Biomedical risk assessment as an aid for smoking cessation
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Setting: 'smoking clinic', USA | |
| Participants | 550 smokers (defined as >=5 cpd for >=1 year) out of 1104 eligible. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: 30‐days abstinence | |
| Notes | Per protocol analysis. Distribution of baseline 550 participants among the 3 groups not reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Setting: Seychelles Heart Study II | |
| Participants | 155 smokers (defined as >=1 cpd during previous week). | |
| Interventions | Intervention: Ultrasonography of carotid and femoral arteries. Smokers with >= 1 plaque given 2 photographs of their plaque + explanation. + quit‐smoking counselling. | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: 7‐days abstinence | |
| Notes | Two participants lost to follow up not included in analysis | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Setting: 6 general practices, United Kingdom | |
| Participants | 2110 smoker (defined as a person admitting to smoking cigarettes) out of 6052 screened. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: demonstration of patient exhaled CO + verbal advice + booklet. | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: point prevalence | |
| Notes | Odds ratio based on unvalidated data. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Setting: US Veterans Administration Demonstration Project. | |
| Participants | 90 smokers (not defined) | |
| Interventions | Intervention: spirometry, exhaled CO, discussion of pulmonary symptoms + control intervention. | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: point prevalence | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Setting: 11 United Kingdom general practices | |
| Participants | 751 participants out of 4330 identified smokers (self‐defined) | |
| Interventions | Intervention: exhaled CO measure + discussion of significance + control intervention | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: point prevalence. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Setting: 44 general practices, Italy. | |
| Participants | 923 included out of 1009 screened. smoker definition not given. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: Spirometry prescription + control intervention. | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: 7 days abstinence | |
| Notes | In the intervention group, 124 subjects out of 292 reported to have actually had a spirometry test. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
| Methods | Setting:2 primary care clinics, USA | |
| Participants | 205 included out of 360 smokers (self‐defined). | |
| Interventions | Intervention group: Spirometry and exhaled CO + control intervention | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: sustained quitting rate | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Setting: 'stop‐smoking clinic', USA | |
| Participants | 64 out of 141 eligible. (smoker self‐defined) | |
| Interventions | Intervention: exhaled CO and spirometry feedback + Taste Satiation (TS) (in 50%) or Fopcused smoking (FS) (in 50%) and booster sessions for half of each subgroup. | |
| Outcomes | Definition of abstinence: 10 days abstinence | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
CO: Carbon Monoxide
cpd: cigarettes per day
NRT: Nicotine Replacement Therapy
OPD: Outpatient Department
ppm: parts per million
SoC: stage of change
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Effect of spirometry cannot be isolated. | |
| Effect of CO cannot be isolated. No results available. | |
| Full text not available. | |
| Effect of CO cannot be isolated. | |
| Effect of CO cannot isolated. | |
| Effect of spirometry cannot isolated. | |
| Effect of spirometry cannot be isolated. | |
| Effect of spirometry cannot be isolated. | |
| Effect of genetic biomarker feedback cannot be isolated. | |
| Smoking cessation is not considered as an outcome. | |
| Effect of biomarker feedback cannot be isolated. | |
| Effect of CO feedback cannot be isolated. | |
| Effect of biomarker feedback (CO and urinary cotinine) cannot be isolated, combined with 1 counselling session and 4 follow‐up calls. | |
| Biomarker feedback given on the subject's child health, not on his own health. The motivational component here differs from the approach in the other included studies. |
CO: carbone monoxide
NRT: Nicotine Replacement Therapy
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 CO (primary care) Show forest plot | 2 | 1791 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.83, 1.39] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Smoking cessation, Outcome 1 CO (primary care). | ||||
| 2 All interventions Show forest plot | 8 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Smoking cessation, Outcome 2 All interventions. | ||||
| 2.1 CO (primary care) | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 Genetic marker (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 Carotid US (health survey, Seychelles) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.4 Spirometry (primary care) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.5 CO and Spirometry (primary care) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.6 CO and Genetic marker (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.7 CO (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.8 CO and Spirometry (veterans health prom. clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.9 CO and Spirometry (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
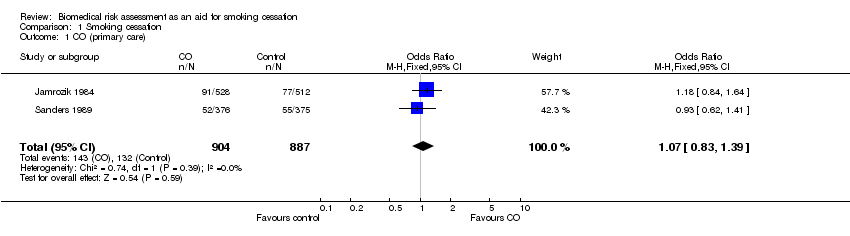
Comparison 1 Smoking cessation, Outcome 1 CO (primary care).

Comparison 1 Smoking cessation, Outcome 2 All interventions.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 CO (primary care) Show forest plot | 2 | 1791 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.83, 1.39] |
| 2 All interventions Show forest plot | 8 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 CO (primary care) | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 Genetic marker (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 Carotid US (health survey, Seychelles) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.4 Spirometry (primary care) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.5 CO and Spirometry (primary care) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.6 CO and Genetic marker (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.7 CO (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.8 CO and Spirometry (veterans health prom. clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.9 CO and Spirometry (smoking clinic) | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |

