Anticoagulación para pacientes con cáncer y catéteres venosos centrales
Appendices
Appendix 1. Full search strategies for the electronic databases ‐ update 2010
| Database | Strategy |
| Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) | #1 heparin OR low molecular weight heparin OR LMWH OR low‐molecular‐weight‐heparin OR nadroparin OR fraxiparin OR enoxaparin OR clexane OR lovenox OR dalteparin OR fragmin OR ardeparin OR normiflo OR tinzaparin OR logiparin OR innohep OR certoparin OR sandoparin OR reviparin OR clivarin OR danaproid OR orgaran #6 1 OR 2 OR 3 OR 4 OR 5 |
| MEDLINE | #1 Heparin/ #12 (Pradaxa or Dabigatran or rivaroxaban or Xarelto or apixaban).tw. |
| Embase | #1 Heparin/ #14 (Pradaxa OR Dabigatran OR rivaroxaban OR Xarelto OR apixaban).tw. |
| ISI (International Scientific Information) the Web of Science | #1 heparin OR low molecular weight heparin OR LMWH OR low‐molecular‐weight‐heparin OR nadroparin OR fraxiparin OR enoxaparin OR clexane OR lovenox OR dalteparin OR fragmin OR ardeparin OR normiflo OR tinzaparin OR logiparin OR innohep OR certoparin OR sandoparin OR reviparin OR clivarin OR danaproid OR orgaran # 5 Pradaxa OR Dabigatran OR rivaroxaban OR Xarelto OR apixaban |
Appendix 2. Full search strategies for the electronic databases ‐ update 2013
| Database | Strategy |
| Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) | #1 MeSH descriptor: [Heparin] explode all trees #2 (LMWH or heparin or nadroparin or fraxiparin or enoxaparin or clexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin or danaproid or orgaran or bemiparin or hibor, badyket, semuloparin, parnaparin, fluxum) #3 MeSH descriptor: [Coumarins] explode all trees #4 (warfarin or coumadin or acenocumarol or phenprocumon or 4‐hydroxicoumarins or oral anticoagulant or vitamin K antagonist or VKA) #5 (fondaparinux or arixtra) #6 (ximelagatran or exanta) #7 (pradaxa or dabigatran or rivaroxaban or xarelto or apixaban or eliquis or edoxaban or lixiana or betrixaban or edoxaban or otamixaban) #8 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 #9 MeSH descriptor: [Neoplasms] explode all trees #10 (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor*) #11 #9 or #10 #12 #8 and #10 |
| MEDLINE | #1 exp Heparin/ #2 (LMWH or heparin or nadroparin or fraxiparin or enoxaparin or clexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin or danaproid or orgaran or bemiparin or hibor, badyket, semuloparin, parnaparin, fluxum).tw. #3 exp Coumarins/ #4 (warfarin or coumadin or acenocumarol or phenprocumon or 4‐hydroxicoumarins or oral anticoagulant or vitamin K antagonist or VKA).tw. #5 (fondaparinux or arixtra).tw. #6 (ximelagatran or exanta).tw. #7 (pradaxa or dabigatran or rivaroxaban or xarelto or apixaban or eliquis or edoxaban or lixiana or betrixaban or edoxaban or otamixaban).tw. #8 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 #9 exp Neoplasms/ #10 (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor*).tw. #11 9 or 10 #12 8 and 11 #13 randomised controlled trial.pt. #14 controlled clinical trial.pt. #15 randomized.ab. #16 placebo.ab. #17 drug therapy.fs. #18 randomly.ab. #19 trial.ab. #20 groups.ab. #21 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 #22 12 and 21 #23 exp animals/ not humans.sh. #24 22 not 23 |
| Embase | #1 heparin/ #2 exp low molecular weight heparin/ #3 (LMWH or heparin or nadroparin or fraxiparin or enoxaparin or clexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin or danaproid or orgaran or bemiparin or hibor, badyket, semuloparin, parnaparin, fluxum).tw. #4 exp coumarin derivative/ #5 (warfarin or coumadin or acenocumarol or phenprocumon or 4‐hydroxicoumarins or oral anticoagulant or vitamin K antagonist or VKA).tw. #6 (fondaparinux or arixtra).tw. #7 (ximelagatran or exanta).tw. #8 (pradaxa or dabigatran or rivaroxaban or xarelto or apixaban or eliquis or edoxaban or lixiana or betrixaban or edoxaban or otamixaban).tw. #9 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 #10 exp neoplasm/ #11 (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor*).tw. #12 10 or 11 #13 9 and 12 #14 crossover procedure/ #15 double‐blind procedure/ #16 randomised controlled trial/ #17 single‐blind procedure/ #18 random*.mp. #19 factorial*.mp. #20 (crossover* or cross over* or cross‐over*).mp. #21 placebo*.mp. #22 (double* adj blind*).mp. #23 (singl* adj blind*).mp. #24 assign*.mp. #25 allocat*.mp. #26 volunteer*.mp. #27 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 #28 13 and 27 #29 (exp animal/ or nonhuman/ or exp animal experiment/) not human/ #30 28 not 29 |
Appendix 3. Full search strategies for the electronic databases ‐ update 2018
| Database | Strategy |
| MEDLINE | RCT search strategy: 1. exp Anticoagulants/ 2. (LMWH* or heparin* or nadroparin* or frixiparin* or enoxaparin* or clexane or klexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin* or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin* or danaproid or danaparoid or orgaran or antixarin or bemiparin* or hibor or zibor or ivor or badyket or semuloparin or parnaparin or tedelparin or fluxum or lohepa or lowhepa or parvoparin or seleparin* or tedelgliparin or lomoparan or orgaran or sulodexide or zivor or embolex or xaparin or clivarine or fondaparinux or Arixtra or UFH or Hepalean or Calcilean or Calciparine or Liquaemin or Liquemin or Multiparin or Novoheparin or Eparina or Hep‐lock or Heparinate or Heparinic acid or Panheprin or Hepalean or Heparin Leo or Heparin Lock).mp. 3. (FR‐860 or FR 860 or FR860 or PK‐10,169 or PK 10,169 or PK10,169 or PK‐10169 or PK 10169 or PK10169 or EMT‐967 or EMT 967 or EMT967 or EMT‐966 or EMT 966 or EMT966 or CY 216 or CY‐216 or CY216 or LMF CY‐216 or LMF CY 216 or LMF CY216).mp. 4. exp Coumarins/ 5. (4‐Hydroxycoumarin* or warfarin* or acenocoumarol or nicoumalone or sinthrome or Sintrom or phenindione or dicoumarol or coumadin or phenprocoumon or phepromaron or ethyl‐biscoumacetate or phenindione or Diphenadione or Tioclomarol or Racumi or Marcoumar or Marcumar or Falithrom or Jantoven or vitamin K antagonist* or VKA or fluindione or difenacoum or coumatetralyl).mp. 6. (Dermatan Sulfate or (Chondroitin Sulfate adj B) or Dermatan Sulphate or DS 435 or MF‐701 or OP‐370 or b‐Heparin or Mistral or Venorix).mp. 7. (thrombin adj inhibitor*).mp. 8. (factor Xa inhibitor* or antithrombin* or anticoagul*).mp. 9. (rivaroxaban or Xarelto or apixaban or Eliquis or dabigatran etexilate or Edoxaban or Savaysa or Betrixaban or ximelagatran or pradaxa or lixiana or exanta or Darexaban or Otamixaban* or Razaxaban or Bivalirudin or Desirudin or Lepirudin or Melagatran or YM 150 or Iprivask or argatrovan or pradax or BIBR‐953 or BIBR‐953ZW or BAY 59‐7939 or BMS‐562247 or DU‐176 or DU‐176b).mp. 10. (TSOAC* or NOAC* or DOAC*).ti,ab,kw. 11. 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 12. exp Neoplasms/ 13. (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor* or glioma* or myeloma* or lymphoma* or leukemia* or leukaemia* or epithelioma* or adenoma*).tw. 14. 12 or 13 15. 11 and 14 16. randomized controlled trial.pt. 17. controlled clinical trial.pt. 18. randomized.ab. 19. placebo.ab. 20. clinical trials as topic.sh. 21. randomly.ab. 22. trial.ti. 23. 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 24. (animals not (humans and animals)).sh. 25. 23 not 24 26. 15 and 25 Systematic Review search strategy: 1. exp Anticoagulants/ 2. (LMWH* or heparin* or nadroparin* or frixiparin* or enoxaparin* or clexane or klexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin* or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin* or danaproid or danaparoid or orgaran or antixarin or bemiparin* or hibor or zibor or ivor or badyket or semuloparin or parnaparin or tedelparin or fluxum or lohepa or lowhepa or parvoparin or seleparin* or tedelgliparin or lomoparan or orgaran or sulodexide or zivor or embolex or xaparin or clivarine or fondaparinux or Arixtra or UFH or Hepalean or Calcilean or Calciparine or Liquaemin or Liquemin or Multiparin or Novoheparin or Eparina or Hep‐lock or Heparinate or Heparinic acid or Panheprin or Hepalean or Heparin Leo or Heparin Lock).mp. 3. (FR‐860 or FR 860 or FR860 or PK‐10,169 or PK 10,169 or PK10,169 or PK‐10169 or PK 10169 or PK10169 or EMT‐967 or EMT 967 or EMT967 or EMT‐966 or EMT 966 or EMT966 or CY 216 or CY‐216 or CY216 or LMF CY‐216 or LMF CY 216 or LMF CY216).mp. 4. exp Coumarins/ 5. (4‐Hydroxycoumarin* or warfarin* or acenocoumarol or nicoumalone or sinthrome or Sintrom or phenindione or dicoumarol or coumadin or phenprocoumon or phepromaron or ethyl‐biscoumacetate or phenindione or Diphenadione or Tioclomarol or Racumi or Marcoumar or Marcumar or Falithrom or Jantoven or vitamin K antagonist* or VKA or fluindione or difenacoum or coumatetralyl).mp. 6. (Dermatan Sulfate or (Chondroitin Sulfate adj B) or Dermatan Sulphate or DS 435 or MF‐701 or OP‐370 or b‐Heparin or Mistral or Venorix).mp. 7. (thrombin adj inhibitor*).mp. 8. (factor Xa inhibitor* or antithrombin* or anticoagul*).mp. 9. (rivaroxaban or Xarelto or apixaban or Eliquis or dabigatran etexilate or Edoxaban or Savaysa or Betrixaban or ximelagatran or pradaxa or lixiana or exanta or Darexaban or Otamixaban* or Razaxaban or Bivalirudin or Desirudin or Lepirudin or Melagatran or YM 150 or Iprivask or argatrovan or pradax or BIBR‐953 or BIBR‐953ZW or BAY 59‐7939 or BMS‐562247 or DU‐176 or DU‐176b).mp. 10. (TSOAC* or NOAC* or DOAC*).ti,ab,kw. 11. 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 12. exp Neoplasms/ 13. (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor* or glioma* or myeloma* or lymphoma* or leukemia* or leukaemia* or epithelioma* or adenoma*).tw. 14. 12 or 13 15. 11 and 14 16. (review or review,tutorial or review, academic).pt. 17. (medline or medlars or embase or pubmed or cochrane).tw,sh. 18. (scisearch or psychinfo or psycinfo).tw,sh. 19. (psychlit or psyclit).tw,sh. 20. cinahl.tw,sh. 21. ((hand adj2 search*) or (manual* adj2 search*)).tw,sh. 22. (electronic database* or bibliographic database* or computeri?ed database* or online database*).tw,sh. 23. (pooling or pooled or mantel haenszel).tw,sh. 24. (peto or dersimonian or der simonian or fixed effect).tw,sh. 25. (retraction of publication or retracted publication).pt. 26. 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 27. 16 and 26 28. meta‐analysis.pt. 29. meta‐analysis.sh. 30. (meta‐analys* or meta analys* or metaanalys*).tw,sh. 31. (systematic* adj5 review*).tw,sh. 32. (systematic* adj5 overview*).tw,sh. 33. (quantitativ* adj5 review*).tw,sh. 34. (quantitativ* adj5 overview*).tw,sh. 35. (methodologic* adj5 review*).tw,sh. 36. (methodologic* adj5 overview*).tw,sh. 37. (integrative research review* or research integration).tw. 38. 28 or 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 39. 27 or 38 41. 15 and 39 |
| Embase | RCT search strategy: 1. exp anticoagulant agent/ 2. (LMWH* or heparin* or nadroparin* or frixiparin* or enoxaparin* or clexane or klexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin* or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin* or danaproid or danaparoid or orgaran or antixarin or bemiparin* or hibor or zibor or ivor or badyket or semuloparin or parnaparin or tedelparin or fluxum or lohepa or lowhepa or parvoparin or seleparin* or tedelgliparin or lomoparan or orgaran or sulodexide or zivor or embolex or xaparin or clivarine or fondaparinux or Arixtra or UFH or Hepalean or Calcilean or Calciparine or Liquaemin or Liquemin or Multiparin or Novoheparin or Eparina or Hep‐lock or Heparinate or Heparinic acid or Panheprin or Hepalean or Heparin Leo or Heparin Lock).mp. 3. (FR‐860 or FR 860 or FR860 or PK‐10,169 or PK 10,169 or PK10,169 or PK‐10169 or PK 10169 or PK10169 or EMT‐967 or EMT 967 or EMT967 or EMT‐966 or EMT 966 or EMT966 or CY 216 or CY‐216 or CY216 or LMF CY‐216 or LMF CY 216 or LMF CY216).mp. 4. exp coumarin derivative/ 5. (4‐Hydroxycoumarin* or warfarin* or acenocoumarol or nicoumalone or sinthrome or Sintrom or phenindione or dicoumarol or coumadin or phenprocoumon or phepromaron or ethyl‐biscoumacetate or phenindione or Diphenadione or Tioclomarol or Racumi or Marcoumar or Marcumar or Falithrom or Jantoven or vitamin K antagonist* or VKA or fluindione or difenacoum or coumatetralyl).mp. 6. (Dermatan Sulfate or (Chondroitin Sulfate adj B) or Dermatan Sulphate or DS 435 or MF‐701 or OP‐370 or b‐Heparin or Mistral or Venorix).mp. 7. (thrombin adj inhibitor*).mp. 8. (factor Xa inhibitor* or antithrombin* or anticoagul*).mp. 9. (rivaroxaban or Xarelto or apixaban or Eliquis or dabigatran etexilate or Edoxaban or Savaysa or Betrixaban or ximelagatran or pradaxa or lixiana or exanta or Darexaban or Otamixaban* or Razaxaban or Bivalirudin or Desirudin or Lepirudin or Melagatran or YM 150 or Iprivask or argatrovan or pradax or BIBR‐953 or BIBR‐953ZW or BAY 59‐7939 or BMS‐562247 or DU‐176 or DU‐176b).mp. 10. (TSOAC* or NOAC* or DOAC*).ti,ab,kw. 11. 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 12. exp neoplasm/ 13. (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor* or glioma* or myeloma* or lymphoma* or leukemia* or leukaemia* or epithelioma* or adenoma*).tw. 14. 12 or 13 15. 11 and 14 16. crossover procedure/ 17. double‐blind procedure/ 18. randomized controlled trial/ 19. single‐blind procedure/ 20. random*.mp. 21. factorial*.mp. 22. (crossover* or cross over* or cross‐over*).mp. 23. placebo*.mp. 24. (double* adj blind*).mp. 25. (singl* adj blind*).mp. 26. assign*.mp. 27. allocat*.mp. 28. volunteer*.mp. 29. 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 30. 15 and 29 Systematic Review search strategy: 1. exp anticoagulant agent/ 2. (LMWH* or heparin* or nadroparin* or frixiparin* or enoxaparin* or clexane or klexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin* or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin* or danaproid or danaparoid or orgaran or antixarin or bemiparin* or hibor or zibor or ivor or badyket or semuloparin or parnaparin or tedelparin or fluxum or lohepa or lowhepa or parvoparin or seleparin* or tedelgliparin or lomoparan or orgaran or sulodexide or zivor or embolex or xaparin or clivarine or fondaparinux or Arixtra or UFH or Hepalean or Calcilean or Calciparine or Liquaemin or Liquemin or Multiparin or Novoheparin or Eparina or Hep‐lock or Heparinate or Heparinic acid or Panheprin or Hepalean or Heparin Leo or Heparin Lock).mp. 3. (FR‐860 or FR 860 or FR860 or PK‐10,169 or PK 10,169 or PK10,169 or PK‐10169 or PK 10169 or PK10169 or EMT‐967 or EMT 967 or EMT967 or EMT‐966 or EMT 966 or EMT966 or CY 216 or CY‐216 or CY216 or LMF CY‐216 or LMF CY 216 or LMF CY216).mp. 4. exp coumarin derivative/ 5. (4‐Hydroxycoumarin* or warfarin* or acenocoumarol or nicoumalone or sinthrome or Sintrom or phenindione or dicoumarol or coumadin or phenprocoumon or phepromaron or ethyl‐biscoumacetate or phenindione or Diphenadione or Tioclomarol or Racumi or Marcoumar or Marcumar or Falithrom or Jantoven or vitamin K antagonist* or VKA or fluindione or difenacoum or coumatetralyl).mp. 6. (Dermatan Sulfate or (Chondroitin Sulfate adj B) or Dermatan Sulfphate or DS 435 or MF‐701 or OP‐370 or b‐Heparin or Mistral or Venorix).mp. 7. (thrombin adj inhibitor*).mp. 8. (factor Xa inhibitor* or antithrombin* or anticoagul*).mp. 9. (rivaroxaban or Xarelto or apixaban or Eliquis or dabigatran etexilate or Edoxaban or Savaysa or Betrixaban or ximelagatran or pradaxa or lixiana or exanta or Darexaban or Otamixaban* or Razaxaban or Bivalirudin or Desirudin or Lepirudin or Melagatran or YM 150 or Iprivask or argatrovan or pradax or BIBR‐953 or BIBR‐953ZW or BAY 59‐7939 or BMS‐562247 or DU‐176 or DU‐176b).mp. 10. (TSOAC* or NOAC* or DOAC*).ti,ab,kw. 11. 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 12. exp neoplasm/ 13. (malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor* or glioma* or myeloma* or lymphoma* or leukemia* or leukaemia* or epithelioma* or adenoma*).tw. 14. 12 or 13 15. 11 and 14 16. exp review/ 17. (literature adj3 review*).ti,ab. 18. exp meta analysis/ 19. exp "Systematic Review"/ 20. 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 21. (medline or medlars or embase or pubmed or cinahl or amed or psychlit or psyclit or psychinfo or psycinfo or scisearch or cochrane).ti,ab. 22. RETRACTED ARTICLE/ 23. 21 or 22 24. 20 and 23 25. (systematic* adj2 (review* or overview)).ti,ab. 26. (meta?anal* or meta anal* or meta‐anal* or metaanal* or metanal*).ti,ab. 27. 24 or 25 or 26 28. 15 and 27 |
| CENTRAL (the Cochrane Library, latest issue) | #1 MeSH descriptor: [Anticoagulants] explode all trees #2 (LMWH* or heparin* or nadroparin* or frixiparin* or enoxaparin* or clexane or klexane or lovenox or dalteparin or fragmin or ardeparin* or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin* or danaproid or danaparoid or orgaran or antixarin or bemiparin* or hibor or zibor or ivor or badyket or semuloparin or parnaparin or tedelparin or fluxum or lohepa or lowhepa or parvoparin or seleparin* or tedelgliparin or lomoparan or orgaran or sulodexide or zivor or embolex or xaparin or clivarine or fondaparinux or Arixtra or UFH or Hepalean or Calcilean or Calciparine or Liquaemin or Liquemin or Multiparin or Novoheparin or Eparina or Hep‐lock or Heparinate or Heparinic acid or Panheprin or Hepalean or Heparin Leo or Heparin Lock) #3 FR‐860 or FR 860 or FR860 or PK‐10,169 or PK 10,169 or PK10,169 or PK‐10169 or PK 10169 or PK10169 or EMT‐967 or EMT 967 or EMT967 or EMT‐966 or EMT 966 or EMT966 or CY 216 or CY‐216 or CY216 or LMF CY‐216 or LMF CY 216 or LMF CY216 #4 MeSH descriptor: [Coumarins] explode all trees #5 (4‐Hydroxycoumarin* or warfarin* or acenocoumarol or nicoumalone or sinthrome or Sintrom or phenindione or dicoumarol or coumadin or phenprocoumon or phepromaron or ethyl‐biscoumacetate or phenindione or Diphenadione or Tioclomarol or Racumi or Marcoumar or Marcumar or Falithrom or Jantoven or vitamin K antagonist* or VKA or fluindione or difenacoum or coumatetralyl) #6 (Dermatan Sulfate or (Chondroitin Sulfate adj B) or Dermatan Sulfphate or DS 435 or MF‐701 or OP‐370 or b‐Heparin or Mistral or Venorix) #7 thrombin near inhibitor* #8 factor Xa inhibitor* or antithrombin* or anticoagul* #9 rivaroxaban or Xarelto or apixaban or Eliquis or dabigatran etexilate or Edoxaban or Savaysa or Betrixaban or ximelagatran or pradaxa or lixiana or exanta or Darexaban or Otamixaban* or Razaxaban or Bivalirudin or Desirudin or Lepirudin or Melagatran or YM 150 or Iprivask or argatrovan or pradax or BIBR‐953 or BIBR‐953ZW or BAY 59‐7939 or BMS‐562247 or DU‐176 or DU‐176b #10 TSOAC* or NOAC* or DOAC* #11 #1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 #12 MeSH descriptor: [Neoplasms] explode all trees #13 malignan* or neoplasm* or cancer* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma* or tumour* or tumor* or glioma* or myeloma* or lymphoma* or leukemia* or leukaemia* or epithelioma* or adenoma* #14 #13 or #14 #15 #11 and #14 |
Appendix 4. GRADE evidence profile: low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH
| Certainty assessment | № of participants | Effect | Certainty | Importance | ||||||||
| № of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | LMWH | No LMWH | Relative | Absolute | ||
| All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 5 | RCTs | Seriousa | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousb | None | 37/689 (5.4%) | 42/547 (7.7%) | RR 0.82 | 14 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 5 | RCTs | Seriousc | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | 17/610 (2.8%) | 32/479 (6.7%) | RR 0.43 | 38 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Critical |
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis measured as asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 5 | RCTs | Seriousd | Not serious | Seriouse | Seriousf | None | 48/610 (7.9%) | 46/479 (9.6%) | RR 0.95 | 5 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Major bleeding (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | Seriousg | Not serious | Not serious | Very serioush | None | 1/575 (0.2%) | 0/443 (0.0%) | RR 1.49 | 0 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| 0.1% | 0 fewer per 1000 | |||||||||||
| Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousi | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousj | None | 15/275 (5.5%) | 11/269 (4.1%) | RR 1.35 | 14 more per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Catheter‐related infection (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousk | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousl | None | 20/300 (6.7%) | 16/174 (9.2%) | RR 0.97 | 3 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | Seriousm | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousn | None | 87/569 (15.3%) | 76/433 (17.6%) | RR 1.03 | 5 more per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
CI: confidence interval; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio.
Explanations
aDowngraded by one level due to serious risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in three studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in four out of five studies.
bDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (36 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (20 per 1000 absolute increase), including 79 events in total.
cDowngraded by one level due to serious risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in four out of five studies.
dDowngraded by one level due to concern about inconsistency, outcome measured as surrogate outcome.
eDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (36 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (40 per 1000 absolute increase), including 94 events in total.
fDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in four out of five studies.
gDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in one study; incomplete outcome data not addressed in four studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in three out of four studies.
hDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for benefit (1 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (35 per 1000 absolute increase), including five events in total. Given the observed baseline risk of 0% we used 0.1% to generate an absolute effect and a confidence interval.
iDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in one study; incomplete outcome data not addressed in two studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in two out of two studies.
jDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (16 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (79 per 1000 absolute increase), including 26 events in total.
kDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; incomplete outcome data not addressed in two studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in one out of two studies.
lDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (35 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (58 per 1000 absolute increase), including 36 events in total.
mDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in two studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in three out of four studies.
nDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (35 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (58 per 1000 absolute increase), including 163 events in total.
Appendix 5. GRADE evidence profile: vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA
| Certainty assessment | № of participants | Effect | Certainty | Importance | ||||||||
| № of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | VKA | No VKA | Relative | Absolute | ||
| All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | Seriousa | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousb | None | 34/353 (9.6%) | 33/348 (9.5%) | RR 0.99 | 1 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 4 | RCTs | Seriousd | Seriouse | Not serious | Not seriousf | None | 36/634 (5.7%) | 51/637 (8.0%) | RR 0.61 | 31 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis measured as asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousg | Not serious | Serioush | Seriousi | None | 8/193 (4.1%) | 14/191 (7.3%) | RR 0.61 | 29 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Major bleeding (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousj | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousk | None | 7/509 (1.4%) | 1/517 (0.2%) | RR 7.14 | 12 more per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousl | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousm | None | 17/509 (3.3%) | 25/517 (4.8%) | RR 0.69 | 15 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Catheter‐related infection (follow‐up: 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | RCT | Seriousn | Not serious | Not serious | Seriouso | None | 22/45 (48.9%) | 18/43 (41.9%) | RR 1.17 | 71 more per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Premature catheter removal (follow‐up: 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | RCT | Seriousn | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousp | None | 6/45 (13.3%) | 7/43 (16.3%) | RR 0.82 | 29 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
CI: confidence interval; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio.
Explanations
aDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in four studies and unclear or no allocation concealment in two out of four studies.
bDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (34 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (52 per 1000 absolute increase), including 67 events in total.
cThe trial WARP showed no overall survival advantage in participants taking warfarin compared with participants in the no‐warfarin group (hazard ratio 0.98, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.25; P = 0.26) (Young 2009)
dDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in four studies and no clear information concerning allocation concealment in one out of four studies).
eDowngraded by one level due to unexplained inconsistency (I2 = 70%). Imprecision was partially driven by the inconsistency between the studies and was taken into consideration when downgrading by two levels for serious risk of bias and serious inconsistency.
fDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (63 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (57 per 1000 absolute increase), including 87 events in total.
gDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies and no clear information about allocation concealment in one out of two studies.
hDowngraded by one level due to concern about inconsistency, outcome measured as surrogate outcome.
iDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (54 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (29 per 1000 absolute increase), including 22 events in total.
jDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies and no clear information about allocation concealment in one out of two studies.
kDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for no effect (0 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (120 per 1000 absolute increase), including eight events in total.
lDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in two out of three studies.
mDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (30 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (16 per 1000 absolute increase), including 42 events in total.
nDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in the included study).
oDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (109 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (356 per 1000 absolute increase), including 40 events in total.
pDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (114 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (202 per 1000 absolute increase), including 13 events in total.
Appendix 6. GRADE evidence profile: low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA)
| Certainty assessment | № of participants | Effect | Certainty | Importance | ||||||||
| № of studies | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | LMWH | VKA | Relative | Absolute | ||
| All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 3 | RCTs | Seriousa | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousb | None | 25/285 (8.8%) | 26/276 (9.4%) | RR 0.94 | 6 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousc | Not serious | Not serious | Very seriousd | None | 6/165 (3.6%) | 3/162 (1.9%) | RR 1.83 | 15 more per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis measured as asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriouse | Not serious | Seriousf | Seriousg | None | 16/159 (10.1%) | 10/158 (6.3%) | RR 1.61 | 39 more per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Pulmonary embolism (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Serioush | Not serious | Not serious | Seriousi | None | 14/165 (8.5%) | 8/162 (4.9%) | RR 1.70 | 35 more per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Major bleeding (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriousj | Not serious | Not serious | Very seriousk | None | 1/147 (0.7%) | 0/142 (0.0%) | RR 3.11 | 0 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| 0.1% | 2 more per 1000 | |||||||||||
| Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | RCTs | Seriousl | Not serious | Not serious | Very seriousm | None | 3/120 (2.5%) | 3/114 (2.6%) | RR 0.95 | 1 fewer per 1000 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Critical |
| Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months)n | ||||||||||||
| 2 | RCTs | Seriouso | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | 61/165 (37.0%) | 35/162 (21.6%) | RR 1.69 | 149 more per 1000 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Critical |
CI: confidence interval; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio.
Explanations
aDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in three studies; and unclear allocation concealment in two out of three studies.
bDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (41 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (56 per 1000 absolute increase), including 51 events in total.
cDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies and unclear allocation concealment in one out of two studies.
dDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (10 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (122 per 1000 absolute increase), including nine events in total.
eDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and unclear allocation concealment in one out of two studies.
fDowngraded by one level due to concern about inconsistency, outcome measured as surrogate outcome.
gDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (16 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (156 per 1000 absolute increase), including 26 events in total.
hDowngraded by one level due to concern both risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and allocation concealment not clear in one out of two studies.
iDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (13 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (144 per 1000 absolute increase), including 22 events in total.
jDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and allocation concealment not clear in one out of two studies.
kDowngraded by two level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for benefit (1 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (51 per 1000 absolute increase), including one event in total. Given the observed baseline risk of 0% we used 0.1% to generate an absolute effect and a confidence interval.
lDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in the study and unclear allocation concealment).
mDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision (95% CI was consistent with the possibility for benefit (21 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (95 per 1000 absolute increase), including six events in total.
nThe study by Lavau‐Denes and colleagues included all grades of thrombocytopenia (even mild cases) (Lavau‐Denes 2013).
oDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and allocation concealment not clear in one out of two studies.
Appendix 7. Detailed results of sensitivity analysis
| Systematic review | CVC |
| Comparison | LMWH vs no LMWH |
| Outcome | Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis |
| CCA effect estimate | RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.81 |
| Sensitivity analysis | |
| All participants with MPD had the event | RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.52 to 1.22 |
| None of participants with MPD had the event | RR 0.42, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.80 |
| Best‐case scenario (intervention: none; control: all) | RR 0.15, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.32 |
| Worst‐case scenario (intervention: all; control: none) | RR 2.06, 95% CI 0.53 to 7.64 |
| RI 1 intervention 1 control | RR 0.42, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.81 |
| RI 1.5 intervention 1 control | RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.85 |
| RI 2 intervention 1 control | RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.89 |
| RI 3 intervention 1 control | RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.97 |
| RI 5 intervention 1 control | RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.24 to 1.12 |
| Systematic review | CVC |
| Comparison | LMWH vs VKA |
| Outcome | Thrombocytopenia |
| CCA effect estimate | RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.20 to 2.39 |
| Sensitivity analysis | |
| All participants with MPD had the event | RR 1.61, 95% CI 1.17 to 2.22 |
| None of participants with MPD had the event | RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.19 to 2.39 |
| Best‐case scenario (intervention: none; control: all) | RR 1.85, 95% CI 1.31 to 2.60 |
| Worst‐case scenario (intervention: all; control: none) | RR 1.46, 95% CI 1.05 to 2.03 |
| RI 1 intervention 1 control | RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.19 to 2.39 |
| RI 1.5 intervention 1 control | RR 1.67, 95% CI 1.18 to 2.36 |
| RI 2 intervention 1 control | RR 1.66, 95% CI 1.18 to 2.34 |
| RI 3 intervention 1 control | RR 1.64, 95% CI 1.16 to 2.31 |
| RI 5 intervention 1 control | RR 1.61, 95% CI 1.15 to 2.27 |
CCA: complete‐case analysis; CI: confidence interval; CVC: central venous catheter; DVT: deep venous thrombosis; LMWH: low‐molecular‐weight heparin; MPD: missing participant data; RR: risk ratio; VKA: vitamin K antagonist.

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
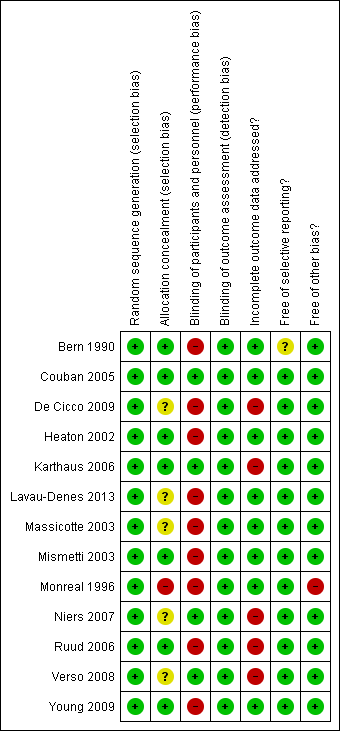
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months).

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 2 Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months).

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 3 Asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months).

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 4 Major bleeding (up to 3 months).

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 5 Minor bleeding (up to 3 months).

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 6 Catheter‐related infection (up to 3 months).

Comparison 1 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus no LMWH, Outcome 7 Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months).
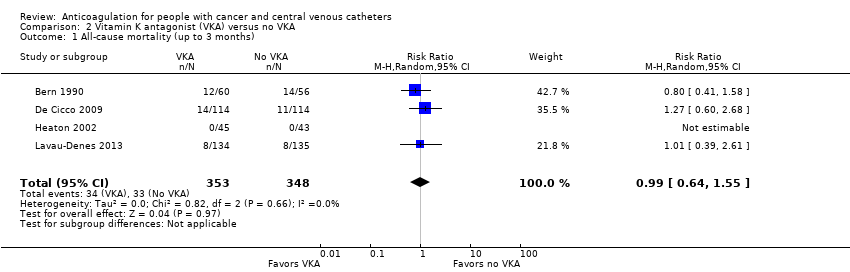
Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months).

Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 2 Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months).

Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 3 Asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis.

Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 4 Major bleeding (up to 3 months).
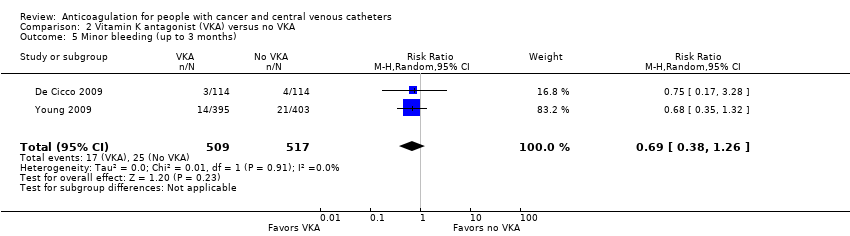
Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 5 Minor bleeding (up to 3 months).
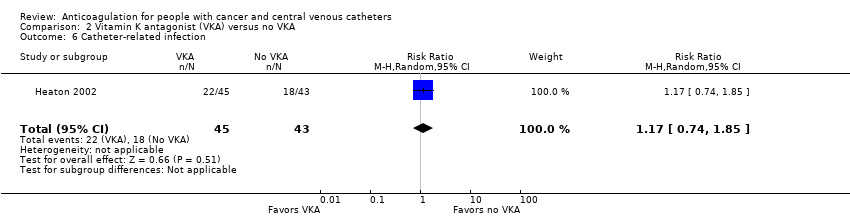
Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 6 Catheter‐related infection.

Comparison 2 Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 7 Premature central venous catheter removal.

Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 1 All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months).
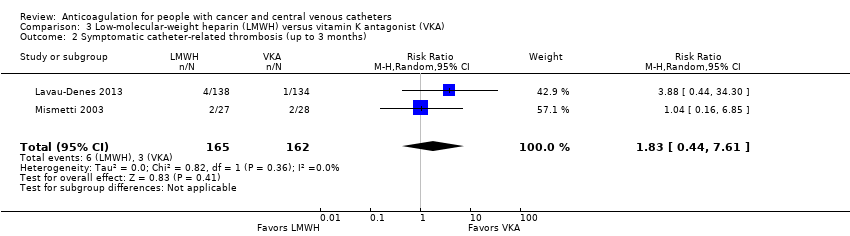
Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 2 Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months).

Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 3 Asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis.

Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 4 Pulmonary embolism (up to 3 months).
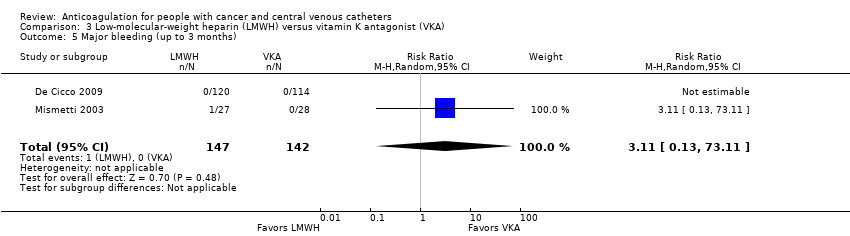
Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 5 Major bleeding (up to 3 months).

Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 6 Minor bleeding (up to 3 months).

Comparison 3 Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) versus vitamin K antagonist (VKA), Outcome 7 Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months).
| Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) compared to no LMWH for people with cancer and central venous catheters | |||||
| Patient or population: people with cancer with thrombosis prophylaxis and central venous catheters Settings: outpatient or inpatient Intervention: LMWH Comparison: no LMWH | |||||
| Outcomes (follow‐up) | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Relative effect | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
| Risk with no LMWH | Risk difference with LMWH | ||||
| All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) | 1236 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.82 | Study population | |
| 77 per 1000 | 14 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | 1089 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | RR 0.43 | Study population | |
| 67 per 1000 | 38 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis measured as asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | 1089 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 0.95 | Study population | |
| 96 per 1000 | 5 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Major bleeding (up to 3 months) | 1018 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 1.49 | Study population | |
| 0 per 1000 | 0 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Low | |||||
| 1 per 1000 | 0 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) | 544 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 1.35 | Study population | |
| 41 per 1000 | 14 more per 1000 | ||||
| Catheter‐related infection (up to 3 months) | 474 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.97 | Study population | |
| 92 per 1000 | 3 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months) | 1002 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 1.03 | Study population | |
| 176 per 1000 | 5 more per 1000 | ||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; LMWH: low‐molecular‐weight heparin; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio. | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| aDowngraded by one level due to serious risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in three studies, incomplete outcome data not addressed in three studies, and unclear or no allocation concealment in four out of five studies. bDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (36 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (20 per 1000 absolute increase), including 79 events in total. cDowngraded by one level due to serious risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in four out of five studies. dDowngraded by one level due to concern about inconsistency, outcome measured as surrogate outcome. eDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (36 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (40 per 1000 absolute increase), including 94 events in total. fDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in four out of five studies. gDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in one study; incomplete outcome data not addressed in four studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in three out of four studies. hDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for benefit (1 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (35 per 1000 absolute increase), including five events in total. Given the observed baseline risk of 0% we used 0.1% to generate an absolute effect and a confidence interval. iDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in one study; incomplete outcome data not addressed in two studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in two out of two studies. jDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (16 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (79 per 1000 absolute increase), including 26 events in total. kDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; incomplete outcome data not addressed in two studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in one out of two studies. lDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (35 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (58 per 1000 absolute increase), including 36 events in total. mDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; incomplete outcome data not addressed in two studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in three out of four studies. nDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (35 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (58 per 1000 absolute increase) including 163 events in total. | |||||
| Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) compared to no VKA for people with cancer and central venous catheters | |||||
| Patient or population: people with cancer with thrombosis prophylaxis and central venous catheters Settings: outpatient or inpatient Intervention: VKA Comparison: no VKA | |||||
| Outcomes (follow‐up) | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Relative effect | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
| Risk with no VKA | Risk difference with VKA | ||||
| All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) | 701 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.99 | Study population | |
| 95 per 1000 | 1 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | 1271 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.61 | Study population | |
| 80 per 1000 | 31 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis measured as asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | 384 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 0.61 | Study population | |
| 73 per 1000 | 29 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Major bleeding (up to 3 months) | 1026 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 7.14 | Study population | |
| 2 per 1000 | 12 more per 1000 | ||||
| Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) | 1026 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.69 | Study population | |
| 48 per 1000 | 15 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Catheter‐related infection | 88 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 1.17 | Study population | |
| 419 per 1000 | 71 more per 1000 | ||||
| Premature CVC removal | 88 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.82 | Study population | |
| 163 per 1000 | 29 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; CVC: central venous catheter; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio; VKA: vitamin K antagonist. | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| aDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in four studies and unclear or no allocation concealment in two out of four studies. bDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (34 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (52 per 1000 absolute increase), including 67 events in total. cThe trial WARP showed no overall survival advantage in participants taking warfarin compared with participants in the no‐warfarin group (hazard ratio 0.98, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.25; P = 0.26) (Young 2009). dDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in four studies and no clear information concerning allocation concealment in one out of four studies). eDowngraded by one level due to unexplained inconsistency (I2 = 70%). Imprecision was partially driven by the inconsistency between the studies and was taken into consideration when downgrading by two levels for serious risk of bias and serious inconsistency. fDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (63 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (57 per 1000 absolute increase), including 87 events in total. gDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies and no clear information about allocation concealment in one out of two studies. hDowngraded by one level due to concern about inconsistency, outcome measured as surrogate outcome. iDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (54 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (29 per 1000 absolute increase), including 22 events in total. jDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies and no clear information about allocation concealment in one out of two studies. kDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for no effect (0 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (120 per 1000 absolute increase), including eight events in total. lDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in three studies; and unclear or no allocation concealment in two out of three studies. mDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (30 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (16 per 1000 absolute increase), including 42 events in total. nDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in the included study). oDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (109 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (356 per 1000 absolute increase), including 40 events in total. pDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (114 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (202 per 1000 absolute increase), including 13 events in total. | |||||
| Low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) compared to vitamin K antagonist (VKA) for people with cancer and central venous catheters | |||||
| Patient or population: people with cancer with thrombosis prophylaxis and central venous catheters Settings: outpatient or inpatient Intervention: LMWH Comparison: VKA | |||||
| Outcomes (follow‐up) | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Relative effect | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
| Risk with VKA | Risk difference with LMWH | ||||
| All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) | 561 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.94 | Study population | |
| 94 per 1000 | 6 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | 327 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 1.83 | Study population | |
| 19 per 1000 | 15 more per 1000 | ||||
| Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis measured as asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) | 317 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 1.61 | Study population | |
| 63 per 1000 | 39 more per 1000 | ||||
| Pulmonary embolism (up to 3 months) | 327 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 1.70 | Study population | |
| 49 per 1000 | 35 more per 1000 | ||||
| Major bleeding (up to 3 months) | 289 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 3.11 | Study population | |
| 0 per 1000 | 0 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Low | |||||
| 1 per 1000 | 2 more per 1000 | ||||
| Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) | 234 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 0.95 | Study population | |
| 26 per 1000 | 1 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months)n | 327 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | RR 1.69 | Study population | |
| 216 per 1000 | 149 more per 1000 | ||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; LMWH: low‐molecular‐weight heparin; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: risk ratio; VKA: vitamin K antagonist. | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| aDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in three studies; and unclear allocation concealment in two out of three studies. bDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (41 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (56 per 1000 absolute increase), including 51 events in total. cDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies and unclear allocation concealment in one out of two studies. dDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (10 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (122 per 1000 absolute increase), including nine events in total. eDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and unclear allocation concealment in one out of two studies. fDowngraded by one level due to concern about inconsistency, outcome measured as surrogate outcome. gDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (16 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (156 per 1000 absolute increase), including 26 events in total. hDowngraded by one level due to concern both risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and allocation concealment not clear in one out of two studies. iDowngraded by one level due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for important benefit (13 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (144 per 1000 absolute increase), including 22 events in total. jDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and allocation concealment not clear in one out of two studies. kDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision; 95% CI was consistent with the possibility for benefit (1 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (51 per 1000 absolute increase), including one event in total. Given the observed baseline risk of 0% we used 0.1% to generate an absolute effect and a confidence interval. lDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in participants and personnel in the study and unclear allocation concealment). mDowngraded by two levels due to concern about imprecision (95% CI was consistent with the possibility for benefit (21 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (95 per 1000 absolute increase), including six events in total. nThe study by Lavau‐Denes and colleagues included all grades of thrombocytopenia (even mild cases) (Lavau‐Denes 2013). oDowngraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias; lack of blinding in participants and personnel in two studies; and allocation concealment not clear in one out of two studies. | |||||
| Term | Definition |
| Adjuvant therapy | Assisting in the amelioration, or cure of disease |
| Anticoagulation | Process of hindering the clotting of blood especially by treatment with an anticoagulant. |
| Antithrombotic | Used against or tending to prevent thrombosis (clotting) |
| Bacteremia | Presence of bacteria in the blood |
| Central venous line | Synthetic tube that is inserted into a central (large) vein to provide temporary intravenous access for the administration of fluid, medication, or nutrients. |
| Coagulation | Clotting |
| Deep venous (vein) thrombosis (DVT) | Condition marked by the formation of a thrombus within a deep vein (as of the leg or pelvis) that may be asymptomatic or be accompanied by symptoms (as swelling and pain) and that is potentially life threatening if dislodgment of the thrombus results in pulmonary embolism |
| Fibrin | White insoluble fibrous protein formed from fibrinogen by the action of thrombin especially in the clotting of blood |
| Fondaparinux | Anticoagulant medication |
| Hemostatic system | System that shortens the clotting time of blood and stops bleeding |
| Heparin | Enzyme occurring especially in the liver and lungs that prolongs the clotting time of blood by preventing the formation of fibrin. 2 forms of heparin that are used as anticoagulant medications are: unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low‐molecular‐weight heparin (LMWH) |
| Impedance plethysmography | Technique that measures the change in blood volume (venous blood volume as well as the pulsation of the arteries) for a specific body segment |
| Kappa statistics | Measure of degree of non‐random agreement between observers or measurements of a specific categorical variable or both |
| Metastasis | Spread of cancer cells from the initial or primary site of disease to another part of the body |
| Oncogene | Gene having the potential to cause a normal cell to become cancerous |
| Osteoporosis | Condition that affects especially older women and is characterized by decrease in bone mass with decreased density and enlargement of bone spaces producing porosity and brittleness |
| Parenteral nutrition | Practice of feeding a person intravenously, circumventing the gastrointestinal tract |
| Pulmonary embolism (PE) | Embolism of a pulmonary artery or 1 of its branches that is produced by foreign matter and most often a blood clot originating in a vein of the leg or pelvis and that is marked by labored breathing, chest pain, fainting, rapid heart rate, cyanosis, shock, and sometimes death. |
| Stroma | Supporting framework of an organ typically consisting of connective tissue |
| Thrombin | Proteolytic enzyme formed from prothrombin that facilitates the clotting of blood by catalyzing conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin |
| Thrombocytopenia | Persistent decrease in the number of blood platelets that is often associated with hemorrhagic conditions |
| Thrombosis | Formation or presence of a blood clot within a blood vessel |
| Vitamin K antagonists (VKA) | Anticoagulant medications that are used for anticoagulation. Warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist |
| Warfarin | Anticoagulant medication that is a vitamin K antagonist that is used for anticoagulation |
| Ximelagatran | Anticoagulant medication |
| LMWH | Generic name | Prophylactic dose | Therapeutic dose |
| Lovenox | Enoxaparin | 40 mg once daily | 1 mg/kg twice daily |
| Fragmin | Dalteparin | 2500‐5000 U once daily | 200 U/kg once daily or |
| Innohep | Tinzaparin, logiparin | 4500 U once daily | 90 U/kg twice daily |
| Fraxiparine | Nadroparin | 35‐75 anti‐Xa IU/kg/day | 175 anti‐Xa IU/kg/day |
| Certoparin | Sandoparin | 3000 anti‐Xa IU once daily | – |
| Reviparin | Reviparin | 1750‐4200 anti‐Xa IU | 7000‐12,600 anti‐Xa IU |
| IU: international units; U: units; Xa: factor Xa. | |||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 5 | 1236 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.53, 1.26] |
| 2 Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 5 | 1089 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.22, 0.81] |
| 3 Asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 5 | 1089 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.62, 1.46] |
| 4 Major bleeding (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 4 | 1018 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.49 [0.06, 36.28] |
| 5 Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 544 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.62, 2.92] |
| 6 Catheter‐related infection (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 474 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.52, 1.79] |
| 7 Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 4 | 1002 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.80, 1.33] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 4 | 701 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.64, 1.55] |
| 2 Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 4 | 1271 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.23, 1.64] |
| 3 Asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis Show forest plot | 2 | 384 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.27, 1.40] |
| 4 Major bleeding (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 1026 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 7.14 [0.88, 57.78] |
| 5 Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 1026 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.38, 1.26] |
| 6 Catheter‐related infection Show forest plot | 1 | 88 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.74, 1.85] |
| 7 Premature central venous catheter removal Show forest plot | 1 | 88 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.30, 2.24] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 All‐cause mortality (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 3 | 561 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.56, 1.59] |
| 2 Symptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 327 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.83 [0.44, 7.61] |
| 3 Asymptomatic catheter‐related thrombosis Show forest plot | 2 | 317 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.61 [0.75, 3.46] |
| 4 Pulmonary embolism (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 327 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.70 [0.74, 3.92] |
| 5 Major bleeding (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 289 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.11 [0.13, 73.11] |
| 6 Minor bleeding (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 1 | 234 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.20, 4.61] |
| 7 Thrombocytopenia (up to 3 months) Show forest plot | 2 | 327 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.69 [1.20, 2.39] |


