Tratamiento conservador versus intervencionista para el neumotórax espontáneo primario en adultos
Referencias
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en curso
Referencias adicionales
Referencias de otras versiones publicadas de esta revisión
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Not a randomized controlled trial. | |
| Not a randomized controlled trial. | |
| Not a randomized controlled trial. |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Trial name or title | A study to investigate the treatment of pneumothorax (collapsed lung) |
| Methods | Randomized controlled parallel‐group non‐inferiority trial; Participants will be randomized using a secure, centralized web‐based randomization system. Participants will be randomized in real time by computer, stratified by study site, using an adaptive biased coin (Urn) technique. The group allocation will only be revealed when the investigator confirms inclusion criteria have been met and enters the participant's details. Study in Australia (Perth) and New Zealand (4 sites). |
| Participants | Inclusion: Primary spontaneous pneumothorax that is 32% or larger, 14 ‐ 50 years old. Exclusion: 1. Secondary pneumothorax, defined as pneumothorax occurring in the setting of acute trauma (including iatrogenic) or underlying lung disease including but not limited to COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis, lung cancer and asthma that requires regular preventative medication or has been symptomatic within the last 2 years 2. Previous spontaneous pneumothorax on the same side 3. Coexistent haemothorax (i.e. spontaneous haemopneumothorax) 4. Bilateral pneumothorax 5. Instability at any stage suggesting tension pneumothorax; systolic BP (SBP) < 90 mmHg, mean arterial pressure (MAP) < 65 mmHg or heart rate (HR) > SBP 6. Pregnancy at time of enrolment 7. Social circumstances whereby the patient either does not have adequate support after discharge to re‐attend hospital if required, or is unlikely to present for study follow up. 8. Air travel within the next 12 weeks if this cannot be deferred, should the pneumothorax be slow to resolve" |
| Interventions | Intervention: Conservative management of primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Participants will be observed for 4 hours in the emergency department and a repeat x‐ray taken. If they are clinically stable and able to mobilize comfortably they will be discharged home and followed as an outpatient with a review at 24 ‐ 72 hours, and at 2, 4 and 8 weeks. Comparator: Standard interventional treatment of primary spontaneous pneumothorax. An attempted air aspiration procedure will be performed. If unsuccessful, the participant will have an intercostal chest drain inserted and be admitted to hospital. Further management, including the use of suction or need for surgery, will be at the discretion of the treating physician. |
| Outcomes | Primary: Proportion of subjects with complete lung re‐expansion on chest x‐ray at 8 weeks; time in days to symptomatic recovery, defined as: discharge from hospital; resolution of symptoms (chest pain score of 0 on a 1 ‐ 10 visual analogue scale; shortness of breath score of 0 on the Borg scale); cessation of analgesic medication; predefined complication of interventional treatment; proportion of participants with persistent air leak, defined by the presence of a chest drain/catheter in situ for 3 days or longer at 8 weeks. Secondary: Proportion of participants with pneumothorax recurrence at 12 months. |
| Starting date | 14th July 2011; proposed sample size 342 |
| Contact information | Dr Kyle Perrin, Medical Research Institute of New Zealand Level G, CSB Wellington Hospital Riddiford Street Newtown Wellington 6242. +64 4 8050232 . [email protected] |
| Notes | www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=336270 Trial report on 9th June 2014: "Thus far none of the patients randomized to conservative management have needed to cross over into the interventional arm". |
COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
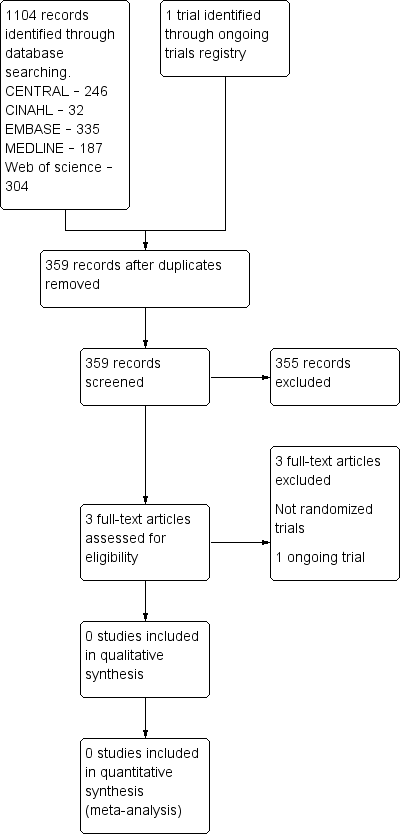
Study flow diagram.

