Tratamiento combinado de primera línea versus monoterapia de primera línea para la hipertensión primaria
References
Referencias de los estudios incluidos en esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en espera de evaluación
Referencias adicionales
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind trial Follow‐up: 36 months | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged ≥ 40 years with hypertension (defined as an untreated systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure ≥ 85 mmHg), history of type 2 diabetes mellitus not exceeding 25 years, urinary albumin excretion rate < 20 μg/min and serum creatinine concentration ≤ 1.5 mg/dL. Exclusion criteria: HbA1c > 11%, non‐diabetic renal disease, heart failure or specific indications or contraindications to ACEI or CCB therapy Country: Italy | |
| Interventions | Monotherapy 1: verapamil SR 240 mg daily Monotherapy 2: trandolapril 2 mg daily Combination therapy: verapamil 180 mg + trandolapril 2 mg daily Target blood pressure 120/80 mmHg. Additional antihypertensive drugs were allowed to achieve the target blood pressure in the following steps: step 1, hydrochlorothiazide or furosemide; step 2, doxazosin, prazosin, clonidine, methyldopa or beta‐blockers (allowed based on of specific indications) and step 3, minoxidil or long‐acting dihydropyridine CCB. Potassium‐sparing diuretics, inhibitors of the renin‐angiotensin system and non‐dihydropyridine CCBs different from the study drugs were not allowed. | |
| Outcomes | Primary endpoint: development of persistent microalbuminuria (urinary albumin excretion ≥ 20 μg/ min at 2 consecutive visits) Other outcomes: urinary albumin excretion, blood pressure after 1 month, major cardiovascular events, overall and cardiovascular mortality, HbA1c, retinal changes, adverse effects and safety laboratory parameters | |
| Funding sources | Abbott GmbH & Co | |
| Declarations of interest | Not reported. | |
| Notes | Trial started March 1997. We used data of participants without previous antihypertensive treatment (verapamil + trandolapril: 115 participants, verapamil: 106 participants, trandolapril: 109 participants) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were assigned to each therapy with a 1:1 ratio according to a computer‐generated randomization list created by the Biometric Unit of Abbott. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The participant randomization number was requested by telephone or fax and was assigned by the Treatment Assignment Secretariat at the Mario Negri Institute (Ranica, Italy) by an independent investigator unaware of treatments' allocation schemes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Study treatments were externally non‐distinguishable pink‐ivory two‐coloured capsules. Investigators, participants, care providers, endpoint evaluators, monitors and data analysts were masked throughout the study. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | All investigators, participants, care providers, endpoint evaluators, monitors and data analysts were masked throughout the study |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Schematic diagram of the trial. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol available. Individual participant data provided. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Inclusion criteria were changed during the trial (from untreated blood pressure ≥ 140/90 mmHg to ≥ 130/85 mmHg). Blood pressure targets were also changed from 130/85 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg (protocol amendment 3; 27 May 1999). Subgroup of participants naive to antihypertensives not predefined. Study not designed for our objectives. |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind trial Follow‐up: 52 weeks | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged 40 to 75 years with type 2 diabetes, hypertension defined as supine systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and <180 mmHg and supine diastolic blood pressure < 110 mmHg, and albumin excretion rate ≥ 20 μg/min and < 500 μg/min in at least 2 of 3 assays Exclusion criteria: HbA1c ≥ 9% within the 3 months before the study, with presumed non‐diabetic kidney disease, serum creatinine ≥ 140 μmol/L, known contraindications to ACEI therapy, or indapamide or other severe disease Countries: Argentina, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Mexico, Morocco, the Netherlands, Poland, Slovakia, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, Tunisia, Turkey, UK | |
| Interventions | Both groups: open 4‐week prerandomization run‐in period of placebo once daily Monotherapy: Enalapril 10 mg daily Combination therapy: perindopril 2 mg + indapamide 0.625 mg once daily Target blood pressure was < 140/90 mmHg. Dose adjustment was permitted after week 12 in double‐blind steps: perindopril 4 mg + indapamide 1.25 mg or enalapril 20 mg then perindopril 8 mg + indapamide 2.5 mg or enalapril 40 mg. Non‐study antihypertensive drugs were not permitted. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: change in the albumin excretion rate after 1 year Secondary outcomes: albumin/creatinine ratio, supine blood pressure and blood pressure response defined as a reduction in systolic blood pressure < 140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg or reduction of systolic blood pressure ≥ 20 mmHg or reduction of diastolic blood pressure ≥ 10 mmHg, or a combination of these. Serious adverse events were predefined as those that were fatal or required prolonged hospitalization. | |
| Funding sources | Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier | |
| Declarations of interest | Not reported | |
| Notes | Trial conducted between March 1997 and January 2001. The trial recruited 481 participants and we used data of 109 participants without previous antihypertensive treatment (perindopril + indapamide: 55 participants; enalapril: 54 participants) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computerized block randomization method used to assign treatments (personal communication). |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | At the beginning of the study, investigators received randomized permutation blocks and the corresponding sealed envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | All study products were supplied in the form of capsules of identical appearance. Prior to the study, the investigator received the therapeutic units and the corresponding coded envelopes. Blister packs and boxes were identified with a unique drug code number for each participant. A 2‐part tear‐off label was affixed to each blister pack and box. When the medication was delivered to the participant, the investigator removed the tear‐off portion of the label and attach it to the participant's case report form. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Investigators provided description of blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | In our subgroup, in monotherapy group there were more withdrawals due to lack of efficacy (6 with monotherapy versus 0 with combination therapy). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Investigators provided results data as requested. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Subgroup of participants naive to antihypertensives not predefined. Study not designed for our objectives. |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind trial Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged 18 to 84 years with essential hypertension defined as a supine systolic blood pressure ≥ 160 mmHg and < 210 mmHg, or a supine diastolic blood pressure ≥ 95 mmHg and < 110 mmHg, or both. In all cases, hypertension was uncomplicated Exclusion criteria: people receiving medication for diabetes, hypocholesteraemia or cardiovascular disease Countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and UK | |
| Interventions | Both groups: 4‐week placebo period Monotherapy: atenolol 50 mg Combination therapy: perindopril 2 mg + indapamide 0.625 mg In both groups, the medication was taken orally in the morning as a single dose. The dosage was then adapted to the blood pressure, and the dose was doubled (2 capsules once daily) after 3 months if systolic blood pressure remained > 160 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg, or both. At the end of the procedure, drug dosage was progressively decreased over 8 to 15 days to avoid any complication caused by atenolol withdrawal. | |
| Outcomes | Brachial systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, pulse pressure, aortic pulse wave velocity, carotid and aortic blood pressures, heart rate, adverse effects Target blood pressure defined as < 140/90 mmHg | |
| Funding sources | INSERM, Association Claude Bernard, GPH‐CV, and Laboratoires Servier | |
| Declarations of interest | Not reported | |
| Notes | Study dates not reported. Trial recruited 471 participants. We used data of 129 participants without previous antihypertensive treatment (perindopril/indapamide: 63 participants; atenolol: 66 participants) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computerized block randomization method used to assign treatments (personal communication) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Prior to the study, the investigator received the therapeutic units and the corresponding coded envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | All study products were supplied in the form of capsules of identical appearance. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | All measurements were analyzed by 2 physicians blinded to treatment, clinical data and physical examination. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | In the whole study, 471 participants were randomized, 354 completed active treatment period but only reasons for 96 withdrawals were provided. There lacked information on 7 participants in the perindopril + indapamide group and 12 participants in the atenolol group. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Investigators provided results data as requested. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Subgroup of participants naive to antihypertensives not predefined. Study not designed for our objectives. |
ACEI: angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor; CCB: calcium channel blocker; HbA1c: glycated haemoglobin; min: minute; SR: slow release.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Follow‐up only 32 weeks | |
| We requested data of participants naive to antihypertensive drugs. Authors provided individual participant data, but there were fewer than 50 participants per group (trandolapril: 39 participants, trandolapril + verapamil: 40 participants). | |
| We requested data of participants naïve to antihypertensive drugs. Authors provided individual participant data, but there were fewer than 50 participants per group (delapril: 33 participants, delapril + manidipine participants: 38). | |
| Single‐blind trial. | |
| Participants entered a run‐in period in which they received ramipril 2.5 mg once daily for 3 days, followed by telmisartan 40 mg + ramipril 2.5 mg once daily for 7 days and then ramipril 5 mg + telmisartan 40 mg for 11 to 18 days; so participants were not naive to antihypertensive treatment at randomization. | |
| We requested data of participants naive to antihypertensive drugs. Authors provided aggregate data, but there were fewer than 50 participants per group (enalapril: 46 participants, perindopril + indapamide: 40 participants). | |
| Not stated that it was a double‐blind trial. No data of any of our primary outcomes. |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, clinical trial Follow‐up: 12 months |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged ≥18 with stage I essential hypertension (defined as sitting systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg and < 160 mmHg and sitting diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg and < 100 mmHg after a 2‐week washout placebo period) Exclusion criteria: type 2 diabetes mellitus, impaired liver or kidney function, anaemia, unstable cardiovascular conditions (e.g. NYHA class I to IV congestive heart failure or a history of myocardial infarction or stroke) or cerebrovascular conditions within 6 months of study enrolment Country: Italy |
| Interventions | Monotherapy 1: olmesartan 20 mg, Monotherapy 2: amlodipine 10 mg Combination therapy: olmesartan 20 mg + amlodipine 5 mg in single tablet |
| Outcomes | Body weight, body mass index, systolic and diastolic blood pressures, fasting plasma glucose, fasting plasma insulin, lipid profile, tumour necrosis factor‐α, retinol binding protein‐4, and interleukins 6 and 7 At baseline, and after 6 and 12 months, participants underwent an euglycaemic, hyperinsulinaemic clamp. |
| Notes | We requested data of outcomes of interest in the subgroup of participants naive to antihypertensive treatment but received no response. There are 6 publications of the trial with the same data, as of February 2016, 5 of them have been retracted. |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, clinical trial Follow‐up: 24 months |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: outpatients aged < 65 years, with a first diagnosed essential hypertension (diastolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg and < 110 mmHg or systolic blood pressure > 140 mmHg and < 180 mmHg, or both), and naive to antihypertensive treatment Exclusion criteria: hypertrophic cardiomyopathies due to aetiologies other than hypertension; history of heart failure, left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 50%, angina, stroke, transient Ischaemic cerebral attack, coronary artery bypass surgery or myocardial infarction any time prior to first visit; concurrent symptomatic arrhythmia; liver dysfunction; creatinine > 1.5 mg/dL; endocrine, infective or inflammatory disorders; use of anti‐inflammatory medications Country: Italy |
| Interventions | Monotherapy 1: enalapril 20 mg once a day Monotherapy 2: lercanidipine 10 mg once a day Combination therapy: enalapril 20 mg + lercanidipine 10 mg once a day |
| Outcomes | Body mass index, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, lipid profile, lipoprotein a, soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products, soluble CD40 ligand, serum myeloperoxidase, high sensitivity C‐reactive protein and tumour necrosis factor‐α |
| Notes | We requested data of outcomes of interest but received no response. There are 2 publications of the trial with the same data, as of February 2016, 1 of them has been retracted. |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, clinical trial Mean follow‐up: 3.5 years |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged 55 to 80 years with hypertension (blood pressure ≥ 150/95 mmHg or ≥ 160 mmHg systolic) and at least 1 additional cardiovascular risk factor: hypercholesterolaemia; smoker (10 cigarettes per day currently or up to 1 year before entry); family history of myocardial infarction in parent or sibling before age 50 years; current left‐ventricular hypertrophy, coronary heart disease; left‐ventricular strain; peripheral vascular disease Countries: Denmark, France, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, UK |
| Interventions | Monotherapy: initially nifedipine 30 mg daily Combination therapy: hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg + amiloride 2.5 mg daily Dose titration was by dose doubling, and addition of atenolol 25 to 50 mg or enalapril 5 to 10 mg in people whose blood pressure fell by < 20/10 mmHg or was > 140/90 mmHg. |
| Outcomes | Primary: cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, heart failure or stroke Secondary: total mortality; death from a vascular cause; and non‐fatal vascular events including transient ischaemic attacks, angina (new or worsening) and renal failure; serious adverse events |
| Notes | We requested data of outcomes of interest in the subgroup of participants without previous antihypertensive treatment but received no response |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, clinical trial |
| Participants | Aged 40 to 70 years, stage 1 hypertension (140 mmHg to 159 mmHg/90 mmHg to 99 mmHg; > 130 mmHg in people with diabetes); no more than 1 antihypertensive, no previous coronary heart disease and severe chronic disease Country: Brazil |
| Interventions | Monotherapy: losartan starting dose 50 mg, up to 100 mg daily. Combination therapy: chlorthalidone 12.5 mg + amiloride 2.5 mg starting dose up to chlorthalidone 25 mg + amiloride 5 mg daily Amlodipine up to 10 mg daily and propranolol up to 160 mg daily, in an open fashion, will be added if blood pressure is not controlled. |
| Outcomes | Primary: blood pressure variation and proportion of use of add‐on drugs, adverse events, development or worsening of microalbuminuria and left ventricular hypertrophy on electrocardiogram Secondary: fatal or major cardiovascular events: myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary interventions, heart failure, duplication of creatinine. Time frame: 18 months. |
| Notes | Number of participants naïve to antihypertensive drugs not reported. |
| Methods | Multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, event‐driven, clinical trial. Median follow‐up: 24.7 months |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged ≥ 18 years who had had acute myocardial infarction (0.5 to 10 days previously) that was complicated by clinical or radiological signs of heart failure or evidence of left ventricular systolic dysfunction Countries: Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Russia, Slovakia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, UK, US |
| Interventions | Monotherapy 1: valsartan 20 mg twice daily Monotherapy 2: captopril 6.25 mg 3 times daily Combination therapy: valsartan 20 mg twice daily + captopril 6.25 mg 3 times daily Doses were gradually increased with the goal of reaching valsartan 160 mg, captopril 50 mg or valsartan 80 mg + captopril 50 mg at 3 months. Investigators increased or decreased the doses of the study drugs at their discretion according to the participant's clinical status. |
| Outcomes | Primary: all‐cause mortality |
| Notes | Participants were candidates to receive also beta‐blockers. Guidelines discourage the studied combination. We requested data of outcomes of interest for the subgroup of people with hypertension without previous treatment and without additional antihypertensive drugs but received no response. |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Total mortality Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.08, 21.72] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 1 Total mortality. | ||||
| 1.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.08, 21.72] |
| 1.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Cardiovascular mortality Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.2 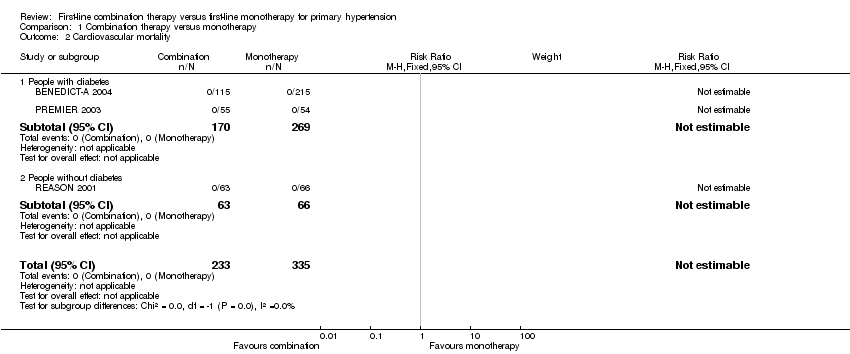 Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 2 Cardiovascular mortality. | ||||
| 2.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Cardiovascular events Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.22, 4.41] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 3 Cardiovascular events. | ||||
| 3.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.10, 3.95] |
| 3.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.14 [0.13, 75.69] |
| 4 Serious adverse events Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.31, 1.92] |
| Analysis 1.4 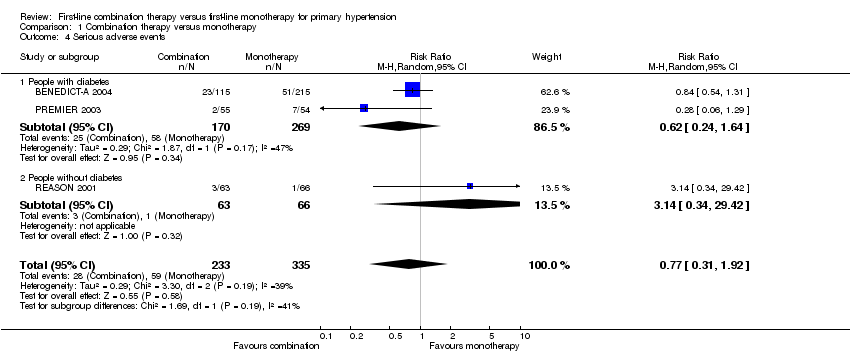 Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 4 Serious adverse events. | ||||
| 4.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.24, 1.64] |
| 4.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.14 [0.34, 29.42] |
| 5 Withdrawals due to adverse effects Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.53, 1.35] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 5 Withdrawals due to adverse effects. | ||||
| 5.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.49, 1.35] |
| 5.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.32, 3.45] |
| 6 Reaching target blood pressure at 1 year Show forest plot | 3 | 548 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.52, 2.54] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 6 Reaching target blood pressure at 1 year. | ||||
| 6.1 People with diabetes, target ≤ 120/80 mmHg | 1 | 314 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.18 [0.01, 3.18] |
| 6.2 People with diabetes, target ≤ 140/90 mmHg | 1 | 105 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [1.24, 3.22] |
| 6.3 People without diabetes, target ≤ 140/90 mmHg | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.62, 1.28] |
| 7 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 3 | 548 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.06 [‐5.39, 1.27] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 7 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year. | ||||
| 7.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 419 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.54 [‐8.27, 3.19] |
| 7.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.33 [‐7.28, 2.62] |
| 8 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 2 | 443 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐1.21, 0.96] |
| Analysis 1.8 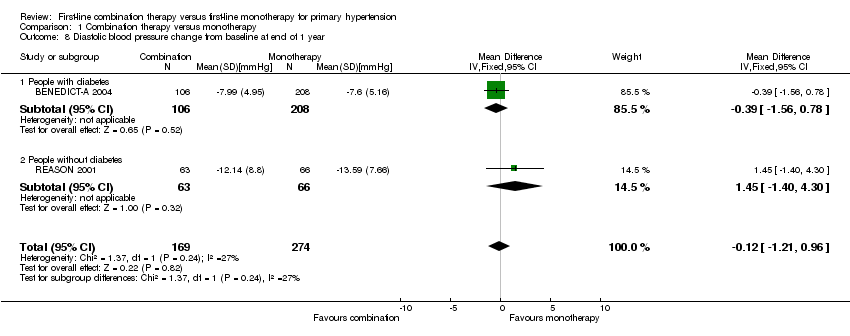 Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 8 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year. | ||||
| 8.1 People with diabetes | 1 | 314 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.39 [‐1.56, 0.78] |
| 8.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.45 [‐1.40, 4.30] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serious adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 1 Serious adverse events. | ||||
| 1.1 Women | 1 | 103 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.52, 3.00] |
| 1.2 Men | 1 | 227 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.75 [0.45, 1.24] |
| 2 Withdrawals due to adverse effects Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 2 Withdrawals due to adverse effects. | ||||
| 2.1 Women | 1 | 103 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [0.43, 3.73] |
| 2.2 Men | 1 | 227 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.42, 1.66] |
| 3 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 3 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year. | ||||
| 3.1 Women | 1 | 97 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.74 [‐2.10, 5.58] |
| 3.2 Men | 1 | 217 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.03 [‐3.25, 1.19] |
| 4 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 4 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year. | ||||
| 4.1 Women | 1 | 97 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [‐1.96, 2.90] |
| 4.2 Men | 1 | 217 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.77 [‐2.08, 0.54] |

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 1 Total mortality.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 2 Cardiovascular mortality.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 3 Cardiovascular events.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 4 Serious adverse events.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 5 Withdrawals due to adverse effects.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 6 Reaching target blood pressure at 1 year.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 7 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year.

Comparison 1 Combination therapy versus monotherapy, Outcome 8 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year.

Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 1 Serious adverse events.

Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 2 Withdrawals due to adverse effects.

Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 3 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year.

Comparison 2 Combination therapy versus monotherapy (men versus women), Outcome 4 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year.
| Combination therapy versus monotherapy for primary hypertension | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with primary hypertension | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Monotherapy | Combination therapy | |||||
| Total mortality | 3 per 1000 | 4 per 1000 | RR 1.35 | 568 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| Cardiovascular mortality | See footnote4 | See footnote4 | Not estimable | 568 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| Cardiovascular events | 9 per 1000 | 9 per 1000 | RR 0.98 | 568 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| Serious adverse events | 176 per 1000 | 136 per 1000 | RR 0.77 | 568 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| Withdrawals due to adverse effects | 128 per 1000 | 109 per 1000 | RR 0.85 | 568 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| *The basis for the assumed is the mean monotherapy group risk across studies. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the combination group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 All data come from subgroups of participants not predefined in the original studies. Outcomes of our review were not the primary outcome in any included trial. | ||||||
| Characteristic | Treatment | Mean (standard deviation) | ||
| Number of participants | Combination | 115 | 55 | 63 |
| Monotherapy | 215 | 54 | 66 | |
| Total participants included in the trial (%) | Combination | 38.08% | 22.78% | 28.09% |
| Monotherapy | 35.54% | 22.54% | 25.82% | |
| Age (years) | Combination | 60.98 (7.62) | 57.27 (8.53) | 52.49 (12.68) |
| Monotherapy | 60.62 (8.36) | 59.93 (8.75) | 50.38 (10.57) | |
| Sex (% men) | Combination | 67.83% | 74.55% | 71.43% |
| Monotherapy | 69.30% | 77.78% | 62.12% | |
| Ethnicity (% white people) | Combination | 100.00% | 96.36% | 98.41% |
| Monotherapy | 100.00% | 88.89% | 93.94% | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | Combination | 28.68 (5.19) | 28.23 (3.18) | 26.85 (3.11) |
| Monotherapy | 28.34 (4.42) | 29.22 (3.51) | 26.99 (2.38) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | Combination | 151.61 (9.70) | 154.56 (9.86) | 162.56 (11.24) |
| Monotherapy | 152.11 (11.57) | 154.04 (11.67) | 158.74 (12.84) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | Combination | 88.72 (7.17) | 90.98 (8.43) | 97.65 (6.89) |
| Monotherapy | 89.54 (6.32) | 91.00 (8.26) | 98.94 (5.07) | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Total mortality Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.08, 21.72] |
| 1.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.08, 21.72] |
| 1.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Cardiovascular mortality Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Cardiovascular events Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.22, 4.41] |
| 3.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.10, 3.95] |
| 3.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.14 [0.13, 75.69] |
| 4 Serious adverse events Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.31, 1.92] |
| 4.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.24, 1.64] |
| 4.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.14 [0.34, 29.42] |
| 5 Withdrawals due to adverse effects Show forest plot | 3 | 568 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.53, 1.35] |
| 5.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 439 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.49, 1.35] |
| 5.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.32, 3.45] |
| 6 Reaching target blood pressure at 1 year Show forest plot | 3 | 548 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.52, 2.54] |
| 6.1 People with diabetes, target ≤ 120/80 mmHg | 1 | 314 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.18 [0.01, 3.18] |
| 6.2 People with diabetes, target ≤ 140/90 mmHg | 1 | 105 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [1.24, 3.22] |
| 6.3 People without diabetes, target ≤ 140/90 mmHg | 1 | 129 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.62, 1.28] |
| 7 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 3 | 548 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.06 [‐5.39, 1.27] |
| 7.1 People with diabetes | 2 | 419 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.54 [‐8.27, 3.19] |
| 7.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.33 [‐7.28, 2.62] |
| 8 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 2 | 443 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐1.21, 0.96] |
| 8.1 People with diabetes | 1 | 314 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.39 [‐1.56, 0.78] |
| 8.2 People without diabetes | 1 | 129 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.45 [‐1.40, 4.30] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serious adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Women | 1 | 103 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.52, 3.00] |
| 1.2 Men | 1 | 227 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.75 [0.45, 1.24] |
| 2 Withdrawals due to adverse effects Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Women | 1 | 103 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [0.43, 3.73] |
| 2.2 Men | 1 | 227 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.42, 1.66] |
| 3 Systolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 Women | 1 | 97 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.74 [‐2.10, 5.58] |
| 3.2 Men | 1 | 217 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.03 [‐3.25, 1.19] |
| 4 Diastolic blood pressure change from baseline at end of 1 year Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.1 Women | 1 | 97 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.47 [‐1.96, 2.90] |
| 4.2 Men | 1 | 217 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.77 [‐2.08, 0.54] |


