Anestésicos locales y anestesia regional versus analgesia convencional para la prevención del dolor posoperatorio persistente en adultos y niños
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to studies awaiting assessment
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participant, provider, outcome assessor) clinical RCT Assignments were computer‐generated Follow‐up: 1 year | |
| Participants | Participants: 260 women aged 18‐85 from 4 cancer hospitals in France Operation: breast cancer surgery (both breast‐conserving and mastectomy with or without axillary or sentinel node dissection) 2 groups, size: 117/119 Age (± SD): 56 (± 12), 57 (± 13) Men/women: 0/117, 0/119 Patient co‐morbidities: breast‐conserving surgery with axillary lymph node dissection, group 1, 2 (± SD) 53 (± 45.3), 62 (± 52.1), mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection or sentinel lymph node dissection, group 1, 2 (± SD): 53 (± 45.3), 48 (± 40.3), mastectomy without axillary lymph node dissection or sentinel lymph node dissection, group 1, 2 (± SD): 11 (± 9.4), 9 (± 7.6) | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): at end of surgery before suturing, 3 mL‐4 mL infiltration of 0.375% ropivacaine along each site of SC and deep layers of breast and axillary incisions, 2nd and 3rd intercostal space, humeral insertion of major pectoralis (received 3 mg/kg of 0.375% ropivacaine) Group 2 (saline): at end of surgery before suturing, 3 mL‐4 mL infiltration of saline along each site of SC and deep layers of breast and axillary incisions, 2nd and 3rd intercostal space, humeral insertion of major pectoralis (receive 0.8 mL/kg saline Both groups: premedicated with oral hydroxyzine (2 mg/kg) 1 h before surgery. GA induction with propofol, sufentanil, maintenance with nitrous oxide in O2, sevoflurane or desflurane, sufentanil bolus as required. Post‐op pain control with oral paracetamol and ketoprofen and rescue with morphine PCA for 24 h (bolus dose 1 mg on demand, lockout 5 min). Ondanestron 4 mg for nausea/vomiting +/‐ droperidol 1.25 mg every 8 h Adjuvants: none Immdiate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 months only Continuous: BPI score at 3, 6, 12 months Other reported: neuropathic pain score, hospital anxiety and depression score at 3, 6, 12 months | |
| Notes | For dichotomous pain, BPI score of ≥ 3 was used as cut off Funding sources: support was from institutional/departmental sources. The study author responded to our request that "Astra Zeneca only paid the insurance for the study and Astra Zeneca had no role in conceiving the study, designing the protocol, executing the trial and or analysing and interpreting the results" Conflicts of interest: there were no other conflicts of interest to report. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a balanced block stratified randomization scheme was used for patient allocation. Stratification was performed on the basis of hospital and type of surgery (conservative or not). Patients were randomized in randomly permuted blocks of four or six patients in each striatum. Assignments were computer generated" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: [Assignments were] "maintained in sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes...the envelope was opened in an isolated room on the day of surgery, and patients were assigned to either the placebo group or the ropivacaine group" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "before induction of anaesthesia, an operating room nurse read the results of randomization to prepare the solution of normal saline or ropivacaine in identical syringes... The solution was prepared in an isolated room and the nurse did not have any further contact with the patient. No other physician or nursing staff member was aware of the contents" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "pain was evaluated by a nurse who was blinded to the treatment group". Patients filled out questionnaires at inclusion and 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after surgery to evaluate chronic pain |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 24 participants were excluded after randomization because of withdrawal of consent or failure to meet inclusion criteria. The groups to which these belonged was not reported, but there were fairly equal numbers in those that were included and received treatment (117 vs 119). At 3 months, there were 6 participants who were lost to follow‐up or had missing outcome data in the ropivacaine group, and 11 participants lost to follow‐up or with missing BPI data in the placebo group. these are low numbers when compared to the total studied population, and fairly balanced and reasons are listed for each group. No report on the exact number of participants with missing data at 6 or 12 months' follow‐up, only states "The maximum percentage of missing data for each point (0, 3, 6, and 12 months) in both arms was less than 5% (range: 0%‐5%). ITT was performed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The primary and secondary outcomes listed in the protocol were all reported. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "measurement of pain on the VAS showed lower scores at rest and during mobilization in the first 90 min after the end of surgery in the ropivacaine group than in the control group (P < 0.001)... Ropivacaine wound infiltration decreased immediate postoperative pain in the PACU and increased the percentage of pain‐free patients (VAS = 0) for the first 48h" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded, clinical RCT Randomization scheme not described Follow‐up: 1 year | |
| Participants | Participants: 200 adults in a hospital setting in Nijmegen, Netherlands Operation: ICBG for cranio‐maxillofacial surgery 2 groups, size: 100/100 Age (range): 56 (21‐74), 57 (21‐80) Men/women: 25/31, 14/28 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (bupivacaine): intraop: after wound closure, participants received a single dose of bupivacaine (10 cc of 2.5 mg/mL bupivacaine with 1:80.000 epinephrine) Group 2 (control): no intervention given Adjuvants: epinephrine Immediate post‐op pain control: no difference between VAS and post‐op NSAID use between groups | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain questionnaire at 1 year Continuous: none Other reported: use of paracetamol (Acetaminophen) and ibuprofen after surgery, duration of surgery, blood loss, and length of incision Adverse events: perforation of the lateral cortex of the iliac crest, haematoma | |
| Notes | Financial support statement: "none." Conflict of interest statement: "none declared" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Randomization scheme was not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "for each patient an envelope was drawn" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of participants and personnel were not described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of the outcome assessors was not described. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "79 questionnaires were sent out . After exclusion of the incorrectly filled and nonreturned questionnaires, 58 remained for evaluation (59%)." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available but all specified outcomes were reported on |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "No statistically significant differences in outcome were detected between these groups...". |
| Methods | Quadruple‐blinded (participant, provider, surgeon, outcome assessor), randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial Sequence generation by random number tables Follow‐up: 1 year (effectively, in treatment group: 17 months, control group 15 months) | |
| Participants | Participants: 96 women included (78 analysed), from 1 university hospital, Besancon, France Operation: breast cancer surgery (mastectomy and lumpectomy with sentinel node biopsy) 2 groups, size: 40/38 Age (groups 1, 2): 52.4 years (SD ± 11.2), 57.7 (SD ± 12.6) Only women | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (postsurgical breast infiltration): GA (sufentanil 0.3 µg/kg), at wound closure single‐shot local infiltration with ropivacaine (0.475%, 40 mL), post‐op: paracetamol (1 g, intravenously, every 6 h), ketoprofen (100 mg, intravenously, every 12 h) rescue analgesic (if VAS > 30/100) nalbuphine 0.2 mg/kg Group 2 (placebo postsurgical breast infiltration): GA (sufentanil 0.3 µg/kg), at wound closure single‐shot placebo infiltration with normal saline (40 mL), post‐op: paracetamol (1 g, intravenously, every 6 h), ketoprofen (100 mg, intravenously, every 12 h) rescue analgesic (if VAS > 30/100) nalbuphine 0.2 mg/kg Adjuvants: none reported Immediate post‐op pain control: analgesic rescue medication and VAS were not different between groups | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 1 year (effectively at 17 months in the experimental and at 15 months in the control group) Continuous: McGill Questionnaire described, but results not reported Effective regional anaesthesia not reported, and treatment did not reduce the severity of immediate postoperative pain or the consumption of rescue pain medication | |
| Notes | Article in French, extracted by authors Funding sources: none reported Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were randomized with the use of a “randomization table” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Participants were randomized “after inclusion”. Unclear how the allocation was concealed. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: “the anaesthetist in charge, the surgeon, the investigator were blinded”. "The anaesthetic was administered with the patients anaesthetized". “The solution was prepared by personnel not taking care of the patient”. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the investigator was blinded". “The solution was prepared by personnel not taking care of the patient". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Significant attrition due to post hoc exclusion/lost participants and lost data that were reported but not analysed with ITT. Unclear how many participants were initially randomized to which group, hence attrition cannot even be assessed. Participants initially excluded for missing data were later included for the 1‐year analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "au cours des 24 premières heures postopératoire, l'EVA a varié significativement au cours du temps...sans différence significative entre les deux groupes... Le nombre de patientes ayant eu recours au traitement antalgiue de secours et la dose de nalbuphine consummée n'était pas statistiquement différente entre les deux groupes". Analogical visual scale pain score, antalgic consumption were similar between groups |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participants, outcome assessors), placebo‐controlled, clinical RCT Sequence generation randomized but not described Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 8 adults in a university setting in Bergen, Norway Operation: bilateral reduction mammoplasty 2 groups, size: 8/8 Age: 28.5 years (range 18‐34) Men/women: 0/8 Remarks: body sides, not participants randomized | |
| Interventions | Breast group 1 (preop infiltration): GA (fentanyl), preincision: infiltration with lidocaine (0.5%, 100 mL with epinephrine 5 µg/mL), post‐op as needed ketobemidone (oral, 5 mg) and paracetamol (1000 mg 3 x daily) Breast group 2 (placebo): GA (fentanyl), preincision: infiltration with normal saline (100 mL with epinephrine 5 µg/mL), post‐op as needed ketobemidone (orally, 5 mg) and paracetamol (1000 mg 3 x daily) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved in treated breasts | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 6 months Continuous: none reported Secondary: thermal thresholds were reported as tables, touch allodynia, or hyperalgesia | |
| Notes | Some details, reported as graphs, are difficult to compare and extract. We acknowledge the study author's response regarding sources of funding and conflict of interest statement. Funding sources: the author informed us that this was an investigator‐initiated study, supported by an unrestricted grant from Astra Zeneca initially to study the effects of ropivacaine. When the study authors could not obtain approval to study this drug, the company maintained their support. The study author wrote that "the results were analysed with the help of a statistician at Astra Zeneca... we were allowed to keep the equipment... and that Astra financed my travel to a conference..." Conflicts of interest: the author had "no conflict of interest... and did not receive any [other] salary or economic compensation from Astra Zeneca." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “patients’ breasts were randomized to test and control groups”, but the method was not described in detail. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Efforts to conceal allocation were not described. Bias is rather unlikely, because body sides, not participants were randomized. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the procedure was performed double blind", however blinding of participants and personnel not explicitly described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "the procedure was performed double blind", however outcome assessor blinding not explicitly described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Withdrawals and attrition reported as none, except one participant excluded for drug spillage. With only one withdrawal, body parts randomized not participants, even though no ITT analysis was performed, bias seems unlikely. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "some details, reported as graphs, are difficult to compare and extract" |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the sum of VAS scores for pain intensity was significantly lower in the lidocaine group than in the placebo group for the entire registration period of 10 h after wound closure" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (patient/outcome assessor), RCT Sequence generation by a computer‐based, random numbers generator Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 120 women in a hospital setting in Ljubljana, Slovenia Operation: axillary lymphadenectomy and breast reconstruction Groups, size: 60/60 Age (lymphadenectomy, reconstruction): 60, 48 All female participants Comorbidities: none | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (levobupivacaine): intraop: before wound closure, a fenestrated wound catheter was placed under the pectoralis major muscle and upon the entire length over the upper side of the wound. The wound catheter was fenestrated along 15 cm in the distal part. A bolus of 15 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine was injected into the wound through the catheter immediately after wound closure. Surgical drains and the fenestrated catheter were clamped for 5 min to enable bolus absorption. Elastomeric pump was connected containing 100 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine. Infusion at 2 mL/h was continuous for 50 h. Group 2 (piritramide): intraop: continuous intravenous infusion with piritramide (30 mg), metoclopramide (20 mg) and metamizole (2.5 g) in 100 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride (3 mL/h‐6 mL/h) until 24 h postoperatively Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: none Dichotomus: overall pain/no pain at 3 months No adverse events reported | |
| Notes | Study characteristics and data combined with Strazisar 2014. Axillary lymphadenectomy and breast reconstruction performed on 60 participants per procedure. Results from both procedures were combined to best represent pain outcomes. Funding sources: financial support was not described. Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was provided. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the research nurse performed randomization using random numbers generated by a computer..." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomization and numbers were placed in sealed opaque envelopes to ensure concealment of allocation at enrollment" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "participants were randomly grouped" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "clinicians who recorded data about chronic pain were blinded about randomisation group of patients." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All participants completed the follow‐up evaluation. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "a smaller portion of patients treated with local anesthetics had chronic pain in comparison to the control group." "Chronic pain three months after operation is less frequent in the test group." |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participant, provider, outcome assessor) randomized placebo‐controlled clinical trial Sequence generation via randomized list Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 36 adult participants at a university clinic in Zurich, Switzerland Operation: Bakart repair for shoulder instability using autogenous bone graft, harvested from iliac crest 2 groups, size: 18/18 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 25 (± 5), 26 (± 4) Men/women, group 1, 2: 14/4, 13/5 Comorbidities: none reported Remarks: autogenous bone harvested through lateral oblique incision just cephalic to anterior iliac crest using classical surgical technique | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): at end of surgery, bolus of 30 mL ropivacaine 0.5% via iliac crest catheter and in PACU, continuous infusion 0.2% ropivacaine at 5 mL/h started, continued for total of 48 h. Group 2 (placebo): at end of surgery, bolus of 30 mL saline via iliac crest catheter, in PACU, continuous infusion saline 5 mL/h started, continued for total of 48 h. Both groups: premedicated with midazolam 1 h before arrival to induction room, and interscalene brachial plexus block performed. GA with propofol, rocuronium and fentanyl. Autogenous bone harvested through lateral oblique incision cephalad to anterior iliac crest using classical surgical technique. Catheter placed in direct contact with self‐resorbing foam pad dressing touching bone, tunnelled and secured to skin using sutures and adhesive dressing. In PACU, all participants also received continuous interscalene analgesia with 0.2% ropivacaine at 10 mL/h 6 h after initial block. Both groups got IV PCA containing 1 mg/mL morphine, 2 mg dose lockout interval 15, no baseline, or 4 h limit, with 2 mg IV morphine top up by nurse for VAS > 30. After discharge, 25 mg oral rofecoxib/d and 2 mg oral paracetamol as needed during 3 weeks post‐op Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: pain significantly lower at the iliac crest donor site at rest (except at t40 h) and during motion (except at t48 h) in the ropivacaine group with significantly decreased morphine consumption at 24 h and 48 h. | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: VAS at rest and on motion at iliac crest at 3 months Other reported: post‐op pain at shoulder and presence of numbness/paraesthesias/neurologic damage at 3 months Adverse events: post‐op nausea/vomiting, pruritis, inflammation at catheter site | |
| Notes | Interscalene block performed in both groups. Comparison of interest is ropivacaine vs placebo continuous infusion at iliac crest donor site. Funding sources: "support was provided solely from institutional and/or departmental sources." Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were given a number between 1 and 36...according to a randomization list" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were given a number between 1 and 36 by choosing a sealed envelope containing a number.. Each patient’s number was passed on to a pharmacist, who prepared the anaesthetic set (bolus and maintenance package) of either ropivacaine or placebo, according to a randomization list" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "double‐blind study". Participants, block performers/anaesthesiologists, post‐op providers all blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all the patients were observed independently by a surgeon and an anaesthesiologist 3 months after surgery to assess the pain (anaesthesiologist) at rest and during motion at the operated IC and operated shoulder". Only pharmacy was aware of contents of anaesthetic set based on randomization list. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all patients completed the study. All interscalene catheters were successfully placed, and no disconnection or other technical problems were encountered during the course of the study" |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "pain was significantly lower at the donor site at rest (except at t40hrs) and during motion (except at t48hrs) in the ropivacaine group" |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participant, provider, outcome assessor) RCT Sequence generation with computer‐generated list of random numbers Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 90 healthy non‐labouring pregnant women from Maternity Hospital in Sao Paulo, Brazil Operation: caesarean delivery, scheduled (under SA with Pfannenstiel incision) Three groups, size: 30/25/26 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: 30.5 (± 6.7), 31.8 (± 4.5), 29.5 (± 6.7) Only female participants Comorbidities: previous caesarean delivery (%), group 1, 2, 3: 46/48/35. Gestational age in weeks, mean (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: 38 (± 1), 38 (± 1), 38 (± 1.5) | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (placebo/control): TAP block with 20.5 mL 0.9% NaCL per side. Group 2 (bupivacaine TAP): TAP block with 20 mL bupivacaine 0.375% + 0.5 mL NaCl 0.9% per side. Group 3 (bupivacaine + clonidine group): TAP block with 20 mL bupivacaine 0.375% + 75 µg (0.5 mL) clonidine per side All TAP blocks were performed in PACU within 1 h post‐op All groups: spinal anaesthetic with 12 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine, 25 µg fentanyl, 100 µg morphine. IV ketoralac at skin closure. Post‐op analgesia: in PACU, IV morphine as needed; in postpartum unit paracetamol (1 g every 6 h standing) and diclofenac (75 mg every 8 h standing), with tramadol 50 mg as needed Adjuvants: clonidine (group 3 only) Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly reduced morphine use in TAP groups compared to placebo in PACU but no change in resting pain scores. Effective regional anaesthesia: reported. "Block success and dermatomal extent of the sensory analgesia were assessed bilaterally by pinprick after recovery from the spinal anaesthetic". | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3, 6, 12 months Continuous: short‐form McGill Pain questionnaire at 3, 6 and 12 months | |
| Notes | We contacted the study author who provided dichotomous pain data for 3, 6, and 12 months' follow‐up. Funding sources: no financial support was received for the study. Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare no conflict of interest." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a computer‐generated list of random numbers was used (www.randomizer.org) for group allocation of the participants". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "each woman was assigned a study number upon enrolment and received a TAP block with the corresponding numbered syringe. The allocation sequence was concealed from investigators and patients". While it does not state method with which allocation was concealed, it states it was concealed thus little risk of bias. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "an investigator with no clinical involvement in the trial prepared the solutions following exact preparation guidelines. All syringes were labelled with the amount and concentrations of all possible contents, as well as a study number. Both operator [who performed TAP block] and patient were blinded to the study group." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "hyperalgesia was evaluated by the same research investigator (who was not involved in placement or evaluation of the TAP blocks in the PACU)". "At 3, 6, and 12 months, telephone interviews were performed to assess development of chronic postoperative pain using the Short‐Form McGill Pain Questionnaire 2 (SF‐MPQ‐2)". While it does not explicitly state chronic pain assessment was performed by a blinded investigator, based on the other descriptions of how participants were assigned to groups and blinding was maintained, it seems very unlikely the telephone interviewers knew which group they were assigned to. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "five women from [group 2] and 4 women from [group 3] were excluded from the study because of block failure (absence of sensory block on the abdomen assessed by pinprick after recovery from the spinal anesthetic)". No ITT analysis was performed, only per‐protocol. Flow diagram depicts loss of follow‐up for each group at 3‐, 6‐, 12‐month periods, with 2 participants in the control, 6 participants in [group 2] and 5 participants in [group 3] lost at 12 months, and fewer in each group at 3 and 6 months. SF‐36 survey reports "return rate" at each time point in terms of percent but does not provide raw numbers. Discordance between flow diagram and numbers included in analysis in neuropathic pain descriptors (table 4) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol reviewed and primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "the incidence of wound hyperalgesia and the WHI were similar among groups at 24 hours (Fig. 2). At 48 hours, the incidence of wound hyperalgesia was not different among groups". |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participant, provider, outcome assessor) clinical RCT Sequence via computer‐generated list Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 100 men at university hospital in Minnesota, USA Operation: elective radical retropubic prostatectomy 2 groups, size: 50/49 (completed) Age ± SD (group 1, 2): 61.0 (± 7.5), 61.6 (± 7.0) All male participants Exclusion criteria: age < 35 or > 85 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (control): after sedation, lumbar region injected with 1% lidocaine SC in one of lumbar interspaces between 2nd‐5th vertebral bodies. SC injection of sterile saline instead of intrathecal injection into subarachnoid space. Received IV fentanyl citrate bolus (4 µg/kg) immediately after induction, followed by continuous infusion (2 µg/kg/h) until fascial closure. Adjuvants: clonidine Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 months Continuous: numerical pain scale, SF‐36 at 3 months Other reported: none | |
| Notes | Funding sources: not reported Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were randomly assigned by a "computer‐generated list that made assignments based on enrolment number" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "assigned to a treatment group using a sealed envelope" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients and providers were masked to treatment assignments...To maximize masking of the study, a consulting anaesthesiologist familiar with the study but not responsible for the intraoperative care of the patient performed the regional procedure. During this time, the anaesthesiologist for the clinical conduct of anaesthesia left the operating room...the anaesthesia team was blinded to the identity of the bolus and infusion" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients and providers were masked to treatment groups" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | One participant assigned to active block group had severe bradycardia after induction and surgery was cancelled. 3 participants in control group, 2 in active block group could not be reached at 12 weeks. Balanced numbers, low attrition rate, low risk of bias |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "iIntrathecal analgesia improved current, least, and worst pain scores on the day of surgery and current and worst pain scores at 06:00 h the next day." |
| Methods | Single‐blinded (outcome assessor), clinical RCT Sequence generation by random number tables Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 34 adults in a university setting in Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Operation: unilateral inguinal hernia repair 2 groups, size: 15/18 Age: not reported Men/women: not reported Remarks: recurrent hernias or bilateral hernias were excluded | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (spinal): spinal with lidocaine (5% with 7.5% dextrose, volume not reported), postincision: illio‐inguinal block with bupivacaine (0.5%, 8 mL to 10 mL), post‐op regimen not reported Group 2 (control): GA (fentanyl), postincision: illio‐inguinal block with bupivacaine (0.5%, 8‐10 mL), post‐op regimen not reported. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none reported Continuous: health status measured by SF‐36 at 6 months, but without randomization list | |
| Notes | We contacted the study author for missing information on SF‐36 outcome. He provided original data and comments, but regretted that the randomization list was no longer available. Therefore the data could not be included. Funding sources: this study was supported by a grant from the Aetna Foundation, Hartford, Conn, USA. Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was provided. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomization was carried out using a blocked and balanced random number table." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a sealed opaque envelope with the randomization assignment was opened only after the patient had given informed consent for the study." The well‐described method makes bias unlikely. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and caregivers were not blinded, but this is acceptable. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Outcome assessor blinding was not reported, but participants filled out the questionnaire alone. Study author responded: "research assistants collecting the data were blinded as to experimental groups during initial data collection. All data collection was by questionnaire. Research assistants were present for early data collection, but at 6 months I think it was only by mail." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Loss to follow‐up reported, but not assigned to groups or outcomes. Initially 34 participants were recruited, but only 23 questionnaires were collected at 6 months. Participants erroneously assigned to the wrong group were analysed with ITT. Bias is likely due to the unclear group allocation of participants lost to follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Unclear risk | Quote: "twelve (80%) of 15 patients in group 1 and 17 (94%) of 18 in group 2 received pain medication in the PACU (P = .3). In group 1, 10 (67%) of 15 patients received narcotic medication, and 6 (40%) of 15 patients received non‐ narcotic medication. In the group 2, 17 (94%) of 18 received narcotic medication, and 7 (39%) of 18 received nonnarcotic medication (P = .07 for narcotic medication; P > 0.99 for nonnarcotic medication)." No significantly decreased analgesic consumption in the PACU, however pain scores not reported. |
| Methods | Double‐blind, clinical RCT Randomization using "the envelope method" but no report on sequence generation technique. Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 adult participants from university‐affiliated hospital in Turkey Operation: thoracotomy, elective 3 groups, size: 20/20/20 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: 52.20 (± 17.05), 45.00 (± 17.46), 50.9 (± 16.12) Men/women, group 1, 2, 3: 15/5, 15/5, 15/5 Comorbidities: no concomitant disease | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (control): preoperative and intraoperative analgesia with 0.25 µg/kg/h to 0.60 µg/kg/h remifentanil infusion. No epidural analgesic medication before or during operation through epidural catheter Group 2 (incision‐sensitized): preoperative analgesia with 0.25 µg/kg/h to 0.60 µg/kg/h remifentanil infusion. 10 min after surgical incision, epidural admin 10 mL to 15 mL 0.1% levobupivacaine and remifentanil infusion then remifentanil continued for 20 more min for a total of 30 min then 10 mL 0.1% levobupivacaine epidural every 45 min Group 3 (pre‐emptive analgesia group): preop analgesia: 0.1% levobupivacaine 10 mL to 15 mL at 2nd dermatome superior and inferior to incision dermatome (between T4 to T10) through epidural catheter prior to induction. Intraop analgesia: 10 mL 0.1% levobupivacaine epidural injection every 45 min. In all groups epidural catheters were placed preoperatively at 6th‐7th or 7th‐8th thoracic intervals. All received the same GA regimen. Postoperatively all received morphine (3 mg) + fentanyl (50 µg) in 15 mL isotonic solution via epidural route at skin closure and every 12 h for 48 h Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 and 6 months Continuous: VAS score 3 and 6 months Other reported: participant satisfaction levels at discharge and at month 6 | |
| Notes | Presence of chronic pain defined as VAS score > 3. Epidural catheters were placed in all participants, and after placement a 3 mL test dose of 2% lidocaine with 1/200,000 adrenalin was injected. Thus, all participants did receive small amount of lidocaine via epidural catheter. We acknowledge the study author's response on allocation concealment, blinding, source of funding and whether there was any conflict of interest. Funding sources: response from study author, "the authors declare... [their] university... funded this study" Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare... that they have no conflict of interest to the publication of this article..." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomized envelopes drawn "when patient come to operation room a staff get an envelope and open it", from study author |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | On questioning, study author responded "Envelopes are opaque and include equal groups symbols. When patient come to operation room a staff get an envelope and open it." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "double blind" study. When questioned, study author responded "The personal collecting the pain data was not involved in the previous study phases" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the outcome assessor collecting pain levels postoperatively and at 1, 3, 6 months was blinded" says the study author |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "2 patients from control group and 1 patient from preemptive analgesia group died and 1 patient from preemptive analgesia and other one patient from incision sensitized group wound infection were excluded" stated author. "New participants that were compliant with the inclusion criteria were enrolled." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available but all specified outcomes were reported on. |
| Null bias | High risk | Table 3 demonstrates no significant difference in VAS scores between the 3 groups at hours 1, 4, 24 or 48 after surgery |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participant, provider, outcome assessor) placebo‐controlled, clinical RCT Sequence generation method not described Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 40 adults at a teaching hospital in New Taipei City, Taiwan Operation: minimally invasive cardiac surgery (coronary artery bypass performed through left thoracotomy via 4th or 5th intercostal space without cardiopulmonary bypass, valvular surgery through a right lateral thoracotomy via 4th intercostal space with cardiopulmonary bypass) 2 groups, size: 19/19 (actually completed) Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 57.4 (± 15.2), 59.7 (± 13.8) Men/women (group 1, 2): 12/7, 13/6 Remarks: 40 participants were randomized, but 2 were excluded, 1 per group, because of protocol violation Surgery type: coronary artery bypass/valve surgery (group 1, 2): 5/14, 6/13 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (placebo): 10 mL saline infused via catheter at end of operation, continuous infusion saline 2 mL/h x 48 h Group 2 (thoracotomy wound infusion): 10 mL 0.15% bupivacaine infused at end of operation then continuous infusion 2 mL/h x 48 h Both groups had same GA regimen with etomidate, fentanyl, rocuronium and sevoflurane and multi‐orifice catheter placed at a SC layer during wound closure. Post‐op breakthrough analgesia for both groups with IV PCA (morphine 0.5 mg/mL, fentanyl 5 µg/mL, tenoxicam 0.8 mg/mL) basal infusion rate 0.1 mL/h, bolus 1 mL, lockout 15 min. After 72 h, oral or parenteral NSAIDs or opioids were used. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: VAS Other reported: IV PCA consumption in first 72 h post‐op | |
| Notes | Funding sources: source of funding not reported. Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "patients were randomly assigned" but no description of method of randomization or at what time point it was done. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Allocation concealment not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the nurse connecting the infusion bag to the catheter, the surgeons, the patient...were all blinded to the nature of the infusion". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | The nurse evaluating the pain score was blinded to the nature of the infusion. Does not explicitly say, but likely the individual evaluating pain score at 90 days after was also blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 1 participant in each group was excluded as a result of "protocol violation (limited consciousness)". No ITT analysis was done. Did not report on the number of individuals assessed at 3‐month follow‐up time point (or if any lost to follow‐up) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available but primary outcomes specified in paper were fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "not only did the bupivacaine wound infusion reduce pain during the first 48‐hour infusion period, but it also provided reduced pain at 24 hours after cessation of the infusion" |
| Methods | Placebo‐controlled, RCT Sequence generation not described Follow‐up for 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 84 adults in a university setting in Korea Operation: robot‐assisted thyroidectomy 2 groups, size: 41/43 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: not described Men/women, group 1, 2: not described Exclusion criteria: not described | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (lidocaine): after induction of anaesthesia, participants received a bolus of 2 mg/kg of lidocaine intravenously followed by continuous infusion at a rate of 3 mg/kg/h during surgery. Further details of anaesthetic regimen were not provided. Group 2 (control): same as above except 0.9% saline was substituted for lidocaine. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no improvement | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: none Other reported: quality of recovery and pain scores during 24 h and 48 h postoperatively | |
| Notes | Study published only as an abstract. We were unable to obtain additional information about methods, randomization or blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: funding of study not described Conflicts of interest: conflicts of interest statement not provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Patients were "randomly allocated" but no further description of sequence generation was included |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of participants and personnel not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Degree of attrition not described |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Use of subgroup analysis not described |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "pain scores for 2 days after surgery were not different between the two groups." |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant, outcome assessor), RCT Sequence generation not described Follow‐up for 3 and 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 adults in a university setting in Turkey Operation: thoracotomy 3 groups, size: 20/20/20 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: 45.95 (18.248), 51.05 (19.324), 44.35 (19.712) Men/women, group 1, 2, 3: 10/10, 15/5, 11/9 Exclusion criteria: no concomitant systemic disease with functional limitations, ASA III‐IV | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (control): an epidural catheter was inserted using an 18 Ga. Tuohy needle with the help of the negative pressure hanging drop method from the levels of thoracic 6‐7 or thoracic 7‐8 in the preoperative period. Following the determination of epidural catheter, 2 mL 2% lidocaine was applied to cases as a test dose. No IV dexketoprofen and pre‐emptive epidural analgesic medication was applied to cases. Intraoperative analgesia was provided with 50‐100 mcg/h fentanyl citrate and O2/N2O 40% to 60% Pre‐oxygenation was provided for all cases with 6 L/min‐8 L/min 100% O2 (3‐5 min) Following 2 mg/kg propofol induction and the sufficient muscle relaxation that was provided with 0.6 mg/kg‐1 mg/kg rocuronium bromide, the cases were intubated using a double‐lumen endobronchial tube. The area of the endobronchial tube was confirmed with fibreoptic bronchoscopy. The maintenance of the anaesthesia was provided with 6%‐8% desflurane within 45% O2, between MAC 1 to1.5. During one‐lung ventilation (OLV), the amount of oxygen was increased according to the saturation of the case. 50 mcg/h fentanyl and O2 + 50%‐60% N2O were given for the analgesia in the intraoperative period. Dosage of the fentanyl was increased to 100 mcg/h during the OLV. At the end of the operation, 1.5 mg neostigmine and 0.5 mg atropine were applied for the antagonism of the muscle relaxant. Postoperative analgesia was provided with 3 mg morphine + 50 mcg fentanyl within 15 mL 0.9% NaCl through epidural catheter shortly before the operation while stitching the skin sutures. Analgesia of the cases was followed for 48 h and postoperative epidural analgesic fluid was applied at intervals of 12 h. When the VAS score became ≥ 3, an additional dose of postoperative epidural analgesic fluid was applied. Group 2 (pre‐emptive epidural): same GA technique used as above. 10 mL to 15 mL 0.125% levobupivacaine was given to cases in 5 mL with intervals of 5 min pre‐emptively through epidural catheter before the anaesthesia induction to provide the analgesia at two dermatome levels below and above the surgical incision dermatome (T4 to T10). Sufficiency of the analgesia was determined by performing hot‐cold test and the anaesthesia induction was then started. Intraoperative analgesia was provided with 10 mL 0.125% levobupivacaine injection, which was repeated every 60 min through epidural catheter. Group 3 (pre‐emptive epidural and dexketoprofen): same GA technique as described for previous 2 groups. Levobupivacaine applied as described in group 2. In addition, 50 mg dexketoprofen trometamol was given within 100 mL 0.9% NaCl with IV infusion in 15 min, and it was finished 15 min before the surgical incision. Adjuvants: dexketoprofen, morphine, and fentanyl Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: VAS Secondary: participant satisfaction scores at 1, 3, 6 months, surgery duration, and VAS scores and frequency of pain at 1 h, 4 h, 24 h, 48 h, discharge, and 1 month | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: funding of study not described Conflicts of interest: study authors had no conflicts of interest | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Sequence generation for randomization not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the cases, who were not informed about which study group they were included in, were divided into 3 groups ... with the random envelope method" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Sham block was used, however the control group did not receive LA or sham saline loading |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Assesors were masked |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | There was no attrition |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Epidurals that were not effective were excluded from the analysis. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "A statistically significant decrease was determined in the VAS score in Group PED ... compared to the other groups." |
| Methods | Data not available | |
| Participants | Participants: 80 women, ASA II, aged 30‐55, in Italy Operation: central quadrantectomy and reconstruction with Grisotti's inferior dermo‐glandular flap for retroareolar breast cancer 2 groups, size: 40/40 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (tramadol): participants of group 1 were administered tramadol 100 mg/20 mL Group 2 (levobupivacaine): participants of group 2 were administered levobupivacaine 2.5% 20 mL Both groups: perioperative pain management was treated with paracetamol 1000 mg/100 mL postoperatively (3 times/d for 48 h) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: data not available | |
| Outcomes | NRS data not available | |
| Notes | Multiple attempts to contact study author were not successful and thus we were unable to obtain results from study Funding sources: funding source not described Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest statement not given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Sequence generation was not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concelament of allocation was not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of participants and personnel was not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors was not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Data collection and outcomes not described |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Selective reporting not described |
| Null bias | Unclear risk | No results reported |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant, outcome assessor), clinical RCT Sequence generation not described Follow‐up for 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 81 adults in a university setting in Turkey Operation: coronary artery bypass graft 2 groups, size: 40/41 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 64.18 (10.46), 60.22 (13.27) Men/women, group 1, 2: 31/9, 32/9 Exclusion criteria: allergy to any of the study medications, severe renal, pulmonary, liver, or endocrine systemic disease, a history of alcohol or drug abuse, a history of chronic pain, psychiatric problems, or difficulty in communication. During the postoperative period, participants who needed postoperative revision for haemostasis, who had haemodynamic instability or infections, or severe bleeding, or who died were also excluded | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (parasternal block): anaesthesia was induced by etomidate 0.2‐0.5 mg/kg and fentanyl 3 µg/kg in addition to rocuronium 0.9 mg/kg for tracheal intubation. For maintenance of anaesthesia, desflurane 1 MAC, remifentanyl infusion (0.25 µg/kg/min) and rocuronium (0.1 mg/kg/h) following induction was used in both groups. The participants were ventilated with a tidal volume of 6‐8 mL/kg, fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2 ) of 50% in air, the respiratory rate was modulated to keep the end‐tidal carbon dioxide at normal values of 35‐45 mm Hg and adjusted to arterial PCO2 values, and a positive end‐expiratory pressure of 5 cm H2O was applied. Coronary artery bypass graft surgery was initiated with a sternotomy incision. The participants were anticoagulated with 300 U/kg of heparin to provide an activated clotting time (ACT) > 400 s. Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) was started following the cannulation of the aorta and the right atrium. Membrane oxygenators (Terumo Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) were primed with 1000‐1500 mL of Ringer’s lactate to maintain a hematocrit level of 26% ± 2%. A nonpulsatile pump flow was set at 2.2 to 2.4 L/min/m2 to maintain mean arterial pressure between 50 and 70 mmHg. CPB was performed at mild hypothermia with a core temperature of 33°C. Intermittent antegrade cardioplegia was used for myocardial protection. The participants were rewarmed to a temperature of 37°C. When the heart was paced in the atrioventricular sequential mode at a rate of 90 beats/min, the participants were weaned from CPB. Protamine sulfate was used to antagonize the heparin. Before sternal wire placement, sternotomy and mediastinal tube sites were infiltrated with 50 mL of study solution (levobupivacaine 25 mL (chirocaine, 50 mg/10 mL, Abbott Lab) + fentanyl 100 µg + 23 mL saline) by the surgeon. This mixture was infiltrated as follows: bilateral 5 costa levels (underside of them) and every level 2 mL on both sides of the sternum, over sternal periosteum 20 mL and the entrance of chest tubes deep infiltration 10 mL. At the end of the surgery, 1 g paracetamol and 1 mg/kg tramadol were given to all participants. At the end of the surgery, all anaesthetics were discontinued and participants were transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU) where they were mechanically ventilated. The participants were extubated if they met the following criteria: participant awake and responsive to commands, fully warmed with core temperature > 36°C, haemodynamically stable without significant dysrhythmias, well‐perfused with adequate urine output ( > 1.0 mL/kg/h), no active bleeding, respiratory rate 10‐30/min, SpO2 > 95 when 50% oxygen + air. Patients were to receive tramadol infusion with an intravenous PCA device for postoperative analgesia when they came to the ICU. The PCA device was set to deliver a 10 mg/h continuous dose and a 20 mg/h demand dose with a lock‐out interval of 30 min and with a maximum 4‐h limit of 200 mg for every participant. All participants were given additional IV NSAID. Group 2 (control): same anaesthetic regimen as described above except no LA was applied before sternal wire placement. Adjuvants: fentanyl Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: VAS Other reported: presence of allodynia, thermal pain, or dysesthesia, tramadol consumption, cross clamp time, duration of operation, left internal mammary artery harvested or not, duration of mechanical ventilation, haemodynamic parameters, VAS at 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 24, and 48 h postoperatively. | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information regarding continuous pain outcomes or about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Pain on a dichotomous scale was defined as Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs > 12 Funding sources: "no financial support was received for this study." Conflicts of interest: "the author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Sequence generation not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were randomly allocated by opening an envelope ... before the entry in the operating room." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of personnel not specified |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "six months after surgery, an investigator who was blinded to acute pain treatment examined the patients' chronic pain." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No participants were lost to follow‐up and ITT analysis was performed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "parasternal block had a beneficial effect on the management of postoperative acute pain." |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participants, providers, outcome assessors) randomized placebo‐controlled clinical trial Sequence generation was randomized but not described Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 46 female participants at a university hospital in Athens, Greece Operation: modified radical mastectomy or lumpectomy and axillary lymph node dissection 2 groups, size: 23/22 (completed) Age ± SD (group 1, 2): 49 ± 6, 49 ± 8 All female participants Exclusion criteria: age > 60 years Remarks: participants undergoing modified radical mastectomy with axillary node dissection/lumpectomy (group 1, 2): 10/13, 7/15. Participants undergoing chemotherapy post‐op (group 1/2): 16/16. Participants undergoing radiotherapy post‐op (group 1/2): 13/8 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (EMLA): 5 g EMLA to sternal area 5 min before induction. Immediately after extubation 5 g EMLA on supraclavicular area, 10 g around axilla (away from site of incision), then covered with Tegaderm. Same total dose of cream (20 g) applied daily on the 4 days after surgery. Group 2 (control/placebo): exactly the same as above, only placebo cream was used. Both groups received premedication with droperidol and metoclopramide and the same GA technique with thiopental and propofol, sevoflurane and nitrous oxide in O2 with rocuronium. No analgesics were given to either group during surgery. Post‐op analgesia in all participants: 75 mg propoxyphene and 600 mg paracetamol IM as needed x 24 h, then paracetamol oral or paracetamol/codeine oral ± hydroxyzine Adjuvants: propoxyphene Immediate post‐op pain control: no significant improvement in post‐op pain or analgesic consumption. Time to first analgesic requirement was significantly longer in EMLA group | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomus: pain/no pain at 3 months (also broken down by site, including chest wall, arm, axilla) Continous: verbal intensity scale of 0 = no pain to 3 = severe pain at 3 months Other reported: absent/decreased sensation, home analgesic use at 3 months | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the response by the study author providing details on allocation concealment, blinding, and sources of support and conflict of interest statement. Funding sources: study author replied, "the study was funded from Departmental sources only." Conflicts of interest: study author replied, "none of the authors has conflict of interest relevant to the study," | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were randomized before induction of anesthesia using sealed opaque envelopes containing code A or B" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: study author responded "sealed opaque envelopes containing code A or B" were used |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the EMLA or the placebo cream was applied by an anaesthesiologist who was not involved in patients' anaesthesia or data collection. All other anaesthesiologists, anaesthetic or ward nurses, as well as the patient, were not aware of the group of assignment" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "an independent observer who was not involved in patient randomization or anaesthesia administration was assessing and recording pain scores" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | One participant in the EMLA group with cutaneous allergy was excluded and not replaced. Otherwise no other participants lost. No ITT analysis was done, only per‐protocol. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available for review but pre‐specified outcomes within manuscript were reported on. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "The VAS scores at rest and after movement recorded 0, 3, 6, 9, and 24 h, as well as 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 days postoperatively did not differ significantly between the 2 groups" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled randomized clinical trial Sequence generation via "coded envelopes", but not explicitly described Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 100 adult women at a university hospital in Athens, Greece Operation: breast cancer surgery (modified radical mastectomy or lumpectomy + axillary node dissection) 4 groups, size: 23/24/25/24 (completed) Age, group 1, 2, 3,4 (SD not reported): 46, 46, 44, 44 All female participants Exclusion criteria: women over 59 years of age or those who received radiotherapy or chemotherapy preoperatively Number of participants who underwent modified radical mastectomy (group 1, 2, 3, 4): 8, 10, 11, 7. Number of participants who underwent radiotherapy post‐op (group 1, 2, 3, 4): 9, 9, 4, 12. Number of participants who underwent chemotherapy post‐op (group 1, 2, 3, 4): 18, 15, 23, 18 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine and mexiletine): mexiletine 200 mg by mouth evening before surgery and 200 mg twice daily for first 6 post‐op days, brachial plexus infiltrated 12 mL ropivacaine 10 mg/mL and 6 mL 3rd‐5th intercostal spaces after axillary dissection. Group 2 (ropivacaine and placebo): placebo tablet oral evening before surgery and twice daily for first 6 post‐op days, brachial plexus infiltrated 12 mL ropivacaine 10 mg/mL and 6 mL 3rd‐5th intercostal spaces after axillary dissection. Group 3 (placebo and mexiletine): mexiletine 200 mg by mouth evening before surgery and 200 mg twice daily for first 6 post‐op days, brachial plexus infiltrated 12 mL saline and 6 mL 3rd‐5th intercostal spaces after axillary dissection. Group 4 (placebo and placebo): placebo tablet oral evening before surgery and twice daily for first 6 post‐op days, brachial plexus infiltrated 12 mL saline and 6 mL 3rd‐5th intercostal spaces after axillary dissection. All groups received IV metoclopramide and droperidol 5 min before induction. Standardized GA regimen with thiopental, propofol, recouronium, sevoflurane, nitrous oxide in O2. All groups received same post‐op analgesia regimen of 75 mg propoxyphene + 600 mg paracetamol IM every 5 h as needed x first 24 h then post‐op day 2, oral tablet of 10 mg codeine + 400 mg paracetamol every 5 h as needed. Adjuvants: mexiletine (2/4 groups), propoxyphene (4/4 groups) Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption in group 2 compared with all other groups | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 months (also reported by site, including chest, axilla) Continuous: VAS at 3 months Other: absent/decreased sensation, analgesic use at 3 months | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the response by the study author providing details on randomization, allocation concealment, blinding of participants, personnel and outcome assessors as well as sources of support and conflicts of interest. Funding sources: study author responded, "The study was funded from Departmental sources only." Conflicts of interest: study author responded, "None of the authors has conflict of interest relevant to the study," | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | The study author stated, "twenty five opaque envelopes were prepared for each group, each containing a note with [a] code...The night before surgery the anaesthesiologist pulled out one envelop from the bag containing the 100 envelops and according to the code inside administered to the patient the capsule from the jar with the same code" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The study author stated: "twenty five opaque envelopes" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | The study author stated: "patients surgeons and anaesthesiologists ALL were blinded except for an anaesthesiologist not participating in the study" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Study author responded that the outcome assessors were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "four patients failed to complete the protocol and were not replaced. Data are unavailable for chronic follow up of two others". Does not state which group specifically the participants belonged to, but can see the numbers of attrition in each group. Overall low numbers and fairly balanced. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No available protocol but primary outcome specified in manuscript completely reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "regional block reduced the number of intramuscular (IM) injections required the first 24 hours (P = 05), the R +PL group requiring less injections versus the PL + M group (P = .037). Three hours postoperatively, the R +PL group had less pain at rest when compared with all other groups" |
| Methods | Double‐blind (participant, outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random number tables Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 50 adults in a university setting in Athens, Greece Operation: breast surgery (modified radical mastectomy and lumpectomy plus axillary dissection) for breast cancer 2 groups, size: 25/25 Age (group 1, 2): 49 years (SD ± 8.4), 48 (SD ± 8.1) Men/women: 0/50 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (multimodal): GA, brachial plexus irrigation with ropivacaine (0.75%, 10 mL), intercostal ropivacaine (0.75%, 3 mL) at intercostal spaces 3‐5, post‐op for 3 d topical (wound, sternum, axilla) EMLA cream (20 g, 2.5% lidocaine/prilocaine), codeine, paracetamol Group 2 (control): GA, brachial plexus irrigation with normal saline, sham intercostal block at intercostal spaces 3‐5, post‐op for 3 d topical (wound and axilla) placebo cream, codeine, paracetamol Adjuvants: Group 1: gabapentin (400 mg, orally every 6 h starting the night before surgery) for 8 d, Group 2: placebo as above Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain, analgesic consumption at 6 months Continuous: none reported Adverse effects, withdrawal and attrition were reported with group allocation. | |
| Notes | We contacted the study author and we acknowledge the response, providing details on source of funding and conflict of interest. Funding sources: study author responded "the study was funded from Departmental sources only." Conflicts of interest: the study author responded "none of the authors has conflict of interest relevant to the study." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "fifty envelopes, 25 containing odd and 25 containing even numbers, obtained from a computer‐generated table, were prepared and sealed...," this is an adequate description of an acceptable randomization technique. Bias is unlikely. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "an independent anesthesiologist, who did not participate in the study or data collection, read the number contained in the envelope and made group assignments." Bias is unlikely. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "except for the independent anesthesiologist, [not involved in the study] no other physician or nursing staff member was aware of the interventions administered to each patient." "Regarding EMLA cream and possible interference with blinding, EMLA or placebo was applied in the morning after pain assessment"... "pain was assessed by an anesthesiologist blinded to group assignment." "Placebo capsules were identical in appearance with the gabapentin capsules. The same number of capsules was packaged in group‐specific bottles and coded as bottle A and bottle B for the control and treatment groups, respectively. A white odourless cream was the control treatment corresponding to the EMLA cream. Similarly, cream for each group was kept in boxes labelled as A and B for the control and treatment groups, respectively." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "except for the independent anesthesiologist, (not involved in the study) no other physician or nursing staff member was aware of the interventions administered to each patient." "Pain was assessed by an anesthesiologist blinded to group assignment." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Study authors provide a good account of attrition, including group allocation, but considered no ITT analysis: dropouts, participants lost to follow‐up, failures, etc were all excluded. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the treatment group consumed less paracetamol in the PACU... and fewer Lonalgal® tablets... than the controls, exhibited lower visual analog scale scores at rest in the PACU... and on postoperative Days 1, 3, and 5" |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participant, provider, and outcome assessor), placebo controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random number tables Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants 110 adults in a university setting in Greece Operation: laparoscopic cholecystectomy 2 groups, size: 55/55 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 51 years (11.2), 48 (SD ± 12.5) Men/women, group 1, 2: 17/38, 14/41 Exclusion criteria: central nervous system, kidney, or liver disease, chronic pain, or consumption of analgesics and/or calcium channel blockers during the last month | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): premedication was omitted in all cases. In the operating room an 18‐G catheter was inserted in a peripheral vein on the dorsum of the left hand and metoclopramide 10 mg, ranitidine 50 mg, and droperidol 0.75 mg were injected IV before induction of anaesthesia. Pulse oximetry, electrocardiogram, noninvasive blood pressure, inspired and end tidal oxygen concentration, capnography, inspired and end tidal sevoflurane concentration, and neuromuscular block were monitored (Datex Ohmeda S/5TM, Anesthesia Monitor, Helsinki, Finland) (Multistim VARIO, Pajunk, Geisingen, Germany). Participants were preoxygenated for 3 min. Thiopental (5‐6 mg/kg) and fentanyl (2 mg/kg) were administered to induce anaesthesia, followed by rocuronium (0.6 mg/kg) to facilitate tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia was maintained with sevoflurane 2%‐3% inspired concentration in an oxygen nitrous oxide mixture of 1:1 L/min. Diclophenac (75 mg IV) was infused slowly within 30 min before pneumoperitoneum. After induction of anaesthesia and before beginning the operation the surgeon inserted SC a “PAINfusor” multihole catheter 75 mm long (PLAN 1 Health, Baxter, Amaro‐UD, Italy) below and parallel to the subcostal area under aseptic conditions. The catheter was connected to a 130 mL elastomeric pump (Baxter Health‐Care Corporation, Deerfield, IL) delivering fluid at 2 mL/h. The pump was filled with 48 mL of 0.75% ropivacaine under sterile conditions by an anaesthetic nurse not participating in the study and having access to the randomization sets. The infusion was maintained for the first 24 h. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy using the 4‐port technique was performed by the same surgeon in all participants. During the pneumoperitoneum the intra‐abdominal pressure ranged between 12 and 14 mmHg. The total amount of CO2 used was recorded. At the end of the procedure each of the 4 holes was infiltrated with 2 mL of ropivacaine 0.75%. After skin closure residual neuromuscular block was reversed with sugammadex (2 mg/kg), and the participant was extubated and transferred to the PACU. In the PACU, the participants were asked to score their pain using the VAS and received paracetamol IV 1 g if VAS was > 40 mm or if the participant asked for analgesia. If paracetamol was not effective then tramadol (100 mg IV) was administered. Participants who experienced vomiting were given ondansetron 4 mg IV. During the first 48 h postoperatively participants were given paracetamol (400 mg) and codeine (10 mg) (Lonarid tablets) on demand or when the VAS scores exceeded the 40 mm in the VAS 100 mm scale. If the participant experienced nausea/vomiting, then ondansetron (4 mg IV) was given. Group 2 (control): the same intervention as above was used except 0.9% saline was substituted for ropivacaine Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no difference | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: VAS scores Other reported: pain at rest and pain during cough recorded 2, 4, 8, 24, and 48 h postoperatively, paracetamol and tramadol consumption in the PACU and cumulative Lonarid tablets consumption during the first postoperative 48 h, incidence of shoulder pain | |
| Notes | Funding sources: source of funding not stated Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare no conflicts of interest." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomization was carried out by means of a computer‐generated table with 1 set of 55 numbers for the range 1‐110. In a second set the remaining 55 numbers were included corresponding to the control group. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Each number for the ropivacaine and the control group remained unique. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The pump was filled with 48 mL of 0.75% ropivacaine or equal volume of saline 0.9% under sterile conditions by an anesthetic nurse not participating in the study and having access to the randomization sets." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Sham block was used to maintain blinding. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition rates were low and ITT analysis was performed. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not discussed |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "Subcutaneous ropivacaine ...was associated with less pain in the PACU and 4 hours after surgery." |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participant, provider, outcome assessor), clinical RCT Sequence generation was randomized but not described Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 80 participants at a university hospital in Portugal Operation: lumpectomy with axillary dissection, modified radical mastectomy (MRM), and mastectomy with or without axillary dissection 2 groups, size: 40/40 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 55.10 (9.8), 52.68 (8.9) All women Exclusion criteria: allergy to NSAIDs, LAs, propofol, opioids, paracetamol, or antiemetics, participants on chronic treatment with antibiotics, obesity (BMI > 30), bilateral or multiple surgical procedures, contraindication to PVB (including coagulation disorders/anatomical changes), severe respiratory disease, pregnancy, inability to understand the VAS | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine PVB): before the induction of anaesthesia, peripheral route catheterization was performed, and participants were monitored according to ASA standards and bispectral index (BIS) anaesthetic depth. PVB was performed with single‐injection, according to the classic technique at the T4 level with Tuohy needle 18 G, with 0.5% ropivacaine + adrenaline 3 g/mL, with a volume of 0.3 mL/kg (maximum total volume of 30 mL). Subsequently, anaesthesia was induced with propofol (1.5 mg kg−1 h−1) and fentanyl (2 g kg−1) and LMA was inserted. Anaesthesia was induced with propofol (1.5 mg kg−1 h−1) and fentanyl (2g kg−1) and LMA was inserted. The maintenance of anaesthesia was performed in both groups with desflurane to maintain BIS values at 45‐60 with a mixture of O2/air. Both groups received parecoxib 40 mg IV before the start of surgery. During maintenance, fentanyl (1.5 g kg−1) was administered if there was an increase of 20% from baseline values of mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR). For maintenance of haemodynamic stability, ephedrine or atropine was administered, at the anaesthesiologist’s discretion, if verified a decreased in MAP > 20% or HR < 50 beats/min of baseline values. The institutional protocol for the prevention of nausea and vomiting was administered, according to the predictive model by Apfel and colleagues, with three antiemetic intervention lines. At the end of surgery, PCA with morphine was initiated, programmed with bolus of 2 mg on demand and 5 min lock‐out and a maximum dose of 6 mg h−1 during the first 24 h postoperatively. Group 2 (general anaesthesia): same anaesthetic technique as above but no PVB was administered Adjuvants: parecoxib, fentanyl, morphine, and adrenaline Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: none Other reported: anxiety was assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale (HADS), pain at rest according to the VAS score (0‐10), as well as pain with mobilization of the ipsilateral arm interpreted as 90° arm abduction 0 h, 1 h, 6 h, and 24 h after surgery, postoperative nausea and vomiting at 24 hours after surgery | |
| Notes | Pain defined as DN4 score > 4 We acknowledge the study author's response regarding blinding and randomization technique. Funding sources: funding for the study was not described. Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare no conflicts of interest." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | The study author responded, quote: "a stratified randomization was performed using Excel software for that purpose." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The study author responded, quote: " in this study the anesthesiologist who proceeded to the technique became aware of the randomization sequence (in groups of 4 patients) the same day of the procedure." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | The study author responded, quote: " the surgical team did not know the group to which the patient belongs." However, "In the first part of the study (assessment of acute pain in the peri‐operative and up to the first 24 hours) the anesthesiologist who proceeded to the technique knew in which group the patient was." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | The study author responded, quote: "the investigator who interviewed the patients and carried out the records in the peri‐operative period.did not know the group to which the patient belongs." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 14 participants were not included in the final analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | Low risk | "The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) values of paravertebral group at rest were lower throughout the 24 h of study" |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participants, providers, outcome assessors) randomized controlled study Sequence generation by computer‐generated codes Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | 36 participants at Cork University Hospital in Cork, Ireland Operation: mastectomy or wide local excision + axillary node dissection, including sentinel node 2 groups, size: 17/19, all women Age (± SD): 55.9 (± 10.4), 56.8 (± 14.4) | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (lidocaine group): immediately after intubation, IV bolus lidocaine (1.5 mg/kg in 10 min) followed by continuous IV infusion (1.5 mg/kg/h), stopped 60 min after skin closure. Group 2 (control group): immediately after intubation, IV bolus saline followed by continuous IV infusion of saline, stopped 60 min after skin closure. Neither group received preanaesthetic medication. Both groups had the same GA protocol, including propofol and fentanyl for induction, sevoflurane and nitrous oxide in O2 for maintenance. The remaining analgesic regimen was identical between groups, including intraoperative paracetamol 1 g and diclofenac 75 mg IV with morphine as needed and postoperative morphine PCA (1 mg max every 5 min), diclofenac (50 mg oral/rectal every 12 h as needed), paracetamol (1 g oral/rectal every 6 h as needed), tramadol (100 mg IM/oral as needed as rescue) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 months Continuous: short form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF‐MPQ) at 3 months Other reported outcomes: measurement of area of peri‐incisional hyperalgesia, pain catastrophizing scale at 3 months post‐op (broken down by question), Hosptial Anxiety and Depression scale at 3 months post‐op | |
| Notes | Funding Sources: source of funding not stated Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare no conflict of interest." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were randomly allocated to 1 of 2 groups based on computer generated codes" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Codes were, quote: "maintained in sequentially numbered opaque envelopes" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "on the morning of surgery an anaesthetist who was not involved in the patient’s evaluation opened the envelope and prepared either 1% lidocaine or normal saline in coded 50mL syringes. None of the investigators involved in patient management or data collection were aware of the group assignment...The anaesthetist, surgeon, and nursing staff were all blinded to the group allocations" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote:"a dedicated investigator, unaware of the patients’ group assignment" performed the outcome assessments. "None of the investigators involved in patient management or data collection were aware of the group assignment". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | There were no dropouts; all participants randomized were included in the final analysis at 3 months. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | A post‐hoc analysis of preoperative factors comparing participants who did and those who did not develop persistent postsurgical pain was done, but this was specified. The rest of listed outcomes were all reported. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "VAS pain scores at rest, 4 hours postoperatively were less in lidocaine group compared with control group" |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participant, provider, outcome assessor) clinical RCT Sequence generation was randomized but not described Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 45 participants (no age requirement) at a university hospital in Kocaeli, Turkey Operation: iliac crest bone harvesting (surgical procedures included vertebral fusion, fracture grafting and grafting for tumour resection) 3 groups, size: 15/15/15 Age (range), group 1, 2, 3: 46 (16‐70), 48 (18‐71), 51 (19‐73) Men/women, group 1, 2, 3: 5/10, 6/9, 6/9 Comorbidities: vertebral fusion (n), group 1, 2, 3: 6, 5, 6. Fracture grafting (n), group 1, 2, 3: 6, 7, 7. Tumour grafting (n), group 1, 2, 3: 3, 3, 2. | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (control): 20 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride solution via iliac crest catheter within 10 min after surgery Group 2 (bupivacaine only): 20 mL of 0.9% NaCl with 50 mg bupivacaine via iliac crest catheter within 10 min after surgery Group 3 (morphine‐bupivacaine group): 20 mL of 0.9% NaCl solution with 5 mg morphine and 50 mg bupivacaine via iliac crest catheter within 10 min after surgery. All groups: standardized general anaesthesia with thiopental, vecuronium, N2 in O2 and isoflurane. Regional infusions via fine bore epidural catheter at iliac crest donor site, tip between muscle and bone at lateral surface of ilium, started 10 min after surgery. Post‐op pain control: participants requested reinjection of LA at iliac crest when donor site became painful (5 mL 0.9% NaCl with 12.5 mg bupivacaine), morphine PCA 1 mg bolus, 5 min lockout, 4‐h limit 20 mg Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain and dysaesthesia vs none at 3 months post‐op Continuous: none Other reported: none | |
| Notes | Postoperatively, all participants in all groups received reinjection of LA (5 mL NaCl and 12.5 mg bupivacaine) into iliac crest when donor site became painful. Thus, control group did receive some bupivacaine in post‐op period. Average number of injections received reported by group. We acknowledge the response provided by the study author regarding blinding, randomization, allocation concealment and source of funding and conflict of interest statement. Funding sources: the study author reports the study was "not funded by any kind of resource." Conflicts of interest: "the authors have no conflict of interests of any kind (financial, commercial or otherwise)." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Study author responded that he "did a simple randomization; as every second patient was included in group two; every third patient was included in group three, then reversing it as every fourth patient in group three, every fifth patient in group two, every sixth patient in group one; and so on". He did not mention this to his collaborators and he did not perform or attend any surgeries in the study. He did not mention his randomization technique to the other collaborators |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Study author responded, quote: "all the medications had been prepared by senior anesthesiology resident, according to me or my chief residents' instructions. All were prepared in 50 cc identical syringes without any label" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Study author responded they, quote: "blinded both the patients and anaesthesiologists" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Study author states "Dr L.K (anaesthesiologist) did the postoperative (24 hour) evaluation of the patient including VAS score without knowing the group of the patient. He also evaluated patients 12 weeks after the surgery, also without knowing the group of the patient. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcome data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Published report includes all expected outcomes |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the VAS score, analgesic consumption and request for reinjection of local anaesthetic into the donor site in the early postoperative period (24th hour) were significantly higher in the control group than in the other two study groups" |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participants, providers, outcome assessors) randomized placebo‐controlled trial Sequene generation by computer‐generated randomized numbers Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 men from a university hospital in Orebro, Sweden Operation: radical retropubic prostatectomy (for prostatic cancer) 2 groups, size: 28/28 (completed) Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 64.5 (± 4.9), 61.1 (± 4.3) All male participants Exclusion criteria: age > 70 Remarks: Gleason score, median (range), group 1, 2: 6 (5‐9), 6 (5‐9) | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (epidural group): on arrival to PACU, ropivacaine‐fentanyl‐adrenaline epidurally at 10 mL/h, IV PCA with 0.9% saline (bolus dose 1 mL, lockout 6 min, used NRS > 3). Group 2 (placebo group): on arrival to PACU, 0.9% saline via epidural at 10 mL/h, IV PCA with 1 mg/mL morphine (bolus dose 1 mg, lockout 6 min, used NRS > 3). In both groups, preoperative anxiolysis with 10 mg diazepam oral 1 h before scheduled surgery and 1 mg‐2 mg midazolam as needed during catheter placement. Standardized placement of epidural at T10 to 12 interspace, tested using 3 mL mepivacaine 2% with adrenaline then bolus dose of 3 mL to 4 mL mepivacaine 2% with adrenaline. Sensory blockade at T8 level. Standardized GA with propofol (participants 1‐55) or thiopentone (participants 56‐60), fentanyl, rocuronium, nitrous oxide in O2, sevoflurane. Intraoperative analgesia with 2% mepivacaine with 2 mL/h‐5 mL/h adrenaline by epidural infusion in all participants. Immediately before transfer to PACU epidural infusion was turned off. In PACU, nurse allowed to administer 1 mg‐2mg morphine bolus as needed if NRS > 5. 1 g paracetamol oral before surgery and every 6 h post‐op during hospitalization. Adjuvants: adrenaline Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: SF‐36 at 3 months Adverse effects: postoperative nausea, vomiting, sedation and bleeding were reported | |
| Notes | We contacted study author for clarification on attrition, source of funding and conflict of interest but received no response. Funding sources: source of funding not reported. Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest statement not provided. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "computer‐generated randomized numbers", randomized "after successful insertion of the epidural catheter" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "every precaution was taken to achieve double blinding...hospital pharmacy sent two double‐blinded bags" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patients and surgeons, anaesthesiologists and nurses involved in patient treatment were unaware of method of analgesia and every precaution was taken to achieve double blinding" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the SF‐36 was given before and 1 and 3 months after the operation to each patient". Participants, as well as providers, were blinded and the participants filled out the questionnaire themselves |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 60 participants were randomized, 4 participants were excluded after randomization with reasons and group assignments listed and balanced between groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "median pain at rest at the incision site was low (< 4) and significantly lower in group E compared with group P at 4–24 h after the operation" |
| Methods | Blinded (PACU nurses, outcome assessor), controlled, randomized clinical trial Computer‐generated randomization in blocks of 2 using sealed, opaque envelopes Follow‐up: 5 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 40 adults in a university hospital setting in Albacete, Spain Operation: radical mastectomy and conservative breast surgery for breast cancer 2 groups, size: 20/20 Age: not reported Men/women: 0/40 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preoperative PVB): single shot PVB at T4 with ropivacaine (0.5% without epinephrine, 25 mL to 30 mL, doses maximum 150 mg; using nerve stimulations according to Naja but only one single injection), GA (LMA using sevoflurane and remifentanil 0.05 to 0.1 mcg/kg/min only in the first 20‐30 min), post‐op: intravenous morphine (0.1 mg/kg), dexketoprofen 50 mg IV plus 25 mg every 8 h as needed for pain and paracetamol (1 g every 6 h) Group 2 (no block): no block, GA (LMA using sevoflurane and remifentanil 0.05 mcg/kg/min to 0. 02 mcg/kg/min), post‐op: IV morphine (0.1 mg/kg), dexketoprofen 50 mg IV plus 25 mg every 8 h as needed for pain and paracetamol (1 g every 6 h) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: number of participants with pain (including detailed number per group on myofascial pain, breast phantom pain or neuropathic pain) at 3 and 5 months per group Continuous: not reported Effective regional anaesthesia: one participant had an unsuccessful block but was NOT excluded, yet PVBs did not reduced the severity of postoperative pain. | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the study author's response regarding randomization, allocation concealment and blinding, dosing and attrition Funding sources: source of funding not stated Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest not reported | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “computer generated list”, “randomization in blocks of two”. Low risk of bias |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “patients were assigned as they arrived in the preoperative clinic”, “The anaesthesiologist [enrolling the participant] did not know in which group the patient was going to be enrolled”. “The anaesthesiologist [in the OR] did not know the group allocation, until the patient reached the operating room.” “The randomization number was included in the chart in a sealed opaque envelope.” Low risk of bias |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: “the recovery room nurses did not know the anaesthetic technique used in each case.” “The surgeon knew” if a block was performed. Participants were not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “the outcome observer conducting the interview did not know the group allocation.” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | The numbers excluded in each group for radiotherapy and lost to follow‐up, respectively are unclear. Significant attrition with unclear group allocation may have caused bias, but no ITT analysis considered. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Expected primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "no significant differences in acute pain were observed" |
| Methods | Double‐blind (participants and outcome assessor), sham epidural‐controlled, clinical RCT Sequence generation was randomized, but not described Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 114 adults in a university setting in Beijing, China Operation: posterolateral thoracotomy for lung and oesophageal disease 2 groups, size: 57/57 Age (group 1, 2): 61.80 years (SD ± 13.78), 61.41 (SD ± 11.78) Men/women (group 1, 2): 41/13, 38/15 (completed the protocol) Remarks: pulmonary/oesophageal operation (group 1, 2): 28/26, 25/28 7 participants with dislodged catheters were excluded. | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preincision epidural): epidural at T6/7/8, preincision epidural ropivacaine (0.5%, bolus 5 mL to 10 mL), GA (fentanyl), post‐op for 72 h PCEA (0.125% bupivacaine + 0.05 mg/mL morphine + 0.02 mg/mL droperidol, basal 3 mL/h, demand 3 mL, lock out 15 min). Group 2 (control/cryotherapy): sham epidural at T6/7/8, GA (fentanyl), cryoalgesia, post‐op for 72 h PCA through sham epidural (SC, 1 mg/mL morphine, demand 2 mL, lock‐out in 30 min, no basal) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not significant | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 6 and 12 months Continuous: not reported Secondary: allodynia at 6 and 12 months | |
| Notes | Funding sources: study supported by grants from Research and Development Foundation of Peking University People's Hospital Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Patients were stratified by disease sites (lung or oesophagus), and blinded randomized to receive either epidural analgesia (Epidural Group, Group E) or intercostal nerve cryoanalgesia (Cryo Group, Group C), in order to ensure that both groups had comparable operation methods." Randomization method not detailed, but otherwise well documented. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants unaware of allocation, concealment of allocation for providers described: "After obtaining ... written informed consent from the prospective patient cases, 114 physical status I or II patients scheduled for posterolateral thoracotomy for lung or oesophagus diseases were enrolled in the study." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Intraoperative anaesthesia providers were not blinded. An effort was made to blind study participants. Quote: "in order to make the patients blinded to the analgesic method, SC infusion catheters were inserted at upper back (T7‐8 level) in Group C." This is acceptable, bias is unlikely. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Outcome assessor "who was blinded to the postoperative pain management, interviewed patients by telephone, using a standard questionnaire." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Attrition was reported, but no ITT analysis was considered. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No protocol was available, but pre‐specified outcomes within manuscript were all reported on. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "no statistically significant differences were found between the two groups with respect to NRS pain scores at rest or on motion within three days following surgery" |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participant, providers, outcome assessor), sham‐ and placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation was not described Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 adults in a university setting in Helsinki, Finland Operation: conservative breast surgery with sentinel lymph node biopsy for cancer 2 groups, size: 30/30 Age: not reported Men/women: 0/60 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preincision PVB): single shot PVB at T3 with bupivacaine (0.5%, 1.5 mL/kg), GA, post‐op: oral ibuprofen (10 mg/kg) and paracetamol (1 g, 3 x daily ) rescue analgesia: paracetamol (500 mg with codeine 30 mg) or tramadol (50‐100 mg) Group 2 (sham PVB): sham PVB at T3 with normal saline, GA, post‐op: oral ibuprofen (10 mg/kg) and paracetamol (1 g, 3 x daily) rescue analgesia: paracetamol (500 mg with codeine 30 mg) or tramadol (50‐100 mg) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: NRS larger 3 at 6 and at 12 months, use of pain medication at 6 and 12 months Continuous: pain at rest and in motion reported as NRS, number of pain descriptors, all at 6 and 12 months Effective regional anaesthesia not reported, but treatment reduced the severity of postoperative pain and oxycodone consumption, postoperatively | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the study author's response regarding randomization and allocation concealment Funding sources: source of funding not reported Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest statement not provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants "were randomly assigned." Sequence generation was "randomized", "performed in a randomized fashion", but the exact method of randomization was not explained. The study author responded "The randomization was done using the opaque sealed envelope method." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Allocation concealment not described in the original report |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patients and the study anaesthesiologists who performed the analysis remained blinded to the use of PVB with bupivacaine or a sham block throughout the entire study period." "Procedure behind a drape curtain" The study author responded, also that "the patient, the anaesthesiologist providing anaesthesia and the staff taking care of the patient were blinded to the study group. The curtains and drapes were hung so that the block was performed behind the curtains on the back side of the patient while the patient's head and front side and her nurse were on the other side of the curtains. The anaesthesiologist and nursing staff giving general anaesthesia were blinded to the study group..." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patients and the study anaesthesiologists who performed the analysis remained blinded to the use of PVB with bupivacaine or a sham block throughout the entire study period.", "telephone interviews by a blinded interviewer." "A group‐blinded study assistant conducted all telephone interviews." The study author responded also that "A non‐medical study assistant blinded to the study group performed the follow‐up telephone interviews at predestined time points up to 12 months postoperatively". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition explained in detail, ITT analysis performed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Primary outcomes fully reported |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the patients given PVB with bupivacaine had less postoperative pain, as indicated by longer times to first analgesic dose, lower VAS scores, and 40% smaller oxycodone consumption in the PACU... On the first postoperative day, the number of patients who experienced continuous aching pain and pain at rest was significantly smaller in the PVB group" |
| Methods | Double‐blind (participants, outcome assessor) placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation was randomized Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 65 adults in a university setting in Patras, Greece Operation: lower limb amputation with pain score > 60/100 VAS 48 h prior to amputation 5 groups, group size: 13 Age: group means ranging 69.2 to 74.3 with largest SD 13 Men/women: 35/53 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (Epi/Epi/Epi): preop: lumbar epidural analgesia bupivacaine (0.2%, fentanyl 2 µg/mL at 4 mL/h to 8 mL/h) for 48 h, GA preincision: epidural bupivacaine (0.5% 10 mL to 15 mL, fentanyl 100 µg), post‐op epidural bupivacaine (0.2% fentanyl 2 µg/mL at 4 mL/h to 8 mL/h) Group 2 (PCA/Epi/Epi): preop: PCA fentanyl (IV, demand 25 µg, lockout 20 min), preincision: epidural bupivacaine (0.5% 10 mL to 15 mL, fentanyl 100 µg), post‐op epidural bupivacaine (0.2%, fentanyl 2 µg/mL at 4 mL/h to 8 mL/h) Group 3 (PCA/Epi/PCA): preop: PCA fentanyl (IV, demand 25 µg, lockout 20 min), preincision: epidural bupivacaine (0.5% 10 mL to 15 mL, fentanyl 100 µg), post‐op PCA fentanyl (IV, demand 25 µg, lockout 20 min) Group 4 (PCA/GA/PCA): preop: PCA fentanyl (IV, demand 25 µg, lockout 20 min), general anaesthesia with LMA, sevoflurane and remifentanil infusion, post‐op PCA fentanyl (IV, demand 25 µg, lockout 20 min) Group 5 (control/GA/control): preop: meperidine (50 mg 4‐6 x/d IM) paracetamol/codeine 30/500 mg orally plus as‐needed IV paracetamol 650 mg 3 x/d and parecoxib 40 mg 2 x/d, GA with LMA, sevoflurane and remifentanil infusion, post‐op: meperidine (IM) paracetamol/codeine 30/500 mg orally plus as‐needed IV paracetamol 650 mg 3 x/d and parecoxib 40 mg 2 x/d Immediate pain control: significantly improved preop and post‐op | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: phantom limb pain at 6 months Continuous: VAS and McGill pain questionnaire and phantom limb pain frequency scores for phantom and stump pain at 6 months Effective regional anaesthesia not reported, but interventions reduced the severity of pain pre‐ and postoperatively. | |
| Notes | There are minor discrepancies regarding the dosing described between the preliminary report of the ongoing registered trial (Karanikolas 2006) and the final report. We reported the treatment according to the latest publication. We contacted the study author for confirmation and additional information, but received no response. Hence, we could only use the data extracted from the publications and the information provided on clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00443404. Funding sources: "support was provided solely from institutional and/or departmental sources." Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Described as "prospective, randomized, clinical trial", with “computer generated blocks with five treatment groups and 13 patients per group.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “sequentially numbered sealed envelope... concealed until after consent was obtain.” Recruitment, outcome assessment and protocol management clearly separated. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | The trial is described as "double‐blind" in the title. Detailed description of blinding procedures. Quote: “control group patients had an epidural catheter placed subcutaneously.” D.A. i.e. the person “responsible for adjusting the epidural...” may not have been blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Detailed description of blinding procedures. Quote: “a second blinded investigator interviewed all participants.” “A third blinded investigator conducted all interviews during the analgesic protocol.” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Only minor attrition is reported, and attributed to groups. Seemingly, attrition affected mainly the control groups. ITT analysis is reported. Per protocol or ITT analysis did not change results. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol review and primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "all patients had severe ischemic pain before analgesia started, but pain scores improved markedly and were significantly lower in all intervention groups compared with control at all times while the protocol was in effect" |
| Methods | Blinded (outcome assessor), RCT Sequence generation by computer‐generated allocation number Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 180 adult women in University Hospital in Hong Kong, China Operation: modified radical mastectomy (including axillary lymph node clearance) 3 groups, size: 60, 57, 60 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: 51 (± 9), 54 (± 9), 53 (± 8) All female participants | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (GA group): standardized GA as described below Group 2 (GA + single shot PVB + placebo infusion): pre‐op thoracic paravertebral catheter placed opposite third thoracic spine, ipsilateral to side of surgery, ropivacaine (2 mg/kg) + epinephrine (5 µg/mL) in total volume of 20 mL with normal saline injected slowly then epidural catheter inserted into thoracic paravertebral space. Intraoperatively, continuous infusion of 0.9% saline started at 0.10 mL/kg/h via catheter and maintained constant until 72 h post‐op. Group 3 (GA+ PVB): pre‐op thoracic paravertebral catheter placed opposite third thoracic spine, ipsilateral to side of surgery, ropivacaine (2 mg/kg) + epinephrine (5 µg/mL) in total volume of 20 mL with normal saline injected slowly then epidural catheter inserted into thoracic paravertebral space. Intraoperatively, continuous infusion of ropivacaine 0.25% started at 0.10 mL/kg/h via catheter, maintained constant until 72 h post‐op. All participants had standardized GA, which included IV fentanyl, propofol and rocuronium. Intraoperative morphine (0.1 mg/kg) IV to every participant, then morphine (1 mg IV) as needed, ondansetron 4 mg IV 30 min before end of surgery. In the PACU, all participants had nurse‐administered IV morphine for rescue analgesia as needed. On post‐op ward, analgesia was with diclofenac (75 mg) oral 2 x 72 h, IM morphine (0.1 mg/kg, as needed every 3 h) or Dologesic (paracetamol 325 mg and dextropropoxyphene 32.5 mg, 2 tablets as needed every 6 h) as rescue. Adjuvants: none Immediate pain control: not significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: incidence of chronic pain at all sites (operated site, axilla, arm) and over operated site at 3 and 6 months Continuous: chronic pain scores at rest and on movement at all sites (operated site, axilla, arm) and over operated site at 3 and 6 months Other reported outcomes: HRQOL (Chinese‐HK version of SF‐36) at 3 and 6 months, Chronic pain symptom and sign score at 3 and 6 months, physical health summary score, mental health summary score (of SF‐36) at 3 and 6 months | |
| Notes | Funding sources: this research work was fully funded by a grant from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China (RGC reference no. CUHK4406/05, project code 2140452). Conflicts of interest: the study authors declare no conflict of interest | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were randomized to 1 of 3 study groups... with a computer‐generated allocation number" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "sequentially numbered, coded, sealed opaque envelopes...The sealed envelopes were prepared by a third party (research assistant) who took no further part in the study" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients in group1, who had received standardized GA with no paravertebral intervention, could not be blinded for obvious reasons..For the other 2 study groups that had a thoracic paravertebral catheter placed, we adopted a double‐blind methodology... The principal investigator performed all the thoracic paravertebral catheter placements, collected procedural data, injected the ropivacaine bolus for the TPVB [thoracic paravertebral block], conducted the GA, and took no further part in data collection.. The paravertebral infusion (ropivacaine 0.25% or 0.9% saline) was prepared.. by a postanaesthetic care unit (PACU) nurse not involved in the study ... A single surgeon, who was also blinded to the group allocation, performed or supervised all the surgical procedures" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a research nurse blinded to the group allocation recorded data preoperatively, in the PACU, and at regular intervals in the postoperative ward...The telephone interview at 3 and 6 months after surgery was also conducted by the same research nurse (blind to group allocation)" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the primary analyses were performed on a modified intention‐to‐ treat basis (i.e., patients were analysed according to their randomized allocated groups but were excluded from the analysis if they did not adhere to the protocol after randomization)". 1 participant lost to follow‐up in group 2 and reason given (returned overseas after surgery). 2 excluded from the analysis in group 2 because of protocol violation/diagnosed contralateral breast cancer. Very small numbers of attrition, with reasons reported for each exclusion and modified ITT protocol used. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All primary outcomes in protocol were fully reported on |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "there was no significant difference in acute pain scores at rest (Fig. 2) or on movement (Fig. 3) between the study groups (both P = 0.22) during the 72 hours after surgery". |
| Methods | clinical RCT Sequence generation randomized, but not described Follow‐up: one year | |
| Participants | Participants: 45 adults in a university setting in Athens, Greece Operation: lower limb amputation 3 groups, size: 15/12/18 Age: not reported Men/women: not reported | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preoperative epidural): for 72 h preop: bupivacaine (0.25% and morphine) via epidural catheter (level not specified), (intraop anaesthesia not specified), post‐op for 72 h epidural bupivacaine infusion (not specified) Group 2 (post‐op epidural): for 72 h preop: opioids and NSAIDs (not specified), (intraop anaesthesia not specified), post‐op for 72 h epidural bupivacaine infusion (not specified) Group 3 (control): for 72 h preop: opioids and NSAID (not specified), (intraop anaesthesia not specified), post‐op opioids and NSAIDs (not specified) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not reported, phantom pain risk not significantly reduced for the first three days | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: phantom limb pain at 6 and 12 months Continuous: none reported | |
| Notes | We were unable to find the contact information for any of the authors using Google and PubMed or the institution and therefore no additional information beyond the abstract could be obtained or extracted. Funding sources: no source of funding reported. Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement given. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Patients were "randomly allocated", but the exact method was not explained. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation was not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding was not reported in the abstract. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding was not reported in the abstract. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Attrition is not reported. ITT analysis is not mentioned. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No protocol available for review and only abstract available |
| Null bias | Unclear risk | Immediate post‐op pain control not reported, however phantom pain risk not significantly reduced for the first three days. |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participants, providers, outcome assessors), sham/placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation was by random number tables Follow‐up: 18 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 30 adults in a university setting in Toronto, Ontario, Canada Operation: lateral thoracotomy for pulmonary or oesophageal disease 2 groups, size: 15/15 Age (group 1, 2): 54.6 years (range 19‐75), 58.9 (range 46‐72) Men/women (group 1, 2): 5/10, 8/7 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preincision intercostal block): placebo rectal suppository, intramuscular midazolam (0.05 per kg), GA (fentanyl 1 µg/kg), preincision intercostal nerve block with bupivacaine (0.5% with epinephrine (1:200.000), 3 mL/interspace) 2 spaces above and below planned incision, post‐op for 72 h PCA morphine (demand 1.5 mg‐2 mg, lockout 6 min, max dose 30 mg/4 h) Group 2 (sham/placebo block): IM morphine (0.15 mg/kg) and perphenazine (0.03 mg/kg), indomethacin (100 mg, rectal suppository), GA (fentanyl 1 µg/kg), preincision sham intercostal nerve block with normal saline (3 mL/level) 2 spaces above and below planned incision, post‐op for 72 h PCA morphine (demand 1.5 mg‐2 mg, lockout 6 min, max dose 30 mg/4 h) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: initial analgesic consumption reduced | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain and analgesic consumption at 18 months Continuous: verbal rating scale at 18 months Secondary: allodynia at 6 and 12 months | |
| Notes | We contacted the study author for missing information. He provided a data table with unpublished data from the follow‐up study to Kavanagh 1994, the second manuscript reporting on (Katz 1996). Funding sources: "this study was supported by a research scholarship from the Medical Research Council of Canada (MRC) and by MRC grant MT‐12052 to Dr Katz." Conflicts of interest: a conflict of interest statement was not given. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a table of random numbers was used to allocate patients." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "..investigator (who had no further involvement with that patient) who administered the medications in accordance with the instructions in the envelope...". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patients and all other personnel involved in subsequent patient management and assessment were completely blinded as to group allocation, ...thus maintain the blind and (patients) also received a placebo rectal suppository." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "other personnel involved in subsequent patient management and assessment were completely blinded as to group allocation...,thus maintain the blind..." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Attrition was described with regards to group allocation. Per‐participant analysis was performed, with no ITT analysis considered. Bias is unlikely, as an ITT analysis would not alter the lack of the statistical significance. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "in the original study, use of preemptive multimodal analgesia during surgery was not found to be more effective than the placebo in reducing the intensity of acute postoperative pain" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded, placebo/sham‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 152 adults in a university setting in Toronto, Canada Operation: laparotomy for major gynaecological surgery 3 groups, size: 49/56/47 Age: 44 years (SD ± 8.9), 47 (SD ± 10.6), 44 (SD ± 9.6) Men/women: women only | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preincisional epidural): epidural catheter at L2/3/4 tested, GA, preincision: lidocaine (2% with epinephrine (1:200,000), 12 mL plus 0.8 mL for each 2.5cm (1 inch) of height above 152cm (60 inch), plus 4 µg/kg fentanyl), 40 min after incision epidural normal saline (12 mL), post‐op morphine PCA (loading dose 4 mg, then bolus 1.0‐1.5 mg, lockout time 5 min, max 40 mg in 4 h, no basal rate) Group 2 (postincision epidural): epidural catheter at L2/3/4 tested, GA, preincision: epidural normal saline (12 mL), 40 min after incision: lidocaine (2% with epinephrine (1:200,000), 12 mL plus 0.8 mL for each inch of height above 60 inch, plus 4 µg/kg fentanyl), post‐op morphine PCA (loading dose 4 mg, then bolus 1.0‐1.5 mg, lockout time 5 min, max 40 mg in 4 h, no basal rate) Group 3 (sham epidural): sham epidural catheter at L2/3/4 tested, GA (fentanyl 1 µg/kg), preincision: epidural normal saline (12 mL), 40 min after incision epidural normal saline (12 mL), post‐op morphine PCA (loading dose 4 mg, then bolus 1.0‐1.5 mg, lockout time 5 min, max 40 mg in 4 h, no basal rate) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not significant | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 6 months, analgesic consumption at 6 months Continuous: Pain Disability Index, Mental Health Inventory‐18 and McGill Pain Questionnaire at 6 months Secondary: allodynia/hyperalgesia | |
| Notes | Funding sources: supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the Canadian Institutes of Health. Conflicts of interest: conflicts of interest were not reported. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “a randomization schedule was computer generated by a biostatistician.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "an opaque envelope containing the patient number and group assignment was prepared, sealed, and numbered for each patient by the hospital pharmacist, not involved in the study otherwise...All patients and personnel involved in patient management and data collection were unaware of the group to which the patient had been allocated. The anesthesiologist in charge of the case was aware of group allocation for control group patients and was not involved in postoperative management or data collection." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all patients and personnel involved in patient management and data collection were unaware of the group to which the patient had been allocated. The anaesthesiologist in charge of the case was aware of group allocation for control group patients and was not involved in postoperative management or data collection." but the anaesthesiologist in charge of the case was aware of group allocation for control group participants. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "neither the person conducting the interview nor the patient was aware of the group to which the patient had been assigned," "personnel involved in ... data collection were unaware of the group to which the patient had been allocated." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "both an intention to treat analysis and a protocol‐compliant analysis were performed." "There was no appreciable difference in the results of the intention‐to‐treat analyses and the protocol compliant analyses. Data and results of significance tests reported below are therefore based on the intention to treat analyses." But ITT was only done for early outcomes, not for questionnaire data at 6 months, when significant attrition occurred. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "preincisional administration of epidural lidocaine and fentanyl was associated with a significantly lower rate of morphine use, lower cumulative morphine consumption, and reduced hyperalgesia compared with a sham epidural condition" |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participants, providers and outcome assessors) placebo‐controlled, group sequential clinical trial Sequence generation with computer‐generated block sequences Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 357 adult participants underwent 403 hernia operations at a teaching hospital in Lucerne, Switzerland Operation: single‐ or double‐sided primary or recurrent inguinal hernia repair 2 groups, participant population size: 162/174 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 50 (± 16), 51 (± 15) Men/women, group 1, 2: 145/8, 161/8 Comorbidities: unilateral/bilateral hernia (n), group 1, 2: 148/14, 162/12 Primary/recurrent hernia (n), group 1, 2: 167/14, 186/12 Remarks: the unit of analysis published was the hernia not the participant | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (placebo): "operative procedures were performed under general or SA at the request of the patient". After closure of the incision, infiltration of 20 mL saline 0.9% in specified region Group 2 (intervention): "operative procedures were performed under general or SA at the request of the patient". After closure of the incision, infiltration of 20 mL bupivacaine 0.25% in specified region Both groups: infiltration started with the laterocranial puncture 1 finger below and 1 finger medial to the anterior superior iliac spine at the lateral end of the incision; 10 mL of study drug was injected in a fan‐shaped manner lateral to and 4 mL medial to the laterocranial puncture. The mediocaudal puncture was located directly above the pubic tubercle; 4 mL of study drug were injected in a fan‐shaped manner lateral to and 2 mL medial to the mediocaudal puncture. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 (and at 12 months, but not published) Continuous: VAS at rest, with various types of movements at 3 and 12 months Other: quality of life at 1 year, neuralgia at 3 and 12 months | |
| Notes | Unit of analysis was the hernia in the original publication. The study authors provided additional information on methodological quality. Absorbed lidocaine from 1 hernia may have mitigated the chronic pain for the other hernia in those with discordant randomization, i.e. participants undergoing bilateral hernia repair in whom one side was treated while the other was not. Funding sources: funding provided by NIH grant NCT00484731 Conflicts of interest: Drs Anita Kurmann, Henning Fischer, Salome Dell‐Kuster, Rachel Rosenthal, Laurent Audigé, Guido Schüpfer, Jürg Metzger, and Philipp Honigmann have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the randomization, based on computer‐generated block randomization sequences, was performed in a 1:1 ratio between investigational and control arms" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the hospital pharmacy provided similar‐looking syringes containing either bupivacaine 0.25% or saline 0.9% solution according to the randomization sequence". In the protocol states the syringes are numbered according to "randomization sequence that is kept confidential" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patient, surgeon, and the physician performing the examinations during follow‐up visits were blinded to the treatment" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patient, surgeon, and the physician performing the examinations during follow‐up visits were blinded to the treatment. Unblinding was performed after completion of the analysis as described in the study protocol". Sham techniques would make it difficult for the practitioner to know which group he or she was working with. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Loss to follow‐up was 16% in intervention group and 11.2% in the placebo group at 3 months post‐op for primary endpoint. One participant was excluded from placebo group because syringe became unsterile. Participants were excluded retrospectively because did not meet inclusion criteria. Numbers lost to follow‐up at each stage clearly delineated. ITT analysis was done, with exception of 1 participant excluded from placebo group described above. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Protocol available and reviewed. Primary outcome of pain at 3 months measured by VAS was fully reported on |
| Null bias | Unclear risk | No data on immediate postoperative pain control. |
| Methods | Placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up for 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 36 adults in a university setting in Alberta, Canada Operation: unilateral total breast mastectomy +/‐ axillary lymph node dissection 2 groups, size: 18/18 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 4: 63.9 years (16.7), 60.2 (13.1) All women Exclusion criteria: not specified | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (PVB): participants received an ultrasound‐guided PVB (regional anaesthetic not specified) or combined with a multimodal regimen consisting of propofol‐based total intravenous anaesthesia with ketorolac, gabapentin, ranitidine, paracetamol, and ondansetron. Group 2 (control): same intervention as above except sham block was substituted for local anaesthesia. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no improvement | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: none Other reported: propofol and fentanyl consumption, postoperative morphine equivalent consumption, frequency of postoperative nausea and vomiting | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: funding for the study not reported Conflicts of interest: there was no statement on conflict of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "following patient allocation with a computer‐generated sequence..." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "consenting patients were randomized to either the treatment group or the control group via sealed envelopes" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Sham block was used and participants were well blinded. No comment on personnel blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Degree of attrition not described |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis noted |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "pain scores were similar at all time points within the first 24 hours" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant, outcome assessor), placebo/sham‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up for 12 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 85 adults in a university setting in Brussels, Belgium Operation: colonic resection (xiphopubic incision) of rectal adenocarcinoma 4 groups, size: 20/20/20/20 Age (group 1, 2, 3, 4): 53 years (SD ± 8), 54 (SD ± 8), 55 (SD ± 8), 53 (SD ± 10) Men/women (total: group 1, 2, 3, 4): 49/31: 12/8, 13/7, 12/8, 12/8 Remarks: intraoperative discovery of an extended tumour resulted in participants' exclusion from the study. | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (IV/IV): epidural catheter at T8, GA (sufentanil 2.5 µg) IV (lidocaine 2 mg/kg + 0.5 mg/kg/h, clonidine 4 µg/kg + 1 µg/kg/h, sufentanil 0.1 µg/kg + 0.07 µg/kg/h) post‐op IV PCA (lidocaine bolus per request 7.5 mg, clonidine bolus per request 15 µg, morphine bolus per request 1.3 mg) (0.75 mL solution per demand, lockout time 7 min, max 15 mL per 4 h) Group 2 (IV/epidural): epidural catheter at T8, GA (sufentanil 2.5 µg); IV (lidocaine 2 mg/kg + 0.5 mg/kg/h, clonidine 4 µg/kg + 1 µg/kg/h, sufentanil 0.1 µg/kg + 0.07 µg/kg/h), before recovery (epidural bolus 7 mL bupivacaine 0.5%, clonidine 1 µg/kg, sufentanil 0.03 µg/kg) post‐op epidural PCEA (bupivacaine 5 mL 0.0675% + 5 mL/h 0.0675%, clonidine 3.5 µg + 3.5 µg/kg/h, sufentanil 0.05 µg + 0.05 µg/h) (continuous infusion of 5 mL and bolus of 5 mL on request, 40 min lockout time) Group 3 (epidural/epidural): epidural catheter at T8, GA (sufentanil 2.5 µg), preincision epidural (bupivacaine 7 mL 0.5% + 5 mL/h 0.125%, clonidine 1 µg/kg + 0.5 µg/kg/h, sufentanil 0.03 µg/kg + sufentanil 0.015 g/kg/h) post‐op epidural PCEA (bupivacaine 5 mL 0.0675% + 5 mL/h 0.0675%, clonidine 3.5 µg + 3.5 µg/kg/h, sufentanil 0.05 µg + 0.05 µg/h) (continuous infusion of 5 mL and bolus of 5 mL on request, 40 min lockout time) Group 4 (epidural/IV): epidural catheter at T8, GA (sufentanil 2.5 µg), preincision epidural (bupivacaine 7 mL 0.5% + 5 mL/h 0.125%, clonidine 1 µg/kg + 0.5 µg/kg/h, sufentanil 0.03 µg/kg + sufentanil 0.015 g/kg/h), post‐op IV PCA (lidocaine bolus per request 7.5 mg, clonidine bolus per request 15 µg, morphine bolus per request 1.3 mg) (0.75 mL solution per demand, lockout time 7 min, max 15 mL per 4 h) Adjuvants: ketamine from skin incision to the end of surgery (0.5 mg/kg bolus followed by continuous infusion at 0.25 mg/kg/h), clonidine as detailed above Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 6 and 12 months Continuous: Pain Disability Index at 6 months, Mental Health Inventory‐18 at 6 months Secondary: punctuate wound hyperalgesia was reported for the first 72 h | |
| Notes | We contacted the study authors for missing data and they responded, but with some data inconsistencies that could not be verified or corrected. The study authors reported an unusually high success rate of epidural analgesia with only 2 failures in 60 participants. Funding sources: "support was provided solely from institutional and/or departmental sources." Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "according to a computer‐generated table of random number assignments, each patient was assigned to one of four double‐blinded groups." Bias is unlikely. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | The timing of allocation and concealment not detailed. Risk of bias is unclear. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "all of the analgesic solutions were prepared by an anesthesiologist who was not involved in the patients' care." Testing the epidural in the PACU "prevented a true double blinding in the postoperative period." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | However, (quote:) "postoperative parameters were recorded by an anesthesiologist who was not aware of the intraoperative treatment administered to the patient", "mobilization assessed by a blinded observer", telephone interviews were "performed by the research nurse." The study author responded: " the research nurse (outcome assessor) was blinded to the group allocation ..." as there was no random code on questionnaire. Bias is unlikely. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Adverse effects and attrition were reported with group allocation. “Absence of thermoanalgesia level as well as intraoperative discovery of an extended tumor resulted in the patient’s exclusion from the study.” ”One was excluded during surgery after discovery of widespread neoplastic disease, and two other patients were excluded for postoperative early dislocation of epidural catheter (before 72‐h follow‐up).” “... one who died of a cardiac arrest at home 2 months" before completion. Results reported on a per‐participant basis, with no ITT analysis considered. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "patients in group 1 (intravenous–intravenous) experienced significantly more severe pain than patients in the three other groups. Cumulative number of satisfied analgesic requirements was significantly higher in group 1 (intravenous–intravenous) than in the other groups " |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participants, provider, outcome assessor), placebo/sham‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 92 adults in a university setting in Brussels, Belgium Operation: elective caesarean section (Pfannenstiel incision) 3 groups, size: 30/30/30 Age (group 1, 2, 3): 33 years (SD ± 5), 31 (SD ± 5), 31 (SD ± 6) Men/women: 0/92 Remarks: no previous caesarean delivery | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): spinal bupivacaine (1.8‐2 mL hyperbaric 0.5%, sufentanil 1 µg/kg), post‐op for 48 h continuous wound irrigation (ropivacaine (0.2%, 5 mL/h), every 12 h diclofenac (75 mg in 50 mL/20 min)), PCA (morphine, no basal rate, demand 1 mg, lockout 5 min, max 25 mg/4 h), as needed paracetamol (1 g/6 h) Group 2 (diclofenac): spinal bupivacaine (1.8 mL‐2 mL hyperbaric 0.5%, sufentanil 1 µg/kg), post‐op for 48 h continuous wound irrigation (diclofenac (300 mg in 240 mL, 5 mL/h) IV saline 50 mL/20 min every 12 h), PCA (morphine, no basal rate, demand 1 mg, lockout 5 min, max 25 mg/4 h), as needed paracetamol (1 g/6 h) Group 3 (saline): spinal bupivacaine (1.8 mL to 2 mL hyperbaric 0.5%, sufentanil 1 µg/kg), post‐op for 48 h continuous wound irrigation (saline (5 mL/h), every 12 h diclofenac (75 mg in 50 mL/20 min)), PCA (morphine, no basal rate, demand 1 mg, lockout 5 min, max 25 mg/4 h), as needed paracetamol (1 g/6 h) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: pain and analgesic consumption significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: "chronic postsurgical pain" and scar/wound pain at 6 months Continuous: none reported Secondary: punctuate wound hyperalgesia for the first 48 h. Analgesic consumption at 6 months. Wound healing and complications such as hypotension, nausea or vomiting | |
| Notes | The study author responded to our request for clarification, but with information differing from the published data. Funding sources: "support was provided solely from institutional and/or departmental sources." Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement was given. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "...according to a randomized, prospective, blinded protocol...The parturients were randomly assigned using computer‐generated random numbers..." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Allocation concealment was not explicitly described. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patient, the person in charge of perioperative management,... were not aware of the patient group assignment." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the staff involved in data collection were not aware of the patient group assignment." The study author responded to our inquiry that "the research nurse was blinded to the group allocation‐ there was no code on the questionnaire, she used." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | A per‐participant analysis was performed, with no attrition reported. But the study author responded: "patients were excluded from the data analysis (intraoperative failure of intrathecal anaesthesia and intra‐wound catheter out, which did not allow a 48h postoperative follow up). We continued the inclusion of patients following the randomisation and at the end of the random list, we add 1 patient in ropivacaine group and 1 patient in diclofenac group (in the same order than those patients were excluded from the study).” Even though no formal ITT analysis was performed, only 2/90 participants were excluded, reducing the likelihood of bias. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study protocol not available but published report includes all the expected outcomes. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "for the first 12 h after surgery, patients receiving a subcutaneous infusion of ropivacaine reported lower VAS pain scores at rest and during movement than those receiving local saline infusion... Wound infiltration with ropivacaine was also more effective than saline to relieve visceral pain at 12 h after surgery." |
| Methods | Single‐blinded (outcome assessor) clinical RCT Sequence generation using random numbers table Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 51 adults in a university setting in Cork, Ireland Operation: breast surgery (mastectomy or breast tumour resection) with axillary node clearance 2 groups, size: 26/25 Age, years (± SD), group 1, 2 : 57.8 (± 14.5), 54.3 (± 11.5) Men/women: all women Comorbidities: wide local excision/mastectomy/mastectomy and reconstruction, n (group 1, 2): 16/9/1, 13/11/1. Chemotherapy, n (group 1, 2): 13, 18. Further surgery, n: None/wide local excision/mastectomy/wide local excision and mastectomy (group 1, 2): 18/4/1/3, 18/3/2/2. Remarks: exclusion criteria included pre‐existing pain conditions other than those due to breast lump biopsy | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (Group C, control): as needed morphine IV intro. Post‐op morphine 2 mg IV as needed in PACU until morphine PCA x 48 h post‐op (2 mg bolus, 5 min lockout, no background, max dose 30 mg 4 h), diclofenac 50 mg oral/PR every 8 h as needed, paracetamol 1 g oral/PR/IV every 6 h as needed Group 2 (Group P, paracetamol and paravertebral): paravertebral catheter inserted prior to induction, 10 mL bupivacaine 0.25% injected with repeat aspiration tests then catheter inserted. 10 mL bupivacaine 0.25% 4 h post‐op then every 12 h x 48 h Both groups: GA induction with propofol 2‐2.5 mg/kg, maintenance with sevoflurane in O2/N2O mixture, vecuronium with 75 mg IV diclofenac sodium and 1 g IV paracetamol intraoperatively. All participants received 100 mg tramadol oral as rescue if required. Adjuvants: pregabalin Immediate post‐op pain control: not significantly improved, but with significantly decreased analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 months Continuous: Short‐form McGill Pain questionnaire at 3 months Secondary: Hospital Anxiety and Depression score, Spielberger Tate‐Trait Anxiety Inventory at 3 months, allodynia/hyperalgesia | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "PL received a research grant from the South of Ireland Association of Anaesthetists." Conflicts of interest: "nothing to declare" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "using a random numbers table, patients were randomly allocated to one of two groups" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Upon contacting study author: quote: "these pieces of paper were then placed in opaque sealed numbered envelopes" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Upon contacting study author: quote: "the envelopes were not opened until all study information was gathered and data analysis had begun" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were interviewed three months postoperatively...by an investigator blinded to their group assignment" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No participants were lost to follow‐up. ITT analysis performed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes were reported on. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "patients in the two groups were similar in terms of reported pain intensity in the early postoperative period," |
| Methods | Assessor‐blinded, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation not described Follow‐up for 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 120 adults in a university setting in China Operation: open thoracotomy 2 groups, size: 60/60 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 61 (10), 58 (10) Men/women, group 1, 2: 33/27, 36/24 Exclusion criteria: paralysis, known allergy to LAs, active bacterial infection, clinically severe liver or kidney diseases, neurologic dysfunction, chronic use of systemic lidocaine, NSAIDs or opioids, insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus and para‐aminobenzoic acid | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine wound infusion): the moment participants entered the operating room, standard monitoring was performed by 5‐lead electrocardiography, pulse oximetry, and non‐invasive arterial pressure measurement. GA was induced with midazolam at 0.05 mg/kg, propofol at 1.5 mg/kg to 2.5 mg/kg and fentanyl at 3 µg/kg. When loss of consciousness was confirmed, a bolus of 0.8 mg/kg rocuronium was intravenously injected for tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia was maintained with continuous infusion of propofol and a bolus of fentanyl at 1 µg/kg/h to 2 µg/kg/h in order to keep the bispectral index monitor (BIS, Aspect 1000, Aspect Medical System Inc., Natick, MA, USA) between 40 and 60. Neuromuscular blockade was conducted by continuous infusion of cis‐atracurium at 0.06‐0.07 mg/kg/h. Participants in both groups were accessible to rescue analgesia via pethidine, if needed, during the postoperative period. The catheter was positioned in the SC tissues above the fascia along the inferior edge of the rib along the incision. The catheter consisted of a multi‐orifice tube that was connected to an elastomeric infusion pump (Beijing tech‐bio‐med medical equipment Corporation, China) for postoperative continuous SC infusion with an anaesthetic at the end of surgery. After skin closure, the infusion pump containing 0.5% ropivacaine (Naropin®‐produced by AstraZeneca) was connected, and the wound was infused at 2 mL/h. Group 2 (control): same intervention induction procedure as above. No catheter was inserted. Sufentanil was injected intravenously via an analgesia pump after surgery, followed by intravenous PCA with sufentanil at 2 mL/h Adjuvants: fentanyl Immediate post‐op pain control: no difference | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: none Secondary: the level of sedation, severity of pain at rest and movement, the amount of opioid analgesics administered, and participants’ satisfaction with their postoperative pain management | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: "this work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Jinling Hospital." Conflicts of interest: the study authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Randomization technique not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Allocation of concealment not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Blinding of participants and personnel not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "postoperative evaluations were performed by an observer blind to this study." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | There was a substantial degree of attrition. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | ITT principle was used and no subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote "There were no statistical differences in the VAS scores... between the two groups" |
| Methods | Double‐blind (participant, outcome assessor) randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated table Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 69 adult women at university hospital in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada Operation: elective caesarean delivery with low transverse incision (under SA) 2 groups, size: 33/33 (completed) Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 35 (± 3), 34 (± 5) All female participants Comorbidities: number of multiparous women (group 1, 2): 25/21 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (intrathecal morphine): 100 µg intrathecal morphine at time of spinal insertion. At end of surgery, sham TAP block with capped needle pushing against skin Group 2 (TAP block): no intrathecal morphine was given. At the end of surgery, TAP block 5 mL increments of ropivacaine into transversus abdominis plane on each side (0.5% ropivacaine, 1.5 mg/kg on each side to max of 100 mg (20 mL)) Both groups received standardized SA with 0.75% hyperbaric bupivacaine 11.25 mg + fentanyl 10 µg and at the end of surgery, rectal naproxen 500 mg + paracetamol 975 mg. Both had same post‐op analgesia regimen with 500 mg naproxen every 12 h standing, oral hydromorphone 2 mg‐4 mg every 4 h as needed with IV PCA (bolus 1.5 mg, lockout 7 min, max 10 mg/h) if needed Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: pain scores were higher in participants receiving a TAP block at all time points but this was only significant at 10 h; statistically significant increase in morphine consumption 24 h post‐op in TAP group, but not at earlier time point | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain "in the operative area" at 3 months Continuous: none Adverse events: incidence of wound infection, nausea/vomiting, pruritus, sedation | |
| Notes | We contacted the study author for clarification on participant flow details, but received no response. Funding sources: "the authors received no external funding for this project." Conflicts of interest: "Dr Joanne Douglas is an Editor of the International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia. She had no involvement with the editorial process or decision to accept this article." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomly assigned using "computer‐generated table" after consent and enrolment |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "group allocation was concealed in an opaque envelope until the woman was consented and enrolled" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "women, postoperative care providers..were blinded to treatment group...The anaesthesiologist caring for the woman, as well as the anaesthesiologist performing the TAP block, were not blinded". Bias during operation by non‐blinded providers possible, e.g. by administering additional morphine, but not very likely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "women, postoperative care providers and research staff collecting postoperative data were blinded to treatment group" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 69 women were randomized, but 1 in intrathecal morphine group and 2 in TAP group were excluded because of protocol violation. 3‐month follow‐up was obtained from 31 (of 33) in group 1 and 28 (of 33) in group 2. Numbers of attrition provided per group, fairly balanced. However, numbers presented in text do not match the numbers presented in the flow chart (reversed groups) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcome in protocol fully reported on. Investigator left the study and this led to premature termination of the study before the intended time. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "pain scores on rest and movement were higher in the TAP block group at all times although this only reached statistical significance at 10 h (P = 0.001)" |
| Methods | Placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation was randomized Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 105 adults in a university setting in Guangdong, China Operation: thoracotomy for tumour resection 3 groups, size randomized (completed): 36 (32)/36 (30)/33 (28) Age (median group 1, 2, 3): 57, 55, 59 years Men/women (group 1, 2, 3): 24/8, 18/12, 20/8 Remarks: 2 participants excluded intraop, 13 participants excluded post‐op with group allocation not specified | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preincision epidural): epidural at T7/8, 3 mL 1% lidocaine (test dose), preincision 10 mL ropivacaine (0.25%, with morphine 0.2 mg/mL) epidurally, GA, post‐op 2 mL/h (0.15% ropivacaine and 1.5 µg/kg/mL morphine) epidurally for 48 h, additional analgesics and rescue medication not described Group 2 (post‐op epidural): epidural at T7/8, 3 mL 1% lidocaine (test dose), GA, post‐op 2 mL/h (0.15% ropivacaine and 1.5 µg/kg/mL morphine) epidurally for 48 h, additional analgesics and rescue medication not described Group 3 (control): GA (0.1 mg fentanyl), post‐op IV fentanyl (0.25 µg/kg/mL at basal 2 mL/h + 0.05 mg/mL demand) for 48 h, additional analgesics and rescue medication not described Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 3 and 6 months Continuous: not reported | |
| Notes | Article published in Mandarin. Data extracted from the abstract and tables, methodological information extracted with the help of a Mandarin‐speaking statistician. Funding sources: source of funding not reported Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest statement not given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | The allocation was by "random numbers generation". Bias is unlikely. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Allocation concealment was not described. Bias is possible, but unclear |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "the attending physician called the patient". No detail provided neither in the English abstract nor the Mandarin methods section. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "the attending physician called the patient". No detail provided neither in the English abstract nor the Mandarin methods section. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Attrition was described with reasons, but it is unclear what the reasons for the attrition were in each group. Attrition was larger in control group. No ITT analysis described. Bias is likely. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available, primary outcomes specified in text fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "VAS scores in the first 48h after operation were significantly lower in group PE and group E than in the group IV (P < 0.05)" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant, outcome assessor) randomized placebo‐controlled clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 74 pregnant women from university hospital in Halifax, Canada Operation: scheduled caesarean delivery (planned SA) 2 groups, size: 35/39 (completed) Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 32.1 (± 5.3), 31.4 (± 5.8) All female participants Comorbidities: gravidity (n) 1/2/3/4/5, group 1, 2: 1/1/11/16/5, 2/1/12/15/9; parity (n) 0/1/2/3, group 1, 2: 7/21/7/0, 10/18/10/1 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): at conclusion of surgery, 20 mL 0.25% ropivacaine injected deep to tissue fascial plane between interior oblique and transversus abdominis Group 2 (placebo): at conclusion of surgery, 20 mL 0.9% saline injected deep to tissue fascial plane between interior oblique and transversus abdominis. All participants received antacid prophylaxis. Standardized spinal anaesthetic technique hyperbaric bupivacaine, fentanyl, morphine. At conclusion of procedure, ketorolac, ondansetron, paracetamol and bilateral TAP blocks under ultrasound. Post‐op pain control with naproxen 250 mg every 8 h, paracetamol 1 g every 6 h, and oxycodone 2.5 mg‐5mg every 6 h as needed. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no significant decrease in pain or morphine consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: SF‐36 Other: adverse effects reported on include nausea, vomiting, pruritus, urine retention | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the study author's response that no dichotomous pain data were collected at 6 months, only SF‐36 Funding sources: "Dr McKeen acknowledges the support of the Canadian Anesthesiologists’ Society (CAS) GE Healthcare Canada Research Award in Perioperative Imaging Operating Grant. Dr George held an IWK Recruitment & Establishment Grant and acknowledges the support of a CAS Career Scientist Award. Dr Allen held a Canadian Institutes of Health Research New Investigator Award and a Dalhousie University Clinical Research Scholar Award. Dr Pink acknowledges Dalhousie University Medical Research Foundation Summer Research Studentship Funding." Conflicts of interest: "none declared" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "computer‐generated block randomized table. Blocks were permuted at ten patients per block with equal allocation of patients between the two groups" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "sealed opaque envelopes" labelled with a study number based on order of recruitment with randomization to 1 of two groups (A or B) inside envelope. The pharmacy supplied sterile blinded study drug syringes labelled TAP Block Study Drug ‘‘A’’ or ‘‘B’’ |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | The pharmacy supplied sterile blinded study drug syringes labelled TAP Block Study Drug ‘‘A’’ or ‘‘B’’. Quote: "prior to each patient’s discharge from the PACU (once spinal motor block had regressed), one of the investigators (D.M. or R.G.) assessed the adequacy of the TAP." This was only known after the participant had left the PACU and was receiving the same ward orders no matter what group. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "research personnel unaware of the patients’ randomization or adequacy of block assessment collected data until the patients left the PACU (minimum two hours), then 24 h and 48 h postoperatively via a ward visit... research personnel contacted patients via telephone at 30 days and six months to complete a five minute Short Form‐36 Health Survey (SF‐36)" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Balanced, low rates of attrition between groups. Reasons for exclusion/missing data are listed for each group. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Quote: "trial registration was not congruent with the final study protocol and did not include cumulative opioid consumption at 24 h postoperatively as a primary outcome". However, this value was not statistically significant and did not add effect to their results, thus low risk of reporting bias. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "pain scores at 24 hr were slightly higher in the TAP 0.25% ropivacaine group. These differences were not statistically significant" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 35 adults in a hospital setting, Athens, Greece Operation: modified radical mastectomy with axillary dissection Groups, size: 17/18 Age: not specified All female participants, 13/7 Comorbidities: none included | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): intra‐op: infiltration before wound closure with 10 mL ropivacaine 7.5 mg/mL. 3 mL of the solution was infiltrated around the route sheath of brachial plexus and the rest of it in the 1st‐7th intercostal spaces. Group 2 (saline): intra‐op: same method as above with infiltration of saline Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no difference | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomus: pain questionnaire at 6 months Continuous: none Other reported: none Adverse events: none reported | |
| Notes | Funding sources: no explanation of financial support Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest statement was not provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Response from study author: "Randomisation was done by means of a computer generated table" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Response from study author: "Mrs Vassi was the only person throughout the study period that was aware of the allocation group. She didn’t participate in any other part of the study pre‐ or postoperatively nor did she have any contact with the patients at any time." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Response from study author: "The anaesthesiologists in the operating room were unaware of the allocation group and so was the surgeon." The participants were also unaware of their group allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Response from study author: "...the record of the pain medicines administered and the telephone contact 6 months postoperatively were performed by me, who I was unaware of the study group throughout the study period." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "thirty‐five patients were enrolled in the study and six of them were excluded (failure to be contacted by phone)." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "no difference was documented...in chronic neuropathic pain." "Ropivacaine infiltration does not seem to attenuate chronic neuropathic pain...after modified radical mastectomy." |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation unclear Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: men in a military teaching hospital in Rabat, Morocco Operation: inguinal hernia repair groups, size: 20/22 Age: years (range ): 46 ± 5; 40 ± 4 Men/women (group 1, 2): 20/0; 22/0 Comorbidities (group 1, 2, 3): none reported Remarks: only ASA I and II | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (bupivacaine wound infiltration): spinal (12.5 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine + 25 µg fentanyl, intrathecally), postincision SC infiltration of the skin with bupivacaine (0.5%, 20 mL), post‐op 1 g paracetamol, ketoprofen (100 mg), morphine 3 mg as needed for breakthrough pain Group 2 (saline/placebo wound infiltration): spinal (12.5 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine + 25 µg fentanyl, intrathecally), postincision SC infiltration of the skin with saline (0.9%, 20 mL), post‐op 1 g paracetamol, ketoprofen (100 mg), morphine 3 mg as needed for breakthrough pain Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 and 6 months, (pain differentiated in mild, moderate and severe) Continuous: none Secondary: | |
| Notes | The report leaves it unclear if postoperative analgesics were given intravenously or orally. We contacted the study author for clarification of randomisation, allocation and blinding methods, but did not get a response. Funding sources: no funding sources specified Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest declared | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “etude prospective randomisee”, (prospective randomized trial) “La randomisation etait realise au cours de la visite preanesethesique par envelopes cachetees et numerotees...” (the randomization was realized during the preoperative visit with numbered and sealed envelopes) Even so the study is reportedly "randomized", the randomization method is not explained, hence bias is possible. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “la randomisation etait realise au cours de la visite preanesethesique par envelopes cachetees et numerotees...” It is unclear if and how and how long the allocation was concealed to the person enrolling the participants or to the anaesthesia provider. Bias is therefore possible. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: “l’anesthesiste remettait au chirurgien une seringue”, “le chirurgien, qui ignorait la solution de infiltration”, (The anesthesiologist passed a syringe to the surgeon, ... the surgeon did not know the solutions to be infiltrated.) Possibly no blinding of the anaesthesia providers, but participant and surgeon were blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote:” a six mois" "evaluee grace a un questionnaire rempli par tous les patients lors de leur consultation de chirurgie de controle?”. (at six months ... evaluated by a questionnaire filled out by all participants during their surgical follow‐up visit) The outcome observer (surgeon) was blinded and the outcome was reported with the use of a questionnaire. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | The uneven numbers of 22 and 20 in both groups leaves open the possibility of an error in the allocation process, cross over, attrition or incorrect randomisation and this is not addressed in the report. Bias seems still unlikely, due to the low attrition. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "there was a significant reduction of postoperative pain in the bupivacaine group at rest as well as with coughing" |
| Methods | Single‐blind (outcome assessor), RCT Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 67 women aged 18‐50 years, gestational age 37‐42 at hospital setting in Lisbon, Portugal Operation: elective caesarean section delivery (with Pfannenstiel incision) Groups, size: 29/29 Age (years ± SD; group 1, group 2): 33 ± 5, 33 ± 5 Men/women (group 1, 2): 0/29, 0/29 Primary caesarean delivery (n, group 1/2): 25/24 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (continuous wound infusion group): anaesthesia was performed through SAB with hyperbaric bupivacaine and sufentanil with single‐shot SA. Intra‐op: catheter placed in wound below fascia after peritoneum closed, 10 mL ropivacaine 10 mg/mL injected during wound closure, then continuous infusion ropivacaine 2 mg/mL at 5 mL/h for 48 h Group 2 (epidural morphine): anaesthesia initiated with combined spinal‐epidural technique to site epidural catheter, single‐shot SA. Intra‐op: upon partial recovery from motor blockade (Bromage score 2), initiated 2 mg/10 mL bolus epidural morphine every 12 h (x 4 times). Neither group received any preanaesthetic medication. Both received standardized post‐op analgesia with paracetamol 1 g every 6 h x 48 h, breakthrough pain (VAS > 3) with IM diclofenac 75 mg every 6 h as needed, ondansetron 4 mg IV for nausea or vomiting as needed Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: presence or absence of "residual pain related to the scar or pain that the patient related to caesarean delivery" at 3 months Dichotomus: none Other reported: neurologic sequelae (paraesthesia, tactile hyperaesthesia), surgical wound healing impairment, surgical wound infection, impact on care provided to newborn/relationship, satisfaction score all at 3 months Adverse events: nausea, vomiting and anti‐emetic therapy requirements, incidence of pruritus, urinary retention, sedation, incidence of neurologic alterations (paraesthesia, tactile hyperaesthesia, headache) | |
| Notes | Because no events were detected in either arm, we could not include the study in the meta‐analysis. Funding sources: "Dr Patricia O'Neill received speaker fees from Baxter Healthscore in 2010. B. Brain and Baxter were contacted simultaneously by authors to provide devices to perform the study. B Braun declined and Baxter showed interest and provided the devices for the study. Dr O'Neill helped design the study, conduct the study, analyse the data and write the manuscript and was paid by the company providing the devices for the study, to speak, after the study was finished being conducted but the results were not yet published. All four other authors reported no conflict of interest." Conflicts of interest: "we do not see a conflict of interest for the authors and no risk of bias of undue sponsor influence." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "computer‐generated random number list" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: " list concealed in an opaque envelope". Randomization was done after consent and prior to initiation of anaesthesia. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | The intraoperative and postoperative anaesthesia managers were not blinded, nor were the surgeons, This is acceptable for inclusion. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Three months after discharge, patients were interviewed by telephone by an investigator blinded to group assignment". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Per protocol analysis done, no ITT analysis. Number of participants in each group who were excluded is given, as well as the reasons for exclusion (e.g. accidental removal of catheter, did not receive allocated intervention, etc). Low overall attrition, fairly balanced numbers between groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes listed in manuscript completely reported on. No protocol available for review. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Pain scores (quote:) "at rest at 2, 6, and 48 hours were lower in the continuous wound infusion group than in the epidural morphine group... (pain scores) evaluated at mobilization were higher in the epidural morphine group at 2 and 6 hours" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation unclear Follow‐up: 4‐6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 40 adults in a university setting, Nashville, TN, USA Operation: ICBG for spinal fusion Groups, size: 20/20 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 66 (± 12), 62 (± 8) Men/women (group 1, 2): 13/7, 13/7 Comorbidities: tobacco use, group 1, 2 (18, 16); alcohol use, group 1, 2 (7, 6) | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (bupivacaine): intra‐op: rectangular window of approximately 4 × 1 cm was created in the cortex of the posterior superior iliac spine using osteotomes and was then hinged open to allow access to cancellous bone. After graft harvest, a gel foam soaked in 10 mL 0.25% bupivacaine was packed into the wound. The cortical bone window was replaced and the wound closed. Group 2 (saline): intra‐op: same method of gel‐foam packing into cortex of posterior superior iliac spine. Gel was soaked in 10 mL 0.9% saline. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: not reported | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: VAS at 4‐6 months Dichotomus: none Other reported: surgical data included the type of surgery, surgical indication, number of levels fused, the use of instrumentation, and the operative time. Health outcomes were back and neck pain, satisfaction with surgical results, and mental/physical states as determined by the Short Form‐12. Adverse events: 1 participant in the saline group had infection | |
| Notes | The reported continuous data were insufficient for inclusion in the additional Bayesian inclusive analysis. Funding sources: "the authors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose." Conflicts of interest: conflicts of interest statement not provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "a block randomization scheme was used," but the method of randomization was not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a sealed envelope containing the group assignment was opened and the appropriate intervention was performed" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Participants and surgeons were blinded, but knowledge of anaesthesia team not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all forms were administered and collected by a research nurse without knowledge of the assigned group" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 19/20 in the treatment group and 17/20 in the control group completed the final evaluation. Quote: "this met the goal of 17 patients per group as determined from the sample size calculation." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The protocol defined the VAS at 3 months as the primary outcome, but it remained unclear from the manuscript if the pain was recorded at rest or at movement and if the current or the average pain was the initial primary outcome. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Experimental treatment was effective in improving immediate postoperative pain control for some outcome measures at least. |
| Methods | Randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by "simple random sampling" Follow‐up for 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 90 adults in a university setting in Turkey Operation: inguinal herniorrhaphy 3 groups, size: 30/30/30 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: not described Men/women, group 1, 2, 3: not described Exclusion criteria: not described | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (spinal): SAB was administered. Further detail about anaesthetic regimen and timing of intervention was not provided. Group 2 (TAP): in addition to SAB, TAP block was performed. No additional detail about anaesthetic regimen or timing of intervention provided. Group 3 (IINB): in addition to SAB, ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block was performed. No additional detail about anaesthetic regimen or timing of intervention provided. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: NRS score Other reported: NRS score and amount of analgesia given in perioperative period | |
| Notes | Published only as abstract. We were unable to obtain data on pain outcomes or additional information about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: funding of study not described Conflicts of interest: the study authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Sequence generation by, quote: "simple random sampling" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of participants and personnel not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Rate of attrition not described |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear if subgroup analysis performed |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "NRS scores ... in TAP block were significantly smaller in all measurements..."." |
| Methods | Double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation "at random", but not described Follow‐up: 12 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 70 adults from a university setting in Belfast, Northern Ireland Operation: vasectomy for contraception 2 groups, size: 70 total, (group size not given) Age: years (range ): 35 years (range 26‐45), 34 years (28‐45) Men/women: 70/0 Remarks: in the intervention group, body sides were randomized to receive treatment or placebo. | |
| Interventions | Group 1a (intervention, body side treated): GA, intraop: bupivacaine (0.5% 1 mL) injected into the lumen of the vas deferens, post‐op NSAID Group 1b (intervention, placebo body side): GA, intraop: normal saline injected into the lumen of the vas deferens, post‐op NSAID Group 2 (control, both sides): GA, intraop: no injection, post‐op NSAID Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: testicular discomfort at 12 months Continuous: duration of testicular discomfort Secondary: none | |
| Notes | No available contact info to email study author to inquire about study sponsorship Funding sources: source of funding not reported Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "randomly....at random..," but exact method of sequence generation not reported. Still, with excellent description of allocation concealment and blinding, we judge that bias is unlikely. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation was done after education and enrolment, (it remains unclear when the vas deferens side was randomized, but this is unlikely to cause bias.) Bias is unlikely. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Bias during operation by non‐blinded providers possible, e.g. by administering additional fentanyl, but not very likely. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all the replies were analysed by one of the authors who was unaware of the treatment". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: "the questionnaire was valid for 61 (91%) patients only." Six participants did not respond and "...three were excluded because of development of wound infection and scrotal haematoma." A per‐participant analysis was performed, withdrawals and attrition were reported, but allocation to groups or subgroup was not reported. Bias is likely, but unlikely to change the result of the study. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available but all specified outcomes were reported on. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the VAS scores for pain on days 1..were significantly lower on the side of the bupivacaine infiltration in the treatment group compared with the saline side of this group and the control group" |
| Methods | Double‐, possibly triple‐blind (participant, provider and possibly outcome assessor), placebo/sham‐controlled randomized clinical trial Sequence generation "with use of a table of random numbers" Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 21 adults, at a university setting, Chicago, Illinois, USA Operation: lower limb amputation because of ischaemic necrosis secondary to peripheral vascular disease 2 groups, size: 11/10 Age: 68.3 years (SD ± 12.96) Men/women: 10/11 Comorbidities: diabetes mellitus in 9 participants | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (treatment): GA or spinal, post‐op nerve sheath irrigation (bupivacaine 0.5%, 1 mL/h) and PCA (morphine, no basal rate, demand 2 mg, lockout 15 min, max 30 mg/4 h) for 72 h Group 2 (placebo): GA or spinal, post‐op nerve sheath irrigation (normal saline, 1 mL/h) and PCA (morphine, no basal rate, demand 2 mg, lockout 15 min, max 30 mg/4 h) for 72 h Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 6 months Continuous: McGill Pain Questionnaire at 6 months Secondary: none | |
| Notes | Reported data not allocated to groups. No graphics that reported data. We contacted the study author for missing information and outcome data. He responded that the data were not accessible. Hence, outcome data could not be included. Funding sources: "no benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. No funds were received in support of this study." Conflicts of interest: no conflicts of interest statement given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were 'divided into two groups with use of a table of random numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patients and the staff were blinded to the contents of the bag, which were known only to the research pharmacist." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Outcome assessor blinding was not described, but (quote:) "the patients and the staff were blinded to the contents of the bag, which were known only to the research pharmacist." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | The study authors report on attrition, (2 participants died, 5 did not participate in the questionnaire), but patients lost to follow up were neither allocated to groups nor considered for an ITT analysis. The authors found no statistically meaningful difference in phantom pain, but it remains unclear which participant numbers were taken as the basis for their analysis. An ITT analysis would likely only have confirmed the lack of significance, however. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes appropriately reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the patients in Group A used significantly less morphine during the first and second days after the operation than did those in Group B" |
| Methods | Randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 adults in a university setting in the UK Operation: vaginal surgery for pelvic floor disorders (tape, repair, or hysterectomy) 2 groups, size: 29/31 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 65.1 (12.5), 60.6 (11.5) All women Exclusion criteria: American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) grade 3, contraindication to Spinal Anesthesia (SA), a lack of capacity to provide consent, and an inability to read and write in English. | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (GA): anaesthesia was induced with propofol (3 mg/kg) and maintained with isoflurane in oxygen‐enriched air to achieve an inspired oxygen fraction (FiO2) of 33%. Ondansetron 4 mg IV was given as prophylaxis against postoperative nausea and vomiting. The operating surgeon was a urogynaecology consultant (JC) or specialist trainee signed off as competent for independent practice for the type of surgery performed. Anaesthesia was provided by 1 of two anaesthetic specialists (NT or AF). Anaesthesia was augmented by surgical infiltration with LA solution comprising 30 mL of 0.5% levobupivacaine, 27 mL of normal saline and 3 mL of adrenaline 1:10,000. Hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 85 mmHg) was treated with metaraminol in aliquots of 0.5 mg and bradycardia (heart rate < 60 beats per min) was treated with glycopyrrolate in aliquots of 200 µg. Women were prescribed ibuprofen 400 mg every 4 h orally with food when required and either co‐codamol (30/500) two tablets every 4 h or paracetamol 1 g IV or orally every 4 h. If pain was not controlled with the above regimen, morphine was prescribed. Postoperative nausea and vomiting were initially treated with prochlorperazine 12.5 mg IM every 6 h with ondansetron 4 mg to8 mg IV if required. Group 2 (SA): a 25‐G Whitacre needle was inserted at the L3‐L4 interspace following skin infiltration with 1% lidocaine, under aseptic conditions, the participant in the sitting position. Initially, the SA regimen consisted of 1 mL of 0.5% hyperbaric bupivacaine with 10 µg of fentanyl diluted to a volume of 3.0 mL using normal saline. Participants remained in the sitting position for 5 min following the introduction of SA. However, owing to suboptimal pain control in the first few participants, the protocol was revised and the spinal anaesthetic mixture was amended to 2.0 mL 0.5% heavy bupivacaine with 10 µg fentanyl, diluted to 3 mL, with the participant’s position immediately changed to semi‐recumbent following spinal injection. Participants’ complaints of pain were treated with IV fentanyl in aliquots of 50 µg. Additional intraoperative sedation was achieved by IV midazolam as required. Levobupivacaine was used to augment anaesthesia as described above. Hypotension was treated as described above. Adjuvants: fentanyl Immediate post‐op pain control: no improvement | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: VAS score, SF‐36 Other reported: VAS in the perioperative period 2 h, 24 h, 2 weeks, Incontinence Modular Questionnaire on Vaginal Symptoms (ICIQ‐VS), data regarding the time taken from the induction of anaesthesia to commencing surgery, operating time, duration of stay in the postoperative recovery room in min, use of analgesia postoperatively, and length of hospital stay | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the response provided by the study author regarding blinding, randomization, allocation concealment and source of funding and conflict of interest statement. Funding sources: "this study was funded by a Research Award from the North Staffordshire Medical Institute, UK." Conflicts of interest: the study authors have no conflicts of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "an internet‐based sequence allocation randomisation was carried out by the Nottingham (UK) Clinical Trials Support Unit with random permuted blocks of randomly varying size." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "The anaesthetist was informed of the random allocation allocated by the computer." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | The study author responded, quote: "Owing to the nature of the interventions, it was not possible to blind either patients or the assessing team to the intervention given." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Outcome assessors not blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Significant attrition |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "no statistically significant differences were noted between the groups with regard to pain..." |
| Methods | Single‐blind (outcome assessor), clinical RCT Sequence generation was random, but not described Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 112 adults at a university setting in Istanbul, Turkey Operation: open thoracotomy for a mix of lung resections 3 groups, size: 28/29/28 Age (group 1, 2, 3): 49 (SD 9), 52 (SD 11), 50 (SD 11) years Men/women: 56/13 (reported at end of study) Comorbidities: not reported | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (preincision): epidural at T7‐8, preincision bupivacaine bolus 10 mL, 7 mL/h infusion (0.1% + 0.1 mg/mL morphine), GA, post‐op 48 h PCEA (0.1% bupivacaine + 0.05 mg/mL morphine, basal rate 5 mL/h, demand 3 mL, lockout 30 min) Group 2 (postsurgery): epidural at T7‐8, GA (fentanyl), postsurgical bupivacaine bolus 10 mL (0.1% + 0.1 mg/mL morphine), post‐op 48 h PCEA (0.1% bupivacaine + 0.05 mg/mL morphine, basal rate 5 mL/h, demand 3 mL, lock time 30 min) Group 3 (control): GA (fentanyl), PCA (morphine, bolus 5 mg, no basal rate, demand 2 mg, lockout 15 min) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain at 6 months, pain affecting daily life at 6 months Continuous: NRS at 6 months Secondary: none | |
| Notes | Regional anaesthesia catheter placement was verified under fluoroscopy. The study author responded and provided additional information regarding randomization allocation concealment, sources of funding and conflicts of interest. Funding sources: "the study was not funded" Conflicts of interest: the authors "have no conflict of interest" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants were "randomly divided into three groups", "using sealed envelopes technique." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “randomization was performed at the first presentation of the patient to our department, i.e. 5‐7 days before the operation (just before the anaesthetic evaluation). The result of the randomization was "hidden" by the secretary of the department until the operation date.” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "patients were not blinded to group, anaesthesia providers aware of allocation at least during treatment." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Outcome assessors "were blinded to the analgesic method." Blinding of only outcome assessors is acceptable. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Allocation of excluded participants is not reported, no ITT analysis was considered. Considerable attrition prior to, during and after intervention make bias likely. Adverse effects were not, but attrition was described albeit without group allocation 27 participants were excluded preoperatively, 6 intraoperatively, and 10 postoperatively, without specification of their group allocation. Comorbidities were the preoperative, inoperability the intraoperative and recurrence of pain due to metastasis & reoperation were the postoperative exclusion criteria. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes included |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "during movement and cough, Group Pre‐TEA had significantly less pain compared with the other two groups during the entire period. At rest, patients in Group Pre‐TEA reported having significantly lower pain scores during the first 12 h compared with those in Group Post‐TEA and during the first 48 h compared with those in Group IV‐PCA. There were statistically significant differences between Group Post‐TEA and Group IV‐PCA during rest from 8 h after surgery until the end of 48 h, but no difference during cough or movement was recorded" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), placebo/sham‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up: 8 months | |
| Participants | Participants: parturients in a university setting in Assiut, Egypt Operation: caesarean section for delivery groups, size: 185/185 Age: 25 years (SD ± 1.5 ) Men/women (group 1, 2): 0/185, 0/185 Comorbidities (group 1/2/3): none reported Remarks: | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (intraperitoneal lidocaine instillation): spinal (details not reported), postincision, preperitoneal closure single‐shot instillation of peritoneal lidocaine (2%, 10 mL) into the pelvis, post‐op paracetamol 1 g intravenously every 6 h for 36 h, rectal suppository of 10 mg followed by oral 400 mg ibuprofen for 72 h, plus intravenous morphine 2 mg for breakthrough pain Group 2 (intraperitoneal placebo/saline instillation): spinal (details not reported), postincision, preperitoneal closure single‐shot instillation of peritoneal saline (0.9%, 10 mL) into the pelvis, post‐op paracetamol 1 g intravenously every 6 h for 36 h, rectal suppository of 10 mg followed by oral 400 mg ibuprofen for 72 h, plus intravenous morphine 2 mg for breakthrough pain Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: overall pain/no pain at 8 months, differentiated also in wound, global abdominal and epigastric pain Continuous: at 8 months: NRS | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "No ... funding acknowledgement was declared by either of the authors." Conflicts of interest: the study authors have no conflict of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐based random allocation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Placed in sealed, opaque, consecutively numbered envelopes... just after providing consent the women were given the next number on the random list..., (allocation) was concealed from the residents and caregivers |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the surgeon involved complied with the instruction but was not further involved" data "collection sheets with corresponding codes,.. a number of syringes equal in size;" "preparation and administration of the medication was carried out by a nurse not involved in the management of the patient", "access to randomization code was only available to the secretary of the statistics department", "randomization code was not broken until the completion of the study". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "access to randomization code was only available to the secretary of the statistics department", "randomization code was not broken until the completion of the study". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Analysis was per protocol, not ITT, but the low number of participants lost to follow‐up with almost equal attrition in both groups and the similar demographics in both groups make bias unlikely. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available but all outcomes specified in the article were reported on. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "control group patients received significantly more morphine injections in the first 24 hours than lidocaine patients". Significantly more participants in the control group reported pain in all sites in the first 24 h than in the lidocaine group. |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participant/provider/outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, clinical RCT Sequence generation by a computer‐based, random numbers generator Follow‐up: mean of 4.7 years (range 4.5–5.4 years) | |
| Participants | Participants : 26 adults in a university setting, Houston, Texas, USA Operation: ICBG for spinal arthrodesis 2 groups, size: 11/14 Age (all, 1, 2): 64 (range 34‐84), 66, 63 years Sex: not reported Comorbidities: not reported Remarks: 11 anterior ICBG included in the initial stage were later excluded | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (treatment): GA, at closure continuous wound irrigation (bupivacaine hydrochloride and epinephrine (Marcaine) 0.5% 2 mL/h) for 48 h post‐op + PCA (hydromorphone hydrochloride (Dilaudid)) (basal, bolus and lock‐out time not specified) Group 2 (control): GA, at closure continuous wound irrigation (normal saline, 2 mL/h) for 48 h post‐op + PCA (Dilaudid) (basal, bolus and lock‐out time not specified) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: graft site pain at around 55 months Continuous: VAS at around 55 months Secondary: pain frequency in days, functional activity score, overall satisfaction with the surgical procedure at around 55 months | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "no funds were received in support of this work" Conflicts of interest: "no benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the method used to generate the randomization consisted of a computer‐based number generator. Moreover, to account for the size of the sample groups, randomization attempted to balance baseline characteristics by stratification, such as age." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the participants were randomized and allocated by a different individual than the one who enrolled the patient." "Randomization and allocation to group type was concealed and not made public to the individual enrolling the patients, the treating physician, or to the nursing staff." "Patients were assigned to receive either one or the other (treatment) solutions at the time of surgery based on a coded sequence enclosed within an envelope." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "blinded and identical in appearance, solutions of saline and Marcaine were prepared." "Physicians, patients, nursing staff, and research personnel conducting the statistical analyses were blinded to the infusion solution until the end of the study to minimize potential for performance and detection bias." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the physician conducting the telephone interview as well as recording the data were blinded to the treatment group." "Research personnel conducting the statistical analyses were blinded to the infusion solution until the end of the study to minimize potential for performance and detection bias." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Study authors report details of attrition with reference to the groups participants were randomized to. "An intent‐to‐treat analysis was considered to preserve randomization and to offer the best representation of the clinical population." "Even if we assume that any treatment patient that was lost to follow‐up (n = 6 patients) was considered to be a failure (chronic dysesthesias, an ICBG VAS score of 8, 15 days of narcotic usage/mo, functional activity score of 4, and an overall dissatisfaction with the procedure), a statistical difference was still noted in the 2 groups (p = 0.05)." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "narcotic dosage, demand frequency, and mean VAS pain score were significantly less in the treatment (Marcaine) group at 24 and 48 hours" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by a computer‐based, random numbers generator Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 women at a university hospital in Ontario, Canada Operation: caesarean section Groups, size: 20/20/20 Age (± SD), group 1, 2, 3: 33 (± 3), 32 (± 7), 33 (± 4) All female participants Comorbidities: previous caesarean delivery, groups 1, 2, 3 (16, 14, 15) Remarks: ASA I, II, and III | |
| Interventions | All participants received SA with 0.75% bupivacaine 10 mg‐12 mg, fentanyl 10 µg and morphine 150 µg Group 1 (high‐ropivacaine): post‐op: a 22‐G, 50 mm or 80mm Pajunk Uniplex nanoline needle was introduced into the fascia between the internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscles. After confirmation of needle placement, the study solution was injected in 5 mL increments after negative aspiration. Study solution for high‐ropivacaine group consisted of 0.5% ropivacaine 3 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 300 mg) plus saline to total 60 mL of fluid. TAP blocks were performed bilaterally. Group 2 (low‐ropivacaine): post‐op: same method as group 1, but study solution consisted of 0.25% ropivacaine 1.5 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 150 mg) plus saline to total 60 mL.TAP blocks were performed bilaterally. Group 3 (placebo): post‐op: TAP blocks consisting of 60 mL of saline were administered bilaterally using same method as groups 1 and 2. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no difference | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomus: none Continuous: NRS at 3 months Other reported: the time to first request for additional analgesia, the total consumption of opioids, antiemetics and anti‐pruritics 72 h postoperatively Adverse events: none reported | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "this study was supported in part by a grant from the Lawson Health Research Institute." Conflicts of interest: "the authors have no conflicts of interest to declare." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were randomly assigned using a computer generated table of random numbers to one of three groups." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "group allocations were concealed in sealed opaque envelopes that were opened only after patient consent was obtained.." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the patients, anesthesiologists, and nursing staff involved in direct patient care were unaware of the study group allocations." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were interviewed at regular intervals by an investigator unaware of group allocation..." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Of the 60 participants enrolled, 59 completed the study. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "neither high‐ or low‐dose TAP blocks as part of a multimodal analgesia regimen including intrathecal morphine improved pain scores." |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), randomized clinical trial Sequence generation not specified Follow‐up: 3, 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 men in a hospital setting in Philadelphia, PA Operation: open radical retropubic prostatectomy Groups, size: 29/31 Age: not specified All male participants | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (multimodal analgesia): pre‐op: PVB with 5 mL of 0.5% ropivacaine per level (T10‐T12) and oral celecoxib (400 mg preoperatively and 200 mg twice daily for 7 days postoperatively). Intra‐op: IV ketamine (10 mg) following induction. Post‐op: all participants had access to morphine (PCA) Group 2 (PCA): pre‐op: participants received placebo equivalents as treatment group ‐ sham tablets and sham saline injections. Post‐op: all participants had access to morphine (PCA) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: SF‐36 at 3, 6 months Dichotomus: none Other reported: VAS at 24 hours, morphine consumption postoperatively Adverse events: none reported | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information regarding pain outcomes or about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: none received Conflicts of interest: conflict of interest not discussed | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Sequence generation not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all patients, staff and physicians were blinded to treatment group assignment." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors not discussed |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Amount of follow‐up and attrition not specified |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "there were no significant differences detected in SF‐36 scores at 2, 12, and 24 weeks." |
| Methods | Single‐blinded (outcome assessor), randomized clinical trial Sequence generation via computer‐generated list Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 89 women from a university hospital in Minnesota, USA Operation: elective vaginal hysterectomy (with or without repair of cystocoele and rectocoele) 2 groups, size: 45/44 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 52.2 (± 11.9), 51.8 (± 12.8) All female participants Comorbidities: postmenopausal, group 1, 2: 21/17. Procedure, group 1, 2: hysterectomy only 27/27, hysterectomy + cystocoele 1/1, hysterectomy + rectocoele 4/4, hysterectomy + cystocoele + rectocoele 13/7 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (regional): sedation with IV midazolam and propofol. SAB performed in lumbar region between 3rd and 5th vertebral bodies. After cerebrospinal fluid free flow, 0.75% hyperbaric bupivacaine (15 mg), preservative‐free clonidine (1 µg/kg), morphine (2 µg/kg, max 200 µg) injected to subarachnoid space. Intraoperative sedation with IV midazolam and propofol as needed. No intraoperative IV opioids. 30 mg ketorolac IV at end of surgery. On floor IV PCA 1.0 mg every 10 min with 4‐h lock out max of 15 mg in regional group (lower than general group, to decrease likelihood of delayed respiratory depression). Additional IV morphine per attending physician as needed Group 2 (general): 2 µg/kg fentanyl after pre‐oxygenation GA with sodium thiopental, succinylcholine, vecuronium bromide, isoflurane and 50% inspired nitrous oxide. A morphine sulphate 0.1 mg/kg IV in divided doses, no additional morphine was allowed. All participants received 30 mg IV ketoralac at end of surgery. On floor IV PCA 1.0 mg every 10 min, 4‐h lockout max of 30 mg Both groups: in PACU 2 mg IV morphine every 5‐10 min as needed for NRS > 3. On floor, morphine PCA, with differences in maximum noted above. Scheduled ketorolac 30 mg IM every 8 h until oral D3. After 24 h, IV PCA stopped and oral paracetamol and codeine (650 mg/30 mg) every 6 h as needed. In both groups, pruritis managed with diphenhydramine then naloxone if needed. Nausea/vomiting managed with droperidol, if later stages ondansetron, then naloxone if persisted. Adjuvants: clonidine (into subarachnoid space) Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: NRS at 3 months, SF‐36 pain subcomponent at 3 months Secondary: none Effective regional anaesthesia: reported. "Confirmation of an adequate dermatomal level of blockade" Adverse events reported on included use of intraoperative pressors, nausea/vomiting, pruritis | |
| Notes | We acknowledge the study author's clarification on blinding methods. Funding sources: "intramural grant from the Mayo Foundation." Conflicts of interest: "none declared." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "computer‐generated list" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients were randomized...using a sealed envelope" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | The anaesthesiologist, participants and providers were not blinded. This is acceptable for our purposes. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | SF‐36 was filled out by participant and mailed in at 12 weeks. Study author contacted, stated the research co‐ordinator performing telephone follow‐up "was blinded regarding the study group" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote. "in three patients in the SAB group, the block failed and the patient received general anesthesia. For all analyses presented in this report these patients are included in the SAB group (intention‐to‐treat)". Fairly balanced, low rate of participants lost to follow‐up at 12‐week follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All primary outcomes fully reported on. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "the patients in the general anesthesia group received more morphine in the PACU... compared to patients receiving SAB" and this continued into the 12 hours after PACU discharge. Numerical pain score values tended to be lower in participants receiving SAB compared to the general anesthesia group through 14:00 hr on postoperative day two (the day after surgery), with significant differences noted at the time of floor arrival and at 14:00 hr on postoperative day two" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by a computer‐based, random numbers generator Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 women in a hospital setting in Ljubljana, Slovenia Operation: breast cancer surgery with axillary lymphadenectomy Groups, size: 30/30 Age (all, 1, 2): 60 (30‐84), 57.4, 62.9 All female participants Comorbidities: diabetes, groups 1, 2 (4, 8); depression, groups 1, 2 (1, 4) Remarks: ASA I, II, and III | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (levobupivacaine): intra‐op: before wound closure, a fenestrated wound catheter was placed near the axillary vein and upon the whole length over the upper side of the wound. The wound catheter was fenestrated along 15 cm in the distal part. A bolus of 15 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine was injected into the wound through the catheter immediately after wound closure. Surgical drains and the fenestrated catheter were clamped for 5 min to enable bolus absorption. Elastomeric pump was connected containing 100 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine. Infusion at 2 mL/h was continuous for 50 h Group 2 (piritramide): intra‐op: continuous IV infusion with piritramide (30 mg), metoclopramide (20 mg) and metamizole (2.5 g) in 100 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride (3 mL/h to 6 mL/h) until 24 h postoperatively Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: none Dichotomus: overall pain/no pain at 3 months Other reported: nausea, opioid consumption, and length of hospital stay and were measured Adverse events: 3 participants (2, 1) underwent additional surgical procedures due to haematoma and 9 participants (5, 4) experienced inflammation postoperatively | |
| Notes | Funding sources: no funding source given Conflicts of interest: "no potential conflicts of interest were disclosed." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomization was performed using random numbers generated by a computer |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomization and numbers were placed in sealed opaque envelopes to ensure concealment of allocation at enrollment." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "participants were randomly grouped." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "clinicians who recorded data about chronic pain were blinded about randomisation group of patients." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All participants completed the follow‐up evaluation. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "pain (at 3 months) was reported by 17% and 50% of patients." Continuous infusion of local anesthetic reduced pain compared to control. |
| Methods | Doubl‐ blinded (participant/outcome assessor), randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by a computer‐based, random numbers generator Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 women in a hospital setting in Ljubljana, Slovenia Operation: radical mastectomy and breast reconstruction Groups, size: 30/30 Age (range, 1, 2): 25‐64, 47.6, 48.0 All female participants Comorbidities: smoking, groups 1, 2 (9, 10); depression, groups 1, 2 (3, 1) Remarks: ASA I, II, and III | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (levobupivacaine): intra‐op: before wound closure, a fenestrated wound catheter was placed under the pectoralis major muscle and upon the entire length over the upper side of the wound. The wound catheter was fenestrated along 15 cm in the distal part. A bolus of 15 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine was injected into the wound through the catheter immediately after wound closure. Surgical drains and the fenestrated catheter were clamped for 5 min to enable bolus absorption. Elastomeric pump was connected containing 100 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine. Infusion at 2 mL/h was continuous for 50 h. Group 2 (piritramide): intra‐op: continuous IV infusion with piritramide (30 mg), metoclopramide (20 mg) and metamizole (2.5 g) in 100 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride (3 mL/h to 6 mL/h) until 24 h postoperatively. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved, significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: none Dichotomus: overall pain/no pain at 3 months Other reported: nausea, opioid consumption, and length of hospital stay were measured. Adverse events: 2 participants (1, 1) underwent additional surgical procedures due to haematoma, 4 participants (1, 3) experienced inflammation postoperatively, and unilateral lymphoedema of the arm was present in 2 participants (1, 1) | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "study was entirely financed by the Institute of Oncology as a part of public service." Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare that they have no competing interests." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomization was made by using random numbers generated by a computer." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomization and numbers were placed in sealed opaque envelopes to ensure concealment of allocation at enrollment." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Participants were blinded, but no description of medical staff's knowledge other than, quote: "after randomization... the principal investigator was informed about the treatment allocation of the patient." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "data about pain were collected by nursing staff, that is, by an independent observer." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All participants completed the follow‐up evaluation. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted. |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "in the test and the control groups of patients, pain was reported in 16.7% (5/30) and 50% (15/30), respectively." "We observed that patients treated with a LA experienced a lower frequency of chronic pain compared to patients treated with standard analgesic." |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant/outcome assessor), randomized clinical trial Sequence generation not described Follow‐up: 3 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 60 women in university hospital in Ankara, Turkey Operation: radical mastectomy (with axillary lymph node dissection) Groups, size: 30/30 Age: not listed All female participants Comorbidities: not listed | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (bupivacaine): intra‐op: intercostobrachial nerve was blocked with 10 cc 0.5% bupivacaine before being sectioned Group 2 (control): intra‐op: intercostobrachial nerve sectioned without blockage Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no difference | |
| Outcomes | Continuous: VAS at 3 months Dichotomus: pain questionnaire at 3 months Other reported: analgesic consumption Adverse events: reported as none | |
| Notes | Pain score ≥ 4 was accepted as pain Funding sources: no explanation of financial support Conflicts of interest: no conflict of interest statement given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Sequence generation not explained |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not explained |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of medical personnel not explained |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Knowledge of outcome assessors not indicated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | All participants completed the follow‐up evaluation |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis or selective reporting was noted |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "this study shows that intercostobrachial nerve block is an effective method to reduce the chronic neuropathic pain development after a breast cancer surgery." |
| Methods | Triple‐blind (participant/provider/outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation using website random number generator Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 61 adult patients at a university hospital in Virginia, USA Operation: mastectomy (including simple and modified radical, with or without axillary dissection) for breast cancer surgery 2 groups, size: 27/34 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 55.2 (± 10.9), 55.0 (± 13.7) All female participants Exclusion criteria: Age > 80 Comorbidities: simple mastectomy (n), group 1, 2: 19/20. Modified radical (n), group 1, 2: 8/14. Axillary direction (n), group 1, 2: 3/13. Breast implant (n), group 1, 2: 5/8. Chemotherapy, (n), group 1, 2: 11/18. Radiotherapy (n), group 1, 2: 9/14. Hormone therapy (n), group 1, 2: 10/7 Remarks: the demographic data above are for participants who were available for follow‐up at 6 months and included in the analysis. | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (placebo): 0.9% NaCl IV infusion beginning before induction, at equal volume to lidocaine group, until 2 h after arrive to PACU or at discharge from PACU (whichever earlier) Group 2 (lidocaine): 2 mg/kg/h IV lidocaine infusion beginning before induction (max 200 mg/h) until 2 h after arrive to PACU or at discharge from PACU (whichever earlier) Both groups: lidocaine bolus before induction, up to 1.5 mg/kg, max 150 mg. Premedication, induction drug, muscle relaxant for GA chosen by anaesthesiologist. Maintenance sevoflurane. Post‐op analgesia fentanyl 50 µg every 10 min as needed or morphine 4 mg every 20 min as needed, with morphine PCA if needed. Nausea treated with ondansetron 4 mg IV as needed then promethazine 6.25 mg IV every 20 min as needed. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no significant improvement | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 6 months Continuous: VAS collected but not reported Other: logistic regression model (Best model) to assess efficacy of lidocaine Adverse events: incidence of lymphoedema, evidence of lidocaine toxicity, post‐surgery infection or complications | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "the study was funded by the Department of Anesthesiology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA." Conflicts of interest: "the authors declare no conflict of interest." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a website random number generator was used (www.randomization.com)...and the patient was asked to select one envelope on the morning of surgery." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "numbers were concealed in opaque sealed envelopes" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "both the patients and research team remained blinded until after all data were analysed." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a research associate, who was blinded to treatment group and management, conducted a telephone interview with the patients 6 months after surgery." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Quote: "seven patients in the placebo group and 3 in the lidocaine group could not be reached for follow‐up, despite multiple phone call attempts (14% dropout). Therefore, we analysed 61 patients, 27 in the placebo group and 34 in the lidocaine group". Slightly higher loss in the placebo group but overall low numbers of attrition. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study maintained a defined protocol, which they did not deviate from. |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "the mean postoperative pain scores at rest (Fig. 2A) were 3.88 ± 2.92 at 2 hours, 2.66 ± 2.66 at 24 hours, and 3.09 ± 2.80 at 48 hours in the placebo group, whereas they were 2.94 ± 2.74 at 2 hours, 2.91 ± 2.21 at 24 hours, and 2.72 ± 2.25 at 48 hours in the lidocaine group. Overall pain scores in both groups were similar with no statistical difference by repeated‐measures ANOVA ". No significant difference in pain scores on movement or perioperative morphine consumption either. |
| Methods | Triple‐blinded (participant, provider, outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up for 3 and 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 78 adults in a university setting in USA Operation: robotic cardiac surgery 2 groups, size: 39/39 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 56 (11), 58 (10) Men/women, group 1, 2: 31/8, 29/10 Exclusion criteria: history of severe psychiatric issues (e.g. depression, somatoform conversion disorder, and borderline personality disorder); addiction to alcohol, opioids, or illegal substances; known history of sensitivity to amide LAs; severe hepatic disease; or pregnant | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (lidocaine): anaesthetic technique not described. The 5% lidocaine transdermal patches contained 700 mg of lidocaine. Each self‐adhesive patch was 10 cm x 14 cm. Up to 3 patches were applied to maximize analgesia while reducing the risk of systemic toxicity. Patches were applied for 12 h, removed for the subsequent 12 h, and then new patches were applied. This process was continued for 6 months or until participants no longer required analgesia. Additional postoperative analgesia was provided by participant‐controlled fentanyl (20 mg bolus, 6‐min lockout, no hourly limit). Morphine or hydromorphone was substituted in participants reporting sensitivity to fentanyl. PCA was continued for up to 3 days, with the exception of a single participant who was treated for 5 days, until participants could tolerate oral opioid medications such as oxycodone 5 mg to 10 mg every 4‐6 hours as needed. Participants who required more than 40 mg of oxycodone, or equivalent, per day were supplemented with fentanyl 25 mg/h transdermal patches Group 2 (control): same intervention as above except sham patches were used. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no improvement | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: VAS/VRS Secondary: VAS at POD 3; VRS at 1 week and 1 month, the Depression Anxiety Stress Score recorded the day before surgery, GPE‐a measure of participant satisfaction, recorded after 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. PDI at 3 and 6 months | |
| Notes | Funding sources: funding for the study was provided by Endo Pharmaceuticals. Conflicts of interest: "none of the authors has a personal financial interest in this research." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "randomization was performed by our Research Pharmacy and was based on computer‐generated codes" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Allocation of concealment was not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "all investigators and clinicians were fully blinded to treatment." |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "incisional pain was evaluated over 6 months with data collected by an independent study coordinator who was blinded to treatment." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | There was no attrition and ITT analysis was performed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "lidocaine 5% patches did not influence any measure of acute or persistent incisional pain" |
| Methods | Single‐blinded (outcome observer) clinical RCT Sequence generation via computer‐generated randomization list Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants children and adolescents ≥ 10 years at a university hospital in Vienna, Austria Operation: pectus excavatum repair (minimally invasive using a thorascope for creation of retrosternal tunnel) 2 groups, size: 20/20 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 16.7 (± 5.2), 14.8 (± 4.2) Men/women, group 1, 2: 17/3, 15/5 Comorbidities: except for 1 participant in TEA group, all procedures were primary operations. Vertebral index (vertebral diameter x 100/sagittal diameter + vertebral diameter), group 1, 2 (± SD) = 32.05 (± 36.2), 31.85 (± 4.15) | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (PCA): post‐op IV PCA 0.02 mg/kg morphine bolus, lockout 6 min, max 6 bolus/h, no continuous rate. Postoperatively, both groups 1 mg/kg diclofenac IV every 8 h scheduled until POD 4, rescue pain medication with IV paracetamol 15 mg/kg, followed by 1.5 mg piritramide IV bolus as needed Group 2 (TEA): catheter placed once in operating room by median approach at T6/7 or T7/8 corresponding with likely insertion site of steel bar. After induction, bolus of 0.2 mg/kg ropivacaine 0.2% with 2 µg/mL fentanyl, then continuous rate of 0.2 mL/h same mixture throughout surgery, continued until POD 4 (96 h). Post‐op scheduled 1 mg/kg diclofenac IV every 8 h until POD 4 rescue pain medication with IV paracetamol 15 mg/kg, followed by epidural bolus of 0.1 mL/kg ropivacaine 0.2% with 2 µg/mL fentanyl as needed. Both groups received standardized GA with propofol, fentanyl, rocuronium. 15 min before end, IV paracetamol bolus Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain/no pain at 3 and 6 months Continuous: VAS pain score 3 and 6 months Secondary: satisfaction with type of anaesthesia at 3 and 6 months Adverse events reported: sedation, nausea, pruritis | |
| Notes | Presence of pain defined by VAS ≥ 3. We acknowledge the study author for providing response regarding VAS cutoff for presence of pain, allocation concealment, blinding and source of funding. Funding sources: "AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers‐Squibb, and Smiths Medical Austria supported the study with an unrestricted grant". We contacted the study author on their specific involvement, who responded, "Funding by the three companies included just paying for the insurance (approximately one third by each company). None of the companies were involved in conducting the study or writing the manuscript." Conflicts of interest: no direct conflicts of interest statement given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "computer generated randomization list" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Study author specified "Group allocation was concealed in an opaque envelope" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants, surgeons and providers were not blinded. The study author clarified that "the PCA pump and the TEA continuous infusion (depending on the study group) were hidden from the persons assessing the VAS scores". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | The study author stated "For postoperative data collection, the PCA pump and the TEA continuous infusion (depending on the study group) were hidden from the persons assessing the VAS scores. The persons who made the follow up questioning [at 3 and 6 months] were unaware to which group the patients were assigned". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Study author specified "All 40 patients were available at three and 6 months for follow‐up". |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported on |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "Patients treated with a thoracic epidural catheter after pectus excavatum repair reported lower postoperative pain scores... than did patients treated with intravenous PCA containing morphine. Postoperative pain scores in the intravenous PCA group were higher despite higher intraoperative fentanyl use in the intravenous PCA group" |
| Methods | Single‐blinded (outcome assessor), clinical RCT Sequence generation using computer‐generated block randomization table Follow‐up: 6 months | |
| Participants | Participants: 162 women aged 18‐60 from five hospitals in Sweden Operation: abdominal subtotal or total hysterectomy (for benign gynaecological disorders) 2 groups, size: 80/82 Age (range), groups 1, 2: 45 (33‐58), 46 (35‐58) All female participants Exclusion criteria: former or concomitant bilateral oophorectomy, postmenopausal without hormone therapy, gynaecological malignancy (cervical dysplasia not included) Comorbidities: indication of hysterectomy, group 1, 2: bleeding disturbances: 46, 46, mechanical symptoms: 27, 29, cervical dysplasia or endometrial hyperplasia: 4, 5, endometriosis or dysmenorrhoea: 3, 2. Total abdominal hysterectomy, group 1, 2: 55/51. Subtotal abdominal hysterectomy, group 1, 2: 25, 31. Mode of skin incision, group 1, 2: midline: 6, 7, low transverse 74, 75 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (GA): GA with propofol, fentanyl, rocuronium. 5 mg IV morphine administered 20 min before surgery complete Group 2 (SA): at L3/4 or L2/3 intervertebral space, 20 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine (5 mg/mL) and 0.2 mg morphine (0.4 mg/mL) administered. 15 min later, confirmed neural blockade with cold test. Sedation throughout operation with continuous IV propofol Both groups, 2 g oral paracetamol 1 h preoperatively. Surgeon injected 40 mL bupivacaine (2.5 mg/mL) SC and pre‐fascially in abdominal wall before end of surgery. Postoperatively, oral paracetamol and diclofenac scheduled 3 x day during hospitalization. Oral or IV opioids given if necessary. Rescue antiemetic with droperidol, then 5‐HT3 receptor antagonist if still necessary. Pruritus treated with clementine and if necessary, naloxone Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly reduced analgesic consumption | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: SF‐36 at 6 months Other reported: list of major and minor complications | |
| Notes | Funding sources: "the Medical Research Council of South East Sweden, Linköping University and the County Council of Östergötland supported the trial financially." Conflicts of interest: "the authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "a computer generated the randomisation sequences into blocks of ten, with an equal number of the two modes of anaesthesia for each of the five participating centres" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "the allocated mode of anaesthesia, written on a label, was sealed in opaque consecutively numbered envelopes. At each centre the envelopes were opened in consecutive number order of patient inclusion in the study" |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "blinding and/or placebo control was not possible in this study. The temporary paralysis of the lower extremities after SA would, for obvious reasons, be observed immediately by the patient, as well as by the staff. The lack of blinding may pose a risk of bias. In order to reduce such potential bias the women were informed and monitored in a standardised fashion, and the mode of incision and type of abdominal hysterectomy were decided prior to randomisation" |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported on whether outcome assessor was blinded or not |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "in the SF‐36, a missing cell was substituted by the truncated mean value of the other items in the specific subscale for the individual. If all cells in a subscale were missing, the cells were substituted by the truncated mean value of each cell in the group. If a questionnaire was missing completely on one occasion, each cell was substituted by the truncated mean value of the cell for the group on that occasion. Missing cells for the SF‐36 on all three occasions made up 0.44%, and a complete SF‐36 was missing in 2.26% (11 of 486 cases). " |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Primary outcomes fully reported |
| Null bias | Low risk | Quote: "spinal anaesthesia was associated with a significantly lower use of opioids" compared to general anaesthesia |
| Methods | Clinical RCT Sequence generation by computer‐generated random numbers Follow‐up for 3 months | |
| Participants | Subjects: 71 adults in a military hospital in China Operation: thoracolumbar spinal surgery 2 groups, size: 35/36 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: 51.91 (11.44), 49.06 (11.20) Men/women, group 1, 2: 19/16, 19/17 Exclusion criteria: a history of cardiopulmonary disease, coagulation and merging with multiple injuries | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): continuous wound infusion with ropivacaine was used as primary analgesia. This group received an initial wound infiltration with 6 mL 1% ropivacaine (100 mg; AstraZeneca AB, Sweden) and followed by continuous infusion with 0.33% ropivacaine via a double lumen catheter system at a rate of 5 mL/h (disposable postoperative local analgesia system, Beijing Heng Yuan Tongji Medical Technology Corporation, China) for 48 h. Participants in this group did not receive postoperative IV continuous constant‐dose analgesia (ICCA) for pain control. Participants were premedicated with phenobarbital 100 mg and atropine 0.5 mg, 30 min before the induction of anesthesia. After baseline measurements of heart rate, noninvasive blood pressure, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation, each participant was preoxygenated for 3 min before induction. All participants received the target‐controlled infusion with propofol 2‐ 3 μg/mL using the Marsh pharmacokinetic model and remifentanil at 3 ng/mL to 4 ng/mL using the Minto pharmacokinetic model for induction. Following the induction of anaesthesia, cisatracurium 0.15 mg/kg was given as an IV injection. After tracheal intubation, mechanical ventilation was initiated with 100% oxygen and adjusted to maintain the end tidal carbon dioxide tension between 35 mmHg and 45 mmHg. Intermittent bolus injection of cisatracurium was used to maintain full muscle relaxation. At the end of surgery, residual neuromuscular block was reversed, if needed, with a mixture of atropine and neostigmine. Participants were given pentazocine 60 mg when surgery was completed prior to extubation. All participants expanded on the use of the supplementary analgesic (flurbiprofen 50 mg IV injection) if necessary (VAS > 4) Group 2 (control): exactly the same as described above except there was no wound infiltration with ropivacaine. Additionally, this group relied on ICCA for postoperative pain control involving flurbiprofen axetil 150 mg, pentazocine 240 mg and palonosetron 0.5 mg in 100 mL normal saline, at a rate of 2 mL/h. All participants expanded on the use of the supplementary analgesic (flurbiprofen 50 mg IV injection) if necessary (VAS > 4) Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: no improvement | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: none Other reported: demographic and operation data including disease, date of birth, gender, operating time, preoperative VAS, perioperative remifentanil and propofol doses, and length of surgical incision, pain score at rest during first 48 h postoperative using VAS, and Ramsay scores, times of rescue analgesia requests, incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, antiemetic therapy requirements and incidence of pruritus (participants were asked about the desire to scratch) at 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, 36 and 48 h postoperatively | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: funding for the study was provided by Guangzhou General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command. Conflicts of interest: "all the authors declare they have no competing of interests." | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "All participants were randomly assigned using a computer‐generated random number table." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No sham was employed and blinding of participants/personnel not described |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "All enrolled patients successfully completed the study and were included in the main analysis." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | High risk | "There were no significant differences in the pain level between the two groups" |
| Methods | Double‐blinded, placebo controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation not described Follow‐up for 3 months | |
| Participants | Subjects: 106 adults in a university setting in China Operation: craniotomy 2 groups, size: 53/53 Age (± SD), group 1, 2: not described Men/women, group 1, 2: not described Exclusion criteria: not described | |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): after the anesthesia induction, skin along the incision was infiltrated with 0.5% ropivacaine. Morphine was used as rescue analgesic postoperatively. Anaesthetic regimen not further described. Group 2 (control): exactly the same as above except 0.9% saline was substituted for ropivacaine. Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: significantly improved | |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: pain vs no pain Continuous: VAS Other reported: morphine consumption, heart rate and mean arterial pressure were recorded before anesthesia induction, after anesthesia induction, after scalp infiltration, during skull drilling, mater cutting, and skin closure | |
| Notes | We were unable to obtain additional information about randomization and blinding methods from the study author. Funding sources: funding of study not described Conflicts of interest: study authors declare no conflicts of interest | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Randomization methods not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not described |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Sham block was used. Blinding of personnel not described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding of outcome assessors not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Rate of attrition not described |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear if subgroup analysis was performed |
| Null bias | High risk | Quote: "the incidence of pain... showed no difference between groups." |
5‐HT3: 5‐hydroxytryptamine; ANOVA: analysis of variance; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiology perioperative risk classification; BPI: brief pain inventory; EMLA: eutectic mixture of local anaesthetics; Epi: epinephrine; GA: general anaesthesia; h: hour; HRQOL: health‐related quality of life; ICBG: iliac crest bone graft harvesting; IM: intramuscular; ITM: intrathecal morphine; ITT: intention‐to‐treat; IV: intravenous; Kg: kilogram; L2: lumbar segment number 2; LA: local anaesthetic; LMA: laryngeal mask airway; MAC: minimum alveolar concentration; mg: milligram; mL: millilitre; NIH: National Institute of Health; NSAID: nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs; NRS: numerical rating scale; paracetamol: acetaminophen; PACU: postanaesthesia care unit; PCA: participant controlled analgesia; PCEA: patient controlled epidural analgesia; POD: postoperative day; PVB: paravertebral block; RCT: randomized controlled trial; SA: spinal anaesthesia; SAB: subarachnoid block; SC: subcutaneous; SD: standard deviation; SF‐36: Short Form (36) Health Survey; SF‐MPQ‐2: Short Form MacGill Pain Questionaire; T4: thoracic segment 4; TAP: transabdominal plane block; TEA: thoracic epidural analgesia; µg: microgram; VAS: visual analogue scale
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Study comparing different epidural LA mixtures for analgesic effect, 2 days after surgery. No long‐term outcomes recorded | |
| Participants undergoing day‐case open inguinal hernia repair with mesh given TAP block or ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block. No control group. VAS scores at 3 and 6 months | |
| Pseudo‐clinical RCT (sequence generation by means of patients' year of birth) investigating epidural analgesia before limb amputation for chronic phantom pain with a follow‐up of 12 months | |
| Outcome was attenuation of (pre‐existing) chronic pelvic pain. The primary outcome of interest for this review, (new onset wound pain persisting for > 3 months after surgery) was not measured | |
| Study assessing effectiveness of preoperative IV lidocaine infusion on post‐op pain, however, no chronic pain outcomes assessed | |
| Follow‐up only 2 months in this RCT of scalp infiltration for craniotomy | |
| Comparing regional technique against combination of regional techniques | |
| Outcome: regional anaesthesia complications associated with interscalene block | |
| Non‐randomized prospective trial of perineural catheter for phantom limb pain | |
| Non‐randomized observational study of continuous infusion through an iliac crest catheter for postoperative analgesia after ICBG harvesting | |
| Preincision epidural anaesthesia vs none for thoracotomy, but no control (as both groups had post‐op epidural anaesthesia) | |
| All participants received local wound infiltration and there was no control group without application of local or regional anaesthesia | |
| Article in French. Single‐dose intraincisional infiltration of levobupivacaine or placebo into wound after scheduled C‐section. Longest pain outcome at 2 months | |
| Excluded for pseudo‐randomization, this prospective trial investigated different anaesthetic techniques for the prevention of regional pain syndrome after carpal tunnel release | |
| Comparing IV ketamine to epidural ketamine to control as adjuvant therapy; all patients receiving LAs via epidural catheter | |
| Comparison of ketamine or placebo in people undergoing thoracotomy. All participants received local ropivacaine administration at the edges of the thoracotomy and chest drainage orifices and in the inter pleural space postoperatively (thus no control group) | |
| RCT comparing intrathecal bupivacaine with ketoralac vs saline for prevention of postoperative pain. All participants received intrathecal bupivacaine thus no control group | |
| Randomized, blinded study comparing outcome of paravertebral block vs thoracic epidural block for post‐thoracotomy incision pain in paediatric patients. The primary objective was evaluation of immediate postoperative analgesia. Secondary objectives included hormonal responses, side effects, failure rate, and pulmonary function. No long‐term outcomes were measured | |
| Comparing different doses of bupivacaine intrapleurally, no long‐term pain outcomes were measured | |
| Patient on chronic opioids preoperatively | |
| Follow‐up only 9.5 weeks, in a double‐blind clinical RCT of 100 people undergoing elective radical retropubic prostatectomy for the treatment of prostate cancer. Epidural bupivacaine, epidural fentanyl, or no epidural drug was administered prior to induction of anaesthesia and throughout the entire operation resulting in more pain‐free participants at 9.5 weeks | |
| Study on prostatectomy with 3 groups: epidural anaesthesia only, combined epidural and general anaesthesia and general anaesthesia only. Total of 6‐month follow‐up. However, excluded because epidural PCA was provided with bupivacaine and fentanyl for all participants in the postoperative period, thus no control group | |
| Not randomized | |
| Not a randomized trial but only a prospective blinded study of TAP block in breast reconstruction | |
| Study designed to investigate differences in backache as complication/adverse effect of labour epidural | |
| Not a clinical RCT, but only case reports on 3 paediatric patients with continuous regional anaesthesia catheters, 2 patients with pain outcomes at 3 months | |
| Comparison of continuous vs single shot (regional vs regional) anesthesia | |
| Prospective, but not randomized study of preoperative epidural anaesthesia for phantom pain after limb amputation | |
| Excluded because chronic pain present at baseline and is reason for surgery | |
| RCT in which all participants received epidural catheter with participant‐controlled ropivacaine administration, comparing IV ketamine vs no ketamine in people undergoing thoracotomy. Follow‐up of 3 months post‐op | |
| Comparing paravertebral block against local infiltration for hernia repair under SA | |
| RCT comparing use of ear acupuncture vs LA in primiparous women with a vaginal delivery at term undergoing surgical repair of lacerations to the labia or the vagina, perineal lacerations of first or second degree or mediolateral episiotomies. Excluded because of traumatic reason for 'surgical' intervention (suturing), not an elective procedure | |
| Non‐randomized pilot study of 20 patients to examine post‐cholecystectomy pain relief of paravertebral block with bupivacaine, with or without adrenaline added. Alternating participants received adrenaline or did not | |
| Men undergoing totally extra‐peritoneal repair of groin hernia were randomized to pre‐peritoneal bupivacaine vs saline after mesh placement. All prospective trocar sites were infiltrated by bupivacaine in all cases, thus no control group without regional analgesia | |
| Comparing regional against regional technique: clinical RCT comparing preoperative epidural vs postoperative perineural catheter for risk reduction of phantom pain after limb amputation | |
| Not comparing regional vs nonregional anaesthesia. 20 healthy parturients undergoing elective caesarean section under SA were randomized to receive spinal clonidine. Outcome was pain up to 6 months and hyperalgesia | |
| RCT of patients undergoing video‐assisted thoracic surgery, with all participants receiving epidural ropivacaine and fentanyl, with or without magnesium sulphate | |
| Controlled clinical trial designed to detect difference in backache as complication/adverse effect of labour epidural | |
| RCT evaluating use of S(+)‐ketamine for prevention of post thoracotomy pain syndrome at 6 months. Patients undergoing thoracotomy under general anaesthesia, with thoracic epidural catheter placed +/‐ IV infusion of ketamine vs IV placebo with 6 months post‐op follow‐up. All participants received epidural catheter with levobupivacaine, thus no control group | |
| Comparison of LA vs LA | |
| Prospective‐double blind RCT investigating haemodynamic effects, quality of surgical field and postoperative analgesia following surgical field infiltration with different concentrations of adrenaline with and without lignocaine in children undergoing cleft lip repair. Only immediate postop pain was recorded, no long‐term outcomes measured | |
| Patients undergoing endoscopic carpal tunnel release under LA (prilocaine) vs IV regional anaesthesia (prilocaine) | |
| Study excluded for pseudo‐randomization as discussed in (Appendix 9). Double‐blinded (patients and outcome assessors), pseudo‐randomized (sequence generation was by "the toss of a coin") controlled clinical trial on preoperative epidural analgesia for limb amputation with a follow‐up of 12 months including 60 adults in a university setting in Aarhus, Denmark | |
| Comparing preincisional vs postincisional epidural anaesthesia for thoracotomy | |
| Comparing preincisional vs postincisional epidural anaesthesia for thoracotomy | |
| Prospective study examining continuous infusion of ropivacaine at iliac crest donor site in paediatric patients undergoing ICBG. However, non‐randomized with only 1 study group, all with same treatment (no control group) | |
| RCT comparing IV vs epidural fentanyl, not LA vs control | |
| RCT of intra‐abdominal LA for abdominal hysterectomy. Follow‐up 3 months. Excluded because all 3 groups used LA infusions | |
| Comparison of awake video‐assisted thoracoscopic bullectomy with pleural abrasion using thoracic epidural anaesthesia vs general anaesthesia (control) in treatment of spontaneous pneumothorax. No long‐term pain outcomes measured; follow‐up at 12 months was to elicit recurrences of pneumothorax | |
| Patients undergoing laparoscopic ventral hernia repair randomized to receive elastomeric pain pump with continuous LA vs saline. Each trocar site injected with LA in either group thus both groups received LAs. Total follow‐up 3 months | |
| Measured outcome was a depression score, no chronic postsurgical pain measured | |
| Comparison of pre‐emptive thoracic epidural analgesia with or without ketamine in people undergoing operations using classic posterolateral thoracotomy incisions. Thus, no control group. Total follow‐up of 3 months post‐op | |
| Follow‐up only 2 months | |
| RCT investigating pre‐ vs postoperative epidural anaesthesia after thoracotomy | |
| Pain outcomes measured < 3 months | |
| Study on effect of adjuvants for LAs to prevent chronic postsurgical pain. All 19 participants received a continuous brachial plexus block for 1 week after the amputation of an upper extremity. In addition they were treated with the NMDA antagonist memantine or placebo for 4 weeks | |
| RCT of 60 men aged 20‐40 years undergoing inguinal herniorrhaphy, comparing preoperative oral gabapentin to placebo and the effects on acute and long‐term pain. All participants received intrathecal bupivacaine. Follow‐up total of 6 moths post‐op | |
| RCT looking at the effect of wound infiltration with bupivacaine before insertion of trocars on post‐op pain and respiratory impairment in people undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. No long‐term pain outcomes measured | |
| Randomized trial investigating pre‐ vs postincisional pre‐emptive thoracic epidural analgesia for thoracotomy with outcomes at 6 months, but with no control group without regional anaesthesia | |
| Pain outcomes measured only until 24 h post‐op; 3‐month follow‐up was only for recurrence and complications | |
| Studying the adjuvant effect of IV ketamine vs placebo in 49 thoracotomy patients, all participants receiving ropivacaine with morphine via epidural analgesia for 2 days | |
| Patients with chronic cholecystitis divided into 4 groups, to receive either saline or different combinations of bupivacaine at gallbladder bed and trocar sites. No long‐term pain outcome measures | |
| Pain outcomes measured only up to 2‐month follow‐up in this RCT on would infiltration after breast surgery | |
| Article in Mandarin. No comparison group without regional anaesthesia | |
| Comparing block vs block with no pain outcome measured | |
| RCT on patients undergoing lower limb amputation received combined intrathecal/epidural anaesthetic for surgery followed by epidural infusion with bupivacaine with ketamine vs bupivacaine with placebo (saline). No control group as both received LA | |
| We acknowledge the study author's response to our inquiry; pain data only measured until 2 months post‐op |
ICBG: iliac crest bone graft; IV: intravenous; NMDA : N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate receptor; PCA: patient controlled analgesia; RCT: randomized controlled trial; SA: spinal anaesthetic; TAP: transabdominal plane block; VAS: visual analogue scale
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (patient and outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, RCT Sequence generation randomized follow‐up: 12 months |
| Participants | Participants : 80 adults, at a teaching hospital, Springfield, MA, USA Operation: lower limb amputation because of ischaemic necrosis, secondary to peripheral vascular disease 2 groups, size: 40/40 Age (group 1, 2): 68 years (SD ± 12 ), 65 years (SD ± 17) Men/women (group 1, 2): 23/17, 25/15 Comorbidities (group 1, 2): BKA:AKA ratio 29:11, 26:14 |
| Interventions | Group 1 (treatment): GA (fentanyl), intra‐op perineural injection of bupivacaine 10 mL 0.25% and clonidine 100 µg, post‐op morphine IV and paracetamol (acetaminophen)/oxycodone orally Group 2 (placebo): GA (fentanyl), intra‐op perineural injection of placebo, post‐op morphine IV and paracetamol/oxycodone orally Adjuvants: clonidine perineurally Immediate post‐op pain control: statistically meaningful reduction in analgesic consumption |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: phantom limb pain and stump pain at 12 months Continuous: not reported Secondary: not reported |
| Notes | The sciatic nerve was infiltrated for AKA or the posterior tibial nerve for BKA. We could not make sense of some numbers reported on attrition. As reported 22 January 2009, SS Reuben was accused of publishing fraudulent data. Up to 22 papers have been or will be retracted by the journals in which they have been published (Retraction notice Anesthesia and Analgesia 20 February 2009 (Shafer 2009)). This article appears not to be among the retracted manuscripts. We placed it in the classification pending section on the advice of Cochrane Anaesthesia, Critical and Emergency Care. |
| Methods | Not yet assessed |
| Participants | Not yet assessed |
| Interventions | Not yet assessed |
| Outcomes | Not yet assessed |
| Notes | Found during top‐up search December 2017 |
AKA: above‐the‐knee amputation; BKA: below‐the‐knee amputation; GA: general anaesthesia
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
| Trial name or title | Study protocol for a double blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial of continuous subpectoral local anaesthetic infusion for pain and shoulder function following mastectomy: SUB‐pectoral Local anaesthetic Infusion following MastEctomy (SUBLIME) study |
| Methods | Single‐blinded (outcome observer) clinical RCT Sequence generation via computer‐generated randomization list follow‐up: 6 months |
| Participants | Participants: all women presenting for unilateral mastectomy surgery at the Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust and Royal Devon and Exeter NHS Foundation Trust, aged ≥ 18 years Operation: mastectomy with or without axillary involvement 2 groups, size: N/A Age (range), groups 1, 2: N/A All female participants Exclusion criteria: inability to give informed consent; primary reconstructive surgery; hypotension, hypovolaemia or any form of shock; known allergy or sensitivity to LA agents, morphine, paracetamol or ondansetron; pregnancy; daily opioid analgesic use; inability to understand or use a PCA device; inability to understand or complete the visual analogue assessment tools; concurrent participation in another interventional study that might conflict with this study |
| Interventions | Group 1 (saline, control arm): 0.9% sodium chloride, is sourced from standard NHS supplies at the participating sites, delivered by means of an infusion catheter and device, supplied as a sterile prepacked kit and licensed for the delivery of LA. At the end of the surgical procedure the surgeon inserts the infusion catheter percutaneously into the subpectoral plane under direct vision within the surgical field. After skin closure, a 20 mL bolus of comparator treatment is given via the catheter, which is then connected to the infusion device to provide an infusion of study treatment at a continuous rate of 5 mL/h for 24 h. Group 2 (levobupivacaine): 0.25% levobupivacaine (chirocaine), an established LA infusion agent, prepared as a 2.5 mg/mL solution and packaged by the manufacturer (Abbott) delivered by means of an infusion catheter and device, supplied as a sterile prepacked kit and licensed for the delivery of LA. At the end of the surgical procedure the surgeon inserts the infusion catheter percutaneously into the subpectoral plane under direct vision within the surgical field. After skin closure, a 20 mL bolus of active or comparator treatment is given via the catheter, which is then connected to the infusion device to provide an infusion of study treatment at a continuous rate of 5 mL/h for 24 h. In the active treatment arm this equates to a 50 mg bolus of levobupivacaine followed by an infusion of 12.5 mg/h. Both groups: paracetamol 1 g IV, ondansetron 4 mg IV, and dexamethasone 3.3 mg (+/‐ 0.1 mg) IV unless clinically contraindicated. Intubation and ventilation at anaesthetist’s discretion ‐ with muscle relaxant of anaesthetist’s choice. Sevoflurane in air: depth of anaesthesia at anaesthetist’s discretion. Fentanyl: 3 µg/kg to 6 µg/kg IV during surgery. Fluids: at anaesthetist’s discretion. All other nonopiate and nonantiemetic drugs: at anaesthetist’s discretion. IV rescue morphine in recovery unit, 2 mg increments IV morphine PCA, 1 mg bolus, 5 min lockout. Paracetamol 1 g 6‐hourly orally. Ibuprofen 400 mg 8‐hourly orally unless contraindicated as needed: ondansetron 4 mg (IV) 8‐hourly and cyclizine 50 mg (IV) 8‐hourly Adjuvants: none Immediate postop pain control: data not available |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: VAS pain scores at rest at 24 h, 14 days and 6 months after surgery; BPI at 6 months. Secondary: total morphine consumption (mg) in the first 24 h (defined as the 24 h following start of the subpectoral infusion), including all morphine given in the recovery unit and cumulative PCA use as recorded by the PCA device and (2) total pain over the first 24 h, as defined by measurement of the area‐under‐the‐curve of each participant’s self‐reported pain scores at rest, measured using a VAS. VAS pain scores are recorded in the recovery unit and then at 4‐hourly intervals for the first 24 h. Secondary outcome measures include the number of PCA attempts in the first 24 h following start of infusion. Incidence of postoperative nausea and/or vomiting and use of supplemental analgesics and postoperative antiemetics in the first 24 h; self‐reported analgesia use at 14 days and 6 months; duration of hospital stay; shoulder movement assessed by goniometry at 24 h, 14 days and 6 months following surgery; shoulder function (as measured by the validated 31) at 6 months. Following the participant’s discharge, the length of stay in hospital is recorded by the research nurse. Adverse events reported: data not available |
| Starting date | 15 October 2012 |
| Contact information | Dr Roger Langford, [email protected]. nhs.uk |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Postoperative pain relief after laparoscopic gynaecological surgery: a pilot study of pre‐emptive superior hypogastric plexus block versus placebo using ropivacaine. The LAP‐HYPOPLEX study |
| Methods | Quote: a "prospective double‐blind randomised controlled trial" with parallel assignment; this is an efficacy study, single centre |
| Participants | Women undergoing (quote:) "gynaecological diseases for complex laparoscopic surgery" |
| Interventions | The superior hypogastric plexus is identified with the laparoscope during surgery, the women receive pre‐emptive infiltration of 20 mL of 0.75% ropivacaine or placebo. |
| Outcomes | Participants are contacted 6 months after surgery with a postal questionnaire and telephone interview to assess chronic pain syndrome. |
| Starting date | Unclear, before 2012 |
| Contact information | Liew A: Anaesthetics, Sydney Women's Endosurgery Centre, St George Private Hospital, Sydney, NSW, Australia |
| Notes | www.aaic.net.au/document/?D=20110649 |
| Trial name or title | Continuous transgluteal sciatic nerve block to prevent phantom limb pain after trans‐femoral amputation |
| Methods | Prospective, randomized double‐blind trial Single centre |
| Participants | Ages eligible for study: not specified Genders eligible for study: both Estimated enrolment: 40 People undergoing trans‐femoral lower limb amputation |
| Interventions | Quote. "a pre‐operative transgluteal sciatic perineural catheter is placed for 5‐days continuous infusion of L‐Bupivacaine vs saline." |
| Outcomes | Quote: "pain assessment via Mc Gill score and OBAS (Overall Benefits of Analgesia Score) test on at 3, 6, and 12 months." |
| Starting date | December 2013 |
| Contact information | Michael Michael, MD e‐mail: [email protected] |
| Notes | We were unable to contact the study author to request more information |
| Trial name or title | Regional anaesthesia and breast cancer recurrence: prospective, randomized, double‐blinded, multicenter clinical trial to compare postoperative analgesia and cancer outcome after combined paravertebral versus thoracic epidural versus general anaesthesia for breast cancer surgery |
| Methods | Prevention, randomized, open‐label, active‐control, parallel‐assignment, efficacy study |
| Participants | Ages eligible for study: 18‐85 years Genders eligible for study: women only Estimated enrolment: 1600 Women undergoing mastectomies or isolated lumpectomy with axillary node dissection |
| Interventions | Combined paravertebral vs thoracic epidural vs general anaesthesia |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome is cancer recurrence with a follow‐up of 5 years. Secondary outcomes include chronic pain, among others, with a follow‐up of 6 and 12 months |
| Starting date | January 2007 |
| Contact information | Nancy Graham, RN Tel: +1216‐445‐7530 e‐mail: [email protected] |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Prevention of phantom limb pain after transtibial amputation (PLATA) |
| Methods | Randomized, double‐blind (participant, caregiver, outcomes assessor), parallel‐assignment, efficacy study, multi‐centred |
| Participants | Ages eligible for study: ≥ 18 years Genders eligible: both Estimated enrolment: 400 |
| Interventions | Quote. "all patients will receive standard optimised intravenous anaesthesia and analgesia (opiate patient‐controlled analgesia (PCA), intravenous ketamine). People in the intervention group will receive additional infusion of local anaesthetic via a sciatic nerve catheter placed under ultrasound guidance." |
| Outcomes | Point prevalence of chronic phantom limb pain (time frame: 12 months after amputation) |
| Starting date | August 2013 |
| Contact information | Philipp Lirk, MD Tel: +31(20)566 ext 4032 Email: [email protected] |
| Notes | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01626755 |
| Trial name or title | Continuous wound infusion of local anaesthetic and steroid after major abdominal surgery: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant and outcome assessor) clinical RCT Sequence via computer‐generated list follow‐up: 3 months |
| Participants | Participants: 120 men and women at university hospital in Italy Operation: major abdominal surgery by laparotomy 2 groups, size: 60/60 Age: 18‐85 years old Men/women: not reported Exclusion criteria: regular use of opioid analgesics, history of drugs or alcohol abuse (or both), postoperative hospitalisation in intensive care with sedation or mechanical ventilation (or both), neurological disorders, any heart conduction disease, any cognitive or mental disorder hindering a participant from providing informed consent, BMI > 30, diabetes (type I or II), allergy to study drugs, and use of epidural analgesia |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine infusion): GA is given using propofol and midazolam (as deemed appropriate by the anaesthesiologist), opioids (fentanyl 0.2 μg/kg or remifentanil 0.1‐0.25 mg/kg/min or both), and muscle relaxants (cisatracurium/rocuronium) and maintained with sevoflurane. A morphine bolus of 0.15 mg/kg is given 30‐45 min before the end of surgery. An infusion catheter is placed by the surgeon in the fascial plane between peritoneum and fascia transversalis, and a 10 mL bolus of 0.2% ropivacaine is administered immediately after muscular plane closure; the catheter is then connected to an electronic pump to give a continuous infusion of pain medications. During the first 24 h, all participants receive ropivacaine 0.2% + methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg, 10 mL/h (total volume of 240 mL in 24 h) continuous wound infusion; additionally, either paracetamol (acetaminophen) 1000 mg or ketorolac 30 mg every 8 h is prescribed. Rescue analgesia in the first 48 h is provided by PCA pump with morphine (0.5 mg/mL, bolus 1 mg, lock‐out 5 min, 20 mg limit every 4 h) Group 2 (control): exactly the same as above, except after 24 h, 10 mL/h continuous infusion of saline 0.9% given to control group Adjuvants: methylprednisolone Immediate post‐op pain control: not reported |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: NRS Other reported: acute postoperative pain, use of morphine equivalents, analgesic consumption, side effects (postoperative nausea and vomiting, sedation, and any signs of LA or steroid systemic toxicity), and differences in terms of wound healing or wound infections. |
| Starting date | October 2013 |
| Contact information | Dario Bugada, M.D. Email: [email protected] |
| Notes | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02002663 |
| Trial name or title | The effect of transversus abdominis plane block on acute and chronic pain after inguinal hernia repair |
| Methods | Double‐blinded (participant, outcome assessor), placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial Sequence generation not described Follow‐up for 6 months |
| Participants | Participants: 35 adults in a university setting in Athens, Greece Operation: inguinal hernia repair 2 groups, size: not specified Age (± SD), group 1, 2: not specified Men/women, group 1, 2: not specified Exclusion criteria: inability to consent to the study; BMI > 40 kg/m2; skin infection at the puncture site; contraindication to monoamide LAs, paracetamol, NSAID's (parecoxib); preoperative use of opioids or NSAIDs for chronic pain conditions |
| Interventions | Group 1 (ropivacaine): during the operation participants all received remifentanil infusion titrated as to maintain heart rate and systolic arterial pressure within 20% of baseline. In the PACU, participants received morphine boluses, until the NRS score was ≤ 3. They also had access to PCA device administering 1 mg doses of morphine as rescue analgesia. TAP block was applied intraoperatively using 20 mL of 0.75% ropivacaine Group 2 (control): same intervention as above except saline was substituted for ropivacaine for TAP block Adjuvants: none Immediate post‐op pain control: meaningful improvement |
| Outcomes | Dichotomous: none Continuous: NRS Secondary: intraoperative dose of remifentanil, mg of IV morphine used in the PACU, and total dose of morphine administered via the PCA device |
| Starting date | January 2014 |
| Contact information | Anne Theodoraki, M.D. Email: [email protected] |
| Notes | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02030223 |
BMI: body mass index; BPI: Brief Pain Inventory; g: gram; GA: general anaesthesia; h: hours; IV: intravenous; mg: milligram; LA: local anaesthetic; N/A: not applicable; NHS: National Health Service; NRS: numerical rating scale; OBAS: overall benefits of analgesia score; PACU: postanaesthesia care unit; PCA: patient controlled analgesia; TAP: transversus abdominis plane; TEA: thoracic epidural anaesthesia; VAS: visual analogue scale; µg: microgram
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 PPP three to 18 months after thoracotomy Show forest plot | 7 | 499 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.52 [0.32, 0.84] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 1 PPP three to 18 months after thoracotomy. | ||||
| 2 PPP three to six months after cardiac surgery Show forest plot | 2 | 116 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.76 [‐1.73, 0.21] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 2 PPP three to six months after cardiac surgery. | ||||
| 3 PPP three to twelve months after breast cancer surgery Show forest plot | 18 | 1297 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.28, 0.68] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 3 PPP three to twelve months after breast cancer surgery. | ||||
| 3.1 Paravertebral block | 6 | 419 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.39, 0.97] |
| 3.2 Intravenous lidocaine | 2 | 97 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.08, 0.69] |
| 3.3 Multimodal block | 4 | 402 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.32, 1.77] |
| 3.4 Local infiltration | 6 | 379 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.12, 0.73] |
| 4 PPP three to eight months after caesarean section Show forest plot | 4 | 551 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.46 [0.28, 0.78] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 4 PPP three to eight months after caesarean section. | ||||
| 5 Pain score three to six months after caesarean section Show forest plot | 2 | 110 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.14 [‐0.34, 0.61] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 5 Pain score three to six months after caesarean section. | ||||
| 6 PPP three to 55 months after Iliac crest bone graft Show forest plot | 3 | 123 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.20 [0.04, 1.09] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 6 PPP three to 55 months after Iliac crest bone graft. | ||||
| 7 PPP six to 12 months after amputation Show forest plot | 2 | 108 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.53 [0.21, 1.33] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 7 PPP six to 12 months after amputation. | ||||
| 8 PPP six to 12 months after laparotomy Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 8 PPP six to 12 months after laparotomy. | ||||
| 9 PPP three to 12 months after hernia repair Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 9 PPP three to 12 months after hernia repair. | ||||
| 10 Pain score three months after prostatectomy Show forest plot | 2 | 150 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.06 [‐0.26, 0.38] |
| Analysis 1.10  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 10 Pain score three months after prostatectomy. | ||||
| 11 SF‐36 bodily pain score at three to six months after hysterectomy Show forest plot | 3 | 297 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.70 [‐1.06, 4.46] |
| Analysis 1.11  Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 11 SF‐36 bodily pain score at three to six months after hysterectomy. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 PPP after thoracotomy Show forest plot | 6 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 1 PPP after thoracotomy. | ||||
| 1.1 Three months follow‐up | 5 | 428 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.40, 1.20] |
| 1.2 Six months follow‐up | 5 | 370 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.24, 0.63] |
| 2 PPP after cardiac surgery Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 2 PPP after cardiac surgery. | ||||
| 2.1 Three months follow‐up | 2 | 116 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.77 [‐1.74, 0.20] |
| 3 PPP after breast cancer surgery Show forest plot | 19 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 3 PPP after breast cancer surgery. | ||||
| 3.1 Three months follow‐up | 11 | 966 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.34 [0.19, 0.61] |
| 3.2 Six months follow‐up | 9 | 515 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.37, 0.84] |
| 3.3 12 months follow‐up | 2 | 113 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.04, 10.47] |
| 4 PPP after caesarean section Show forest plot | 4 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 4 PPP after caesarean section. | ||||
| 4.1 Three months follow‐up | 2 | 137 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.39, 3.07] |
| 4.2 Six months follow‐up | 3 | 492 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.26, 0.74] |
| 5 PPP after amputation Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 2.5  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 5 PPP after amputation. | ||||
| 6 PPP after laparotomy Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 2.6  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 6 PPP after laparotomy. | ||||
| 7 PPP after hernia repair Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 2.7  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 7 PPP after hernia repair. | ||||
| 8 PPP after hysterectomy Show forest plot | 2 | 135 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.23, 5.02] |
| Analysis 2.8  Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 8 PPP after hysterectomy. | ||||
| 8.1 Three months follow‐up | 2 | 135 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.23, 5.02] |
The study flow diagram documents the search and selection process. We included 63 studies. We were able to pool data from 39 of the 63 included studies in our inclusive analysis; data from 24 studies were not available or otherwise could not be pooled (Appendix 11).

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies

Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study
This graph plots attrition versus effect size (log odds ratio) for studies investigating regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent pain after thoracotomy (blue), breast surgery (pink) and caesarean section (green). Symbol size decreases with attrition. Repeated follow‐ups within one study are linked with a black line. We are unable to discern any association between attrition, follow‐up time and effect measure; this lends support to our decision to pool studies reporting outcomes at different follow‐up intervals and with different attrition.

The funnel plot for breast surgery including all outcomes at any follow‐up interval for all breast surgery studies is inconclusive for publication bias.

Forest plot of comparison 1. Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), outcome 1.3, PPP three to 12 months after breast cancer surgery

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 1 PPP three to 18 months after thoracotomy.
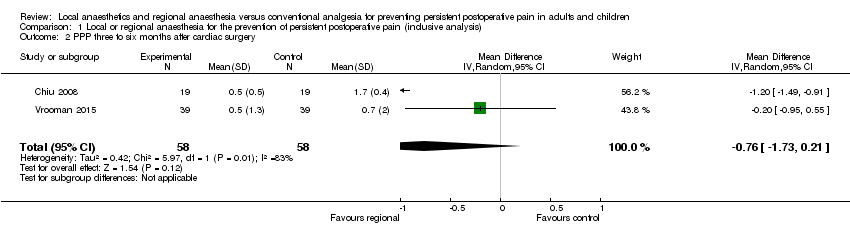
Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 2 PPP three to six months after cardiac surgery.
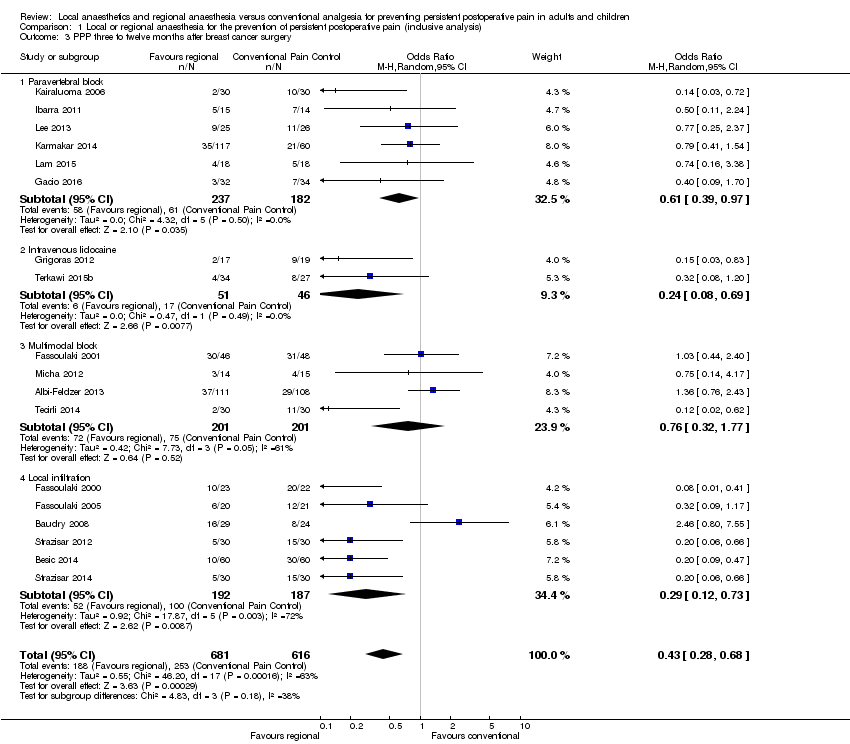
Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 3 PPP three to twelve months after breast cancer surgery.

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 4 PPP three to eight months after caesarean section.

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 5 Pain score three to six months after caesarean section.

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 6 PPP three to 55 months after Iliac crest bone graft.

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 7 PPP six to 12 months after amputation.
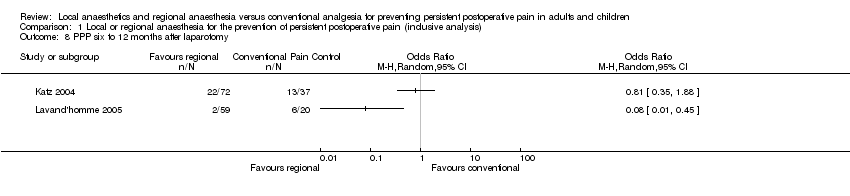
Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 8 PPP six to 12 months after laparotomy.

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 9 PPP three to 12 months after hernia repair.
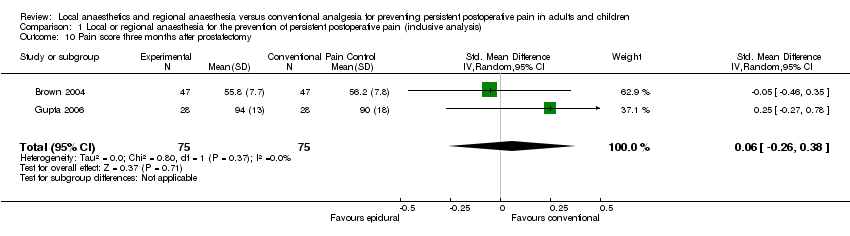
Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 10 Pain score three months after prostatectomy.

Comparison 1 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (inclusive analysis), Outcome 11 SF‐36 bodily pain score at three to six months after hysterectomy.

Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 1 PPP after thoracotomy.

Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 2 PPP after cardiac surgery.

Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 3 PPP after breast cancer surgery.

Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 4 PPP after caesarean section.

Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 5 PPP after amputation.
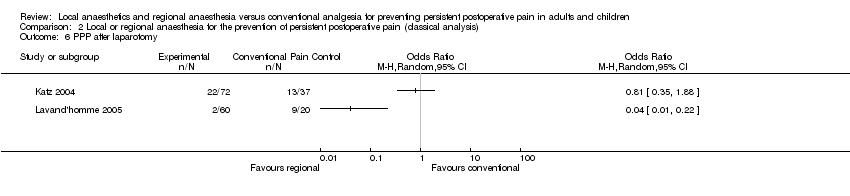
Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 6 PPP after laparotomy.
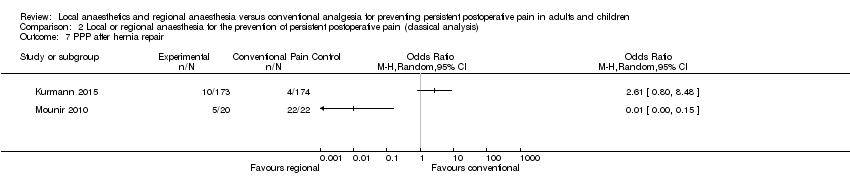
Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 7 PPP after hernia repair.

Comparison 2 Local or regional anaesthesia for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain (classical analysis), Outcome 8 PPP after hysterectomy.
| Should thoracic epidural anaesthesia or conventional pain control be used to prevent persistent pain after open thoracotomy | ||||||
| Patient or population: people undergoing open thoracotomy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Conventional pain control | Thoracic epidural anaesthesia | |||||
| Persistent pain 3 to 18 months after thoracotomy (We defined persistent postsurgical pain as new pain that did not exist before the operation, measured using differences in scores based on validated pain scales; patient interview between 3 to 18 months after surgery.) | Study population | OR 0.52 (0.32 to 0.84) | 499 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | All studies investigated persistent pain after open thoracotomy. The results cannot be extended to video‐assisted thoracotomy or other (minimally invasive) surgeries of the chest. The five of the seven included studies using thoracic epidural anaesthesia showed the strongest effect. The results cannot be extended to other interventions like paravertebral blocks. Conventional pain control with opioids and NSAID was the comparator. Event rates of persistent pain after thoracotomy were reported between 25% to 65% Regional anaesthesia may prevent persistent (chronic) pain after open thoracotomy in one out of seven people treated, thoracic epidural anaesthesia in one out of five people treated. | |
| 525 per 1000 | 332 per 1000 | |||||
| Low | ||||||
| 250 per 1000 | 130 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 500 per 1000 | 310 per 1000 | |||||
| Adverse effects of epidural anaesthesia ‐ not reported | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | ‐ | See comment | Adverse effects of epidural anaesthesia were not systematically reported and due to their low frequency are better investigated in patient registries. |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1While outcome observers' blinding was described, study participants were not blinded; this is acceptable because participant and provider blinding is difficult in regional anaesthesia. | ||||||
| Should regional anaesthesia or conventional pain control be used to prevent persistent pain following breast cancer surgery | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with breast cancer undergoing elective surgery | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Conventional pain control | Paravertebral block | |||||
| Persistent pain 3 to 12 months after breast cancer surgery (We defined persistent postsurgical pain as new pain that did not exist before the operation, measured using differences in scores based on validated pain scales; patient interview between 3 to 12 months after surgery.) | Study population | OR 0.43 (0.28 to 0.68) | 1297 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Conventional pain control with opioids and NSAID was the comparator. Event rates of persistent pain after breast cancer were reported around 30%. Pooling all studies, regional anaesthesia may prevent persistent pain after breast surgery in one out of every seven women. Limiting the analysis to paravertebral block, the number of women needed to treat for one person to benefit was 11. | |
| 427 per 1000 | 239 per 1000 | |||||
| Low | ||||||
| 200 per 1000 | 95 per 1000 | |||||
| High | ||||||
| 600 per 1000 | 387 per 1000 | |||||
| Adverse effects of paravertebral block for breast cancer surgery | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | ‐ | See comment | Adverse effects of regional anaesthesia after breast surgery were not systematically reported and due to their low frequency are better investigated in registries. |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1We downgraded quality of evidence by one level because conclusions may be considerably weakened by performance bias, shortcomings in allocation concealment, considerable attrition and incomplete outcome data. | ||||||
| Should local or regional anaesthesia be used for the prevention of chronic pain after caesarean section | ||||||
| Patient or population: women after caesarean section Comparison: conventional pain control | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Local or regional anaesthesia | |||||
| Persistent pain 3 to 8 months after caesarean section (We defined persistent postsurgical pain as new pain that did not exist before the operation, measured using differences in scores based on validated pain scales; patient interview between 3 to 8 months after surgery.) | Study population | OR 0.46 | 551 participants | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Event rates of persistent pain after caesarean section are reported around 10%. The number of women needed to be treated for one woman to benefit from regional anaesthesia after caesarean section was 19. | |
| 179 per 1000 | 91 per 1000 | |||||
| Low | ||||||
| 50 per 1000 | 24 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 100 per 1000 | 49 per 1000 | |||||
| Adverse effects of local or regional anaesthesia ‐ not reported | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | ‐ | See comment | Adverse effects of local or regional anaesthesia after caesarean section were not systematically reported and due to their low frequency are better investigated in registries. |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1The results are based on only four, mostly smaller studies. Meta‐analysis results based on small numbers tend to overestimate the effects. | ||||||
| Should continuous donor site local anaesthetic infusion or conventional pain control be used for the prevention of persistent postoperative pain after iliac crest bone graft harvesting | ||||||
| Patient or population: people after iliac crest bone graft harvesting Comparison: conventional pain control | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Continous donor site local anaesthetic infusion | |||||
| Persistent pain 3 to 55 months after iliac crest bone graft harvesting (We defined persistent postsurgical pain as new pain that did not exist before the operation, measured using differences in scores based on validated pain scales; patient interview between 3 to 55 months after surgery) | Low | OR 0.20 | 123 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | We accepted study author classification of the presence of persistent postoperative pain. Some assessed only pain vs no pain, others pain and dysaesthesia vs none. Event rates of persistent pain after iliac crest bone graft harvesting were reported between 20% to 40% and was assumed to be around 30%. | |
| 200 per 1000 | 48 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 400 per 1000 | 118 per 1000 | |||||
| High | ||||||
| 600 per 1000 | 231 per 1000 | |||||
| Adverse effects of continuous local anaesthetic infusion ‐ not reported | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | ‐ | See comment | Adverse effects of regional anaesthesia after iliac crest bone graft harvesting were not systematically reported and due to their low frequency are better investigated in registries. |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1The results are based on only three small studies. Meta‐analysis results based on small numbers tend to overestimate the effects. Including an additional RCT with continuous outcomes in a Bayesian evidence synthesis further strengthens the evidence favouring the intervention (Blumenthal 2005). | ||||||
| Should continuous intravenous local anaesthetic infusion or conventional pain control be used for the prevention of persistent pain after breast cancer surgery | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with breast cancer undergoing elective surgery Comparison: conventional pain control | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Continous intravenous local anaesthetic infusion | |||||
| Persistent pain 3 to 6 months after breast cancer surgery (We defined persistent postsurgical pain as new pain that did not exist before the operation, measured using differences in scores based on validated pain scales; patient interview between 3 to 6 months after surgery.) | Study population | OR 0.24 | 97 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Event rates of persistent pain after breast cancer surgery ranged in this population between 20% to 40%. One in three women benefited on average from continuous intravenous infusion of local anaesthetics after breast cancer surgery. | |
| 370 per 1000 | 123 per 1000 | |||||
| Low | ||||||
| 200 per 1000 | 57 per 1000 | |||||
| High | ||||||
| 600 per 1000 | 265 per 1000 | |||||
| Adverse effects of continuous local anaesthetic infusion ‐ not reported | See comment | See comment | Not estimable | ‐ | See comment | Adverse effects of intravenous infusion of local anaesthetics after breast cancer surgery were not systematically reported and due to their low frequency are better investigated in registries. |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1We downgraded quality of evidence by one level because conclusions may be considerably weakened by the small number of studies included. These two studies are however consistent and of high methodological quality. Still, meta‐analysis results based on small numbers tend to overestimate the effects. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 PPP three to 18 months after thoracotomy Show forest plot | 7 | 499 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.52 [0.32, 0.84] |
| 2 PPP three to six months after cardiac surgery Show forest plot | 2 | 116 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.76 [‐1.73, 0.21] |
| 3 PPP three to twelve months after breast cancer surgery Show forest plot | 18 | 1297 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.28, 0.68] |
| 3.1 Paravertebral block | 6 | 419 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.39, 0.97] |
| 3.2 Intravenous lidocaine | 2 | 97 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.08, 0.69] |
| 3.3 Multimodal block | 4 | 402 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.32, 1.77] |
| 3.4 Local infiltration | 6 | 379 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.12, 0.73] |
| 4 PPP three to eight months after caesarean section Show forest plot | 4 | 551 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.46 [0.28, 0.78] |
| 5 Pain score three to six months after caesarean section Show forest plot | 2 | 110 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.14 [‐0.34, 0.61] |
| 6 PPP three to 55 months after Iliac crest bone graft Show forest plot | 3 | 123 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.20 [0.04, 1.09] |
| 7 PPP six to 12 months after amputation Show forest plot | 2 | 108 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.53 [0.21, 1.33] |
| 8 PPP six to 12 months after laparotomy Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 PPP three to 12 months after hernia repair Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10 Pain score three months after prostatectomy Show forest plot | 2 | 150 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.06 [‐0.26, 0.38] |
| 11 SF‐36 bodily pain score at three to six months after hysterectomy Show forest plot | 3 | 297 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.70 [‐1.06, 4.46] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 PPP after thoracotomy Show forest plot | 6 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Three months follow‐up | 5 | 428 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.40, 1.20] |
| 1.2 Six months follow‐up | 5 | 370 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.24, 0.63] |
| 2 PPP after cardiac surgery Show forest plot | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Three months follow‐up | 2 | 116 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.77 [‐1.74, 0.20] |
| 3 PPP after breast cancer surgery Show forest plot | 19 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 Three months follow‐up | 11 | 966 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.34 [0.19, 0.61] |
| 3.2 Six months follow‐up | 9 | 515 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.37, 0.84] |
| 3.3 12 months follow‐up | 2 | 113 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.04, 10.47] |
| 4 PPP after caesarean section Show forest plot | 4 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.1 Three months follow‐up | 2 | 137 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.39, 3.07] |
| 4.2 Six months follow‐up | 3 | 492 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.44 [0.26, 0.74] |
| 5 PPP after amputation Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6 PPP after laparotomy Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7 PPP after hernia repair Show forest plot | 2 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 PPP after hysterectomy Show forest plot | 2 | 135 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.23, 5.02] |
| 8.1 Three months follow‐up | 2 | 135 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.23, 5.02] |

