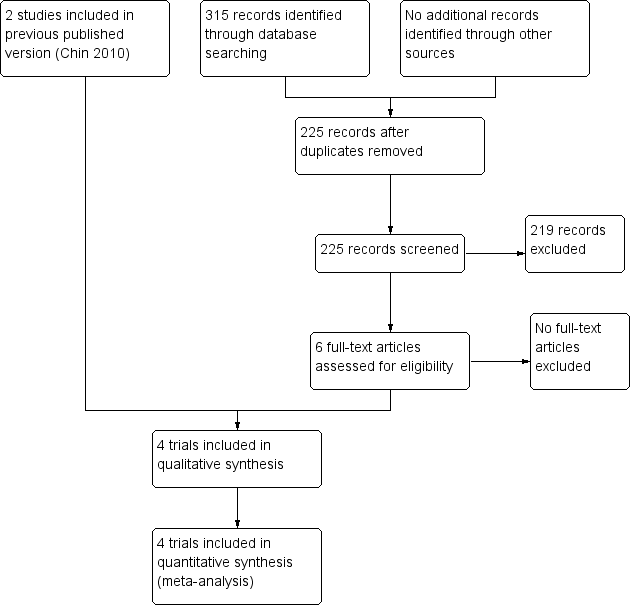
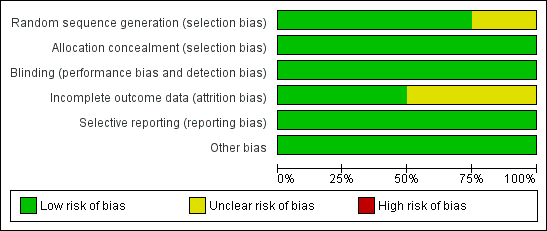
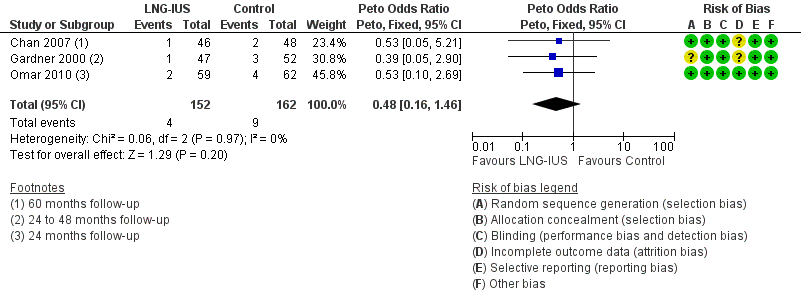
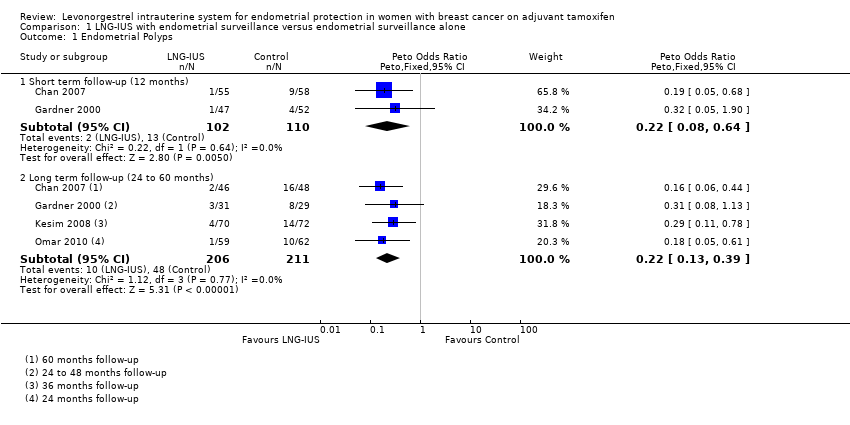
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Sally AD Romero, Katie Young, Martha Hickey, H Irene Su | 21 diciembre 2020
Susan Furness, Helen Roberts, Jane Marjoribanks, Anne Lethaby | 15 agosto 2012
Giulio Formoso, Enrica Perrone, Susanna Maltoni, Sara Balduzzi, Jack Wilkinson, Vittorio Basevi, Anna Maria Marata, Nicola Magrini, Roberto D'Amico, Chiara Bassi, Emilio Maestri | 12 octubre 2016
Hunain Shiwani, Naomi S Clement, Jane P Daniels, William Atiomo | 2 mayo 2024
Theresa Mittermeier, Charlotte Farrant, Michelle R Wise | 6 septiembre 2020
Yunhai Chuaia, Ivana Rizzutoa, Xia Zhanga, Ying Li, Guanghai Dai, Sophie J Otter, Rasiah Bharathan, Alexandra Stewart, Aiming Wang | 4 marzo 2021
Ussanee S Sangkomkamhang, Pisake Lumbiganon, Porjai Pattanittum | 23 noviembre 2020
Li Luo, Bing Luo, Ying Zheng, Heng Zhang, Jing Li, Neil Sidell | 4 diciembre 2018
Rafael M Moroni, Wellington P Martins, Rui A Ferriani, Carolina S Vieira, Carolina O Nastri, Francisco José Candido Dos Reis, Luiz Gustavo Brito | 20 marzo 2015
Elvira C van Dalen, Helena JH van der Pal, Leontien CM Kremer | 3 marzo 2016
Respuestas clínicas Cochrane
Simone Mocellin | 23 septiembre 2019