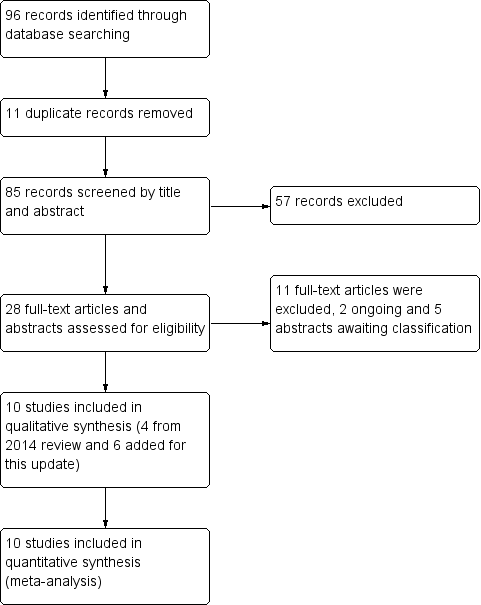
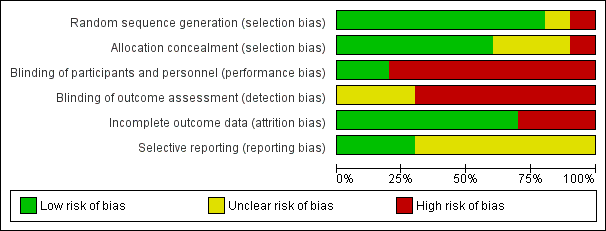
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Ulugbek Nurmatov, Iris Venderbosch, Graham Devereux, F Estelle R Simons, Aziz Sheikh | 12 septiembre 2012
Joanne P Yeung, Lorie A Kloda, Jason McDevitt, Moshe Ben‐Shoshan, Reza Alizadehfar | 14 noviembre 2012
Juan Jose Yepes‐Nuñez, Yuan Zhang, Marta Roqué i Figuls, Joan Bartra Tomas, Juan M Reyes Sanchez, Fernando Pineda de la Losa, Ernesto Enrique | 9 noviembre 2015
Michael J Abramson, Robert M Puy, John M Weiner | 4 agosto 2010
Jamie Hartmann‐Boyce, Kate Cahill, Dorothy Hatsukami, Jacques Cornuz | 15 agosto 2012
Moises A Calderon, Bernadette Alves, Mikila Jacobson, Brian Hurwitz, Aziz Sheikh, Stephen Durham | 24 enero 2007
Nicola Lindson, Elias Klemperer, Bosun Hong, José M Ordóñez‐Mena, Paul Aveyard | 30 septiembre 2019
Suzana Radulovic, Moises A Calderon, Duncan Wilson, Stephen Durham | 8 diciembre 2010
Robert J Boyle, Mariam Elremeli, Juliet Hockenhull, Mary Gemma Cherry, Max K Bulsara, Michael Daniels, J.N.G. Oude Elberink | 17 octubre 2012
Daniel T Tsoi, Mamta Porwal, Angela C Webster | 28 febrero 2013
Respuestas clínicas Cochrane
What are the benefits and harms of oral immunotherapy for children and adolescents with egg allergy?
Adarsh Gupta | 19 noviembre 2018