Diclorhidrato de zuclopentixol para la esquizofrenia
Appendices
Appendix 1. Previous searches
1. Electronic searches: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's study‐based Register (December 2004) using the phrase:[ ( (**zuclopenthixol* or *ciatyl* or *cisordinol* or *clopenthixol* or *clopixol* or *sordinol*) in REFERENCE) and ( (clopenthixol* or 0‐108* or cisordinol* or clopixol* or zuclopenthix*) in STUDY)]
This register is compiled by systematic searches of major databases, hand searches and conference proceedings (see Group Module).
1.2. Reference searching
We inspected references of all identified studies for more studies.
1.3. Personal contact
We contacted the first author of each included study for more information regarding unpublished trials.
1.4. Drug companies
We contacted the Lundbeck Limited for further data.
2. Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Trials Register (July 2012)
The Trials Search Co‐ordinator searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group’s Trials Register (10 July 2012).
1.1 Intervention search
The ‘Intervention’ field will be searched using the phrase:
((*zuclopenthix* or *ciatyl* or *cisordinol* or *clopenthixol* or *clopixol* or *sordinol*) AND *placebo*)
The Cochrane Schizophrenia Group’s Trials Register is compiled by systematic searches of major databases, handsearches of relevant journals and conference proceedings (see group module).
Trials identified through the searching activities are each assigned to awaiting classification of relevant review titles.
Appendix 2. Previous methods
1. Selection of trials
We independently inspected the citations identified from the search. We identified potentially relevant abstracts and ordered full papers and reassessed these for inclusion and methodological quality. We discussed and reported any disagreement.
2. Quality assessment
We allocated trials to three quality categories, as described in the Cochrane Collaboration Handbook (Higgins 2011). When disputes arose as to which category a trial was allocated, again, we attempted resolution by discussion. When this was not possible and further information was necessary to clarify into which category to allocate the trial, we did not enter data but allocated the trial to the list of those awaiting assessment. We only included trials in Category A or B in the review.
3. Data management
3.1 Data extraction
We independently extracted data from selected trials. When disputes arose, we attempted resolution by discussion. When this was not possible and further information was necessary to resolve the dilemma, we did not enter data but added this outcome of the trial to the list of those awaiting assessment.
3.2 Intention to treat analysis
We excluded data from studies where more than 50% of participants in any group were lost to follow up, except for the outcome of 'leaving the study early'. In studies with less than 50% dropout rate, everyone allocated to the intervention was counted whether or not they completed follow up. We considered those leaving early to have had the negative outcome, except for the event of death and adverse effects.
Where attrition rates were high (25‐50%), we analysed the impact of including this type of data in a sensitivity analysis. If inclusion of high attrition data resulted in a substantive change in the estimate of effect, then we did not pool this data, but presented the data separately.
4. Data analysis
4.1 Binary data
For binary outcomes we calculated a standard estimate of the relative risk (RR) and its 95% confidence intervals (CI) (fixed effect). Where possible, we estimated the number needed to treat (NNT) using an on‐line calculator (http://www.nntonline.net/). If heterogeneity was found (see section 5) we used a random‐effects model.
4.2 Continuous data
4.2.1 Intention‐to‐treat analyses versus analyses that only take into account those who completed the study: in the case of continuous data, it was supposed that in many cases an intention‐to‐treat analysis would not be available, so an analysis was presented on those who completed the study.
4.2.2 Rating scales: A wide range of instruments are available to measure mental health outcomes. These instruments vary in quality and it has been shown that the use of rating scales which have not been described in a peer‐reviewed journal (Marshall 2000) are associated with bias, or may not be valid, or even ad hoc. Therefore, some minimum standards were set: (a) the psychometric properties of the instrument should have been described in a peer‐reviewed journal; (b) the instrument should either be a self‐report, or completed by an independent rater or relative (not the therapist); and (c) the instrument should be a global assessment of an area of functioning.
4.2.3 Normal distribution of data: mental health continuous data are often not normally distributed. Most statistics assume a normal distribution. To avoid including non‐normally distributed data in the statistical analysis we applied the following criteria to all data before inclusion:
a. Standard deviations and means were reported or derivable from data in the paper, or were obtainable from the authors.
b. When a scale started from zero, the standard deviation, when multiplied by two, was less than the mean (as otherwise the mean was unlikely to be an appropriate measure of the centre of the distribution (Altman 1996)). Endpoint scores on scales often have a finite start and end point and this rule can be applied to them.
c. When continuous data are presented on a scale which includes a possibility of negative values (such as change on a scale) it is impossible to tell whether data are non‐normally distributed (skewed) or not. It is thus preferable to use scale end point data, which typically cannot have negative values. If end point data were not available, we chose to use change data, because the statistics used in Metaview are rather robust towards skew.
d. If a scale starts from a positive value (such as PANSS, which can have values from 30‐210) the calculation described above in (b) should be modified to take the scale starting point into account. In these cases skew is present if 2SD> (S‐Smin), where S is the mean score and Smin is the minimum score.
4.2.4 Endpoint versus change data: where possible, we presented endpoint data and if both endpoint and change data were available for the same outcomes then we only reported the former in this review.
4.2.5 Summary statistic: For continuous outcomes we calculated weighted mean differences (WMD) and respective 95% CI (fixed effect). If heterogeneity was found (see section 5) we used a random effects model.
4.3 Cluster trials
Studies increasingly employ 'cluster randomisation' (such as randomisation by clinician or practice) but analysis and pooling of clustered data poses problems. Firstly, authors often fail to account for intra class correlation in clustered studies, leading to a 'unit of analysis' error (Divine 1992) whereby p values are spuriously low, confidence intervals unduly narrow and statistical significance overestimated. This causes type I errors (Bland 1997, Gulliford 1999).
Where clustering was not accounted for in primary studies, we presented the data in a table, with a (*) symbol to indicate the presence of a probable unit of analysis error. In subsequent versions of this review we will seek to contact first authors of studies to obtain intra‐class correlation co‐efficients of their clustered data and to adjust for this using accepted methods (Gulliford 1999). Where clustering has been incorporated into the analysis of primary studies, we will also present these data as if from a non‐cluster randomised study, but adjusted for the clustering effect.
We have sought statistical advice and have been advised that the binary data as presented in a report should be divided by a 'design effect'. This is calculated using the mean number of participants per cluster (m) and the intraclass correlation co‐efficient (ICC) [Design effect = 1+(m‐1)*ICC] (Donner 2002). If the ICC was not reported it was assumed to be 0.1 (Ukoumunne 1999).
Where cluster studies were appropriately analysed taking into account intra‐class correlation coefficients and relevant data documented in the report, synthesis with other studies was possible using the generic inverse variance technique.
5. Test for inconsistency
Firstly, consideration of all the included studies within any comparison was undertaken to estimate clinical heterogeneity. Then visual inspection of graphs was used to investigate the possibility of statistical heterogeneity. This was supplemented employing, primarily, the I‐squared statistic. This provides an estimate of the percentage of inconsistency thought to be due to chance. Where the I‐squared estimate included 75% this was interpreted as evidence of high levels of heterogeneity (Higgins 2003). Data were then re‐analysed using a random effects model to see if this made a substantial difference. If it did, and results became more consistent, falling below 75% in the estimate, the studies were added to the main body trials. If using the random effects model did not make a difference and inconsistency remained high, data were not summated, but were presented separately and reasons for heterogeneity investigated.
6. Addressing publication bias
We entered all data from the included studies into a funnel graph (trial effect against trial size) in an attempt to investigate the likelihood of overt publication bias (Egger 1997).
7. Sensitivity analyses
The effect of including studies with high attrition rates was analysed in a sensitivity analysis.
8. General
Where possible, we entered data in such a way that the area to the left of the line of no effect indicated a favourable outcome for zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride.
Appendix 3. Previous effects of interventions
1. The search
We found a total of 85 citations using the search strategy. Out of these 85 only 26 fulfilled the criteria for our review.
2. COMPARISON 1. ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO
This comparison included two studies (total n=74). Neither study reported global or mental state outcomes.
2.1 Adverse effects
Serafetinides 1972 showed that zuclopenthixol is associated with less orthostatic adverse effects than placebo but not to conventional levels of statistical significance (n=28, 1 RCT, RR 0.29, CI 0.01 to 6.60). The two studies, Serafetinides 1972 and Kordas 1968, reported different extrapyramidal adverse effects but overall zuclopenthixol did increase a persons risk of having any of these symptoms compared with placebo (n=64, RR 5.37, CI 1.12 to 29.34 NNH 2 CI 2 to 31). Other adverse effects reported by Serafetinides 1972 were excitation, sleepiness/sedation and weight change. Excitation, sleepiness/sedation were more prominent with zuclopenthixol than placebo (n=28, 1 RCT, RR 2.89, CI 1.01 to 8.30 NNH 3 CI 2 to 435). However weight gain/loss of ten pounds showed that people in the placebo group were no more prone to lose/gain weight than those in the zuclopenthixol group (n=28, 1 RCT, RR 0.43 CI 0.17 to 1.11).
2.2 Leaving the study early
Serafetinides 1972 reported leaving the study early due to adverse effects and we found fewer people allocated zuclopenthixol left in the short term compared with those given placebo. However these did not meet conventional levels of statistical significance (n=28, RR 0.29 CI 0.01 to 6.6).
3. COMPARISON 2. ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus OTHER TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS (only short term)
This comparison included ten studies (total n=478).
3. 1 Global state
Seven studies presented categorical data on global state and reported these in different ways. We were most frequently able to extract data on the short term outcome of unchanged or worse. Being allocated to the various control drugs was significantly associated with being unchanged or worse, compared with being given zuclopenthixol (n=357, 7 RCTs, RR 0.72 CI 0.53 to 0.98, NNT 10 CI 6 to 131).
3.2 Mental state
There appeared to be no significant difference between about 122 mg/day zuclopenthixol and about 435 mg/day chlorpromazine, on BPRS as a continuous outcome measure (n=41, 1 RCT, WMD ‐2.66 CI ‐9.09 to 3.77). Other BPRS and CPRS data that were too skewed to present graphically also did not point to any difference between groups.
3.3 Adverse effects
Several studies report general adverse effects. None of the findings suggest any clear difference between zuclopenthixol and other typical antipsychotics across a whole range of effects, including movement disorders (n=280, 6 RCTs, RR needing additional antiparkinsonian medication 1.07 CI 0.86 to 1.33) and general agitation (n=162, 3 RCTs, RR needing treatment with hypnotic/sedative drugs 1.09 CI 0.76 to 1.56).
Zuclopenthixol did not clearly cause more adverse effects than other typical antipsychotics.
3.4 Leaving the study early
Although two studies did report the reasons for leaving the study early, most simply stated that people had left and did not specify causes. Fewer people allocated zuclopenthixol left in the short term compared with those given other typical antipsychotics (n=424, 22% vs 30%, 8 RCTs, RR 0.70 CI 0.51 to 0.95, NNT 12 CI 7 to 67).
4. COMPARISON 3. ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS (only short term)
This comparison included three studies (total n=233).
4.1 Global state
Only Huttunen 1995 presented categorical data on global state. We were able to extract data on the short term outcome of unchanged or worse. There was no clear difference between zuclopenthixol and risperidone for the outcome of being 'unchanged or worse' (n=98, 1 RCT, RR 1.30 CI 0.80 to 2.11).
4.2 Mental state
There appeared to be no significant difference between zuclopenthixol and risperidone on 'no clinical response' (n=98, 1 RCT, RR not achieving at least 20% reduction in PANSS total score 1.39 CI 0.92 to 2.10). Other, skewed data, for BPRS also did not show any difference between groups.
4.3 Adverse effects
Three studies comparing zuclopenthixol with atypical antipsychotics reported different adverse effects. Huttunen 1995 reported general adverse effects (n=98) but showed no difference between the two groups. Fischer 1976 reported different specific autonomic adverse effects (n=74): gastrointestinal adverse effects, anticholinergic adverse effects, orthostatic reaction, headache, hypersalivation and dizziness. Again we found no significant differences between those allocated zuclopenthixol and those given atypical antipsychotics.
Huttunen 1995 and Fischer 1976 recorded the different aspects of extrapyramidal adverse effects: needing antiparkinsonian medication, hypokinesia, hyperkinesia, rigor, tremor and akathisia. Huttunen 1995 showed that the zuclopenthixol group had been prescribed with antiparkinsonian medication more frequently compared to people treated with risperidone (n=98, 1 RCT, RR 1.92 CI 1.12 to 3.28, NNH 3 CI 3 to 17). Psychic adverse effects (drowsiness, stimulation, confusion) reported by Fischer 1976, were not different between zuclopenthixol and clozapine (n=74).
Mahadevan 1991 reported weight change as continuous data. We found no significant difference between people allocated zuclopenthixol and those given sulpiride (n=61, 1 RCT, WMD 1.60 CI 8.35 to 5.15).
4.4 Leaving the study early
Huttunen 1995 and Mahadevan 1991 reported the outcome leaving the study early (45% vs 30%) and we found that fewer people allocated atypical antipsychotics left in the short term compared with those given zuclopenthixol but not to conventional levels of statistical significance (n=159, 2 RCTs, RR 1.48 CI 0.98 to 2.22).
5. COMPARISON 4. CIS‐ (Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS (Z)+TRANS (E) FORM OF ZUCLOPENTHIXOL (only short term)
This comparison included four studies (total n=140).
5.1 Global state
Three studies Gravem 1978, Gravem 1981, Heikkila 1981a reported the outcome unchanged or worse in the category of global state but found no difference between the groups (n=131, RR 1.08 CI 0.76 to 1.52).
5.2 Adverse effects
General adverse effects were reported by the same studies. None of the findings suggest any clear difference between cis (z) clopenthixol and cis (z)+ trans (e) clopenthixol (n=131, 3 RCTs, RR interfering with functioning/outweighing therapeutic effect 0.75 CI 0.46 to 1.22).
Gravem 1981 (n=20) found no difference for the frequency of treatment of extrapyramidal adverse effects between the isomers (n=20, RR 1.40, CI 0.67 to 2.94). Gravem 1978 (n=57) provided data for the outcome 'sedation'. Again these researchers found no clear differences between the isomers (RR 0.19 CI 0.02 to 1.55).
5.3 Leaving the study early
Aaes‐Jorgensen 1981b and Gravem 1981 did not show any significant difference for the outcome leaving the study early by only one week (n=29, 2 RCTs, RR 5.0 CI 0.27 to 92.62).
Appendix 4. Previous discussion
1. The studies
Zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride has been widely proposed as a product specifically designed for the management of schizophrenia for inpatients and outpatients (Bhattacharya 1987). Low frequency of adverse effects and good tolerability has also been stressed by open clinical studies and materials produced for marketing purposes (Gravem 1981). In this systematic search for controlled clinical trials we found a small number of studies, some presenting important methodological flaws.
1.1 Applicability of findings
The studies were conducted either in Europe or North America. The majority of trials involved inpatient participants with little in the way of physical and psychiatric co‐morbidity and with well‐defined schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Such people are a minority in everyday care, where it is the norm to find people (not in a hospital setting) who suffer from less well defined illnesses combined with problems such as depression and substance abuse.
1.2 Limited data, confusing data
The collection and quality of the data reported was very variable. All included studies reported data only for the short term (less than 12 weeks). To further undermine the value of the studies, many reported mean figures without giving the standard deviation and therefore these averages were meaningless.
Among the 12 groups of defined outcomes, only five were addressed by the studies. We found no data on hospital and services outcomes, engagement with services, satisfaction with treatment and economic outcomes. There was a lack of information on outcomes that are clinically important such as death, general functioning, behaviour, treatment and hospitalisation. For such a widely used drug there are surprisingly few data. Outcomes were commonly reported using graphs and p‐values instead of tables and confidence intervals. The excessive use of graphs did not allow us to acquire sufficient numbers to calculate many measures of effectiveness.
1.3 Quality of studies
We appreciate that studies in this population group bring unique difficulties. There were however important methodological difficulties with the trials and therefore any conclusions must be viewed with caution. There is a danger of inclusion of at least a moderate risk of bias in these results (Higgins 2011).
2. ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO (only short term)
This comparison included two short, small studies (total n=74) but it is a pity that neither reported global or mental state outcomes. Even from the few data there is indication that zuclopenthixol increases a persons risk of having extrapyramidal adverse effects compared with placebo (NNH 2 CI 2 to 31). Zuclopenthixol is also sedating (NNH 3 CI 2 to 435) but does not definitely cause weight gain in the short term. These may not be unexpected results to clinicians who frequently administer this drug, but as far as we are aware, this is the first time that these effects have been quantified from the best available data.
3. ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus OTHER TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS (only short term)
3.1 Global state
It has often been stated that there is little to choose between one antipsychotic and another. The older drugs are now often placed in one large category but this review does suggest that the compounds may have different levels of efficacy and zuclopenthixol is statistically significantly better than other older drugs in terms of a broad global outcome (n=357, 7 RCTs, RR unchanged or worse 0.72 CI 0.53 to 0.98, NNT 10 CI 6 to 131). However this result comes from small short trials and needs to be replicated. Real differences between drugs could point to subtle effects that can inform future drug design. It is obvious that, like many others, this is an under researched drug and we would be able to ascertain much more concrete evidence regarding the effects of this compound from larger, longer trials.
3.2 Mental state
Data relevant to mental state are few and there is insufficient information on this outcome for us to use in this review.
3.3 Adverse effects
Zuclopenthixol did not clearly cause greater or lesser adverse effects than other typical antipsychotics. At these moderately high doses however, over half of both the treatment and control groups required additional drugs to offset movement disorders. In comparison to newer treatment regimens and more modern drugs, this must be seen as disadvantage of using oral zuclopenthixol, but no more so than for other older drugs given in similar doses.
3.4 Leaving the study early
Many people left these short studies early (22% zuclopenthixol vs 30% control) and data were lost. Although there was less attrition from the zuclopenthixol groups (NNT 12 CI 7 to 67) we would hope, with more modern trial designs, such low follow up could be avoided in the future. It might well be that despite its disadvantages zuclopenthixol is more acceptable than other older drugs which would be an important finding in need of replication.
4. ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS (only short term)
We were surprised to find that zuclopenthixol had been compared to the newer generation of drugs. The new generation are most commonly compared to themselves or older drugs such as haloperidol or chlorpromazine. However the studies were too small and short to be truly informative.
4.1 Global and mental state
With a study size of more than 98, conducted over a longer period of time, we may have been able to ascertain more definite results in the comparison zuclopenthixol versus risperidone. However, at the present time, in terms of global measures and mental state scores given in the trials we uncovered, zuclopenthixol compares favourably with risperidone.
4.2 Adverse effects
If there had been greater standardisation of studies the three relevant trials would not have all reported different adverse effects. With the exception of the movement disorders in terms of general and specific autonomic effects (gastrointestinal, anticholinergic, orthostatic, headache, hypersalivation, dizziness and weight changes), zuclopenthixol was not clearly different from the newer generation of drugs. People did need more additional antiparkinsonian medication however compared to those treated with risperidone (n=98, 1 RCT, RR 1.92 CI 1.12 to 3.28, NNH 3 CI 3 to 17). This is a real practical disadvantage of using zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride, but no more so than for the other older generation drugs.
4.3 Leaving the study early
Normal clinical care would not expect loss to follow up of about 38% across six to ten weeks so it is likely that overall study design promotes attrition. Two studies however did suggest that taking zuclopenthixol may be less acceptable than taking either risperidone or sulpiride (45% vs 30% attrition) and that this did not reach conventional levels of statistical significance (n=159, 2 RCTs, RR 1.48 CI 0.98 to 2.22) may be a function of study size and duration.
5. CIS‐ (Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS (Z)+TRANS (E) FORM OF ZUCLOPENTHIXOL (only short term)
Three studies attempted to highlight differences between the isomers of zuclopenthixol hydrochloride. Studies were small and short and found no clear differences in terms of global state, adverse effects or attrition. Any differences were always likely to be small and therefore studies would have had to be very large, probably with thousands of participants, to highlight clear disparity in effect. In current circumstances, whether or not there really is a clinically meaningful difference between the two isomers is likely to remain unanswered.
6. Missing data
There are no data on outcomes relating to service use (e.g. hospitalisation), relapse, satisfaction with care, behaviour and social function. It would be ideal if newer generation drugs were not widely circulated without such data, but we are sceptical that this is the case considering that three of the studies included in this review are trials of zuclopenthixol versus new compounds.
Note: the 8 citations in the awaiting classification section of the review may alter the conclusions of the review once assessed.
Appendix 5. Previous conclusions
Implications for practice
1. For people with schizophrenia
There is evidence that zuclopenthixol causes movement disorders, perhaps more so than newer drugs, but no more frequently than the other older generation antipsychotics. There is some suggestion from this review that oral zuclopenthixol may have some clinical advantage over other older drugs in terms of global state, at least in the short term. If an older drug is going to be used, zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride is a viable option but may be best taken with additional medication to offset movement disorders that occur in about half the people taking this drug. If the clinical advantage is real, zuclopenthixol does come in a depot form, and these data support those in the review of the depot zuclopenthixol (Coutinho 2004) suggesting a moderate advantage over other similar compounds.
2. For clinicians
There is no evidence that zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride is any worse than other compounds and some indications that it is in fact better. Any difference in the isomers is speculative, but there are some data to suggest a real advantage in comparison with other older drugs. As with other older generation drugs, the use of zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride is tainted by the need for drugs to counter movement disorders. If the advantage, in terms of global effect, over its fellow older generation drugs is real, then zuclopenthixol could be a preferred choice of these older generation drugs. However in light of just these few trials, there does appear to be an advantage for the newer generation of drugs in terms of extrapyramidal adverse effects.
3. For managers/policy makers
There are no data on service outcomes and no medium or long term data. In the context of finite resources, the lack of good quality data leaves managers and policy makers with difficult decisions to make. However, the short term data do favour zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride over several of the older drugs and therefore it should remain a choice in the treatment of people for whom older generation drugs are indicated.
Implications for research
1. General
If the recommendations of the CONSORT statement (Moher 2001) had been anticipated by trialists much more data would have been available. Allocation concealment is essential for the result of a trial to be considered valid and gives the assurance that selection bias is kept to the minimum. Well‐described and tested blinding could have encouraged confidence in the control of performance and detection bias. It is also important to know how many, and from which groups, people were withdrawn, in order to evaluate exclusion bias. It would have been helpful if authors had presented data in a useful manner which reflects association between intervention and outcome, for example, relative risk, odds‐ratio, risk or mean differences, as well as raw numbers. Binary outcomes should be calculated in preference to continuous results, as they are easier to interpret. If p‐values are used, the exact value should be reported.
2. Specific
We do think that more trials are indicated. These should not only be large and long but should also adhere to a pragmatic design in order to increase applicability. Methods should be strict and involve good concealment of allocation and follow up. Participants should be people recognisable in everyday life and not those who are so strictly diagnosed as to render them unrecognisable to routine care. Interventions should involve standard doses of zuclopenthixol and a control drug that is a real choice in the region of the study. This could equally be a new generation drugs such as risperidone, or an older medication such as chlorpromazine. Outcomes should be measured over months rather than weeks as this is the usual period a person would be asked to take the drug. We suggest that if scales are to be used, validated and clinically meaningful outcomes are pre‐defined. Routine outcomes such as relapse, employment, housing status, satisfaction with care, serious or troubling adverse effects can all be easily recorded without the use of scales and we would suggest that these are included in the design of the study.
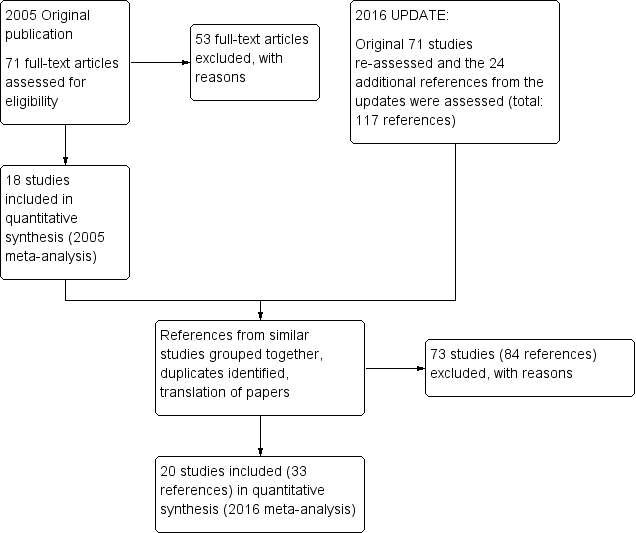
Study flow diagram ‐ update 2016.
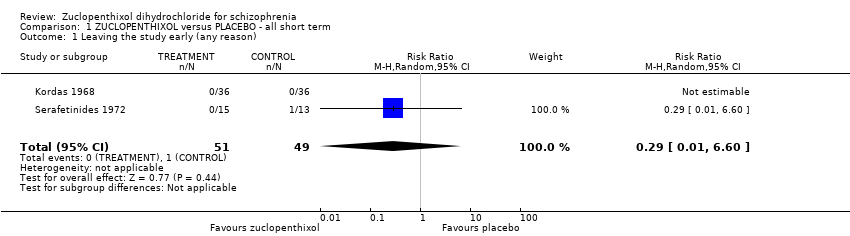
Comparison 1 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Leaving the study early (any reason).
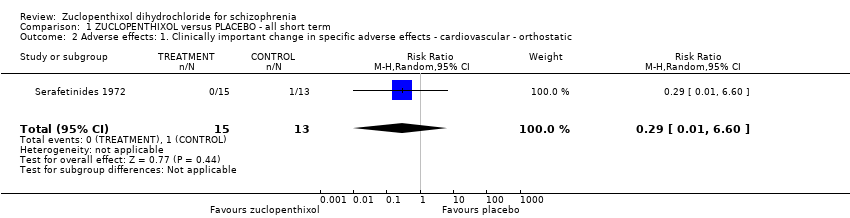
Comparison 1 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO ‐ all short term, Outcome 2 Adverse effects: 1. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ cardiovascular ‐ orthostatic.

Comparison 1 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO ‐ all short term, Outcome 3 Adverse effects: 2. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ central nervous system ‐ arousal state.

Comparison 1 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO ‐ all short term, Outcome 4 Adverse effects: 3. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ endocrine ‐ menstruation started.

Comparison 1 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO ‐ all short term, Outcome 5 Adverse effects: 4a. Any general adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs (UKU side effect rating scale, no scores).

Comparison 1 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PLACEBO ‐ all short term, Outcome 6 Adverse effects: 4b. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs.

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Global state: 1. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI, scores not reported).

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 2 Global state: 2. Average endpoint global state score ‐ No Recovery.

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 3 Global state: 3a. Average endpoint global state score (GAS, high score not reported, average score = 63.4).
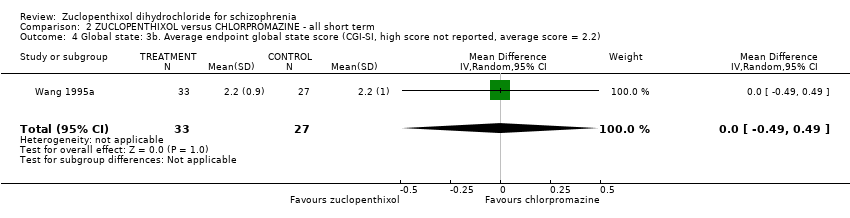
Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 4 Global state: 3b. Average endpoint global state score (CGI‐SI, high score not reported, average score = 2.2).

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 5 Mental state: 1. No clinically important change in general mental state ‐ Not improved (PANSS, scores not reported).
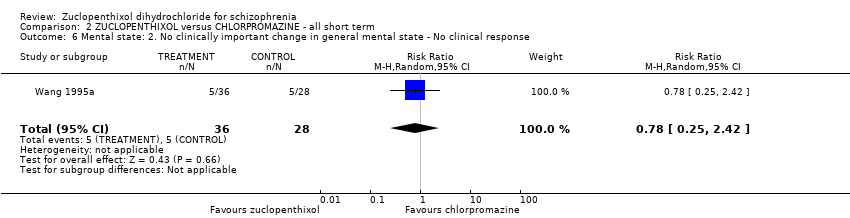
Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 6 Mental state: 2. No clinically important change in general mental state ‐ No clinical response.

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 7 Mental state: 3. Average endpoint general mental state score (BPRS, high score = 34.2).

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 8 Leaving the study early (any reason).
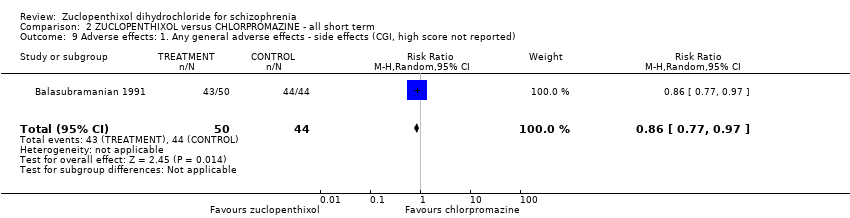
Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 9 Adverse effects: 1. Any general adverse effects ‐ side effects (CGI, high score not reported).
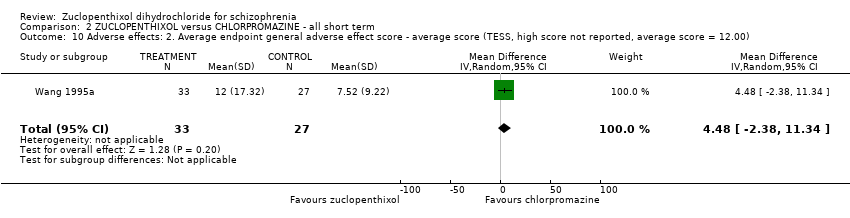
Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 10 Adverse effects: 2. Average endpoint general adverse effect score ‐ average score (TESS, high score not reported, average score = 12.00).
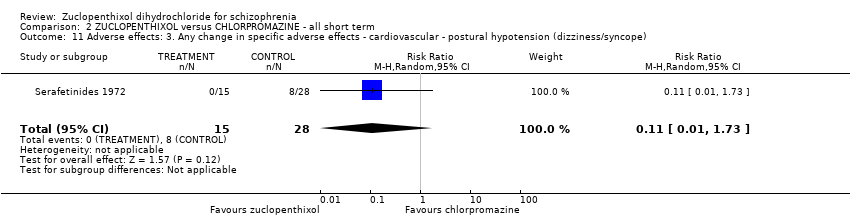
Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 11 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ cardiovascular ‐ postural hypotension (dizziness/syncope).

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 12 Adverse effects: 4. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ central nervous system ‐ arousal.

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 13 Adverse effects: 5. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ metabolic ‐ weight change ‐ loss or gain of weight of 10 pounds.

Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 14 Adverse effects: 6a. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs.
| Study | Zuclopenthixol | Chlorpromazine |
| Kingstone 1970 | n = 5, authors do not state which additional medication. | n = 2, authors do not state which additional medication. |
| Kordas 1968 | Benzhexol and diazepam if necessary. | Benzhexol and diazepam if necessary. |
| Wang 1995a | Trihexphenidyl or scopolamine used if necessary. Authors do not report frequency of use or which group used which. | Trihexphenidyl or scopolamine used if necessary. Authors do not report frequency of use or which group used which. |
Comparison 2 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROMAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 15 Adverse effects: 6b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ additional medication use.
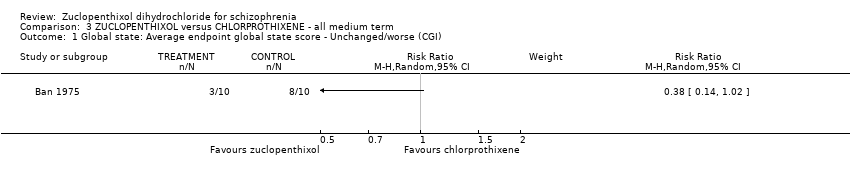
Comparison 3 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROTHIXENE ‐ all medium term, Outcome 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI).

Comparison 3 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CHLORPROTHIXENE ‐ all medium term, Outcome 2 Leaving the study early (any reason).

Comparison 4 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CLOZAPINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Leaving the study early (any reason).
| Study | Zuclopenthixol (n = 36) | Clozapine (n = 38) |
| Fischer‐Cornelssen 1976 | Drowsiness (12%); Stimulation (14%); Confusion (1%); GI (1%); anticholinergic (14%); dizziness (6%); Orthostatic reaction (1%); Headache (2%); Hypersalivation (2%); hypokinesia (4%); hyperkinesia (2%); dyskinesia (0.4%); rigor (5%); tremor (5%); akathisia (3%) | Drowsiness (12%); Stimulation (21%); Confusion (3%); GI (8%); anticholinergic (8%); dizziness (15%); Orthostatic reaction (6%); Headache (3%); Hypersalivation (4%); hypokinesia (2%); hyperkinesia (4%); dyskinesia (0%); rigor (1%); tremor (3%); akathisia (3%) |
Comparison 4 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CLOZAPINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 2 Adverse effects: Any general adverse effects ‐ side effects ‐ frequency per day.
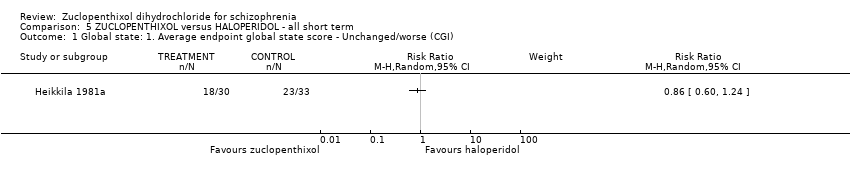
Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Global state: 1. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI).

Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 2 Global state: 2. Average endpoint global state score (CGI, mean score = 1.25).
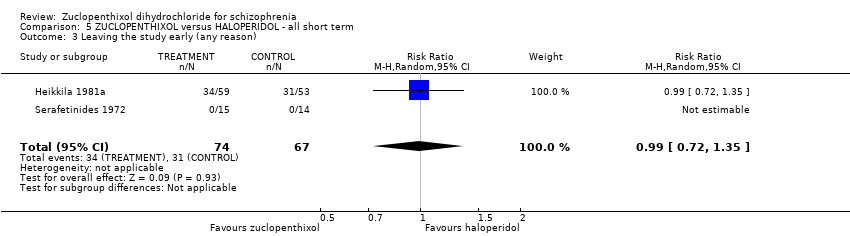
Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 3 Leaving the study early (any reason).

Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 4 Adverse effects: 1. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ interference with functioning.

Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 5 Adverse effects: 2. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs ‐ requiring medication.
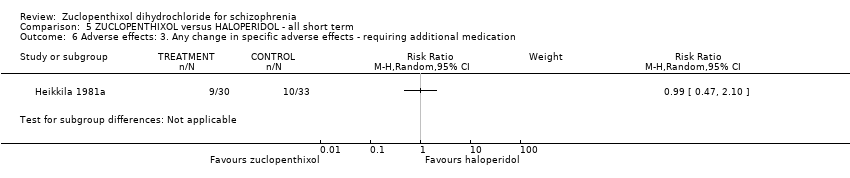
Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 6 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ requiring additional medication.

Comparison 5 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus HALOPERIDOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 7 Adverse effects: 4. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ requiring hypnotics/sedatives.
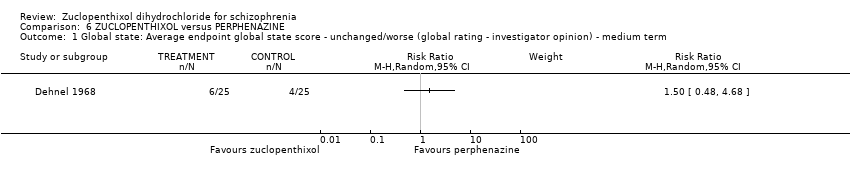
Comparison 6 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PERPHENAZINE, Outcome 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ unchanged/worse (global rating ‐ investigator opinion) ‐ medium term.

Comparison 6 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PERPHENAZINE, Outcome 2 Leaving the study early (any reason) ‐ short/medium term.

Comparison 6 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PERPHENAZINE, Outcome 3 Adverse effects: 1. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ central nervous system ‐ arousal ‐ requiring medication ‐ medium term.
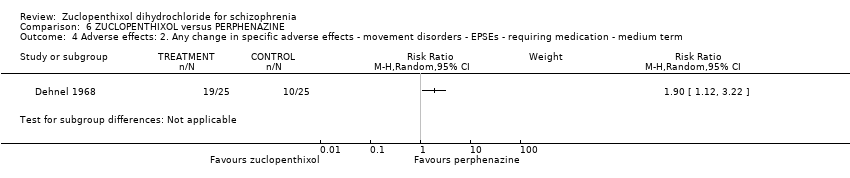
Comparison 6 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus PERPHENAZINE, Outcome 4 Adverse effects: 2. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs ‐ requiring medication ‐ medium term.

Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 1 Mental State: 1. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS, average score = 45.8) ‐ medium term.
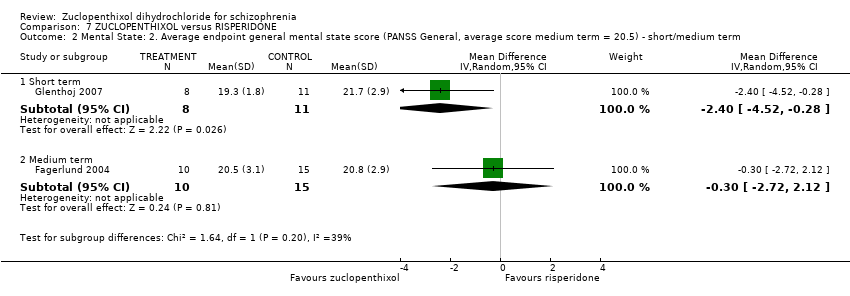
Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 2 Mental State: 2. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS General, average score medium term = 20.5) ‐ short/medium term.
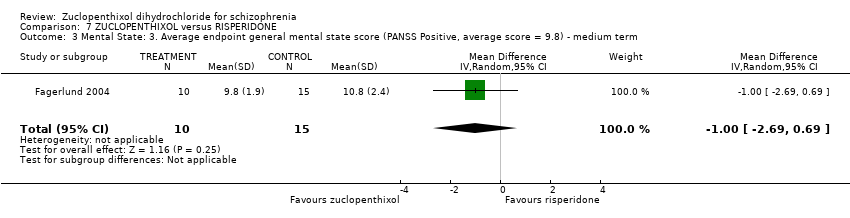
Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 3 Mental State: 3. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS Positive, average score = 9.8) ‐ medium term.

Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 4 Mental State: 4. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS Negative, average score 11.5) ‐ medium term.

Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 5 Leaving the study early (any reason) ‐ short/medium term.
| Study | Zuclopenthixol | Risperidone |
| Fagerlund 2004 | Benzodiazepines n = 7 Anticholinergics n = 11 | Benzodiazepines n = 8 Anticholinergics n = 7 |
| Glenthoj 2007 | Anticholinergic n = 10, Benzodiazepines n = 11, Antidepressant n = 1 | Authors do not differentiate the use of additional medication between the two groups, totals only given. |
Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 6 Adverse Effects: 1. Any change in general adverse effects ‐ additional medication use ‐ short/medium term.

Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 7 Adverse effects: 2a. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs ‐ requiring medication ‐ short term.

Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 8 Adverse Effects: 2b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs (ESRS) ‐ short term.
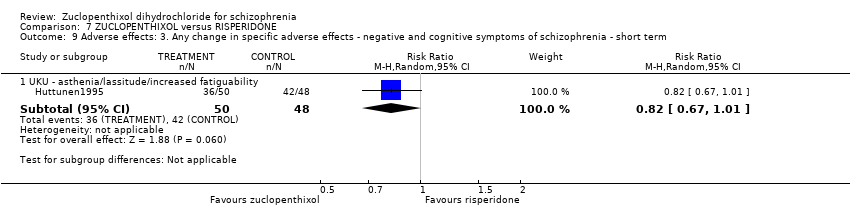
Comparison 7 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus RISPERIDONE, Outcome 9 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia ‐ short term.

Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Global state: 1. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI).

Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 2 Global State: 2. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Moderately or severely ill (CGI).

Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 3 Mental State: Average endpoint general mental state score (BPRS, average = 5.7).
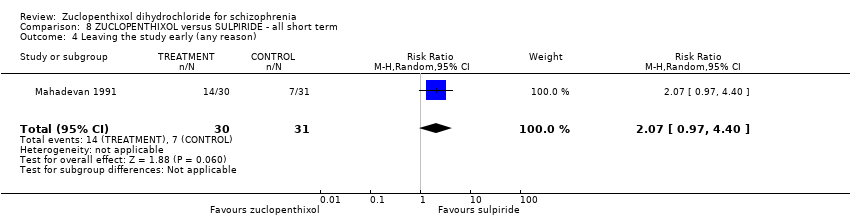
Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 4 Leaving the study early (any reason).
| Study | Zuclopenthixol | Sulpiride |
| Mahadevan 1991 | n = 4 Amitriptyline | n = 4 Amitryptyline |
Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 5 Adverse Effects: 1. Any change in general adverse effects ‐ additional medication use.
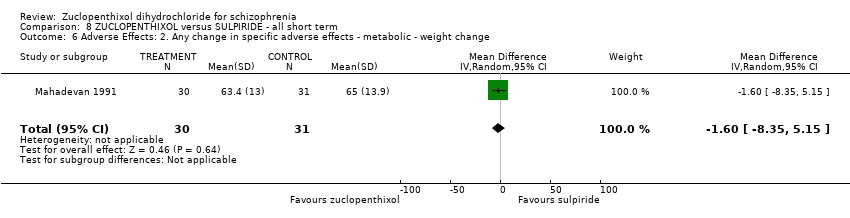
Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 6 Adverse Effects: 2. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ metabolic ‐ weight change.

Comparison 8 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus SULPIRIDE ‐ all short term, Outcome 7 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ requiring additional medication ‐ hypnotics/sedatives.

Comparison 9 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus THIOTHIXENE ‐ all medium term, Outcome 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ unchanged/worse (CGI).
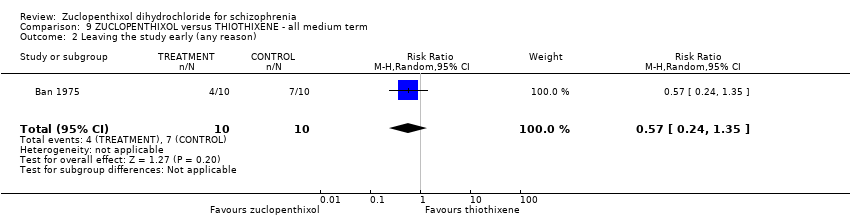
Comparison 9 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus THIOTHIXENE ‐ all medium term, Outcome 2 Leaving the study early (any reason).
Comparison 10 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus TRIFLUOPERAZINE ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Leaving the study early (any reason).
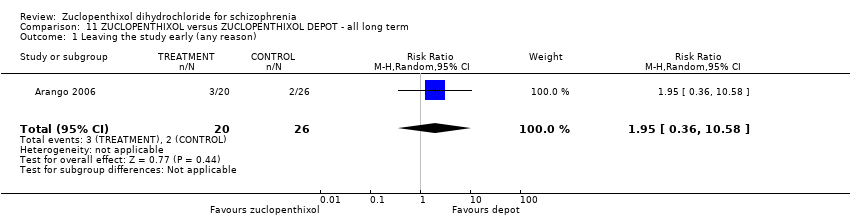
Comparison 11 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus ZUCLOPENTHIXOL DEPOT ‐ all long term, Outcome 1 Leaving the study early (any reason).
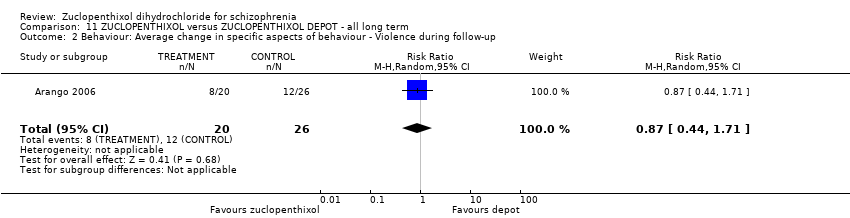
Comparison 11 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus ZUCLOPENTHIXOL DEPOT ‐ all long term, Outcome 2 Behaviour: Average change in specific aspects of behaviour ‐ Violence during follow‐up.
| Study | Zuclopenthixol | Depot |
| Arango 2006 | n = 1 Propanolol | n = 1 venlafaxine n = 1 Lithium |
Comparison 11 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus ZUCLOPENTHIXOL DEPOT ‐ all long term, Outcome 3 Adverse Effects: 1a. Any general adverse effects ‐ additional medication use.

Comparison 11 ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus ZUCLOPENTHIXOL DEPOT ‐ all long term, Outcome 4 Adverse Effects: 1b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ additional medication use ‐ benzodiazepine use at least once.

Comparison 12 CIS‐(Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS(Z)/TRANS(E) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unwell.

Comparison 12 CIS‐(Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS(Z)/TRANS(E) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 2 Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score ‐ Not improved.

Comparison 12 CIS‐(Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS(Z)/TRANS(E) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 3 Leaving the study early (any reason).

Comparison 12 CIS‐(Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS(Z)/TRANS(E) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 4 Adverse Effects: 1a. Any general adverse effects ‐ side effects reported.
| Study | Cis Z | Cis(Z)/Trans(E) |
| Gravem 1981 | EPSEs most frequent. Authors state no significant difference between two isomers. | EPSEs most frequent. |
| Heikkila 1981 | Dry mouth, Disturbance of accommodation, Disturbance of urination, Constipation, Dizziness, Headache, Increased sweating, Drowsiness, Anxiety, Parkinsonism, Akathisia, Tardive dyskinesia and others | Dry mouth, Disturbance of urination, Constipation, Dizziness, Drowsiness, Parkinsonism, Akathisia, Tardive dyskinesia, others |
Comparison 12 CIS‐(Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL versus CIS(Z)/TRANS(E) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL ‐ all short term, Outcome 5 Adverse Effects: 1b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ individual side effects.
| Patient or population: people with schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with PLACEBO (short term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (extrapyramidal effects ‐ UKU side effect rating scale) | 80 per 1000 | 486 per 1000 | RR 6.07 | 28 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Risk assumed to be moderate and rounded from 7.69% to 8%. |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: Duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 40 per 1000 | 12 per 1000 | RR 0.29 | 100 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Risk assumed to be moderate and rounded from 3.85% to 4%. Low number of events in both RCTs. |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated 'very serious' ‐ possible selection bias, blinding may have been single, attrition bias and reporting bias. 2 Risk of bias: rated 'very serious' ‐ selection, attrition and reporting bias 3 Risk of inconsistency: rated 'not serious' ‐ suspected but not found. 4 Risk of publication bias: rated 'strongly suspected' ‐ multiple papers published with the same patient cohort. 5 Risk of large effect: rated 'very large' ‐ RR 6.07, small n number but result likely when versus placebo. 6 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with CHLORPROMAZINE (short term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (CGI‐SI, high score not reported, average score = 2.2) | The mean CGI‐SI endpoint score in the intervention group (MD) was 0 (‐0.49 lower to 0.49 higher) | ‐ | 64 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Translated study. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (EPSEs) | 300 per 1000 | 282 per 1000 | RR 0.94 | 199 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Risk control rounded to 30% and set to moderate. Mixture of inpatient and outpatient, though predominantly hospitalised patients. |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (BPRS, high score = 34.2) | The mean mental state: average endpoint score (BPRS, high score = 34.2) in the intervention group was 0.4 more (2.43 fewer to 3.23 more) | ‐ | 221 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Mixture of inpatient and outpatient, though predominantly hospitalised patients. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 70 per 1000 | 38 per 1000 | RR 0.54 | 766 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Mixture of inpatient and outpatient, though predominantly hospitalised patients. Risk control set to moderate and rounded to 7%; extreme values not likely. |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated 'serious' ‐ Selection and attrition bias likely. 2 Risk of bias: rated 'serious' ‐ Selection attrition bias. 3 Risk of bias: rated 'serious' ‐ Selection, attrition and reporting bias. 4 Risk of bias: rated 'serious' ‐ Selection, attrition and reporting bias. Risk of inconsistency: rated as 'serious' ‐ All three papers reported on differing population sizes and obtained different levels of EPSEs in the experimental and control groups. 5 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers 6 Risk of indirectness: rated 'very serious' ‐ mixed samples For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with CHLORPROTHIXENE (medium term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 400 per 1000 | 400 per 1000 | RR 1.00 | 20 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ selection, reporting bias likely. 2 Risk of publication bias: rated as 'strongly suspected' ‐ several papers published using the same cohort of patients. 3 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with CLOZAPINE (short term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 | not estimable | 407 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Multi‐centre, multi‐drug trial with disproportionate numbers of people in different arms of the study. The authors did not report that anybody left the study in the Zuclopenthixol and clozapine arms. |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ selection, attrition, reporting and performance bias likely. 2 Risk of indirectness: rated 'serious' ‐ Multiple study arms For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with HALOPERIDOL (short term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (CGI, mean score = 1.25) | The mean CGI endpoint score in the intervention group (MD) was 0.13 more (‐0.3 fewer to 0.55 more) | ‐ | 49 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Small study, multiple scales used (NOSIE30, BPRS, CGI). Paper only reported outcomes of some of these scales. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 300 per 1000 | 297 per 1000 | RR 0.99 | 141 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Risk control rounded to 30% from 29.25% and, as extreme values unlikely, it was set to moderate. |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'very serious' ‐ likely selection, attrition, reporting and diagnostic purity bias. 2 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ likely selection, attrition, reporting and diagnostic purity bias. Risk of inconsistency: rated as 'serious' ‐ both papers generated differing values for people leaving the study and do not appear consistent (face validity). 3 Risk of imprecision: rated 'serious' ‐ low n numbers 4 Risk of indirectness: rated 'serious' ‐ not all scales reported For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with PERPHENAZINE (short and medium term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (EPSEs requiring medication ‐ medium term) | 400 per 1000 | 760 per 1000 | RR 1.90 | 50 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason, short and medium term) | 207 per 1000 | 130 per 1000 | RR 0.63 | 104 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ likely selection and reporting bias. 2 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with RISPERIDONE (short and medium term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect ‐ short term (EPSEs requiring medication) | 271 per 1000 | 520 per 1000 | RR 1.92 | 98 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (PANSS, average score = 20.5) ‐ medium term | The mean PANNS endpoint score in the intervention group (MD) was 3.2 fewer (‐7.71 fewer to 1.31 more) | ‐ | 25 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Small study. Standard deviations may be standard errors. Open label trial. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason, short and medium term) | 310 per 1000 | 403 per 1000 | RR 1.30 | 154 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Risk control taken as mean of extremes: high + low / 2 (changed from 21.43% to 31%) |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'very serious' ‐ open label trial, likely selection bias. 2 Risk of imprecision: rated as 'very serious' ‐ strongly suspect reported standard deviations are standard errors, low n numbers 3 Risk of publication bias: rated as 'strongly suspected' ‐ all studies published findings across several consecutive years in different journals and at conferences. 4 Risk of bias: rated as 'very serious' ‐ study 1 (selection, reporting, diagnostic purity and attrition bias likely ‐ author emailed); study 2 (open label); study 3 (reporting and attrition bias). 5 Risk of publication bias: rated as 'strongly suspected' ‐ multiple papers over consecutive years published with the same data. 6 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ diagnostic purity and attrition bias; likely selection and reporting bias (authors contacted) For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with SULPIRIDE (short term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (CGI ‐ unchanged/worse) | 226 per 1000 | 266 per 1000 | RR 1.18 | 61 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | The study did not report clinical improvement so unchanged/worse is reported for this outcome. Usually we report clinical improvement. |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect ‐ requiring hypnotics/sedatives | 419 per 1000 | 252 per 1000 | RR 0.60 | 61 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (BPRS) | The mean BPRS endpoint score in the intervention group (MD) was 1.3 fewer (‐5.08 fewer to 2.48 more) | ‐ | 61 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 230 per 1000 | 476 per 1000 | RR 2.07 | 61 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Control of risk rounded up from 22.58% to 23%. |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ diagnostic purity, attrition bias. Per‐Protocol analysis suspected. 2 Risk of imprecision: rated as ' very serious' ‐ percentages used to describe data and comparisons are made against an assumption of baseline measurements. Low n numbers. For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with THIOTHIXENE (medium term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (unchanged/worse ‐ CGI) | 600 per 1000 | 300 per 1000 | RR 0.50 | 20 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | The study did not report clinical improvement so unchanged/worse is reported for this outcome. Usually we report clinical improvement. |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported on this outcome. | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported on this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported on this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported on this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 700 per 1000 | 399 per 1000 | RR 0.57 | 20 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No studies reported on this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ likely selection and reporting bias. 2 Risk of publication bias: rated as 'strongly suspected' ‐ several papers published using the same cohort. 3 Risk of imprecision: rated as 'serious' ‐ low n numbers For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with TRIFLUOPERAZINE (short term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 | not estimable | 72 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Multi‐centre and multi‐drug trial with low numbers in each arm. |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ selection, attrition, reporting and performance bias likely. 2 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers 3 Risk of indirectness: rated 'very serious' ‐ multiple arms, some missing For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | |||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | ||
| Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL DEPOT (long term) | Risk with ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | ||||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | ||
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | ||
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | ||
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | ||
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | ||
| Leaving the study early (any reason) | 80 per 1000 | 156 per 1000 | RR 1.95 | 46 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Control of risk rounded from 7.69% to 8%. | |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | ||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'very serious' ‐ single researcher did randomisation, selection bias likely, open label trial and incomplete outcome data. 2 Risk of publication bias: rated as 'strongly suspected' ‐ several papers published using the same data and cohort. 3 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | |||||||
| Patient or population: schizophrenia | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with CIS(Z)/TRANS(E) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL (short term) | Risk with CIS‐(Z) ZUCLOPENTHIXOL | |||||
| Global state: Average endpoint global state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Adverse effects: Clinically important general adverse effect | 470 per 1000 | 630 per 1000 | RR 1.34 | 57 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Control of risk set at moderate and rounded up from 46.4% to 47%. |
| Death: Suicide and natural causes (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Service outcomes: duration of stay in hospital (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| Leaving the study early: Any reason | 28 per 1000 | 61 per 1000 | RR 2.15 | 140 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| General functioning: Average endpoint general functioning score (clinically improved) (no data) | not pooled | not pooled | not estimable | (0 studies) | No study reported this outcome. | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Risk of bias: rated as 'serious' ‐ selection bias throughout. Very difficult to ascertain from published materials if selection bias has been minimised. 2 Risk of imprecision: rated 'very serious' ‐ low n numbers For risks rated as serious, we downgraded by 1. For risks rated as very serious we downgraded by 2. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 2 | 100 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.01, 6.60] |
| 2 Adverse effects: 1. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ cardiovascular ‐ orthostatic Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.01, 6.60] |
| 3 Adverse effects: 2. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ central nervous system ‐ arousal state Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 excitation | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.62 [0.12, 59.40] |
| 3.2 sleepiness / sedation | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.89 [1.01, 8.30] |
| 4 Adverse effects: 3. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ endocrine ‐ menstruation started Show forest plot | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 7.0 [0.39, 126.48] |
| 5 Adverse effects: 4a. Any general adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs (UKU side effect rating scale, no scores) Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 6.07 [0.86, 43.04] |
| 6 Adverse effects: 4b. Clinically important change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 6.1 parkinsonism | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.00 [0.26, 97.37] |
| 6.2 oculogyric crisis | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.13, 69.09] |
| 6.3 tremor | 1 | 36 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.00 [0.26, 97.37] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: 1. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI, scores not reported) Show forest plot | 2 | 135 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.75, 1.13] |
| 2 Global state: 2. Average endpoint global state score ‐ No Recovery Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.89, 1.16] |
| 3 Global state: 3a. Average endpoint global state score (GAS, high score not reported, average score = 63.4) Show forest plot | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.60 [‐8.12, 6.92] |
| 4 Global state: 3b. Average endpoint global state score (CGI‐SI, high score not reported, average score = 2.2) Show forest plot | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.49, 0.49] |
| 5 Mental state: 1. No clinically important change in general mental state ‐ Not improved (PANSS, scores not reported) Show forest plot | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.81, 1.18] |
| 6 Mental state: 2. No clinically important change in general mental state ‐ No clinical response Show forest plot | 1 | 64 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.25, 2.42] |
| 7 Mental state: 3. Average endpoint general mental state score (BPRS, high score = 34.2) Show forest plot | 3 | 221 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.40 [‐2.43, 3.23] |
| 8 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 6 | 766 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.54 [0.36, 0.81] |
| 9 Adverse effects: 1. Any general adverse effects ‐ side effects (CGI, high score not reported) Show forest plot | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.77, 0.97] |
| 10 Adverse effects: 2. Average endpoint general adverse effect score ‐ average score (TESS, high score not reported, average score = 12.00) Show forest plot | 1 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 4.48 [‐2.38, 11.34] |
| 11 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ cardiovascular ‐ postural hypotension (dizziness/syncope) Show forest plot | 1 | 43 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.01, 1.73] |
| 12 Adverse effects: 4. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ central nervous system ‐ arousal Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 12.1 excitation | 1 | 43 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.07, 5.47] |
| 12.2 sedation | 2 | 163 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.73, 1.70] |
| 13 Adverse effects: 5. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ metabolic ‐ weight change ‐ loss or gain of weight of 10 pounds Show forest plot | 1 | 29 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.22, 1.75] |
| 14 Adverse effects: 6a. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs Show forest plot | 3 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.61, 1.45] |
| 15 Adverse effects: 6b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ additional medication use Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 1 | 20 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.34, 2.93] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 1 | 407 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Adverse effects: Any general adverse effects ‐ side effects ‐ frequency per day Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: 1. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2 Global state: 2. Average endpoint global state score (CGI, mean score = 1.25) Show forest plot | 1 | 49 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.13 [‐0.30, 0.55] |
| 3 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 2 | 141 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.72, 1.35] |
| 4 Adverse effects: 1. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ interference with functioning Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5 Adverse effects: 2. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs ‐ requiring medication Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 6 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ requiring additional medication Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 7 Adverse effects: 4. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ requiring hypnotics/sedatives Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ unchanged/worse (global rating ‐ investigator opinion) ‐ medium term Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2 Leaving the study early (any reason) ‐ short/medium term Show forest plot | 2 | 104 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.27, 1.47] |
| 3 Adverse effects: 1. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ central nervous system ‐ arousal ‐ requiring medication ‐ medium term Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4 Adverse effects: 2. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs ‐ requiring medication ‐ medium term Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Mental State: 1. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS, average score = 45.8) ‐ medium term Show forest plot | 1 | 25 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐3.20 [‐7.71, 1.31] |
| 2 Mental State: 2. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS General, average score medium term = 20.5) ‐ short/medium term Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Short term | 1 | 19 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.40 [‐4.52, ‐0.28] |
| 2.2 Medium term | 1 | 25 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.30 [‐2.72, 2.12] |
| 3 Mental State: 3. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS Positive, average score = 9.8) ‐ medium term Show forest plot | 1 | 25 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐2.69, 0.69] |
| 4 Mental State: 4. Average endpoint general mental state score (PANSS Negative, average score 11.5) ‐ medium term Show forest plot | 1 | 25 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.5 [‐4.05, 1.05] |
| 5 Leaving the study early (any reason) ‐ short/medium term Show forest plot | 3 | 154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.30 [0.84, 2.02] |
| 6 Adverse Effects: 1. Any change in general adverse effects ‐ additional medication use ‐ short/medium term Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 7 Adverse effects: 2a. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs ‐ requiring medication ‐ short term Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 8 Adverse Effects: 2b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ movement disorders ‐ EPSEs (ESRS) ‐ short term Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 4.5 [0.67, 8.33] |
| 9 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia ‐ short term Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 9.1 UKU ‐ asthenia/lassitude/increased fatiguability | 1 | 98 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.67, 1.01] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: 1. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unchanged/worse (CGI) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2 Global State: 2. Average endpoint global state score ‐ Moderately or severely ill (CGI) Show forest plot | 1 | 61 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.75, 1.30] |
| 3 Mental State: Average endpoint general mental state score (BPRS, average = 5.7) Show forest plot | 1 | 61 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.30 [‐5.08, 2.48] |
| 4 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 1 | 61 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.07 [0.97, 4.40] |
| 5 Adverse Effects: 1. Any change in general adverse effects ‐ additional medication use Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 6 Adverse Effects: 2. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ metabolic ‐ weight change Show forest plot | 1 | 61 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.60 [‐8.35, 5.15] |
| 7 Adverse effects: 3. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ requiring additional medication ‐ hypnotics/sedatives Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ unchanged/worse (CGI) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 1 | 20 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.57 [0.24, 1.35] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 1 | 72 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.95 [0.36, 10.58] |
| 2 Behaviour: Average change in specific aspects of behaviour ‐ Violence during follow‐up Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.44, 1.71] |
| 3 Adverse Effects: 1a. Any general adverse effects ‐ additional medication use Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||
| 4 Adverse Effects: 1b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ additional medication use ‐ benzodiazepine use at least once Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.3 [0.59, 2.86] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global state: Average endpoint global state score ‐ Unwell Show forest plot | 3 | 131 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.80, 1.17] |
| 2 Mental state: Average endpoint general mental state score ‐ Not improved Show forest plot | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.45, 2.07] |
| 3 Leaving the study early (any reason) Show forest plot | 4 | 140 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.15 [0.49, 9.41] |
| 4 Adverse Effects: 1a. Any general adverse effects ‐ side effects reported Show forest plot | 1 | 57 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.34 [0.82, 2.18] |
| 5 Adverse Effects: 1b. Any change in specific adverse effects ‐ individual side effects Show forest plot | Other data | No numeric data | ||

