Infusión continua versus intermitente para la prevención de la pérdida de función de los catéteres intravenosos periféricos utilizados para la administración de fármacos en recién nacidos
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Multi‐centre randomised controlled trial with treatment group allocation determined by computer generated randomisation. Assessment of the following key criteria: | |
| Participants | Neonates in the neonatal nursery who do not require IV fluids. Number of infants = 95 Number of catheters = 238 | |
| Interventions | Continuous infusion (CI) using 0.5‐1 mL of 10% Dextrose; or | |
| Outcomes | Proportion of catheters with: | |
| Notes | The infants were randomised and allocated to either group, but the data were analysed and reported by catheter. The lead author of this study was contacted for further information regarding this study: additional data were available on the duration of patency for the first catheter used per infant. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial. The randomisation method was not stated. Assessment of the following key criteria: | |
| Participants | Newborn infants who were admitted to the 'intermediate care' nursery who either 1. required intravenous medications but no additional intravenous fluids, or 2. had an umbilical arterial catheter in situ and required an intravenous cannula for medications. Number of infants = 39 | |
| Interventions | Continuous infusion (CI) using 10% dextrose (without heparin) at a rate of 1.5 to 3.0 ml/hr; or | |
| Outcomes | Outcome measures included: | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Abbreviations
CI‐continuous infusion
IF‐intermittent infusion
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Did not compare continuous infusion with intermittent flushes. | |
| Historical cohort comparison only; did not compare continuous infusion with intermittent flushes. | |
| Did not compare continuous infusion with intermittent flushes. | |
| Did not compare continuous infusion with intermittent flushes. | |
| Did not compare continuous infusion with intermittent flushes. |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Duration of cannula patency for the first cannula used per infant (hours) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.1 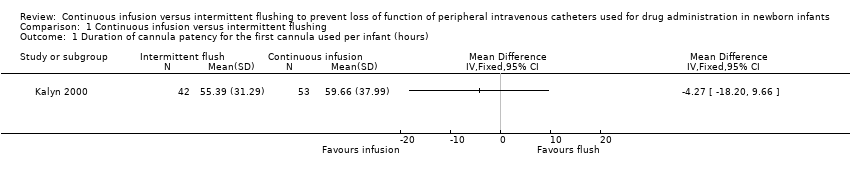 Comparison 1 Continuous infusion versus intermittent flushing, Outcome 1 Duration of cannula patency for the first cannula used per infant (hours). | ||||
| 2 Number of cannulas used per infant in the first 48 hours Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Continuous infusion versus intermittent flushing, Outcome 2 Number of cannulas used per infant in the first 48 hours. | ||||
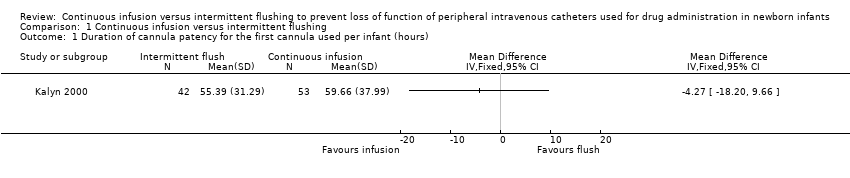
Comparison 1 Continuous infusion versus intermittent flushing, Outcome 1 Duration of cannula patency for the first cannula used per infant (hours).

Comparison 1 Continuous infusion versus intermittent flushing, Outcome 2 Number of cannulas used per infant in the first 48 hours.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Duration of cannula patency for the first cannula used per infant (hours) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2 Number of cannulas used per infant in the first 48 hours Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |

