| Study ID (report) | MN device | Duration of exposure to MN intervention | Conditioning protocol used to adapt participants to MN use | MN use/daily use for increasing the activities and participation in the home or community context |
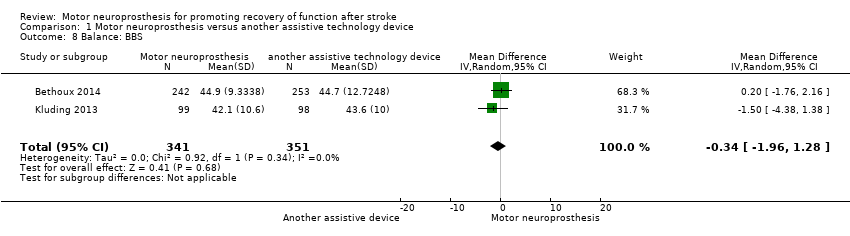
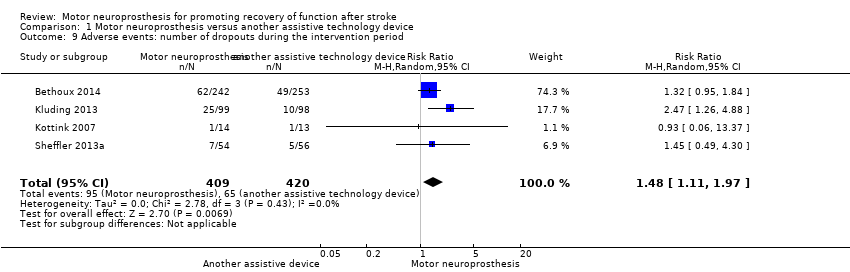
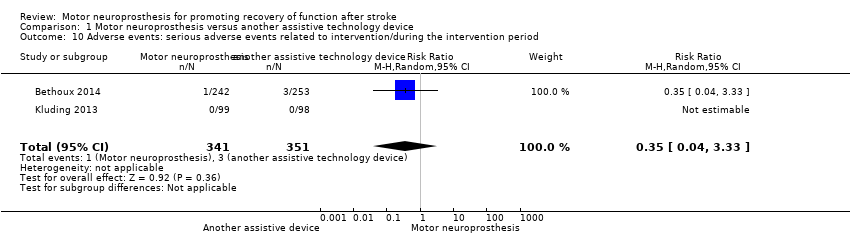
| Bethoux 2014 | The MN used was the WalkAide device (Innovative Neurotronics, Austin, TX, USA). It is a commercially available, battery‐operated, single‐channel surface peroneal nerve stimulator that consists of a cuff worn around the proximal part of the lower leg, which holds the control module and surface electrodes. This device uses a tilt sensor and an accelerometer to trigger ankle dorsiflexion and control the timing and duration of peroneal nerve stimulation during the swing phase of gait to alleviate foot drop. | The duration of MN intervention was 12 months. The conditioning protocol occurred in the first 2 weeks, after which participants started daily use of MN device. | The first part consisted of fitting and programming the MN device as well as patient education performed by WalkAide‐certified orthotist or licensed physical therapist. The conditioning protocol included a 2‐week progressive wearing schedule of MN device. | Participants were instructed to wear MN device on a full‐time basis (quote: "ie, for all walking activities throughout the day"). |
| Kluding 2013 | The MN used was the NESS L300 device (Bioness Inc, Valencia, CA, USA). It is a commercially available, battery‐operated, single‐channel surface peroneal nerve stimulator that consists of a cuff with integrated stimulation unit and electrodes, a control unit, and an in‐shoe pressure sensor. The pressure sensor detects heel off and initial contact events during gait. It transmits wireless signals to the stimulation cuff, which initiates or pauses the stimulation of deep and superficial branches of the peroneal nerve via 2 surface electrodes that activate dorsiflexors and evertors muscles to ensure foot clearance during the swing phase of gait and prevent excessive ankle inversion during early stance. | The duration of MN intervention was 30 weeks. The conditioning protocol occurred in the first 6 weeks. Participants used the MN device all day between week 4 and week 30. | The first part consisted of initial fitting of the device, gait training, wearing schedule, home exercise program, and participant education based on manufacturer standardized protocols. For the first 3 weeks, participants followed the standard conditioning protocol (gradually increasing walking with the MN from 15 minutes each day to all‐day use). During the same period, participants also used the MN for cyclic stimulation while not walking in order to gradually strengthen and condition the muscles to avoid fatigue when using the device (Dunning 2013).* During the first 6 weeks of the study, participants also received 8 dose‐matched sessions of physical therapy. The first 2 to 4 therapy visits focused on education on device use, initial gait training, and an individualized home exercise program. The remaining physical therapy sessions focused on gait training (Kluding 2013). | Participants used the MN all day for ambulation (Dunning 2013).* |
| Kottink 2007 | The MN used was the STIMuSTEP device (FineTech Medical Ltd, Hertfordshire, UK). It is a commercially available, battery‐operated, 2‐channel implantable device composed of implantable components such as a stimulator, 2 leads, and bipolar intraneural electrodes, and non‐implantable components such as an external transmitter with a built‐in antenna and a pressure sensor. 1 electrode is surgically positioned under the epineurium of the superficial peroneal nerve and the other under the epineurium of the deep peroneal nerve. This device promotes the ankle dorsiflexion/eversion during gait to correct foot drop, and a pressure sensor placed inside the shoe determines the on and off switching of the stimulation. | The duration of MN intervention was 26 weeks. The intervention began with the surgical procedure for placement of the implant. After 2 weeks of the surgery, the wound was checked and first test stimulation took place. The conditioning protocol began at the third week, and all‐day MN use began at the sixth week. | Quote: "Two weeks after the surgery the wound was checked and a first test stimulation took place. In the third week, stimulation during walking was tested and the stimulator was taken home by the patient. The use of the stimulator was gradually increased over 2 weeks to prevent severe muscle pain and fatigue. After this period patients were allowed to use the system all day." | Participants were allowed to use the system all day between week 6 and week 26. |
| Sheffler 2013a | The MN used to correct foot drop was the Odstock Dropped‐Foot Stimulator (ODFS) device (Odstock Medical Ltd, Salisbury Wiltshire, UK). The ODFS is a commercially available, battery‐operated, single‐channel surface peroneal nerve stimulator consisting of an electrical stimulator, a control module, pressure sensors, and surface electrodes. The stimulation is triggered by an insole pressure‐sensing foot switch that detects heel rise at pre‐swing. | The duration of MN intervention was 12 weeks. The conditioning protocol occurred over the 12 weeks. Daily MN use began once device safety was demonstrated by participants. | In the first 5 weeks the Functional Training phase (2 x 1‐hour sessions per week) took place, in which participants were trained to use MN device for home and community mobility with an assistive device, if needed. Activities included passive and active range‐of‐motion exercises, lower extremity strengthening, standing balance and weight‐shifting activities to the affected limb with transition to least‐restrictive assistive device, and refinement of a reciprocal gait pattern. Exercises were done with multiple repetitions with an increase in difficulty and a decrease in cues, with and without the MN device, as appropriate. In the last 7 weeks the Post‐Functional Training Phase (3 x 1‐hour sessions) took place, in which device function, application, and usage guidelines were reviewed with each participant to maximize MN compliance. | The article did not explicitly mention when participants started all‐day MN use, but reported that as soon as participants demonstrated safe use of the device, it was used up to 8 hours per day. |