59, 2.04] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.19  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 19 Cognitive state: 1. Treatment response (BACS). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 Cognitive state: 2. Average change score ‐ short term (Stroop test, high difference from baseline=good) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.20  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 20 Cognitive state: 2. Average change score ‐ short term (Stroop test, high difference from baseline=good). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20.1 Stroop ‐ color naming time | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐29.45 [‐53.69, ‐5.21] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20.2 Stroop ‐ color naming error | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐8.28 [‐12.85, ‐3.71] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20.3 Stroop ‐ word reading time | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [‐10.81, 12.03] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20.4 Stroop ‐ word reading error | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.33 [‐2.46, 1.80] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 Cognitive state: 3. Average change score ‐ short term (BACS, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.21
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 21 Cognitive state: 3. Average change score ‐ short term (BACS, high change=good, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 Leaving the study early ‐ short term Show forest plot | 5 | 537 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.71, 1.29] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.22  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 22 Leaving the study early ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 Adverse effects: 1. Death, self harm, ideation about harm to self or others ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.23  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 23 Adverse effects: 1. Death, self harm, ideation about harm to self or others ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23.1 death | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23.2 any one or more fatalistic acts/impulses | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.38 [0.90, 6.30] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23.3 suicide attempt | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23.4 ideation ‐ homicidal | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.95 [0.24, 102.01] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23.5 ideation ‐ suicidal | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.15, 7.06] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 Adverse effects: 2a. Specific ‐ any adverse effect ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.19 [1.02, 1.38] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.24  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 24 Adverse effects: 2a. Specific ‐ any adverse effect ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 Adverse effects: 2b. Specific ‐ cardiovascular ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.25  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 25 Adverse effects: 2b. Specific ‐ cardiovascular ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25.1 chest pain | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.68 [0.18, 15.99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25.2 electrocardiogram abnormal | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25.3 hypertension | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.50 [0.50, 12.60] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25.4 tachycardia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 Adverse effects: 2c. Specific ‐ dermatological ‐ short term Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.26  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 26 Adverse effects: 2c. Specific ‐ dermatological ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26.27 hair loss | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.13, 69.09] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26.34 itching | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.0 [0.49, 32.39] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26.45 rash | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.24, 2.28] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 Adverse effects: 2d. Specific ‐ gastrointestinal ‐ short term Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.27  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 27 Adverse effects: 2d. Specific ‐ gastrointestinal ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.1 constipation | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.04, 3.15] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.2 decreased appetite | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.01, 2.02] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.3 diarrhea | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.56 [0.39, 6.16] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.4 dyspepsia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.0 [0.45, 35.20] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.5 nausea | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.26 [1.05, 4.88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.6 vomiting | 2 | 253 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.17 [0.77, 13.02] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 Adverse effects: 2e. Specific ‐ metabolic parameters ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.28  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 28 Adverse effects: 2e. Specific ‐ metabolic parameters ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28.1 alanine aminotransferase increase | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28.2 aspartate aminotransferase | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28.3 blood creatine phosphokinase | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28.4 blood glucose increase | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.5 [0.26, 8.80] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 Adverse effects: 2f. Specific ‐ neurological ‐ short term Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.29  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 29 Adverse effects: 2f. Specific ‐ neurological ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.1 ataxia | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.00 [0.26, 97.37] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.2 blurred vision | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.20, 20.15] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.3 dizziness | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.51, 2.70] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.4 headache | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [0.88, 2.08] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.5 loss of consciousness | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.0 [0.24, 102.92] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.6 paraesthesia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.7 hypoaesthesia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 7.00 [0.37, 133.88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29.8 tremor | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.95 [0.59, 41.71] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 Adverse effects: 2g. Specific ‐ psychiatric ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.30  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 30 Adverse effects: 2g. Specific ‐ psychiatric ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.1 aggression | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.2 agitation | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.09, 2.67] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.3 anxiety | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.73 [0.09, 5.76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.4 crying | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.5 hallucination, auditory | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 10.90 [0.61, 194.74] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.6 insomnia | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.02 [0.04, 96.25] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.7 paranoia | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.99 [0.37, 10.75] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30.8 somnolence | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.51, 2.87] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 Adverse effects: 2h. Specific ‐ respiratory ‐ short term Show forest plot | 1 | 424 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.48, 18.89] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.31  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 31 Adverse effects: 2h. Specific ‐ respiratory ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31.1 cough | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.0 [0.37, 133.88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31.2 influenza | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.06, 15.78] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 Adverse effects: 2i. Specific ‐ others ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.32  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 32 Adverse effects: 2i. Specific ‐ others ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.1 abnormal dreams | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.02] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.2 asthenia | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.02] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.3 back pain | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.30, 3.33] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.4 dry mouth | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.21, 4.84] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.5 fatigue | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.45, 4.24] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.6 lymphadenopathy | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.99 [0.31, 28.48] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.7 urine abnormality | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.8 weight increase | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 Adverse effects: 3. Events ‐ co‐incident with trial ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.33  Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 33 Adverse effects: 3. Events ‐ co‐incident with trial ‐ short term. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.1 abscess | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.2 arthropod bite | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.3 endometrial cancer | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.5 joint injury | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.6 local swelling | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.7 nasopharyngitis | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.42 [0.28, 7.15] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.8 pharyngolaryngeal pain | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.9 post‐procedural pain | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.10 tooth abscess | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.11 toothache | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.08, 2.00] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33.12 upper respiratory tract infection | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.22, 4.94] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 Adverse effects: 4a. Movement disorders ‐ average endpoint score (ESRS, high = poor, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.34
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 34 Adverse effects: 4a. Movement disorders ‐ average endpoint score (ESRS, high = poor, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35 Adverse effects: 4b. Movement disorders ‐ average dose (biperiden, mg, high = poor, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis 1.35
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 35 Adverse effects: 4b. Movement disorders ‐ average dose (biperiden, mg, high = poor, data skewed). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Post‐hoc subgroup analysis: Heterogenous data for average change scores (PANSS total scores, high = poor)
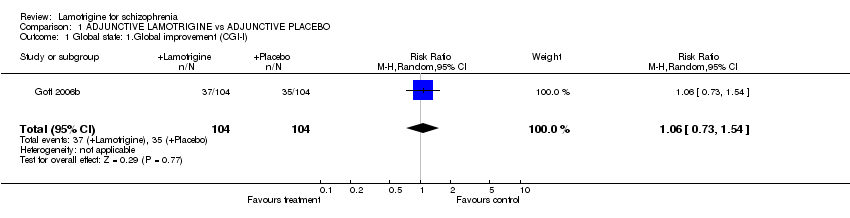
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 1 Global state: 1.Global improvement (CGI‐I).
| Study | Intervention | Least Mean Square | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐0.2 | 0.82 | 101 | |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | ‐0.5 | 0.82 | 104 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐0.5 | 0.72 | 104 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐0.4 | 0.72 | 104 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 2 Global state: 2. Average total change score ‐ short term (CGI‐S, high change=good, data skewed).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | 0.07 | 7.18 | 87 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐0.31 | 7.22 | 88 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 3 Global state: 3. Average physical health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | 0.21 | 8.21 | 87 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | 1.32 | 8.16 | 88 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 4 Global state: 4. Average mental health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 5 Mental state: 1.Treatment responders (> 20% reduction in PANSS total).
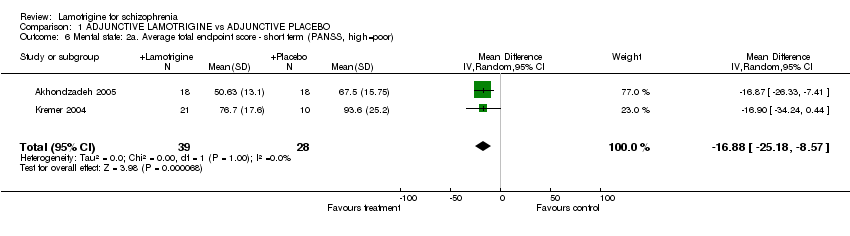
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 6 Mental state: 2a. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor).
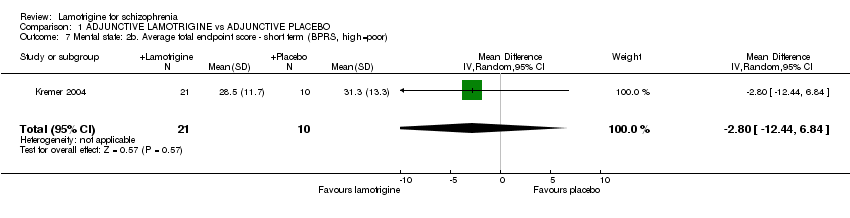
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 7 Mental state: 2b. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (BPRS, high=poor).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐6.0 | 13.77 | 101 | |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | ‐8.2 | 13.84 | 104 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐12.9 | 12.34 | 103 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐12.0 | 12.40 | 104 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 8 Mental state: 2c. Average total change score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor, data skewed).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 9 Mental state: 3a. Average positive endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐2.2 | 4.39 | 101 | |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | ‐3.2 | 4.51 | 104 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐4.4 | 4.18 | 103 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐3.9 | 4.20 | 104 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 10 Mental state: 3b. Average positive change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high change=good, data skewed).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 11 Mental state: 4a. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 12 Mental state: 4b. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (SANS, high=poor).
| Study | Intervention | Least Mean Square | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐2.6 | 12.65 | 97 | |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | ‐6.2 | 13.16 | 100 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐4.8 | 11.69 | 101 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐5.7 | 11.69 | 102 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 13 Mental state: 4c. Average negative change score ‐ short term (SANS, high change=good, data skewed).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 14 Mental state: 5a. Average general psychopathology endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor).
| Study | Intervention | Least Mean Squares | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐2.4 | 7.45 | 101 | High change=good |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | ‐3.7 | 7.48 | 104 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐5.5 | 6.63 | 103 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐5.3 | 6.56 | 104 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 15 Mental state: 5c. Average general psychopathology change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, data skewed).
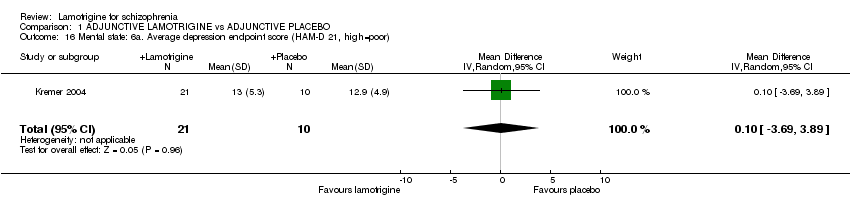
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 16 Mental state: 6a. Average depression endpoint score (HAM‐D 21, high=poor).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐0.2 | 3.57 | 97 | |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | ‐0.8 | 3.59 | 101 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | ‐0.8 | 2.96 | 100 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | ‐1.2 | 2.97 | 102 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 17 Mental state: 6b. Average depression change score (CDSS, high change=good, data skewed).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | 2.7 | 22.8 | 86 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | 1.8 | 22.71 | 86 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 18 Mental state: 6c. Average depression change score ‐ short term (WHO‐5, high change=good, data skewed).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 19 Cognitive state: 1. Treatment response (BACS).

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 20 Cognitive state: 2. Average change score ‐ short term (Stroop test, high difference from baseline=good).
| Study | Intervention | Least Square mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant lamotrigine | 0.22 | 0.61 | 74 | |
| Goff 2006a | Adjuvant placebo | 0.23 | 0.51 | 84 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant lamotrigine | 0.44 | 0.68 | 103 | |
| Goff 2006b | Adjuvant placebo | 0.19 | 0.70 | 103 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 21 Cognitive state: 3. Average change score ‐ short term (BACS, high change=good, data skewed).
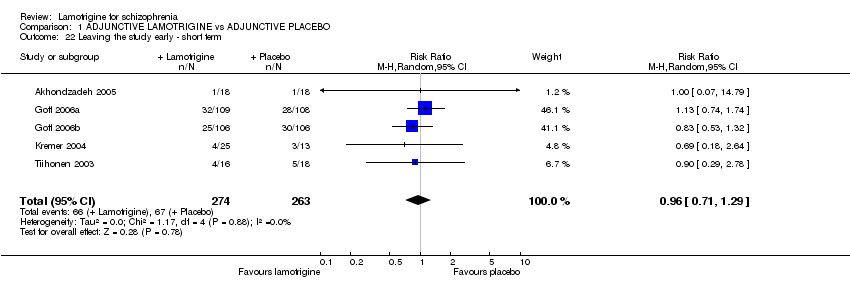
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 22 Leaving the study early ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 23 Adverse effects: 1. Death, self harm, ideation about harm to self or others ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 24 Adverse effects: 2a. Specific ‐ any adverse effect ‐ short term.
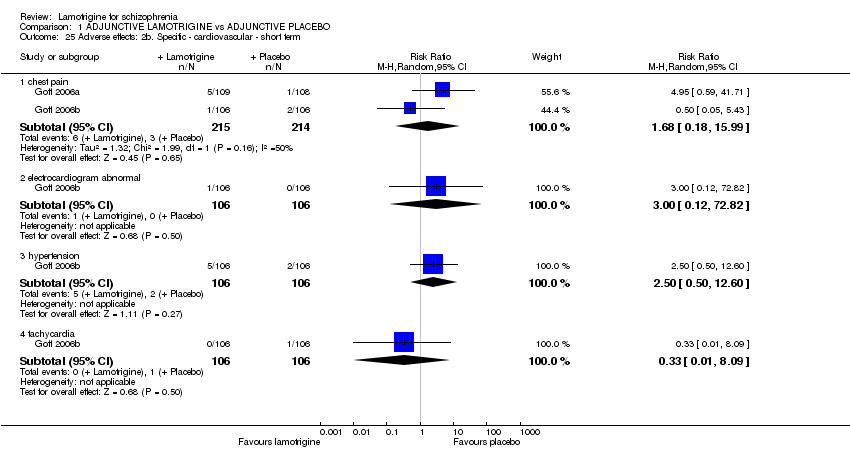
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 25 Adverse effects: 2b. Specific ‐ cardiovascular ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 26 Adverse effects: 2c. Specific ‐ dermatological ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 27 Adverse effects: 2d. Specific ‐ gastrointestinal ‐ short term.
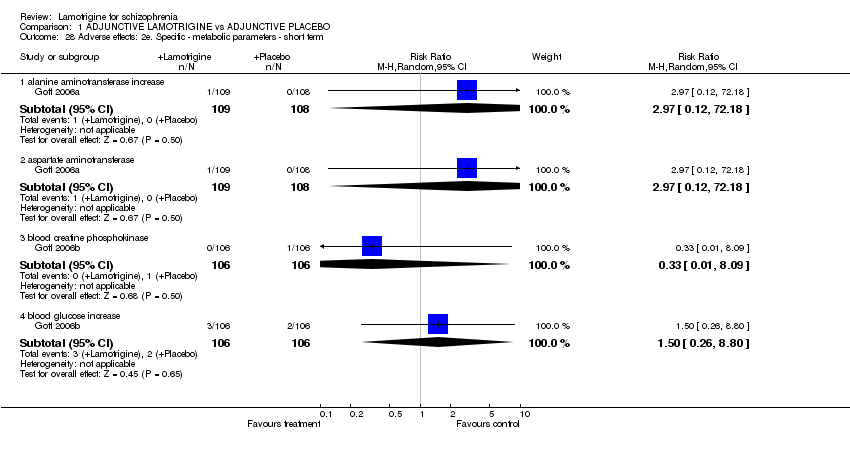
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 28 Adverse effects: 2e. Specific ‐ metabolic parameters ‐ short term.
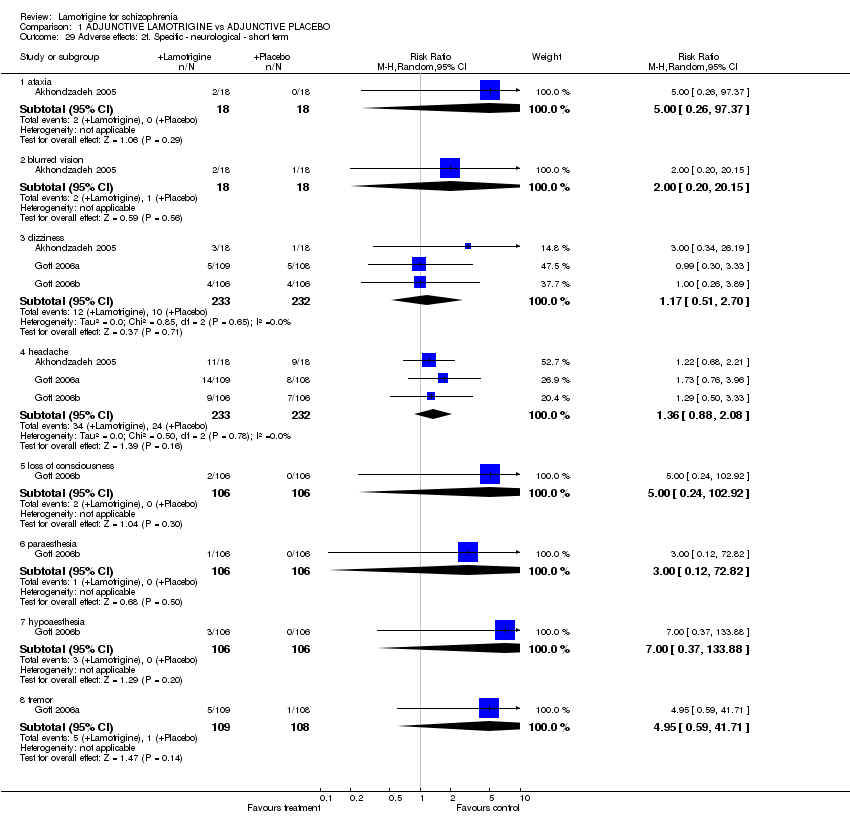
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 29 Adverse effects: 2f. Specific ‐ neurological ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 30 Adverse effects: 2g. Specific ‐ psychiatric ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 31 Adverse effects: 2h. Specific ‐ respiratory ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 32 Adverse effects: 2i. Specific ‐ others ‐ short term.

Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 33 Adverse effects: 3. Events ‐ co‐incident with trial ‐ short term.
| Study | Intervention | Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Akhondzadeh 2005 | Lamotrigine | 2.93 | 2.99 | 18 | p=0.78 |
| Akhondzadeh 2005 | Placebo | 3.25 | 3.27 | 18 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 34 Adverse effects: 4a. Movement disorders ‐ average endpoint score (ESRS, high = poor, data skewed).
| Study | Intervention | Mean | SD | N | Notes |
| Akhondzadeh 2005 | Lamotrigine | 100.33 | 81.38 | 17 | p=0.19 |
| Akhondzadeh 2005 | Placebo | 137.66 | 87.00 | 17 | |
Comparison 1 ADJUNCTIVE LAMOTRIGINE vs ADJUNCTIVE PLACEBO, Outcome 35 Adverse effects: 4b. Movement disorders ‐ average dose (biperiden, mg, high = poor, data skewed).
| Methods | Participants | Interventions | Outcomes | Notes |
| Allocation: centralised sequence generation with table of random numbers or computer generated code, stratified by severity of illness, sequence concealed till interventions assigned. | Diagnosis: schizophrenia (DSM IV), subtypes and schizoaffective disorder included and numbers in each category clearly reported. | 1. Lamotrigine: dose 400 mg/ day + routine antipsychotic therapy. N=150. | Qualtiy of life: healthy days,** SF‐36. | * size of study to detect a 10% difference in improvement with 80% certainity. |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: 1.Global improvement (CGI‐I) Show forest plot | 1 | 208 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.73, 1.54] |
| 2 Global state: 2. Average total change score ‐ short term (CGI‐S, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 3 Global state: 3. Average physical health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 4 Global state: 4. Average mental health change score ‐ short term (SF‐36, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 5 Mental state: 1.Treatment responders (> 20% reduction in PANSS total) Show forest plot | 3 | 297 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.81, 1.97] |
| 6 Mental state: 2a. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 67 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐16.88 [‐25.18, ‐8.57] |
| 7 Mental state: 2b. Average total endpoint score ‐ short term (BPRS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 1 | 31 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.80 [‐12.44, 6.84] |
| 8 Mental state: 2c. Average total change score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 9 Mental state: 3a. Average positive endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 65 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.10 [‐8.86, ‐1.34] |
| 10 Mental state: 3b. Average positive change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 11 Mental state: 4a. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 67 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.25 [‐7.07, ‐3.43] |
| 12 Mental state: 4b. Average negative endpoint score ‐ short term (SANS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 1 | 31 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐8.80 [‐19.73, 2.13] |
| 13 Mental state: 4c. Average negative change score ‐ short term (SANS, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 14 Mental state: 5a. Average general psychopathology endpoint score ‐ short term (PANSS, high=poor) Show forest plot | 2 | 67 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐10.74 [‐16.53, ‐4.96] |
| 15 Mental state: 5c. Average general psychopathology change score ‐ short term (PANSS subscale, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 16 Mental state: 6a. Average depression endpoint score (HAM‐D 21, high=poor) Show forest plot | 1 | 31 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐3.69, 3.89] |
| 17 Mental state: 6b. Average depression change score (CDSS, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 18 Mental state: 6c. Average depression change score ‐ short term (WHO‐5, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 19 Cognitive state: 1. Treatment response (BACS) Show forest plot | 2 | 329 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.59, 2.04] |
| 20 Cognitive state: 2. Average change score ‐ short term (Stroop test, high difference from baseline=good) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 20.1 Stroop ‐ color naming time | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐29.45 [‐53.69, ‐5.21] |
| 20.2 Stroop ‐ color naming error | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐8.28 [‐12.85, ‐3.71] |
| 20.3 Stroop ‐ word reading time | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [‐10.81, 12.03] |
| 20.4 Stroop ‐ word reading error | 1 | 36 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.33 [‐2.46, 1.80] |
| 21 Cognitive state: 3. Average change score ‐ short term (BACS, high change=good, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 22 Leaving the study early ‐ short term Show forest plot | 5 | 537 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.71, 1.29] |
| 23 Adverse effects: 1. Death, self harm, ideation about harm to self or others ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 23.1 death | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 23.2 any one or more fatalistic acts/impulses | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.38 [0.90, 6.30] |
| 23.3 suicide attempt | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 23.4 ideation ‐ homicidal | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.95 [0.24, 102.01] |
| 23.5 ideation ‐ suicidal | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.15, 7.06] |
| 24 Adverse effects: 2a. Specific ‐ any adverse effect ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.19 [1.02, 1.38] |
| 25 Adverse effects: 2b. Specific ‐ cardiovascular ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 25.1 chest pain | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.68 [0.18, 15.99] |
| 25.2 electrocardiogram abnormal | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 25.3 hypertension | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.50 [0.50, 12.60] |
| 25.4 tachycardia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] |
| 26 Adverse effects: 2c. Specific ‐ dermatological ‐ short term Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 26.27 hair loss | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.13, 69.09] |
| 26.34 itching | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.0 [0.49, 32.39] |
| 26.45 rash | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.24, 2.28] |
| 27 Adverse effects: 2d. Specific ‐ gastrointestinal ‐ short term Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 27.1 constipation | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.04, 3.15] |
| 27.2 decreased appetite | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.01, 2.02] |
| 27.3 diarrhea | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.56 [0.39, 6.16] |
| 27.4 dyspepsia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.0 [0.45, 35.20] |
| 27.5 nausea | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.26 [1.05, 4.88] |
| 27.6 vomiting | 2 | 253 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.17 [0.77, 13.02] |
| 28 Adverse effects: 2e. Specific ‐ metabolic parameters ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 28.1 alanine aminotransferase increase | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 28.2 aspartate aminotransferase | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 28.3 blood creatine phosphokinase | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] |
| 28.4 blood glucose increase | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.5 [0.26, 8.80] |
| 29 Adverse effects: 2f. Specific ‐ neurological ‐ short term Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 29.1 ataxia | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.00 [0.26, 97.37] |
| 29.2 blurred vision | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.20, 20.15] |
| 29.3 dizziness | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.51, 2.70] |
| 29.4 headache | 3 | 465 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [0.88, 2.08] |
| 29.5 loss of consciousness | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.0 [0.24, 102.92] |
| 29.6 paraesthesia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 29.7 hypoaesthesia | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 7.00 [0.37, 133.88] |
| 29.8 tremor | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.95 [0.59, 41.71] |
| 30 Adverse effects: 2g. Specific ‐ psychiatric ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 30.1 aggression | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 30.2 agitation | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.5 [0.09, 2.67] |
| 30.3 anxiety | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.73 [0.09, 5.76] |
| 30.4 crying | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] |
| 30.5 hallucination, auditory | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 10.90 [0.61, 194.74] |
| 30.6 insomnia | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.02 [0.04, 96.25] |
| 30.7 paranoia | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.99 [0.37, 10.75] |
| 30.8 somnolence | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.51, 2.87] |
| 31 Adverse effects: 2h. Specific ‐ respiratory ‐ short term Show forest plot | 1 | 424 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.48, 18.89] |
| 31.1 cough | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.0 [0.37, 133.88] |
| 31.2 influenza | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.06, 15.78] |
| 32 Adverse effects: 2i. Specific ‐ others ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 32.1 abnormal dreams | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.02] |
| 32.2 asthenia | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.02] |
| 32.3 back pain | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.30, 3.33] |
| 32.4 dry mouth | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.21, 4.84] |
| 32.5 fatigue | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.39 [0.45, 4.24] |
| 32.6 lymphadenopathy | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.99 [0.31, 28.48] |
| 32.7 urine abnormality | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 32.8 weight increase | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 33 Adverse effects: 3. Events ‐ co‐incident with trial ‐ short term Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 33.1 abscess | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 33.2 arthropod bite | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.09] |
| 33.3 endometrial cancer | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 33.5 joint injury | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 33.6 local swelling | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 33.7 nasopharyngitis | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.42 [0.28, 7.15] |
| 33.8 pharyngolaryngeal pain | 1 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.12, 72.82] |
| 33.9 post‐procedural pain | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 33.10 tooth abscess | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.97 [0.12, 72.18] |
| 33.11 toothache | 1 | 217 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.08, 2.00] |
| 33.12 upper respiratory tract infection | 2 | 429 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.22, 4.94] |
| 34 Adverse effects: 4a. Movement disorders ‐ average endpoint score (ESRS, high = poor, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 35 Adverse effects: 4b. Movement disorders ‐ average dose (biperiden, mg, high = poor, data skewed) Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||

