Krioterapi utama untuk kanser prostat tempatan atau lanjutan tempatan
Información
- DOI:
- https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005010.pub3Copiar DOI
- Base de datos:
-
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- Versión publicada:
-
- 30 mayo 2018see what's new
- Tipo:
-
- Intervention
- Etapa:
-
- Review
- Grupo Editorial Cochrane:
-
Grupo Cochrane de Urología
- Copyright:
-
- Copyright © 2018 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cifras del artículo
Altmetric:
Citado por:
Autores
Contributions of authors
Jae Hung Jung (JHJ): acquired trial reports, performed trial selection, data extraction, data analysis, data interpretation, and drafted the review.
Michael C Risk (MCR): provided clinical and methodological advice on the review, and final approval.
Robert Goldfarb (RG): drafted the protocol, developed the search strategy, acquired trial reports, and performed trial selection.
Balaji Reddy (BR): performed trial selection, data extraction, data analysis, data interpretation, and drafted the review.
Bernadette Coles (BC): developed the search strategy and acquired trial reports.
Philipp Dahm (PD): responsible for conception and study design, provided clinical and methodological advice on the review, and final approval.
Sources of support
Internal sources
-
Department of Urology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Korea, South.
-
Minneapolis VA Health Care System, USA.
-
Department of Urology, University of Minnesota, USA.
External sources
-
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
JHJ: none known.
MCR: none known.
RG: none known.
BR: none known.
BC: none known.
PD: none known.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Francisco Donis, Julio Pow‐Sang, and Timothy McClure for having served as peer reviewers. We would like to thank Cochrane Urology and our editors Mari Imamura and Alea Miller for supporting this review.
Version history
| Published | Title | Stage | Authors | Version |
| 2018 May 30 | Primary cryotherapy for localised or locally advanced prostate cancer | Review | Jae Hung Jung, Michael C Risk, Robert Goldfarb, Balaji Reddy, Bernadette Coles, Philipp Dahm | |
| 2007 Jul 18 | Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer | Review | Mike Shelley, Timothy J Wilt, Bernadette Coles, Malcolm Mason | |
| 2004 Oct 18 | Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer | Protocol | Norman Dublin, Mike Shelley, Timothy Wilt, Malcolm Mason | |
Differences between protocol and review
The protocol for this review was published in 2008. Therefore, considerable changes were necessary to align this update with Cochrane's current methodological standards, including more specific definitions of primary and secondary outcomes, their measurement, planned secondary analyses, the details of the search and the use of GRADE on a per outcome basis to assess the quality of evidence. Specific issues are highlighted below:
-
Title: as cryotherapy also is used in the salvage situation, we added the word ”Primary” to the title.
-
Type of outcome measures: we have revised the outcomes included in the review. In the prior version of the review, outcomes were listed as: "The main outcome measures of interest included biochemical disease‐free survival, disease‐free survival and treatment‐induced complications. Secondary outcomes included disease specific survival, overall survival, QoL outcome measures and economic impact measures." These were now prioritized based on perceived patient‐importance.
-
Type of outcome measures: we have renamed the oncologic outcomes to time to death from prostate cancer, any cause, or biochemical failure to reflect them representing time‐to‐event outcomes.
-
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies: we have described the method to assess risk of bias in detail. In addition, we grouped all outcomes that have a similarly susceptibility to performance bias in one group.
-
Subgroup and sensitivity analysis: we have limited these analyses to the primary outcomes.
Notes
We have based parts of the Methods section of this protocol on a standard template developed by the Cochrane Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Group, which has been modified and adapted for use by Cochrane Urology.
Keywords
MeSH
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Keywords
Medical Subject Headings Check Words
Aged; Humans; Male;
PICO
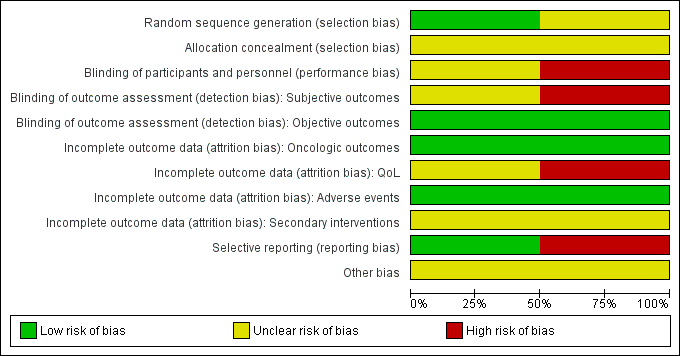
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
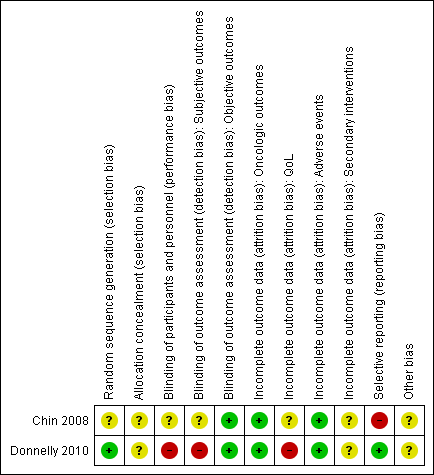
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
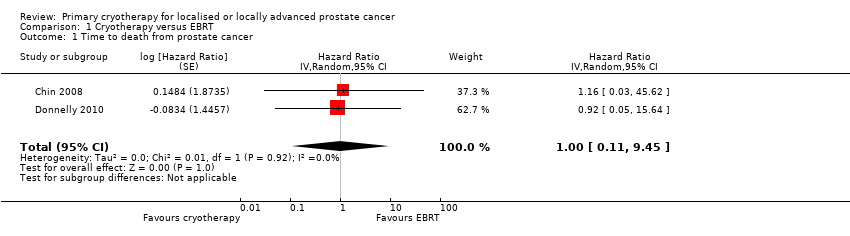
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 1 Time to death from prostate cancer.
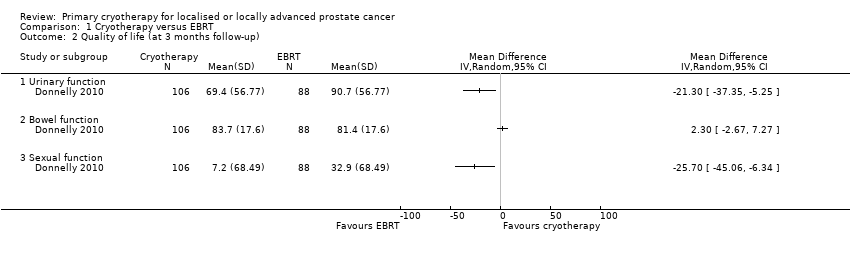
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 2 Quality of life (at 3 months follow‐up).
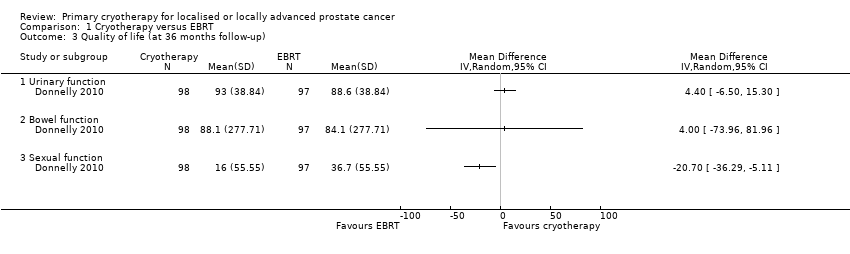
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 3 Quality of life (at 36 months follow‐up).
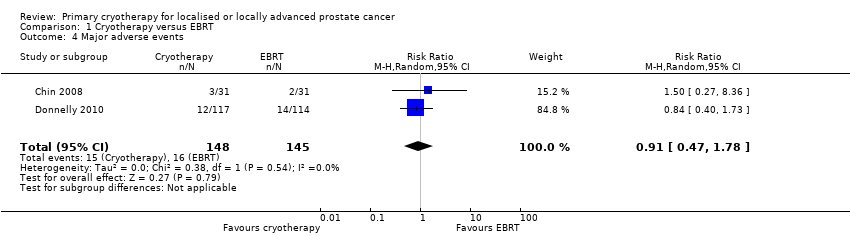
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 4 Major adverse events.
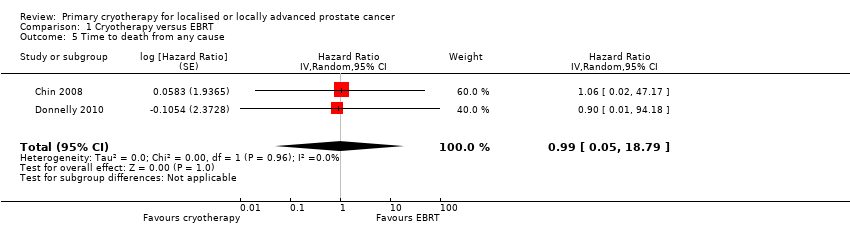
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 5 Time to death from any cause.
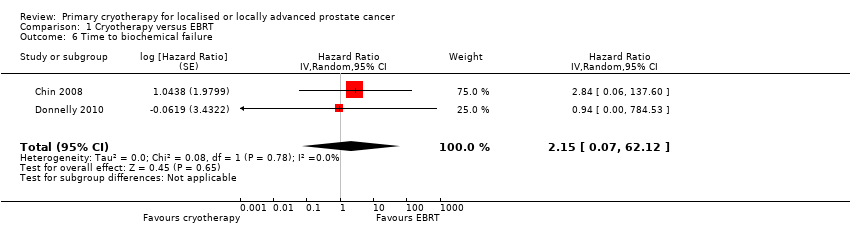
Comparison 1 Cryotherapy versus EBRT, Outcome 6 Time to biochemical failure.
| Participants: men with localised or locally advanced prostate cancer Setting: single institution in Canada Intervention: whole gland cryotherapy Comparator: external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) | |||||
| Outcomes | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Relative effect | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
| Risk with EBRT | Risk difference with cryotherapy | ||||
| Time to death from prostate cancer (absolute effects: disease‐specific mortality)1 | 293 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | HR 1.00 | Study population | |
| 97 per 1000 | 0 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Quality of life ‐ urinary function Follow‐up: mean 36 months | 195 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ | The mean quality of life ‐ urinary function was 88.6 | MD 4.4 higher |
| Quality of life ‐ bowel function Follow‐up: mean 36 months | 195 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ | The mean quality of life ‐ bowel function was 84.1 | MD 4 higher |
| Quality of life ‐ sexual function Follow‐up: mean 36 months | 195 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | ‐ | The mean quality of life ‐ sexual function was 36.7 | MD 20.7 lower |
| Major adverse events | 293 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 0.91 | Study population | |
| 110 per 1000 | 10 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Time to death from any cause (absolute effects: overall mortality)1 | 293 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | HR 0.99 | Study population | |
| 166 per 1000 | 2 fewer per 1000 | ||||
| Secondary interventions for treatment failure ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| 1 Mortality instead of survival to estimate anticipated absolute effect is reported for methodological reason. 2 Downgraded by one level for study limitations: unclear or high risk of bias in half of domains in included studies. 3 Downgraded by one level for indirectness (differences in intervention): prescribed dose of radiotherapy in the included studies was lower than 74 Gy as recommended by current guidelines (EAU 2017). Also, radiotherapy should be given in combination with long‐term androgen deprivation therapy (two to three years) in patients with high risk prostate cancer. 4 Downgraded by two levels for imprecision: wide confidence interval cross assumed threshold of clinically important differences. 5 UCLA‐Prostate Cancer Index contains six domains (urinary function (4 items), urinary bother (1 item), sexual function (5 items), sexual bother (1 item), bowel function (3 items), bowel bother (1 item)) which are scored separately (low score = worst, high score = better) (Litwin 1998). 6 Downgraded by one level for imprecision: confidence interval crosses assumed threshold of clinically important difference. | |||||
| Study name | Trial period | Setting/ country | Participants | Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Age (median, years) | No of men with clinical tumour stage (T2a; 2b; 2c; 3a; 3b) | Biopsy Gleason score (<7; 7; >7) | PSA (median, ng/mL) | Median follow‐up (months) |
| Chin 2008 | 1999 to 2002 | Single institution in Canada | Histologically proven prostate cancer, clinically staged as T2c, T3a or T3b with no evidence of lymph node or distant metastasis and serum PSA < 25 ng/mL | Whole gland cryotherapy | 70.4 | ‐; ‐; 12; 17; 2 | 2; 24; 5 | 11.1 | 105 |
| EBRT | 70.5 | ‐; ‐; 8; 15; 8 | 1; 24; 6 | 8.6 | |||||
| Donnelly 2010 | 1997 to 2003 | Single institution in Canada | Histologically proven adenocarcinoma of the prostate, a biopsy tumour classification of T2 or T3, no evidence of lymph node or distant metastases, a pretreatment PSA level < 20 ng/mL, and a gland volume < 60 cm3 | Whole gland cryotherapy | 69.4 | 22; 28; 49; 17; 6 | 42; 69; 11 | 8.1 | 100 |
| EBRT | 68.6 | 20; 23; 57; 18; 4 | 44; 65; 13 | 9.0 | |||||
| EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; PSA: prostate specific antigen | |||||||||
| Study name | Intervention(s) and comparator(s) | Screened/ eligible | Randomised | Treatment completed | Treatment analysed |
| Chin 2008 | Whole gland cryotherapy | NR/140 | 32 | NR | 31 (96.8%) |
| EBRT | 31 | 31 (100.0%) | |||
| Total | 63 | NR | 62 (98.4%) | ||
| Donnelly 2010 | Whole gland cryotherapy | NR/764 | 122 | NR | 117 (95.9%) |
| EBRT | 122 | 114 (93.4%) | |||
| Total | 244 | NR | 231 (94.6%) | ||
| Grand total | 307 | NR | 293 (95.4%) | ||
| EBRT: external beam radiotherapy; NR: not reported | |||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Time to death from prostate cancer Show forest plot | 2 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.11, 9.45] | |
| 2 Quality of life (at 3 months follow‐up) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Urinary function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 Bowel function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 Sexual function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Quality of life (at 36 months follow‐up) Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Urinary function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 Bowel function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.3 Sexual function | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Major adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 293 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.47, 1.78] |
| 5 Time to death from any cause Show forest plot | 2 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.05, 18.79] | |
| 6 Time to biochemical failure Show forest plot | 2 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 2.15 [0.07, 62.12] | |