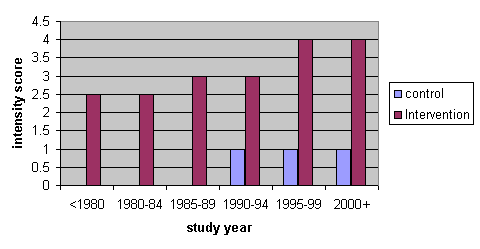
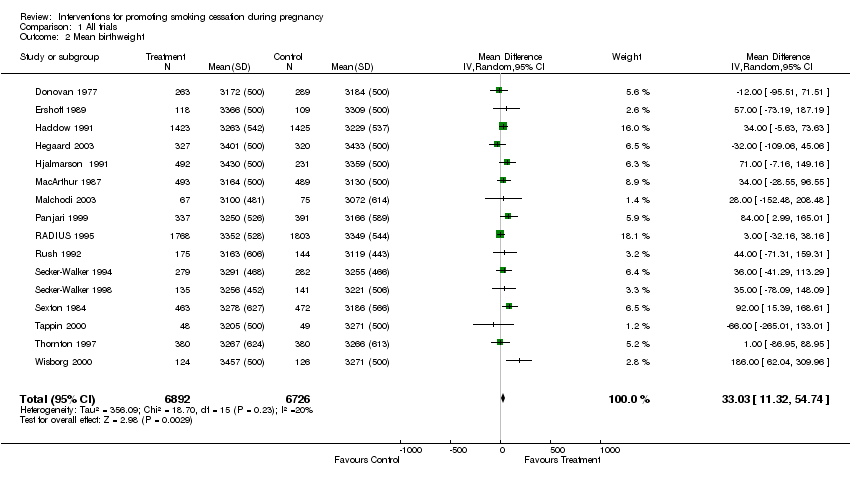
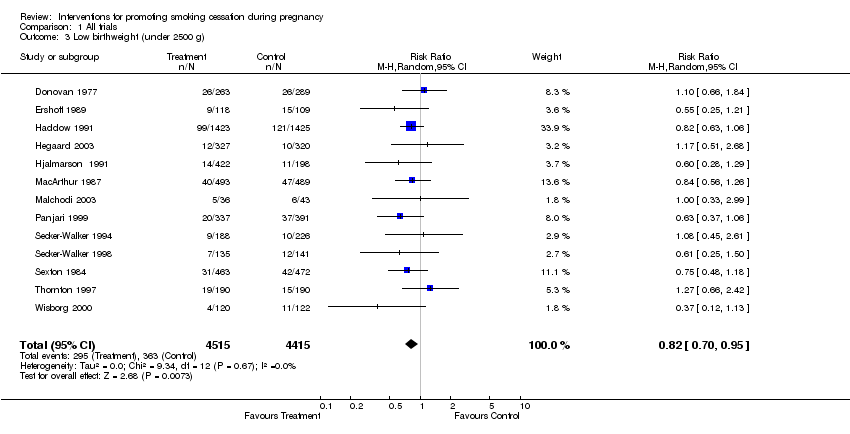
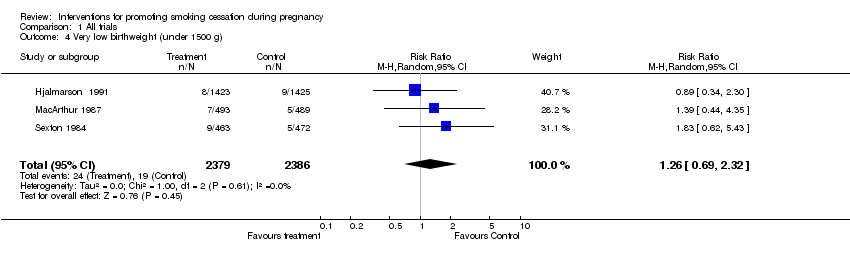
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Catherine Chamberlain, Alison O'Mara‐Eves, Jessie Porter, Tim Coleman, Susan M Perlen, James Thomas, Joanne E McKenzie | 14 febrero 2017
Christine E East, Mary A Biro, Suzanne Fredericks, Rosalind Lau | 1 abril 2019
Heather C Brown, Helen J Smith, Rintaro Mori, Hisashi Noma | 14 octubre 2015
Olukunmi O Balogun, Elizabeth J O'Sullivan, Alison McFadden, Erika Ota, Anna Gavine, Christine D Garner, Mary J Renfrew, Stephen MacGillivray | 9 noviembre 2016
Katharina da Silva Lopes, Yo Takemoto, Erika Ota, Shinji Tanigaki, Rintaro Mori | 6 marzo 2017
Melissa Whitworth, Siobhan Quenby, Ruth O Cockerill, Therese Dowswell | 7 septiembre 2011
Diana M Bond, Philippa Middleton, Kate M Levett, David P van der Ham, Caroline A Crowther, Sarah L Buchanan, Jonathan Morris | 3 marzo 2017
Christine Urquhart, Rosemary Currell, Francoise Harlow, Liz Callow | 15 febrero 2017
Julie Brown, Nisreen A Alwan, Jane West, Stephen Brown, Christopher JD McKinlay, Diane Farrar, Caroline A Crowther | 4 mayo 2017
Shanshan Han, Caroline A Crowther, Philippa Middleton | 18 enero 2012