Shengmai (una hierba medicinal china tradicional) para la insuficiencia cardíaca
Referencias
Referencias de los estudios incluidos en esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en espera de evaluación
Referencias adicionales
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (100mL + 5% glucose solution 150mL intravenously daily) + usual treatment | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement >1 class: 81% in Shengmai group; 55% in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Quasi‐random (sequence of visit hospital) controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Suzhong, the proportion from three herbs: Radix ginseng rubra, Radix ophiopogonis, Schisandra chinensis is 1:3.12:1.56) 40 to 60mL + 5% glucose solution 250˜500mlLintravenously daily) + co‐interventions | |
| Outcomes | Death: 3 in shengmai group, 12 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Suzhong, 25 mL+ 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Symptoms and sign no improvement or worsening of heart failure; 4 in shengmai group, 12 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Quasi‐randomised (sequence of visit hospital) controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Suzhong, from three herbs: Radix ginseng rubra, Radix ophiopogonis, Schisandra chinensis) 40 to 60 mL + 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < I class: 5 in shengmai group, 12 in control group | |
| Notes | Single blinding: participants | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, 20 to 40 mL + 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenouly daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 3 in shengmai group, 7 in control group The outcomes were measured at the end of treatment. | |
| Notes | Single blinding: participants | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Suzhong, proportion from three herbs: Radix ginseng rubra, Radix ophiopogonis, Schisandra chinensis is 1:3.12:1.56. 10 mL + 5% glucose solution 200 mL intravenously every 12 hours) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 2 in shengmai group, 12 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, 40 mL + 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement <class 1: 4 in shengmai group, 12 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Quasi‐random (sequence of visit hospital) controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, 30‐50 mL + 10% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement <class 1: 6 in shengmai, 6 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent Suzhong, 30 mL + 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement <class 1: 6 in shengmai, 25 in control group | |
| Notes | Single blinding: participants | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Quasi‐random (sequence of visit hospital) controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Hehuang, shengmai injection/mL: Ranax ginseng 1 g, Radix ophiopogonis 3.12 g, Fructus schisandra chinensis1.56 g 60 mL + 5% glucose solution 250‐500 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | B‐type natriuretic peptide: before treatment: 928.17+/‐534.46 in shengmai group, 934.35 +/‐570.54 in control group; after treatment: 167.56 +/‐96.88 in shengmai group, 383.83 +/‐ 226.69 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (50 mL + 5%glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement <class 1: 1in Shengmai, 8 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Quasi‐random (sequence of visit hospital) controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, from three herbs/10mL: Radix ginseng rubra 1 g, Radix ophiopogonis 3.12 g, Schisandra chinensis1.56 g. 100mL + 5% glucose solution 200mL iv gtt qd) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 2 in shengmai, 10 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Yibing, 100 mL + 5% glucose solution 250‐500 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 2 in shengmai, 9 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai A1, A2, A3 groups: shengmai injection (agent: Yibing, 20, 40, 60 mL intravenously daily ) + co‐intervention A | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 7/60 in all shengmai, 2/20 in control group. | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, 50 mL + 10% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 2 in shengmai, 7 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (20 mL + 10% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 3 in shengmai, 11 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, 60 mL + 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐interventions | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 6 in shengmai, 13 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Quasi‐random (sequence of visit hospital) controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Suzhong, 20‐30 mL + 5% glucose solution 250 mL intravenously daily) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 5 in shengmai, 14 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial | |
| Participants | Ethnic: Chinese | |
| Interventions | Shengmai group: shengmai injection (agent: Huaxi, from three herbs/10 mL: Panax ginseng 1 g, Ophiopogon japonicus 3.12 g and Schisandra chinensis 1.56 g. 60 mL + 5% GS250 mL iv gtt qd ) + co‐intervention | |
| Outcomes | Heart function improvement < class 1: 8 in shengmai, 20 in control group | |
| Notes | No blinding | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CHD= coronary heart disease; RHD=rheumatic heart disease; PHD=pulmonary heart disease; DCM=dilated cardiomyopathy; HCM=hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; PaO2=oxygen partial pressure; PaCO2 =carbon dioxide partial pressure; kPa=blood pressure measure unit, 1kPa=7.6mmHg; p.o=by mouth; NYHA=New York Heart Association
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial (confirmed by contacting to the author by telephone) | |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial | |
| Shengmai + Chinese drug + usual treatment versus usual treatment | |
| Shengmai versus another drug | |
| Outcome reported from 27 patients, but only 20 patients included at entry in control group | |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial (confirmed by contacting to the author by telephone) | |
| A before‐after study | |
| Outcome reported from 51 patients, but only 50 patients included at entry in shengmai group | |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial | |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial (confirmed by contacting to the author by telephone) | |
| A before‐after study | |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial (confirmed by contacting to the author by telephone) | |
| Not a randomiszd or quasi‐randomized controlled trial (confirmed by contacting to the author by telephone) | |
| Not a randomized or quasi‐randomized controlled trial (confirmed by contacting to the author by telephone) | |
| Descriptive study |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
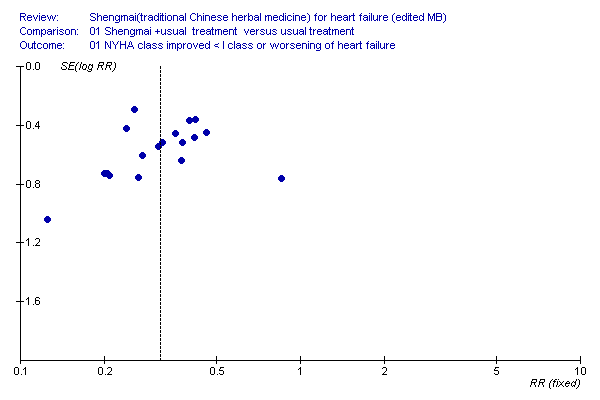
| 1 Lack of improvement in heart failure ( NYHA class improved < I class or worsening of heart failure) Show forest plot | 18 | 1606 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.25, 0.40] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 1 Lack of improvement in heart failure ( NYHA class improved < I class or worsening of heart failure). | ||||
| 2 mortality at the end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 2 mortality at the end of treatment. | ||||
| 3 cardiac output (L/min) change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 3 cardiac output (L/min) change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 4 stroke volume (ml) change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 4 stroke volume (ml) change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 5 cardiac index change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 5 cardiac index change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 6 eject fraction change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 6 eject fraction change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 7 system vascular resistance change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 7 system vascular resistance change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 8 left ventricular minor axis shortened rate change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 8 left ventricular minor axis shortened rate change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 9 ventricular wall thickened rate change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 9 ventricular wall thickened rate change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 10 Exercise time in movement tolerance test at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.10  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 10 Exercise time in movement tolerance test at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 11 heart rate multiply systolic blood press (mmHg) at the end of movement tolerance test at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.11  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 11 heart rate multiply systolic blood press (mmHg) at the end of movement tolerance test at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 12 flow mediated dilation of brachial artery volume change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 12 flow mediated dilation of brachial artery volume change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 13 eletrocardiogram QT dispersion change at 20 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.13  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 13 eletrocardiogram QT dispersion change at 20 days. | ||||
| 14 electrocardiogram JT dispersion change at 20 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.14  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 14 electrocardiogram JT dispersion change at 20 days. | ||||
| 15 tumor necrosis factor‐alpha change at 14 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.15  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 15 tumor necrosis factor‐alpha change at 14 days. | ||||
| 16 endogenous digitalis‐like factors change at 14 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.16  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 16 endogenous digitalis‐like factors change at 14 days. | ||||
| 17 Plasma P‐selectin change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.17  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 17 Plasma P‐selectin change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 18 von Willebrand's factor change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.18  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 18 von Willebrand's factor change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 19 D‐dimer change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.19  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 19 D‐dimer change at 2 weeks. | ||||
| 20 partial pressure of oxygen increase at 10 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.20  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 20 partial pressure of oxygen increase at 10 days. | ||||
| 21 partial pressure of carbon dioxide decrease at 10 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.21  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 21 partial pressure of carbon dioxide decrease at 10 days. | ||||
| 22 B‐type natriuretic peptide change at 15 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.22  Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 22 B‐type natriuretic peptide change at 15 days. | ||||
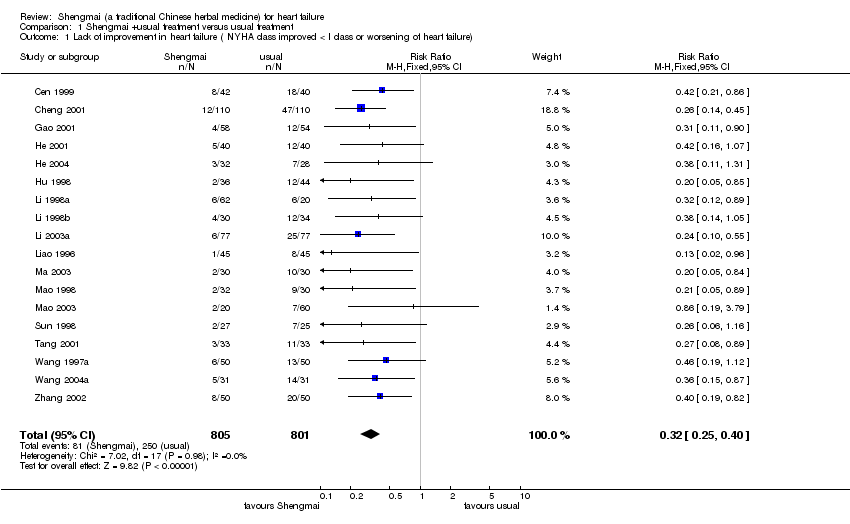
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 1 Lack of improvement in heart failure ( NYHA class improved < I class or worsening of heart failure).

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 2 mortality at the end of treatment.
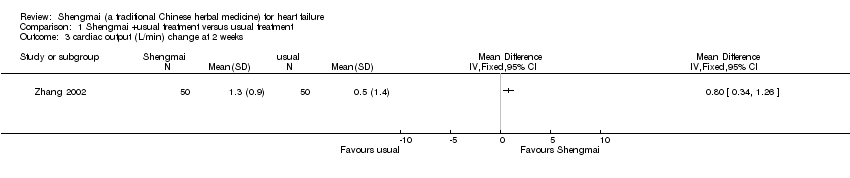
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 3 cardiac output (L/min) change at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 4 stroke volume (ml) change at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 5 cardiac index change at 2 weeks.
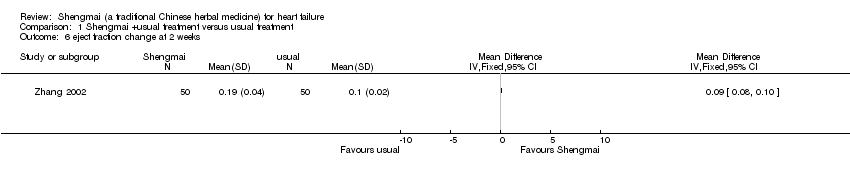
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 6 eject fraction change at 2 weeks.
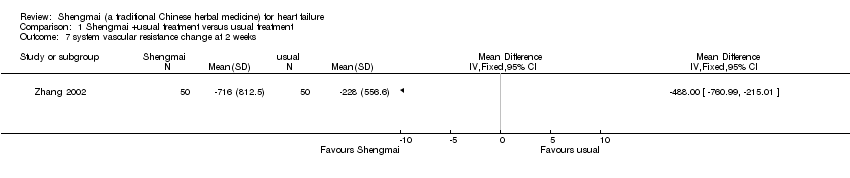
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 7 system vascular resistance change at 2 weeks.
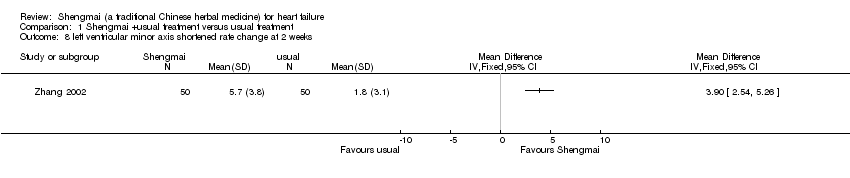
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 8 left ventricular minor axis shortened rate change at 2 weeks.
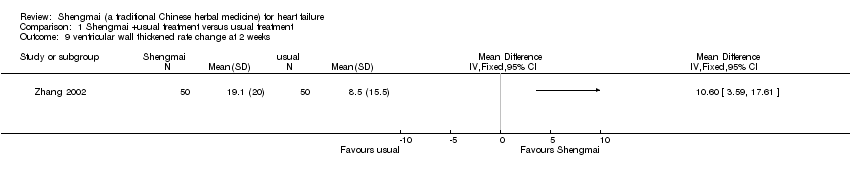
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 9 ventricular wall thickened rate change at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 10 Exercise time in movement tolerance test at 2 weeks.
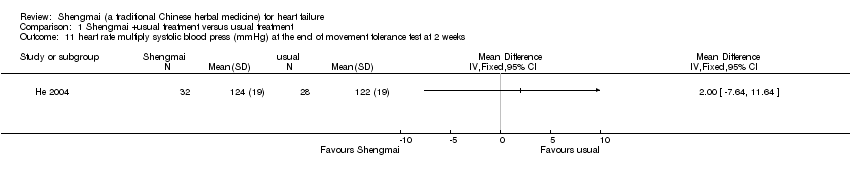
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 11 heart rate multiply systolic blood press (mmHg) at the end of movement tolerance test at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 12 flow mediated dilation of brachial artery volume change at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 13 eletrocardiogram QT dispersion change at 20 days.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 14 electrocardiogram JT dispersion change at 20 days.
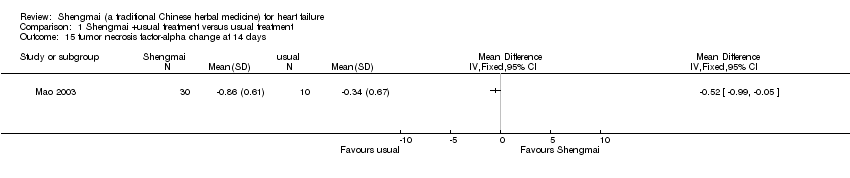
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 15 tumor necrosis factor‐alpha change at 14 days.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 16 endogenous digitalis‐like factors change at 14 days.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 17 Plasma P‐selectin change at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 18 von Willebrand's factor change at 2 weeks.
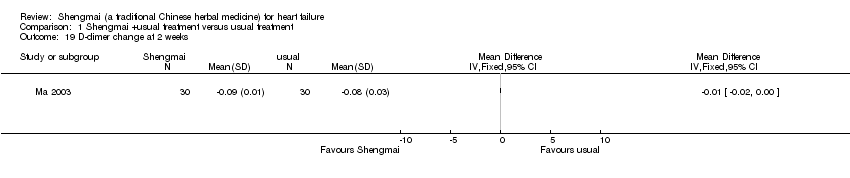
Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 19 D‐dimer change at 2 weeks.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 20 partial pressure of oxygen increase at 10 days.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 21 partial pressure of carbon dioxide decrease at 10 days.

Comparison 1 Shengmai +usual treatment versus usual treatment, Outcome 22 B‐type natriuretic peptide change at 15 days.
| 1.shengmai* |
| 1.shengmai* |
| 1.shengmai$ |
| 1.shengmai$ |
| Study | Number | Sex | Average age | Duration of HF | Original disease | Heart Function |
| Gao 2001 | 112 | M/F 81/31 | 66.8 | PHD 112 | ||
| Ma 2003 | 60 | M/F 32/28 | 65‐67 | 5.4‐6.3 years | CHD/RHD/HBP/DCM 47/5/6/2 | II/III/IV 13/32/15 |
| Sun 1998 | 52 | M/F 29/23 | 55‐57 | CHD/RHD/HBP 20/14/11 | III/IV 23/29 | |
| Zhang 2002 | 100 | M/F 59/41 | 58‐60 | 6 months‐8 years | DCM 100 | II/III/IV 20/71/9 |
| Cen 1999 | 82 | M/F 67/15 | 69‐70 | CHD/RHD/HBP/DCM/PHD 38/12/17/1/14 | ||
| He 2004 | 60 | 41 | CHD/RHD/HBP/DCM 21/12/15/12 | II/III/IV 8/34/18 | ||
| Mao 2003 | 80 | II/III 27/53 | ||||
| Liao 1996 | 90 | M/F 57/33 | 65‐66 | average 8 years | CHD/RHD/HBP/DCM/PHD/others 38/9/4/7/27/5 | I/II/III 17/33/40 |
| Cheng 2001 | 220 | M/F144/76 | 56‐57 | average 9.5‐9.7 years | PHD 220 | |
| Wang 2004 | 62 | M/F 44/18 | 59‐60 | average 7.5‐7.8 years | CHD/RHD/HBP/DCM/PHD 18/9/17/9/9 | II/III/IV 18/25/19 |
| Li 2003 | 154 | M/F 82/72 | 63 | PHD 154 | III/IV 102/52 | |
| Hu 1998 | 80 | M/F 64/16 | 56‐58 | III/IV 68/10 | ||
| He 2001 | 80 | M/F 54/26 | 48‐50 | |||
| Li 2004 | 57 | M/F 32/25 | 72‐73 | average 7.5‐7.9 years | CHD/HBP/DCM 37/18/2 | III/IV 19/38 |
| Wang 1997b | 100 | M/F 54/46 | 49‐50 | CHD/RHD/DCM 31/51/18 | II/III/IV 5/64/31 | |
| Li 1998b | 64 | M/F 42/22 | 69‐72 | PHD 64 | ||
| Tang 2001 | 66 | M/F 41/25 | 64‐65 | 2‐12 years | CHD/RHD/HBP/DCM/PHD 23/19/7/4/13 | |
| Li 1998a | 82 | M/F 54/28 | 56‐64 | 1‐14 years | CHD/RHD/PHD 40/34/8 | II/III/IV 20/32/30 |
| Mao 1998 | 62 | M/F 53/9 | 67‐68 | 5‐41 years |
| Study | Agent | Dose | Form | Duration of treat |
| Gao 2001 | 25 mL + 5% GS 250ml/iv gtt qd | injection | 10d | |
| Ma 2003 | Huaxi | 100 mL + 5% GS 200ml/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d |
| Sun 1998 | Huaxi | 50 mL +1 0% GS 250ml/iv gtt qd | injection | 10d |
| Zhang 2002 | Huaxi | 60 mL + 5% GS 250ml/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d |
| Cen 1999 | 100mL + 5% GS 150ml/iv gtt qd | injection | 20d | |
| He 2004 | Huaxi | 20‐40 mL + GS /iv gtt qd | injection | 14d |
| Mao 2003 | Yibin | 20,40,60 mL + 5% 200 mL polarized solution /iv gtt qd | injection | 14d |
| Liao 1996 | 50 mL + 10% GS 250 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 10d | |
| Cheng 2001 | Suzhong | 40‐60 mL + 5% GS 250‐500 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | (10‐15d)*1.5 |
| Wang 2004 | Suzhong | 20‐30 mL +5% GS 250 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d |
| Li 2003 | Suzhong | 30 mL +5 % GS 250 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 21d |
| Hu 1998 | Suzhong | 10 mL + 5% GS 200 mL/iv gtt q12h | injection | 10d |
| He 2001 | Suzhong | 40‐60 mL + 5% GS 250 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d |
| Li 2004 | Hehuang | 60 mL + 5% GS 250‐500 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 15d |
| Wang 1997b | 60 mL +5% GS 250 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d | |
| Li 1998b | Huaxi | 40 mL /iv gtt qd | injection | 10d |
| Tang 2001 | 20 mL +10% GS 250 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d | |
| Li 1998a | Huaxi | 30‐50 mL + 10% GS 250 mL/iv gtt q12h | injection | 15d |
| Mao 1998 | Yibin | 100 mL +5% GS 250‐500 mL/iv gtt qd | injection | 14d*(1‐2) |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Lack of improvement in heart failure ( NYHA class improved < I class or worsening of heart failure) Show forest plot | 18 | 1606 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.25, 0.40] |
| 2 mortality at the end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3 cardiac output (L/min) change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4 stroke volume (ml) change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5 cardiac index change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6 eject fraction change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7 system vascular resistance change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 left ventricular minor axis shortened rate change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 ventricular wall thickened rate change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10 Exercise time in movement tolerance test at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11 heart rate multiply systolic blood press (mmHg) at the end of movement tolerance test at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 12 flow mediated dilation of brachial artery volume change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 13 eletrocardiogram QT dispersion change at 20 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 14 electrocardiogram JT dispersion change at 20 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 15 tumor necrosis factor‐alpha change at 14 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 16 endogenous digitalis‐like factors change at 14 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 17 Plasma P‐selectin change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 18 von Willebrand's factor change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 19 D‐dimer change at 2 weeks Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 20 partial pressure of oxygen increase at 10 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 21 partial pressure of carbon dioxide decrease at 10 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 22 B‐type natriuretic peptide change at 15 days Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |