Extracto de Cyclamen europaeum para la sinusitis aguda
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Randomised, parallel, double‐blind; intention‐to‐treat | |
| Participants | Age: 18 to 65 years, N = 99 Inclusion criteria: men/women, moderate or severe acute rhinosinusitis symptoms > 7 days and < 12 weeks, at least 2 of: nasal obstruction, nasal secretion, facial pain/tension/pressure, impaired or loss of smell and mucus oedema, nasal obstruction or mucopurulent secretion on nasal endoscopy Exclusion criteria: chronic rhinosinusitis, nasal polyposis, severe mechanical nasal obstruction, severe asthmatic patients, intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid, treatment with anticoagulants or anticholinergic drugs, topical nasal corticosteroids within 72 hours of study start, or antibacterial agent within 48 hours | |
| Interventions | 1. Treatment: Cyclamen europaeum nasal spray, lyophilised extract, 1.3 mg once daily each nostril, N = 48 2. Control: placebo matching, once daily, N = 51 Concomitant amoxycillin 500 mg 3 times daily for 8 days or alternative if allergic to penicillin in both groups Treatment duration: 15 days Follow‐up: 15 days | |
| Outcomes | Change from baseline in mean total symptom score on days 5 to 7 Individual symptoms scores on days 5 to 7 and 15 Total symptom score at day 15, endoscopic findings on days 5 to 7 and 15 Treatment failure/need for additional treatment Complications Sleep quality Overall treatment satisfaction | |
| Notes | Similar baseline characteristics, 13 centres in Germany, informed consent, intensity of rhinosinusitis symptoms assessed by visual analogue scale (0 to 10 cm). Subjective assessment; no concomitant treatment with corticosteroids or decongestants was allowed; symptom diaries completed by participants; endoscopic findings assessed by 4‐point Likert scales from 0 to 3; adverse events and complications of rhinosinusitis were monitored. Grant from Hartington Pharmaceutical Spain. We tried to contact trial authors for more information regarding the randomisation method and for data on participants, i.e. whether participants were inpatients, outpatients, or both, as this was not mentioned in the paper, but did not receive a reply. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Randomly assigned, method not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Double‐blind, placebo matching |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Dropouts described. Treatment group 8 total: 2 adverse events, 3 discontinued treatment, 1 immunosuppressive treatment, 2 other. Placebo group 9 total: 1 adverse event, 2 discontinued treatment, 1 consent withdrawal, 5 other. Dropouts balanced between study groups, reasons reported, analyses by intention‐to‐treat. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Not observed |
| Other bias | Low risk | Not observed |
| Methods | Randomised, parallel, double‐blind; intention‐to‐treat | |
| Participants | Age: 18 to 70 years, N = 48 Inclusion criteria: men/women, outpatients with symptoms and endoscopy + radiology acute rhinosinusitis or acute exacerbation of chronic rhinosinusitis, total symptom score ≥ 3 (nasal obstruction/congestion, facial pain/fullness/pressure), endoscopy ‐ mucopurulence and inflammation, CT scan ‐ air fluid levels and/or air bubbles in at least 1 maxillary sinus Exclusion criteria: pregnant, hypogammaglobulinaemia, immotile cilia syndrome, cystic fibrosis, atrophic rhinitis, rhinitis medicamentosa, hypersensitivity to Primulaceae, serious comorbidity, expansile mass or bony erosion on radiologic examination, viral upper respiratory tract infection in past 2 weeks, high fever, facial or periorbital oedema or local complications, recent nasal/sinus surgery within 3 months, radiation treatment or chemotherapy within 1 year, intranasal antibiotics within 30 days, systemic antibiotics within 15 days, oral/topical nasal decongestants within 7 days | |
| Interventions | 1. Treatment: Cyclamen europaeum nasal spray, 10% lyophilised (Sinuforte), 1.3 mg (0.13 mL) once daily each nostril, N = 24 2. Control: placebo spray sterile water, once daily, N = 24 Treatment duration: 7 days Follow‐up: 90 days | |
| Outcomes | Change from baseline in % sinus opacification on CT scans at days 15, 29 or endpoint Reduction in total symptom score (6‐point scale: nasal obstruction, congestion, facial pain, pressure, fullness) Other symptoms scores changes from baseline Endoscopic inflammation at day 8 | |
| Notes | Similar baseline characteristics; outpatients 25 US centres; November 2007 to September 2008; intranasal/systemic antibiotics, oral/inhaled steroids, decongestants were not allowed. Visit 1: randomisation, visit 2: 7 days, follow‐up visit 3: 15 days, visit 4: 29 days, telephone follow‐up: 90 days; participants' diaries for symptoms, adverse events, concomitant medication. CT scans at visits 1, 3, 4, endoscopy at visits 1, 2, no serious adverse events. Funded by Hartington Pharmaceutical, Spain and Dey Pharma, LP, Napa, CA, USA | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomly assigned, computer‐generated scheme |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Double‐blind, matching product vials labelled to obscure the contents |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Mentioned only for 1 outcome, central reader of CT scans was blinded to treatment assignment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Dropouts described. Treatment group 16 total dropouts: 11 excluded: 9 chronic rhinosinusitis, 2 unclassified; 13 included in analyses (5 discontinued: 2 protocol violation, 3 other); 8 completed study. Placebo group 13 total dropouts: 8 excluded: 4 chronic rhinosinusitis, 4 unclassified; 16 included in analyses (1 lost to follow‐up; 4 discontinued: 1 protocol violation, 3 other); 11 completed study. Reasons for dropout reported, analysis by intention‐to‐treat. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Not observed |
| Other bias | Low risk | Not observed |
CT: computed tomography
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| The comparison did not meet inclusion criteria: combined interventions were used in the control group that differed from the intervention group. | |
| The comparison did not meet inclusion criteria: combined interventions were used in the control group that differed from the intervention group. | |
| The comparison did not meet inclusion criteria: combined interventions were used in the control group that differed from the intervention group. | |
| Not randomised, combined different treatments in the intervention and control groups. | |
| Randomisation not clear; we contacted the author, who confirmed quasi‐randomisation by odd/even numbers. | |
| The comparison did not meet inclusion criteria: combined interventions were reported as "standard treatment" for the intervention and control groups, and the control group used punctures of the maxillary sinuses as comparison. | |
| Not randomised, no control group | |
| Not randomised, no control group |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ intention‐to‐treat Show forest plot | 2 | 147 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.11 [1.35, 3.29] |
| Analysis 1.1 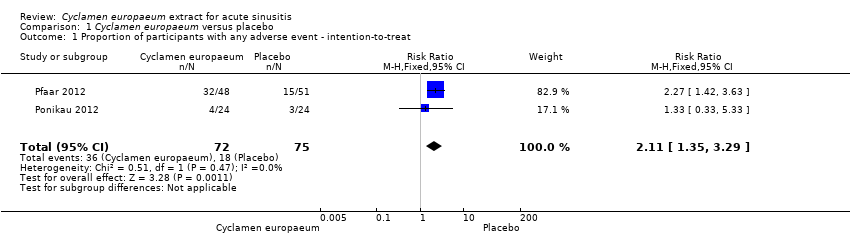 Comparison 1 Cyclamen europaeum versus placebo, Outcome 1 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ intention‐to‐treat. | ||||
| 2 Proportion of participants with any adverse events ‐ best‐case sensitivity analysis Show forest plot | 2 | 147 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.68, 1.30] |
| Analysis 1.2 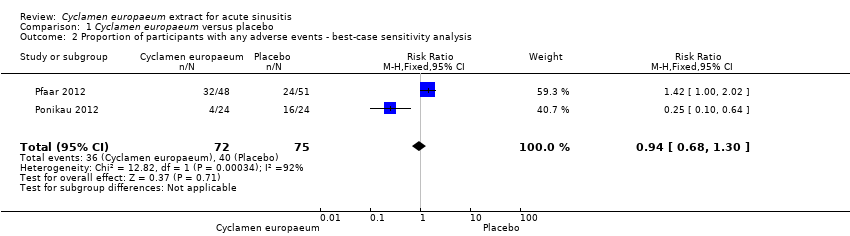 Comparison 1 Cyclamen europaeum versus placebo, Outcome 2 Proportion of participants with any adverse events ‐ best‐case sensitivity analysis. | ||||
| 3 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ worst‐case sensitivity analysis Show forest plot | 2 | 147 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.49 [2.30, 5.30] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Cyclamen europaeum versus placebo, Outcome 3 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ worst‐case sensitivity analysis. | ||||

Study flow diagram.
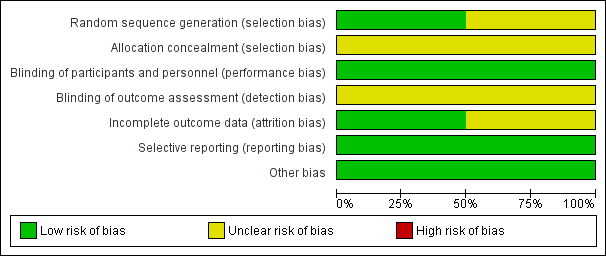
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Cyclamen europaeum versus placebo, Outcome 1 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ intention‐to‐treat.

Comparison 1 Cyclamen europaeum versus placebo, Outcome 2 Proportion of participants with any adverse events ‐ best‐case sensitivity analysis.

Comparison 1 Cyclamen europaeum versus placebo, Outcome 3 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ worst‐case sensitivity analysis.
| Cyclamen europaeum compared to placebo for acute sinusitis | ||||||
| Patient or population: adults with acute sinusitis | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with placebo | Risk with Cyclamen europaeum | |||||
| Proportion of participants with resolution or improvement of symptoms up to 30 days | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | No studies reported this outcome. |
| Proportion of participants with any adverse event | Study population | RR 2.11 | 147 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Moderate | We downgraded the quality of the evidence as concealment of allocation to treatment and blinding of outcome assessors were not reported in the studies. Also, 1 study had a small sample size with a high attrition rate. | |
| 240 per 1000 | 506 per 1000 | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI) CI: confidence interval; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RR: risk ratio | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| Study ID | Cyclamen europaeum | Placebo |
| 67% total 50% nasal irritation mild/moderate 27% mild epistaxis 4% sneezing 3 discontinued treatment | 29% total 4% nasal irritation 14% mild epistaxis 4% vertigo 2 discontinued treatment | |
| 15.4% total Influenza, throat irritation, migraine, sneezing No serious adverse events Did not discontinue treatment | 12.5% total Headache, ear pain, gastritis, back pain, conjunctival haemorrhage No serious adverse events Did not discontinue treatment |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ intention‐to‐treat Show forest plot | 2 | 147 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.11 [1.35, 3.29] |
| 2 Proportion of participants with any adverse events ‐ best‐case sensitivity analysis Show forest plot | 2 | 147 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.68, 1.30] |
| 3 Proportion of participants with any adverse event ‐ worst‐case sensitivity analysis Show forest plot | 2 | 147 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.49 [2.30, 5.30] |

