Фототерапия для лечения язв стопы у людей с диабетом
Appendices
Appendix 1. Glossary
Cytochrome oxidase: an oxidizing enzyme containing iron and a porphyrin, found in mitochondria and important in cell respiration as an agent of electron transfer from certain cytochrome molecules to oxygen molecules.
Mitochondria: a spherical or elongated organelle in the cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material and many enzymes important for cell metabolism. Mitochondria make most of the energy for cells.
Adenosine triphosphate: a nucleotide that is the primary source of energy in all living cells because of its function in donating a phosphate group during biochemical activities.
Oxidative metabolism: the catabolic first half of metabolism in which the cell breaks down molecules into energy, or adenosine triphosphate.
Angiogenesis: the growth of blood vessels from the existing vasculature.
Vasodilation: widening of blood vessels that results from relaxation of the muscular walls of the vessels.
Appendix 2. Search strategies
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)
#1 MeSH descriptor: [Leg Ulcer] explode all trees
#2 MeSH descriptor: [Skin Ulcer] explode all trees
#3 MeSH descriptor: [Foot Ulcer] explode all trees
#4 {or #1‐#3}
#5 MeSH descriptor: [Diabetes Mellitus] explode all trees
#6 {and #4‐#5}
#7 MeSH descriptor: [Diabetic Foot] explode all trees
#8 {or #6‐#7}
#9 diabet*:ti,ab,kw
#10 ((ulcer* or wound* or defect*) near/3 (foot or feet or sole or plantar)):ti,ab,kw
#11 {and #9‐#10}
#12 (diabet* near/3 ulcer*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#13 (diabet* near/3 (foot or feet)):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#14 (diabet* near/3 wound*)
#15 (diabet* near/3 defect*)
#16 {or #8, #11‐#15}
#17 MeSH descriptor: [Phototherapy] explode all trees
#18 MeSH descriptor: [Laser Therapy] explode all trees
#19 (laser* or ultraviolet or phototherap* or photoradiation next therap* or photon next therap* or light next therap* or heat next therap* or LLLT or LED):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#20 {or #17‐#19}
#21 {and #16, #20} in Trials
Ovid MEDLINE
1 exp Leg Ulcer/
2 Skin Ulcer/
3 Foot Ulcer/
4 or/1‐3
5 exp Diabetes Mellitus/
6 and/4‐5
7 exp Diabetic Foot/
8 or/6‐7
9 diabet*.ti,ab.
10 ((ulcer* or wound* or defect*) adj3 (foot or feet or sole or plantar)).ti,ab.
11 and/9‐10
12 (diabet* adj3 ulcer*).tw.
13 (diabet* adj3 (foot or feet)).tw.
14 (diabet* adj3 wound*).tw.
15 (diabet* adj3 defect*).tw.
16 or/8,11‐15
17 exp Phototherapy/
18 exp Laser Therapy/
19 (laser* or ultraviolet or phototherap* or photoradiation therap* or photon therap* or light therap* or heat therap* or LLLT or LED).tw.
20 or/17‐19
21 and/16,20
22 randomized controlled trial.pt.
23 controlled clinical trial.pt.
24 randomi?ed.ab.
25 placebo.ab.
26 clinical trials as topic.sh.
27 randomly.ab.
28 trial.ti.
29 or/22‐28
30 exp animals/ not humans.sh.
31 29 not 30
32 21 and 31
Ovid Embase
1 exp leg ulcer/
2 skin ulcer/
3 foot ulcer/
4 plantar ulcer/
5 or/1‐4
6 exp diabetes mellitus/
7 and/5‐6
8 diabetic foot/
9 or/7‐8
10 diabet*.ti,ab.
11 ((ulcer* or wound* or defect*) adj3 (foot or feet or sole or plantar)).ti,ab.
12 and/10‐11
13 (diabet* adj3 ulcer*).tw.
14 (diabet* adj3 (foot or feet)).tw.
15 (diabet* adj3 wound*).tw.
16 (diabet* adj3 defect*).tw.
17 or/9,12‐16
18 exp phototherapy/
19 low level laser therapy/
20 (laser* or ultraviolet or phototherap* or photoradiation therap* or photon therap* or light therap* or heat therap* or LLLT or LED).tw.
21 or/18‐20
22 and/17,21
23 Randomized controlled trials/
24 Single‐Blind Method/
25 Double‐Blind Method/
26 Crossover Procedure/
27 (random* or factorial* or crossover* or cross over* or cross‐over* or placebo* or assign* or allocat* or volunteer*).ti,ab.
28 (doubl* adj blind*).ti,ab.
29 (singl* adj blind*).ti,ab.
30 or/23‐29
31 exp animals/ or exp invertebrate/ or animal experiment/ or animal model/ or animal tissue/ or animal cell/ or nonhuman/
32 human/ or human cell/
33 and/31‐32
34 31 not 33
35 30 not 34
36 22 and 35
EBSCO CINAHL Plus
S33 S20 AND S32
S32 S21 or S22 or S23 or S24 or S25 or S26 or S27 or S28 or S29 or S30 or S31
S31 MH "Quantitative Studies"
S30 TI placebo* or AB placebo*
S29 MH "Placebos"
S28 TI random* allocat* or AB random* allocat*
S27 MH "Random Assignment"
S26 TI randomi?ed control* trial* or AB randomi?ed control* trial*
S25 AB ( singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl* ) and AB ( blind* or mask* )
S24 TI ( singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl* ) and TI ( blind* or mask* )
S23 TI clinic* N1 trial* or AB clinic* N1 trial*
S22 PT Clinical trial
S21MH "Clinical Trials+"
S20 S15 AND S19
S19 S16 OR S17 OR S18
S18 TX (laser* or ultraviolet or phototherap* or photoradiation therap* or photon therap* or light therap* or heat therap* or LLLT or LED)
S17 (MH "Laser Therapy+")
S16 (MH "Phototherapy+")
S15 S7 OR S10 OR S11 OR S12 OR S13 OR S14
S14 TX (diabet* N3 defect*)
S13 TX (diabet* N3 wound*)
S12 TX (diabet* N3 (foot or feet))
S11 TX (diabet* N3 ulcer*)
S10 S8 AND S9
S9 TI (((ulcer* or wound* or defect*) N3 (foot or feet or sole or plantar))) OR AB (((ulcer* or wound* or defect*) N3 (foot or feet or sole or plantar)))
S8 TI (diabet*) OR AB (diabet*)
S7 S5 OR S6
S6 (MH "Diabetic Foot")
S5 S3 AND S4
S4 (MH "Diabetes Mellitus+")
S3 S1 OR S2
S2 (MH "Skin Ulcer")
S1 (MH "Leg Ulcer+")
CNKI
(AB='糖尿病足' OR AB='糖尿病肢端坏疽' OR AB='糖尿病血管病变' OR AB='糖尿病溃疡' OR AB='烂脚' OR AB='烂腿' OR SU='糖尿病足' OR SU='糖尿病肢端坏疽' OR (AB='糖尿病' AND (AB='坏疽' OR AB='足' OR AB='血管神经病变' OR AB='微血管病变' OR AB='溃疡'))) AND (SU='激光' OR AB='低强度激光' OR AB='激光' OR AB='红光' OR AB='光疗' OR SU='蓝光' OR AB='光学治疗') AND (SU='随机对照试验' OR SU='临床试验'OR AB='随机'OR AB='对照' OR AB='盲法' OR AB='双盲'OR AB='单盲' OR AB='随机对照试验' OR AB='临床试验' OR SU='多中心临床试验')
Terms used for searching clinical trials registries
-
Phototherapy
-
LLLT
-
Laser
-
Light
-
Diabetic Foot
-
Diabetic ulcer
Appendix 3. Cochrane's tool for assessing risk of bias
1. Was the allocation sequence randomly generated?
Low risk of bias
The investigators describe a random component in the sequence generation process such as: referring to a random number table; using a computer random number generator; coin tossing; shuffling cards or envelopes; throwing dice; drawing of lots.
High risk of bias
The investigators describe a non‐random component in the sequence generation process. Usually, the description would involve some systematic, non‐random approach, for example: sequence generated by odd or even date of birth; sequence generated by some rule based on date (or day) of admission; sequence generated by some rule based on hospital or clinic record number.
Unclear
Insufficient information about the sequence generation process to permit judgement of low or high risk of bias.
2. Was the treatment allocation adequately concealed?
Low risk of bias
Participants and investigators enrolling participants could not foresee assignment because one of the following, or an equivalent method, was used to conceal allocation: central allocation (including telephone, web‐based, and pharmacy‐controlled randomisation); sequentially numbered drug containers of identical appearance; sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes.
High risk of bias
Participants or investigators enrolling participants could possibly foresee assignments and thus introduce selection bias, such as allocation based on: use of an open random allocation schedule (e.g. a list of random numbers); assignment envelopes without appropriate safeguards (e.g. envelopes were unsealed, non‐opaque, or not sequentially numbered); alternation or rotation; date of birth; case record number; any other explicitly unconcealed procedure.
Unclear
Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk of bias. This is usually the case if the method of concealment is not described or not described in sufficient detail to allow a definite judgement, for example if the use of assignment envelopes is described, but it remains unclear whether envelopes were sequentially numbered, opaque, and sealed.
3. Blinding ‐ was knowledge of the allocated interventions adequately prevented during the study?
Low risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
No blinding, but the review authors judge that the outcome and the outcome measurement are not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding.
-
Blinding of participants and key study personnel ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken.
-
Either participants or some key study personnel were not blinded, but outcome assessment was blinded and the non‐blinding of others unlikely to introduce bias.
High risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
No blinding or incomplete blinding, and the outcome or outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding.
-
Blinding of key study participants and personnel attempted, but likely that the blinding could have been broken.
-
Either participants or some key study personnel were not blinded, and the non‐blinding of others likely to introduce bias.
Unclear
Either of the following:
-
Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk of bias.
-
The study did not address this outcome.
4. Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?
Low risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
No missing outcome data.
-
Reasons for missing outcome data unlikely to be related to true outcome (for survival data, censoring unlikely to be introducing bias).
-
Missing outcome data balanced in numbers across intervention groups, with similar reasons for missing data across groups.
-
For dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with observed event risk not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on the intervention effect estimate.
-
For continuous outcome data, plausible effect size (difference in means or standardised difference in means) among missing outcomes not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on observed effect size.
-
Missing data have been imputed using appropriate methods.
High risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
Reason for missing outcome data likely to be related to true outcome, with either imbalance in numbers or reasons for missing data across intervention groups.
-
For dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with observed event risk enough to induce clinically relevant bias in intervention effect estimate.
-
For continuous outcome data, plausible effect size (difference in means or standardised difference in means) among missing outcomes enough to induce clinically relevant bias in observed effect size.
-
‘As‐treated’ analysis done with substantial departure of the intervention received from that assigned at randomisation.
-
Potentially inappropriate application of simple imputation.
Unclear
Either of the following:
-
Insufficient reporting of attrition/exclusions to permit judgement of low or high risk of bias (e.g. number randomised not stated, no reasons for missing data provided).
-
The study did not address this outcome.
5. Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting?
Low risk of bias
Either of the following:
-
The study protocol is available and all of the study’s prespecified (primary and secondary) outcomes that are of interest in the review have been reported in the prespecified way.
-
The study protocol is not available, but it is clear that the published reports include all expected outcomes, including those that were prespecified (convincing text of this nature may be uncommon).
High risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
Not all of the study’s prespecified primary outcomes have been reported.
-
One or more primary outcomes are reported using measurements, analysis methods, or subsets of the data (e.g. subscales) that were not prespecified.
-
One or more reported primary outcomes were not prespecified (unless clear justification for their reporting is provided, such as an unexpected adverse effect).
-
One or more outcomes of interest in the review are reported incompletely so that they cannot be entered in a meta‐analysis.
-
The study report fails to include results for a key outcome that would be expected to have been reported for such a study.
Unclear
Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk of bias. It is likely that the majority of studies will fall into this category.
6. Other sources of potential bias
Low risk of bias
The study appears to be free of other sources of bias.
High risk of bias
There is at least one important risk of bias. For example, the study:
-
had a potential source of bias related to the specific study design used; or
-
has been claimed to have been fraudulent; or
-
had some other problem.
Unclear
There may be a risk of bias, but there is either:
-
insufficient information to assess whether an important risk of bias exists; or
-
insufficient rationale or evidence that an identified problem will introduce bias.
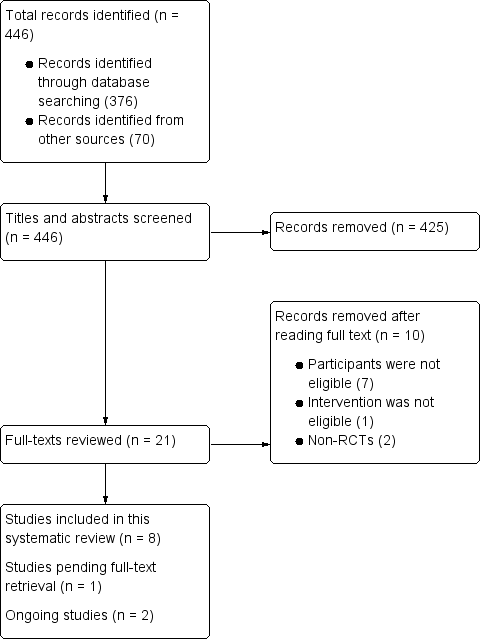
Flow chart of study selection.
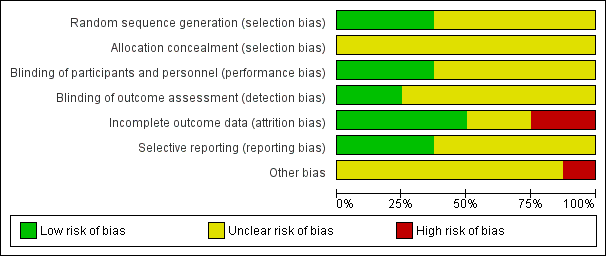
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Phototherapy versus no phototherapy/placebo, Outcome 1 Proportion of wounds completely healed during follow‐up (4 to 20 weeks).
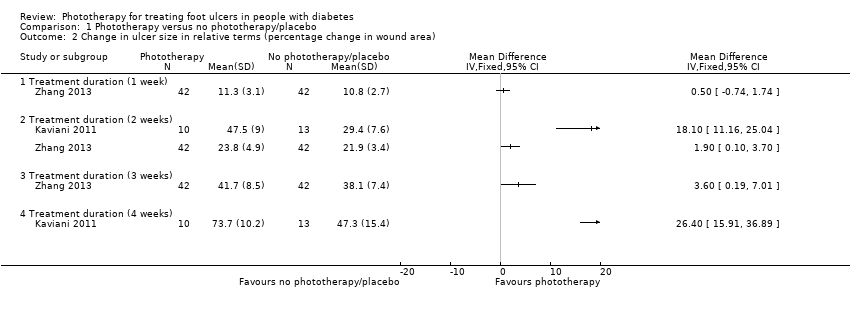
Comparison 1 Phototherapy versus no phototherapy/placebo, Outcome 2 Change in ulcer size in relative terms (percentage change in wound area).
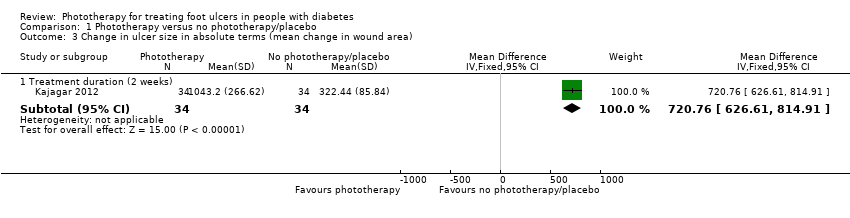
Comparison 1 Phototherapy versus no phototherapy/placebo, Outcome 3 Change in ulcer size in absolute terms (mean change in wound area).

Comparison 1 Phototherapy versus no phototherapy/placebo, Outcome 4 Number of amputations at study end (20 weeks).
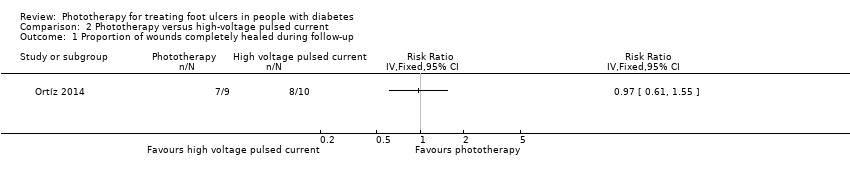
Comparison 2 Phototherapy versus high‐voltage pulsed current, Outcome 1 Proportion of wounds completely healed during follow‐up.
| Phototherapy compared with placebo/no phototherapy for foot ulcers in people with diabetes | ||||||
| Patient or population: Diabetes with foot ulcers Settings: Clinics and hospitals Intervention: Phototherapy Comparison: Placebo/no phototherapy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects*(95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed absolute effect | Corresponding absolute effect | |||||
| Placebo/no phototherapy | Phototherapy | |||||
| Wound healing ‐ time to complete wound healing (weeks) | No study provided reliable data for this outcome. | |||||
| Wound healing ‐ proportion of wounds completely healed during follow‐up | 330 per 1000 | 568 per 1000 | RR 1.57 (1.08 to 2.28) | 116 (4 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| Adverse events | See comment | See comment | See comment | See comment | See comment | In Landau 2011, there were no device‐related adverse events. In Londahl 2013, the authors suggested that there was no difference in adverse events between intervention and control groups, but the number of adverse events was not reported. |
| *The basis for the assumed absolute effect (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding absolute effect (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed absolute effect in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; RR: risk ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded one level for study limitations (high risk of bias for incomplete outcome data in two studies and potential influence of imbalance in baseline characteristics in one study) and one level for imprecision (small sample size). | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Proportion of wounds completely healed during follow‐up (4 to 20 weeks) Show forest plot | 4 | 116 | Risk Ratio (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.57 [1.08, 2.28] |
| 2 Change in ulcer size in relative terms (percentage change in wound area) Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Treatment duration (1 week) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 Treatment duration (2 weeks) | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 Treatment duration (3 weeks) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.4 Treatment duration (4 weeks) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Change in ulcer size in absolute terms (mean change in wound area) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 Treatment duration (2 weeks) | 1 | 68 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 720.76 [626.61, 814.91] |
| 4 Number of amputations at study end (20 weeks) Show forest plot | 1 | 23 | Risk Ratio (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.01, 2.95] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Proportion of wounds completely healed during follow‐up Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |

