Ventilasi mekanikal untuk sklerosis lateral amiotrofik/penyakit neuron motor
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | 41 participants with ALS Age: 63.7 ± 10.3 and 63.0 ± 8.1 years Male sex 64% and 53% Disease duration 1.9 ± 1.3 and 2.0 ± 1.1 years Baseline characteristics: vital capacity (% predicted) 55.6 ± 18.7% and 48.8 ± 20.7%, maximum inspiratory pressure ‐ Pimax (% predicted) 31.1 ± 11.0% and 31.0 ± 10.6%, SNIP (% predicted) 22.6 ± 11.4% and 24.4 ± 10.8%, PaCO2 (mmHg) 6.1 ± 1.1 and 6.4 ± 1.2 in NIV and standard care group respectively at randomisation (mean ± SD) | |
| Interventions | Intervention: NIV (n = 22) Control: standard care (n = 19) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: overall survival after initiation of assisted ventilation Secondary outcomes: survival at 1 and 6 months, SF‐36, and SAQLI | |
| Funding | ResMed UK Ltd and the Motor Neurone Disease Association provided funding for the study. | |
| Conflicts of interest for primary investigators | No reported conflicts of interest | |
| Notes | Protocol: ISRCTN76330611 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Immediate allocation following randomisation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not possible to blind delivery of the non‐invasive ventilation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | No information given on whether outcome assessors were blinded to knowledge of allocation intervention when assessing the data. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 13 withdrawals during surveillance, but no participants withdrew after randomisation. 1 participant alive 45 months after randomisation; all others were followed up to death. All outcome measures were measured by intention to treat. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is available, and all of the study’s prespecified (primary and secondary) outcomes that are of interest in the review were reported. The report and protocol do not state whether the choice of primary quality of life outcomes in the trial report or the choice of analyses were prespecified, but data were provided for all domains. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other bias identified. |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study | |
| Participants | 7 participants with ALS in early NIPPV group and 6 participants in late NIPPV group No age or sex provided. Baseline characteristics: FVC = 77 ± 13% (mean ± SD) in early NIPPV group at baseline and time of randomisation. FVC = 77 ± 6% (mean ± SD) in late NIPPV at baseline. The time to randomisation (FVC < 50% predicted) for the late NIPPV group = 59 ± 38 days (mean ± SD). | |
| Interventions | Early NIPPV (FVC 70% to 100%) and late ("standard of care") NIPPV (FVC < 50%) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: not available Secondary outcomes: survival at 3 months, SF‐36, ALSFRS‐R, and SAQLI | |
| Funding | National Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Association. Respironics for provision of equipment | |
| Conflicts of interest for primary investigators | No conflicts of interest statement given in the manuscript. | |
| Notes | Pilot study that failed to develop further, due to lack of funding. The study was deemed as at high risk of bias due to selective reporting. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Described as randomised but no method of randomisation stated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | 2 sets of random assignments in blocks of 4 for each centre were prepared by a statistician. Randomisation was carried out separately for bulbar‐ and limb‐onset participants. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants were not blinded to their treatment allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Trial described as a single‐blind study, with pulmonary assessments, ALSFRS‐R, SAQLI, and SF‐36 repeated every 3 months by a blinded clinical evaluator. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Only early NIPPV group analysed, outcome of 1 participant not clear. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Study protocol not available. Numerical data not systematically reported. |
| Other bias | High risk | Nocturnal hypoventilation not defined as per the universally accepted criteria. |
ALS: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
ALSFRS‐R: revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale
FVC: forced vital capacity
NIPPV: non‐invasive positive pressure ventilation
NIV: non‐invasive ventilation
PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood
SAQLI: Sleep Apnea Quality of Life Index
SD: standard deviation
SF‐36: 36‐Item Short Form Health Survey
SNIP: sniff nasal inspiratory pressure
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Not a randomised trial. Observational cohort study of 18 NIV tolerant and 21 NIV non‐tolerant participants with ALS | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study of 89 people with ALS. No control group | |
| Not a randomised trial. Study of the effect of NIV on survival and pulmonary function decline across MND/ALS phenotypes using data from 929 people with ALS/MND | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study without control group. 38 people with ALS received intermittent nasal mechanical ventilation using pressure‐ and volume‐cycled respirators. | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study. 29 people with ALS used nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation, and 50 used tracheostomy intermittent positive pressure ventilation. | |
| Not a randomised trial. No control group. 28 participants received BPAP, and 7 received mechanical ventilation via tracheostomy. | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study without control group. 13 people with ALS received BPAP. | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study of 16 people with ALS receiving assisted ventilation | |
| Primary aim was early initiation of NIV. Once current standard criteria for NIV initiation were reached, both arms were offered NIV. Study did not assess NIV use in people with ALS with respiratory muscle weakness causing ventilator failure or nocturnal hypoventilation with sleep‐disordered breathing. | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study of 13 people with ALS receiving mechanical ventilation | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study of 122 people with ALS. 38 participants used BPAP for more than 4 hours day, 32 participants used BPAP for less than 4 hours a day, and 52 participants refused to try BPAP. | |
| Not a randomised trial. Prospective study of 44 NIV tolerant ALS participants and 27 NIV non‐tolerant participants | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study of 33 consecutive ALS patients in acute respiratory failure receiving tracheostomy intermittent positive pressure ventilation | |
| Not a randomised trial. Prospective cohort study of 16 people with ALS on NIV and 11 normal age‐matched controls | |
| Not a randomised trial. A prospective 1‐year study of the efficacy of NIV for ALS. Comparison group declined NIV. Not blinded | |
| Described in trial registry as a randomised comparison of NIV at night or usual care. Investigator responded to review authors' enquiry in November 2015 that the trial had recruitment problems, was not completed, and there have been no publications. | |
| Does not compare ventilation to no ventilation or standard care; compared high‐level ventilation versus low‐level ventilation (each for 2 hours) | |
| Does not compare ventilation to no ventilation or standard care; this was a comparison of pressure support versus volume‐assisted mode NIV delivered by home care providers. No publication identified. | |
| Listed in trial registry as a randomised controlled trial of non‐invasive ventilation (BPAP) versus no non‐invasive ventilation. The contact person (Dr Lee) informed the review authors that the study was converted into an observational study, as participants were not willing to be randomised, hence the study was not eligible for inclusion. | |
| Randomised trial. Does not compare ventilation to no ventilation or standard care. Polysomnography‐guided adjustment of NIV versus standard initiation of NIV | |
| Randomised trial. Does not compare ventilation to no ventilation or standard care; compared home pressure ventilator model Vivo 40 (BREAS Medical AB) initiated early (when FVC is less than 75% predicted) versus standard initiation (when FVC is less than 50% predicted). No outcome data on NIV, survival, or quality of life available in abstract. | |
| Randomised trial. Does not compare ventilation to no ventilation or standard care; compared different modes of ventilation (intelligent Volume‐Assured Pressure Support (iVAPS) versus standard built‐in self test (BiST) mode) | |
| Randomised trial. Assessment of adaptation to NIV via home‐ or clinic‐based training | |
| Not a randomised trial. Prospective study of 9 people with ALS with hypoventilation given NIPPV, compared with 10 normal age‐matched controls without ventilation problems | |
| Randomised trial terminated early due to problems recruiting participants | |
| Not a randomised trial. Prospective controlled study of 20 consecutive patients, first 10 received standard care and following 10 received NIV | |
| Not a randomised trial. Controlled study of exercise in people with ALS with respiratory insufficiency. 8 participants on NIV and 12 ALS controls | |
| Not a randomised trial. Historical controls | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective review of 25 cases using positive pressure ventilation with tracheostomy | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective review of 13 cases | |
| Not a randomised trial. Anecdotal study | |
| Not a randomised trial. Retrospective study without control group. 20 ALS participants received NIPPV. |
ALS: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
BPAP: bilevel positive airway pressure
MND: motor neuron disease
NIPPV: non‐invasive positive pressure ventilation
NIV: non‐invasive ventilation
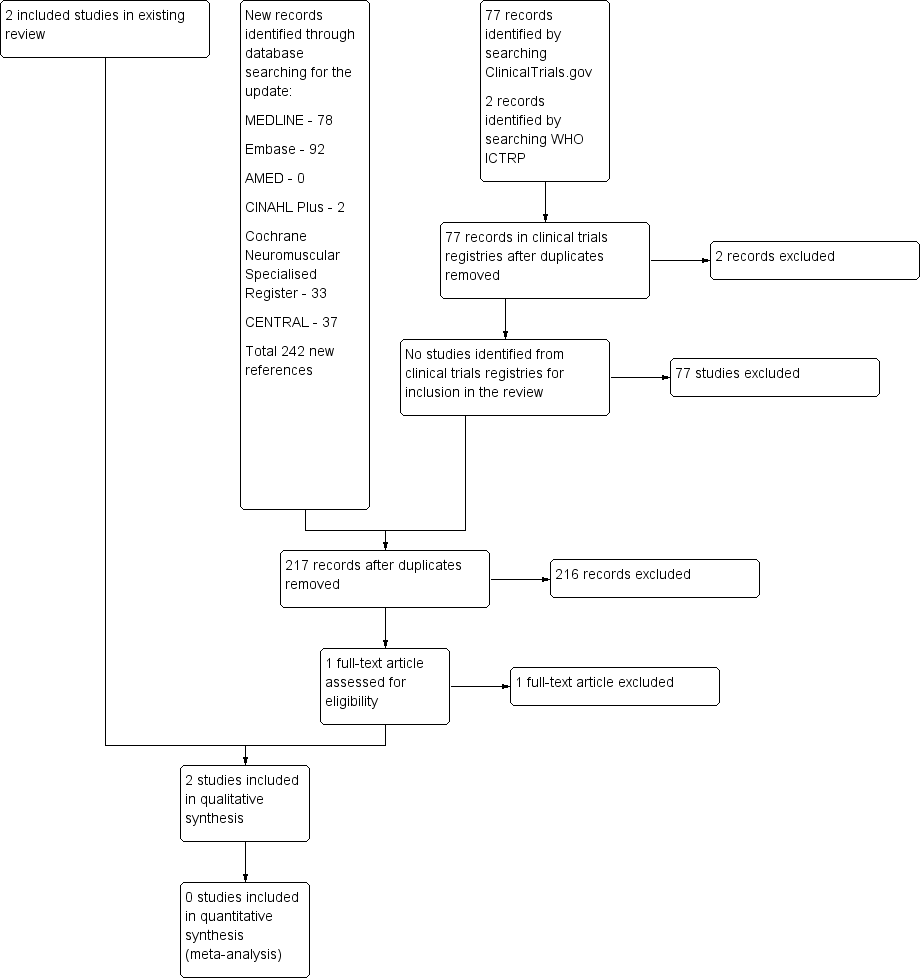
A flow diagram illustrating the study selection process.

Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study. A green plus sign indicates low risk of bias; a red minus sign indicates high risk of bias; and a yellow question mark indicates unclear risk of bias.
| Non‐invasive ventilation compared with standard care for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with ALS Settings: people with ALS attending a single regional care centre Intervention: non‐invasive ventilation Comparison: standard care | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No. of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Standard care | Non‐invasive ventilation (NIV) | |||||
| Survival | All participants Median survival was 171 days. | All participants Median survival was 48 days longer (12 to 91 days1 longer). | ‐ | 41 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Moderate2 | 21 of the 41 participants had poor bulbar function. P = 0.0059 better bulbar function, P = 0.92 poor bulbar function |
| Participants with better (good or moderately impaired) bulbar function Median survival was 11 days. | Participants with better (good or moderately impaired) bulbar function Median survival was 205 days longer (CI not given). | |||||
| Participants with poor bulbar function Median survival was 261 days. | Participants with poor bulbar function Median survival was 39 days shorter (CI not given). | |||||
| Quality of life (SF‐36 MCS) | All participants Median duration that SF‐36 MCS remained above 75% of baseline was 99 days. | All participants Median duration that SF‐36 MCS remained above 75% of baseline was 69 days longer (45 to 667 days longer). | ‐ | 41 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Low2,3 | ‐ |
| Participants with better (good or moderately impaired) bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 MCS remained above 75% of baseline was 4 days. | Participants with better (good or moderately impaired) bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 MCS remained above 75% of the baseline was 195 days longer (P = 0.001, CI not given). | |||||
| Participants with poor bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 MCS remained above 75% of baseline was 164 days. | Participants with poor bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 MCS remained above 75% of the baseline was 37 days shorter (P = 0.64, CI not given). | |||||
| Quality of life (SF‐36 PCS) | All participants Median duration that SF‐36 PCS remained above 75% of baseline was 81 days. | All participants Median duration that SF‐36 PCS remained above 75% of baseline was 69 days longer (P = 0.004). | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | CI not given |
| Participants with better (good or moderately impaired) bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 PCS remained above 75% of baseline was 4 days. | Participants with better (good or moderately impaired) bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 PCS remained above 75% of the baseline was 175 days longer (P < 0.001). | |||||
| Participants with poor bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 PCS remained above 75% of baseline was 132 days. | Participants with poor bulbar function Median duration that SF‐36 PCS remained above 75% of the baseline was 18 days longer (P = 0.88). | |||||
| Quality of life (SAQLI) | All participants Median duration that SAQLI remained above 75% of baseline was 99 days. | All participants Median duration that SAQLI remained above 75% of baseline was 74 days longer (P = 0.031). | ‐ | 41 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Low2,3 | CI not given |
| Participants with good or moderately impaired bulbar function Median duration that SAQLI remained above 75% of baseline was 4 days. | Participants with good or moderately impaired bulbar function Median duration that SAQLI remained above 75% of the baseline was 195 days longer (P = < 0.001). | |||||
| Participants with poor bulbar function Median duration that SAQLI remained above 75% of baseline was 132 days. | Participants with poor bulbar function Median duration that SAQLI remained above 75% of the baseline was 29 days shorter (P = 0.77). | |||||
| Adverse events (not reported) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Calculated CIs are approximate. | ||||||
| All participants (n = 41) | Better bulbar function (n = 20) | Poor bulbar function (n = 21) | |||||||
| NIV (n = 22) | Standard care | P | NIV | Standard care | P | NIV (n = 11) | Standard care | P value | |
| SF‐36 MCS | 168 (45 to 1357) | 99 (0 to 690) | 0.0017 | 199 (48 to 552) | 4 (0 to 196) | 0.001 | 127 (45 to 1357) | 164 (2 to 690) | 0.64 |
| SF‐36 PCS | 150 (27 to 908) | 81 (0 to 273) | 0.0014 | 179 (36 to 548) | 4 (0 to 94) | < 0.001 | 150 (27 to 908) | 132 (2 to 273) | 0.88 |
| SAQLI symptoms | 192 (48 to 1357) | 46 (0 to 703) | 0.0013 | 205 (69 to 629) | 4 (0 to 143) | < 0.001 | 143 (48 to 1357) | 100 (2 to 703) | 0.26 |
| SAQLI score | 173 (25 to 1357) | 99 (0 to 645) | 0.031 | 199 (61 to 595) | 4 (0 to 193) | < 0.001 | 103 (25 to 1357) | 132 (2 to 645) | 0.77 |
| Data are median (range). Data from Bourke 2006. Abbreviations: NIV: non‐invasive ventilation; SAQLI: Sleep Apnea Quality of Life Index; SF‐36 MCS: 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey Mental Component Summary; SF‐36 PCS: 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey Physical Component Summary | |||||||||
| All participants (n = 41) | Better bulbar function (n = 20) | Poor bulbar function (n = 21) | |||||||
| NIV | Standard care (n = 19) | P | NIV (n = 11) | Standard care (n = 9) | P | NIV | Standard care (n = 10) | P value | |
| SF‐36 MCS | 2.31 (0 to 11.54) | 0 (0 to 5.23) | 0.0082 | 2.18 (0 to 11.54) | 0 (0 to 1.39) | 0.0052 | 4.47 (0 to 7.75) | 0.88 (0 to 5.23) | 0.24 |
| SF‐36 PCS | 0.18 (0 to 10.62) | 0 (0 to 6.73) | 0.51 | 0.14 (0 to 10.62) | 0 (0 to 0.39) | 0.031 | 0.21 (0 to 5.41) | 0.48 (0 to 6.73) | 0.37 |
| SAQLI symptoms | 1.07 (0 to 3.20) | 0 (0 to 1.14) | < 0.001 | 1.73 (0.52 to 2.95) | 0 (0 to 0) | < 0.001 | 0.90 (0 to 3.20) | 0.04 (0 to 1.14) | 0.018 |
| SAQLI score | 0.44 (0 to 1.59) | 0 (0 to 0.42) | < 0.001 | 0.50 (0 to 0.88) | 0 (0 to 0.07) | < 0.001 | 0.28 (0 to 1.59) | 0.04 (0 to 0.42) | 0.066 |
| Data are median (range) values of area under the curve above baseline divided by time from randomisation to death. Data from Bourke 2006. Abbreviations: NIV: non‐invasive ventilation; SAQLI: Sleep Apnea Quality of Life Index; SF‐36 MCS: 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey Mental Component Summary; SF‐36 PCS: 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey Physical Component Summary | |||||||||

