E‐learning para profissionais de saúde
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategies
Medline (OVID)
Epub Ahead of Print, In‐Process & Other Non‐Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE(R) Daily and Ovid MEDLINE(R) 1946 to present
| No. | Search terms | Results |
| 1 | ("e‐learning" or elearning).ti. | 857 |
| 2 | ("e‐learning" or elearning).ab. | 1376 |
| 3 | or/1‐2 | 1662 |
| 4 | *internet/ and *education/ | 55 |
| 5 | ((electronic or internet or internet‐based or online or "on line" or remote or distance or mobile or web or "web 2*" or web‐based or web deliver*) adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or course‐work or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop? or work‐shop?)).ti,ab. | 7437 |
| 6 | ((computeri?ed or computer‐assisted or computer‐mediated* or computer‐based) adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or coursework or course‐work or education or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop?)).ti,ab. | 1743 |
| 7 | ((e‐mail* or email* or e‐mail‐based or email‐based) adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or course‐work or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop? or work‐shop?)).ti,ab. | 83 |
| 8 | (e‐education or e‐instruction or elearning or "e learning" or "e train*" or "e curricul*" or "e program*" or m‐learn*).ti,ab. | 1792 |
| 9 | (virtual adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or course? or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or instructor? or learning or seminar? or teacher? or teaching or training or trainer? or workshop*)).ti,ab. | 1243 |
| 10 | ((3g or 4g or ipad or iphone or handheld or (tablet adj5 computer?) or android or cell phone or mobile phone) adj4 (educational or class)).ti,ab. | 27 |
| 11 | (distributed adj3 (curricul* or education or learning)).ti,ab. | 298 |
| 12 | spaced learning.ti,ab. | 35 |
| 13 | ("remote course*" or "remote education" or "remote seminar?" or "remote learning" or "remote workshop*" or (remote participation adj4 (education? or workshop or course or learning))).ti,ab. | 40 |
| 14 | (virtual or online or web or internet).ti. | 51312 |
| 15 | or/4‐14 | 59766 |
| 16 | *postgraduate education/ or *continuing education/ or *in service training/ or *professional development/ | 3449 |
| 17 | (post‐graduate or graduate education or graduate degree? or ((master? or doctoral) adj2 degree?) or doctorate or doctoral or post‐professional).ti,ab. | 8089 |
| 18 | (continuing adj2 (medical or nursing or pharmacist? or physician? or doctor? or allied health) adj3 education?).ti,ab. | 5321 |
| 19 | (inservice training or professional development or cme).ti,ab. | 11093 |
| 20 | or/16‐19 | 26273 |
| 21 | (15 and 20) not 3 | 913 |
| 22 | *nurse/ or exp *paramedical personnel/ or exp *physician/ or *medical personnel/ | 132064 |
| 23 | (continuing adj2 education?).ti,ab,hw. | 62702 |
| 24 | (and/15,22‐23) not (or/3,21) | 77 |
| 25 | *dental education/ or *medical education/ or *nursing education/ | 68626 |
| 26 | 25 not (undergraduate? or first year or second year or third year or preclinical or pre‐clinical).ti,ab,hw. | 63971 |
| 27 | (26 and 15) not (or/3,21,24) | 1166 |
| 28 | controlled clinical trial/ or controlled study/ or randomized controlled trial/ | 510348 |
| 29 | randomi?ed.ti. or ((random* or control) adj3 (group? or cohort? or patient? or hospital* or department?)).ab. or (controlled adj2 (study or trial)).ti. | 641737 |
| 30 | (multicenter and (study or trial)).ti. | 20362 |
| 31 | (random sampl* or random digit* or random effect* or random survey or random regression).ti,ab. not randomized controlled trial/ | 62344 |
| 32 | (exp animals/ or exp invertebrate/ or animal experiment/ or animal model/ or animal tissue/ or animal cell/ or nonhuman/) and (human/ or normal human/ or human cell/) | 16144262 |
| 33 | (exp animals/ or exp invertebrate/ or animal experiment/ or animal model/ or animal tissue/ or animal cell/ or nonhuman/) not 32 | 4275233 |
| 34 | (or/28‐30) not (or/31,33) | 841718 |
| 35 | 3 and 34 | 176 |
| 36 | 21 and 34 | 58 |
| 37 | 24 and 34 | 9 |
| 38 | 27 and 34 | 54 |
| 39 | or/35‐38 | 297 |
Embase (OVID)
Embase 1974 to 2016 July 07
| No. | Search terms | Results |
| 1 | ("e‐learning" or elearning).ti. | 1157 |
| 2 | ("e‐learning" or elearning).ab. | 2220 |
| 3 | or/1‐2 | 2597 |
| 4 | computer‐assisted instruction/ | 62027 |
| 5 | ((electronic or internet or internet‐based or online or "on line" or remote or distance or mobile or web or "web 2*" or web‐based or web deliver*) adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or course‐work or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop? or work‐shop?)).ti,ab. | 9126 |
| 6 | ((computeri?ed or computer‐assisted or computer‐mediated* or computer‐based) adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or coursework or course‐work or education or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop?)).ti,ab. | 2086 |
| 7 | ((e‐mail* or email* or e‐mail‐based or email‐based) adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or course‐work or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop? or work‐shop?)).ti,ab. | 156 |
| 8 | (e‐education or e‐instruction or elearning or "e learning" or "e train*" or "e curricul*" or "e program*" or m‐learn*).ti,ab. | 2778 |
| 9 | (virtual adj2 (class or classes or classroom? or course? or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or instructor? or learning or seminar? or teacher? or teaching or training or trainer? or workshop*)).ti,ab. | 1632 |
| 10 | ((3g or 4g or ipad or iphone or handheld or (tablet adj5 computer?) or android or cell phone or mobile phone) adj4 (educational or class)).ti,ab. | 45 |
| 11 | (distributed adj3 (curricul* or education or learning)).ti,ab. | 352 |
| 12 | spaced learning.ti,ab. | 46 |
| 13 | ("remote course*" or "remote education" or "remote seminar?" or "remote learning" or "remote workshop*" or (remote participation adj4 (education? or workshop or course or learning))).ti,ab. | 55 |
| 14 | (virtual or online or web or internet).ti. | 59771 |
| 15 | or/4‐14 | 128433 |
| 16 | education, medical, continuing/ or education, medical, graduate/ or exp "internship and residency"/ or education, nursing, continuing/ or education, nursing, graduate/ or education, pharmacy, continuing/ or education, pharmacy, graduate/ or pharmacy residencies/ or inservice training/ or staff development/ | 660488 |
| 17 | (post‐graduate or graduate education or graduate degree? or ((master? or doctoral) adj2 degree?) or doctorate or doctoral or post‐professional).ti,ab. | 10031 |
| 18 | (continuing adj2 (medical or nursing or pharmacist? or physician? or doctor? or allied health) adj3 education?).ti,ab. | 6614 |
| 19 | (inservice training or professional development or cme).ti,ab. | 15275 |
| 20 | or/16‐19 | 674033 |
| 21 | (15 and 20) not 3 | 49387 |
| 22 | exp allied health personnel/ or exp *dentists/ or exp medical staff/ or exp nurses/ or pharmacists/ or exp physicians/ | 907485 |
| 23 | (continuing adj2 education?).ti,ab,hw. | 43200 |
| 24 | (and/15,22‐23) not (or/3,21) | 176 |
| 25 | education, dental/ or education, medical/ or education, nursing/ or education, pharmacy/ | 537908 |
| 26 | 25 not (undergraduate? or first year or second year or third year or preclinical or pre‐clinical).ti,ab,hw. | 514219 |
| 27 | (26 and 15) not (or/3,21,24) | 27 |
| 28 | (randomized controlled trial or controlled clinical trial).pt. or randomized.ab. or placebo.ab. or clinical trials as topic.sh. or randomly.ab. or trial.ti. | 981031 |
| 29 | exp animals/ not humans.sh. | 21860327 |
| 30 | 28 not 29 | 92471 |
| 31 | (3 or 21 or 24 or 27) and 30 | 232 |
The Cochrane Library (Wiley)
| No. | Search terms | Results |
| #1 | ("e‐learning" or elearning):ti | 117 |
| #2 | ("e‐learning" or elearning):ab | 188 |
| #3 | {or #1‐#2} | 216 |
| #4 | [mh "computer‐assisted instruction"] | 1039 |
| #5 | ((electronic or internet or internet‐based or online or "on line" or remote or distance or mobile or web or "web 2*" or web‐based or web deliver*) near/2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or course‐work or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop? or work‐shop?)):ti,ab | 656 |
| #6 | ((computeri?ed or computer‐assisted or computer‐mediated* or computer‐based) near/2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or coursework or course‐work or education or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop?)):ti,ab | 276 |
| #7 | ((e‐mail* or email* or e‐mail‐based or email‐based) near/2 (class or classes or classroom? or class‐room? or course or courses or course‐work or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or learning or seminar? or teaching or workshop? or work‐shop?)):ti,ab | 25 |
| #8 | (e‐education or e‐instruction or elearning or "e learning" or "e train*" or "e curricul*" or "e program*" or m‐learn*):ti,ab | 275 |
| #9 | (virtual near/2 (class or classes or classroom? or course? or education* or inservice or in‐service or instruction* or instructor? or learning or seminar? or teacher? or teaching or training or trainer? or workshop*)):ti,ab | 174 |
| #10 | ((3g or 4g or ipad or iphone or handheld or (tablet near/5 computer?) or android or cell phone or mobile phone) near/4 (educational or class)):ti,ab | 4 |
| #11 | (distributed near/3 (curricul* or education or learning)):ti,ab | 15 |
| #12 | spaced learning:ti,ab | 52 |
| #13 | ("remote course*" or "remote education" or "remote seminar?" or "remote learning" or "remote workshop*" or (remote participation near/4 (education? or workshop or course or learning))):ti,ab | 3 |
| #14 | (virtual or online or web or internet):ti | 5035 |
| #15 | {or #4‐#14} | 6458 |
| #16 | [mh "education, medical, continuing"] or [mh "education, medical, graduate"] or [mh "internship and residency"] or [mh "education, nursing, continuing"] or [mh "education, nursing, graduate"] or [mh "education, pharmacy, continuing"] or [mh "education, pharmacy, graduate"] or [mh "pharmacy residencies"] or [mh "inservice training"] or [mh "staff development"] | 2528 |
| #17 | (post‐graduate or graduate education or graduate degree? or ((master? or doctoral) near/2 degree?) or doctorate or doctoral or post‐professional):ti,ab | 225 |
| #18 | (continuing near/2 (medical or nursing or pharmacist? or physician? or doctor? or allied health) near/3 education?):ti,ab | 2 |
| #19 | (inservice training or professional development or cme):ti,ab | 730 |
| #20 | {or #16‐#19} | 3340 |
| #21 | (#15 and #20) | 339 |
| #22 | [mh "allied health personnel"] or [mh *dentists] or [mh "medical staff"] or [mh nurses] or [mh pharmacists] or [mh physicians] | 4047 |
| #23 | (continuing near/2 education?):ti,ab,kw | 2 |
| #24 | #15 and #22 and #23 | 0 |
| #25 | [mh "education, dental"] or [mh "education, medical"] or [mh "education, nursing"] or [mh "education, pharmacy"] | 3454 |
| #26 | #25 not (undergraduate? or first year or second year or third year or preclinical or pre‐clinical):ti,ab,kw | 2873 |
| #27 | #26 and #15 | 456 |
| #28 | #3 or #21 or #24 or #27 | 720 |
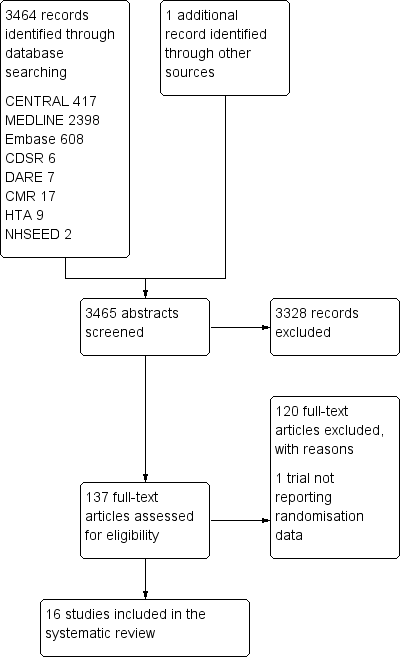
Study flow diagram
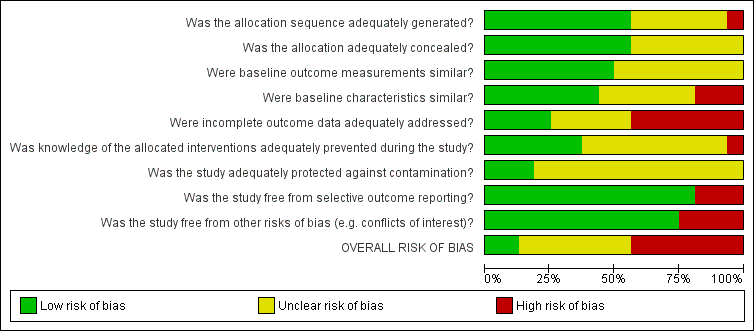
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item for each included study.
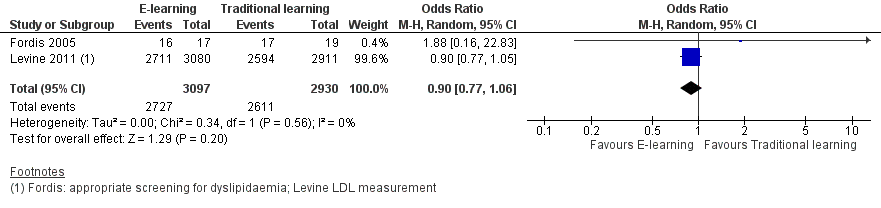
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Behaviours, outcome: 1.1 Patients appropriately screened (Fordis 2005 ‐ screening for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ LDL measurement).

Forest plot of comparison: 1 Behaviours, outcome: 1.2 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ statin prescription).
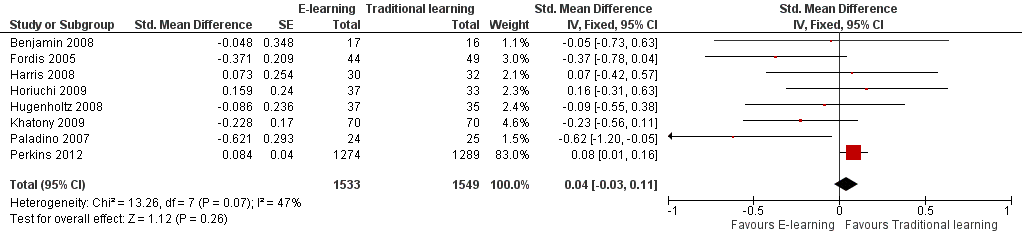
Forest plot of comparison: 3 Knowledge, outcome: 3.1 At any time (fixed‐effect).

Forest plot of comparison: 3 Knowledge, outcome: 3.2 At any time (random‐effects).

Comparison 1 Behaviours, Outcome 1 Patients appropriately screened (Fordis 2005 ‐ screening for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ LDL measurement).

Comparison 1 Behaviours, Outcome 2 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ statin prescription).

Comparison 1 Behaviours, Outcome 3 Patients appropriately screened (Fordis 2005 ‐ screening for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ HbA1c measurement).
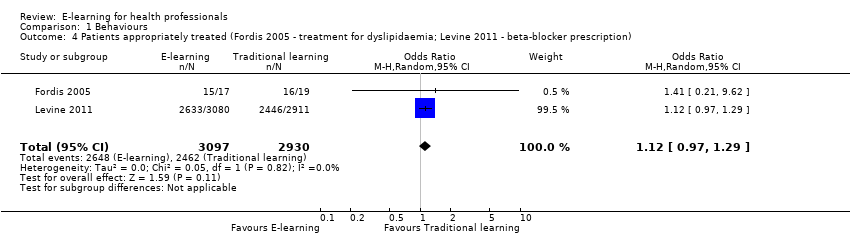
Comparison 1 Behaviours, Outcome 4 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ beta‐blocker prescription).

Comparison 1 Behaviours, Outcome 5 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ ACEI/ARB prescription).

Comparison 2 Skills, Outcome 1 Drug dose calculation accuracy (Simonsen 2014); ulcer classification accuracy (Bredesen 2016).

Comparison 2 Skills, Outcome 2 Cardiac arrest simulation test (CASTest).
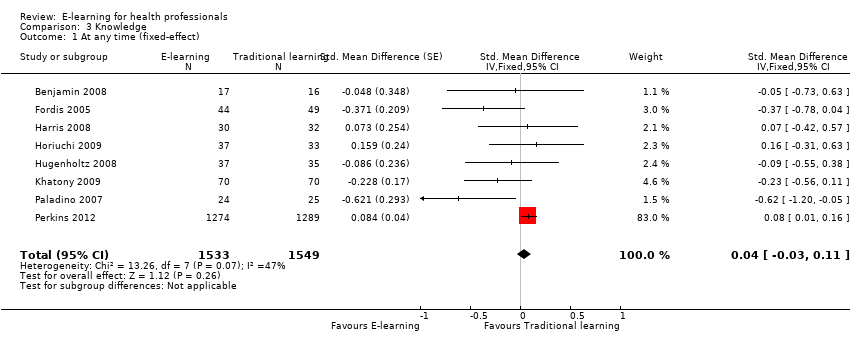
Comparison 3 Knowledge, Outcome 1 At any time (fixed‐effect).

Comparison 3 Knowledge, Outcome 2 At any time (random‐effects).
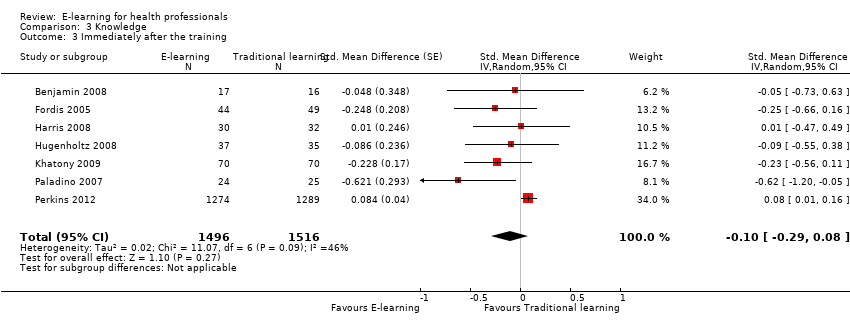
Comparison 3 Knowledge, Outcome 3 Immediately after the training.

Comparison 3 Knowledge, Outcome 4 After 3 or more months.
| E‐learning versus traditional learning for health professionals | ||||
| Patient or population: licensed health professionals (doctors, nurses and allied health professionals fully licensed to practice without supervision) Settings: postgraduate education in any setting Intervention: e‐learning (any intervention in which clinical content is distributed primarily by the Internet, Extranet or Intranet) Comparison: traditional learning (any intervention not distributed through the media mentioned above) | ||||
| Outcomes | Impact* | No of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Comments |
| Patient outcomes Follow‐up: 12 months | E‐learning may make lead to little or no difference between the groups in proportion of patients with LDL cholesterol < 100 mg/dL (adjusted difference 4.0% (95% CI −0.3 to 7.9; 6399 patients) or glycated haemoglobin level < 8% (adjusted difference 4.6%, 95% CI −1.5 to 9.8; 3114 patients) | 168 primary care clinics; 847 health professionals (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | — |
| Health professionals' behaviours Follow‐up: 3‐12 months | E‐learning may make little or no difference between the groups in terms of screening for dyslipidaemia (OR 0.90, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.06, 6027 patients) or treatment for dyslipidaemia (OR 1.15, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.48; 5491 patients) | 950 health professionals (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Studies reported multiple outcomes without specifying the primary outcome: to assess consistency, we explored 3 other possible combinations between the 2 study indicators. |
| Health professionals' skills Follow‐up: 0‐12 weeks | We are uncertain whether e‐learning improves or reduces health professionals' skills (SMD 0.03, 95% CI −0.25 to 0.31, I2 = 61%, 201 participants, 12 weeks' follow‐up). | 2912 health professionals (6 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowc | The results from the largest trial and 2 more trials, favouring traditional learning (2640 participants), and from one trial favouring e‐learning could not be included in the meta‐analysis. The meta‐analysis included 2 trials studying different professional skills (drug dose calculation and accuracy in pressure ulcers classification). |
| Health professionals' knowledge Any follow‐up: 0‐12 weeks | E‐learning may make little or no difference in health professionals' knowledge: 8 trials provided data to the meta‐analysis (SMD 0.04, 95% CI ‐0.03 to 0.11, I2 = 47%, 3082 participants). | 3236 health professionals (11 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | 3 additional studies (154 participants) reported this outcome but no data were available for pooling. |
| CI: confidence interval; LDL: low‐density lipoprotein; OR: odds ratio; SD: standard deviation; SMD: standardised mean difference. *We interpreted SMDs using the following rules suggested by Higgins 2011a: < 0.40 represents a small effect size; 0.40 to 0.70, a moderate effect size; and > 0.70, a large effect size. | ||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence: | ||||
| aDowngraded for study limitations (risk of bias and imprecision) and imprecision surrounding surrogate outcomes. Important benefits cannot be ruled out. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Patients appropriately screened (Fordis 2005 ‐ screening for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ LDL measurement) Show forest plot | 2 | 6027 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.77, 1.06] |
| 2 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ statin prescription) Show forest plot | 2 | 5491 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.89, 1.48] |
| 3 Patients appropriately screened (Fordis 2005 ‐ screening for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ HbA1c measurement) Show forest plot | 2 | 3056 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.69, 1.06] |
| 4 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ beta‐blocker prescription) Show forest plot | 2 | 6027 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.12 [0.97, 1.29] |
| 5 Patients appropriately treated (Fordis 2005 ‐ treatment for dyslipidaemia; Levine 2011 ‐ ACEI/ARB prescription) Show forest plot | 2 | 6027 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.94, 1.19] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Drug dose calculation accuracy (Simonsen 2014); ulcer classification accuracy (Bredesen 2016) Show forest plot | 2 | 201 | Std. Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.25, 0.31] |
| 2 Cardiac arrest simulation test (CASTest) Show forest plot | 1 | 2562 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.46 [1.22, 1.76] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 At any time (fixed‐effect) Show forest plot | 8 | 3082 | Std. Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.04 [‐0.03, 0.11] |
| 2 At any time (random‐effects) Show forest plot | 8 | 3082 | Std. Mean Difference (Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.09 [‐0.27, 0.09] |
| 3 Immediately after the training Show forest plot | 7 | 3012 | Std. Mean Difference (Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐0.29, 0.08] |
| 4 After 3 or more months Show forest plot | 3 | 225 | Std. Mean Difference (Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.41, 0.27] |

