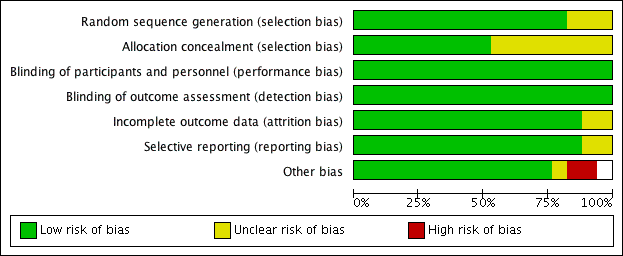
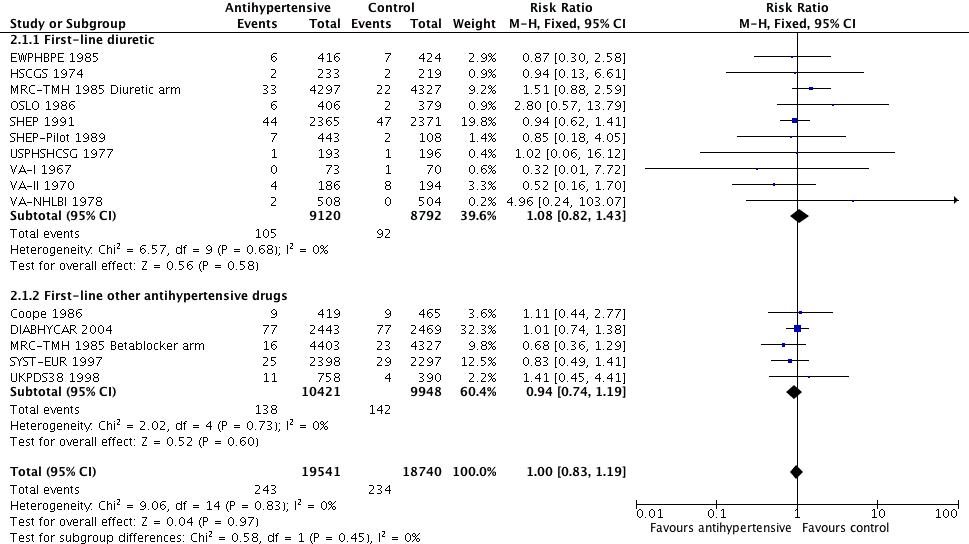
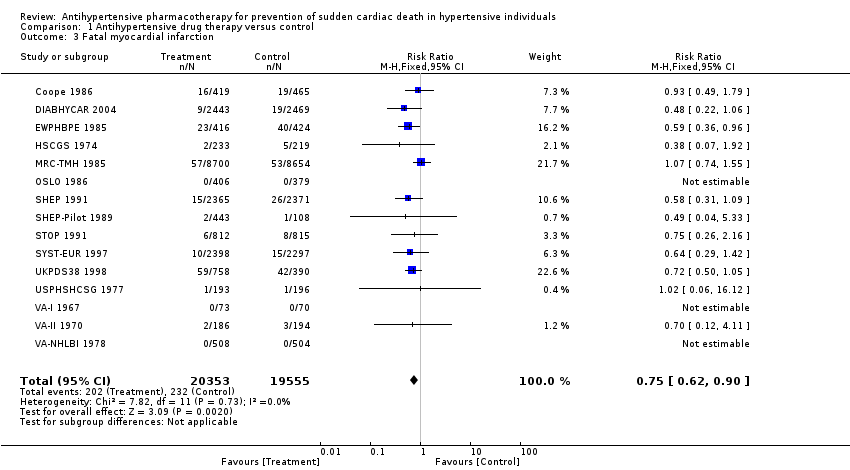
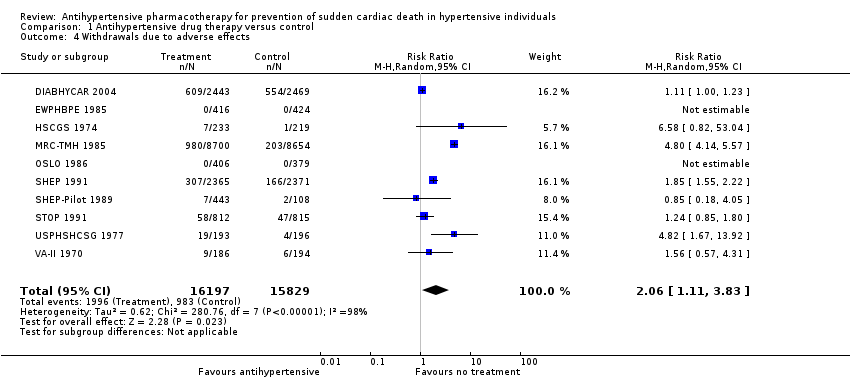
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Vijaya M Musini, Francois Gueyffier, Lorri Puil, Douglas M Salzwedel, James M Wright | 16 agosto 2017
Emily Reeve, Vanessa Jordan, Wade Thompson, Mouna Sawan, Adam Todd, Todd M Gammie, Ingrid Hopper, Sarah N Hilmer, Danijela Gnjidic | 10 junio 2020
Vijaya M Musini, Aaron M Tejani, Ken Bassett, Lorri Puil, James M Wright | 5 junio 2019
Jose Agustin Arguedas, Viriam Leiva, James M Wright | 17 diciembre 2020
Yu Jie Chen, Liang Jin Li, Wen Lu Tang, Jia Yang Song, Ru Qiu, Qian Li, Hao Xue, James M Wright | 14 noviembre 2018
Sarah N Stabler, Aaron M Tejani, Fong Huynh, Claire Fowkes | 15 agosto 2012
Diana Diao, James M Wright, David K Cundiff, Francois Gueyffier | 15 agosto 2012
Anna P Quan, Karla Kerlikowske, Francois Gueyffier, Jean‐Pierre Boissel, INDANA Investigators | 24 abril 2000
Marco I Perez, Vijaya M Musini, James M Wright | 23 enero 2008
Lee Hooper, Christopher Bartlett, George Davey Smith, Shah Ebrahim | 26 enero 2004
Respuestas clínicas Cochrane
Jane Burch, Benilde Cosmi | 19 abril 2017