Le lavage intra‐cavité et l'irrigation de la plaie pour la prévention de l'infection du site opératoire
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to studies awaiting assessment
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: NR; appears to be single hospital in Saudi Arabia Participants reportedly followed up for 1 month, no additional details | |
| Participants | 254 adults and children (aged 5‐80 years, mean age 21 (Group I) and 24 years (Group II)) undergoing appendectomy for acute appendicitis were randomised; 249 analysed Inclusion criteria: people undergoing appendectomy through gridiron incision for clinically suspected acute appendicitis Exclusion criteria: allergy to ampicillin; systemic diseases requiring systemic antibiotic administration | |
| Interventions | Group I: (saline): wound irrigation with 100 mL normal sterile saline at closure (134 participants randomised; 132 analysed; 2 participants withdrawn post‐randomisation) Group II: (Ampicillin): wound irrigation with 1 g Ampicillin powder dissolved in 100 mL normal sterile saline (120 participants randomised; 117 analysed; 3 participants withdrawn post‐randomisation) Co‐interventions: IV metronidazole (500 mg for adults; 15 mg/kg for children) and gentamicin (75 mg for adults and 1.5 mg/kg for children) 1 h before surgery. If appendix was found to be gangrenous or perforated antibiotics were continued for 5 ds postoperatively. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (defined as presence of purulent discharge in wound, regardless of culture results, or as occurrence of serous discharge with a positive culture) within 1 month Group I (Saline): 7/132 (134 randomised) Group II (Ampicillin): 1/117 (120 randomised) Secondary outcome: adverse events including abscess: Abscess Group I (saline): 0/132 Group II (Ampicillin): 0/117 Other specific post‐operative complications were reported but total number of participants with adverse events was not clear. Secondary outcome: hospital stay: reported to be reduced by 2.5 d by avoidance of wound infection. Median reported for participants with (5.5, range 3‐11 d) and without infection (3.0, range 2‐11 d) but not for each treatment group. | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "254 patients fulfilled the criteria and were randomized into two groups using sealed envelopes" Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was generated. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "254 patients fulfilled the criteria and were randomized into two groups using sealed envelopes that were opened intraoperatively" Comment: although sealed envelopes were used it is not clear that they were opaque or that the allocation sequence was fully concealed at all times. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: no direct quote but it is clear that personnel were made aware of allocation once the envelopes were opened. Unclear if participants were aware |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote but it is unclear whether the outcome assessment was performed by individuals aware of group allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Comment: there were a small number of post‐randomisation exclusions for protocol violations described. However there were low numbers of events relative to these exclusions, increasing the risk of attrition bias impacting the results. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: rhe data for one of the secondary outcomes (bed‐stay) were not reported on a per‐group base making this outcome difficult to evaluate. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was not clear enough to be certain. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single centre; 1 surgical unit in UK Follow‐up: close monitoring during hospital stay; full inquiry into possible infection signs at 6‐week outpatient clinic follow‐up | |
| Participants | 330 participants undergoing elective colorectal surgery (mean ages 61 (Group I) and 63 years (Group II)); 300 analysed Inclusion criteria: participants undergoing elective colorectal surgery Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I (taurolidine PVP): peritoneal lavage in 2 stages with 250 mL 2% taurolidine in 5% PVP (150 participants) Group II (saline): peritoneal lavage in 2 stages with 250 mL normal saline (150 participants) In each group 250 mL lavage solution diluted in a further 250 mL normal saline was placed in the abdomen as a washout and then removed with suction. This was followed by instillation of a second 250 mL undiluted lavage solution, which was left in the abdomen. If abdominal drains were present these were clamped for at least 20 min. Cointerventions: all participants (except 11 who had severe constricting colonic lesions and were in imminent danger of bowel obstruction) received up to 8 doses of magnesium sulphate (4 g by mouth) for 48 h starting 72 h before surgery followed by 2 sachets of sodium picosulphate (Picolax; Fering Pharmaceutical, Feltham, UK) given in the 24 h immediately before surgery. Participants with severe constricting colonic lesions were prepared according to the wishes of the surgeon; 8 received Klean‐Prep (Norgine, Oxford, UK) in place of Picolax and 3 no preparation. All participants received cefotaxime 1 g and metronidazole 500 mg IV at induction of anaesthesia, and 8 h and 16 h later. 5 participants with penicillin allergy received gentamicin 160 mg on induction, and 120 mg at 8 h and 16 h after induction; doses were individually adjusted according to body mass, renal function and age. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (defined as spontaneous or incisional discharge from the wound, either of pus or serous fluid, with an infective organism positively identified on culture) Group I (taurolidine PVP): 17/150 (10 superficial, 7 deep) Group II (saline): 17/150 (12 superficial, 5 deep) Secondary outcome: 30‐day mortality Group I (taurolidine PVP): 4/150 Group II (saline): 4/150 Secondary outcome: adverse events including abscess: Pelvic abscess Group I (taurolidine PVP): 2/150 Group II (saline): 1/150 Other specific post‐operative complications were reported but total number of participants with adverse events was not clear. Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay Group I (taurolidine PVP): median 11 d for 133 participants without infection; 18 d for 17 with infection (paper reports N = 134, error suspected) Group II (saline): median 11 d for 133 participants without infection; 18 d for 17 with infection (mean NR, range NR) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "This paper reports a randomized controlled trial.....Bottles of lavage fluid were dispensed in identical containers according to a computer‐generated randomized code held by the hospital pharmacy with no stratification for severity of contamination or procedure. " Comment: appears there was a computer‐generated randomisation sequence |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Bottles of lavage fluid were dispensed in identical containers according to a computer‐generated randomized code held by the hospital pharmacy with no stratification for severity of contamination or procedure." Comment: although the allocation sequence was held by the hospital pharmacy it is not clear whether it was adequately concealed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Bottles of lavage fluid were dispensed in identical containers according to a computer‐generated randomized code held by the hospital pharmacy... The trial and control solutions were indistinguishable to users." Comment: personnel appear to have been blinded; although there is no direct information on participants it is likely that they were also blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "All patients were monitored closely after operation until hospital discharge for clinical signs of abdominal sepsis and wound infection by an independent (non‐operating) trained assessor (J.AJ.)." Comment: |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "Sixteen patients were withdrawn from the trial after consent because the operative procedure performed did not constitute elective colorectal surgery ....... A further eight patients were withdrawn as lavage was not undertaken for logistical reasons, such as breakage of solution bottles. A further six patients were withdrawn at the time of surgery because of overt sepsis or severe faecal spillage, which rendered the intraoperative lavage a therapeutic rather than a prophylactic measure. Thus 300 patient reports were available for analysis." Comment: almost 10% of randomised participants were not included in the analysis. Although full reasons are given for this the number of withdrawals is almost equivalent to the number of events. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: the data for one of the secondary outcomes (bed‐stay) were not fully reported (measure of variance lacking) but no other evidence of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was not clear enough to be certain. |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single hospital in USA Follow‐up: 6 weeks (review of records after discharge) | |
| Participants | 223 women undergoing cesarean section Inclusion criteria: women delivered by caesarean section Exclusion criteria: allergy to penicillin or cephalosporins, taken an antibiotic within 7 d of surgery or required antibiotics around time of surgery for other reasons. Participants with temperature elevated to 38oC or with foul amniotic fluid prior to or immediately after surgery were considered to have infection and excluded. High risk and low risk participants were separated according to duration of labor prior to cesarean section, with 6 h arbitrarily chosen as the division point. Each group contained both high risk (more than 6 h labour) and low risk (less than 6 h labour) participants | |
| Interventions | Group I: irrigation with 2 g cefamandole in 1000 mL normal saline (73 participants) Group II: irrigation with 1000 mL normal saline (75 participants) Group III: no irrigation (75 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I: low risk: 5.2 (0.3) d (N = 46); high risk: 5.3 (0.2) (N = 27) Group II: low risk: 5.9 (0.4) d (N = 40); high risk 6.8 (0.6) (N = 35) Group III: low risk 5.8 (0.3) d (N = 44); high risk: 6.9 (0.4) (N = 31) Secondary outcome: adverse events Only a specific event (metritis) was reported Group I: low risk: 2 (4.3% of 46); high risk: NR Group II: low risk: 4 (10% of 40); high risk: NR Group III: low risk: 9 (20.5% of 44); high risk: NR Infection data were also reported but were not clearly SSI and were not reported for all participants Group I: low risk: NR; high risk: 3 (11.1% of 27) Group II: low risk: NR; high risk: 17 (48.6% of 35) Group III: low risk: NR; high risk: 17 (54.8% of 31) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "members of each group were then assigned to a cohort according to a computer‐generated table of random numbers under the direction of the hospital pharmacy" Comment: appropriate method used to generate randomisation sequence; randomisation stratified by duration of labour: > 6 h vs < 6 h |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "under the direction of the hospital pharmacy" Comment: unclear whether adequate methods were used to conceal allocation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "Physicians who performed the operation and provided postoperative care were unaware of the type of irrigation provided" Comment: physicians were unaware of the type of irrigation used but are likely to have been aware of whether irrigation was used or not. It is unclear whether participants were aware of treatment allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were followed postoperatively by the resident and attending physicians on service" Comment: not clear whether outcomes were determined by personnel blinded to treatment allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "of all 451 patients who had cesarean sections during the study period, 223 were included" Comment: it appears that the 223 participants described as included were all included in the analyses but it's not completely clear that this is the total number who were randomised. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: not all data relating to outcomes of infection, adverse events and postoperative hospitalisations were reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no obvious source of additional bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: 16 referral centres in the USA Follow‐up: 28‐56 d | |
| Participants | 449 women (age 32.6 years in Adept group vs 32.3 in lactated Ringer's solution group) undergoing laparoscopic gynaecological surgery. Primary diagnoses included pelvic pain, infertility endometriosis and known adhesions. Inclusion criteria: aged > 18 years and in good health. Laparoscopic surgery was planned for a gynaecologic procedure that included adhesiolysis followed by a second follow‐up laparoscopy 4–8 weeks later. Exclusion criteria: preoperative: the use of concomitant systemic corticosteroids, antineoplastic agents, and/or radiation; pregnancy; diagnosis of an active pelvic or abdominal infection, or cancer; and a known allergy to starch‐based polymers. Intraoperative exclusion criteria included women requiring an additional non obstetric/gynaecologic surgical procedure to be performed during the laparoscopic procedure; unplanned surgery necessitating opening the bowel (excluding appendectomy); any laparotomy procedure; and use of another adhesion reduction agent. Adhesion site exclusion criteria included women having < 3 of the available anatomical study sites with adhesions or, if fewer than three were lysed, removal of any anatomical sites being scored for the purposes of the study; and an inability to visualise clearly all available anatomical score sites. | |
| Interventions | Group I: irrigated with a minimum 100 mL Adept (icodextrin 4% solution) solution every 30 min during surgery; any remaining solution at end of surgery was aspirated and then 1 L instilled from a fresh supply of solution (227 ITT, 205 PP participants) Group II: irrigated with a minimum 100 mL lactated Ringer's solution every 30 min during surgery; any remaining solution at end of surgery was aspirated and then 1 L instilled from a fresh supply of solution (222 ITT 205 PP participants) | |
| Outcomes | Postoperative infections were reported but unclear whether these referred to SSI Group I (icodextrin): 1% of 227 calculated as 2 Secondary outcome: adverse events Group I (icodextrin): 221/227 of which 44 serious; 55 considered related, reported as serious 8 participants (25 events) Group II (Ringer's solution): 218/222 of which 36 serious; 38 considered related, reported as serious 11 participants (19 events) Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (icodextrin): 0/227 Group II (Ringer's solution): 0/222 | |
| Notes | Funding: Innovata Limited, Vectura Group | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Treatment was randomized by computer‐generated randomization on a 1:1 basis" Comment: an appropriate method of generating the randomisation sequence was reported. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patient numbers were allocated to treatment group before labelling of the blinded study treatment Comment: adequate method for concealment of treatment allocation reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Double‐blinding was possible because Adept and LRS are both clear and odourless solutions Comment: blinding appears to have been undertaken for personnel and participants. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Safety was assessed by serious adverse events (SAEs), adverse events, and changes in laboratory values. Patients completed Comment: safety outcomes were assessed by participants who were blinded to treatment allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Safety was assessed in the intent‐to‐treat (ITT) population, which included all patients who had the study solution instilled. Comment: the outcomes relevant to this review were assessed using the ITT population so almost all randomised participants were included in the analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: outcomes were prespecified; all planned outcomes appeared fully reported. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias and reporting is sufficient to be reasonably confident that this is the case |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single hospital in UK Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 35 participants with gross peritonitis or frank fecal soiling and a positive culture swab at operation Inclusion criteria: gross peritonitis or frank fecal soiling and a positive culture swab at operation Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: 2% taurolin in 5% PVP solution (normal saline) up to 200 mL instilled prior to closure of abdomen or afterwards through a tube drain. Additional 200 mL could be instilled daily if required for 7 d (17 participants) Group II: 5% PVP solution (normal saline) to 200 mL instilled prior to closure of abdomen or afterwards through a tube drain. Additional 200 mL could be instilled daily if required for 7 d (18 participants) Additional antibiotic use was documented as including gentamycin, lincomycin, cephalosporin [cephalosporine], ampicillin | |
| Outcomes | Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (taurolin): 3/17 Group II (PVP): 0/18 | |
| Notes | Outcome was classed as "good" or "bad" where a normal recovery with normal wound healing and no sepsis was a good result and all other outcomes were bad | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Envelopes containing cards, previously randomly arranged were available in theatre for selection of solution A or solution B" Comment: no information on how the random sequence arrangement was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Envelopes containing cards, previously randomly arranged were available in theatre for selection of solution A or solution B" Comment: no information on whether or how the random sequence arrangement was concealed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Two solutions were prepared ....in identical bottles labelled A and B" Comment: it appears that measures were taken to blind personnel and participants. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Thirty‐five patients entered the trial. It was intended to include a much larger number but at this stage there was a marked difference in results which was statistically significant..... so the code was broken" Comment: it appears that measures were taken to ensure blinded outcome assessment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: it appears that all randomised participants were included in the analysis. However many fewer participants than planned were randomised (see other sources of bias). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Outcomes were not prespecified and "a good result" was defined only in the results section. |
| Other bias | High risk | Quote: "For ethical reasons it was decided the trial should be stopped as soon as a statistically significant difference between the two groups emerged............Thirty‐five patients entered the trial. It was intended to include a much larger number but at this stage there was a marked difference in results which was statistically significant..... so the code was broken." Trial was stopped very early (a long way short of planned recruitment). Although this was preplanned this approach to early stopping is highly likely to produce an artefactual difference between groups |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single hospital in Norway Follow‐up: 6 weeks postoperatively | |
| Participants | 85 participants with perforated appendicitis and generalised peritonitis Inclusion criteria: diagnosis of perforated appendicitis and generalised peritonitis verified at laparotomy Exclusion criteria: age < 6 years; known allergy to ampicillin or tinidazole, localised infiltration or abscess around the appendix. | |
| Interventions | Group I: 24 hs postoperative lavage with 0.9% saline 1 L x 20 for adults, 0.5 L for children (39 participants) Group II: no postoperative lavage (44 participants) Cointerventions: intra‐operative peritoneal lavage with 2 L of saline; 2 g ampicillin every 6 hs and 800 mg tinidazole daily until oral fluids commenced then pivampicillin 500 mg 3/d and 1 g tinidazole daily orally; children received pivampicillin 100 mg/kg/d and tinidazole 400 mg daily (rectal) for 5 d | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (wound infection defined as temperature > 38.5 C for > 24 h plus localised, drainage‐confirmed accumulation of fluid in the abdominal incision Group I (postoperative lavage): 9/39 Group II (no postoperative lavage): 2/44 Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I (postoperative lavage): median 5 d (range 3‐11) 39 participants Group II (no postoperative lavage): median 5 d (range 4 ‐12) 44 participants | |
| Notes | Treatment (postoperative lavage) was discontinued early in 10/39 participants | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "As soon as the diagnosis of perforated appendicitis with generalized peritonitis was verified at laparotomy, the patient was randomized..." Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was produced. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "As soon as the diagnosis of perforated appendicitis with generalized peritonitis was verified at laparotomy, the patient was randomized..." Comment: no information as to whether allocation was adequately concealed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: allocation to postoperative lavage versus no postoperative lavage would be evident to both personnel and participants. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: unclear whether outcome assessment was performed by blinded individuals |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: 2/85 randomised participants were withdrawn for a documented reason (ampicillin allergy); although both were in the same group the number is low and is unlikely to have been a source of bias. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes were not all prespecified in the methods although a priori definitions for intra‐abdominal and wound infection were given. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other source of bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: appears to be single hospital in USA Follow‐up: 4‐6 weeks postoperatively | |
| Participants | 40 women undergoing caesarean section at high risk of infection | |
| Interventions | Group I: irrigation with cefazolin; 2 g in 1000 cc normal saline; 700 cc intrauterine 100 cc in each gutter and 100 cc subcutaneously (20 participants) Group II: irrigation with 1000 cc normal saline 700 cc; intrauterine 100 cc in each gutter and 100 cc subcutaneously (20 participants) Cointerventions: none reported | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (defined only as "wound infection") Group I (cefazolin): 1/20 Group II (saline): 1/20 | |
| Notes | Abstract only. Funding NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients at high risk of infection were randomly placed in two groups" Comment: no information as to how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients at high risk of infection were randomly placed in two groups" Comment: no information as to whether there was adequate concealment of allocation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no specific quote, no information as to whether these groups were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no information as to who performed the outcome evaluation or whether they were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Only 2 of 40 high risk patients who received prophylactic irrigation developed...." Comment: it appears that all randomised participants were included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The objective of this study is to determine the impact of copious antibiotic irrigation versus normal saline (ns) on the incidence of post‐cesarean wound infections" Comment: the primary outcome was specified and reported but it is not clear from the abstract which other outcomes the study may have planned to assess. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there were no additional sources of bias noted but the abstract reporting was insufficient to be certain. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single centre; 1 surgical unit in the UKm Follow‐up: included outpatient assessment 6 weeks post‐surgery | |
| Participants | 54 women undergoing planned Patey mastectomy for carcinoma of the breast (mean age 56; range 32‐75 years) randomised (52 women and 53 breasts analysed) Inclusion criteria: Patey mastectomy Exclusion criteria: participants with allergy to tetracycline | |
| Interventions | Group I (tetracycline): lavage of 1 g tetracycline in 100 mL saline (23 women) Group II (saline): lavage of 100 mL saline (30 women) Lavage was given at wound closure and was contained within the axilla and skin flaps as much as possible during closure. Cointerventions: drainage was standardised to Vygon suction drains to axilla and skin flaps; drains removed at request of surgical staff when drainage for previous 24 hs appeared minimal | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (not defined) Group I (tetracycline): 0/23 Group II (saline): 1/30 Primary outcome: wound dehiscence Group II (saline): 1/30 (described as "minor") | |
| Notes | One woman underwent bilateral mastectomy and was randomised for each breast. Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "....were randomized to receive at wound closure" Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "....were randomized to receive at wound closure" Comment: no information on whether allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote but no information on whether participants and personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Records were kept on a standard form by the nursing staff, who were unaware of the patient's randomization." Comment: no information on whether the blinded nursing staff performed outcome assessment at follow‐up. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Two women were excluded after randomization because they subsequently did not undergo Patey mastectomy" Comment: the number of exclusions was very small and both were accounted for by a substantive operative protocol deviation |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no evidence of selective reporting but because most outcomes were not specified in the methods section it is not clear whether it may have occurred |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | There may be a minor unit of analysis issue due to the randomisation of one woman twice for each breast. Otherwise there is no evidence of other bias but the reporting is not full enough to be sure. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single centre, Emergency Department in Mexico Follow‐up: 2 and 4 weeks after operation | |
| Participants | 350 participants entered into study; 283 considered evaluable (mean age of 27.99 years (SD 12.81 years), range from 9‐82 years); (67 rejected from final analysis due to finding of another pathology different from appendix) Inclusion criteria: adults and children of both sexes admitted with a clinical diagnosis of acute abdomen suggestive of acute appendicitis with aid of laboratory and X‐ray, confirmed during operation and by histopathologic study Exclusion criteria: age < 5 years, allergy to metronidazole or aminoglycosides, antibiotic therapy within 72 h preceding operation, pregnancy, those with other intraperitoneal bacterial infection not originating from the appendix, and those with any immune deficiency (diabetes mellitus, chronic renal insufficiency, malnourishment, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, corticosteroid therapy, asplenism) | |
| Interventions | Group I: no irrigation (156 participants) Group II: syringe pressure irrigation with saline: after closure of the fascial planes, subcutaneous fat tissue irrigated with 300 mL of normal saline solution, delivered with a 20‐mL syringe with a 19‐gauge IV catheter, applying to the embolus the force of one hand, at a distance of 2 cm from the wound tissues, aspirating the fluid collected in the wound with a bulb syringe (127 participants) Cointerventions: each participant was administered metronidazole (30 mg/kg/day) 3/d, plus amikacin (15 mg/kg/d) once daily IV 30–45 min before skin incision. In cases of uncomplicated appendicitis they were stopped within the first 24 h, whereas in cases of complicated appendicitis they were maintained for a minimum of 7 d | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (Definition: "A wound was considered to be infected...when there was a collection of pus or a positive bacteriologic culture from a wound discharge") Group I: (no irrigation): 39/156 Group II: (syringe pressure irrigation): 11/127 Secondary outcome: adverse events. The authors stated that "Antibiotics used for prophylaxis were well tolerated without any case of allergy or intolerance." The proportion of participants with any adverse event was not reported. | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "All patients included were randomly assigned by a computerized assignment system into 2 groups of the trial." Comment: randomisation sequence generated by computer |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The randomization chart was kept by our statistician, who was blind to the follow‐up, until June 1995." Comment: appears that allocation sequence was concealed from trial personnel |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "Statistical analysis of the results...was conducted by our statistician who was blind to the surgical procedures and follow‐up." Comment: control arm did not include comparator intervention and so unable to conceal allocation to staff present at operation. Study design indicated as "double blind," so assumption that participants were not told of their treatment allocation High risk of physicians not being blinded; unclear or low risk for participants |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "...sought by daily examination of all patients by one of the members of the research team who was blind to the random allocation and the surgical procedures, until discharge." Quote: "...reevaluated at the outpatient consultation 2 and 4 weeks after operation by the responsible author who was blind to the random assignment and the surgical procedures." Comment: appears that outcome assessment for SSI was conducted by blinded assessor |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "A total of 350 patients were entered into the study, and 283 (80.9%) were considered evaluable. The reason for rejection of the 67 (19.1%) patients from the final analysis was the finding of another pathology different from the appendix." Comment: the number of exclusions was high and the study did not achieve its aim of including 133 participants in each arm. Therefore confirmation of appendicitis during surgery appears to be an inclusion criterion and so exclusions based on pathology do not violate inclusion criteria. There was a high rate of exclusion relative to event rate for the primary outcome. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: main end point (defined surgical wound infection) was reported overall and for complicated and uncomplicated types of appendicitis. It is unclear whether there were any other end points specified in the study protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was insufficient to be certain. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single centre at hospital in Taiwan Follow‐up: at 2 weeks, 1 month and 3 months after operation, and then every 3 months until end of study (approximately 19 months) | |
| Participants | 244 participants (age range 20‐89 years; Group I: average 67.1 years, (range 20‐82 years); Group II: average 65.4 years (range 22‐89 years)). Inclusion criteria: primary instrumented lumbosacral posterolateral fusion for degenerative spinal disorder with lumbar or lumbosacral segmental instability defined by chronic back, buttock and/or leg pain and degenerative spondylolisthesis, degenerative scoliosis or isthmic spondylolisthesis Exclusion criteria: prior spinal surgery, spinal trauma, malignant tumour, infectious spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, metabolic bone disease, skeletal immaturity or immunosuppressive treatment | |
| Interventions | Group I (povidone‐iodine): wounds irrigated with 0.35% povidone‐iodine solution to soak for 3 min, followed by irrigation with 2000 cc normal saline to remove povidone‐iodine solution (120 participants) Group II (saline): wounds irrigated with only 2000 cc normal saline (124 participants) Cointerventions: wound closure by layer after suction drainage applied; drain removed 48 h or 72 h post‐operatively. Routine analgesic pain control applied for 3 d. Pre‐operative IV bolus injection of cefazolin (1000 mg) and gentamicin (60 mg); additional cefazolin (1000 mg/6 h) and gentamicin (60 mg/12 h) also given for 48 hs after surgery, and then oral cefazolin (500 mg/6 h) for 3 d | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (Definition: "Infections were classified as superficial (above lumbosacral fascia) or deep (below lumbosacral fascia), and as early onset (within 2 weeks postoperatively) or late onset (otherwise). All deep infections were confirmed by laboratory parameters including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and level of C‐reactive protein (CRP) and a positive culture of biopsy." Group I (povidone‐iodine): 0/120 Group II (saline): 6/124 (2 early onset; 4 late onset) Primary outcome: wound dehiscence within 30 d (time NR but it says all others healed with sutures removed on day 14 so can presume < 30 d. No infection found in wounds) Group I: 1/120 Group II: 2/124 Secondary outcome: proportion of participants with postoperative SSI using systemic antibiotics within 30 d of surgery Group II: (saline): "After radical debridement and parenteral antibiotics (according to sensitivities) for 6 weeks and oral antibiotics for 2 months, a satisfactory outcome has been reached except in two cases." Secondary outcome: occurrence of infections showing antibiotic resistance Group II: (saline): MRSA cultured from 5/6 cases Secondary outcome: surgical re‐intervention rates Group I: (povidone‐iodine): 3 participants underwent exploration of the non‐union site and re‐arthrodesis with autogenous bone graft Group II: (saline): 4 participants underwent exploration of the non‐union site and re‐arthrodesis with autogenous bone graft Group II: (saline): "After radical debridement and parenteral antibiotics (according to sensitivities) for 6 weeks and oral antibiotics for 2 months, a satisfactory outcome has been reached except in two cases." These 2 cases had implants removed 4 months post‐operatively as infection could not be eradicated | |
| Notes | Interventions: no information given on duration of irrigation of wounds with normal saline for either group. Funding: Quote: "No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients...were randomly assigned to either treatment group. An independent person unaware of the subject characteristics and the study design delivered pre‐coded sealed enveloped randomly (containing serial numbers from 1 to 300) to the assignment of the subjects into the two groups." Comment: clearly states how sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "An independent person unaware of the subject characteristics an the study design delivered pre‐coded sealed enveloped randomly (containing serial numbers from 1 to 300) to the assignment of the subjects into the two groups. The sealed envelope was not opened until the middle of the surgery before wound irrigation." Comment: although sealed envelopes were used it is not clear that they were opaque or that the allocation sequence was fully concealed at all times. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote, but no information on how personnel might have been blinded to the treatment performed. Unclear whether participants were blinded, but report states it was "single blind" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "All clinical and radiographic assessments were made by independent observers other than the treating surgeons." Comment: unclear whether observers were aware of treatment group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: no direct quote, but no evidence of attrition |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of selective reporting but not enough information to be certain |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single centre at hospital in Taiwan Follow‐up: at 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 2 months after operation, and then every 3 months until end of study (mean follow‐up 15.5 months for both groups) | |
| Participants | 417 consecutive eligible participants enrolled. 3 who died during the follow‐up period were excluded (1 case in Group I and 2 cases in Inclusion criteria: pre‐operative diagnosis of degenerative scoliosis or stenosis; degenerative disc disease; disc prolapse; traumatic spinal fracture; spinal metastasis lesion. Undergoing procedure such as decompression for degenerative stenosis; decompression, fusion and fixation for degenerative scoliosis or stenosis; fixation of traumatic spinal fracture; discectomy for disc prolapse; excision with fixation for spinal metastatic lesions. Exclusion criteria: those with overt or suspected pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis, discitis, or any form of pre‐operative spinal infection were excluded. Those with fever or other suspected sources of infection also excluded | |
| Interventions | Group I (povidone‐iodine): surgical wound soaked with dilute povidone‐iodine solution for 3 min after operation. Commercially available Betadine solution used had a concentration of 10% povidone‐iodine (100 mg povidone‐iodine per 1 mL solution). Approximately 5 mL povidone‐iodine was diluted with normal saline to achieve a 0.35% povidone‐iodine (3.5% Betadine) solution for use during the operation. The wound was irrigated with copious amounts of normal saline (2000 mL) after Betadine solution irrigation (208 participants) Group II (saline): irrigation with copious normal saline (2000 mL) performed alone (206 participants) Cointerventions: each participant received 1 dose of parenteral cefazolin (1000 mg) and gentamicin (60 mg) 1 h before surgery. Cefazolin (1000 mg) every 6 hs and gentamicin (60 mg) every 12 hs were then given for 48 hs after surgery. Additional doses of antibiotics were given to maintain antibiotics levels during prolonged surgery. Following IV antibiotics, cefazolin (500 mg every 6 hs) was continued orally for 3 d. Drains were retained until < 100 mL of output was observed. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (Definition: "Infection was suspected when unusual pain, tenderness, erythema, induration, fever, or wound drainage was noted. Such findings were investigated with measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C‐reactive protein, and bacteriological cultures from the operative site or blood. Cultures were obtained from blood and wound discharge by aseptic methods.") Group I (povidone‐iodine): 0/208 Group II (saline): 7/206 (one superficial and 6 deep) Secondary outcome: occurrence of infections which show antibiotic resistance Group II (saline): MRSA cultured from 5/7 cases Secondary outcome: surgical re‐intervention rates Group II (saline): 7/206 (all those with highly suspected wound infection underwent surgical debridement) | |
| Notes | Funding: Quote: "No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients were randomly assigned to two groups, using pre‐coded sealed envelopes containing serial numbers from 1 to 500. Patients with odd serial numbers were group 1 (study group) and those with even serial number were group 2 (controls)." Comment: clearly states how sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomly assigned to two groups, using pre‐coded sealed envelopes containing serial numbers from 1 to 500. Envelopes were not opened until the end of surgery, before wound irrigation. Patients with odd serial numbers were group 1 (study group) and those with even serial number were group 2 (controls) Comment: although sealed envelopes were used it is not clear that they were opaque or that the allocation sequence was fully concealed at all times. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote, but no information on how personnel might have been blinded to the treatment performed. Unclear whether participants were blinded, but report states it was "single blind" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote; no information given regarding who collected outcome assessment data |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "Three patients who died during the follow‐up period were excluded (one case in group 1 and two cases in Comment: number of exclusions is low but similar to number of events |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of selective reporting but not enough information to be certain |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was not clear enough to be certain |
| Methods | Parallel RCT Setting: single centre in Republic of Korea Follow‐up: 2 weeks | |
| Participants | 34 patients undergoing gastrectomy Inclusion criteria: naive stomach cancer patients Exclusion criteria: history of diabetes, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, chemotherapy | |
| Interventions | Group I: saline exchange after gastrectomy (17 participants) Group II: no saline exchange during surgery (17 participants) Co‐interventions: preoperative cefametazol 1 g | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Superficial, deep SSI defined by Horan 1992 Group I (saline exchange): 1/17 Group II (no saline exchange): 3/17 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR Reported in Korean. Data extraction and risk of bias assessment performed by translator | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Comment: random number table was used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: method of allocation concealment was not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: personnel were blinded because they were under anaesthesia but personnel would have been aware of the allocation due to the nature of the comparison |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Comment: outcome assessors were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all participants were included |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: pre‐specified outcomes were reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: not detected |
| Methods | Parallel‐group, 5‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in USA Follow‐up: unclear | |
| Participants | 360 women undergoing caesarean section. Both caesareans in labour and without labour were included. Mean ages between 24.59 and 27.52 years. Gestational ages between 37.85 and 39.31 weeks Inclusion criteria: women undergoing caesarean section Exclusion criteria: history of penicillin or cephalosporin allergy, taking antibiotics, known infectious process (e.g. chorioamnionitis or urinary tract infection) | |
| Interventions | Group 1: saline lavage (800 mL) Group 2: 2 g cephapirin sodium lavage Group 3: 2 g cefamandole nafate lavage Group 4: 2 g moxalactam disodium lavage Group 5: 2 g ampicillin sodium lavage Inferred that each antibiotic lavage used 800 mL Cointerventions: none reported | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (wound breakdown with positive culture or presence of cellulitis) Group 1 (saline): 3/77 Group 2 (cephapirin): 3/70 Group 3 (cefamandole): 2/64 Group 4 (moxalactam): 2/79 Group 5 (ampicillin): 0/70 Secondary outcome: adverse events including abscess There were 0 abscess events; other adverse events reported were infection‐related morbidity as follows Group 1 (saline): 22/77 Group 2 (cephapirin): 17/70 Group 3 (cefamandole): 8/64 Group 4 (moxalactam): 19/79 Group 5 (ampicillin): 10/70 | |
| Notes | Funding NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "A computer‐generated table of pseudo‐random numbers.... was used by the pharmacy to assign each patient to one of five groups" Comment: an acceptable method of sequence generation was reported. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "A computer‐generated table of pseudo‐random numbers.... was used by the pharmacy to assign each patient to one of five groups" Comment: there was no information on how allocation concealment was undertaken. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "A vitamin .... was added to each solution for disguise" "The patients and physicians were unaware of the group assignment until after completion of the study and chart review by the authors" Comment: blinding of both participants and physicians was undertaken. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no specific quote but it was unclear who performed the outcome assessments and hence whether they were blinded to group allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants were included in the analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the outcomes were not defined in the methods section so it is unclear whether all planned outcomes were fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no apparent sources of additional bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT with 2 phases Setting: NR, but appears to be a general surgery department at a hospital in the Netherlands Follow‐up: at 4, 8 and 14 d, and 4 weeks after surgery | |
| Participants | 592 participants, of which 34 excluded (18 in the control group and 16 in the povidone‐iodine group) because they died before the end of the control period or had to be operated upon again through the same wound during this period. 2 wounds were present in 21 participants (9 in the control group and 12 in the povidone‐iodine group). A total of 582 wounds were evaluated in 558 participants. Inclusion criteria: all elective and acute patients who underwent intra‐abdominal operations or operations for inguinal hernia Exclusion criteria: children < five years of age and those undergoing vascular reconstruction. | |
| Interventions | Group I (control): quote "No special measures were taken" Group II (povidone‐iodine): carried out in 2 phases. Subcutaneous tissues irrigated with a povidone‐iodine solution at the end of the operation. Lavage with an ample amount of 1% aqueous povidone‐iodine solution (Phase 1) or 10% aqueous povidone‐iodine solution (Phase 2). Lavage was performed after closure of the fascia with interrupted polyglactin 910 sutures. After lavage for 1 min, excess fluid was aspirated and skin closed with interrupted with nylon sutures. If present, drains were brought out through a second wound. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (Definition: "Diagnosis of wound infection made if a purulent discharge form the wound was seen within a period of four weeks after the operation or if culturing of fluid from the wound was positive.") Group I (control): Phase 1: 21/142 wounds Phase 2: 15/137 wounds (270 participants? ‐ participant numbers unclear) Group II (povidone‐iodine): Phase 1: 17/154 wounds Phase 2: 22/149 wounds (291 participants? ‐ participant numbers unclear) | |
| Notes | Participants: age NR Outcomes: these appear to refer to number of wounds, not participants Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The patients were divided at random into two groups." Comment: it is unclear how randomisation was performed. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The patients were divided at random into two groups." Comment: no information on whether the randomisation sequence was concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "In the first group, no special measures were taken." Comment: the control arm did not involve an intervention as a comparator, and so unable to conceal allocation to staff present at the operation. Unclear whether all staff were aware of the different phases of the study (and concentrations of solution used as the intervention). Unclear whether participants were aware of treatment allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Postoperatively, all wounds were assessed by the same investigator..." Comment: unclear as to whether the investigator was blinded to the treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "34, 18 in the control group and 16 in the povidone‐iodine group, were excluded because they either died before the end of the control period or had to be operated upon again through the same wound during this period." Comment: number of exclusions is high. No reasons given for cause of death or re‐operations |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No evidence of reporting bias, but report is not complete enough to be sure |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was not clear enough to be certain |
| Methods | 4‐arm RCT Setting: 2 hospitals in USA Follow‐up: 6 weeks | |
| Participants | 'High risk' patients (for developing post operative febrile morbidity) undergoing cesarean section for a variety of reasons 158 women included in study Inclusion criteria: women in active labour or with ruptured membranes, at least one digital vaginal examination (i.e. high risk from developing postoperative febrile morbidity) Exclusion criteria: allergy to cephalosporins or penicillin, presence of fever ≥ 37.8 C during labour with suspicion of chorioamnionitis, maternal use of antibiotics in 2‐week period before delivery | |
| Interventions | Group I: 8 doses of IV cefoxitin 2 g (1st dose after umbilical cord clamp, then every 6 hs) (39 participants) Group II: irrigation of uterus and peritoneum with 2 g cefoxitin (in 1000 mL of normal saline). After delivery of the placenta, the fundus of the uterus was irrigated with 300 mL, the uterine incision with 150 mL, after closure of the first layer 150 mL, bladder flap 150 mL, remainder used to irrigate peritoneal cavity and excess suctioned away before closure of the abdomen (42 participants) Group III: combination of IV antibiotic (8 doses of 2 g cefoxitin) and irrigation with cefoxitin (in 1000 mL of normal saline) i.e. treatments of groups I and II combined (38 participants) Group IV: control group who received no prophylactic antibiotics (39 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (wound infection) Group I (IV antibiotics only): 0/39 Group II (irrigation with antibiotics only): 0/42 Group III (IV antibiotics plus irrigation with antibiotics): 0/38 Group IV (no IV and no irrigation):1/39 Secondary outcome: hospital stay (mean (SD) d) Group I: 4.8 (1.1) Group II: 4.9 (1.0) Group III 4.9 (1.2) Group IV: 5.4 (1.4) Secondary outcome: adverse events Infectious (endomyometritis, urinary tract infection, wound infection (1 case, see above), pulmonary infection, septicaemia) Group I: 2/39 Group II: 3/42 Group III: 2/38 Group IV: 14/39 Non‐infectious (seroma, transfusion reaction, atelectasis) Group I: 1/39 Group II: 1/42 Group III: 1/38 Group IV: 0/39 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Randomization into one of four treatment groups was performed by using a table of random numbers" Comment: an appropriate method appears to have been used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no information about allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: there is no information about blinding. It is possible that participants were blinded, but personnel would be aware of treatment as the protocols are quite different. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no information about blinding or who performed outcome assessment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all participants are accounted for in the results |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the outcomes do not appear to have been pre‐specified, although febrile morbidity was extensively defined |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no evidence of additional sources of bias but the reporting is insufficient to be confident that there were none. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in UK Follow‐up: 1 month | |
| Participants | 129 patients undergoing elective and emergency colorectal surgery Age: unknown; Type of operations: unknown Inclusion criteria: NR Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: 1000 mL saline lavage at the end of the operation (65 participants) Group II: 1000 mL saline lavage with 1 g cefotetan at the end of the operation (64 participants) Co‐interventions: Groups I and II both received 500 mg metronidazole and 120 mg gentamicin IV at anaesthesia induction | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (defined as discharge of pus from the wound "wound sepsis") Group I (saline): 18/65 Group II (cefotetan): 15/64 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR Limited information from paper | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomly allocated to receive either 1 liter of saline lavage or 1 liter of saline containing 1g of cefotetan..." Comment: the method of randomisation is not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no mention of allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no mention of blinding of participants or personnel |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Post‐operatively, patients were assessed regularly by a single observer for the development of wound sepsis..." Comment: there is no mention of blinding of the observer |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: participants are all accounted for in the outcome data of interest |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the outcome of interest (SSI) is reported but it is not clear that related results are fully reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is not enough methodological information to judge whether there were any additional sources of bias |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Turkey Follow‐up: participants were examined at 2 and 6 weeks after surgery. Wounds examined twice daily during hospitalisation. After discharge, women were instructed to contact investigators immediately if any of the listed symptoms appeared. Women who contacted the investigators were examined within 12 h | |
| Participants | 520 women with indications for elective or emergency caesarean section (incidence of emergency surgery (45.5 vs 51.5%; P = 0.53)) Inclusion criteria: past 37 weeks' gestation and required a caesarean section (elective or emergency). Exclusion criteria: anaemia (haemoglobin: < 7 g/dL), chorioamnionitis and fever on admission | |
| Interventions | Group I: underwent wound irrigation before wound closure with 100 mL of sterile saline with a 30–60 mL syringe (260 participants) Group II: no wound irrigation before wound closure (260 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes: SSI (wound drained purulent material or serosanguineous fluid in association with induration, warmth and tenderness) Group I (saline): 17/260 Group II (no irrigation): 19/260 Secondary outcomes: mean length of hospital stay Group I (saline): 2.05 (0.21) d Group II (no irrigation): 2.04 ( 0.20) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Consenting patients were preoperatively randomised using numerically ordered cards in sealed envelopes" Comment: method of sequence generation is not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quotes: "Consenting patients were preoperatively randomised using numerically ordered cards in sealed envelopes" "The investigator was not blinded to the procedure allocation" "The allocated envelope was opened by the clinician just before surgery" Comment: the use of sealed envelopes suggests an attempt to conceal some aspect of allocation but the authors state that the investigator was not blinded to allocation; envelopes are not stated to be opaque |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "The allocated envelope was opened by the clinician just before surgery. The procedure allocation was recorded in the women's charts" Comment: personnel and participants were both aware of treatment |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Quote: "The procedure allocation was recorded in the women's charts" "The investigator was not blinded to the procedure allocation" Comment: it is not explicitly stated but the report suggests the outcome assessors were not blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: data are reported for all participants |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: apart from SSI, it is unclear which outcomes were prespecified |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other bias |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single hospital in UK Follow‐up: 4 weeks postoperatively | |
| Participants | 192 participants undergoing appendectomy via grid iron incision Inclusion criteria: appendectomy via a right iliac fossa incision Exclusion criteria: female participants of child bearing age not adequately protected by contraceptive practice | |
| Interventions | Group I: 50 mL 2% taurolin in 5% PVP in "saline sufficient to produce solutions of equal tonicity"; wound irrigated for 2 min; then 10 mL instilled through a quill after closure of the skin Group II 50 mL of 5% PVP in "saline sufficient to produce solutions of equal tonicity" wound irrigated for 2 min; then 10 mL instilled through a quill after closure of the skin Cointerventions: antibiotics and drains as required | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (wound sepsis) defined as a wound discharging pus Group I (taurolin): 18/99 Group II (placebo): 29/93 Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I (taurolin): 6.4 d (mean, no SD) Group II (placebo): 6.6 d (mean, no SD) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "the taurolin and placebo being randomly allocated to sequential numbers 1 to 200" Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "the taurolin and placebo being randomly allocated to sequential numbers 1 to 200" Comment: no information on whether allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "neither solution was distinguishable to users" Comment: it appeared that personnel (and participants) were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote:"During the hospital stay the wound was observed be a member of the medical staff participating in trial" Comment: it was unclear whether the individual who assessed the outcomes was blinded to treatment group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: the 8 participants who were not included in the analyses were clearly documented. Although 7 of these were placebo group‐allocated participants it appears unlikely that these exclusions would have affected the results. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the primary outcome was specified but it was unclear which other outcomes were planned to be recorded |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting was insufficient to be certain. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: multicentre trial: 4 UK hospitals in the "South of England" Study period: 18‐months Follow‐up: 30 d post surgery or discharge from unit (1 assessor in each hospital reviewed participants' wounds twice a week until discharge) | |
| Participants | 356 participants with a displaced intracapsular fractured neck of femur, due to be treated with a hemiarthroplasty, were randomised into 2 groups Inclusion criteria: displaced intracapsular fractured neck of femur, due to be treated with a hemiarthroplasty Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: the ‘pulse lavage’ group had a 2‐L normal saline wash delivered via pulsatile lavage in stages throughout the procedure (164 participants) Group II: the control group had a 2‐L normal saline wash delivered by a jug or a syringe according to the surgeon's preference with 1 L being given before prosthesis insertion and 1 L after insertion (192 participants) Co‐interventions: NR | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound infections were diagnosed using criteria from the Nosocomial Infection National Surveillance Survey and graded as superficial or deep. Group I (pulse lavage): 9/164 (3/164 'deep') Group II (control): 30/192 (10/192 'deep') Secondary outcome: occurrence of infections with antibiotic resistance No group data but quote: "Half of the deep space infections were due to methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus" Secondary outcome: mortality NR by group. There were 25 deaths within the study period (7%); 18 of these were associated with American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA) scores of 3 or below | |
| Notes | Funding: no records | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "...all patients... were randomized into two groups" Comment: no details about method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: no mention of blinding, but nature of intervention and control means personnel would not be blind to treatment |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "One assessor in each hospital reviewed patients' wounds twice a week until discharge" Comment: no mention of blinding and it is unclear if the assessor would have been aware of treatment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "the difference in size between the two groups was due to 'start up' problems within the hospitals where pulse lavage had not been previously associated with hemiarthroplasty operations" "In cases where hemiarthroplasties were due to have pulse lavage but this was forgotten, the cases were struck from the study" Comment: the authors describe issues with implementing the pulse lavage intervention and although they describe participants being excluded at some point for this reason (presumably post‐randomisation) there are no details about them. It is probable that this introduced bias to the study. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: data are fully reported for some outcomes but others are not reported by group |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is insufficient information to judge |
| Methods | 2‐arm, parallel‐group RCT Setting: single centre in USA Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 196 women undergoing caesarean delivery. 94 were elective repeat procedures, age 27.5 vs 28.2 years Inclusion criteria: women presenting with term (> 37 weeks) singleton pregnancies undergoing routine caesarean delivery for arrest of dilation, arrest of descent, foetal malpresentation or as an elective repeat procedure Exclusion criteria: women diagnosed with chorioamnionitis, type I diabetes, placenta previa, placenta accreta, maternal coagulopathy, multiple gestation, HIV–positive status, prior severe gastrointestinal disease, or non‐reassuring fetal monitoring requiring immediate delivery | |
| Interventions | Group I: irrigation with 500‐1000 mL warm saline after closure of the uterine incision but before closure of the abdominal wall (97 participants) Group II: no irrigation (99 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (undue tenderness, erythema, discharge, or separation of the incision accompanying maternal fever) Group I (saline irrigation): 1/97 Group II (no irrigation): 2/99 Secondary outcome: length of stay (d) Group I (saline irrigation): 2.9 (1.0) Group II (no irrigation): 2.8 (0.9) Secondary outcome: adverse events (postpartum complications including SSI) Group I (saline irrigation): 14/97 Group II (no irrigation): 13/99 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Assignment was performed by pulling sequentially numbered opaque envelopes containing computer‐randomized individual allocations." Comment: an appropriate method of random sequence generation was reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Assignment was performed by pulling sequentially numbered opaque envelopes containing computer‐randomized individual allocations." Comment: an appropriate method of allocation concealment was reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "This randomization was carried out by research staff before initiation of the study, and the patients were blinded to treatment once assigned." Comment: although participants were blinded to treatment allocation it is unclear whether personnel were also blinded, the nature of the intervention groups suggests that they were not. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Postoperative care providers were blinded to group assignment to minimize potential bias. .... The randomizing physician collected the initial data. Data entry was performed by data technicians who did not participate in the design or execution of the study; these technicians also reviewed the charts of each randomized patient to assess the accuracy of information provided by the treating physician. The senior investigator performed periodic reviews of data entry to ensure completeness and accuracy of information in the computer database. The data analysis was performed by an investigator blinded to group assignment." Comment: blinded outcome assessment was conducted |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants were included in the analyses |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The primary outcome measure was the incidence of maternal morbidity, defined as the presence of at least one of the following:..." Comment: primary and secondary outcomes were clearly specified and fully reported. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there were no other sources of bias evident and reporting was sufficient to be reasonably confident that this was the case. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Slovakia Follow‐up: 7.8 months (mean) 2‐14 months (range): follow‐up at 2 weeks, 6 weeks and then 3‐monthly | |
| Participants | 162 children (undergoing 182 surgical procedures on soft and bone tissues in the proximal femur, hip and pelvic regions. mean age was 7.9 vs 7.5 years Types of procedures: adductor tenotomy, femoral or pelvic osteotomy, extraction of metal materials, open reductions, epiphysiodesis, resection or biopsy. Children had the following long‐term conditions: developmental dysplasia of the hip, cerebral palsy, tumours, Perthes disease Inclusion criteria: children undergoing surgery of the femur, hip or pelvis Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: lavage with 3.5% Betadine solution (0.35% povidone iodine) diluted in 30 mL sterile saline Group II: lavage with 30 mL sterile saline Cointerventions: antibiotic prophylaxis begun preoperatively in participants with femoral or pelvic osteotomy or massive surgery of soft tissues and continued for 48‐72 hs postoperatively (dose determined by weight). Drains left in until second postoperative day where necessary | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (positive bacteriological examination) Group I (Betadine lavage): 0/89 Group II (saline lavage): 2/73 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR Slovak; data entry and risk of bias based on information provided by translator | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information about the sequence generation process but stated that the participants were allocated to 2 groups randomly |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information on whether the allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information on whether personnel or participants were blinded to the interventions |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information on who assessed the presence of SSI or whether they were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote "In the first group (89 patients) [we] found no peri‐ or post‐operative infection. In the second group of patients (73) [we] brought to light two surface infection[s] (2.7%)" Comment: it appears that all participants were included in the analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes were not specified in the methods section so difficult to be certain whether all planned outcomes were assessed |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No evidence of additional bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: NR, appears to be single centre in Japan Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 16 children (aged 2‐12 years) undergoing appendectomy for perforated appendicitis Inclusion criteria: generalised peritonitis or nonlocalised abscess Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | After appendectomy, the peritoneal cavity was lavaged with 100 mL/kg (1500‐4000 mL) of the following warmed lavage solutions: Group I : normal saline (8 participants) Group II: acidic oxidative water (AOPW), a strong acidic water produced by the electrolysis of tap water containing 10% W/V sodium chloride (8 participants) Co‐interventions: antibiotics moxalactam [reported as LMOX] (100 mg/kg/d) or cefazolin [reported as CEZ] (50 mg/kg/d) were given in both groups for 5 d or until serum C‐reactive protein was at a normal level | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI No definition given for wound infection Group I (saline): 4/8 Group II (APOW): 1/8 Secondary outcome: adverse events: abscess formation Group I (saline): 1/8 Group II (APOW): 0/8 Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay (mean (SD) d) Group IS (saline): 22.7 (11.1) Group II (APOW): 12.1 (5.1) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "They were randomly divided into two groups" Comment: no details of randomisation method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of blinding |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of who performed the assessment of outcomes or whether blinding occurred |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all participants are included in the results |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: outcomes were not prespecified beyond "effectiveness and safety" |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is not enough methodological detail to judge |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: appears to be multiple centres, Japan ("our affiliated hospitals") Follow‐up: 30 d Duration of study: 2008‐2012 | |
| Participants | 44 children aged 3‐14 Group I: 16 boys and 4 girls, ranging in age from 4‐11 years Group II: 12 boys and 12 girls, ranging in age from 3‐14 years Inclusion criteria: children (age not defined) appendectomy for perforated appendicitis with extensive or panperitonitis Exclusion criteria: pre‐operative antibiotics or requirement of antibiotics due to massive abscess formation | |
| Interventions | After appendectomy, the peritoneal cavity was lavaged with 100 mL/kg saline or SAEW (strong acid electrolysed water, generated by electrolysis of tap water containing 0.2% NaCl), in Groups I and II, respectively. After closure of the fascial layer, the wound was washed out with 200 mL same solution before skin suture Group I: 100 mL/kg saline (20 participants) Group II: 100 mL/kg SAEW (24 participants) Co‐intervention: cefmetazole, 100 mg/kg/d, was given initially to both groups, which was replaced by the most sensitive antibiotics after identification of causative pathogens for 5 or 7 d depending on response. The abdominal wall was disinfected with povidone iodine, and laparotomy was performed via a pararectal incision, saving the muscle layers, followed by appendectomy, carried out in the same manner in both groups. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Defined as infection at the operation site, occurring up to 30 d after surgery, with confirmed causative pathogen(s) identical to those of the appendicitis. Group I (saline): 4/20 Group II (SAEW): 0/24 Secondary outcome: adverse events (intraperitoneal abscess) Group I (saline): 1/20 Group II (SAEW): 1/24 Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay (mean (SD) d) Group I (saline): 9.4 (4.7) Group II (SAEW): 8.7 (4.0) | |
| Notes | 34 participants were excluded from the study because some had received antibiotics before the operation and some had required antibiotics for massive abscess formation to be resected primarily with appendectomy Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were allocated randomly to one of two treatment groups" Comment: no details about method of randomisation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of blinding |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of who performed the outcome assessment or whether blinding occurred |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "34 patients were excluded from the study..." Comment: it is unclear if the exclusions were before or after randomisation |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: all outcomes of interest appear to be reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is not enough methodological information to judge |
| Methods | 3‐arm RCT Setting: Kaiser‐Permanente Medical Center ‐ Santa Clara, USA Follow‐up: at least 8 weeks | |
| Participants | 128 women undergoing cesarean section for various indications including repeat, breech and cephalopelvic disproportion. (132 entered study but 4 were excluded for irrigation protocol deviation and data are only presented for 128) Inclusion criteria: undergoing cesarean section Exclusion criteria: fever or other evidence of infection in labour, history of sensitivity to cephapirin or cefoxitin | |
| Interventions | Group I: following delivery of the placenta, the uterine cavity and incision, bladder flap, pelvic gutters, and subcutaneous tissue were irrigated with 2 mg cephapirin in 1000 mL normal saline (44 participants) Group II: irrigation with 2 mg cefoxitin in 1000 mL normal saline (41 participants) Group III: irrigation with 1000 mL normal saline only (43 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (defined as purulent wound discharge with or without wound separation) Group I (cephapirin): 0/44 Group II (cefoxin): 0/41 Group III (saline): 3/43 Secondary outcome: endometritis (defined as persistent fever, uterine tenderness, foul‐smelling lochia, with no other obvious source of infection) Group I (cephapirin):4/44 Group II (cefoxin): 1/41 Group III (saline): 5/43 (one of these also had wound infection) Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay (mean (SD) d) Group I (cephapirin): 4.8 (1.2) Group II (cefoxin): 4.9 (1.9) Group III (saline): 5.2 (2.1) | |
| Notes | 4 excluded from the analysis for protocol deviation Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "... bags were sequenced randomly by a lottery method and used in numerical order" Comment: the method is not explained in enough detail to know whether it was appropriate |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "... bags were sequenced randomly by a lottery method and used in numerical order" Comment: there is not enough detail about the method of randomisation and allocation concealment to judge |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "...bags of irrigant were prepared by pharmacy personnel" "One millilitre of multivitamin infusion was added to create an identical appearance of all solutions" "Patients, physicians, operating room personnel, and data collectors were thus blinded to the group assignment." Comment: steps were have been taken to ensure blinding of participants and personnel |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients, physicians, operating room personnel, and data collectors were thus blinded to the group assignment." Comment: steps appear to have been taken to ensure blinding of outcome assessors |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "One hundred thirty‐two patients were entered in the study. Four patients were eliminated from the statistical analysis because of deviations from the protocol of irrigation technique" Comment: there are only a few participants lost during the study but no details of these participants are reported and since numbers of events are small this could potentially have an impact. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: the outcomes of interest appear to be fully reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other bias |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: NR; appears to be single hospital in USA Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 200 participants undergoing elective and emergency gastrointestinal surgery (procedures on biliary tract 63/100 vs 57/100; gastroduodenal 14 vs 19 and colon 23 vs 24). Mean age was 61.7/61.6 years (range 17‐93). Malignancy present in 29/100 versus 25/100; diabetes 6/100 vs 8/100; obesity 30/100 vs 18/100 Inclusion criteria: elective or emergency procedures on the gastrointestinal tract Exclusion criteria: parenteral antibiotics had been administered preoperatively or intraoperatively; a colostomy was required; if frank pus was encountered at operation | |
| Interventions | Group I (kanamycin sulphate and cephalothin sodium): operative site was irrigated intermittently from the beginning to completion of the operation with a solution containing 1 g of kanamycin sulphate and 1 g of cephalothin sodium in 1000 mL of normal saline solution (100 participants) Group II (saline): operative site was irrigated intermittently from the beginning to completion of the operation with a solution of normal saline (100 participants) Cointerventions: the average volume of irrigant used for each operation was 750 mL. No cointerventions were reported | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (postoperative wound infection) Group I (kanamycin sulphate and cephalothin sodium): 3/100 Group II (saline): 9/100 Secondary outcome: mortality (postoperative deaths‐ last recorded 43 d post‐op) Group I (kanamycin sulphate and cephalothin sodium): 5/100 Group II (saline): 3/100 Note: 2 participants who died had wound infections but sepsis was not the cause of the deaths Secondary outcome: antibiotic resistance Details of individual species recovered from wounds of participants with SSI were reported together with their sensitivity or resistance where this was tested for. Multiple species reported for each participant Secondary outcome: adverse events Postoperative peritonitis: Group I (kanamycin sulphate and cephalothin sodium): 0/100 Group II (saline): 1/100 Secondary outcome: antibiotic resistance Resistance of specific organisms to kanamycin sulphate and cephalothin sodium reported for each type of surgery. Large numbers of samples reported as not tested | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Designation was made by computer‐generated listing using a standard table of random numbers." Comment: sequence generation used an appropriate method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Designation was made by computer‐generated listing using a standard table of random numbers." Comment: no indication as to whether allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "a prospective, randomized, double‐blind study" Comment: it was unclear who was blinded; while participants would probably be blinded it is unclear if personnel were |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "a prospective, randomized, double‐blind study" Comment: it was unclear whether the double‐blinding referred to outcome assessors |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants were included in the analyses |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes were not defined in the methods section so it is difficult to be sure whether all planned outcomes were fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT (factorial) Setting: single hospital in the USA Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 100 women undergoing caesarean section Inclusion criteria: women undergoing caesarean section; indications for surgery included elective repeat caesarean, failed trial of labour after prior caesarean, abnormal presentation, failure to progress, cephalopelvic disproportion, and severe pre‐eclampsia without thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy | |
| Interventions | Group I: saline irrigation (500 mL) of pelvis and subcutaneous tissue at uterine and fascial closure (50 participants) Group II: cefazolin irrigation (1 g in 500 mL saline) of pelvis and subcutaneous tissue at uterine and fascial closure (50 participants) Cointerventions: factorial randomisation to 2 alternative skin preparations: povidone iodine 7.5% scrub followed by povidone iodine 10% solution (standard skin preparation) versus 5‐min scrub with parachlorometaxylenol followed by povidone iodine scrub and solution (special skin preparation). No additional interventions were reported. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (hyperemic skin incision and fluctuant mass which when opened contained purulent material) Group I (saline): 4/50 (3/25 with standard skin preparation; 1/25 with special skin preparation) Group II (cefazolin): 2/50 (2/25 with standard skin preparation) Secondary outcome: adverse events (endometritis) Group I (saline): 30/50 (16/25 with standard skin preparation; 14/25 with special skin preparation) Group II (cefazolin): 11/50 (8 with standard skin preparation; 3/25 with special skin preparation) | |
| Notes | Funding: supported in part by the Vicksburg Hospital Medical Foundation | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Random assignment was achieved by card selection from sealed opaque envelopes with group appointment derived from a random number table" Comment: it appeared that an appropriate method was used to generate the randomisation sequence |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Random assignment was achieved by card selection from sealed opaque envelopes with group appointment derived from a random number table" Comment: it was not clear that enough measures were taken to ensure adequate concealment of allocation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no information on whether personnel and participants were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no information on who performed the outcome assessment or whether they were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants were included in the analyses |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes were not clearly prespecified so difficult to determine if all planned outcomes were fully assessed |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no obvious additional sources of bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Australia Follow‐up: letter or text message 4 weeks after surgery (following discharge from hospital) | |
| Participants | 3270 women undergoing caesarean section. Of those followed up 1508 had elective surgery and 1519 had surgery during labour. Mean age was 28.5 years in the Betadine group vs 28.6 years in the no Betadine group. 13.8% versus 12.9% had diabetes Inclusion criteria: women undergoing caesarean section either elective or during labour (stratified randomisation) Exclusion criteria: suspected or known allergy to iodine | |
| Interventions | Group I: wound irrigation with 50 mL of 10% aqueous povidone iodine (Betadine) solution just before skin closure (1634 participants randomised; 1634 received allocated intervention; 1520 analysed) Group II: no irrigation (1636 participants randomised; 1636 received allocated intervention; 1507 analysed) Cointerventions: alcoholic povidone iodine for skin preparation unless an allergy to iodine present, in which case chlorhexidine was used. Prophylactic cephalothin administered to all women soon after spinal anaesthesia | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (wound abscess or wound draining pus or sero‐sanguinous fluid, or redness, induration, warmth and tenderness or if woman’s general practitioner had seen her and prescribed antibiotics for presumed infection) Group I (povidone iodine irrigation): 144/1520 Group II (no irrigation): 147/1507 Secondary outcome: return to theatre Group I (povidone iodine irrigation): 7/1520 Group II (no irrigation): 9/1507 Secondary outcome: hospital readmission Group I (povidone iodine irrigation): 39/1520 Group II (no irrigation): 30/1507 Completed case analyses reported here: ITT population 1634 vs 1636 ‐ used in analyses for SSI | |
| Notes | Funding: states "we had no funding for this study..." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The allocation was prepared using computer generated list of random numbers using a variable block of 10 and performed by a staff member not part of the clinical team" Comment: acceptable method of sequence generation; randomisation also stratified by elective versus non‐elective procedure |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Women were randomised to ‘Betadine’ or ‘no Betadine’ group using sequentially numbered sealed opaque envelopes that contained the allocation..... After all layers were sutured and just prior to starting skin closure, the envelope with the allocation was opened by one of the theatre nurse[sic]" Comment: appropriate measures appear to have been taken to ensure allocation concealment. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote "In the control group (no Betadine group), layers would be sutured in exactly the same manner right up to the point of skin closure as it was only at this point that the allocation was revealed to the surgical team." Comment: surgical personnel were aware of group allocation; unclear whether participants were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Information on outcome measures was obtained by the research team blinded to the allocation and also not involved in clinical care of the women" Comment: blinded outcome assessment for all outcomes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Of the total number randomised, 243 women were inadequately followed up either due to change of address, wrong telephone number or just not receiving the text messages" Comment: 7% of women were lost to follow‐up; this was balanced between the arms (114 versus 129) and between the types of surgery (elective versus non‐elective) undertaken. Although this is close to the wound infection rate it does not appear likely to have impacted on the risk ratio of infection. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote "Primary outcome was the incidence of SSI as a whole but also specifically readmission for intravenous antibiotics and/ or return to theatre for wound infection" Comment: The outcomes were specified in the methods section and then fully reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: no specific quote but no evidence of other bias and reporting sufficient to be reasonably confident. |
| Methods | Three‐arm RCT Setting NR; appears to be single hospital in Switzerland Follow‐up: not clear beyond 4 d/discharge from hospital | |
| Participants | 162 participants with appendicitis Inclusion criteria: people undergoing appendectomy carried out through an incision at McBurney's point, without the use of drains and without the use of pre‐, peri‐ or post‐operative systemic antibiotics Exclusion criteria: people with perforated or gangrenous appendices or with peritonitis | |
| Interventions | Group I (saline): irrigation with 500 mL saline (0.9%) after the closure of the peritoneum. The liquid was re‐aspirated and the wound was not swabbed. The skin was then closed. Group II: (epicillin): irrigation with 500 mL saline with 1 g epicillin (Spectacilline) in solution as for Group I Group III: (lincomycine): irrigation with 500 mL saline with 600 mL lincomycine (Lincocin) in solution as for Group I Cointerventions: NR | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (septic complications with spontaneous or induced purulent discharge): results only reported for all groups together (1/162) compared with a non‐randomised group without irrigation (7/158) Secondary outcome: adverse events including abscess: results only reported for all groups together: 1/162 abscess from one of the antibiotic groups | |
| Notes | Funding: NR Paper in French; data extracted by one review author, checked by a fluent speaker | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "162 appendicectomies were randomised to treatment by blindly drawn lots" Comment: acceptable method of sequence generation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "162 appendicectomies were randomised to treatment by blindly drawn lots" Comment: unclear whether there was adequate concealment of allocation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No direct quote; no information on whether any personnel were blinded after the treatment allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Quote "In the irrigated groups a questionnaire was sent to the treating physician to establish whether postoperative wound infections developed" Comment: no information as to whether the physicians were aware of treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants appeared in the analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: the results for the three randomised groups were reported together and contrasted only with a non‐randomised comparison group |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No other sources of bias were apparent but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: a single hospital in Iran Follow‐up: 1, 2, 4 and 6 weeks post surgery | |
| Participants | 102 participants (mean age: Group I: 50.63 years, Group II: 50.28 years) undergoing open cholecystectomy surgery Inclusion criteria: cholecystitis diagnosed by surgeon Exclusion criteria: age > 80 years, diabetes, immunosuppression (acquired or hereditary), history of immunosuppressive therapy, use of antibiotics during referral time for other reasons, history of recurrent cholecystitis, laparoscopic cholecystectomy, limitation for follow up [sic] | |
| Interventions | Group I: open cholecystectomy, then before wound closure irrigation with 1 g cefazolin IV [sic] antibiotics (51 participants) Group II: open cholecystectomy with no antibiotic irrigation before wound closure (51 participants) Co‐interventions: same surgery and general anaesthesia | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Signs of infection included erythema, induration, tenderness, warmth, suppurative discharge Group I: 6/51 Group II: 6/51 | |
| Notes | Funding: none reported Reported in Persian. Data extraction and 'Risk of bias' assessment performed by translator | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Comment: they used a random number table |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Translator did not identify any information |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Translator did not identify any information |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Translator did not identify any information |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Translator judged all randomised participants included in analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Translator did not identify any information |
| Other bias | High risk | Comment: had a potential source of bias related to the specific study design used, they did not have well‐defined outcome, the evaluation of some participants by telephone! |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: NR; appears to be single hospital in Malaysia Follow up at 2, 4 and 6 weeks post‐operatively for wound infection and adverse events | |
| Participants | 190 participants (178 analysed) undergoing CABG surgery. Mean age was 61.6 (7.6) years. Comorbidiities documented were diabetes (44.4%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (37.1%), end stage renal failure (18%) and obesity (11.2%) Inclusion criteria: scheduled for elective CABG Exclusion criteria: emergency cases, those who underwent other surgical procedures in addition to CABG, those allergic to Dermacyn, and those who had infective or other skin lesions over anterior chest wall area | |
| Interventions | Group I (Dermacyn): Dermacyn wound irrigation (15‐min soak) upon chest closure and after insertion of sternal wires before subcutaneous tissue and skin closure (88 participants analysed) Group II (povidone‐iodine): povidone‐iodine would irrigation (15‐min soak) upon chest closure and after insertion of sternal wires before subcutaneous tissue and skin closure (90 participants analysed) Cointerventions: IV prophylaxis with 1.2 g Augmentin (amoxicillin and clavulanate) at induction. 2 drains were normally left in the mediastinal cavity. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (sternotomy wound infection, which was defined according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention system. Wound infections were graded as superficial (involving the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the incision), deep (involving fascia, muscle layers, and sternum), or deep organ space. Group I (Dermacyn): 5/88 (5 superficial; 0 deep) Group II (povidone‐iodine): 14/90 (10 superficial; 4 deep) Secondary outcome: need for reoperation Group I (Dermacyn): 0/88 Group II (povidone‐iodine): 4/90 (sternal dehiscence requiring surgical debridement and repair) Secondary outcome: mortality 12 participants were described as having "dropped out"; 4 owing to postoperative mortality and 8 dropped for re‐opening of chest due to bleeding Group I (Dermacyn): 7/95 Group II (povidone iodine): 5/95 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "patients were consecutively randomized into 2 groups" Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "patients were consecutively randomized into 2 groups" Comment: no information on whether allocation concealment was adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information on whether the participants or personnel were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The sternotomy wounds were inspected on postoperative day 2 and daily until discharge. Patients were then followed up at 2, 4, and 6 weeks postoperatively to assess for the presence of wound infection and Dermacyn side effects." Comment: no information on whether the inspections and follow‐up were carried out by blinded assessors |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "We recruited 190 patients for this trial, 95 patients in each group. Twelve patients, however, dropped out owing to postoperative mortality (4 cases, 2 deaths due to poor left ventricular function of < 20% and 2 deaths due to cerebrovascular accident) and chest re‐opened for bleeding (8 cases)" Comment: the number of dropouts (exclusions) was close to the number of primary outcome events. The outcome of mortality can be assessed using the ITT population so is at low risk but the SSI outcome is at high risk. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The primary outcome was the presence of sternotomy wound infection," Comment: only the primary outcome was prespecified and it is difficult to be certain whether other planned outcomes were fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in USA Follow‐up: carried out daily until discharge | |
| Participants | 260 randomised participants undergoing enterotomy during abdominal surgery. No further information on participant characteristics. Inclusion criteria: enterotomy during abdominal surgery Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I (kanamycin): lavage prior to closure of the abdominal incision with 100 mL of 1% kanamycin; excess allowed to enter the peritoneal cavity (124 analysed participants; number randomised unclear) Group II (saline): lavage prior to closure of the abdominal incision with 100 mL of saline; excess allowed to enter the peritoneal cavity (116 analysed participants; number randomised unclear) Cointerventions: concomitant systemic antibiotics in approximately one fifth of wounds | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (not defined) Group I (kanamycin): 12/124 Group II (saline): 23/116 Secondary outcomes: mortality, reoperation 20 participants were excluded for early postoperative death, reoperation or delayed primary closure. Group allocations and numbers excluded for each reason were not reported Secondary outcome: antibiotic resistance to kanamycin in wound culture Group I (kanamycin): 12/12 Group II (saline): "over half" of 23 Secondary outcome: adverse events Respiratory depression was only event reported on: Group I (kanamycin): 2/124 Group II (saline):4/116 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The solution, either 1% kanamycin or saline, was administered according to an established randomized schedule" Comment: no information on how the randomisation schedule was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The solution, either 1% kanamycin or saline, was administered according to an established randomized schedule" Comment: no information on whether the allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "an established randomized schedule under a double‐blind protocol" Comment: unclear who was blinded to the allocations |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The appearance of the wound was graded daily until discharge by a single observer and any deviation from optimal healing was documented serially with photographs" Comment: unclear whether the single observer was blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "of the 260 patients admitted to the study, 20 were excluded for reasons of early postoperative death, reoperation or delayed primary wound closure" Comment: the number of exclusions was comparable to the numbers of infections in each group; the group allocation of excluded participants was not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: outcomes were not defined in the methods section so it is difficult to be sure whether all planned outcomes were fully reported. Some outcomes were not fully reported with data for each treatment group. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: unclear but appears to be a single centre in Germany Follow up: NR | |
| Participants | 197 participants undergoing elective colorectal resection Inclusion criteria: NR Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: irrigation with polyhexanide 0.04% solution before final wound closure (101 participants) Group II: irrigation with Ringer's solution before final wound closure (concentration not given) (96 participants) Cointerventions: NR | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (not defined) Group I (polyhexanide): 19/101 Group II (Ringer's solution): 22/96 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR Abstract only States "interim analysis was done after 250 patients were screened and is presented here." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "This study was conducted as a double blind, randomized, single center study" Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "This study was conducted as a double blind, randomized, single center study" Comment: no information on whether the allocation sequence was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "This study was conducted as a double blind, randomized, single center study" Comment: although described as double‐blind it is unclear who was blinded and whether the blinding was adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "This study was conducted as a double blind, randomized, single center study" Comment: although described as double‐blind it is unclear who was blinded and whether the blinding was adequate |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "A total number of 197 elective colorectal resections were randomized. 101 patients received verum. Univariate analysis was followed by multivariate analysis where appropriate. Results: There were 41 wound infections in 197 patients (20.8%). 19 in the verum group, 22 in the control group (p=0.478)." Comment: it appeared that all randomised participants were included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Primary endpoint was the rate of SSI in each group" Comment: there is too little information to be sure if all planned outcomes were assessed and reported. |
| Other bias | High risk | Comment: an interim analysis. This is an abstract and there is too little information to determine if there were other additional sources of potential bias. |
| Methods | Setting: 2 tertiary hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery units in Australia Follow‐up: at 1 and 2 weeks following surgery, and thereafter as indicated. Minimum follow‐up 1 month after surgery | |
| Participants | 137 consecutive participants enrolled, undergoing major elective open abdominal operative procedures; 128 assigned to treatment (median age 63 years, range 18‐86 years) Inclusion criteria: adults undergoing an elective open abdominal operation anticipated to extend beyond 2 h Exclusion criteria: those undergoing laparoscopic procedures | |
| Interventions | In all cases, prior to abdominal closure, the peritoneal cavity was irrigated with least 3 L of warm saline without any added antibiotics. participants then received the following treatment after randomisation: Group I (pulse irrigation): surgical irrigation device (Stryker Instruments, Portage, MI) used after fascia closure to irrigate the surgical wound with 2 L of normal saline at room temperature; pressure close to (but not exceeding) 15 psi delivered through cone‐shaped applicator Group II (saline): following closure of the fascia in the standard group, 2 L of normal saline at room temperature was poured into the subcutaneous tissue without any agitation Excess fluid was removed from the subcutaneous tissue with application of a dry pack. Subcutaneous drainage or closure was not undertaken. The skin was reapproximated with continuous subcuticular 3/0 Monocryl sutures. Skin staples were not used in any case. A Duoderm dressing was applied to the wound. Cointerventions: all participants received dexamethasone phosphate 8 mg IV as part of routine antiemetic prophylaxis. At induction of anaesthesia all participants received ampicillin 1 g IV, gentamicin IV (2 mg/kg), and metronidazole 500 mg IV. Antibiotics were continued for 24 h postoperatively. In cases of penicillin allergy, vancomycin 1 g IV or cefazolin [cephazolin] 1 g IV was administered according to the particular sensitivity reaction. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound infection defined as: (1) purulent drainage, with or without laboratory confirmation, from the superficial incision; (2) organisms isolated from an aseptically obtained culture of fluid or tissue from the superficial incision; (3) at least one of the following signs or symptoms of infection: pain or tenderness, localised swelling, redness, or heat and superficial incision is deliberately opened by surgeon, unless the incision was culture‐negative; (4) diagnosis of superficial incisional SSI by the surgeon or the attending physician Group I (pulse irrigation): 4/66 (all superficial) Group II (saline): 12/62 (2 required major debridement with prolonged course of dressings; one had partial abdominal wall dehiscence) Primary outcome: wound dehiscence within 30 d of operation Group I (pulse irrigation): 0/4 Group II (saline): 1/12 Secondary outcome: participants with postoperative SSI using systemic antibiotics within 30 d of surgery 14/16 participants; no data regarding which treatment group these were associated with Secondary outcome: antibiotic‐resistant infections Details of organisms isolated but not of resistance were reported, this was not group data Secondary outcome: adverse events Cellulitis (without wound cultures): 1/16; no data regarding which treatment group this was associated with Any non‐wound‐related complication Group I (pulse irrigation): 32/66 Group II (saline): 23/62 Secondary outcome: surgical reintervention Relaparotomy Group I (pulse irrigation): 3/66 Group II (saline): 3/62 Debridement of wounds with SSI Group I (pulse irrigation): 0/4 Group II (saline): 2/12 Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I (pulse irrigation): median 9 (range 4‐71) d Group II (saline): median 9 (range 5‐45) d Secondary outcome: hospital readmissions Group I (pulse irrigation): 9/66 Group II (saline): 6/62 | |
| Notes | Funding: supported by a University of Melbourne, Early Career Development Grant, awarded to lead author. No supplementary support was provided by Stryker | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Grouping allocation was determined by a sealed envelope selection. Blocks of 20 patients were randomized at one time. Diabetic patients were randomized separately to achieve close to even distribution in each group." Comment: no information on how randomisation schedule was generated. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Grouping allocation was determined by a sealed envelope selection." Comment: unclear whether opaque envelopes were used |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No direct quote; no information on blinding Comment: it is unclear whether participants and personnel were blinded; personnel unlikely to be blinded after randomisation due to difference in intervention procedures between arms |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were monitored by a dedicated acute pain service and reviewed daily for any complications arising from their analgesic regime." Comment: unclear whether personnel were blind to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "A total of 137 patients were enrolled, as 8 cases did not reach the 2 h duration required for randomization." Comment: study flow diagram indicates that 9 were excluded because they did not conform to inclusion criterion of needing to be > 2 h in duration; there is a discrepancy in the report text stating 8 were excluded for this reason. Attrition bias judged to be low risk given that all others conforming to inclusion criteria were analysed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: unclear whether all prescribed outcomes were reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Switzerland Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 540 randomised participants undergoing surgery Inclusion criteria: participants undergoing surgery Exclusion criteria: oto‐rhino‐laryngeal surgical cases; thyroid surgeries; day‐case surgeries | |
| Interventions | Group I (saline): irrigation with saline. 2 rinses were performed; the first of the operative site, and the second performed before skin closure (273 participants ‐ information derived from graph) Group II (povidone‐iodine): irrigation with Betadine‐R solution (10% PVP‐iodine with 1% available iodine, diluted in a 1/10 solution). 2 rinses were performed; the first of the operative site, and the second performed before skin closure. (267 participants ‐ information derived from graph) Cointerventions: after 1 min the excess liquid was re‐aspirated. In all participants skin disinfection was carried out using a standard Betadine‐R solution. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (not defined) Group I (saline): 15/273 Group II (Betadine): 16/267 | |
| Notes | Paper in French; data extracted by one review author, checked by a fluent speaker SSI data presented graphically across 2 figures; these data extracted using graph‐reader software Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "A prospective randomized study was undertaken......a draw of two groups on the basis of a pre‐established list, was carried out at entrance to theatre" Comment: not clear how the randomisation sequence was established |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "A prospective randomized study was undertaken......a draw of two groups on the basis of a pre‐established list, was carried out at entrance to theatre" Comment: not clear whether allocation sequence was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote " all information about the participant, the type of interventions, the personnel, the bacteriological findings and the antibiotic therapies was stored on a computer" Comment: no information as to whether personnel were blinded to interventions |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No direct quote but no information as to who determined the presence of SSI or whether they were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No direct quote: no attrition is reported but results are presented only graphically and it is difficult to determine whether all randomised participants were represented in the results. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | No direct quote: results are not adequately reported for each group and it is very unclear if all outcome data are fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No other source of bias was apparent but the reporting was insufficient to be certain. |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single hospital in Denmark Follow‐up: mean 8 d (5‐16 d) | |
| Participants | 33 participants undergoing surgery for perforated appendix Inclusion criteria: all patients admitted for surgery for perforated appendix with diffuse peritonitis. Visible perforation of appendix with free pus in peritoneum, verified by microbiological culture of extracted peritoneal material. Normal function of kidneys in serum‐creatinin concentration demanded. Exclusion criteria: pregnant women, < 15 and > 75 years, with malignant disorders and known allergy to penicillin | |
| Interventions | Group I: no irrigation Group II: postoperative peritoneal flushing with 1 g ampicillin per L flushing fluid Group III: postoperative peritoneal flushing without ampicillin in the flushing fluid Cointerventions: all participants had systemic antibiotics: ampicillin 2 g 4/d IV, gentamycin 1.5 mg/kg weight as the first dose – then 1 mg/kg weight 3/d IM, and clindamycin 600 mg 3/d IM | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Group I (no irrigation): 4/10 Group II (ampicillin irrigation): 3/10 Secondary outcome: adverse events (intra‐abdominal abscess) Group I (no irrigation): 1/10 Group II (ampicillin irrigation): 010 Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I (no irrigation): 14 d (8‐22) Group II (ampicillin irrigation): 13 d (9‐20) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR Data extraction and 'Risk of bias' assessment performed by translator from the Danish; some aspects discussed with a review author | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: described by one Danish word; the envelope system |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: described by one Danish word; the envelope system |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: Groups II and III had additional catheter added for flushing fluids. Group II also had ampicillin added to the flushing fluid. Personnel would therefore be aware of allocation, unclear if participants were also aware |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no description of whether assessors were the same as the personnel |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all 30 participants were included in analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: all outcomes mentioned in the methods section were reported. In the discussion they reported that no kidney or liver dysfunction was observed |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: none identified |
| Methods | Three‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Spain Follow‐up: unclear | |
| Participants | 51 women undergoing axillary lymph node dissection for breast neoplasm. Mean age 55.6 years Inclusion criteria: diagnosis of breast neoplasm and plans to undergo an elective axillary lymph node dissection of Berg’s levels I and II because of axillary metastases determined pre‐operatively by core biopsy or evidence of metastasis in the sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in the intra‐operative or differential analysis Exclusion criteria: allergy to any of the antibiotic drugs to be used, chronic renal failure secondary to possible toxicity of gentamicin, and planned modified radical mastectomy | |
| Interventions | Group I: 2 lavages with 500 mL of physiologic saline (17 participants) Group II: lavage with 500 mL of saline followed by lavage with 500 mL of a 240‐mg gentamicin solution (17 participants) Group III: lavage with 500 mL of saline followed by lavage with 500 mL of a 600‐mg clindamycin solution (17 participants) Cointerventions: pre‐operative systemic antibiotics (amoxicillin‐clavulanic acid 2 g IV; a single dose within 30 min of incision) were employed in all groups. Once the dissection was finished, a Redon drain was placed and connected to a low‐pressure vacuum device (primary closure was undertaken) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (incisional, not further defined) Group I (2 x saline lavages) 0/17 Group II (saline then 240 mg gentamicin lavages) 0/17 Group III (saline then 600 mg clindamycin lavages) 0/17 Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (2 x saline lavages) 0/17 Group II (saline then 240 mg gentamicin lavages) 0/17 Group III (saline then 600 mg clindamycin lavages) 0/17 Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay Group I (2 x saline lavages) median 3 d (range 1‐3) Group II (saline then 240 mg gentamicin lavages) median 3 d (range 1‐3) Group III (saline then 600 mg clindamycin lavages) median 3 d (range 1‐3) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "The patients were randomized by means of an Internet module into three groups" Comment: mechanism of the internet module used for randomisation unclear |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "The patients were randomized by means of an Internet module into three groups" Comment: no information as to whether the allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The patients were blinded as to whether they received saline, gentamicin, or clindamycin." Comment: participants were blinded but unclear whether personnel were also blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is insufficient information to determine who performed the assessment of outcomes and whether they were blinded to treatment allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: it appears that all the randomised participants were included in the analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: the outcomes reported were not prespecified in the methods so it is difficult to determine whether all planned outcomes were fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other sources of bias but reporting is insufficiently detailed to be sure. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: NR but appears to be a hospital in Turkey Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 14 participants with perforated appendix (among 279 undergoing appendectomy for acute appendicitis) Inclusion criteria: perforated appendix, undergoing appendectomy for acute appendicitis Exclusion criteria: appendix not perforated | |
| Interventions | Group I: peritoneal lavage with irrigation and aspiration (7 participants) Group II: aspiration alone (7 participants) Co‐interventions: NR | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound infection Group I (lavage): 2/7 Group II (aspiration only): 0/7 Secondary outcome: adverse events (1 intra‐abdominal abscess, 1 postoperative ileus) Group I (lavage): 1/7 Group II (aspiration only): 1/7 | |
| Notes | Abstract only but further information received via study author correspondence Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote (via correspondence): "The randomisation method is envelope method" Comment: unclear how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: insufficient information on use of envelopes to be sure whether allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: no information on whether participants or personnel were blinded but personnel must have been aware due to differences in intervention |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information on who performed the assessment or whether they were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | It appears that all randomised participants were included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | It is unclear whether all planned outcomes were fully reported; we contacted the study author in order to fully report SSI outcome on a per‐group basis. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Abstract only and reporting insufficient to be certain there were no other sources of bias. |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single medical centre in USA Follow‐up: at least 2 weeks postoperatively | |
| Participants | 207 women undergoing caesarean section Inclusion criteria: non elective caesarean section Exclusion criteria: allergic to penicillin or cephalosporins, already on antibiotics, ongoing infection, requiring bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis | |
| Interventions | Group I: cefazolin lavage; 2 g in 1000 mL saline administered to the uterine incision (300 mL), bladder flap (200 mL), abdominal gutters (200 mL) and abdominal incision (remaining fluid) Group II: cefamandole lavage; 2 g in 1000 mL saline administered to the uterine incision (300 mL), bladder flap (200 mL), abdominal gutters (200 mL) and abdominal incision (remaining fluid) 2 additional groups were included in the trial using the same antibiotics delivered IV with saline lavage. These groups are not relevant to this review and we did not extract any data relating to them. Cointerventions: normal saline bolus IV after cord clamped | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (presence of cellulitis and/or purulent exudate) Group I (cefazolin): 2/59 Group II (cefamandole) 0/54 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomly assigned to one of four treatments" Comment: no information on how the randomisation sequence was generated or whether an appropriate method was used. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomly assigned to one of four treatments" Comment: no information on whether there was adequate allocation concealment. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The operating‐room nurses prepared the 1000 mL lavage solutions, to which all surgeons and patients were blinded" Comment: participants and personnel were blinded to treatment allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no specific quote but it was not clear who performed the outcome assessment and whether they were blinded to treatment allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all 207 randomised participants were included in the analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes were not clearly specified in the methods so it is unclear whether all planned outcomes were fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no obvious sources of additional bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | Within‐subject design ‐ all participants received both treatment and control Setting: single hospital in UK Follow‐up: 1, 4 and 8 weeks | |
| Participants | 30 women undergoing bilateral breast reduction. Participants had breasts randomised to the 2 treatment groups. Mean age 33 years (range 18‐65), mean BMI 26.3 Inclusion criteria: BMI ≤ 30, undergoing bilateral breast reduction Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I (saline): breast washed out with saline for approximately 2 min just prior to wound closure (30 participants, 30 breasts) Group II (control): no wash out with saline (same 30 participants as Group I, 30 breasts) Co‐interventions: each breast was preinfiltrated with 300 mL saline containing adrenaline diluted to 1:500,000, lignocaine and hyaluonidase. Infiltration was performed uniformly through the breast using a spinal needle and syringe, sparing the pedicle. All wounds were closed over corrugated drains which were removed 24 hs after surgery. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound discharge, invasive infection Group I (saline): 0/30 Group II (control): 0/30 Primary outcome: wound dehiscence Minor wound breakdown in 13/60 breasts (7 < 1 cm wide, 6 > 1 cm) 11/60 participants affected, 9 unilaterally, 2 bilaterally Group I (saline): 7/30 Group II (control): 6/30 | |
| Notes | Generalisability: outcomes were related to BMI and this group were preselected based on BMI Some methodological details were provided via study author correspondence Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote (from text): "The side to be washed out with normal saline was randomised so that the contralateral breast acted as each patient's own control" Quote (from author correspondence): "I think we used sealed envelopes" Comment: not enough detail about the method to judge whether appropriate method of sequence generation was used. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote (from author correspondence): "I think we used sealed envelopes" Comment: not enough detail about the method to judge whether there was adequate allocation concealment. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: there is no mention of blinding. The participants may have been blinded but the personnel would be aware of the different treatments. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote (from author correspondence): "Assessors were blind to the side washed out but could include the surgeons." Comment: although some assessors were blind to treatment, they could also have included the surgeons who were not blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote (from author correspondence): "All people enrolled were included in the study." Comment: all participants accounted for in the results |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is insufficient information to judge whether all planned outcomes were appropriately assessed. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: the study design means that the 2 groups are not independent. It's not clear whether the analysis was adjusted for paired data. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in USA Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 94 patients undergoing surgery for peritonitis. Mean age Group I: 40.1 years, Group II: 40.3 years Inclusion criteria: participants deemed by surgeon, at time of operation, that irrigation would be helpful for mechanical cleansing of peritoneal cavity or for direct application of an antibiotic to a grossly contaminated peritoneum. Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I (cephalothin): irrigation with solution containing 4 g/L cephatholin (43 participants irrigated with 4 L of solution, 1 participant irrigated with 2 L of solution) Group II (saline and multivitamin): irrigation with 0.9% saline solution containing 0.25 mL/L of IV multivitamin solution (Betalin, Eli Lilly, Indiana) (48 participants irrigated with 4 L of solution, 2 participants irrigated with 2 L of solution) Cointerventions: use of concomitant antibiotics (cephaolthin; cephalothin plus other antibiotic; penicillin and streptomycin; miscellaneous) was at surgeon's discretion | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (no definition provided) Group I (cephalothin): 11/44 Group II (saline and multivitamin): 13/50 Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (cephalothin): 5/44 Group II (saline and multivitamin): 8/50 Secondary outcome: antibiotic‐resistant infections Group I (cephalothin): 7 organisms reported to be resistant; 28 to be sensitive Group II (saline and multivitamin): 12 organisms reported to be resistant; 49 to be sensitive It was not clear how this related to participant‐level data; individual organism types were reported Secondary outcome: adverse events Abscess/peritonitis: Group I (cephalothin): 8/44 Group II (saline and multivitamin): 10/50 | |
| Notes | Participants: "Two patients had irrigation of the peritoneal cavity on two separate occasions, each of which was counted as a distinct clinical entity unto itself" Funding: NR Time points for all assessments unknown | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients were assigned by the pharmacy to the cephalothin or to the control group by use of a table of random numbers." Comment: sequence generation used an appropriate method. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quotes: "Patients were assigned by the pharmacy to the cephalothin or to the control group by use of a table of random numbers;" "The study was double blind, and the charts were fully evaluated prior to breaking the code, which was kept by the pharmacy;" Comment: participants allocated to treatment group by pharmacy who held the randomisation schedule, but unknown whether pharmacy staff were blinded to the allocation sequence |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quotes: "The study was double blind, and the charts were fully evaluated prior to breaking the code, which was kept by the pharmacy." Comment: appears that treating staff and participants were unaware of treatment allocation until after data collection |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The study was double blind, and the charts were fully evaluated prior to breaking the code, which was kept by the pharmacy." Comment: appears that staff were unaware of the allocation until after data collection |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: no evidence of attrition, as data reported for all randomised patients |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: all outcomes specified in study methods are reported in the results, but not enough information to determine whether all outcomes in the study protocol are reported |
| Other bias | High risk | Quote: "Patients were admitted to the study if their surgeon, at the time of operation, believed that irrigation would be helpful for mechanical cleansing of the peritoneal cavity or for direct application of an antibiotic to a grossly contaminated peritoneum." Comment: potential bias relating to participant selection, based on subjective rather than objective criteria. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Spain Follow‐up: NR | |
| Participants | 128 participants Inclusion criteria: colorectal surgery for neoplasms Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: intraperitoneal irrigation with normal saline (64 participants) Group II: intraperitoneal irrigation with solution containing gentamicin (240 mg) and clindamycin [clindamicin] (600 mg) (64 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (not defined) Wound infection (unsure of calculation to numbers as whole numbers/64 do not round to these %) Group I (saline): 41.9%; 27/64 (extrapolated from percentage and rounded to nearest whole number) Group II (antibiotic): 9.5%; 6/64 (extrapolated from percentage and rounded to nearest whole number) Intra‐abdominal infection (excluding 5% cases diagnosed with anastomotic leak) (intra‐abdominal abscess?) Group I (saline): 16.3%; 10/64 (extrapolated from percentage and rounded to nearest whole number) Group II (antibiotic): 0%; 0/64 | |
| Notes | Abstract only Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "A prospective randomized study of all the patients undergoing colorectal surgery for neoplasms at Hospital General Universitario de Elche during 2010 was performed. Patients were divided in 2 groups..." Comment: not clear how the randomisation sequence was generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "A prospective randomized study of all the patients undergoing colorectal surgery for neoplasms at Hospital General Universitario de Elche during 2010 was performed. Patients were divided in 2 groups..." Comment: not clear whether allocation was adequately concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote but no information on blinding of either participants or personnel |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote but no information on how the outcomes were assessed or whether the assessors were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "128 patients were analyzed, 64 in each group." Comment: the number of participants randomised is not stated, only the number analysed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Wound infection and intrabdominal abscess were investigated." Comment: both these outcomes were reported but it is not clear whether they were the only planned outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other bias but reporting insufficient to be confident (abstract only) |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Spain Follow‐up: 30 d after discharge | |
| Participants | 108 participants with adenocarcinoma (5 excluded postoperatively due to anastomotic leak). Mean (SD) age 69.9 (11.3) years. Comorbidities: diabetes mellitus (34%), high blood pressure (48%), dyslipedaemia (32%), cardiopathies (21%), chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (11%), nondecompensated liver cirrhosis (1%). Inclusion criteria: diagnosis of colorectal neoplasms and due to undergo elective operation with curative aims Exclusion criteria (preoperative): diagnosis of chronic renal failure Exclusion criteria (postoperative): anastomotic leak identified by computed tomography (CT) scan with rectal contrast enema | |
| Interventions | Group I (saline): irrigation of entire abdominal cavity with 500 mL normal saline, followed by aspiration of the liquid and abdominal wall closure (54 participants) Group II (antibiotics): irrigation with 500 mL normal saline, aspiration, then lavage with antibiotic solution (gentamicin 240 g and clindamycin 600 mg dissolved in 500 mL normal saline) for 3 min, aspiration and abdominal wall closure (54 participants) Co‐interventions: perioperative antibiotics given to all (ciprofloxacin 400 mg and metronidazol 1500 mg, single dose within 30 min of incision with redose after 4 h if surgery prolonged) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound infection defined as presence of purulent discharge from the surgical wound, confirmed with microbiologic culture Group I (saline): 14% (calculated as7/51 analysed participants) Group II (antibiotic): 4% (calculated as 2/52 analysed participants) Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (saline): 2 (unclear whether this is out of 51 analysed or 54 randomised participants) [we will assume completed case here] Group II (antibiotic): 1 (unclear whether this is out of 52 analysed or 54 randomised participants) Secondary outcome: intra‐abdominal abscess Defined as the presence of a fluid collection at CT scan in symptomatic participant (fever, abdominal pain, prolonged postoperative ileus or septic status) Group I (saline): 6% (calculated as 3/51 analysed participants) Group II (antibiotic): 0 (presumably 0/52 analysed participants) Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay (median (range) d) Group I (saline): 6 (5‐32) Group II (antibiotic): 6.5 (5‐14) | |
| Notes | Funding: financial support provided by Fundacion Navarro Tripodi | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The patients were randomized by means of an Internet randomization module" Comment: appropriate method of sequence generation appears to have been used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: there is no mention of blinding participants or personnel but differences in treatment mean personnel would not have been blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Wound infection was determined by an epidemiology nurse blinded to treatment groups" "The diagnosis of intra‐abdominal abscess was determined by a radiologist blinded to the treatment groups" Comment: outcome assessors were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "Exclusion criteria were... or an anastomotic leak in the postoperative course, which would represent a bias in the diagnosis of intra‐abdominal infection" Comment: 5 participants were excluded from the analysis as they were considered to be at high risk of infection and represent a bias ‐ however it is not clear what bias they would introduce as their results are not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes are not clearly reported as they are presented as percentages and do not clarify participant numbers. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other bias. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single breast unit at hospital in Spain Follow‐up: 2 weeks after surgery | |
| Participants | 40 female participants (mean age 54.8 (SD 13.7) years) undergoing axillary lymph node dissection Inclusion criteria: diagnosis of breast neoplasms and plans to undergo elective axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) of Berg’s levels I and II due to axillary metastasis determined preoperatively by core biopsy or evidence of metastasis in the sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in the intraoperative or in the differed analysis. Exclusion criteria: chronic renal failure due to possible toxicity of gentamicin and participants undergoing a modified radical mastectomy. | |
| Interventions | Group I (saline): lavage performed immediately prior to closure, after placement of drain and a first swab for microbiological culture. First lavage with 500 mL normal saline, which was aspirated and a second swab for culture obtained. Second lavage with 500 mL normal saline, which was aspirated prior to third swab for culture Group II (gentamicin): lavage performed immediately prior to closure, after placement of drain and a first swab for microbiological culture. First lavage with 500 mL normal saline, which was aspirated and a second swab for culture obtained. Second lavage with 240 mg gentamicin dissolved in 500 mL normal saline, which was aspirated prior to third swab for culture. Cointerventions: perioperative systemic antibiotics (single dose amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 2 g IV, within 30 min of incision) were administered in both groups. Redon drain was left in place and connected to a low pressure vacuum device, and removed when drainage volume was < 30 mL/d | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI ("wound infection" ‐ not defined) Group I (saline): 0/20 Group II (gentamicin): 0/20 Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay (median (range) d) Group I: 3 (1‐3) Group II: 3 (1‐3) Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (saline): 0/20 Group II (gentamicin): 0/20 Secondary outcome: adverse events (all types) Group I (saline): 0/20 Group II (gentamicin): 0/20 | |
| Notes | Funding: Fundación Navarro Tripodi | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients were randomized by means of an Internet randomization module into 2 groups." Comment: sequence generation used an appropriate method |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomized by means of an Internet randomization module into 2 groups." Comment: unclear whether randomisation schedule was concealed from staff |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were blinded as to whether they received gentamicin or not." Comment: unclear whether staff were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no direct quote; no information on who performed outcome assessment or whether they were blinded to treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: no evidence of attrition bias |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of selective reporting but not enough information to be certain |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias, but reporting is not sufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: several hospitals in Spain and 1 hospital in UK ("at our institutions" ‐ not stated how many ‐ it isn't clear from authorship) Follow‐up: minimum 42 months post surgery (infection surveillance was for 30 d following discharge) | |
| Participants | 106 participants undergoing elective surgery for colon neoplasms (data only presented for 104 as 2 who died perioperatively were excluded). Mean (SD) age: Group I 69.1 (10.2) years, Group II 68.5 (10.2) years. Co‐morbidities included diabetes mellitus (Group I 33%, Group II 29%), high blood pressure (Group I 46%, Group II 50%), dyslipidemia (Group I 33%, Group II 29%), cardiopathy (Group I 23%, Group II 27%). Groups were balanced in terms of tumour stage and surgical technique used. Inclusion criteria: diagnosis of colon neoplasms, undergoing elective surgery with curative aims Exclusion criteria: pre‐operative diagnosis of renal failure, allergy to gentamicin or clindamycin, diagnosis of rectal cancer | |
| Interventions | Group I: immediately prior to closure of the abdominal wall, lavage was performed with an antibiotic solution (gentamicin 240 mg and clindamycin 600 mg dissolved in 500 mL normal saline). The solution was allowed to sit in the abdominal cavity for 3 min, then aspirated (53 participants) Group II: as above but with 500 mL normal saline (53 participants) Co‐interventions: perioperative systemic antibiotics (ciproflaxin 400 mg and metronidazole 1500 mg, single dose given within 30 min of incision, additional dose after 4 h if surgery prolonged) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Incisional SSI (defined as the presence of a purulent discharge from the surgical incision and confirmed with microbiological culture) Group I (antibiotic): 3.8% (calculated as 2/52) Group II (saline): 13.5% (calculated as 7/52) Organ‐space SSI Group I (antibiotic): 0% (0/52) Group II (saline): 5.8% (calculated as 3/52) Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay (median (range) d) Group I (antibiotic): 6.5 (5‐14) Group II (saline): 6 (5‐32) Secondary outcome: adverse events Anastomotic leak Group I (antibiotic): 2/52 Group II (saline): 3/52 Secondary outcome: mortality 1 participant from each group died perioperatively and was excluded from the analysis. Survival analysis is reported for remaining participants as the primary outcome of the study was disease‐free survival, but 30‐day survival is not reported. 30‐day mortality Group I (antibiotic): 1/53 Group II (saline): 1/53 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients were randomly assigned using a random number table" Comment: appropriate method used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no mention of allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: There is no mention of blinding of participants and personnel. It is unlikely that personnel were blinded but possible |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Incisional SSI was determined by an epidemiology nurse blinded to the treatment groups" Comment: outcome assessor was blinded (for SSI) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: 1 participant in each group died perioperatively and was excluded from analysis. This is unlikely to have biased results but no details about these participants are included so it is difficult to judge. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: there does not appear to have been selective outcome reporting and the primary outcomes of the study are reported in detail |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other bias |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Setting: single hospital in Spain Follow‐up: 30 d after discharge | |
| Participants | 80 participants undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) as a bariatric procedure. Mean age 43.1 years; mean BMI 47.8 kg/m2 Inclusion criteria: BMI either > 40 kg/m2 or > 35 kg/m2 with comorbidities associated with obesity and undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) as a bariatric procedure. Exclusion criteria (preoperative): documented gastroesophageal reflux (these underwent laparoscopic Roux‐en‐Y gastric bypass), uncontrolled psychiatric disorders, active infection or malignant disease, and any other concomitant pathology considered to be a contraindication to bariatric surgery diagnosis of chronic renal failure. Post‐operative complications were also excluded from the analysis. | |
| Interventions | Group I: intra‐abdominal lavage with 500 mL saline (40 participants) Group II: intra‐abdominal lavage with a gentamicin–clindamycin solution: gentamicin (240 mg) and clindamycin (600 mg) dissolved in 500 mL (40 participants) Cointerventions: Peri‐operative systemic antibiotics (cefuroxime 3 g; single dose pre‐operatively within 30 min of incision, repeated after 4 h when the surgery exceeded that time) | |
| Outcomes | Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (saline): 1/40 Group II (clindamycin‐gentamicin): 0/40 Secondary outcome: adverse events ‐ complications of surgery Group I (saline): 2/40 Group II (clindamycin‐gentamicin): 1/40 | |
| Notes | Declaration of no competing financial interests, funding otherwise NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The patients were randomized by means of an Internet randomization module into two groups" Comment: appropriate means of randomisation sequence generation reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The patients were randomized by means of an Internet randomization module into two groups" Comment: unclear if appropriate measures were taken to conceal allocation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there was no information on whether personnel and participants were blinded to group allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Incisional SSI was determined by an epidemiology nurse blinded to the treatment groups. Infection surveillance was extended for 30 d after discharge. The diagnosis of organ‐space SSI and leak was determined by a radiologist blinded to the treatment group." Comment: outcome assessment was performed in a blinded manner |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Exclusions due to postoperative complications (3 participants) from some analyses were fully reported and accounted for; all participants could be included in analysis of SSI |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes were clearly predefined and appeared to be fully reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence of other sources of bias and reporting sufficient to suggest there were none |
| Methods | 3‐arm RCT Setting: 1 surgical unit in South Africa Follow‐up: at least 2 weeks after operation | |
| Participants | 87 participants undergoing surgery for peritonitis (mean age 53 years, range 18‐91 years) Inclusion criteria: confirmed diffuse or localised intra‐abdominal infection Exclusion criteria: those with nonruptured, localised abscesses and those participants undergoing appendectomy through right iliac fossa incisions; those with diffuse fecal peritonitis, infected pancreatic necrosis, or postoperative peritonitis | |
| Interventions | Group I (control): all peritoneal contamination was sucked out or picked out manually; the peritoneal cavity was then swabbed gently with large abdominal swabs (29 participants) Group II (saline): all peritoneal contaminants were sucked out, and the peritoneal cavity was generously irrigated with no less than 5 L of saline solution (29 participants) Group III (chloramphenicol succinate): all peritoneal contaminants were sucked out, and the peritoneal cavity was generously irrigated with no less than 5 L of saline solution; 2 g of chloramphenicol succinate was added to the last L of the lavage fluid (29 participants) Cointerventions: all participants received systemic antibiotics penicillin G potassium, amikacin sulfate and metronidazole. Therapy with antibiotics was started preoperatively and continued after operation for 24 hs and more, depending on the operative finding and each participant's clinical course. Intraperitoneal drains were placed only when abscesses were found. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI "Wound infection" defined as a discharge of pus from the wound; considered to be minor in cases where no early removal of sutures was necessary and primary healing was achieved; considered to be major when wounds required premature removal of sutures and drainage of pus and that healed by secondary intention. Group I (control): 6/29 (4 minor, 2 major) Group II (saline): 5/29 (3 minor, 2 major) Group III (chloramphenicol succinate): 5/29 (3 minor, 2 major) Secondary outcome: mortality Group I (control): 6/29 Group II (saline): 6/29 Group III (chloramphenicol succinate): 3/29 Secondary outcome: adverse events Surgical complications Group I (control): 3/29 (one pelvic abscess) Group II (saline): 7/29 (one pelvic abscess) Group III (chloramphenicol succinate): 2/29 Medical complications Group I (control): 8/29 Group II (saline): 9/29 Group III (chloramphenicol succinate): 5/29 Secondary outcome: mean length of hospital stay Group I (control): 13 d Group II (daline): 13 d Group III (chloramphenicol succinate): 10 d | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomized into one of the following three treatment groups..." Comment: unclear how randomisation was performed |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were randomized into one of the following three treatment groups..." Comment: unclear whether randomisation schedule was concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: no direct quote; no information on whether participants or personnel were blinded to treatment |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were monitored closely after operation and followed up in the outpatient clinic for at least 2 weeks after the operation." Comment: Nno information on whether personnel performing outcome assessments were blinded to treatment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: no evidence of attrition bias |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of selective reporting, but not enough information to be certain |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias, but reporting not sufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: neurosurgical department in Japan Follow up: 10 d post surgery | |
| Participants | 20 participants (mean age 60 years) admitted for clipping surgery for unruptured cerebral aneurysms; indications for clipping surgery are age < 70 years, no significant systemic risk for general anaesthesia, and aneurysm size > 5 mm. In 2 participants, 2 aneurysms were clipped in one surgery. Inclusion criteria: age between 20 and 70 years; planned surgery for aneurysm(s) of the internal carotid artery territory through a unilateral pterional approach; no steno‐occlusive lesions (> 50%) in cerebral arteries as evaluated by magnetic resonance (MR) angiography and/or conventional angiography; and aneurysms that presented no significant surgical difficulty Exclusion criteria: aneurysms presenting more surgical difficulty than usual; aneurysms suitable for approaches other than the pterional approach; aneurysms suitable for intravascular surgery; history of cerebrovascular diseases causing any disability (modified Rankin scale score 1 or worse); and significant medical problems | |
| Interventions | Group I (artificial CSF): brain surfaces and basal and sylvian cisterns irrigated during surgery with Artcereb, an artificial CSF (10 participants) Group II (saline): brain surfaces and basal and sylvian cisterns irrigated during surgery with physiological saline (10 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI NR Secondary outcome: adverse events: (postoperative, all types, includes MRI findings) Group I (artificial CSF): 2/10 Group II (saline): 2/10 (2/10 participants with 2 events each) | |
| Notes | Published paper does not report any of specified primary outcomes for this review Funding: Nihon Medi‐Physics Co, Ltd, Tokyo, Japan, provided N‐isopropyl‐p‐[123I]iodoamphetamine and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Tokyo, Japan, provided Artcereb. The study did not receive any other financial support. Contacted lead study author to find out if there are any further data relating to our outcomes | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The patient was randomly assigned to irrigation fluid A or B during surgery to irrigate the basal and sylvian cisterns and the brain surface." Comment: unclear how randomisation was performed |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "A total of 20 bottles each containing 500 mL of Artcereb (Artcereb group, n = 10) or physiological saline (saline group, n = 10) were prepared. The bottles of Artcereb were labelled A, and those of physiological saline were labelled B, without the knowledge of the study participants. The assignment was kept in a shielded envelope and only opened after all study data were collected." Comment: unclear whether allocation sequence was concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The bottles of Artcereb were labelled A, and those of physiological saline were labelled B, without the knowledge of the study participants. The assignment was kept in a shielded envelope and only opened after all study data were collected." Comment: unclear whether personnel were blind to treatment allocation |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "All 20 patients were serially evaluated on postoperative days 1, 3 to 5, and 7 to 10." Potentially amend this after obtaining more information from study authors, as it may not specifically relate to assessment of wound. Comment: study author contacted to determine if this relates to wound assessment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: no evidence of attrition |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of selective reporting, but not enough information to be certain |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other sources of bias, but reporting not sufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: a general hospital, UK Follow‐up: 6 weeks post surgery (close monitoring in post‐operative period, then outpatient review at 6 weeks) Also a 1‐year follow‐up (see notes) | |
| Participants | 159 patients undergoing elective or emergency transperitoneal intestinal surgery of various types and for a range of conditions (e.g. colorectal neoplasm, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticular disease). Mean (range) age: Group I (saline): 51 (16‐89) years, Group II (tetracycline): 50 (19‐85) years. Stratification 1) high risk and low risk operation category 2) IV antibiotic used (three regimes) Inclusion criteria: elective or emergency transperitoneal intestinal surgery (small bowel, colon and rectum) Exclusion criteria: allergy to penicillin or cephalosporins | |
| Interventions | Group I (saline): prior to closing the abdomen at the conclusion of the operation, peritoneal lavage was performed with 2 L 0.9% sterile saline. The lavage fluid was washed around the peritoneal cavity for at least 2 min and then sucked out with a sump sucker (74 participants) Group II (tetracycline): same method as above but with lavage fluid 2 L 0.9% sterile saline containing 2 g tetracycline (85 participants) Co‐interventions: all participants received IV antibiotic at the beginning of the operation (metronidazole 1.5 g and either gentamicin 120 mg (55 participants), ceftriaxone 2 g (55 participants), or mezlocillin 5 g (49 participants)). All participants had abdomen closed with a mass suture technique and primary skin closure with suction drainage to the pelvis | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound infection was defined as a discharge of pus from the wound. (Abdominal minor/major and perineal infection, and IV antibiotic groups also reported separately) Group I (saline): 24/74 Group II (tetracycline): 10/85 Secondary outcome: adverse events Intra‐abdominal abscess Group I (saline): 10/74 Group II (tetracycline): 11/85 Septicemia Group I (saline): 0/74 Group II (tetracycline): 2/85 Secondary outcome: surgical re‐intervention rate Reoperation for adhesive obstruction within 1 year of surgery (reported in the discussion rather than results) Group I (saline): 0/74 Group II (tetracycline): 3/85 | |
| Notes | Surgical re‐intervention rate was reported in the discussion rather than the results and is from 1‐year follow‐up. Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Each patient was assigned a study number on a consecutive basis. The hospital pharmacist then dispensed... according to a computed‐generated randomization code." "Randomization was stratified so that patients classified as 'high risk' or 'low risk' were distributed equally between the two lavage groups and also among the three intravenous antibiotic regimens" Comment: appropriate methods used to generate the sequence |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The hospital pharmacist then dispensed the intravenous antibiotics and the lavage fluid according to a computer‐generated randomization code. All drugs were in numbered ampoules, the pharmacist being the sole possessor of the code" Comment: the allocation sequence appears to have been concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The hospital pharmacist then dispensed the intravenous antibiotics and the lavage fluid according to a computer‐generated randomization code. All drugs were in numbered ampoules, the pharmacist being the sole possessor of the code" Comment: suggests that there may have been blinding of participants and personnel but not explicitly stated |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "All patients were monitored... by assessors independent of the surgical team" Comment: suggests they may have been blind to treatment but not explicitly stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all participants are included in the results |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: some outcomes were NR by group, or were only reported in the discussion (re‐operation rate) and it is not clear which outcomes were decided prospectively |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: no evidence of other bias but reporting insufficient to be certain |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in USA Follow‐up: 12 weeks post surgery (daily examination for 7 d, then at least weekly) | |
| Participants | 500 patients undergoing operative procedures (age reported as groups rather than mean ‐ there are participants of all age groups from < 9 years to > 80 years). Surgery categories included clean, potentially contaminated, contaminated and dirty. Inclusion criteria: elective or emergency surgery, abdominal and gastrointestinal procedures, oncologic procedures, vascular reconstructions, head and neck operations, thoracic procedures, genitourinary procedures, trauma operations Exclusion criteria: amputations for ischaemic disease, drainage of subcutaneous abscesses, skin grafting, anorectal procedures, a history of iodine sensitivity, thyroid disease or significant renal impairment | |
| Interventions | Group I (povidone‐iodine): following closure of the fascia, subcutaneous tissues were irrigated for 60 s with 10% povidone‐iodine solution (242 participants) Group II (saline): following closure of the fascia, subcutaneous tissues were irrigated for 60 s with saline solution (258 participants) Co‐interventions: wounds categorised as dirty had close system suction wound catheters placed in the subcutaneous space, which were removed 48 h postoperatively. Systemic antibiotics (clindamycin and gentamycin, or doxycycline for those with a history of allergy or suspected early impaired renal function) were given preoperatively to participants in potentially contaminated, contaminated, and dirty wound categories. If there were clinical indications of sepsis, systemic antibiotics were continued in some participants beyond 48 h postoperatively. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI An incision was considered infected if any amount of pus was discharged within 12 weeks of operation. Serous drainage from questionable wounds was cultured and the wound was classified as infected if any bacterial growth was recovered. Group I (povidone‐iodine): 7/242 Group II (saline): 39/258 Results also reported by wound category (clean, potentially contaminated, contaminated, dirty) for both groups | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "...eligible patients...were randomly allocated into treatment and control groups" Comment: there are no details on how participants were randomly allocated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no information about allocation concealment |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no mention of blinding |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "All wounds were examined daily by a single observer" Comment: there is no mention of blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: data from all randomised participants are included in the analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: the only outcome of interest was SSI and these data are fully reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is not enough methodological detail to judge |
| Methods | 2‐arm equivalence RCT Setting: single hospital (2 sites) in Australia Follow‐up: 6 weeks by phone call and state‐wide record searching | |
| Participants | 83 adults with intraoperative finding of acutely inflamed appendix undergoing laparoscopy for suspected appendicitis. Mean age 20 years (suction only group) versus 32 years (irrigation and suction group) Inclusion criteria: adult patients (English‐speaking), > 18 years, undergoing laparoscopy for clinically or radiologically suspected appendicitis meeting the following intra‐operative case definition: "Intra‐operative finding of an acutely inflamed appendix, with suppuration or perforation localized to the right iliac fossa, paracolic gutter or pelvis, and when the surgery is completed via a laparoscopic approach." Exclusion criteria: pathology not satisfying the case definition, pregnant, interval appendectomy, appendectomy following percutaneous drainage for abscess, appendectomy for reasons other than appendicitis (for example, tumour) | |
| Interventions | Group I: saline irrigation and suction. Median volume 675 mL (minimum 500 mL); irrigation deployment to contaminated areas at surgeon's discretion (41 participants allocated; 40 received intervention; 40 analysed) Group II: suction only (no irrigation) (42 participants allocated; 41 received intervention; 41 analysed) Cointerventions: all participants were treated with pre‐operative, IV, broad‐spectrum antibiotics. Continuation post‐operatively for purulent or perforated appendicitis, with transition to oral antibiotics recommended for 5 d but at the discretion of the treating surgeon: 17/41 vs 21/40 received these | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Group I (saline irrigation): 0/40 Group II (no irrigation): 0/41 Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I (saline irrigation): 2.0 (1 ‐ 3) Group II (no irrigation): 2.0 (1 ‐ 2.25) Secondary outcome: adverse events ‐ abscess formation Group I (saline irrigation): 2/40 Group II (no irrigation): 2/41 | |
| Notes | Funding: no funding was received | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Following enrolment, patients underwent simple randomization to either “suction only” (SO) or “irrigation and suction” (IS), with the use of computer‐generated random number sequencing." Comment: it appears that an appropriate method was used to generate the randomisation sequence. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Group allocation and data‐collection forms were stored in identical, opaque sealed envelopes" Comment: it appears that an appropriate method was used to conceal the allocation sequence. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: personnel (surgeons) were aware of the allocation to intervention groups. It is unclear if participants were also aware of allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote "Data collection was performed by an individual not involved in clinical treatment of enrolled patients." Comment: it appears that blinded outcome assessment was undertaken |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "All enrolled patients were accounted for in follow‐up through hospital medical records and searching the statewide admission database" Comment: 1 participant in each group converted to open surgery and therefore did not receive the intended intervention. All other participants were included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: both primary and secondary outcomes were predefined and appear to be fully reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | There were no other sources of bias apparent, and reporting was sufficiently detailed to be reasonably confident that this was the case. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single study in USA Follow‐up: early follow‐up by clinic follow‐up or phone call at 2‐4 weeks | |
| Participants | 220 children < 18 years with perforated appendicitis undergoing laparoscopic appendectomy Inclusion criteria: children < 18 years who were found to have perforated appendicitis. Perforation was defined as a hole in the appendix or fecalith in the abdomen Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I: saline irrigation, minimum 500 mL volume plus suction, mean volume 867 (327) (110 participants) Group II: no irrigation, suction only (110 participants) Cointerventions: 50 mg/kg dose of ceftriaxone (maximum dose 2 g) and 30 mg/kg dose of metronidazole (maximum dose 1 g) before the operation. Once daily dosing of ceftriaxone and metronidazole continued postoperatively | |
| Outcomes | Secondary outcome: adverse events ‐ abscess formation Group I (saline irrigation): 20/110 (calculated from 18.3% of 110) Group II (no irrigation): 21/110 (calculated from 19.1% of 110) Secondary outcome: length of stay Group I (saline irrigation): 5.4 (2.7) Group II (no irrigation): 5.5 (3.0) Secondary outcome: readmission Group I (saline irrigation): 0/110 Group II (no irrigation): 3/110 Secondary outcome: reoperation Group I (saline irrigation): 0/110 Group II (no irrigation): 1/110 | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "A computer‐generated individual unit of randomization was utilized in a nonstratified sequence in blocks of 10" Comment: an appropriate method was used to generate the randomisation sequence. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "After consent for study enrolment was obtained, the randomization sequence was accessed to identify the next allotment. The attending surgeon did not obtain consent and was blind to the allotment throughout the enrolment process." Comment: it seems that allocation concealment was used but procedures are not clear enough to be sure it was adequate. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: no specific quote but it appears that personnel could not be blinded; it is unclear whether participants were blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no specific quote; no information on whether outcome assessors were blinded to treatment allocation. It is stated that "Surgeons were not blinded during the postoperative course" but it is unclear if they were performing the outcome assessment. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all eligible randomised participants were included in the analysis. There were a large number of participants who consented but were excluded because of the intraoperative inclusion criterion. As this was prespecified this is unlikely to be a source of bias. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "This was a definitive trial design using postoperative abscess as the primary outcome variable." Comment: only the primary outcome was prespecified in the methods so it is difficult to determine if all planned outcomes were fully reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other sources of bias but the reporting is insufficiently detailed to be certain. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: a single centre in Japan Follow‐up: 3 months post surgery. (After the operation, there was wound inspection daily by nurses, once a week by an infection control nurse and surgeon during hospital stay, and at 4 week and 3 month post operative visits) | |
| Participants | 400 participants undergoing elective colorectal surgery for a variety of conditions (e.g. colorectal cancer, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease). 37 randomised participants were excluded for protocol violations (e.g. inappropriate bowel preparation, inappropriate antimicrobial prophylaxis, colon was not opened) therefore baseline data include 363 participants. Mean (SD) age: Group I (ESAAS) 51.8 (17.4) years, Group II (saline) 51.9 (17.7) years; diabetes 14/180 vs 13/183; colorectal cancer 82/180 vs 90/183 Inclusion criteria: participants undergoing elective colorectal surgery Exclusion criteria: dirty/infected wound, emergency surgery, laparoscopic surgery, stoma creation without bowel resection, transrectal operation, use of antibiotics within 10 d preceding surgery | |
| Interventions | Group I (ESAAS): the surgical wound was irrigated with at least 500 mL of ESAAS (electrolysed strongly acidic aqueous solution, produced by the electrolysis of tap water containing 0.12% NaCl) after the completion of fascial suture (200 participants, of whom 20 excluded due to protocol violation) Group II (saline): the surgical wound was irrigated with at least 500 mL of saline solution after the completion of fascial suture (200 participants, of whom 17 excluded due to protocol violation) Co‐interventions: all participants received Magcorol P (68 g magnesium citrate) for bowel preparation, antimicrobial prophylaxis 30 min before surgery with 1 g of second generation cephalosporins IV. If surgery was > 3 h, these were redosed. The same antibiotics were continued for 24 h after the operation (3‐4 doses). Povidone‐iodine was used for skin preparation. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Diagnosis based on guidelines issued by the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system. Infection had to occur within 30 d of the operation. Group I (ESAAS): 19/180 Group II (saline): 29/183 Incisional SSI Group I (ESAAS): 11/180 Group II (saline): 21/183 Organ/space SSI Group I (ESAAS): 8/180 Group II (saline): 8/183 Primary outcome: wound dehiscence Superficial wound dehiscence defined as > 1 cm separation of the incision above the fascia with or without infection that required packing and healing by secondary intention. Fascial dehiscence involved disruption of the fascia. (Superficial incisions deliberately opened to treat SSI were excluded.) Group I (ESAAS): 17/180 (15 superficial; 2 fascial) Group II (saline): 12/183 (10 superficial; 2 fascial) Secondary outcome: antibiotic resistance MRSA Group I (ESAAS): 4/14 Group II (saline): 8/24 MSSA Group I (ESAAS): 0/14 Group II (saline): 3/24 (other organisms are reported but without sensitivity) | |
| Notes | Funding: none reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Computer generated sequence allocation was used" Comment: approriate methods appear to have been used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "concealment was achieved by use of opaque envelopes opened at operating room by a third party" Comment: appropriate steps were taken to conceal allocation with opaque envelopes and third party |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "some surgeons could make the distinction between ESAAS and saline solution during application to the wound" Comment: authors state that personnel were not blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "the diagnosis of SSI was made by our infection control team" Comment: it is not clear whether personnel knew treatment allocation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Comment: 37/400 randomised participants were excluded at baseline due to protocol violation. This is a large number and it is possibly biased as personnel were not blinded, even though reasons for exclusion appear similar in the 2 treatment groups. No participants were lost to follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: all results are reported for the stated outcomes of interest |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence for other sources of bias |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single centre in Japan Follow‐up: 4 weeks post surgery | |
| Participants | 193 participants undergoing elective liver resection surgery (200 randomised, 7 excluded due to complications during surgery). Median age 68.5 years (range 21‐87 years), mean age 66.4 (11.2) vs 66.8 (11.3) years. Diabetes mellitus co‐morbidity: Group I 24.0%, Group II 19.6%. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Group I 35/96, Group II 37/97. Cholangiocellular carcinoma: Group I 3/96. Group II 2/97. Liver metastases: Group I 45/96, Group II 52/96 Inclusion criteria: elective liver resection without resection/reconstruction of the bile duct or intestine Exclusion criteria: resection/reconstruction of the bile duct and/or intestine, an operation designated Class III or higher according to CDC guidelines, detection of peritoneal dissemination of cancer | |
| Interventions | Group I (lavage): after removal of resected liver and confirmation of haemostasis, irrigation with sterile saline (37º C) directed at the dissected area. 3000 mL was used in open surgery and 1000 mL in laparoscopic surgery (96 participants) Group II (no lavage): no intraoperative lavage performed (97 participants) Co‐interventions: prophylactic antibiotic (flomoxef sodium) 1 g IV 30 mins before surgery, 1 g every 3 h during surgery, 1 g 2h after surgery, then 2 g daily for 4 d. A closed suction drain was placed near the transection plane of the liver parenchyma for all participants, and wound washout was performed using sterile saline after fascial closure but before skin closure | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Incisional infection (either superficial or deep) or organ/space infection. Incisional infection defined by clinically apparent cellulitis, induration, or purulent discharge from the closure site. Organ/space infection defined by radiologic evidence of a fluid collection necessitating drainage or antibiotic therapy. Total SSI Group I (lavage): 21/96 Group II (no lavage): 13/97 Superficial/deep SSI Group I (lavage): 7/96 Group II (no lavage): 6/97 Organ/space SSI Group I (lavage): 16/96 Group II (no lavage): 7/97 Secondary outcome: mortality (90 d) Group I (lavage): 2/96 Group II (no lavage): 1/97 Secondary outcome: morbidity (post‐operative complications) Group I (lavage): 37/96 Group II (no lavage): 36/97 Secondary outcome: hospital stay (mean (SD) d) (median (range) also reported) Group I (lavage): 15.2 (13.4) Group II (no lavage): 15.2 (13.1) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "..simple randomization was carried out by comparing a number within a sealed envelope with numbers in a computer‐generated random number table" Comment: use of a random number table |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "...a number within a sealed envelope.." Comment: it appears that steps were taken to conceal allocation in some way, but it is not known if envelopes were opaque and consecutively numbered |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "By its nature this study was unblinded" Comment: no blinding of personnel, appears to state that participants were also unblinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Quote: "By its nature this study was unblinded" Comment: no blinding of personnel, appears to state that outcome assessors were also unblinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all participants reported at baseline accounted for in analysis (but 7 excluded during surgery; probably too few to impact analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: all outcomes of interest appear to have been reported for all participants |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence of other sources of bias |
| Methods | 3‐arm RCT Setting: a single hospital in Thailand Follow‐up: minimum 2 weeks post surgery | |
| Participants | 374 participants randomised in total, 252 in the 2 arms of interest. Mean age (range): Group I (control) 27 (15‐65) years, Group II (Savlon) 24.5 (15‐55) years Inclusion criteria: > 15 years of age with acute appendicitis requiring emergency operation Exclusion criteria: known penicillin sensitivity, preoperative antibiotics received, microscopically normal appendices, periappendicitis due to inflammation elsewhere | |
| Interventions | Group I (control): no local treatment during operation (124 participants) Group II (Savlon): each layer was irrigated with 1% solution of cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (Savlon) and possibly also chlorhexidine, but this is unclear; and swabbed dry before closure (128 participants) Co‐interventions: "The use of peritoneal drainage and postoperative antibiotics was left to the surgeon's discretion" drains were used for 4 participants in group I (control) and 8 in group II (Savlon), all but 1 were for participants with a perforated appendix | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI "A wound was considered to be infected when there was a collection of pus which emptied itself spontaneously or after incision" Group I (control): 3/108 participants with non‐perforated appendix, 9/16 participants with perforated appendix Total 12/124 Group II (Savlon): 5/111 participants with non‐perforated appendix, 8/17 participants with perforated appendix Total 13/128 | |
| Notes | There is an additional trial arm in which ampicillin powder is applied to wounds. Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "At operation patients were randomly allocated into three groups by drawing cards" "randomisation may not have been adequate because more perforated appendices were found in the ampicillin group, which suggests that a large number of junior staff on rotation may have disregarded randomisation in what they took (rightly) to be the patient's interest" Comment: it is not clear whether allocation was random, the study authors express doubt |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "At operation patients were randomly allocated into three groups by drawing cards" "randomisation may not have been adequate because more perforated appendices were found in the ampicillin group, which suggests that a large number of junior staff on rotation may have disregarded randomisation in what they took (rightly) to be the patient's interest" Comment: it is not clear whether allocation was random, the study authors express concern |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: there is no information about blinding. The participants may have been blinded to treatment, but it is clear the personnel were not. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is no information about blinding of outcome assessment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants are accounted for in the results |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: there is not enough information to judge |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: there is not enough information to judge |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single hospital in Turkey Follow up: NR | |
| Participants | 430 women undergoing elective caesarean section. Mean age was 27.7 years (irrigation group) vs 28.2 years (mean number of previous births was 1)39% vs 36% had a comorbidity such as asthma or thyroid dysfunction. Inclusion criteria: women with gestational age > 38 weeks and elective cesarean delivery. Elective caesarean was defined as being performed before the presence of labour with or without previous history of caesarean delivery Exclusion criteria: women with emergency cesarean delivery, chorioamnionitis, type I diabetes, placenta previa, placenta accreta, maternal coagulopathy, or prior severe gastrointestinal disease | |
| Interventions | Group I: saline irrigation of the abdominal cavity using 500 mL of warm normal saline after closure of the uterine incision but before closure of the abdominal wall. All blood clots, vernix, and other debris were evacuated from the paracolic gutters, anterior and posterior cul‐de sacs, and under the bladder flap when employed. Group II: no irrigation; all clots, vernix and other debris were left in place. Cointerventions: 5 IU IV bolus of oxytocin over 5–10 s when the umbilical cord was clamped. Then, 30 IU of oxytocin in 500 mL lactated Ringer solution administered at a rate of 125 mL/h, and continued for 4 h. A total of 1 g cefazolin diluted in 20 mL normal saline administered over a 5‐min period | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI (partial or total separation of the incision, as well as the presence of purulent or serous wound discharge with induration, warmth, and tenderness) Group I (saline irrigation): 1/215 Group II (no irrigation): 2/215 | |
| Notes | Funding: Departmental funds only | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The participants were randomized to either an irrigation group or a control group. Assignment to one of the two treatment groups was determined using a random number table." Comment: an appropriate method was used to generate the randomisation sequence |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The assigned treatments were written on cards and sealed in secure opaque envelopes numbered in sequence." Comment: appropriate measures to ensure allocation concealment appear to have been followed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "The surgeons were not blinded to the procedure allocation. The allocated envelope was opened by the surgeon just before surgery, and the procedure allocation was recorded on each woman’s chart." Comment: personnel were not blinded; unclear if participants were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quotes: "Postoperative physicians were blinded to group assignment to avoid any potential bias; however, the surgeon who performed the operative procedure cared for the patient in the postoperative period, thus, was not blinded to the study group." "All data were recorded and analyzed by another researcher, who was blinded to the group assignments." Comment: some elements of outcome assessment were undertaken by a blinded assessor but it's not clear whether all assessment was. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants were included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The primary outcome measured was the rate of antiemetic drugs required in the postoperative period following cesarean delivery. Secondary outcome measures included the rate of PIM. Other outcomes evaluated were nausea and emesis occurring during the postoperative hospitalization." Comment: additional outcomes to those specified were also reported so it is difficult to determine whether all planned outcomes were assessed and reported. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Comment: there is no evidence of any other bias and reporting is detailed. |
| Methods | 3‐arm RCT Setting: a single hospital in Ireland Follow‐up: not stated | |
| Participants | 131 participants undergoing appendectomy (age range 3.5‐74 years) Inclusion criteria: all participants undergoing appendectomy over a stated time period Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Group I (Betadine): following appendectomy, participants were irrigated with 150 mL 1% Betadine (main constituent povidone iodine) solution intraperitoneally and 50 mL to the wound following closure of the peritoneum (49 participants) Group II (sterile water): participants were irrigated with approximately 150 mL sterile water intraperitoneally and 50 mL to the wound following closure of the peritoneum (31 participants) Group III (no irrigation): no irrigation following appendectomy (51 participants) | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI "Wound infection was defined as the presence of pus either spontaneously or on probing. All infections were confirmed bacteriologically" There were 17 wound infections among the 131 participants. Results are not given by trial arm. The authors state "when broken down according to type of irrigation, there was no significant difference between the three groups" Secondary outcome: systemic antibiotic use 53/131 participants "distributed evenly across the groups" Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay Participants with infection: 10 d Participants without infection 6 d Results NR by group | |
| Notes | Results are only provided for the whole group, by appendix histology or for participants with infected wounds vs uninfected, not by treatment group. Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The randomization took place in theatre following induction of anaesthesia by selecting a disc from a box" Comment: not enough information to judge whether this method was adequate |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The randomization took place in theatre following induction of anaesthesia by selecting a disc from a box" Comment: not enough information to judge whether this method was adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: no information provided about blinding. The participants may have been blinded but personnel would be aware of treatment |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information provided about who performed outcome assessment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no participants appear to have dropped out of the study |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: results are not reported for study arms so there are no data provided to back up authors' claim of no difference between groups. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: not enough information to judge |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: 25 centres in Europe Follow‐up: 4‐16 weeks post surgery (follow‐up laparoscopy) | |
| Participants | 498 participants randomised, of whom 72 were excluded from study before or during surgery due to failure to meet pre‐operative or intra‐operative inclusion criteria Inclusion criteria: female, aged 18‐45 years, undergoing primary removal of myomas or endometriotic cysts, using adequate contraceptive and not pregnant (negative test and agreement to use adequate contraception) Exclusion criteria (pre‐operative): pregnancy, serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase and/or bilirubin > 20% above normal range and considered clinically significant; blood urea nitrogen and creatinine > 30% above normal range and considered clinically significant; systemic corticosteroids, antineoplastic drugs and/or radiation; gonadotropin‐releasing hormone agonist/antagonist (except oral contraceptive) in 4 weeks prior to study; active pelvic/abdominal infection; known allergy to starch polymers; known/suspected intolerance to study materials; prior surgery for endometriotic cysts or myomas; non‐gynaecological surgical procedure planned during laparoscopic procedure; > 4 myomas, largest myoma < 2 or > 8 cm diameter, or endometriotic cysts < 3 or > 7 cm on pre‐operative ultrasound; history of alcohol or other substance abuse within last year; use of another investigational agent; participation in another clinical trial within last 30 d; (at centres in France, diabetes mellitus was also an exclusion criterion) Exclusion criteria (intra‐operative and post‐operative): clinical evidence of cancer, pregnancy, rectovaginal endometriosis, endometriosis class III or IV other than endometrial cysts (American Fertility Society (AFS) classification), conversion to laparotomy, unplanned surgery involving opening of the bowel (excluding appendectomy), extensive pelvic adhesions (AFS scores moderate or severe), use during procedure of any anti‐adhesion agent, use of O2 enhanced insufflation, adhesions requiring lysing during planned myomectomy or planned endometrial cyst removal (other than those around the ovarian fossa), endometriotic cysts not removed and ovary not left open, suturing the ovarian capsule, pedunculated cysts, use of glue, peritoneum sutured to fascia, use of drains, and post‐operative ovarian histology consistent with a non‐endometriotic cyst | |
| Interventions | At surgery, the abdomen was washed with warm study solution and this washing/irrigation of the abdominal cavity was repeated/continued with a minimum of 100 mL at intervals of at least once every 30 min. At the end of surgery, after a final irrigation with a minimum of 100 mL and evacuation of intraoperative solution, a final 1000 mL was instilled from a fresh treatment bag. Group I (Adept): study solution was Adept, a 4% icodextrin solution (217 participants) (non‐antibacterial) Group II (LRS): study solution was lactated Ringer's solution (209 participants) (non‐antibacterial) Co‐interventions: none specifically mentioned. There was standardised surgical management and all trocar ports ≥ 10 mm were double sutured to the fascia to help minimise any leakage. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI 'Wound infection' listed in treatment‐related adverse events table VII Group I (Adept): 1/217 Group II (LRS): 1/209 'Wound infection and vomiting' listed in adverse events designated serious table VIII (none deemed treatment‐related) Group I (Adept): 2/217 (1 with faecal impaction) Group II (LRS): 0/209 Secondary outcome: mortality Mentioned within adverse events section Group I (Adept): 0/217 Group II (LRS): 0/209 Secondary outcome: adverse events Group I (Adept): 71/217 of which 18 considered treatment‐related Group II (LRS):72/209 of which 15 considered treatment‐related | |
| Notes | Outcomes: the objective of the study was to examine the effect of irrigation on adhesion formation hence this was the primary outcome and infection and mortality were only mentioned among adverse events and are reported for the designated safety population Funding: Shire Pharmaceutical Development Ltd was the original study sponsor, providing research funding to all hospital departments involved, and funding was also provided by Baxter BioSurgery (Shire and Baxter are the previous and current distributors of Adept) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Treatment was randomized through a 24‐h central randomisation telephone system" "Patients were stratified according to their diagnosis of either myomas or endometriotic cysts and were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to separate randomisation lists" "The system was administered by the study Clinical Research Organisation" Comment: method of sequence generation is not explicitly stated but appropriate service and method for stratification appear to have been used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The system was administered by the study Clinical Research Organisation" "the treatment pack assigned was not permitted for allocation to any other patient in the study" Comment: use of 3rd party and other steps to conceal allocation |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Double‐blinding was possible as both fluids are clear and odourless solutions with similar viscosities to water and they were packaged identically" Comment: adequate methods used to blind participants and personnel |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: (referring to primary outcome) "Reviewers were blinded to the study treatment assignment" Comment: it appears steps were taken to blind outcome assessors for the primary outcome however blinding is not mentioned for safety assessment (our outcomes of interest) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "The safety population consisted of all consenting patients who received randomized treatment" Comment: 72/498 randomised participants were excluded from the study before (27) or during (45) surgery. There does not appear to be any bias in this exclusion but it is possible. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: our primary outcome of interest (infection) is not clearly defined or reported as it not a primary outcome of the study. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Comment: the study was funded by pharmaceutical companies which may have influenced reporting of safety data. |
| Methods | 3‐arm RCT Setting: 2 hospitals in the UK Follow‐up: 3, 7, 10 d, and 1 month post‐surgery | |
| Participants | 53 participants undergoing operations for generalised purulent or faecal peritonitis. Mean (range) age: Group I 56.1 (10‐84) years, Group II 49.7 (10‐83) years, Group III 56.0 (18‐79) years Inclusion criteria: generalised purulent or faecal peritonitis confirmed at laparotomy Exclusion criteria: NR | |
| Interventions | Following completion of surgical procedure, participants were given a thorough peritoneal toilet and lavage until solutions ran clear with the following protocols: Group I (saline): warm saline solution lavage, with a further 100 mL saline inserted into the abdominal cavity before wound closure (20 participants) Group II (chlorhexidine): warm chlorhexidine gluconate (Hibitane) 1:5000 solution lavage, with 100 mL inserted before wound closure (19 participants) Group III (PVP‐I): warm saline solution lavage, with 100 mL PVP‐I solution ('Betadine' peritoneal lavage solution) inserted before wound closure (14 participants) Co‐interventions: broad spectrum antibiotics (metronidazole and either gentamicin or cefuroxime) were given pre‐operatively and continued for at least 5 d postoperatively. Abdominal drains were inserted in all participants as required by the focus of primary sepsis or nature of surgery performed | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Wound abnormalities indicative of infection presented (can be added as each participants is only counted once) Pus in wound Group I (saline): 5/16 Group II (chlorhexidine): 4/16 Group III (PVP‐I): 4/13 Sero‐sanguinous discharge Group I (saline): 4/16 Group II (chlorhexidine): 6/16 Group III (PVP‐I): 5/13 Inflammation or induration Group I (saline): 1/16 Group II (chlorhexidine): 2/16 Group III (PVP‐I): 2/13 Summed data Group I (saline):10/16 Group II chlorhexidine): 12/16 Secondary outcome: mortality 12 participants died, 8 within 4 d of the operation (data below), and 4 died 8‐52 d postoperatively but group assignment was not reported. Authors state "all deaths were due either to the severity of the presenting disease or co‐existing complicating conditions" Mortality (within 4 d of surgery) Group I (saline): 4/20 Group II (chlorhexidine): 3/19 Group III (PVP‐I): 1/14 Secondary outcome: length of hospital stay Mean (SD) d (unclear on numbers of participants in groups (see mortality) 41 survivors included in total) Group I (saline): 11.4 (4.4) Group II (chlorhexidine): 9.3 (4.3) Group III (PVP‐I): 12.6 (3.8) | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote "Patients were randomized to receive..." Comment: no details about method of randomisation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information in report |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information in report |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: no information in report |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Comment: 12/53 participants died, thus removing some outcome data e.g. length of hospital stay. Causes of death were reported and there was no attrition for other reasons. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: details of deaths are provided but it is not reported which groups some of these participants were assigned to. Outcomes are not fully reported and may have been selectively reported. |
| Other bias | High risk | Quote: "the random allocation of patients to the different lavage groups resulted in an uneven distribution of the causes of peritonitis between the groups" Comment: due to small numbers of participants and broad inclusion criteria the groups may be too different to demonstrate a treatment effect. |
| Methods | Parallel‐group RCT Single hospital in the USA | |
| Participants | 236 women undergoing caesarean section Inclusion criteria: "pregnant English‐speaking women, ≥ 18 years, presenting for labour or scheduled cesarean delivery Exclusion criteria: "declining consent or urgent and emergent clinical situations in which the staff caring for the patient determined the | |
| Interventions | Group I: lavage with 500‐1000 mL warm saline after closure of the hysterotomy, but before the closure of the abdominal wall (110 participants) Group II: no lavage (126 participants) Cointerventions: blood clots and other debris manually evacuated. 1 g cefazolin IV as antibiotic prophylaxis before the start of surgery. Participants with cefazolin allergy received 900 mg clindamycin. | |
| Outcomes | Secondary outcome: length of stay (reported as day of discharge) Group I (saline lavage): 3 d Group II (no lavage): 3 d | |
| Notes | Funding: NR | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Assignment was performed by opening a sequentially numbered opaque envelope containing Comment: appropriate method of sequence generation reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Assignment was performed by opening a sequentially numbered opaque envelope containing Comment: appropriate method of allocation concealment reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "The original randomization was performed by research staff before the initiation of the study using a random number table generator, and the participants were blinded to treatment once assigned." "The envelope was opened by the circulation nurse in the operating room and silently viewed by the surgeons after closure of the hysterotomy." Comment: participants were blinded to the treatment allocation but personnel were not. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Quote: "This was recorded by nursing staff not blinded to the randomization....Postoperative nursing staff were blinded to group assignment to avoid any potential bias; however, the surgeon who performed the operative procedure cared for the patient in the postoperative period and, thus, was not blinded to the study group". Comment: some outcome assessors were not blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: all randomised participants were included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: outcomes assessed were clearly prespecified and mostly fully reported but measures of variance were not given for some outcomes. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Quote "Our study was stopped halfway through to allow for planned midpoint data analysis for resident research day" Comment: unclear if the study was stopped early and if so whether this was on the basis of a specific stopping rule. No evidence of other sources of bias and reporting sufficient to be reasonably confident of this. |
BMI: body mass index; CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; ITT: intention‐to‐treat; IM: intramuscular; IV: intravenous; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; MRSA: methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MSSA: methicillin‐susceptible Staphylococcus aureus; NR: not reported; PP: per‐protocol; PVP: polyvinyl pyrrolidine; RCT: randomised controlled trial; SSI: surgical site infection
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Different indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Different indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible intervention: extremely small volume of liquid | |
| Different intervention: lavage was not the intervention of interest | |
| Different indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Ineligible intervention: differences in lavage procedure were not the only difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Ineligible intervention: extremely small volume of liquid | |
| Different indication; study author contact confirmed that no relevant outcome data were collected and purpose of study was to evaluate pain and WBC | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible intervention: extremely small volume of liquid | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible intervention: extremely small volume of liquid | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible intervention: extremely small volume of liquid | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Ineligible indication: healing by delayed primary or secondary intention in some or all participants | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Ineligible population: some or all participants did not undergo surgery | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Quasi‐randomised RCT | |
| Use of peri‐operative irrigation/lavage was not the only systematic difference between the groups | |
| Different indication: used for anaesthesia purposes |
RCT: randomised controlled trial; WBC: white blood count
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT |
| Participants | 20 women undergoing surgery for endometriosis |
| Interventions | Group I: lavage performed routinely Group II: lavage performed until liquid was clear |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: C‐reactive protein concentration White blood cell count Temperature Complications |
| Notes | We have contacted study author who confirms relevant outcome data were collected; these are currently unpublished although a publication is being prepared. Study author unable to supply data in advance of publication |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT |
| Participants | 80 people receiving knee or hip replacement surgery |
| Interventions | Group I: iodophore irrigation of wound during surgery (40 participants) Group II: physiologic salt solution irrigation of wound during surgery (40 participants) |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: contamination of suction device used during surgery Group I: 13/40 Group II: 14/40 |
| Notes | 2 records for this study; one in Dutch. Notes from translator on methodology, "The authors say it is randomised, however there is no description as to how this was done and the allocation is not reported" "Very low quality, bad methodology, baseline not clearly described" Unclear whether any relevant outcomes were collected. Unable to contact study author to date |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: "private hospital" in Turkey Follow‐up: 40 d Duration of study: 2004‐2007 |
| Participants | 1272 women undergoing cesarean section Loss to follow‐up: 17 participants were lost from follow‐up Age range: 23.1‐33.7 years Inclusion criteria: women undergoing cesarean section Exclusion criteria: coincident remote site infections or colonisation, diabetes, cigarette smoking, systemic steroid use, obesity (> 20% ideal body weight), excessive subcutaneous scar tissue due to previous operations, perioperative transfusion of blood products and altered immune response were excluded from the study (33 women). Operation time, > 2 h or blood loss > 1 L or having premature rupture of membrane > 6 hs were discharged from the study (26 women) |
| Interventions | Group I: povidone‐iodine 10% was used for preoperative antisepsis of skin and after closure of skin (600 participants) Group II: povidone‐iodine was used in the same way but also subcutaneous tissue was irrigated with rifamycin SV/ 250 mg, before closure of subcutaneous tissue (596 participants) Amount of irrigation fluid: not stated Cointervention: single dose of 1 g ceftriaxone was given to all participants for prophylaxis in perioperative period after clamping of umbilical cord |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: SSI Group I: 12/600. All of them were superficial incisional SSI Group II: 0/596 Secondary outcome: cost [costs were given in dollars, we have assumed these to be USD] Group I: total cost of 12 participants with SSI was USD 5386 P value: not stated for cost alone When groups were compared, surgical site infection and cost were significantly lower in study group ( P <0.05) |
| Notes | Funding: not stated Not clear whether randomisation was adequate. Study author contact attempted but so far unsuccessful |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: appears to be single hospital in Spain Follow‐up: 1 year |
| Participants | 79 Participants with orthopaedic (hip and knee) implant infection undergoing surgery for the infection |
| Interventions | Group I: low‐pressure pulsatile lavage Group II: high‐pressure pulsatile lavage Cointerventions: after open debridement, a broad‐spectrum intravenous antimicrobial regimen was started and maintained until obtaining definitive microbiological results. The definitive oral antibiotic treatment was selected according to the antibiogram. The duration of intravenous and oral antibiotics was not standardised and this was decided according to the clinical manifestations and the C‐reactive protein values of each case |
| Outcomes | Remission of infection; relapse of infection; retention of prosthesis; reinfection; success rate |
| Notes | The source of funding did not play any role in the investigation. Unclear whether any relevant outcomes were reported. Study author contact attempted but so far unsuccessful. |
| Methods | 2‐arm RCT Setting: single UK hospital Follow‐up: none reported |
| Participants | 44 participants undergoing hip fracture fixation Inclusion and exclusion criteria not reported |
| Interventions | Group I: 0.05% chlorhexidine jet lavage (number of participants not reported) Group II: no intervention (number of participants not reported) Co‐interventions: not reported |
| Outcomes | Air bacterial counts and mean operating times |
| Notes | Unclear whether any relevant outcomes were reported. Unable to contact study author to date No funding reported |
RCT: randomised controlled trial
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
| Trial name or title | Does Peritoneal lavage influence the rate of complications in paediatric laparoscopic appendicectomy? A prospective randomised clinical trial |
| Methods | Parallel‐group (2‐arm) RCT |
| Participants | Children with perforated appendicitis |
| Interventions | Peritoneal lavage with 0.9% saline then suction No lavage (suction only) |
| Outcomes | Length of hospital stay in days, including any days of re‐admission Intra‐abdominal abscess |
| Starting date | 20 May 2010 |
| Contact information | Charles Keys Department of Paediatric Surgery Southern Health Monash Medical Centre 246 Clayton Road Clayton Vic 3168 Australia |
| Notes | No updates registered |
| Trial name or title | Dilute Betadine lavage in the prevention of postoperative infection |
| Methods | Parallel‐group (2‐arm) RCT |
| Participants | People who are scheduled to undergo a revision total knee arthroplasty |
| Interventions | Betadine lavage: dilute Betadine lavage prior to surgical closure for 3 min followed by 2000 mL of sterile saline irrigation Saline lavage: (2000 mL) prior to closure |
| Outcomes | Infection |
| Starting date | 2 August 2010 |
| Contact information | Darren R Plummer, BBA, MBA; [email protected] Rush University Medical Center Chicago, Illinois, United States, 60612 |
| Notes | Currently recruiting |
| Trial name or title | Antibiotic irrigation for pancreatoduodenectomy |
| Methods | Parallel‐group (2‐arm) RCT |
| Participants | Adults undergoing pancreatoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) |
| Interventions | Antibiotic irrigation via peritoneal lavage (polymyxin B (500,000 U) in 1 L of 0.9% normal saline) Placebo irrigation via peritoneal lavage (0.9 % normal saline) |
| Outcomes | Infections Fistulas |
| Starting date | 1 July 2014 |
| Contact information | Michael G. House, Associate Professor of Surgery, Indiana University Indianapolis, Indiana, United States, 46202 |
| Notes | Recruiting |
| Trial name or title | Incidence of surgical site infection after irrigation of surgical pocket with 0.05% chlorhexidine compared with triple antibiotic solution in post‐mastectomy breast reconstruction |
| Methods | Intra‐individual (split‐body) (2‐arm) RCT |
| Participants | Women with breast cancer undergoing bilateral breast reconstruction |
| Interventions | 0.05% chlorhexidine solution (IrriSept®) commercially prepared in 450 mL bottles Triple antibiotic solution will contain 1 g of cefazolin, 50,000 U of bacitracin, and 80 mg of gentamicin in 500 mL of normal saline Each participant will receive triple antibiotic solution on one breast and the chlorhexidine on the other breast |
| Outcomes | Surgical site infection |
| Starting date | 17 March 2015 |
| Contact information | Kent Higdon, MD 615‐936‐0160 Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee, United States, 37232 |
| Notes | Recruiting |
| Trial name or title | Bacterial contamination: iodine vs saline irrigation in pediatric spine surgery |
| Methods | Parallel (2‐arm) RCT |
| Participants | Children aged 3‐18 years undergoing surgery for diagnosis of spinal deformity |
| Interventions | Povidone‐iodine ‐ 0.35% povidone‐iodine (Betadine) Normal saline ‐ sterile sodium chloride (NaCl) solution |
| Outcomes | Postoperative infection |
| Starting date | 7 August 2015 (received), anticipated start date February 2017 |
| Contact information | Principal investigator: Michael Glotzbecker, MD; Boston Children’s Hospital |
| Notes | Not yet open to recruitment |
| Trial name or title | Water and saline head‐to‐head in the blinded evaluation study trial (WASHITBEST) |
| Methods | Parallel‐group (2‐arm) RCT |
| Participants | Participants diagnosed with acute appendicitis aged at least 6 years |
| Interventions | Irrigation of the abdomen during surgery with normal saline Irrigation of the abdomen during surgery with sterile water |
| Outcomes | Postoperative deep space organ infection as defined by the Surgical Infection Society (time frame: 30 d) Infection after surgery within the peritoneal space Temperature > 38.5º C (time frame: 30 d) > 2 d to return of bowel function as evident by either flatus or bowel movement (time frame: 30 d) Length of hospital stay (time frame: 30 d) |
| Starting date | 8 March 2016 (information received). Study start date April 2013 |
| Contact information | Arthur Rawlings, MD University of Missouri‐Columbia |
| Notes | Completed |
RCT: randomised controlled trial
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 SSI Show forest plot | 14 | 6106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.68, 1.11] |
| Analysis 1.1 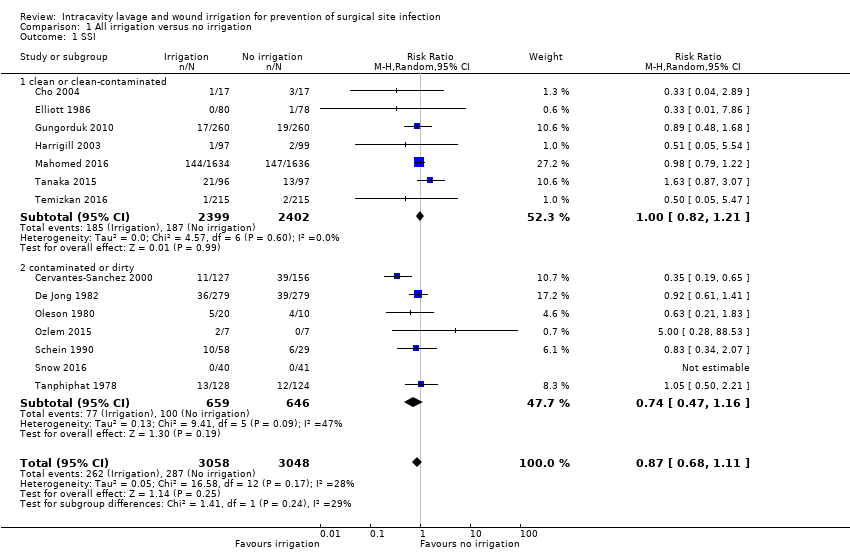 Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 1 SSI. | ||||
| 1.1 clean or clean‐contaminated | 7 | 4801 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.82, 1.21] |
| 1.2 contaminated or dirty | 7 | 1305 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.47, 1.16] |
| 2 Adverse events Show forest plot | 3 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.76, 1.44] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 2 Adverse events. | ||||
| 3 Abscess Show forest plot | 3 | 331 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.54, 1.54] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 3 Abscess. | ||||
| 4 Mortality Show forest plot | 2 | 280 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.36, 2.04] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 4 Mortality. | ||||
| 5 Hospital stay Show forest plot | 7 | 1597 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.13 [‐0.38, 0.12] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 5 Hospital stay. | ||||
| 6 Return to theatre (reoperation) Show forest plot | 2 | 3247 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.28, 1.84] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 6 Return to theatre (reoperation). | ||||
| 7 Readmission to hospital Show forest plot | 2 | 3247 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.10, 4.90] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 7 Readmission to hospital. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 SSI Show forest plot | 30 | 5141 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.57 [0.44, 0.75] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 1 SSI. | ||||
| 1.1 clean | 4 | 680 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.03, 0.89] |
| 1.2 clean‐contaminated | 13 | 2210 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.57 [0.40, 0.79] |
| 1.3 contaminated or dirty | 13 | 2251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.40, 0.92] |
| 2 Wound dehiscence Show forest plot | 3 | 660 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.65, 2.45] |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 2 Wound dehiscence. | ||||
| 3 Adverse events Show forest plot | 3 | 178 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.55 [0.22, 1.34] |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 3 Adverse events. | ||||
| 4 Abscess Show forest plot | 9 | 1309 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.42, 1.62] |
| Analysis 2.4 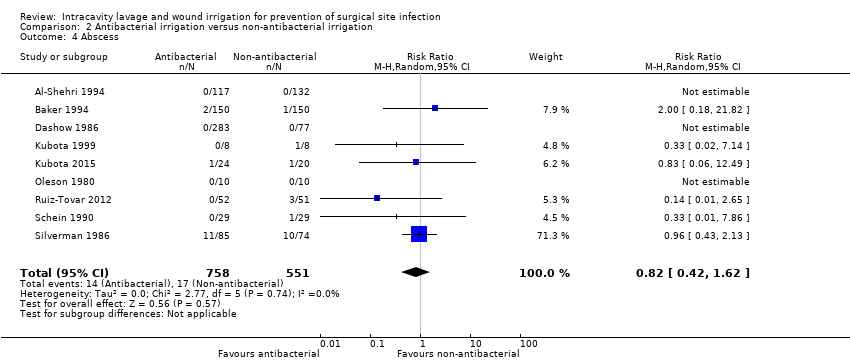 Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 4 Abscess. | ||||
| 5 Mortality Show forest plot | 11 | 1121 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.48, 1.36] |
| Analysis 2.5  Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 5 Mortality. | ||||
| 6 Hospital stay Show forest plot | 7 | 635 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.85 [‐1.60, ‐0.09] |
| Analysis 2.6  Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 6 Hospital stay. | ||||
| 7 Return to theatre (reoperation) Show forest plot | 2 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.12, 13.60] |
| Analysis 2.7  Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 7 Return to theatre (reoperation). | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Mortality Show forest plot | 2 | 875 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 Icodextrin versus lactated Ringer's solution, Outcome 1 Mortality. | ||||
| 2 Adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 875 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.96, 1.02] |
| Analysis 3.2 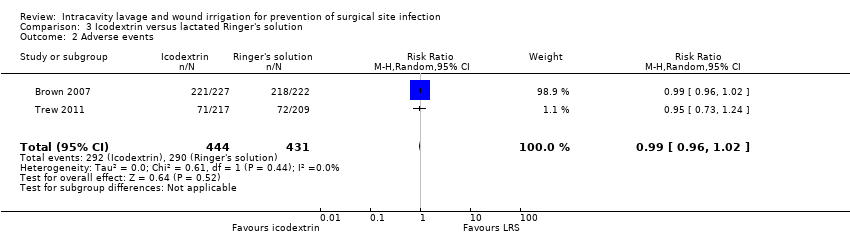 Comparison 3 Icodextrin versus lactated Ringer's solution, Outcome 2 Adverse events. | ||||
| 3 Treatment‐related adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 875 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.98, 1.86] |
| Analysis 3.3  Comparison 3 Icodextrin versus lactated Ringer's solution, Outcome 3 Treatment‐related adverse events. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 SSI Show forest plot | 2 | 484 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.34 [0.19, 0.62] |
| Analysis 4.1  Comparison 4 Standard irrigation versus pulsatile irrigation, Outcome 1 SSI. | ||||

Study flow diagram
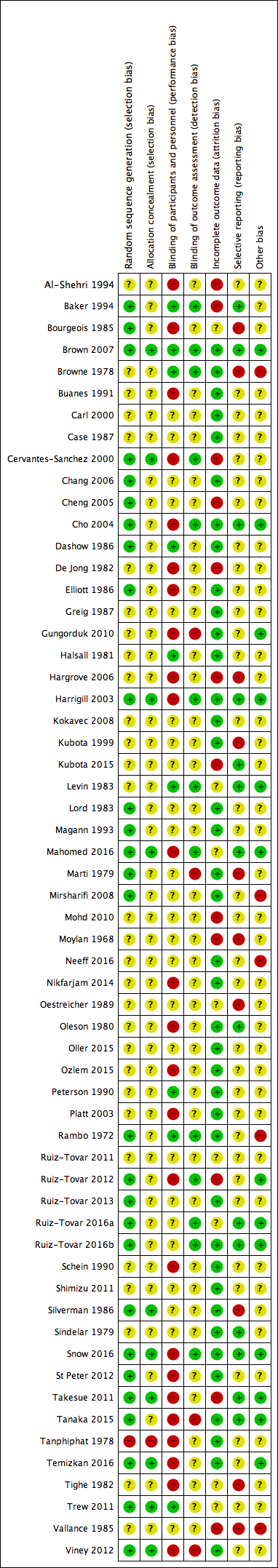
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study
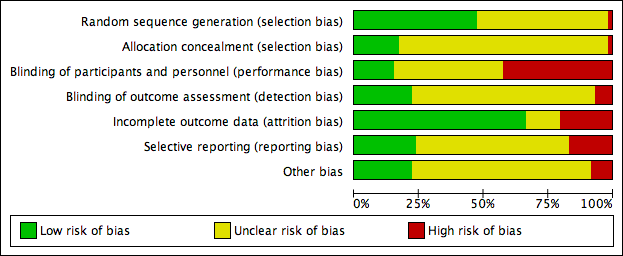
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies

Funnel plot of comparison 1: all irrigation versus no irrigation, outcome: 1.1 surgical site infection

Funnel plot of comparison 2: antibacterial versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, outcome: 2.1 surgical site infection

Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 1 SSI.
Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 2 Adverse events.
Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 3 Abscess.

Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 4 Mortality.
Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 5 Hospital stay.

Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 6 Return to theatre (reoperation).

Comparison 1 All irrigation versus no irrigation, Outcome 7 Readmission to hospital.

Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 1 SSI.

Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 2 Wound dehiscence.

Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 3 Adverse events.

Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 4 Abscess.
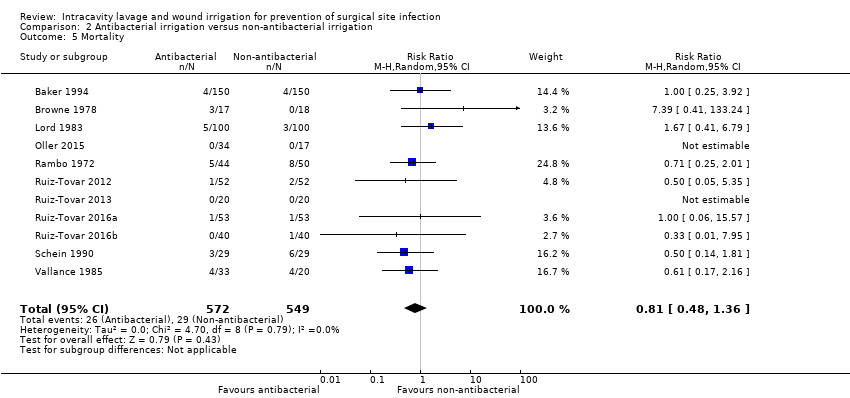
Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 5 Mortality.
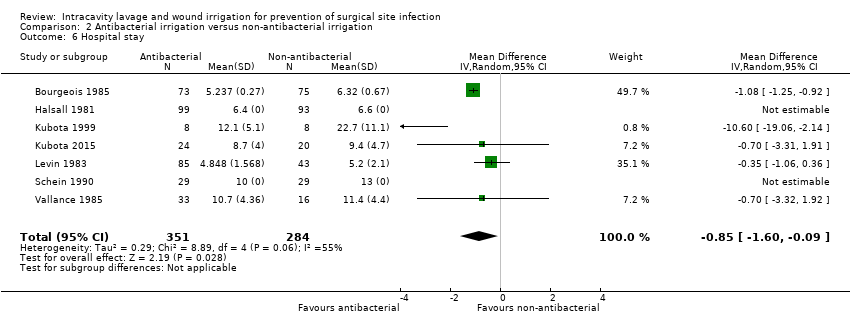
Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 6 Hospital stay.
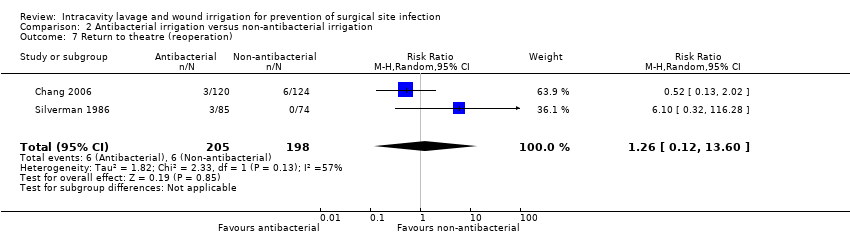
Comparison 2 Antibacterial irrigation versus non‐antibacterial irrigation, Outcome 7 Return to theatre (reoperation).

Comparison 3 Icodextrin versus lactated Ringer's solution, Outcome 1 Mortality.

Comparison 3 Icodextrin versus lactated Ringer's solution, Outcome 2 Adverse events.

Comparison 3 Icodextrin versus lactated Ringer's solution, Outcome 3 Treatment‐related adverse events.

Comparison 4 Standard irrigation versus pulsatile irrigation, Outcome 1 SSI.
| All irrigation compared with no irrigation for prevention of surgical site infection | ||||||
| Patient or population: participants undergoing clean, clean‐contaminated, contaminated or dirty surgical procedures Setting: hospitals | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with no irrigation | Risk with irrigation | |||||
| SSI | Study population: participants undergoing clean‐contaminated, contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | RR 0.87 | 6106 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | On the basis of the included studies there is no clear difference between the intervention and comparison groups in the incidence of SSI. | |
| 98 per 1000 | 85 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 13 fewer SSI occur per 1000 with irrigation than with no irrigation (31 fewer to 10 more) | ||||||
| Wound dehiscence | Study population: participants undergoing clean procedures (split‐body design) | RR 1.17 | 30 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There is no clear difference between surgical sites treated with irrigation and those in the control condition. This is based on a single split‐body design with small numbers of participants. | |
| 200 per 1000 | 234 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 34 more wound dehiscences occur per 1000 with irrigation than with no irrigation (112 fewer to 412 more) | ||||||
| Adverse events | Study population: participants undergoing clean‐contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | RR 1.05 (0.76 to 1.44) | 403 (3 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There is no clear difference in the number of adverse events between participants treated with irrigation and those in the control condition. | |
| 247 per 1000 | 259 per 1000 (187 to 355) | |||||
| Risk difference: 12 more per 1000 (from 59 fewer to 108 more) | ||||||
| Adverse events: abscess formation | Study population: participants undergoing dirty or contaminated surgical procedures | RR 0.91 (0.54 to 1.54) | 331 (3 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Moderate4 | There is no clear difference in the number of adverse events between participants treated with irrigation and those in the control condition. | |
| 149 per 1000 | 136 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 13 fewer per 1000 (from 69 fewer to 80 more) | ||||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded once for risk of bias in one or more domains other than performance bias in studies that account for more than 50% of the analysis weight; downgraded once for imprecision because confidence intervals include both benefit and harm. Publication bias could not be clearly ruled out but was not additionally downgraded for as the evidence was unclear. | ||||||
| Irrigation with antibacterial compared with non‐antibacterial solution for prevention of surgical site infection | ||||||
| Patient or population: participants undergoing clean, clean‐contaminated, contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with non‐antibacterial | Risk with antibacterial | |||||
| SSI | Study population: participants undergoing clean‐contaminated, contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | RR 0.57 | 5141 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | The included studies found that there may be fewer SSIs in participants treated with antibacterial irrigation compared with those treated with non‐antibacterial irrigation. | |
| 140 per 1000 | 80 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 60 fewer SSI occur per 1000 with antibacterial irrigation than with non‐antibacterial (78 to 35 fewer) | ||||||
| Wound dehiscence | Study population: participants undergoing clean or clean‐contaminated surgical procedures | RR 1.26 | 660 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | The effect of antibacterial compared with non‐antibacterial irrigation on wound dehiscence is very uncertain. | |
| 45 per 1000 | 56 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 11 more wound dehiscences occur per 1000 with antibacterial irrigation than with non‐antibacterial (16 fewer to 64 more) | ||||||
| Adverse events | Study population: participants undergoing clean, clean‐contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | RR 0.55 (0.22 to 1.34) | 178 (3 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | It is unclear whether there is a difference in the incidence of all adverse events between participants treated with antibacterial irrigation compared with those treated with non‐antibacterial irrigation. | |
| 67 per 1000 | 37 per 1000 (15 to 90) | |||||
| Risk difference: 30 fewer adverse events occur per 1000 with antibacterial irrigation than with non‐antibacterial (53 fewer to 23 more) | ||||||
| Adverse events: abscess formation | Study population: participants undergoing clean‐contaminated, contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | RR 0.82 (0.42 to 1.62) | 1309 (9 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | The effect of antibacterial compared with non‐antibacterial irrigation on abscess formation is very uncertain | |
| 31 per 1000 | 25 per 1000 (13 to 50) | |||||
| Risk difference: 6 fewer abscesses form per 1000 with antibacterial irrigation than with non‐antibacterial (18 fewer to 19 more) | ||||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded once for risk of bias due to high risk of bias for at least one domain in studies contributing over 50% of the weight and once for probable publication bias. We did not further downgrade for inconsistency because the inconsistency present appeared due to the difference between larger and smaller studies and hence was accounted for by the downgrade for potential publication bias. | ||||||
| Standard irrigation compared with pulsatile irrigation for prevention of surgical site infection | ||||||
| Patient or population: participants undergoing clean, clean‐contaminated, contaminated or dirty surgical procedures | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with standard irrigation | Risk with pulsatile irrigation | |||||
| SSI | Study population: participants undergoing clean or clean‐contaminated surgical procedures | RR 0.34 | 484 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Included studies show that there may be fewer SSIs in participants treated with pulsatile saline irrigation compared with standard techniques; the evidence is low certainty due to high risk of biases in the study contributing the majority of participants and weight to the analysis. | |
| 165 per 1000 | 56 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 109 fewer SSI occur per 1000 with pulsatile irrigation than with standard (134 fewer to 62 fewer) | ||||||
| Wound dehiscence | Study population: participants undergoing clean‐contaminated surgical procedures | RR 0.31 | 128 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There is no clear difference in the incidence of wound dehiscence between groups treated with standard or pulsatile techniques of saline irrigation. Confidence intervals include both benefit and harm and are wide and fragile. | |
| 16 per 1000 | 5 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 11 fewer wound dehiscences occur per 1000 with pulsatile irrigation than with standard (16 fewer to 106 more) | ||||||
| Adverse events | Study population: participants undergoing clean‐contaminated surgical procedures | RR 1.31 (0.87 to 1.97) | 128 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There is no clear difference in the incidence of adverse events between groups treated with standard or pulsatile techniques of saline irrigation. Confidence intervals include both benefit and harm and are wide and fragile. | |
| 486 per 1000 | 371 per 1000 | |||||
| Risk difference: 115 fewer adverse events occur per 1000 with pulsatile irrigation (360 fewer to 48 more) | ||||||
| Adverse events: abscess formation | There were no reported data on abscess formation | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded twice for high risk of bias in multiple domains for study contributing most of the weight. | ||||||
| Comparison | Surgery | Participants (studies) | SSI RR (95% CI) | GRADE judgement: certainty of the evidence | Reason for downgrading |
| Icodextrin vs Ringer's solution | Clean‐contaminated (uterine) | 426 (1 RCT) | 2.89 (0.30 to 27.56) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Povidone iodine vs Dermacyn | Clean (cardiac) | 190 (1 RCT) | 2.80 (1.05 to 7.47) | Low | Downgraded once for high risk of bias and once for imprecision |
| Povidone iodine vs chlorhexidine | Dirty (peritonitis) | 53 (1 RCT)1 | 1.13 (0.78 to 1.63) | Very low | Downgraded twice for high risk of bias in multiple domains and once for imprecision |
| Cepharin vs cefoxitin | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 132 (1 RCT)1 | Not estimable (no events in either group) | No assessment possible | ‐ |
| Epicillin vs lincomycin | Contaminated (appendicitis) | 162 (1 RCT)1 | Not estimable (data not reported for groups) | No assessment possible | ‐ |
| Gentamicin vs clindamycin | Clean (breast) | 51 (1 RCT)1 | Not estimable (no events in either group) | No assessment possible | ‐ |
| Cephapirin versus moxalactam | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 149 (total 360) (1 RCT)2 | 1.69 (0.29 to 9.84) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Cephapirin versus cefamandole | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 134 (total 360) (1 RCT)2 | 1.37 (0.24 to 7.95) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Cephapirin versus ampicillin | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 140 (total 360) (1 RCT)2 | 7.00 (0.37 to 133.06) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Cefamandole versus moxalactam | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 143 (total 360) (1 RCT)2 | 1.23 (0.18 to 8.52) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Cefamandole versus ampicillin | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 134 (total 360) (1 RCT)2 | 5.46 (0.27 to 111.65) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Moxalactam versus ampicillin | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 149 (total 360) (1 RCT)2 | 4.44 (0.22 to 90.88) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| Cefazolin versus cefamandole | Clean‐contaminated (caesarean section) | 207 (1 RCT) | 4.58 (0.22 to 93.38) | Low | Downgraded twice for very serious imprecision |
| 1Three‐armed trial; not all participants relevant to this comparison. CI: confidence interval; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RR: risk ratio; SSI: surgical site infection | |||||
| Study | Surgical category/type | Participants | Interventions | Definition of SSI | Follow‐up | SSI events | Risk ratio (95% CI) | Wound dehiscence risk ratio (95% CI) |
| Comparison of irrigation compared with no irrigation | ||||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 223 | Antibiotic irrigation/saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | |||||
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 35 | Saline postoperative irrigation No postoperative irrigation | Temperature > 38.5C for > 24 h plus localised, drainage‐confirmed accumulation of fluid | 6 weeks | 9/39 2/44 | 5.08 (1.17 to 22.09) Not included in pooled analysis ‐ intervention too different | NR | |
| Contaminated Appendicitis | 283 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Collection of pus or positive bacteriologic culture from wound discharge | 4 weeks | 11/127 39/156 | 0.25 (0.19 to 0.65) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Gastrectomy | 34 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria | 2 weeks | 1/17 3/17 | 0.33 (0.04 to 2.89) | NR | |
| Mixed Abdominal/inguinal hernia | 592 | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation | Purulent discharge seen within 4 weeks or culturing of fluid from the wound was positive | 4 weeks | 36/279 39/279 | 0.92 (0.61 to 1.41) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 158 | Antibiotic irrigation No irrigation | NR | 6 weeks | 0/80 1/78 | 0.33 (0.01 to 7.86) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 520 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Wound drained purulent material/serosanguineous fluid plus induration, warmth and tenderness | 6 weeks | 17/260 19/260 | 0.89 (0.48 to 1.68) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 196 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Undue tenderness, erythema, discharge, or separation of the incision accompanying fever | NR | 1/97 2/99 | 0.51 (0.05 to 5.54) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 3270 | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation | Abscess or wound draining pus or sero‐sanguinous fluid, or redness, induration, warmth and tenderness or general practitioner prescribed antibiotics | 4 weeks | 144/1520 147/1507 | 0.97 (0.78 to 1.21) | NR | |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 33 | Antibiotic irrigation/saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | Mean 8 d (5‐16) | 5/20 4/10 | 0.63 (0.21 to 1.83) | NR | |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 14 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | NR | 2/7 0/7 | 5.00 (0.28 to 88.53) | NR | |
| Clean Breast | 30 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Wound discharge, invasive infection | 8 weeks | 0/30 0/30 | Not estimable Not included in pooled analysis ‐ split‐body design | 1.15 (0.44 to 3.06) | |
| Dirty Abdominal infection | 87 | Saline irrigation/ Antibiotic irrigation No irrigation | Discharge of pus | 2 weeks | 10/58 6/29 | 0.83 (0.34 to 2.07) | NR | |
| Mixed Appendix | 83 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | 6 weeks | 0/40 0/41 | Not estimable | NR | |
| Dirty Appendix | 220 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | NR | ||||
| Clean‐contaminated Liver resection | 193 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Incisional or organ/space infection Incisional infection: clinically apparent cellulitis, induration, or purulent discharge. Organ/space infection: radiologic evidence of fluid collection necessitating drainage or antibiotic therapy | 4 weeks | 21/96 13/97 | 1.63 (0.87 to 3.07) | NR | |
| Contaminated Appendix | 374 | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation | Collection of pus that emptied itself spontaneously or after incision | 2 weeks | 13/128 12/124 | 1.05 (0.50 to 2.21) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 430 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | Partial or total separation of incision, plus purulent or serous wound discharge with induration, warmth, and tenderness | NR | 1/215 2/215 | 0.50 (0.05 to 5.47) | NR | |
| Contaminated Appendix | 131 | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation Non‐antibacterial irrigation | Prescence of pus either spontaneously or on probing. All infections confirmed bacteriologically | NR | 17/131 Results are not given by intervention group; no effect estimate calculable | NR | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 236 | Saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | NR | ||||
| Comparison of antibacterial irrigationwith non‐antibacterial irrigation | ||||||||
| Mixed Appendicits | 254 | Antibiotic Saline | Purulent discharge in wound, regardless of culture results, or occurrence of serous discharge with positive culture | 1 month | 1/120 7/134 | 0.16 (0.02 to 1.28) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 330 | Antiseptic Saline | Spontaneous or incisional discharge from wound, pus or serous fluid, with infective organism identified on culture | 6 weeks | 17/150 17/150 | 1.00 (0.53 to 1.88) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 223 | Antibiotic irrigation Saline irrigation (No irrigation) | NR | NR | ||||
| Dirty Peritonitis | 35 | Antiseptic irrigation Saline irrigation | NR | NR | ||||
| Clean‐contaminated | 40 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | 4‐6 weeks | 1/20 1/20 | 1.00 (0.07 to 14.90) | NR | |
| Clean Breast | 54 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | 6 weeks | 0/23 1/30 | 0.43 (0.02 to 10.11) | 0.43 (0.02 to 10.11) | |
| Clean Spinal | 244 | Antiseptic Saline | Superficial (above lumbosacral fascia) or deep (below lumbosacral fascia), early onset (within 2 weeks) or late onset (otherwise). Deep infections confirmed by laboratory parameters: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, level of C‐reactive protein, and positive biopsy culture | 2 weeks, long‐term follow‐up to 19 months | 0/120 6/124 | 0.08 (0.00 to 1.40) Only included in sensitivity analysis due to suspected data overlap with Cheng 2005 | 0.52 (0.05 to 5.62) | |
| Clean Spinal | 417 | Antiseptic Saline | Unusual pain, tenderness, erythema, induration, fever, or wound drainage; investigated with erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C‐reactive protein, and bacteriological cultures from operative site or blood | 2 weeks', long‐term follow‐up to mean 15.5 months | 0/208 7/206 | 0.07 (0.00 to 1.015) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caesarean | 360 | 4 antibiotics Saline | Wound breakdown with positive culture or presence of cellulitis | NR | 7/283 3/77 | 0.63 (0.17 to 2.40) | NR | |
| Mixed Colorectal | 129 | Antibiotic Saline | Discharge of pus from the wound "wound sepsis" | 1 month | 15/64 18/65 | 0.85 (0.47 to 1.53) | NR | |
| Mixed Appendicitis | 192 | Antiseptic Saline | Wound discharging pus | 4 weeks | 18/99 29/93 | 0.58 (0.35 to 0.98) | NR | |
| Clean Orthopaedic | 162 | Antiseptic Saline | Positive bacteriological examination | 6 weeks then mean 7.8 (2‐4) months | 0/89 2/73 | 0.16 (0.01 to 3.37) | NR | |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 16 | Antiseptic Saline | NR | NR | 1/8 4/8 | 0.25 (0.04 to 1.77) | NR | |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 44 | Antiseptic Saline | Infection at operation site, up to 30 d after surgery; confirmed causative pathogen(s) identical to those of appendicitis | 30 d | 0/24 4/20 | 0.09 (0.01 to 1.64) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 128 | 2 Antibiotics Saline | Purulent wound discharge with or without wound separation | 8 weeks | 0/85 3/43 | 0.07 (0.00 to 1.38) | NR | |
| Mixed Gastrointestinal/colorectal | 200 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | NR | 3/100 9/100 | 0.33 (0.09 to 1.20) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 100 | Antibiotic Saline | Hyperemic skin incision and fluctuant mass which when opened contained purulent material | NR | 2/50 4/50 | 0.50 (0.10 to 0.50) | NR | |
| Contaminated Appendicitis | 162 | 2 Antibiotics Saline | Septic complications with spontaneous or induced purulent discharge | 4 d; longer follow‐up unclear | Results are not given by intervention group; no effect estimate calculable | NR | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Cholecystectomy | 102 | Antibiotic Saline | Erythema, induration, tenderness, warmth, suppurative discharge | 6 weeks | 6/51 6/51 | 1.00 (0.35 to 2.89) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Abdominal | 260 | Antibiotic Saline | NR, wounds were monitored with daily photographs | Until discharge | 12/124 23/116 | 0.49 (0.25 to 0.94) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 197 | Antiseptic Non‐antibacterial | NR | NR | 19/101 22/96 | 0.82 (0.48 to 1.42) | NR | |
| Mixed General surgery | 540 | Antiseptic Saline | NR | NR | 16/267 15/273 | 1.09 (0.55 to 2.16) | NR | |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 33 | Antibiotic irrigation Saline irrigation No irrigation | NR | mean 8 d (5‐16) | 3/10 2/10 | 1.50 (0.32 to 3.09) | NR | |
| Clean Breast | 51 | 2 Antibiotics Saline | NR | NR | 0/34 0/17 | Not estimable | NR | |
| Dirty Peritonitis | 94 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | NR | 11/44 13/50 | 0.96 (0.48 to 1.92) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 128 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | NR | 6/64 27/64 | 0.22 (0.10 to 0.50) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 108 | Antibiotic Saline | Presence of purulent discharge, confirmed with microbiologic culture | 30 d | 2/52 7/51 | 0.29 (0.06 to 1.31) | NR | |
| Clean Breast | 40 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | 2 weeks | 0/20 0/20 | Not estimable | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 106 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | 30 d | 2/52 7/52 | 0.20 (0.05 to 1.87) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Bariatric surgery | 80 | Antibiotic Saline | NR | 30 d after discharge | NR | NR | ||
| Dirty Abdominal infection | 87 | Antibiotic Saline (No irrigation) | Discharge of pus | 2 weeks | 5/29 5/29 (6/29) | 1.00 (0.32 to 3.09) | NR | |
| Mixed Gastrointestinal/colorectal | 159 | Antibiotic Saline | Discharge of pus | 6 weeks | 10/85 24/74 | 0.36 (0.19 to 0.71) | NR | |
| Mixed General Surgery | 500 | Antiseptic Saline | Pus discharged within 12 weeks or serous drainage from questionable wounds plus positive culture | 12 weeks | 7/242 39/258 | 0.19 (0.09 to 0.42) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 400 | Antiseptic Saline | National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance system | 30 d (total 3 months) | 19/180 29/183 | 0.67 (0.39 to 1.14) | 1.44 (0.71 to 2.93) | |
| Contaminated Appendix | 131 | Antiseptic irrigation Non‐antibacterial irrigation (No irrigation) | Prescence of pus either spontaneously or on probing. All infections confirmed bacteriologically | NR | 7/131 Results are not given by intervention group; No effect estimate calculable | NR | ||
| Dirty Peritonitis | 53 | 2 Antiseptics Saline | Pus in wound, sero‐sanguinous discharge, Inflammation or induration | 1 month | 23/29 10/16 | 0.61 (0.40 to 0.92) | NR | |
| Comparisons of two different agents in the same class | ||||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Uterine | 449 | 2 non‐antibacterials Icodextrin Ringer's solution | NR clearly; data on infection ambiguous | NR | ||||
| Clean‐contaminated Caesarean | 360 | 4 antibiotics (Saline) Cephapirin Cefamandole Moxalactam Ampicillin | Wound breakdown with positive culture or presence of cellulitis | NR | 3/70 2/64 2/79 0/70 | Cephapirin: cefamandole 1.37 (0.24 to 7.95) Cephapirin: moxalactam 1.69 (0.29 to 9.84) Cephapirin: ampicillin 7.00 (0.37 to 133.06) Cefamandole: moxalactam 1.23 (0.18 to 8.52) Cefamandole: ampicillin 5.46 (0.27 to 111.65) Moxalactam: ampicillin 4.44 (0.22 to 90.88) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caesarean | 128 | 2 antibiotics (Saline) Cephapirin cefoxitin | Purulent wound discharge with or without wound separation | 8 weeks | 0/44 0/41 | Not estimable; zero events | NR | |
| Contaminated Appendicitis | 162 | 2 antibiotics (Saline) Epicillin Lincomycin | Septic complications with spontaneous or induced purulent discharge | 4 d; longer follow‐up unclear | Not estimable; number of participants and events per group not reported | NR | ||
| Clean Cardiac | 190 | 2 antiseptics Povidone iodine Dermacyn | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria | 6 weeks | 14/90 5/88 | 2.80 (1.05 to 7.47) | NR | |
| Clean Breast | 51 | 2 antibiotics Clindamycin Gentamicin | NR | NR | 0/17 0/17 | Not estimable; zero events | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Caesarean | 207 113 in relevant groups | 2 antibiotics Cefazolin Cefamandole | Presence of cellulitis and/or purulent exudate | > 2 weeks | 2/59 0/54 | 4.58 (0.22 to 93.38) | NR | |
| Clean Brain | 20 | 2 non‐antibacterials Saline Artificial CSF | NR | NR | ||||
| Clean‐contaminated Uterine | 498 | 2 non‐antibacterials Icodextrin Ringer's solution | NR | 4‐16 weeks | 3/217 1/209 | 2.89 (0.30 to 27.56) | NR | |
| Dirty Peritonitis | 53 | 2 antiseptics (Saline) Povidone iodine Chlorhexidine | Pus in wound, sero‐sanguinous discharge, Inflammation or induration | 1 month | 4/16 4/13 | 1.13 (95% CI 0.78 to 1.63) | NR | |
| Comparison of pulsatile versus standard irrigation delivery | ||||||||
| Clean Orthopaedic | 356 | Pulsatile saline Standard saline | Nosocomial Infection National Surveillance Survey | 30 days or discharge | 9/164 30/192 | 0.35 (0.17 to 0.72) | NR | |
| Clean‐contaminated Abdominal | 137 | Pulsatile saline Standard saline | Purulent drainage, with or without laboratory confirmation; organisms isolated from aseptically obtained culture of fluid or tissue; at least 1 of the following: pain or tenderness, localised swelling, redness, or heat and incision is deliberately opened by surgeon, unless incision is culture‐negative; diagnosis of superficial incisional SSI by surgeon or attending physician | 1 month | 4/66 12/62 | 0.31 (0.11 to 0.92) | 0.31 (0.01 to 7.55) | |
| 1Elliott is a 4‐armed trial with a factorial design, arms with and without intravenous antibiotics are combined CI: confidence interval; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; NR: not reported; RR: risk ratio | ||||||||
| Comparison | Subgroup basis | Pre‐specified or exploratory | Subgroups used | Subgroup results | I2 & Chi2 subgroup differences | I2 & Chi2 overall |
| Irrigation vs no irrigation | Surgical classification | Pre‐specified | Clean‐contaminated Contaminated/Dirty/Mixed | 1.00 (0.82, 1.21) 0.74 (0.47 to 1.16) | I2 = 29.1%. Chi2 = 1.41 | I2 = 28% Chi2 = 16.58 |
| Irrigation vs no irrigation | Type of irrigation | Exploratory | Non‐antibacterial Antiseptic Antibiotic | 0.80 (0.46 to 1.41) 0.97 (0.81 to 1.17) 0.92 (0.42 to 1.99) | I2 = 0% Chi2 = 0.39 | I2 = 28% Chi2 = 16.58 |
| Antibacterial vs non‐antibacterial | Surgical classification | Pre‐specified | Clean Clean‐contaminated Contaminated/Dirty/Mixed | 0.17 (0.03 to 0.89) 0.57 (0.40 to 0.79) 0.61 (0.40 to 0.92) | I2= 9.7% Chi2 = 2.21 | I2 = 53% Chi2 = 56.94 |
| Antibacterial vs non‐antibacterial | Type of irrigation | Exploratory | Antiseptic Antibiotic | 0.63 (0.40 to 0.95) 0.57 (0.44 to 0.75) | I2= 0% Chi2 = 0.38 | I2 = 53% Chi2 = 56.94 |
| CI: confidence interval; RR: risk ratio | ||||||
| Study Surgical category/type | Participants (N) Follow‐up | Interventions | Mortality | Systemic antibiotics | Antibiotic resistance | Adverse events | Reoperation | Readmission | Length of stay (days (95% CI)) |
| Irrigation compared with no irrigation | |||||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 223 6 weeks | Antibiotic irrigation/Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means ‐0.46 (‐0.64 to ‐0.29) |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 85 6 weeks | Saline postoperative irrigation No postoperative irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Medians 5 (3‐11) vs 5 (4‐12) |
| Contaminated Appendicitis | 283 4 weeks | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | No group data | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean‐contaminated Gastrectomy | 34 2 weeks (primary outcome) | Saline irrigation No irrigation | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Mixed Abdominal/inguinal hernia | 592 4 weeks (primary outcome) | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 158 6 weeks | Antibiotic irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means ‐0.20 (‐0.57 to 0.17) |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 520 6 weeks | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means 0.01 (‐0.03 to 0.05) |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 196 NR | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Overall RR 1.10 (0.55 to 2.22) | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means 0.10 (‐0.17 to 0.37) |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 3270 4 weeks | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | RR 0.77 (0.29 to 2.07) | RR 1.29 (0.81 to 2.06) | ‐ |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 33 mean 8 days (5‐16) | Antibiotic irrigation/Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 0.17 (0.01 to 3.94) | ‐ | ‐ | Medians 14 (8‐22) vs 13 (9‐22) |
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 14 NR | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Overall RR 1.00 (0.08 to 13.02) Abscess but no group data | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean Breast | 30 8 weeks | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Dirty Abdominal infection | 87 2 weeks | Saline irrigation Antibiotic irrigation No irrigation | RR 0.75 (0.30 to 1.90) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means not estimable 11.5 vs 13 |
| Mixed Appendix | 83 6 weeks | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 1.02 (0.15 to 6.93) | ‐ | ‐ | Medians 2.0 (1‐3) vs 2.0 (1‐2.25) |
| Dirty Appendix | 220 2‐4 weeks | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 0.95 (0.55 to 1.65) | RR 0.33 (0.01 to 8.09) | RR 0.14 (0.01 to 2.73) | Difference in means ‐0.10 (‐0.85 to 0.65) |
| Clean‐contaminated Liver resection | 193 4 weeks | Saline irrigation No irrigation | RR 2.02 (0.36 to 2.04) | ‐ | ‐ | Overall RR 1.04 (0.72 to 1.49) | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means 0.00 (‐3.74 to 3.74) |
| Contaminated Appendix | 374 2 weeks | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 430 NR | Saline irrigation No irrigation | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Contaminated Appendix | 131 NR | Antiseptic irrigation No irrigation Non‐antibacterial irrigation | ‐ | 53/131 participants "distributed evenly across the groups" | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | No group data |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 236 NR | Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Median discharge day: 3 in both groups |
| Antibacterial irrigation vs non‐antibacterial irrigation | |||||||||
| Mixed Appendicits | 254 1 month | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR not estimable 0 events | No group data | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 330 6 weeks | Antiseptic Saline | RR 1.00 (0.25 to 3.92) | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 2.0 (0.18 to 21.82) | No group data | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 223 6 weeks | Antibiotic irrigation Saline irrigation (No irrigation) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means ‐1.08 (‐1.25 to ‐0.92) |
| Dirty Peritonitis | 35 NR | Antiseptic irrigation Saline irrigation | RR 7.39 (0.41 to 133.24) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 40 4‐6 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| Clean Breast | 54 6 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| Clean Spinal | 244 2 weeks, long‐term follow‐up to 19 months | Antiseptic Saline | ‐ | All 6 participants with SSI received these; all in saline group | 5/6 infections positive for MRSA | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| Clean Spinal | 417 2 weeks long ‐term follow ‐up to mean 15.5 months | Antiseptic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 360 NR | 4 antibiotics Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR not estimable 0 events | ‐ | ||
| Mixed Colorectal | 129 1 month | Antibiotic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Mixed Appendicitis | 192 4 weeks | Antiseptic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means not estimable (6.4 vs 6.6) | ||
| Clean Orthopaedic | 162 mean 7‐8 months (range 2‐14 months) (primary outcome) | Antiseptic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ‐ | |||||
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 16 NR | Antiseptic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 0.33 (0.02 to 7.14) | Difference in means ‐10.60 (‐19.06 to ‐2.14) | ||
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 44 30 days | Antiseptic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 0.83 (0.06 to 12.49) | Difference in means ‐0.70 (‐3.31 to 1.91) | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 128 8 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | Difference in means ‐0.35 (‐1.06 to 0.36) | ||
| Mixed Gastrointestinal/colorectal | 200 NR | Antibiotic Saline | RR 1.67 (0.41 to 6.79) | ‐ | Specific organisms | Specific complication only | ‐ | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 100 NR | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | ‐ | ||
| Contaminated Appendicitis | 162 4 days; longer follow‐up unclear | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | ‐ | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Cholecystectomy | 102 6 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Abdominal | 260 Until discharge | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | Kanamycin resistance Kanamycin: 12/12 Saline: "over half" of 23 | Specific complication only | ‐ | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 197 NR | Antiseptic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Mixed General surgery | 540 NR | Antiseptic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ‐ | |||||
| Dirty Perforated appendicitis | 33 Mean 8 days (5‐16 | Antibiotic irrigation Saline irrigation No irrigation | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR not estimable 0 events | Medians 13 (9‐20 13 (10‐22) | ||
| Clean Breast | 51 NR | Antibiotic 1/ Antibiotic 2 Saline | RR not estimable, 0 events | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Medians 3 (1‐3) 3 (1‐3) | ||
| Dirty Peritonitis | 94 NR | Antibiotic Saline | RR 0.71 (0.25 to 2.01) | ‐ | Specific organisms | Abscess grouped with another event ‐ not estimable | ‐ | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 128 NR | Antibiotic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 108 30 days | Antibiotic Saline | RR 0.50 (0.05 to 5.35) | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 0.14 (0.01 to 2.65) | Medians 6 (5‐32) 6.5 (5‐14) | ||
| Clean Breast | 40 2 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | RR not estimable, 0 events | ‐ | ‐ | Overall RR not estimable 0 events | Medians 3 (1‐3) 3 (1‐3) | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 106 30 days | Antibiotic Saline | RR 1.00 (0.06 to 15.57) | ‐ | ‐ | Specific complication only | Medians 6.5 (5‐14) 6 (5‐32) | ||
| Clean‐contaminated Bariatric surgery | 80 30 days | Antibiotic Saline | RR 0.33 (0.01 to 7.95) | ‐ | ‐ | Overall RR 0.50 (0.05 to 5.30) | ‐ | ||
| Dirty Abdominal infection | 87 2 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | RR 0.50 (0.14 to 1.81) | ‐ | ‐ | Overall RR 0.56 (0.21 to 1.46) Abscess RR 0.33 (0.01 to 7.86) | Difference in means not estimable 10 vs 13 | ||
| Mixed Gastrointestinal/colorectal | 159 6 weeks | Antibiotic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess RR 0.96 (0.43 to 2.13) Specific additional complication | RR 6.10 (0.32 to 116.28) | ‐ | |
| Mixed General Surgery | 500 12 weeks | Antiseptic Saline | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Colorectal | 400 30 days (total 3 months) | Antiseptic Saline | ‐ | ‐ | MRSA 4/14 vs 8/24 MSSA 0/14 vs 3/24 | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| Contaminated Appendix | 131 NR | Antiseptic Non‐antibacterial (No irrigation) | ‐ | 53/131 participants "distributed evenly across the groups" | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | No group data |
| Dirty Peritonitis | 53 1 month | Antiseptic Saline | RR 0.61 (0.17 to 2.16) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means ‐0.70 (‐3.32 to 1.92) | ||
| Comparisons of two different agents in the same class | |||||||||
| Clean‐contaminated Uterine | 449 28‐56 days | 2 non‐antibacterials Icodextrin Ringer's solution | RR not estimable ‐ 0 events | ‐ | ‐ | Total: RR 0.99 (0.96 to 1.02) Treatment‐related RR 1.42 (0.98 to 2.05) Serious RR 1.20 (0.80 to 1.78) Serious treatment‐related RR 0.71 (0.29 to 1.73) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 360 NR | 4 antibiotics (Saline) Cephapirin Cefamandole Moxalactam Ampicillin | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Abscess: no effect estimate calculable ‐ 0 events Other specific events | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 128 8 weeks | 2 antibiotics (Saline) Cephapirin Cefoxitin | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Specific event data only | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means 0.10 (‐0.78 to 0.58) |
| Contaminated Appendicitis | 162 4 days; longer follow‐up unclear | 2 antibiotics (Saline) Epicillin Lincomycin | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | 1 abscess in antibiotic groups; no group data | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean Cardiac | 190 6 weeks | 2 antiseptics Povidone iodine Dermacyn | 4 deaths but no group data; group data for composite outcome with reopening of chest | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | RR 8.80 (0.48 to 161.11) | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean Breast | 51 NR | 2 antibiotics Clindamycin Gentamicin | RR not estimable, 0 events | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Median 3 (1‐3) in each group |
| Clean‐contaminated Caeasarean section | 207 113 in relevant groups 2 weeks + (primary outcome) | 2 antibiotics Cefazolin Cefamandole | No secondary outcomes were reported | ||||||
| Clean Brain | 20 10 days | 2 non‐antibacterials Saline Artificial CSF | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | 2 participants in each group, included MRI data. RR not calculated | ‐ | ‐‐ | ‐ |
| Clean‐contaminated Uterine | 498 4‐16 weeks | 2 non‐antibacterials Icodextrin Ringer's solution | RR not estimable ‐ 0 events | ‐ | Total: RR 0.95 (0.73 to 1.24) Treatment‐related RR 1.16 (0.60 to 2.23) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | |
| Dirty Peritonitis | 53 1 month | 2 antiseptics (Saline) Povidone iodine Chlorhexidine | RR 0.45 (0.05 to 3.90) within 4 days, no group data for later events | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Difference in means 3.30 (0.53 to 3.90) |
| Comparison of pulsatile versus standard irrigationdelivery | |||||||||
| Clean Orthopaedic | 356 30 days or discharge | Pulsatile saline Standard saline | No group data | ‐ | No group data "half" SSI positive for MRSA | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Clean‐contaminated Abdominal | 137 1 month | Pulsatile saline Standard saline | ‐ | No group data: 14/16 SSI treated | Qualitative data on organisms isolated | Complications, not wound infections RR 1.31 (0.87 to 1.97) | RR 0.56 (0.14 to 2.26) | RR 1.41 (0.53 to 3.73) | Median 9 (5 ‐45) 9 (4‐71) |
| More details of interventions can be found in Table 1 and Characteristics of included studies 1 Elliott is a four‐armed trial with a factorial design, arms with and without iv antibiotics are combined CI: confidence interval; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; MRSA: methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus; RR: risk ratio; SSI: surgical site infection | |||||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 SSI Show forest plot | 14 | 6106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.68, 1.11] |
| 1.1 clean or clean‐contaminated | 7 | 4801 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.82, 1.21] |
| 1.2 contaminated or dirty | 7 | 1305 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.47, 1.16] |
| 2 Adverse events Show forest plot | 3 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.76, 1.44] |
| 3 Abscess Show forest plot | 3 | 331 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.54, 1.54] |
| 4 Mortality Show forest plot | 2 | 280 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.36, 2.04] |
| 5 Hospital stay Show forest plot | 7 | 1597 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.13 [‐0.38, 0.12] |
| 6 Return to theatre (reoperation) Show forest plot | 2 | 3247 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.28, 1.84] |
| 7 Readmission to hospital Show forest plot | 2 | 3247 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.10, 4.90] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 SSI Show forest plot | 30 | 5141 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.57 [0.44, 0.75] |
| 1.1 clean | 4 | 680 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.03, 0.89] |
| 1.2 clean‐contaminated | 13 | 2210 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.57 [0.40, 0.79] |
| 1.3 contaminated or dirty | 13 | 2251 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.40, 0.92] |
| 2 Wound dehiscence Show forest plot | 3 | 660 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.65, 2.45] |
| 3 Adverse events Show forest plot | 3 | 178 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.55 [0.22, 1.34] |
| 4 Abscess Show forest plot | 9 | 1309 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.42, 1.62] |
| 5 Mortality Show forest plot | 11 | 1121 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.48, 1.36] |
| 6 Hospital stay Show forest plot | 7 | 635 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.85 [‐1.60, ‐0.09] |
| 7 Return to theatre (reoperation) Show forest plot | 2 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.12, 13.60] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Mortality Show forest plot | 2 | 875 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 875 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.96, 1.02] |
| 3 Treatment‐related adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 875 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.98, 1.86] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 SSI Show forest plot | 2 | 484 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.34 [0.19, 0.62] |

