Tratamiento con microondas para el ectropión cervical
Referencias
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en espera de evaluación
Referencias adicionales
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐ randomised controlled trial) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (through call to the author) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (through call to the author) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (Although called for the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (Through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (Through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| RCT ( There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (Through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (Through called for the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| RCT ( There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic.) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial)l) | |
| There was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (Through called for the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| RCT ( there was no documentation as to whether the women who had cervical ectropion were symptomatic.) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT ( According to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (Through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (Through called for the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Retrospective clinical trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (Through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Duplicate publication literature (It was the same study with "Zhang 2006b") | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (Although called for the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Quasi‐randomised controlled trial (through call to the author) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) | |
| Non‐RCT (Through called for the author, we found it was a pseudo randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (through call to the author, we found it was a pseudo‐randomised controlled trial) | |
| Non‐RCT (according to looking up study in detail) |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | RCT duration: not yet known Randomisation method not stated Blinding: not yet known Number of women randomised: n = 204 Number of women analysed: n = 204 Unit of comparison: individuals. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical erosion without cervical cancer and infusorium, neisseria gonorrhoeae vaginitis and mould infection Microwave group (n = 106): Grade I: 22; Grade II: 58; Grade III: 26 Age: 32y; No.of pregnancy: 2.2; No. of births: 1.2 Electrocautery group (n = 98): Grade I: 28; Grade II: 50; Grade III: 20 Age: 30y; No. of pregnancy: 3.1; No. of births: 1.6 Source of participants: medical outpatients. |
| Interventions | Treatment: microwave tissue coagulation (MTC) Time of treatments: during 3 to 7 days after menstrual period. |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) Adverse reaction: bleeding during operation, bellyache pain during operation, more bleeding during decrustation than menstruation The follow‐up period: 8 to 12 weeks |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of Nanyou Hospital, Zhanjiang City and No. 422 Liberation Army Hospital Funding: unclear Failed to contact the author, and it is unclear whether the trial is an authentic RCT. |
| Methods | RCT duration: not yet known Randomisation method not stated Blinding: not yet known Number of women randomised: n = 360 Number of women analysed: n = 360 Unit of comparison: individuals. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical erosion without cervical cancer and infusorium and mould infection Interferon suppository group: n = 120 Microwave group: n = 120 Interferon suppository plus microwave group: n = 120 Grade I. interferon suppository group: 24; microwave group: 24; interferon suppository plus microwave group: 24 Grade II. interferon suppository group: 63; microwave group: 63; interferon suppository plus microwave group: 63 Grade III. interferon suppository group: 33; microwave group: 33; interferon suppository plus microwave group: 33 Source of participants: medical outpatients. |
| Interventions | 1. Interferon suppository 2. Microwave 3. Interferon suppository plus microwave |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) The time of vaginal fluid and the status of vaginal bleeding The follow‐up period: 8 weeks |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, Nanjing first hospital affiliated to Nanjing Medical University Funding: unclear Failed to contact the author, and it is unclear whether the trial is an authentic RCT. |
| Methods | RCT duration 5 years from Jan 2000 to Dec 2005 Randomisation method not stated Single centre Blinding: not yet known Number of women randomised: n = 188 Number of women analysed: n = 188 Unit of comparison: individuals. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with severe cervical erosion without cervical cancer and infusorium, mould infection and venereal disease Microwave group: n = 98 Interferon suppository plus microwave group: n = 90 Exclusion criteria: excluded women with cervical cancer, diagnosed through Papanicolaou test. Excluded women with infusorium, mould infection and venereal disease Source of participants: medical outpatients. |
| Interventions | 1. Microwave group: 45W (power) 2. Interferon suppository plus microwave group: after microwave, interferon suppository one pill once every other day, course of treatment for 15 days |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: Cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) The follow‐up period: not yet known |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of Mudanjiang Railway Central Hospital in Heilongjiang Funding: unclear Failed to contact the author, and it is unclear whether the trial is an authentic RCT. |
| Methods | Randomisation method: not yet known Single centre Blinding: not yet known. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with severe cervical erosion |
| Interventions | 1. Treatment: microwave group 2. Control: not yet known |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) The follow‐up period: not yet known |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of Yiwu Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Funding: unclear Failed to find the full text. |
| Methods | RCT duration: not yet known Randomisation method: not yet known Single centre Blinding: not yet known Number of women randomised: n = 260 Number of women analysed: n = 260 Unit of comparison: individuals. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical erosion Microwave group: n = 130 Electrocautery group: n = 130 Source of participants: medical outpatients. |
| Interventions | 1. Microwave group 2. Electrocautery group |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) The follow‐up period: not yet known |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: The Third People's Hospital of Xiaoshan City, Zhejiang province Funding: unclear Failed to contact the author, and it is unclear whether the trial is an authentic RCT. |
| Methods | Randomisation method: not yet known Single centre Blinding: not yet known. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with severe cervical erosion |
| Interventions | 1. Treatment: microwave group 2. Control: not yet known |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate The follow‐up period: not yet known |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Women and Children's Hospital of Jinzhou City Funding: unclear Failed to find the full text. |
| Methods | Randomisation method: not yet known Single centre Blinding: not yet known. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with severe cervical erosion |
| Interventions | 1.Treatment: microwave group 2. Control: not yet known |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) The follow‐up period: not yet known |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Women and Children's Hospital of Nantong City Funding: unclear Failed to find the full text. |
| Methods | RCT duration 2.5 years from Jul 1997 to Dec 1999 Randomisation method not stated Single centre Blinding: not yet known Number of women randomised: n = 150 Number of women analysed: n = 150 Unit of comparison: individuals. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical erosion without cervical cancer and infusorium, neisseria gonorrhoeae vaginitis and mould infection Microwave group (n = 106): Grade I: 18; Grade II: 47; Grade III: 25 Age: 32y (20 to 40) Electrocautery group (n = 90): Grade I: 12; Grade II: 31; Grade III: 17 Age: 33y (19 to 56) Source of participants: medical outpatients. |
| Interventions | 1. Microwave group 2. Electrocautery group The follow‐up period: 8 and 36 months. Once a week after treatment, once 4 weeks, once 8 weeks, then once 3 months for going on 1 year. And then once half yearly. |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix) The time of vaginal fluid and the status of vaginal bleeding Bleeding during operation and after operation, more bleeding during decrustation than menstruation |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: The first hospital affiliated to Qiqihaer Medical College of Heilongjiang Funding: unclear Failed to contact the author, and it is unclear whether the trial is an authentic RCT. |
| Methods | Randomisation method: not yet known Single centre Blinding: not yet known |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with severe cervical erosion |
| Interventions | 1. Treatment: microwave group 2. Control: not yet known |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate The follow‐up period: not yet known |
| Notes | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of Shuangya People's Hospital Funding: unclear Failed to find the full text. |
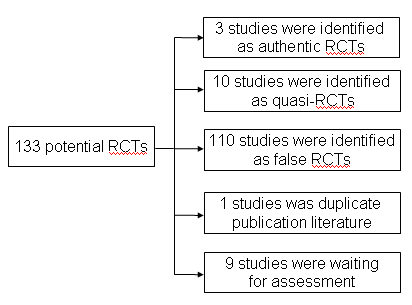
Flow chart of the study excluded process
| Process | Questions |
| Question 1 | Introduce myself and purpose: How do you do? I was a student of Lanzhou University, was doing a review about microwave tissue coagulation in the treatment of cervical ectropion. Purpose of my study was to compare the effects of variety randomisation methods. I had searched out a paper that published in (time, journal) written by you. Could you please tell me what method to be used in this trial? |
| Question 2 | If the subject cannot describe the method clearly, change the question like this: could you please tell me when a new participant enrolled, how did you decide which group the participant should be allocated to? |
| Question 3 | If there was any problem about the first author, the second author or others should be interviewed. |
| Question 4 | Next two questions aim to understand the category of support source for investigated study, I selected one of them or both: (1) Was your study funded by government or any other source? (2) Was your study for new drug development? |
| Question 5 | Judgment should be made immediately for whether it was a real RCT or not. If it be judged as real RCT, next questions aim to understand the status of allocation concealment: (1) Do you know allocation concealment? If so, please clarify. (2) Did you use any method to mask allocation sequence? If any, please clarify. |
| Question 6 | Next question aims to understand the validity of blinding particularly pay attention to whether the detector was blinded or not: Please tell me who were blinded in your trial? |
| Question 7 | We said "thank you" to author. |
| Question 8 | Finally, We needed to judge whether the subject knew well the trial principle or not: if anyone persisted in the method of randomisation as correct but actually wrong or ineligible, it should be judged didn't know; if anyone claimed that "I knew we performed not good enough" or "it was impossible to perform a completely correct RCT" and so on, it should be judged as knew well about the principle of trial but violated knowingly claimed the non‐RCT as RCT. |
| Question 9 | Put all of record in the form. |
| RCTs: randomised controlled trials | |
| Study | |
| Methods | Randomization method not stated. RCT duration: from Jan 1991 to May 1992 |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical ectropion. Macroscopic examination: discriminating acute with chronic cervicitis. |
| Interventions | Treatment: MTC; |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix). |
| Note | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of Chaoyang Hospital Funding: unclear |
| MTC: microwave tissue coagulation CIN: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia | |
| Study | |
| Methods | Randomisation: random digits table; RCT duration: from Aug 2001 to Oct 2001. |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical ectropion. |
| Interventions | Treatment: MTC; Control: CO2 laser. |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: Cure rate (According to appearance of cervix); |
| Note | Location: China. Setting: Shiyan Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Hubei. Funding: unclear. |
| MTC: microwave tissue coagulation CIN: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia | |
| Study | |
| Methods | Randomisation: random digits table; |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with cervical ectropion. Papanicolaou test: Grade I or II. |
| Interventions | Treatment: MTC (once); |
| Outcomes | Efficacy: cure rate (according to appearance of cervix); |
| Note | Location: China Setting: Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics of The First Hospital of Nanping, Fujian. Funding: unclear |
| MTC: microwave tissue coagulation CIN: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia | |
| Study ID | |||
| Design | Parallel single‐centre. | Parallel single‐centre. | Parallel single‐centre. |
| Adequate sequence generation? | Yes. | Yes(random number table). | Yes(random number table). |
| Allocation concealment? | Yes(envelopes). | No. | No. |
| Blinding? | Yes (Single: participants). | No. | No. |
| Incomplete outcome data addressed? | Unclear. | Unclear. | Unclear. |
| Free of selective reporting? | Unclear. | Unclear. | Unclear. |
| Free of other bias? | Unclear. | Unclear. | Unclear. |
| Power calculation | Unclear. | Unclear. | Unclear. |

