Pentoxifilina para la nefropatía diabética
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not describe sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not describe allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not describe blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not describe sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not describe allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not describe blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information. Some clinically important outcomes, such as adverse events, not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
Patients were stratified based on DKD stage
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Participants randomised = 86, but number analysed = 80. ITT analysis not conducted |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
Patients were stratified based on DKD stage
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Participants and outcome assessors were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Participants randomised = 37, but number analysed = 34. ITT analysis not conducted |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided: adverse events not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided: e.g., adverse events were not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | After basal measurements, patients with DM were randomly assigned using a computer‐generated random‐number table to either a control (no treatment) or pentoxifylline (treatment) group based on a 1:2 split |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided: e.g. adverse events were not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | After an initial 2 weeks run‐in period, patients were randomised using a computer‐generated random‐number table into a control group or an active treatment group |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report on allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report on blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment method |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report some important clinical outcomes, such as possible adverse events of pentoxifylline |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated random numbers were used to assign participants to pentoxifylline or captopril groups |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Outcomes assessors were blinded to group assignment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated random numbers used to assign participants to pentoxifylline or placebo groups |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | All participants and outcomes assessors were blinded to group assignment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided: e.g., adverse events were not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided e.g. adverse events were not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Participants randomised = 72, but number analysed = 69. ITT analysis not conducted |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Participants randomised = 84, but number analysed = 77. ITT analysis was not conducted |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Free of selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Treatment group
Control group
| |
| Outcomes |
| |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report sequence generation process |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report allocation concealment |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Study did not report blinding |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No missing outcomes data reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided: e.g. adverse events were not reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided for assessment |
ACEi: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; AMI: acute myocardial infarction; ARB: angiotensin receptor blockers; BP: blood pressure; CCB: calcium channel blockers; CrCl: creatinine clearance; CVA: cardiovascular accident; DKD: diabetic kidney disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; gtt: guttae (drops); IV: intravenous; MI: myocardial infarction; NS: not stated; RCT: randomised controlled trial; SCr: serum creatinine; UAE: urinary albumin excretion; UTI: urinary tract infection
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Questionable randomisation | |
| Questionable randomisation | |
| Participants were kidney transplant recipients with unknown underlying kidney diseases | |
| Questionable randomisation | |
| Not RCT | |
| Participants Included diabetic retinopathy and/or DKD. Separate data not available for DKD | |
| Haemodialysis patients | |
| Participants diagnosed with type 2 DM and diabetic neuropathy, not DKD | |
| Participants with moderate‐advanced CKD due to multiple causes. Separate data not available for DKD | |
| Participants diagnosed with type 2 DM, not DKD | |
| Questionable randomisation | |
| Participants diagnosed with advanced kidney failure due to multiple causes. Separate data not available for DKD | |
| Not RCT | |
| Participants diagnosed with progressive CKD due to multiple causes. Separate data not available for DKD |
CKD: chronic kidney disease; DKD: diabetic kidney disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; RCT: randomised controlled trial
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 117 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐0.17, ‐0.03] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment. | ||||
| 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.18 [‐15.55, 5.18] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment. | ||||
| 2.1 Type 2 microalbuminuria | 1 | 30 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐12.0 [‐27.42, 3.42] |
| 2.2 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐21.66, 19.66] |
| 2.3 Type 1 albuminuria | 1 | 18 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [‐21.59, 25.59] |
| 2.4 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.0 [‐31.19, 33.19] |
| 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 117 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.28 [‐3.85, ‐0.70] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment. | ||||
| 4 Overt proteinuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐428.58 [‐661.65, ‐195.50] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 4 Overt proteinuria at end of treatment. | ||||
| 4.1 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐552.0 [‐656.57, ‐447.43] |
| 4.2 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐314.0 [‐367.36, ‐260.64] |
| 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 126 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.29 [‐11.80, 9.23] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment. | ||||
| 5.1 Type 2 microalbuminuria | 2 | 62 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 10.15 [‐15.27, 35.58] |
| 5.2 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 5.0 [‐4.19, 14.19] |
| 5.3 Type 1 microalbuminuria | 1 | 18 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐6.0 [‐11.08, ‐0.92] |
| 5.4 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐22.0 [‐31.41, ‐12.59] |
| 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 126 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.75 [‐9.56, ‐1.94] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment. | ||||
| 6.1 Type 2 microalbuminuria | 2 | 62 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐3.17 [‐7.98, 1.64] |
| 6.2 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐8.07, 6.07] |
| 6.3 Type 1 microalbuminuria | 1 | 18 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐9.0 [‐14.55, ‐3.45] |
| 6.4 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐11.0 [‐18.23, ‐3.77] |
| 7 Any adverse events at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 83 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐0.10, 0.30] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 7 Any adverse events at end of treatment. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment Show forest plot | 5 | 199 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.06, 0.07] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment. | ||||
| 2 Change in albuminuria Show forest plot | 4 | 220 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.18, 1.07] |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 2 Change in albuminuria. | ||||
| 3 Change in proteinuria Show forest plot | 5 | 192 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.46 [0.17, 0.74] |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 3 Change in proteinuria. | ||||
| 4 Systolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 5 | 240 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.28 [‐2.20, 1.63] |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 4 Systolic BP at end of treatment. | ||||
| 5 Diastolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 5 | 240 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.15 [‐1.44, 1.14] |
| Analysis 2.5  Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 5 Diastolic BP at end of treatment. | ||||
| 6 Any adverse events at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | 190 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐0.01, 0.22] |
| Analysis 2.6  Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 6 Any adverse events at end of treatment. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 166 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.08, 0.07] |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment. | ||||
| 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 3.2  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment. | ||||
| 2.1 Compared with ACEi | 2 | 145 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 3.26 [‐1.05, 7.58] |
| 2.2 Compared with clonidine or methyldopa | 1 | 21 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 10.90 [1.40, 20.40] |
| 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 233 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐8.79 [‐27.18, 9.59] |
| Analysis 3.3  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment. | ||||
| 4 Proteinuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 145 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.03, 0.01] |
| Analysis 3.4  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 4 Proteinuria at end of treatment. | ||||
| 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | 272 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.46 [‐0.57, 3.50] |
| Analysis 3.5  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment. | ||||
| 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | 272 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.37 [‐0.23, 2.98] |
| Analysis 3.6  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment. | ||||
| 7 Plasma fibrinogen at end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.7  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 7 Plasma fibrinogen at end of treatment. | ||||
| 8 Adverse events at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 166 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.15, 0.01] |
| Analysis 3.8  Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 8 Adverse events at end of treatment. | ||||
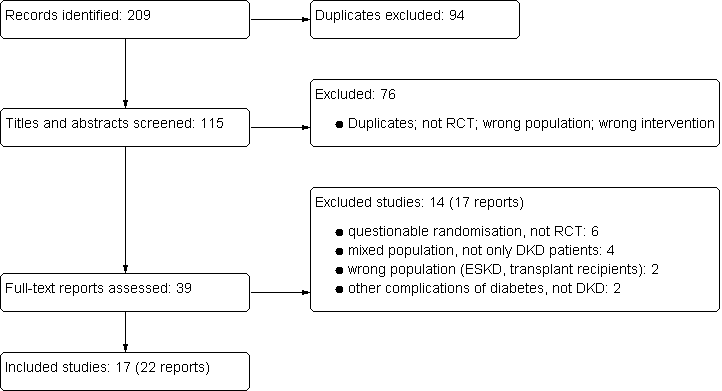
Study flow diagram: pentoxifylline for diabetic kidney disease (DKD)

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
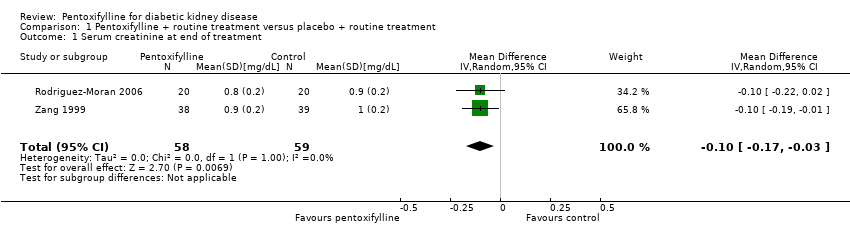
Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment.

Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment.
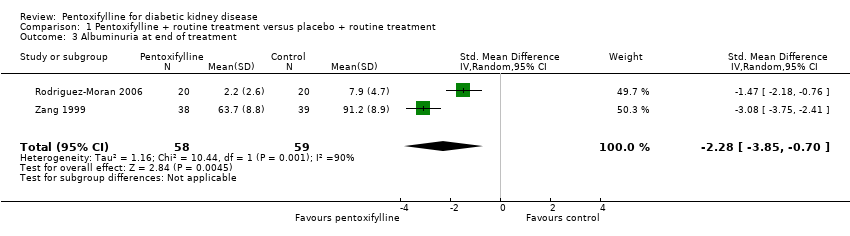
Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment.

Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 4 Overt proteinuria at end of treatment.

Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment.

Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment.
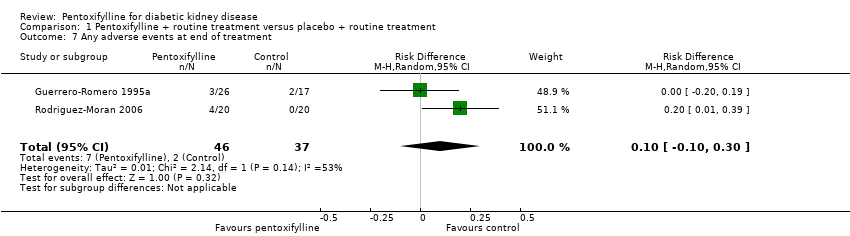
Comparison 1 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus placebo + routine treatment, Outcome 7 Any adverse events at end of treatment.

Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment.
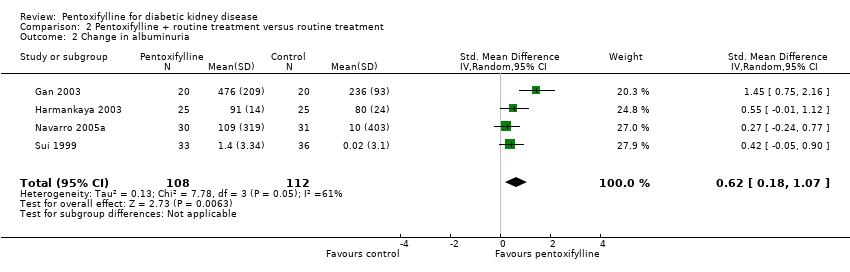
Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 2 Change in albuminuria.

Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 3 Change in proteinuria.
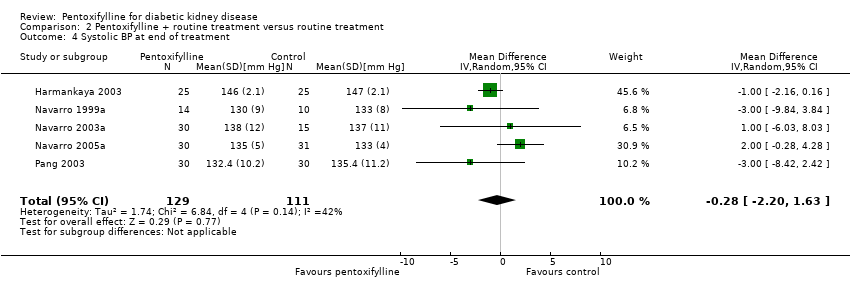
Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 4 Systolic BP at end of treatment.

Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 5 Diastolic BP at end of treatment.
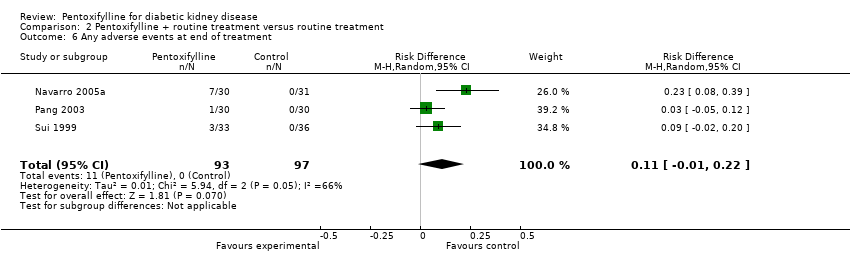
Comparison 2 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus routine treatment, Outcome 6 Any adverse events at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 4 Proteinuria at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 7 Plasma fibrinogen at end of treatment.

Comparison 3 Pentoxifylline + routine treatment versus other drugs + routine treatment, Outcome 8 Adverse events at end of treatment.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 117 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐0.17, ‐0.03] |
| 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.18 [‐15.55, 5.18] |
| 2.1 Type 2 microalbuminuria | 1 | 30 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐12.0 [‐27.42, 3.42] |
| 2.2 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐21.66, 19.66] |
| 2.3 Type 1 albuminuria | 1 | 18 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [‐21.59, 25.59] |
| 2.4 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.0 [‐31.19, 33.19] |
| 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 117 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.28 [‐3.85, ‐0.70] |
| 4 Overt proteinuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐428.58 [‐661.65, ‐195.50] |
| 4.1 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐552.0 [‐656.57, ‐447.43] |
| 4.2 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐314.0 [‐367.36, ‐260.64] |
| 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 126 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.29 [‐11.80, 9.23] |
| 5.1 Type 2 microalbuminuria | 2 | 62 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 10.15 [‐15.27, 35.58] |
| 5.2 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 5.0 [‐4.19, 14.19] |
| 5.3 Type 1 microalbuminuria | 1 | 18 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐6.0 [‐11.08, ‐0.92] |
| 5.4 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐22.0 [‐31.41, ‐12.59] |
| 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 126 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐5.75 [‐9.56, ‐1.94] |
| 6.1 Type 2 microalbuminuria | 2 | 62 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐3.17 [‐7.98, 1.64] |
| 6.2 Type 2 proteinuria | 1 | 22 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐1.0 [‐8.07, 6.07] |
| 6.3 Type 1 microalbuminuria | 1 | 18 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐9.0 [‐14.55, ‐3.45] |
| 6.4 Type 1 proteinuria | 1 | 24 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐11.0 [‐18.23, ‐3.77] |
| 7 Any adverse events at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 83 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐0.10, 0.30] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment Show forest plot | 5 | 199 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.06, 0.07] |
| 2 Change in albuminuria Show forest plot | 4 | 220 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.18, 1.07] |
| 3 Change in proteinuria Show forest plot | 5 | 192 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.46 [0.17, 0.74] |
| 4 Systolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 5 | 240 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.28 [‐2.20, 1.63] |
| 5 Diastolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 5 | 240 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.15 [‐1.44, 1.14] |
| 6 Any adverse events at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | 190 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐0.01, 0.22] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Serum creatinine at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 166 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.08, 0.07] |
| 2 Creatinine clearance at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Compared with ACEi | 2 | 145 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 3.26 [‐1.05, 7.58] |
| 2.2 Compared with clonidine or methyldopa | 1 | 21 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 10.90 [1.40, 20.40] |
| 3 Albuminuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 233 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐8.79 [‐27.18, 9.59] |
| 4 Proteinuria at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 145 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.03, 0.01] |
| 5 Systolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | 272 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.46 [‐0.57, 3.50] |
| 6 Diastolic BP at end of treatment Show forest plot | 3 | 272 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.37 [‐0.23, 2.98] |
| 7 Plasma fibrinogen at end of treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8 Adverse events at end of treatment Show forest plot | 2 | 166 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.15, 0.01] |

