Administración de heparina subcutánea lenta versus rápida para la prevención de la equimosis y la intensidad del dolor en el sitio de inyección
Appendices
Appendix 1. CENTRAL search strategy
| Search run on Mon Mar 20 2017 | ||
| #1 | MESH DESCRIPTOR Heparin EXPLODE ALL TREES | 3883 |
| #2 | *heparin*:TI,AB,KY | 9079 |
| #3 | LMWH:TI,AB,KY | 847 |
| #4 | (nadroparin* or fraxiparin* or enoxaparin* or Clexane or klexane or lovenox or dalteparin* ):TI,AB,KY | 2110 |
| #5 | (ardeparin or normiflo or tinzaparin or logiparin or Innohep or certoparin or sandoparin or reviparin or clivarin* or danaproid or danaparoid ):TI,AB,KY | 371 |
| #6 | (Fragmin or Kabi 2165 or Kabi2165 or FR 860 or FR860):TI,AB,KY | 209 |
| #7 | (antixarin or ardeparin* or bemiparin* or Zibor or cy 222 or cy222 or embolex or monoembolex or parnaparin* or rd 11885 or tedelparin or Kabi 2165 or Kabi2165 ):TI,AB,KY | 154 |
| #8 | (emt 966 or emt966 or emt 967 or emt967 or pk 10169 or pk10169):TI,AB,KY | 8 |
| #9 | (cy 216 or cy216 or seleparin* or tedegliparin or seleparin* or tedegliparin* or tedelparin or calciparin*):TI,AB,KY | 70 |
| #10 | (kb 101 or kb101 ):TI,AB,KY | 3 |
| #11 | (lomoparan or orgaran):TI,AB,KY | 28 |
| #12 | (parnaparin or fluxum or lohepa or lowhepa or parvoparin ):TI,AB,KY | 34 |
| #13 | (op 2123 or op2123 ):TI,AB,KY | 1 |
| #14 | (AVE5026 or AVE 5026):TI,AB,KY | 2 |
| #15 | #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 | 10033 |
| #16 | MESH DESCRIPTOR Injections, Subcutaneous EXPLODE ALL TREES | 3847 |
| #17 | subcutan*:TI,AB,KY | 16583 |
| #18 | (sc or s.c):TI,AB,KY | 7296 |
| #19 | #16 OR #17 OR #18 | 19485 |
| #20 | MESH DESCRIPTOR Contusions | 93 |
| #21 | bruis*:TI,AB,KY | 486 |
| #22 | contus*:TI,AB,KY | 537 |
| #23 | indurat*:TI,AB,KY | 858 |
| #24 | MESH DESCRIPTOR Hematoma | 402 |
| #25 | haematoma*:TI,AB,KY | 525 |
| #26 | hematoma*:TI,AB,KY | 2882 |
| #27 | MESH DESCRIPTOR Pain EXPLODE ALL TREES | 34252 |
| #28 | pain*:TI,AB,KY | 94480 |
| #29 | #20 OR #21 OR #22 OR #23 OR #24 OR #25 OR #26 OR #27 OR #28 | 102440 |
| #30 | #15 AND #19 AND #29 | 303 |
| #31 | * NOT SR‐PVD:CC AND 31/08/2013 TO 28/02/2017:DL | 79662 |
| #32 | #30 AND #31 | 63 |
Appendix 2. Trials registries searches
ClinicalTrials.gov
12 studies found for: heparin AND subcutaneous AND pain
4 studies found for: heparin AND subcutaneous AND bruising
World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform
5 records for 5 trials found for: heparin AND subcutaneous AND bruising (2 NEW and not NCT)
6 records for 6 trials found for: heparin AND subcutaneous AND pain (2 new not in NCT)
ISRCTN Register
3 results subcutaneous AND heparin AND pain (0 new)
1 results subcutaneous AND heparin AND bruising (0 new)
Appendix 3. Authors' Iranian search strategy
| 1 | Heparin AND Subcutaneous AND Injection (title or abstract) | 12 |
Appendix 4. Google Scholar search strategy
| 1 | ((heparin OR enoxaparin OR LMWH) AND subcutaneous AND injection AND (duration OR speed) AND (bruising OR pain) AND trial)) ABSTRACT | 3900 |

Study flow diagram.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
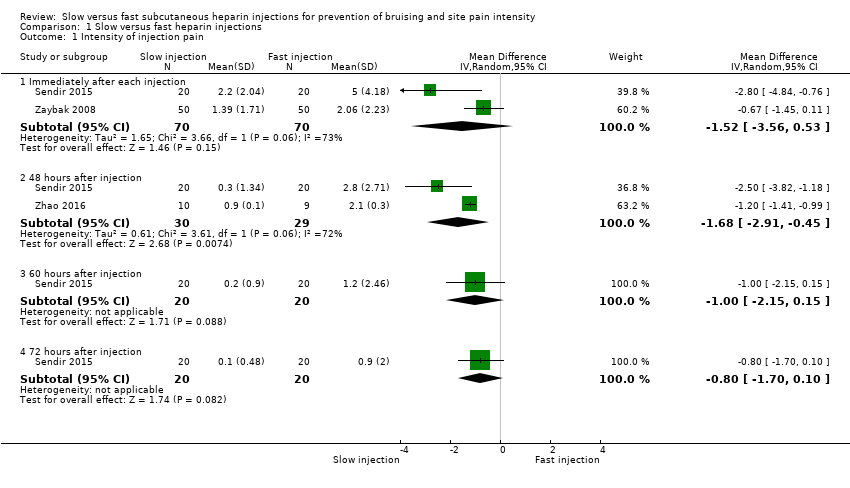
Comparison 1 Slow versus fast heparin injections, Outcome 1 Intensity of injection pain.
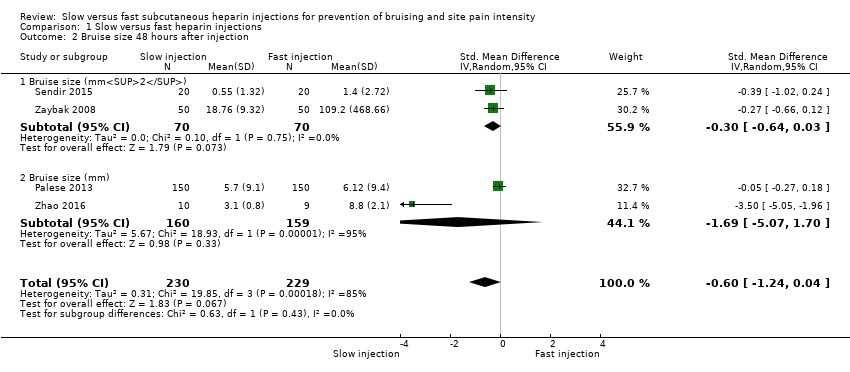
Comparison 1 Slow versus fast heparin injections, Outcome 2 Bruise size 48 hours after injection.
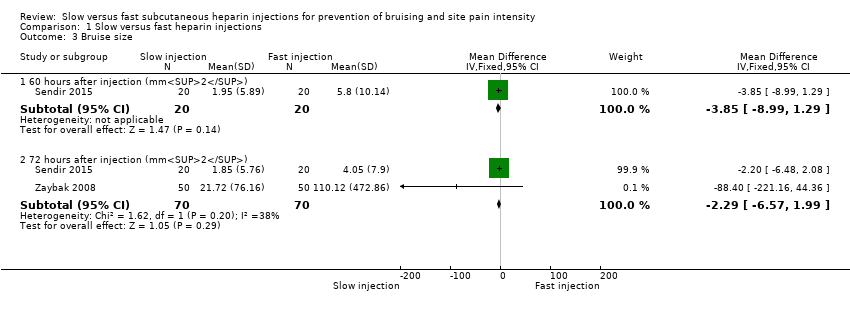
Comparison 1 Slow versus fast heparin injections, Outcome 3 Bruise size.
| Slow vs fast subcutaneous heparin injection for prevention of bruising and site pain intensity | |||||
| Patient or population: patients treated with subcutaneous heparin injections Settings: hospital outpatient and inpatient units Intervention: slow injection (injection speed of 20 or more seconds) Comparison: fast injection (injection speed of less than 20 seconds) | |||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk with fast injection | Corresponding risk with slow injection | ||||
| Intensity of injection pain immediately after injection (VAS 0 to 10 cm) 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain) | Mean pain intensity reported by the 2 studies ranged across fast injection groups from 2 to 5. | Mean pain intensity in the slow injection group was 1.52 points less than in the fast group (3.56 lower to 0.53 higher; P = 0.15). | 140 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝a | |
| Intensity of injection pain 48 hours after injection (VAS 0 to 10 cm) 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain) | Mean pain intensity ranged across fast injection groups from 2.1 to 2.8. | Mean pain intensity in the slow injection group was 1.68 points less than in the fast group (2.91 lower to 0.45 lower; P = 0.007). | 59 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝b | |
| Bruise size 48 hours after injection (mm/mm2) | See comment. | Mean bruising size in the slow injection group was 0.6 SD lower than in the fast injection group (1.24 lower to 0.04 higher; P = 0.07). | 459 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝c | Bruise size was measured on different scales; therefore we used the SMD to pool data. |
| Haematoma at injection site | See comment. | No studies measured this outcome. | |||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) for pain intensity was the range of mean pain score reported following fast injection by the 2 studies. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the mean difference of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. | |||||
| aWe downgraded the quality of evidence by two steps owing to study limitations, as we identified few studies with small numbers of participants (imprecision) and high heterogeneity (I2 = 73%) (inconsistency). | |||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Intensity of injection pain Show forest plot | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Immediately after each injection | 2 | 140 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.52 [‐3.56, 0.53] |
| 1.2 48 hours after injection | 2 | 59 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.68 [‐2.91, ‐0.45] |
| 1.3 60 hours after injection | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐2.15, 0.15] |
| 1.4 72 hours after injection | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.8 [‐1.70, 0.10] |
| 2 Bruise size 48 hours after injection Show forest plot | 4 | 459 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.60 [‐1.24, 0.04] |
| 2.1 Bruise size (mm2) | 2 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.30 [‐0.64, 0.03] |
| 2.2 Bruise size (mm) | 2 | 319 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.69 [‐5.07, 1.70] |
| 3 Bruise size Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 60 hours after injection (mm2) | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.85 [‐8.99, 1.29] |
| 3.2 72 hours after injection (mm2) | 2 | 140 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.29 [‐6.57, 1.99] |

