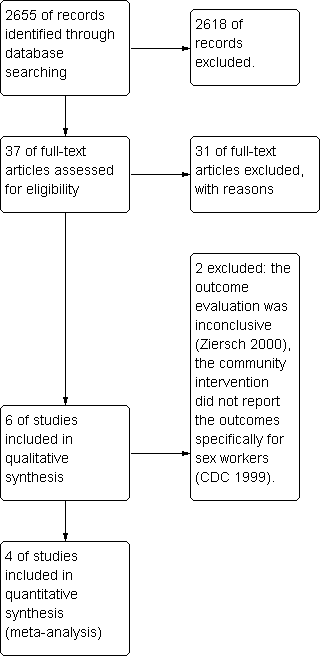
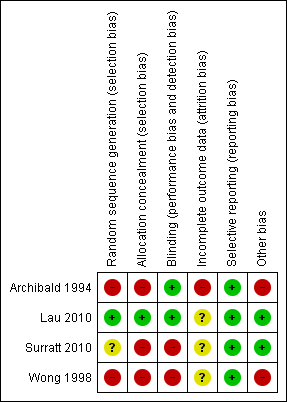
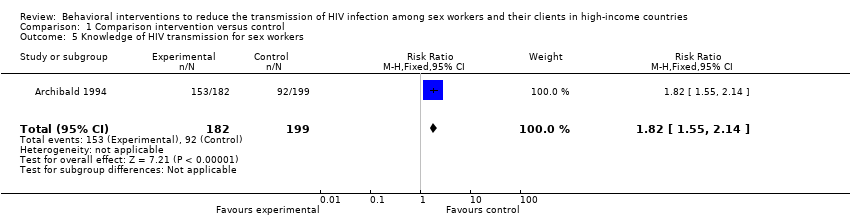
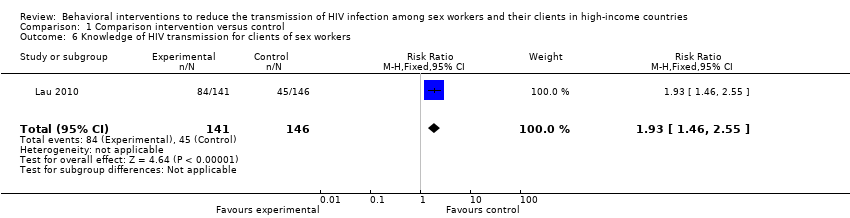
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Windy MV Wariki, Erika Ota, Rintaro Mori, Ai Koyanagi, Narumi Hori, Kenji Shibuya | 15 febrero 2012
Wayne D Johnson, Rafael M. Diaz, William D Flanders, Michael Goodman, Andrew N Hill, David Holtgrave, Robert Malow, William M McClellan | 16 julio 2008
Programas de abstinencia plus para la prevención de la infección por VIH en países de ingresos altos
Kristen Underhill, Paul Montgomery, Don Operario | 23 enero 2008
Olumuyiwa Ojo, Jos H Verbeek, Kimmo Rasanen, Jarmo Heikkinen, Leena K Isotalo, Nomusa Mngoma, Eija Ruotsalainen | 7 diciembre 2011
Kristen Underhill, Don Operario, Paul Montgomery | 17 octubre 2007
Serena Brusamento, Elena Ghanotakis, Lorainne Tudor Car, Michelle HMMT van‐Velthoven, Azeem Majeed, Josip Car | 17 octubre 2012
Fernanda T Carvalho, Tonantzin R Gonçalves, Evelise R Faria, Jean A Shoveller, C A Piccinini, Mauro C Ramos, Lídia RF Medeiros | 7 septiembre 2011
Virginia A Fonner, Julie Denison, Caitlin E Kennedy, Kevin O'Reilly, Michael Sweat | 12 septiembre 2012
Lorainne Tudor Car, Michelle HMMT van‐Velthoven, Serena Brusamento, Hoda Elmoniry, Josip Car, Azeem Majeed, Rifat Atun | 15 junio 2011
Ralfh Moreno, Herfina Y Nababan, Erika Ota, Windy MV Wariki, Satoshi Ezoe, Stuart Gilmour, Kenji Shibuya | 29 julio 2014