Rehabilitación cardíaca para pacientes con cardiopatía: una revisión global de las revisiones sistemáticas Cochrane
Referencias
Referencias de las revisiones incluidas
Referencias de las revisiones excluidas
Referencias adicionales
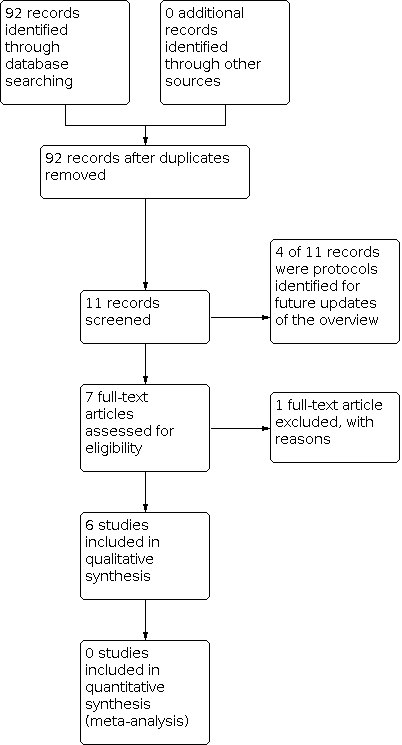
Study flow diagram.
| Review short title (reference) | Exercise for CHD | Exercise for HF | Psychological for CHD | Education for CHD | Home vs. centre | Uptake and adherence |
| Main objective | To determine the effectiveness of exercise‐based CR (exercise training alone or in combination with psychosocial or educational interventions) on mortality, morbidity and HRQoL of people with CHD | To determine the effectiveness of exercise‐based interventions compared with usual medical care by focusing on mortality, hospital admission rate, morbidity and HRQoL in people with HF | To determine the independent effects of psychological interventions in people with CHD | To assess the effects of patient education on mortality, morbidity, HRQoL and healthcare costs in people with CHD | To determine the effectiveness of home‐based CR programmes compared with supervised centre‐based CR on mortality and morbidity, HRQoL and modifiable cardiac risk factors in people with CHD | To determine the harms and benefits of interventions to increase patient uptake of, and adherence to, CR |
| Search time frame | November 2000 to December 2009 | 2008 to March 2013 | 2001 to January 2009 | 1990 to August 2010 | 2008 to November 2012 | 2008 to January 2013 |
| Study design | RCTs (follow‐up ≥ 6 months) | RCTs (follow‐up ≥ 6 months) | RCTs (no minimum follow‐up) | RCTs (follow‐up ≥ 6 months) | RCTs (no minimum follow‐up) | RCTs (no minimum follow‐up) |
| Population | Inclusion Post‐MI Post revascularisation CHD defined by angiography Exclusion Heart valve surgery HF Heart transplantation CRT or ICD implant | Inclusion HF Exclusion Previous CR | Inclusion Post‐MI Post revascularisation Angina CHD defined by angiography Exclusion None | Inclusion Post‐MI Post revascularisation Angina CHD defined by angiography | Inclusion Post‐MI Post revascularisation Angina HF Exclusion Heart transplantation CRT or CD implant Previous CR | Inclusion Post‐MI Post revascularisation Angina HF CHD Exclusion Heart transplantation CRT or ICD implant |
| Intervention | Exercise training with or without the addition of psychosocial or educational interventions (or both) | Exercise training with or without the addition of psychosocial or educational interventions (or both) | Psychological interventions delivered by healthcare workers with specific training in psychological techniques | Patient education interventions involving direct contact with a health professional and including structured knowledge transfer about CHD | CR programmes delivered in a home‐based setting | CR plus any intervention with the specific aim of increasing patient uptake of, or adherence to, CR or any of its component parts |
| Comparator | No exercise training control that could include psychological, educational interventions, standard medical care or a combination | No exercise training control that could include psychological, educational interventions, standard medical care or a combination | No psychological intervention control that could include exercise interventions or standard medical care | No education intervention control that could include exercise interventions or standard medical care | CR programmes delivered in a centre‐based setting | CR programmes without the intervention |
| Outcomes |
|
|
|
|
| Uptake of, or adherence to, CR (primary)
|
| Funding source | NIHR, UK Cochrane Collaboration Programme Grant, UK | None specified | Department of Social Medicine, University of Bristol, UK Health Services Research Focus, University of Wales College of Medicine, UK British Heart Foundation, UK ESCR, UK NIHR, UK Cochrane Collaboration Heart Programme Grant, UK | NIHR, UK Cochrane Collaboration Programme Grant, UK | NIHR Cochrane Heart Programme grant, UK Transparency of the National Health System Drug Reimbursement Decisions, Poland, EU | NIHR programme grant, UK |
| Authors' declarations of interest | Authors were authors of the original Cochrane review. RST was a co‐investigator on a number of CR RCTs | ‐ | None declared | None declared | RST was a co‐author of the original Cochrane review and was a co‐investigator on a number of CR RCTs | None declared |
| CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; CAD: coronary artery disease; CHD: coronary heart disease; CR: cardiac rehabilitation; CRT: cardiac resynchronisation therapy; CV: cardiovascular; ESCR: Economic and Social Research Council; HF: heart failure; HRQoL: health‐related quality of life; ICD: implantable cardioverter defibrillator; MI: myocardial infarction; NIHR: National Institute of Health Research; PTCA: percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty; RCT: randomised controlled trial. | ||||||
| Review short title (reference) | Exercise for CHD | Exercise for HF | Psychological for CHD | Education for CHD | Home vs. centre | Uptake and adherence |
| RCTs (participants) | ||||||
| Number | 47 RCTs (10,794) | 33 RCTs (4740) | 24 RCTs (9296) | 13 RCTs (68,556) | 17 RCTs (2172) | 18 RCTs (2505) |
| Nature of intervention* | ||||||
| Exercise only | 17 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 6 | Interventions aimed at increasing patient uptake of CR (10 RCTs) Interventions designed to increase adherence to exercise (7 RCTs) or supervised CR (1 RCT) |
| Psychological only | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | |
| Education only | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 0 | |
| > 1 intervention | 29* | 12 | 10 (psychological and education) | 0 | 11 | |
| Sample size | ||||||
| Median (range) | 142 (28 to 2304) | 54 (19 to 2331) | 133 (44 to 2481) | 288 (87 to 46,606) | 104 (20 to 525) | 110 (16 to 597) |
| Intervention duration [months] | ||||||
| Median (range) months | 3 (1 to 30) | 6 (1 to 120) | NR | 6 (1 to 30) | 3 (1.5 to 6) | NR |
| Publication year (number of RCTs) | ||||||
| 1970‐1979 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1990‐1999 | 11 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 1990‐1999 | 20 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| 2000‐2009 | 14 | 20 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 8 |
| 2010+ | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| % male | ||||||
| Median (range) | 88 (0 to 100) | 80 (36 to 100) | 84 (0 to 100) | 60 (0 to 100) | 80 (60 to 100) | 84 (0 to 100) |
| % white | ||||||
| Median (range) | NR | 85 (60 to 100) from 8 RCTs | NR | 86 (55 to 97) from 6 RCTs | 80 from 1 RCT | 79 (43 to 95) from 6 RCTs |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| Median (range) | 55 (49 to 70) | 60 (51 to 81) | 57 (51 to 62) | 62 (51 to 73) | 60 (52 to 69) | 62 (51 to 77) |
| Indication (number of RCTs) | ||||||
| MI only | 28 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Angina only | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Revascularisation only | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| MI or revascularisation (or both) | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
| MI or angina | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Mixed CHD | 9 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 7 |
| HF | 0 | 33 | 0 | 3 CHD or HF | 3 | 1 |
| Arrhythmia | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Study location (number of RCTs (%)) | ||||||
| Europe | 20 (43) | 20 (64) | 11 (46) | 7 (54) | 10 (58) | 6 (33) |
| North America | 3 (6) | 11 (30) | 11 (46) | 6 (46) | 5 (29) | 11 (61) |
| Asia/Australia | 7 (15) | 1 (3) | 2 (8) | 0 | 1 (6) | 1 (6) |
| Other | ‐ | 1 (3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (6) | 0 |
| NR | 17 (36) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Single centre | ||||||
| Number of RCTs (%) | 23 (49) | 30 (91) | 8 (33) | 4 (31) | 15 (88) | 10/16 (63)** |
| Follow‐up duration [months] | ||||||
| Median (range) | 24 (6 to 120) | 6 (6 to 120) | NR | 18 (6 to 60) | 6 (2 to 72) | 3 (1.5 to 12) |
| CHD: coronary heart disease; HF: heart failure; MI: myocardial infarction; NR: not reported; RCT: randomised controlled trial. * 1 RCT randomly assigned to exercise‐only or comprehensive intervention. ** 2 studies were unavailable to us as they were unpublished degree dissertations. | ||||||
| Review short title (reference) | Exercise for CHD | Exercise for HF | Psychological for CHD | Education for CHD | Home vs. centre | Uptake and adherence |
| 1. Was an 'a priori' design provided? | ||||||
| (A) 'a priori' design | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) Statement of inclusion criteria | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) PICO/PIPO research question (population, intervention, comparison, prediction, outcome) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Score | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 2. Was there duplicate study selection and data extraction? | ||||||
| (A) There should be at least 2 independent data extractors as stated or implied | Yes | *Yes | *Yes | *Yes | *Yes | Yes |
| (B) Statement of recognition or awareness of consensus procedure for disagreements | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) Disagreements among extractors resolved properly as stated or implied | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Score | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Yes |
| 3. Was a comprehensive literature search performed? | ||||||
| (A) At least 2 electronic sources should be searched | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) The report must include years and databases used (e.g. CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) Key words or MESH terms (or both) must be stated AND where feasible the search strategy outline should be provided such that one can trace the filtering process of the included articles | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (D) In addition to the electronic databases (PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE), all searches should be supplemented by consulting current contents, reviews, textbooks, specialised registers, or experts in the particular field of study, and by reviewing the references in the studies found | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| (E) Journals were "hand‐searched" or "manual searched" (i.e. identifying highly relevant journals and conducting a manual, page‐by‐page search of their entire contents looking for potentially eligible studies) | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Score | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 4. Was the status of publication (i.e. grey literature) used as an inclusion criterion? | ||||||
| (A) The authors should state that they searched for reports regardless of their publication type | *No | *No | No | *No | Yes | *No |
| (B) The authors should state whether or not they excluded any reports (from the systematic review), based on their publication status, language, etc. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) "Non‐English papers were translated" or readers sufficiently trained in foreign language | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| (D) No language restriction or recognition of non‐English articles | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Score | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| 5. Was a list of studies (included and excluded) provided? | ||||||
| (A) Table/list/figure of included studies, a reference list does not suffice | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) Table/list/figure of excluded studies, either in the article or in a supplemental source (i.e. online). (Excluded studies refers to those studies seriously considered on the basis of title and/or abstract, but rejected after reading the body of the text) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) Author satisfactorily/sufficiently stated the reason for exclusion of the seriously considered studies | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (D) Reader was able to retrace the included and the excluded studies anywhere in the article bibliography, reference or supplemental source | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Score | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 6. Were the characteristics of the included studies provided? | ||||||
| (A) In an aggregated form such as a table, data from the original studies should be provided on the participants, interventions AND outcomes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) Provide the ranges of relevant characteristics in the studies analysed (e.g. age, race, sex, relevant socioeconomic data, disease status, duration, severity or other diseases should be reported) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) The information provided appears to be complete and accurate (i.e. there was a tolerable range of subjectivity here. Is the reader left wondering? If so, state the needed information and the reasoning) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Score | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 7. Was the scientific quality of the included studies assessed and documented? | ||||||
| (A) 'A priori' methods of assessment should be provided (e.g. for effectiveness studies if the author(s) chose to include only randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled studies, or allocation concealment as inclusion criteria); for other types of studies alternative items will be relevant | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) The scientific quality of the included studies appeared to be meaningful | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) Discussion/recognition/awareness of level of evidence | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (D) Quality of evidence should be rated/ranked based on characterised instruments. (Characterised instrument is a created instrument that ranks the level of evidence, e.g. GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation)) | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Score | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 8. Was the scientific quality of the included studies used appropriately in formulating conclusions? | ||||||
| (A) The results of the methodological rigor and scientific quality should be considered in the analysis and the conclusions of the review | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) The results of the methodological rigor and scientific quality were explicitly stated in formulating recommendations | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| (C) To have conclusions integrated/drives towards a clinical consensus statement | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (D) This clinical consensus statement drives towards revision or confirmation of clinical practice guidelines | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Score | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 9. Were the methods used to combine the findings of studies appropriate? | ||||||
| (A) Statement of criteria that were used to decide that the studies analysed were similar enough to be pooled? | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) For the pooled results, a test should be done to ensure the studies were combinable, to assess their homogeneity (i.e. Chi2 test for homogeneity, I2 statistic) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | NA |
| (C) Is there a recognition of heterogeneity or lack of thereof | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (D) If heterogeneity exists a "random‐effects model" should be used or the rationale (i.e. clinical appropriateness) of combining should be taken into consideration (i.e. is it sensible to combine?), or stated explicitly (or both) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | NA |
| (E) If homogeneity exists, author should state a rationale or a statistical test | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | Yes | NA |
| Score | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| 10. Was the likelihood of publication bias (a.k.a. "file drawer" effect) assessed? | ||||||
| (A) Recognition of publication bias or file‐drawer effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) An assessment of publication bias should include graphical aids (e.g. funnel plot, other available tests) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| (C) Statistical tests (e.g. Egger regression test) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Score | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| 11. Was the conflict of interest stated? | ||||||
| (A) Statement of sources of support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (B) No conflict of interest. This is subjective and may require some deduction or searching | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| (C) An awareness/statement of support or conflict of interest in the primary inclusion studies | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Score | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Total score (n/44) | 39 | 39 | 39 | 41 | 40 | 35 |
| CHD: coronary heart disease; HF: heart failure. * Studies were screened independently by 2 review authors. Data were extracted by 1 review author and checked by a second review author. ** While the authors did not explicitly state that they searched for reports regardless of publication type, it was clear from the included studies or text (or both) that a search of grey literature was conducted. | ||||||
| Review short title (reference) | Exercise for CHD | Exercise for HF | Psychological for CHD | Education for CHD | Home vs. centre | Uptake and adherence | Total |
| Number of RCTs with low risk of bias (%) | |||||||
| Random sequence generation | 8 (17) | 10 (30) | 7 (29) | 9 (69) | 4 (24) | 9 (50) | 47 (31) |
| Allocation concealment | 7 (15) | 6 (18) | 7 (29) | 7 (54) | 7 (41) | 8 (44) | 41 (27) |
| Groups balanced at baseline | a27 (57) | 32 (97) | a10 (42) | 12 (92) | 14 (82) | ab9 (56) | 103 (68) |
| Outcome blinding | 4 (9) | 11 (33) | 5 (21) | 4 (31) | 7 (41) | 5 (28) | 36 (24) |
| Selective reporting | 0 (0) | 31 (94) | 16 (67) | 12 (92) | 16 (94) | 15 (83) | 90 (59) |
| Loss to follow‐up < 20% | 33 (70) | 29 (88) | 13 (54) | 10 (77) | 11 (65) | 4 (22) | 99 (65) |
| Intention‐to‐treat analysis | a19 (40) | 29 (88) | 22 (92) | 11 (85) | 14 (82) | ab7 (44) | 101 (66) |
| Groups received same treatment apart from intervention* | a21 (45) | 21 (64) | a16 (67) | 11 (85) | 15 (88) | ab15 (94) | 100 (66) |
| CHD: coronary heart disease; HF: heart failure; RCT: randomised controlled trial. a Risk of bias was not reported within the review, but was assessed by the authors of this overview. b Denominator = 16 as 2 studies were unavailable to us as they were unpublished degree dissertations. | |||||||
| Exercise‐based cardiac rehabilitation for coronary heart disease | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with CHD | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Exercise‐based CR | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.82 | 6000 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 65 per 1000 | 53 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.87 | 5790 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 126 per 1000 | 109 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Cardiovascular mortality | Study population | RR 0.93 | 4130 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 51 per 1000 | 48 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Cardiovascular mortality | Study population | RR 0.74 | 4757 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 129 per 1000 | 96 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Hospitalisations | Study population | RR 0.69 | 463 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 324 per 1000 | 224 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Hospitalisations | Study population | RR 0.98 | 2009 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 342 per 1000 | 335 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| MI | Study population | RR 0.92 | 4216 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 45 per 1000 | 41 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| MI | Study population | RR 0.97 | 5682 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 89 per 1000 | 87 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| CABG | Study population | RR 0.91 | 2312 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 67 per 1000 | 61 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| CABG | Study population | RR 0.93 | 2189 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 69 per 1000 | 64 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| PTCA | Study population | RR 1.02 | 1328 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 69 per 1000 | 71 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| PTCA | Study population | RR 0.89 | 1322 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 124 per 1000 | 110 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Random sequence generation and allocation concealment were poorly described; bias likely. | ||||||
| Exercise‐based cardiac rehabilitation for heart failure | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with HF Settings: | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Exercise‐based CR | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.93 | 1871 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 75 per 1000 | 70 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.88 | 2845 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 196 per 1000 | 173 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Hospitalisations | Study population | RR 0.75 | 1328 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 227 per 1000 | 170 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Hospitalisations | Study population | RR 0.92 | 2722 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 604 per 1000 | 556 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Hospitalisations (HF‐specific admissions) | Study population | RR 0.61 | 1036 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 182 per 1000 | 111 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| HRQoL | ‐ | The mean HRQoL in the intervention groups was | ‐ | 1270 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| HRQoL | ‐ | The mean HRQoL in the intervention groups was | ‐ | 3240 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| HRQoL | ‐ | The mean HRQoL in the intervention groups was | ‐ | 329 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Random sequence generation and allocation concealment were poorly described; bias likely. | ||||||
| Psychological‐based interventions for coronary heart disease | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with CHD | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Psychological‐based interventions | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.89 | 6852 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 93 per 1000 | 83 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Cardiovascular mortality | Study population | RR 0.80 | 3893 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 85 per 1000 | 68 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| MI (non‐fatal) | Study population | RR 0.87 | 7534 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 83 per 1000 | 72 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| Revascularisation (CABG and PTCA combined) | Study population | RR 0.95 | 6670 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 121 per 1000 | 115 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Random sequence generation and allocation concealment were poorly described; bias likely. | ||||||
| Education‐based interventions forcoronary heart disease | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with CHD | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Education‐based interventions | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.79 | 2330 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 96 per 1000 | 76 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| Hospitalisations | Study population | RR 0.83 | 12,905 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 64 per 1000 | 53 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| MI | Study population | RR 0.63 | 209 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 118 per 1000 | 74 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| CABG | Study population | RR 0.58 | 209 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 78 per 1000 | 45 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| All‐cause withdrawal | Study population | RR 1.03 | 2862 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 181 per 1000 | 186 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 The 95% CIs include both no effect and appreciable benefit or harm (i.e. RR < 0.75 or > 1.25). | ||||||
| Home‐based cardiac rehabilitation compared with centre‐based cardiac rehabilitation for heart disease | ||||||
| Patient or population: people with heart disease | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Centre‐based CR | Home‐based CR | |||||
| Total mortality | Study population | RR 0.79 | 1166 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ‐ | |
| 27 per 1000 | 22 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| All‐cause withdrawal | Study population | RR 1.04 | 1984 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ‐ | |
| 874 per 1000 | 909 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| ‐ | ‐ | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Random sequence generation and allocation concealment were poorly described; bias likely. | ||||||
| Review short title (reference) | Exercise for CHD | Exercise for HF | Psychological for CHD | Education for CHD | Home vs. centre | Uptake and adherence |
| Total mortality | Follow‐up < 12 months 19 RCTs (6000 participants), RR 0.82; 95% CI 0.67 to 1.01 I2 = 0% Follow‐up > 12 months 16 RCTs (5790 participants) RR 0.87; 95% CI 0.75 to 0.99 I2 = 0% | Follow‐up < 12 months 25 RCTs (1871 participants) RR 0.93; 95% CI 0.697 to 1.27 I2 = 0% Follow‐up > 12 months 6 RCTs (2845 participants) RR 0.88; 95% CI 0.75 to 1.02 I2 = 34% | 17 RCTs (6852 participants) RR 0.89; 95% CI 0.75 to 1.05 I2 = 2% | 6 RCTs (2330 participants) RR 0.79; 95% CI 0.55 to 1.13 I2 = 16% | Follow‐up < 12 months 7 RCTs (1166 participants) RR 0.79; 95% CI 0.43 to 1.47 I2 = 0% Follow‐up > 12 months 1 RCT (525 participants) RR 1.99; 95% CI 0.50 to 7.88 | 3 RCTs (211 participants) 0/3 RCTs reported a significant difference between intervention and control groups (no pooling of data) |
| Cardiovascular mortality | Follow‐up < 12 months 9 RCTs (4130 participants) RR 0.93; 95% CI 0.71 to 1.21 I2 = 0.0% Follow‐up > 12 months 12 RCTs (4757) RR 0.74; 95% CI 0.63 to 0.87 I2 = 0% | "Studies did not consistently report deaths due to heart failure or sudden death" | 5 RCTs (3893 participants) RR 0.80; 95% CI 0.6 to 1.00 I2 = 0.0% | NR | NR | NR |
| Hospitalisation | Follow‐up < 12 months 4 RCTs (463 participants) RR 0.69; 95% CI 0.51 to 0.93 I2 = 12% Follow‐up > 12 months 7 RCTs (2009 participants) RR 0.98; 95% CI 0.87 to 1.11 I2 = 56% | Follow‐up < 12 months 15 RCTs (1328 participants) RR 0.75; 95% CI 0.62 to 0.92 I2 = 0% Follow‐up > 12 months 5 RCTs (2722 participants) RR 0.92; 95% CI 0.66 to 1.29 I2 = 63% | NR | At end of follow‐up period 4 RCTs (12,905 participants) RR 0.83; 95% CI 0.65 to 1.07 I2 = 32% | 1 RCT No difference between home‐based and centre‐based CR | 3 RCTs (numbers NR) No significant difference between intervention and control groups (no pooling of data) |
| HF‐specific admissions | NR | Follow‐up > 12 months 12 RCTs (1036 participants) RR 0.61; 95% CI 0.46 to 0.80 I2 = 34% | NR | 1 RCT Participants in the intervention group had 41% fewer (P value = 0.05) and 61% fewer heart‐related inpatient days (P value = 0.02) than in the control group | NR | NR |
| Events MI | Fatal or non‐fatal(or both) MI Follow‐up < 12 months 12 RCTs (4216 participants) RR 0.92; 95% CI 0.70 to 1.22 I2 = 19% Follow‐up > 12 months 16 RCTs (5682 participants) RR 0.97; 95% CI 0.82 to 1.15 I2 = 25% | NR | Non‐fatal MI 12 RCTs (7534 participants) RR 0.87; 95% CI 0.67 to 1.13 I2 = 31% | MI at the end of the follow‐up period 2 RCTs (209 participants) RR 0.63; 95% CI 0.26 to 1.48 I2 = 0% | 2 RCTs No difference between home‐based and centre‐based CR (no pooling of data performed) | CHD event rates 3 RCTs (414 participants) 2/3 RCTs reported no difference between intervention and control groups 1 RCT (228 participants) RR 1.66, P value < 0.01 |
| CABG | Follow‐up < 12 months 14 RCTs (2312 participants) RR 0.91; 95% CI 0.67 to 1.24 I2 = 0% Follow‐up > 12 months 9 RCTs (2189 participants) RR 0.93; 95% CI 0.68 to 1.27 I2 = 0% | NR | Revascularisation (CABG and PTCA combined) 12 RCTs (6670 participants) RR 0.95; 95% CI 0.80 to 1.13 I2 = 13% | At end of follow‐up period 2 RCTs (209 participants) RR 0.58; 95% CI 0.19 to 1.71 I2 = 0% | Not reported by RCTs | ‐ |
| PTCA | Follow‐up < 12 months 7 RCTs (1328 participants) RR 1.02; 95% CI 0.69 to 1.50 I2 = 12% Follow‐up > 12 months 6 RCTs (1322 participants) RR 0.89; 95% CI 0.66 to 1.19 I2 = 20% | NR | Revascularisation (CABG and PTCA combined) 12 RCTs (6670 participants) RR 0.95; 95% CI 0.80 to 1.13 I2 = 13% | Not reported by RCTs | Not reported by RCTs | ‐ |
| HRQoL | 10 RCTs 7/10 RCTs reported evidence of a significantly higher level of HRQoL with intervention at follow‐up | 20 RCTs Follow‐up < 12 months 13 RCTs (1270 participants) MLWHF score: MD ‐5.8; 95% CI ‐9.2 to ‐2.4 I2 = 70% Follow up > 12 months 3 RCTs (329 participants) MD ‐9.5; 95% CI ‐17.54 to ‐1.5 I2 = 73% All HRQoL measures pooled 20 RCTs (3240 participants) SMD ‐0.5; 95% CI ‐0.7 to ‐0.3 I2 = 79% | 7 RCTs 1/7 RCTs reported evidence of a significantly higher level of HRQoL with intervention at follow‐up | Across 11 RCTs, 81 HRQoL outcome scores/sub‐scores reported: 14/81 in favour of intervention compared to control 67/81 no significant difference between intervention and control 5/11 RCTs reported evidence of a significantly higher level of some HRQoL domains with intervention at follow‐up No consistent difference in HRQoL total or domain score at follow‐up between intervention and control | 10 RCTs 8/10 RCTs reported improvements in HRQoL at follow‐up with both home‐based and centre‐based CR compared with baseline No strong evidence of difference in overall HRQoL outcomes or domain score at follow up between home‐based and centre‐based CR | 2 RCTs 1/2 RCTs reported improvement in HRQoL with intervention (not significant) 1/2 RCTs reported improvement in both groups but no significant difference between intervention and control |
| Economics Costs Cost‐effectiveness | Costs 3 RCTs 2/3 studies reported total healthcare costs were not statistically significantly different between groups Cost‐effectiveness 1 RCT Authors concluded that rehabilitation was an efficient use of healthcare resources and may be economically justified | 3 RCTs 2 studies undertook a cost effectiveness analysis and 1 reported costs There was no evidence of significantly different costs or outcomes | NR | 5 RCTs reported healthcare utilisation costs 2/5 RCTs reported an overall mean net saving of USD965 per participant at 6 months follow‐up and USD1420 per participant at 24 months follow‐up 1/5 RCTs reported an increase in mean net costs of USD52 per participant 2/5 RCTs reported no difference between groups No RCTs reported cost‐effectiveness | 3/4 RCTs reported healthcare costs associated with CR were lower for the home‐based than centre‐based programmes 1/4 RCTs reported that home‐based CR was more costly than centre‐based CR but costs would be the same if participant travel costs and travel time were included 8 studies reported different aspects of consumption of healthcare resources No significant between group differences were seen | NR |
| All‐cause withdrawal /drop‐out at follow‐up | NR | NR | NR | At follow‐up 8 RCTs (2862 participants) RR 1.03; 95% CI 0.83 to 1.27 I2 = 34% | At follow‐up 18 (1894 participants) RR 1.04; 95% CI 1.00 to 1.08 I2 = 44% | NR |
| Uptake | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 10 RCTs (1338 participants) 8/10 RCTs reported uptake was significantly higher in intervention group |
| Adherence | NR | NR | NR | NR | 14 RCTs *3/14 RCTs reported adherence was significantly higher in home‐based CR | 8 RCTs (1150 participants) 3/8 RCTs reported adherence was significantly higher in intervention group |
| CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; CHD: coronary heart disease; CR: cardiac rehabilitation; HF: heart failure; HRQoL: health‐related quality of life; MD: mean difference; MI: myocardial infarction; MLWHF: Minnesota Living with Heart Failure questionnaire; NR: not reported; PTCA: percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RR: risk ratio; SMD: standardised mean difference. * As reported in the 'Summary of findings' table. Effects of interventions section states 4/14. | ||||||

