درمان دارویی برای یبوست مرتبط با مصرف داروهای آنتیسایکوتیک
Referencias
منابع مطالعات واردشده در این مرور
منابع مطالعات خارجشده از این مرور
منابع مطالعات در انتظار ارزیابی
منابع اضافی
منابع دیگر نسخههای منتشرشده این مرور
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Allocation: Unclear. Described by the authors as "Randomly divided in treatment order with numbers” Blinding: Not described. Unlikley to have occurred. Duration: 14 days. Design: A parallel design trial comparing acupuncture, tuina and glycerol suppository for treating antipsychotic‐related constipation. Setting: Inpatient. Country: China.. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: CCDMD‐3 criteria for schizophrenia (N = 205), affective disorders (N = 30), neurosis (N = 5). Age: 20 to 61 years. History: Antipsychotics included clozapine (N = 166), chlorpromazine (N = 48), sulpiride (N = 12), perphenazine (N = 8), and haloperidol (N = 6). Included: Adult inpatients in a Chinese hospital who had received oral antipsychotic drugs for at least two weeks and who had not defecated for between 2 and 9 days. Excluded: Participants with physical co‐morbidities. | |
| Interventions | 1. Glycerin suppository: 40 mL per day. N = 60. 40 mL glycerin suppository (N = 60) compared with acupuncture alone (N = 60); tuina massage alone (N = 60); and combined with acupuncture and tuina massage (N = 60). Interventions occurred daily for 14 days. | |
| Outcomes | Global or clinical change in constipation: defecation by 2 days and defecation by 3 days (both compared with not cured). Unable to use Global or clinical change in constipation: time to effectiveness (unclearly defined subset of participants). Adverse effects: no data provided. | |
| Notes | Overall, the study was methodologically poor and methods were poorly described. We had concerns that ethics approval was not reported, and there was no mention of any informed consent process. Attempts were made to contact the authors at the host institution, but no response was received. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Randomisation was implied; sequence generation methods not specified. "All the cases were randomly divided in treatment order with numbers”. Comment: We suspect quasi‐randomisation (sequential allocation resulting in exactly 60 participants in each of the four groups), but this remains unclear. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No description of blinding participants and personnel. Considered unlikely due to the different natures of the treatment. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No description of blinding of outcome assessment, but it is plausible this could have occurred. It is not clear how response to laxatives was assessed and whether it was self‐reported or clinician‐reported. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | There were no comments on missing outcome data. It was unclear if this was because there were no missing data, or because they were not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | There was no evidence a pre‐specified study protocol was agreed and followed. Outcome data provided only at 14 days – uncertain whether this was chosen a priori or post hoc. Alongside the three outcome categories mentioned in the methods sections, time‐to‐effect was also reported. It appears time may have been only provided for the subset of participants who were deemed cured, but this was unclear. No adverse event data were provided. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Funding source was not reported. |
| Methods | Allocation: Not clear. Described by the authors as “equally divided into two groups according to their types of psychosis and the drugs they took”. Blinding: Not described. Unlikely to have occurred. Duration: 1 day. Parallel design trial comparing mannitol with rhubarb soda or phenolphthalein. Setting: Female psychiatric inpatient unit. Country: China. | |
| Participants | Diagnosis: Reported as 192 schizophrenia, 40 affective psychosis, 2 hysteria (6 unaccounted for). N = 240. Sex: Female. Age: 14 to 56 years. Included: Hospitalised female Chinese psychiatric patients with antipsychotic‐related constipation, treated with antipsychotics for at least a week, no bowel movements for at least 4 days. Excluded: Participants with physical co‐morbidities. | |
| Interventions | 1. Mannitol: one single 10% mannitol oral 250 mL dose twice over the course of one day (N = 120). 2. Rhubarb soda twice daily or phenolphthalein 6 to 8 tablets twice over the course of one day (N = 120). | |
| Outcomes | Global or clinical change constipation: change in frequency by 24 hrs. Unable to use Time to defecation (unclear participant numbers). | |
| Notes | Statistical analysis was poorly reported, with errors evident. Phenolphthalein and rhubarb soda data were combined. Attempts were made to contact the authors at the host institution, but no response was received. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | While randomisation was mentioned in the abstract, the methods stated participants were "equally divided into two groups according to their types of psychosis and the drugs they took". We suspect quasi or non‐randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No description of blinding participants and personnel. Considered unlikely due to the different natures of the interventions. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No description of blinding of outcome assessment. It is not clear how response to laxatives was assessed and whether it was self‐reported or clinician‐reported. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Some data were missing but not accounted for (e.g. diagnoses are only reported for 234 participants). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | There was no evidence a pre‐specified study protocol was agreed and followed. Outcome data provided after only one day – uncertain whether these were chosen a priori or post hoc. |
| Other bias | High risk | The statistical analysis had errors. A P > 0.05 was reported as being significant, the mean and range of times‐ to‐defecation for each intervention contradicted the reported frequencies of defecation within 24 hours. Funding source was not reported. |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Clozapine‐treated patients. Interventions: Orlistat versus placebo. Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria. The prevalence of constipation was compared between the treatment and non‐treatment groups. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Psychiatric inpatients with psychosis. Interventions: Laxatives (senna or glycerol) versus warm salt water, vitamin B, and soap enema. Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was psychiatric inpatients with psychosis. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Chlorpromazine‐treated patients with gastric adverse reaction, e.g. dry mouth, bitter taste in mouth, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation. Interventions: Self‐made Chinese medicine ‘smoothing‐nervous‐and‐strengthen‐spleen syrup’ versus placebo Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was antipsychotic‐related gastric adverse reactions. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Patients with psychosis and constipation. Interventions: Mannitol versus senna tea. Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was psychosis and constipation, not all participants were prescribed antipsychotics. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Clozapine‐treated patients. Interventions: TCM treatment qihuangkongxian versus cyproheptadine. Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was clozapine‐treated patients, study investigated the prevalence of hypersalivation and constipation. | |
| Allocation: Randon allocation. Participants: Patients with antipsychotic‐related constipation. Interventions: sit ups (30/day) versus no sit ups. Reason for exclusion: Not a pharmacological intervention; investigated sit ups. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Patients with schizophrenia. Interventions: Diversity of health education versus general health education. Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was patients with schizophrenia. Not a pharmacological intervention; investigated health education. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Antipsychotic‐induced adverse reactions of digestive tract. Interventions: Anshejianpi syrup versus no syrup. Reason for exclusion: Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was antipsychotic induced gastrointestinal side effects, could not identify number of participants with constipation. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: Antipsychotic‐induced adverse reactions of digestive tract. Interventions: Anshejianpi syrup versus no syrup. Reason for exclusion: Duplicate paper of Lu 2001. Antipsychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was antipsychotic induced gastrointestinal side effects, could not identify numbers of participants with constipation. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: People with psychosis and constipation. Interventions: Laxatives (not specified) versus abdominal massage and health education. Reason for exclusion: Antispychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was people with psychosis and constipation, not all taking antipsychotics. Laxative type not specified. | |
| Allocation: Random allocation. Participants: People with schizophrenia. Interventions: Daily living skills training versus no daily living skills training. Reason for exclusion: Antispychotic‐related constipation was not an inclusion criteria; population of interest was people with schizophrenia. Inteverntion was not a pharmacological intervention; investigated daily living skills. | |
| Allocation: Sequential allocation. Participants: Antipyschotic related constipation. Interventions: Abdominal massage, physical exercise and warm foot baths versus laxatives (not specified). Reason for exclusion: Not a randomised trial. |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Parallel design trial comparing a single dose of senna with rhubarb and alcohol paste applied topically to the umbilicus. |
| Participants | 104 Chinese hospitalised psychiatric patients who had not defecated for more than three days, who had been treated with antipsychotics (type and dose not specified) for at least two weeks. All fulfilled CCMD‐2‐R criteria for psychosis. Included 48 males, 56 females, with a mean age of 38.65 years, range 18 to 66 years. |
| Interventions | Intervention described as liquid senna in the abstract (but as a single 3 g dose of senna granules, sennoside dose unclear, in the methods section) versus rhubarb and alcohol paste topically applied to umbilicus (TCM shenque point). |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome reported was defecation within 24 hours. Adverse events were reported as a collective category when the participant reported painful abdomen and diarrhoea. |
| Notes | Overall methods were poorly described. Randomisation unclear. We had concerns that ethics approval was not reported, and there was no mention of any informed consent process. The dose and preparation of the pharmacological treatment for antipsychotic‐related constipation (senna) were not clearly reported, with contradictory descriptions (liquid and granules). About 80% of the text of the paper was identical to Zhang 2004 (but had none of the same authors). Data not usable without further information and clarification. Attempts were made to contact the authors at the host institution, but no response has been received. |
| Methods | Parallel design trial comparing a single dose of senna with aloe and alcohol paste applied topically to the umbilicus. |
| Participants | 96 hospitalised Chinese patients with antipsychotic‐related constipation who had not defecated for more than three days, all treated with antipsychotics (type and dose not specified) for at least two weeks, aged 18 to 66 years (mean: 39 years), 56 males, 40 females. |
| Interventions | Intervention described as liquid senna in the abstract (but as a single 3 g dose of senna granules, sennoside dose unclear, in the methods section) versus aloe and alcohol paste topically applied to umbilicus (TCM shenque point). |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome reported was defecation within 24 hours. Adverse events were reported as a collective category when the participant reported painful abdomen and diarrhoea. |
| Notes | Overall methods were poorly described. Randomisation unclear. We had concerns that ethics approval was not reported, and there was no mention of any informed consent process. The dose and preparation of the pharmacological treatment for antipsychotic‐related constipation (senna) were not clearly reported, with contradictory descriptions (liquid and granules). About 80% of the text of the paperwas identical to Liang 2002 (but had none of the same authors). Data not usable without further information and clarification. Attempts were made to contact the authors at the host institution, but no response has been received. |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Glycerol laxative versus Tuina massage, Outcome 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation. | ||||
| 1.1 no defecation by 2 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.88 [1.89, 4.39] |
| 1.2 no defecation by 3 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.8 [1.96, 11.74] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Glycerol laxative versus acupuncture, Outcome 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation. | ||||
| 1.1 no defecation by 2 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.5 [2.18, 5.62] |
| 1.2 no defecation by 3 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.0 [2.54, 25.16] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation Show forest plot | 1 | 240 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.27] |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 Mannitol versus phenolphthalein or rhubarb soda, Outcome 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation. | ||||
| 1.1 no defecation by 24 hours | 1 | 240 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.27] |
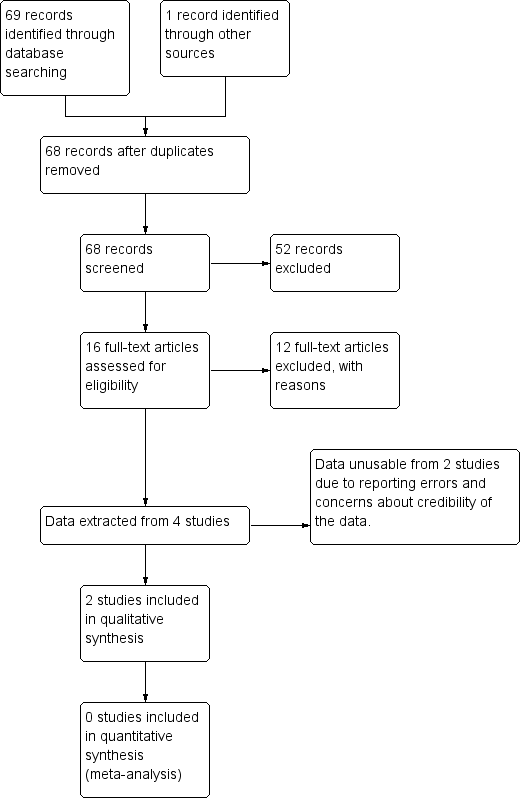
Study flow diagram.
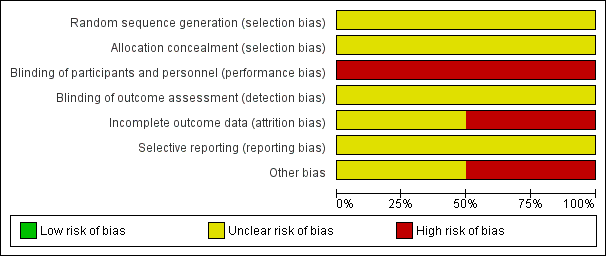
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
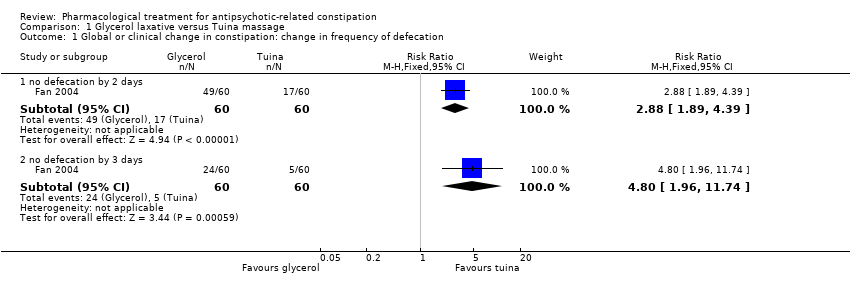
Comparison 1 Glycerol laxative versus Tuina massage, Outcome 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation.
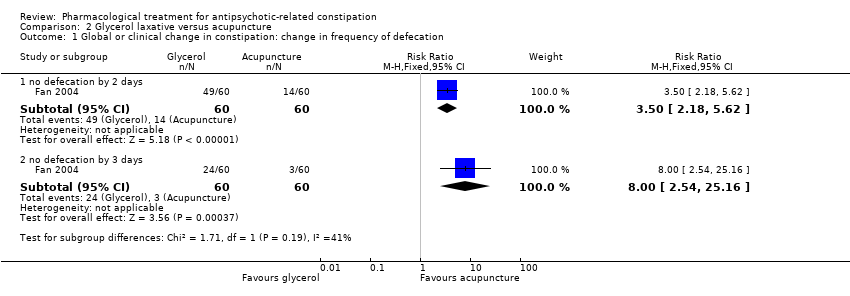
Comparison 2 Glycerol laxative versus acupuncture, Outcome 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation.
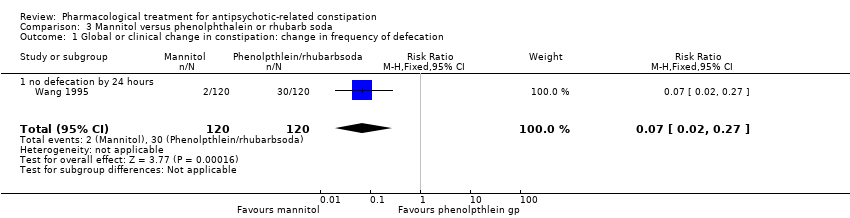
Comparison 3 Mannitol versus phenolphthalein or rhubarb soda, Outcome 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation.
| Methods | Allocation: centralised, randomised, sequence generation described. Blinding: participants, personnel recruiting and assigning participants, and assessors. Blinding can be tested by asking participants and raters to guess the assigned treatment. Study duration: 12 weeks. Setting: Inpatients and outpatients |
| Participants | Diagnosis: antipsychotic‐related constipation or antipsychotic induced gastrointestinal hypomotility N = sample size obtained through power calculation* Age: any Sex: both |
| Intervention | Any of the interventions listed in Appendix 1 compared against any other intervention or placebo, |
| Outcomes | Primary Outcomes 1. Global or clinical change in constipation 1.1 Change in the frequency of defecation (e.g. complete spontaneous bowel movements per week) Secondary outcomes
|
| Notes | * Size of study with sufficient power to detect a approximate 10% difference between the two groups for the primary outcome with 80% certainty. |
| Glycerol laxative versus tuina massage | ||||||
| Patient or population: antipsychotic‐related constipation | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with Tuina | Risk with Glycerol | |||||
| 1. Global or clinical change in constipation (a) as defined by the study Still constipated (no defecation) at 2 days | Study population | RR 2.88 | 120 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 283 per 1000 | 816 per 1000 | |||||
| Global or clinical change in constipation (a) as defined by the study Still constipated (no defecation) at 3 days | Study population | RR 4.80 | 120 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 83 per 1000 | 400 per 1000 | |||||
| (b) Change in the frequency of defecation | No studies reported these important outcomes | |||||
| (c) Change in straining at defecation | ||||||
| (d) Change in the frequency of lumpy or hard stools | ||||||
| (e) Change in the frequency of manual manoeuvres to facilitate defecation | ||||||
| 2. Need for rescue medication | ||||||
| 3. Presence of antipsychotic‐related constipation complications such as bowel obstruction | ||||||
| 4. Quality of life (changed to any extent) | ||||||
| 5. Adverse events | ||||||
| 6. Leaving the study early | ||||||
| 7. Economic costs | ||||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Randomisation and allocation concealment methods unclear. Management of incomplete outcome data unclear. Blinding unlikely to have occurred ‐ rated as very serious ‐ downgraded by 2. 2 No validated method used for measuring constipation. Unclear how reported defecation was assessed (e.g. stool chart, participant recall from memory). No recording of any of the other ROME constipation symptoms (e.g. straining, stool consistency, manual manoeuvres) ‐ rated as serious ‐ downgraded by 1. | ||||||
| Glycerol laxative versus acupuncture | ||||||
| Patient or population: antipsychotic‐related constipation | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with acupuncture | Risk with glycerol laxative | |||||
| 1. Global or clinical change in constipation (a) as defined by the study Still constipated (no defecation) at 2 days | Study population | RR 3.50 | 120 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 233 per 1000 | 817 per 1000 | |||||
| Still constipated (no defecation) at 3 days | Study population | RR 8.00 | 120 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 50 per 1000 | 400 per 1000 | |||||
| (b) Change in the frequency of defecation | No studies reported these important outcomes | |||||
| (c) Change in straining at defecation | ||||||
| (d) Change in the frequency of lumpy or hard stools | ||||||
| (e) Change in the frequency of manual manoeuvres to facilitate defecation | ||||||
| 2. Need for rescue medication | ||||||
| 3. Presence of antipsychotic‐related constipation complications such as bowel obstruction | ||||||
| 4. Quality of life (changed to any extent) | ||||||
| 5. Adverse events | ||||||
| 6. Leaving the study early | ||||||
| 7. Economic costs | ||||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Randomisation and allocation concealment methods unclear. Management of incomplete outcome data unclear. Blinding unlikely to have occurred ‐ rated as very serious ‐ downgraded by 2. 2 No validated method used for measuring constipation. Unclear how reported defecation was assessed (e.g. stool chart, participant recall from memory). No recording of any of the other ROME constipation symptoms (e.g. straining, stool consistency, manual manoeuvres) ‐ rated as serious ‐ downgraded by 1. | ||||||
| Mannitol versus phenolphthalein or rhubarb soda | ||||||
| Patient or population: antipsychotic‐related constipation | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with phenolphthalein or rhubarb soda | Risk with Mannitol | |||||
| 1. Global or clinical change in constipation as defined by the study a) Still constipated (no defecation) at 24 hours | Study population | RR 0.07 | 240 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | Results from the phenolphthalein and rhubarb soda groups were combined by the study authors. | |
| 250 per 1000 | 18 per 1000 | |||||
| (b) Change in the frequency of defecation | No studies reported these important outcomes | |||||
| (c) Change in straining at defecation | ||||||
| (d) Change in the frequency of lumpy or hard stools | ||||||
| (e) Change in the frequency of manual manoeuvres to facilitate defecation | ||||||
| 2. Need for rescue medication | ||||||
| 3. Presence of antipsychotic‐related constipation complications such as bowel obstruction | ||||||
| 4. Quality of life (changed to any extent) | ||||||
| 5. Adverse events | 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 | Not estimable | 240 (1 RCT) | ‐ | It is highly questionable how well adverse effects were monitored and recorded. The study simply notes "No side‐effects were detected in the two groups after treatment". |
| 6. Leaving the study early | No studies reported these important outcomes | |||||
| 7. Economic costs | ||||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Randomisation and allocation concealment methods unclear. Management of incomplete outcome data unclear. Blinding unlikely to have occurred ‐ rated as very serious ‐ downgraded by 2. 2 No validated method used for measuring constipation. Unclear how reported defecation was assessed (e.g. stool chart, participant recall from memory). No recording of any of the other ROME constipation symptoms (e.g. straining, stool consistency, manual manoeuvres) ‐ rated as serious ‐ downgraded by 1. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 no defecation by 2 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.88 [1.89, 4.39] |
| 1.2 no defecation by 3 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.8 [1.96, 11.74] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 no defecation by 2 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.5 [2.18, 5.62] |
| 1.2 no defecation by 3 days | 1 | 120 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.0 [2.54, 25.16] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Global or clinical change in constipation: change in frequency of defecation Show forest plot | 1 | 240 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.27] |
| 1.1 no defecation by 24 hours | 1 | 240 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.27] |

