تقویت عضلات کف لگن همراه با درمانهای فعال در برابر همان درمانهای فعال به تنهایی برای بیاختیاری ادراری زنان
Referencias
منابع مطالعات واردشده در این مرور
منابع مطالعات خارجشده از این مرور
منابع اضافی
منابع دیگر نسخههای منتشرشده این مرور
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | 2‐arm parallel RCT | |
| Participants | 48 women with SUI | |
| Interventions | A. PFMT + electrical stimulation (ES) (N = 24) PFMT was individually designed by physiotherapist. No other details were provided about PFMT, including duration of treatment. ES was delivered with vaginal electrodes, with 50 Hz of frequency, 1 ms pulse and fixed 20 mA B. Electrical stimulation (ES) (N = 24) ES was delivered with vaginal electrodes, with 50 Hz of frequency, 1 ms pulse and fixed 20 mA | |
| Outcomes | 1. Improvement in urinary symptoms This outcome was assessed using voiding diary, no other details were reported A. 5/15; B. 3/19 2. Satisfaction with treatment No detail was reported on how this outcome was measured Immediately after treatment A. 8/15; B. 12/19 After 12 months A. 7/15; B. 9/19 | |
| Notes | This study is a conference abstract with little detail reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Details not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Details not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Impossible to blind participants and personnel to PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Details not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | proportions of withdrawals differ between the 2 treatment groups; reasons for withdrawals were not reported and it was not clear whether or not analysis was based on ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Unclear risk | Details not reported |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | It was stated that there was no source of funding |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Details not reported |
| Methods | 2‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 64 women with urgency predominant incontinence | |
| Interventions | A: Drug therapy alone group (N = 32). Individuals in this group received oxybutynin 5 mg daily with dose gradually increased during visits to the maximum level the individual could tolerate (dose range: 5 to 30 mg) B: Behavioural therapy + drug therapy (N = 32): participants in this group received drug therapy as described above and behavioural therapy. Behavioural therapy included PFMT and urge suppression strategies. PFMT consisted of 3 sessions of 15 exercises daily (total of 45 exercises). During each session, participants were instructed to contract for 10 seconds and relax for another 10 seconds (maximum duration of 10 seconds was achieved on a gradual basis). They were also taught the skills on urge suppression strategies | |
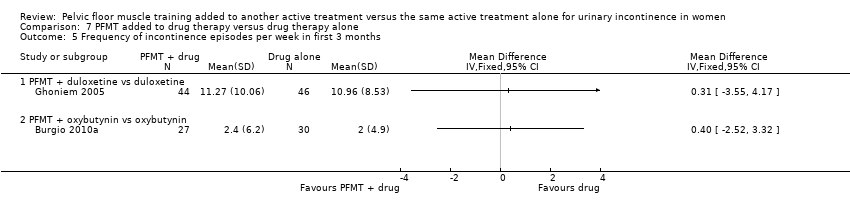
| Outcomes | 1. Patient global perception of improvement: this was measured using the Global Perception of Improvement rating. Success was defined as the proportion of participants who felt 'much better' at the end of the treatment At 8 weeks: A: 28/31; B: 21/27 2. Condition‐specific quality of life: assessed using the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and Urogenital Distress Inventory (reported as mean score and SD; details of data not reported) 3. Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome: success was defined as the proportion of participants who were completely satisfied with the treatment outcome. It was assessed using the Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire At 8 weeks: A: 27/31; B: 21/27 4. Frequency of incontinence episodes per week: mean (SD) of incontinence episodes frequency was assessed at endpoint using the 7‐day bladder diary At 8 weeks: A: 2.0 (4.9), N = 30: B: 2.4 (6.2), N = 27 At 12 months: A: 1.7 (3.9), N = 27; B: 4.5 (11.4), N = 22 5. Frequency of micturition per 24 hours (in mean and SD) At 8 weeks: A: 8.2 (1.9), N = 31; B: 8.4 (3.0), N = 27 6. Volumes of urine voided per 24 hours (in mean and SD) At 8 weeks: A: 256.7 (86.7), N = 31; B: 240.4 (129.1), N = 27 | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Stated as "stratified block randomisation". Exact process not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | It was not stated whether or not the allocations were concealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Completed questionnaires were submitted in sealed envelopes and given to the nurses who administered the intervention. However, it is not specified whether the same or different nurses assessed the outcomes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 5/64 dropped out of the trial: A 1/32; B 4/32. Reasons not specified |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Approved by the institutional review board |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | Stated (received grants from public institutions) |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Some of the authors had financial and other relationships with some pharmaceutical companies |
| Methods | 2‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 29 women with over‐active bladder | |
| Interventions | A: Drug alone (N = 14): details of drug including name and dose not stated B: PFMT + drug (N = 15). PFMT was assisted by perineal surface electromyography and was taught inially. Participants were then instructed to perform 3 sets of PFMT per day, 15 contractions per set, continuously at home for 8 weeks. Drug regimen: as stated above | |
| Outcomes | 1. Urgency episodes per 24 hours: this was determined at baseline and endpoint using the 3‐day voiding diary and mean percentage change was calculated for the 2 groups (no useable data) 2. Daytime frequency per 24 hours: this was obtained before and after treatment using the 3‐day voiding diary and mean percentage change calculated (no useable data) 3. Treatment benefit: this was determined 4 weeks post‐treatment using the 'Benefit Questionnaire' and proportion of participants with perceived benefits calculated for each group A: 4/14; B: 11/15 4. Symptom bothersome: scores were obtained before and after treatment and mean percentage change in bothersome scores was obtained for the 2 groups (no useable data) 5. Quality of life: total scores were calculated for different domains of the quality of life (such as sleeping, concern and coping) before and after treatment. Mean percentage increase was calculated for the 2 groups (no useable data) | |
| Notes | Dropouts: not reported, only the number of participants who completed the trial was stated | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Process involved in randomisation was not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Process involved in allocation concealment was not stated |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible (assumed not done) |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported, only the number of participants who completed the trial was stated |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Approved by the Ethics committee |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | Stated "none" according to the authors |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not declared |
| Methods | 4‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 201 women with predominant symptoms of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) | |
| Interventions | A: No active treatment (N = 47). Received placebo plus imitation (sham) PFMT for 12 weeks. Imitation PFMT consisted of initial therapist‐supervised instructions on how to train the hip abductors. Participants were then given written instructions and a training log with the recommendation of 3 sets of 10 long and 2 sets of 10 rapid contractions 4 days weekly. However, no instructions were given to the participants to contract the pelvic floor muscles with physical activities associated with urine leakage (skill training) B. PFMT only (N = 50). Received placebo plus PFMT for 12 weeks. PFMT comprised 30 minutes of initial therapist supervised instructions on how to contract the pelvic floor muscles. The correct type of contraction was confirmed by pelvic examination. Then participants received instructions to perform 3 sets of 10 long (6 to 8 seconds) and 2 sets of 10 rapid (1 to 2 seconds) contractions 4 days weekly (total of 200 contractions per week). At 4 and 8 weeks, participants received 15 minutes of re‐instruction and manual feedback and a training log was completed. Finally, skill training was giving by instructing participants to contract the pelvic floor muscles with physical events usually associated with urine loss C: Duloxetine + sham PFMT (N = 52). This group received duloxetine and sham PFMT. Duloxetine was given at a dose of 40 mg twice daily for 12 weeks. Sham PFMT (as described above) D: PFMT + duloxetine (N = 52). This is the combined group. Participants in this group received PFMT and duloxetine as described above For this review comparison D versus C is relevant | |
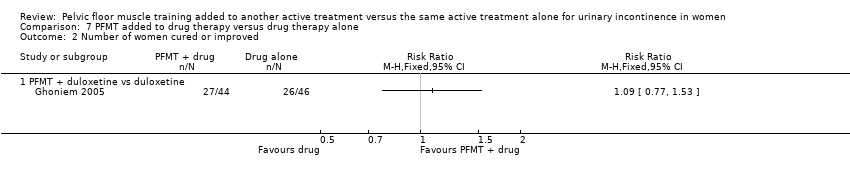
| Outcomes | 1. Incontinence episode frequency (IEF) per week. This was computed from participant completed paper diaries at each visit. Mean (SD) weekly IEF at the endpoint was calculated for each treatment group A: 18.50 (17.10), N = 44; B: 20.93 (16.26), N = 46; C: 10.96 (8.53), N = 46; D: 11.27 (10.06), N = 44 2. Improvement (IEF responder rate): this was defined as the proportion of participants who had a 50% or greater decrease in IEF with treatment as computed from the paper diaries A: 11/44; B: 12/46; C: 26/46; D: 27/44 3. Number of continence pads used. Mean (SD) pads per week was calculated for each treatment group at endpoint A: 10.22 (7.56), N = 44; B: 11.48 (8.36), N = 46; C: 7.23 (5.98), N = 46; D: 7.84 (7.41), N = 44 4. Condition‐specific quality of life: this was assessed at endpoint using the Incontinence Quality of Life (I‐QoL) score questionnaire and mean (SD) score was obtained for each group A: 69.34 (20.69), N = 45; B: 68.76 (22.70), N = 49; C: 68.23 (20.87), N = 50; D: 74.07 (19.70), N = 51 5. Patient Global Impression of Improvement (PGI‐I): this was defined as the proportion of participants with a PGI‐I score in one of the following 3 categories: 1. 'very much better', 2. 'much better' or 3. 'a little better'. This was obtained using the validated PGI‐I questionnaire A: 19/45; B: 32/49; C: 27/50; D: 36/51 | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "...treatments were assigned using a centralised computer voice response" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "...treatments were assigned using a centralised computer voice response" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Duloxetine and placebo were given in double‐blind fashion. However, it is not specified who exactly was blinded. Participants were blinded to PFMT or sham PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated whether or not outcome assessors were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Dropouts: all: 56/201; A: 10/47; B: 10/50; C: 19/52; D: 17/52 No differential loss to follow‐up between group C and D. However, there is excessive loss to follow‐up as 56/201 participants were dropped‐out. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Trial protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Approved by the ethics committee |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | Stated, supported by private organisations |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Stated but some of the authors had financial and other relationships with one of the organisations which supported the trial |
| Methods | 4‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 43 women with urodynamic evidence of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) | |
| Interventions | A. PFMT + electrical stimulation (ES) (N = 11): participants in this group received both PFMT and ES. PFMT was part of an exercise programme which also included abdominal and hip exercise and was administered twice weekly for 20 minutes by a therapist in addition to a daily home exercise programme. Electrical stimulation consisted of vaginal and lumbar electrodes which were administered for 10 minutes, 3 times weekly for a total of 6 weeks. Output was increased until noticeable contraction was achieved and participant then added voluntary effort B. PFMT alone (N = 11): as described above C. Electrical stimulation (ES) alone (N = 11): as described above D. Sham electrical stimulation (N = 10): as for ES above but current was so low that no effect (contraction) was possible For this review comparison A versus C is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. Cure: this is the proportion of participants who became continent (free of symptoms of incontinence) at the end of the treatment as reported by the participants At 10 to 12 weeks from the onset of treatment: A: 3/11; B: 6/11; C: 1/11; D: 0/11 2. Improvement: proportion of participants who reported improvement in the symptoms of incontinence; success threshold not defined At 10 to 12 weeks from the onset of treatment: A: 4/11; B: 1/11; C: 2/11; D: 0/11 3. Success rate: this is the proportion of participants who reported cure of or significant improvement in the symptoms of incontinence At 10 to 12 weeks from the onset of treatment: A: 7/11; B:7/11; C: 3/11; D: 0/11 | |
| Notes | Dropouts: not stated | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Reported as "prospektiv randomisierten". No additional information provided. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Reported as "prospektiv randomisierten". No additional information provided. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants undergoing PFMT not possible |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Dropouts: not reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Ethical approval | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Source of funding or support | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 61 women with symptoms of stress, urinary incontinence | |
| Interventions | A. Drug therapy (DT) group (N = 18). Participants in this group received clenbuterol tablets 20 µg twice daily B. PFMT group (N = 20). Participants in this group received instructions on PFMT from gynaecologic specialists until they understood the technique. They were then instructed to perform the exercise for 10 minutes daily (other details not reported). Video tapes that demonstrated the proper method of performing PFMT were also given to the participants C. PFMT + DT group (N = 23): participants in this group received both clenbuterol and PFMT as described above For this review comparison C versus A is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. Cure: as reported by participants and is the proportion of participants who reported 100% reduction in symptoms of incontinence (i.e. no incontinence at all) A: 10/13; B: 10/19; C: 17/19 2. Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome: defined as the proportion of participants who were completely satisfied with treatment outcome. Scale used for the assessment not stated A: 11/13; B: 6/19; C: 13/19 | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | The envelope method was used to randomise participants to treatment groups; not stated whether envelopes were sequentially numbered, opaque and sealed |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | The envelope method was used to randomise participants to treatment groups; not stated whether envelopes were sequentially numbered, opaque and sealed |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants undergoing PFMT not possible |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Dropouts: all: 10/61; A: 5/18, B: 1/20; C: 4/23 Differential loss to follow‐up: not fully reported (2 and 3 participants withdrew from groups A and C respectively due to adverse drug effects; other reasons for withdrawal not reported) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Trial protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Approved by the ethics committee |
| Source of funding or support | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 16 women with stress incontinence | |
| Interventions | A. Electrical stimulation (ES) group (N = 6): participants in this group used electrical stimulator for 1 hour a day every day (except when menstruating) B. Pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) alone (N = 7): PFMT consisted of individualised exercise regimen with instruction to the participants to carry out a minimum of 3 exercises per day with progression over the treatment period. Biofeedback was provided by means of a Periform probe. Other details not given C. PFMT + ES (combined) (N = 6). Participants in this group received both PFMT and ES as described above For this review comparison C versus A is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. Severity of incontinence assessed using 24‐hour pad test and 3‐day voiding diary 2. Condition‐specific quality of life assessed using Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ) and Urogenital Distress Inventory (UDI). | |
| Notes | No useable data were reported in the trial (data reported in median and range) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible. Assumed not done |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Not explicitly reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Ethical approval | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Source of funding or support | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 242 women with urodynamic evidence of over‐active bladder | |
| Interventions | A. Drug alone (N = 82). Participants in this group received oral solifenacin 5 mg once daily B. PFMT alone (N = 80). Participants in this group performed PFMT once daily; other details were not given C. PFMT + drug (N = 80). Participants in this group received both PFMT and drug as stated above For this review comparison C versus A is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. Frequency of micturition per 24 hours (no useable data) 2. Number of episodes of over‐active bladder in 24 hours (no useable data) 3. Volume of urine voided per micturition in 24 hour (no useable data) 4. Adverse events: proportion (%) of participants who reported adverse events (mainly dry mouth) with solifenacin A: 17/82; B: 0/80; C: 14/80 | |
| Notes | Dropouts: not reported All participants randomised at baseline included in analysis | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible for PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Trial protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | "ethics not required" according to the authors Trial was conducted in accordance with Helsinki declaration Informed consent was obtained from participants |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | No funding source according to the authors |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Methods | 2‐arm parallel RCT | |
| Participants | 132 women with SUI, UUI and MUI from 2 centres in Turkey | |
| Interventions | A. PFMT + bladder training (N = 67): Participants in this group completed a progressive home‐based exercise program consisting of strength and endurance training. They were taught both fast (2‐s) and slow voluntary PFM contractions (VPFMCs). One slow contraction took 15 s (5‐s contraction, 5‐s hold, 5‐s relaxation). One set of exercises involved ten fast and ten slow VPFMCs. During week 1, participants were instructed to perform five sets of exercises per day (5×10 fast and 10 slow = 50 fast and 50 slow VPFMCs daily), which was progressively increased by five sets/week: ten sets per day at week 2; 15 at week 3; 20 at week 4; 25 at week 5, and 30 at week 6 [600 VPFMCs daily (300 fast and 300 slow)]. Patients were advised to exercise while in the supine, seated, and upright positions and to integrate these exercises into their daily activities, e.g., while watching television, waiting for something, travelling. B. Bladder training (N = 65) Based on the three frequency‐volume charts obtained at baseline, the longest voiding interval achieved several times was deemed the initial voiding interval. During week 1, participants were encouraged to hold urine for 30 min beyond the initial voiding interval. Then, the schedule was increased by 15 min per week depending on the patient’s tolerance to the schedule. Urgency suppression strategies, including distraction, relaxation, and PFM contraction, were explained to each participant. Techniques to control urgency were: (1) Deep and slow breathing (2) Contracting PFMs while relaxing other body parts (3) Using mental imagery or self‐motivational statements, such as “I can wait” and “I can take control” (4) Incorporating mental distractions, such as mathematical calculation | |
| Outcomes | 1. Global rating of improvement A four‐point scale (worse, unchanged, improved, cured) was used to determine participants’ global perception of UI improvement at the end of the intervention period compared with baseline. Improvement was defined as the proportion of women 'cured' or 'improved 'At 6 weeks A. 56/56; B. 43/52 2. Frequency and volume of incontinence (no usable data) 3. Symptom distress and quality of life (no usable data) 4. Incontinent episodes (No../day) (no usable data) 5. Micturition frequency (No./day) (no usable data) | |
| Notes | 6‐week treatment protocol was implemented for both groups by an experienced physical therapist over four visits (baseline and weeks 2, 4, and 6 of the program) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | “A stratified block randomization procedure was used to assign blocks of four participants to either treatment arm using opaque and sealed envelopes that contained a group allocation number from a computer generated random‐number table.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation was concealed using sealed and opaque envelope |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Impossible to blind participants and personnel to PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Proportions of withdrawals and reasons for withdrawals differ between the 2 groups and data analysis was not based on ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Ethics approval was said to be obtained |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | Source of funding was declared |
| Conflict of interest | Low risk | It was reported that there was no known conflict of interest |
| Methods | 4‐arm randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | 147 women with stress, urge or mixed UI from a single centre in Tokyo | |
| Interventions | A. General education (GE) group (N = 36): general education classes were held (topics including cognitive function, osteoporosis and oral hygiene) once a month, a total of 3 times B. Heat and steam generating sheet (HSGS) group (N = 37): participants in this group received HSGS, a thin, flexible, filmed sheet that generated heat and steam. When placed on the skin surface. It raises the temperature to 38 to 40°C by generating heat and steam continuously for up to 5 hours. Participants were asked to place the HSGS on their lower back once daily immediately after waking period, taking note of the time they started and ended C. Exercise (Ex) group (N = 37): this group received stretching exercise, fitness exercise and PFM exercise. Participants were initially instructed to perform 10 fast contractions (3 seconds) with a 5‐second rest and 10 sustained contractions (8 to 10 seconds) with a 10‐second rest between the contractions D. Ex + HSGS group (N = 37): participants in this group received both exercise and HSGS as described above For this review comparison D versus B is relevant | |
| Outcomes | Cure of urine loss episodes (assessed by interview, with cure defined as the proportion of participants with complete cessation of urine loss episodes) At 3 months: A: 1/34; B: 8/37; C: 12/35; D: 19/37 | |
| Notes | Changes in frequency of urine loss episodes: assessed based on changes on a 5‐point scale obtained in the interviews conducted at baseline (before treatment) and at 3 months after treatment. Data not available, only graphical presentation | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Used "computer‐generated random numbers" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Used "computer generated random numbers", however, no further information provided |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of the participants not possible |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 4/147 dropped out of the trial. However, there were no dropouts in the comparison of interest and there was no differential loss to follow‐up in the other group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Source of funding or support | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Conflict of interest | Low risk | Declared (no conflict of interest) |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 446 women with symptoms of stress urinary incontinence | |
| Interventions | A. Continence pessary alone group (N = 149). Individuals in this group were fitted with a continence ring or dish either by a physician or a nurse. Most participants were fitted successfully in 1 clinic visit while up to 3 visits at 1 to 2‐week intervals were allowed for others to achieve optimal fitting. At the end of the 8‐week treatment period, participants were encouraged to continue to use the pessary B. Behavioural therapy (PFMT + continence strategies) (N = 146). Intervention in this group consisted of pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) and exercise and additional skills and strategies on the use of muscles to prevent urgency and stress incontinence. Treatment was administered by registered nurses, nurse practitioners and physical therapists and was implemented in 4 visits at 2‐week intervals. During each visit, participants received instructions on PFMT and exercise and also acquired additional skills and strategies on stress urge incontinence prevention. They were then given individualised prescriptions for daily PFM exercise and practice. At the end of the 8‐week treatment period, participants received an individualised home maintenance programme to enable them sustain their skills and muscle strength C. Continence pessary + behavioural therapy (combined) (N = 150). Treatment regimen was as described for both pessary and behavioural therapy groups. In addition, participants in this group could continue in the trial with only 1 of the therapies at the end of the 8‐week treatment period For this review comparison C versus A is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. The patient global impression of improvement (PGI‐I) was assessed for the 3 groups using a validated PGI‐I questionnaire with success defined as the proportion of participants with a response of 'much better' or 'very much better' At 3 months: A: 59/110; B: 72/124; C: 80/132 At 6 months: A: 52/102; B: 59/116; C: 63/123 At 12 months: A: 47/96; B: 48/99; C: 49/111 2. Condition‐specific quality of life (in form of the Pelvic Floor Distress inventory): this was assessed using the Urogenital Distress Inventory ‐ stress incontinence sub‐scale with success defined as the proportion of participants with absence of bothersome stress incontinence symptoms (indicated by an answer of 'no' to all 6 items on the sub‐scale or a response of 'yes' but with a bother of 'not at all' or 'somewhat' At 3 months: A: 49/110; B: 71/124; C: 66/132 At 6 months: data not reported At 12 months: A: 52/96; B: 59/99; C: 49/111 3. Frequency of incontinence episodes per week (self reported improvement) assessed by using the 7‐day diary with success defined as the proportion of women with 75% or more reduction in frequency of incontinence episodes At 3 months: A: 69/110; B: 68/124; C: 80/132 At 6 months: data not reported At 12 months: A: 51/96; B: 54/99; C: 52/111 4. Patient satisfaction with treatment: this was assessed using the validated Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire At 3 months: A: 94/110; B: 110/124; C: 118/132 At 6 months: A: 87/102; B: 95/116; C: 104/123 At 12 months: A: 75/96; B: 79/99; C: 81/111 | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Permuted block randomisation schedule was used |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation contained in sealed envelopes, opened by the interventionist only after the participants met all the inclusion/exclusion criteria |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible especially for PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | All outcome assessors were blinded to the treatment group assignment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Dropouts: at 3 months: all 79/445, C: 18/150, B: 22/146, A: 39/149; at 6 months: all 104/445, C: 27/150, B: 30/146, A: 47/149; at 12 months: all: 139/445; C: 39/150; B: 47/146; A: 53/149 "After randomization, dropout patterns differed among the three treatment groups (P = 0.015) with the pessary only group having the highest attrition rate ..." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Trial protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Approved by the ethics committee |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | Disclosed, funded by "Eunice Kennedy Shriver" |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Declared some of the authors were associated with a major pharmaceutical company |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 62 women with urodynamically proven genuine stress, urinary incontinence (GSI) | |
| Interventions | A. Maximal electrical stimulation alone (N = 20). Participants in this group received a battery‐powered vaginal stimulator (impulse frequency: 20 Hz; duration: 0.75 ms; current intensity: 0 to 90 mA) at home daily for 20 minutes B. Vaginal cones alone (N = 21). Participants in this group were instructed to use cones twice daily for 15 minutes and to increase the weight of the cones when successful on 2 occasions. They did not undergo vaginal examination. It was not reported whether participants were instructed to contract PFMs in order to hold the cones C. Kegel exercise + vaginal cones (N = 21). Participants in this group received vaginal cones as stated above. In addition, they were taught by vaginal examination to voluntarily contract their pelvic floor muscles and carried out 10 sessions of 10 contractions daily. No further details were reported For this review comparison C versus B is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. Improvement: threshold not defined, unclear whether self reported, detailed data not reported, only the level of significance was given for each treatment group 2. Reduction in urine leakage: this was assessed objectively (using pad testing); success threshold was not defined, details of data not reported, only P values were given 3. Decrease in pad weight: only the P values were reported, other details not given 4. Improvement on pad testing: objective assessment of improvement using pad testing; only proportions of participants were reported, success threshold was not defined A: 12/16; B: 14/19; C: 14/15 | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible, especially for PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Dropouts: all 12/62; C: 6/21, B: 2/21; A: 4/20 There is differential loss to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Trial protocol not available |
| Ethical approval | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Source of funding or support | Unclear risk | Not disclosed |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not disclosed |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomised controlled trial, parallel design | |
| Participants | 204 women with urodynamic evidence of stress urinary incontinence (GSI), detrusor instability (DI) or both (mixed incontinence). | |
| Interventions | A. Bladder training (BT) group (N = 68): involved a progressive voiding schedule that was altered every week for the first 6 weeks of the programme but remained unchanged for the last 6 weeks. The voiding interval was initially set at 30 or 60 minutes, depending on the baseline voiding diary and increased by 30 minutes each week if there was reduction in episodes of incontinence B. Pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) alone (N = 69). PFMT was also structured and it consisted of an initial teaching session (which also included instructions on continence strategies) followed by a graded home exercise with audio cassette practice tapes and 4 office biofeedback sessions. In all, 10 fast (3‐second) contractions and 40 sustained (10‐second) contractions (a total of 50 contractions) with 10‐second rest periods between contractions were performed daily by the third week. Patients received 4 weekly 30‐minute sessions of visual and verbal biofeedback. Visual biofeedback was provided via a strip‐chart recorder demonstrating vaginal and abdominal pressures as measured by vaginal balloons C. PFMT + BT (combined) (N = 67). Treatment regimen was as described for the BT and PFMT groups. BT was implemented initially while PFMT was added during the third week, including instructions on continence strategies (urge inhibition and preventive contractions) For this review comparison C versus A is relevant | |
| Outcomes | 1. Incontinence episodes per week (mean (SD)): this was assessed at endpoint using the records in a standardised diary Immediately after treatment: A: 10.6 (16.3), N = 68; B: 9.6 (10.8), N = 64; C: 6.8 (10.7), N = 61 3 months after treatment: data not reported 2. Cure rates: cure was defined as the proportion of participants who had 100% reduction in incontinence episodes, assessed using the standardised diary Immediately after treatment: A: 12/67; B: 8/62; C: 19/61 3 months after treatment: A: 10/63; B: 13/65; C: 16/59 3. Improvement rates: improvement was defined as the proportion of participants who had 50% or greater reduction in incontinence episodes, assessed using the standardised diary Immediately after treatment: A: 35/67; B: 36/63; C: 43/61 3 months after treatment: A: 28/61; B: 36/64; C: 35/59 4. Patient perceived improvement: instrument used in assessment not stated, success threshold was not defined but will be taken as the proportion of participants who were 'much better' or 'somewhat better' for the purpose of this review Immediately after treatment: A: 43/66; B: 48/63; C: 55/61 3 months after treatment: A: 37/60; B: 45/64; C: 44/59 5. Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome: instrument used in assessment not stated, success threshold was not defined but will be taken as the proportion of participants who were 'very satisfied' or 'slightly satisfied' with treatment outcome for the purpose of this review Immediately after treatment: A: 48/66; B: 56/63; C: 57/61 3 months after treatment: A: 47/60; B: 53/64; C: 51/58 6. Condition‐specific quality of life assessed at endpoint using: i. Urogenital Distress Inventory (UDI); reported as mean (SD): Immediately after treatment: A: 95.5 (54.4), N = 67; B: 90.8 (52.0), N = 63; C: 64.4 (48.6), N = 61 3 months after treatment: A: 91.7 (55.0), N = 60; B: 85.0 (52.4), N = 64; C: 72.8 (50.4), N = 58 ii. Incontinence Impact Questionnaire‐Revised (IIQ‐R); reported as mean (SD): Immediately after treatment: A: 72.1 (75.2), N = 66; B: 56.8 (61.4), N = 63; C: 46.6 (65.3), N = 61 3 months after treatment: A: 65.7 (80.2), N = 60; B: 59.3 (67.7), N = 64; C: 59.8 (83.9), N = 58 7. Treatment adherence: this was defined as the proportion of participants adhering to the voiding schedule; assessed using treatment logs or standardised questionnaire (no useable data were: only percentages, without the actual proportions, were reported) 8. Number of women requiring further treatment (relapse): women were followed up for a mean time of 3.2 years and the overall number of women requiring additional treatment such as surgery, drug, etc. was determined for each treatment group A: 19/48; B: 29/52: C: 18/48 | |
| Notes | Dropouts in each treatment group were not reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants not possible especially to PFMT |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Dropouts: immediately after treatment 9/204; 3 months after treatment 16/204 Differential loss to follow‐up: not reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | According to the authors, one pre‐specified outcome (pad weight) was eventually not reported due to large number of missing data |
| Ethical approval | Low risk | Approved by the ethics committee |
| Source of funding or support | Low risk | Disclosed (public institutions) |
| Conflict of interest | Unclear risk | Not stated |
BT: bladder training
DT: drug therapy
ES: electrical stimulation
Ex: exercise
GE: general education
HSGS: heat and steam generating sheet
IEF: incontinence episode frequency
PFM: pelvic floor muscle
PFMT: pelvic floor muscle training
SD: standard deviation
UI: urinary incontinence
SUI˜: Stress Urinary Incontinence
UUI: Urgency Urinary Incontinence
MUI: Mixed Urinary Incontinence
Hz: Hertz
mA: milliampere
µg: microgram
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Participants and intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Systematic review | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Participants not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Design not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Post‐prostatectomy patients | |
| Systematic review | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Design not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| The study is about the efficacy of a self management promotion programme and the participants were not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Design not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant; recruited both men and women with no separate data for women | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Design not relevant | |
| Participants were provided with a leaflet and were not under a structured PFMT programme and included both men and women (no separate data for women) | |
| Participants were provided with a leaflet and were not under a structured PFMT programme and included both men and women (no separate data for women) | |
| Participants were provided with a leaflet; were not under a structured PFMT programme; included both men and women (no separate data for women) | |
| Participants were provided with a leaflet and were not under a structured PFMT programme; included both men and women (no separate data for women) | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Design not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Design not relevant | |
| Randomisation was not done for intervention (incontinence versus no incontinence) | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Participants and intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Participant and intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant | |
| Intervention not relevant |
PFMT: pelvic floor muscle training
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured or improved (objective assessment) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 PFMT added to vaginal cones versus vaginal cones alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured or improved (objective assessment). | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured. | ||||
| 1.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.2  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 2 Number of women cured or improved. | ||||
| 2.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on IIQ‐R Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.3  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on IIQ‐R. | ||||
| 3.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.4  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 4 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI. | ||||
| 4.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Number of women cured or improved using patient global impression of improvement Show forest plot | 2 | 354 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [1.14, 1.41] |
| Analysis 3.5  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 5 Number of women cured or improved using patient global impression of improvement. | ||||
| 5.1 Immediately after treatment | 2 | 235 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [1.15, 1.45] |
| 5.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | 119 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.94, 1.55] |
| 6 Incontinence episode per week Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.6 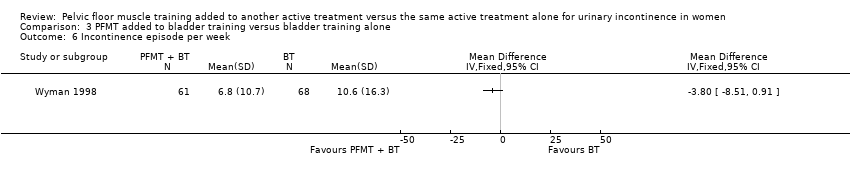 Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 6 Incontinence episode per week. | ||||
| 7 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.7  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 7 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome. | ||||
| 7.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Number of women requiring further treatment (relapse) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.8  Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 8 Number of women requiring further treatment (relapse). | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 4.1  Comparison 4 PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes), Outcome 1 Number of women cured. | ||||
| 2 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 2 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.06 [0.79, 5.38] |
| Analysis 4.2  Comparison 4 PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes), Outcome 2 Number of women cured or improved. | ||||
| 3 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome Show forest plot | 1 | 68 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.57, 1.43] |
| Analysis 4.3  Comparison 4 PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes), Outcome 3 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome. | ||||
| 3.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.47, 1.52] |
| 3.2 After 12 months | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.48, 2.02] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 6.1  Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured or improved. | ||||
| 1.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 6.2  Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 2 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI. | ||||
| 2.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Number of women improved using patient global impression of improvement Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 6.3  Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 3 Number of women improved using patient global impression of improvement. | ||||
| 3.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 At 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 6.4  Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 4 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome. | ||||
| 4.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 At 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.3 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.1  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured. | ||||
| 1.1 PFMT + clenbuterol vs clenbuterol | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.2  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 2 Number of women cured or improved. | ||||
| 2.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on I‐QoL questionnaire Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.3  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on I‐QoL questionnaire. | ||||
| 3.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Number of women improved on patient global impression of improvement in first 3 months Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.4  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 4 Number of women improved on patient global impression of improvement in first 3 months. | ||||
| 4.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week in first 3 months Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.5  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 5 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week in first 3 months. | ||||
| 5.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week at 12 months Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.6 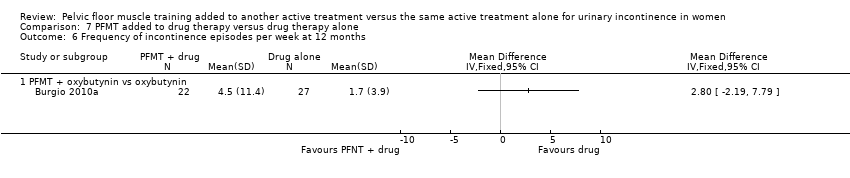 Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 6 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week at 12 months. | ||||
| 6.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7 Frequency of micturitions per 24 hours Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.7  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 7 Frequency of micturitions per 24 hours. | ||||
| 7.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Volumes of urine per micturition Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.8  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 8 Volumes of urine per micturition. | ||||
| 8.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 9 Number of continence pads used per week Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.9  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 9 Number of continence pads used per week. | ||||
| 9.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 10 Treatment adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.10  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 10 Treatment adverse events. | ||||
| 10.1 PFMT + solifenacin vs solifenacin | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome in first 3 months Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.11  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 11 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome in first 3 months. | ||||
| 11.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11.2 PFMT + clenbuterol vs clenbuterol | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 12 Treatment benefit Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 7.12  Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 12 Treatment benefit. | ||||
| 12.1 PFMT + ?drug vs ?drug (drug name not reported) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 9.1  Comparison 9 PFMT added to other treatment versus other treatment alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured. | ||||
| 1.1 PFMT + heat and steam generating sheet versus heat and steam generating sheet alone | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |

PRISMA study flow diagram.

'Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias domain for each included study.

Comparison 1 PFMT added to vaginal cones versus vaginal cones alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured or improved (objective assessment).

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 2 Number of women cured or improved.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on IIQ‐R.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 4 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 5 Number of women cured or improved using patient global impression of improvement.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 6 Incontinence episode per week.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 7 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome.

Comparison 3 PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone, Outcome 8 Number of women requiring further treatment (relapse).

Comparison 4 PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes), Outcome 1 Number of women cured.

Comparison 4 PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes), Outcome 2 Number of women cured or improved.

Comparison 4 PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes), Outcome 3 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome.

Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured or improved.

Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 2 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI.

Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 3 Number of women improved using patient global impression of improvement.

Comparison 6 PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone, Outcome 4 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured.
Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 2 Number of women cured or improved.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on I‐QoL questionnaire.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 4 Number of women improved on patient global impression of improvement in first 3 months.
Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 5 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week in first 3 months.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 6 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week at 12 months.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 7 Frequency of micturitions per 24 hours.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 8 Volumes of urine per micturition.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 9 Number of continence pads used per week.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 10 Treatment adverse events.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 11 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome in first 3 months.

Comparison 7 PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone, Outcome 12 Treatment benefit.

Comparison 9 PFMT added to other treatment versus other treatment alone, Outcome 1 Number of women cured.
| PFMT added to vaginal cones versus vaginal cones alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to vaginal cones versus vaginal cones alone | |||||
| Number of women cured or improved (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (pad test) | Study population | RR 1.27 | 34 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 737 per 1000 | 936 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women experiencing pain ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life assessed by patient questionnaire such as Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ), King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Random sequence generation and allocation concealment unclear. | ||||||
| PFMT added to lifestyle intervention versus lifestyle intervention alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to lifestyle intervention versus lifestyle intervention alone | |||||
| Number of women cured or improved (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting adverse events ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to bladder training versus bladder training alone | |||||
| Number of women cured ‐ 3 months after treatment | Study population | RR 1.71 | 122 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 159 per 1000 | 271 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women experiencing pain ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life ‐ 3 months after treatment | The mean condition‐specific quality of life ‐ 3 months after treatment in the intervention groups was 5.9 lower (35.53 lower to 23.73 higher) | 118 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | lower scores imply lower impact of incontinence on quality of life | ||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) | 396 per 1000 | 376 per 1000 | RR 0.95 | 96 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Random sequence generation and allocation concealment is unclear. | ||||||
| PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes) for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to electrical stimulation versus electrical stimulation alone (excluding implanted electrodes) | |||||
| Number of women cured | Study population | RR 2.06 | 56 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 167 per 1000 | 343 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women experiencing pain ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life assessed by patient questionnaire such as Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ), King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Random sequence generation and allocation concealment unclear. | ||||||
| PFMT added to magnetic stimulation versus magnetic stimulation alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to magnetic stimulation versus magnetic stimulation alone | |||||
| Number of women cured or improved (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting adverse events ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life assessed by patient questionnaire such as Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ), King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to continence pessary versus continence pessary alone | |||||
| Number of women cured or improved (subjective) at 12 months | Study population | RR 0.88 | 207 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 531 per 1000 | 468 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting adverse events ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life at 12 months | Study population | RR 0.81 | 207 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 542 per 1000 | 439 per 1000 | |||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Wide confidence interval (0.67 to 1.16). | ||||||
| PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to drug therapy versus drug therapy alone | |||||
| Number of women cured ‐ PFMT + clenbuterol versus clenbuterol | Study population | RR 1.16 | 32 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ||
| 769 per 1000 | 892 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting adverse events | 207 per 1000 | 174 per 1000 | RR 0.84 | 162 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Condition‐specific quality of life on I‐QoL Questionnaire ‐ PFMT + duloxetine versus duloxetine | The mean condition‐specific quality of life on I‐QoL questionnaire ‐ PFMT + duloxetine versus duloxetine in the intervention groups was 5.84 higher | 101 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Higher scores mean less symptom impact on the quality of life (better) | ||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Random sequence generation and allocation concealment is unclear. | ||||||
| PFMT prior to surgical intervention versus surgical intervention alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT prior to surgical intervention versus surgical intervention alone | |||||
| Number of women cured or improved (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women reporting adverse events ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life assessed by patient questionnaire such as Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ), King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| PFMT added to HSGS versus HSGS alone for urinary incontinence in women | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with urinary incontinence | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | PFMT added to other versus other treatment alone | |||||
| Number of women cured | Study population | RR 2.38 | 74 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 216 per 1000 | 515 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women reporting incontinence at 1 year or more after treatment (subjective) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Objective measure of urine leakage (e.g. pad test) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women experiencing pain ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Condition‐specific quality of life assessed by patient questionnaire such as Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ), King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| General health status evaluation e.g. Short Form (SF)‐36 ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| Number of women requiring further treatment such as surgery, drugs, mechanical devices (relapse) ‐ not reported | Not estimable | Not reported | ||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Allocation concealment unclear. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured or improved (objective assessment) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on IIQ‐R Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Number of women cured or improved using patient global impression of improvement Show forest plot | 2 | 354 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [1.14, 1.41] |
| 5.1 Immediately after treatment | 2 | 235 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [1.15, 1.45] |
| 5.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | 119 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.94, 1.55] |
| 6 Incontinence episode per week Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7.2 3 months after treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Number of women requiring further treatment (relapse) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 2 | 56 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.06 [0.79, 5.38] |
| 3 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome Show forest plot | 1 | 68 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.57, 1.43] |
| 3.1 Immediately after treatment | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.47, 1.52] |
| 3.2 After 12 months | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.48, 2.02] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Condition‐specific quality of life on UDI Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Number of women improved using patient global impression of improvement Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 At 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 At 3 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 At 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.3 At 12 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 PFMT + clenbuterol vs clenbuterol | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Number of women cured or improved Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Condition‐specific quality of life on I‐QoL questionnaire Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Number of women improved on patient global impression of improvement in first 3 months Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4.2 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week in first 3 months Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5.2 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Frequency of incontinence episodes per week at 12 months Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7 Frequency of micturitions per 24 hours Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Volumes of urine per micturition Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 9 Number of continence pads used per week Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.1 PFMT + duloxetine vs duloxetine | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 10 Treatment adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.1 PFMT + solifenacin vs solifenacin | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11 Patient satisfaction with treatment outcome in first 3 months Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11.1 PFMT + oxybutynin vs oxybutynin | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11.2 PFMT + clenbuterol vs clenbuterol | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 12 Treatment benefit Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 12.1 PFMT + ?drug vs ?drug (drug name not reported) | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women cured Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 PFMT + heat and steam generating sheet versus heat and steam generating sheet alone | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |

