برنامههای مختلف دوزبندی برای کاهش سمیّت قلبی در افراد مبتلا به سرطان تحت شیمیدرمانی با آنتراسیکلین
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategy for EMBASE/Ovid
For anthracycline chemotherapy the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
exp doxorubicin derivative/ or exp doxorubicin/ or exp daunorubicin derivative/ or exp daunorubicin/ or exp epirubicin/ or exp idarubicin/ or anthracycline antibiotic agent/ or anthracycline/ or exp anthracycline derivative/
For the updates we added the following to the search: or anthracyclines.mp or anthracyclin$.mp or anthracycline antibiotics.mp or doxorubicin.mp or adriablastin$.mp or adriblastin$.mp or adriamycin.mp or doxorubicin hydrochloride.mp or doxorubic$.mp or adriamyc$.mp or doxil.mp or caelyx.mp or myocet.mp or liposomal doxorubicin.mp or exp idarubicin derivative/ or idarubicin.mp or (4 demethoxydaunomycin or 4 demethoxydaunorubicin or 4 desmethoxydaunomycin or 4 desmethoxydaunorubicin).mp or idarubicin hydrochloride.mp or idarubic$.mp or epirubicin.mp or (epirubic$ or farmorubicin$).mp or (epirubicin hydrochloride or 4' epirubicin or epidoxorubicin or 4' epidoxorubicin or epiadriamycin or 4' epiadriamycin or 4 epiadriamycin).mp or daunorubicin.mp or daunorubic$.mp or (rubidomycin or rubomycin).mp or (cerubidin$ or daunoblastin$ or rubidomyc$ or daunoxome or daunosom$ or daunomycin or daunorubimycin or daunorubidomycin or daunorubicin hydrochloride or daunomycin hydrochloride).mp
For the different dosage schedules the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
(administration and dosage).mp or exp drug administration/ or exp intravenous drug administration/ or peak dose.mp or infusion duration.mp
For the updates we added the following to the search: or drug administration schedule.mp or exp drug administration/ or drug administration route.mp or exp drug administration route/ or drug administration routes.mp or drug administration method.mp or drug administration schedule.mp or drug administration schedules.mp or intravenous drug administration.mp or cumulative.mp or dosage.mp
For heart damage the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
exp heart ventricle failure/ or exp heart left ventricle function/ or exp congestive heart failure/ or exp heart right ventricle failure/ or exp heart failure/ or exp heart/ or exp forward heart failure/ or exp heart right ventricle function/ or exp heart disease/ or exp cardiotoxicity/ or exp cardiomyopathy/ or exp congestive cardiomyopathy/ or exp heart ventricle function/ or exp congestive heart failure/
For the updates we added the following to the search: or heart.mp or heart ejection fraction/ or exp heart right ventricle ejection fraction/ or exp heart function/ or exp forward heart failure/ or exp heart function test/ or exp heart left ventricle failure/ or exp heart ventriculography/ or exp heart left ventricle ejection fraction/ or congestive heart failure.mp or cardiomyopathy.mp or cardiotoxicity.mp or heart disease.mp or cardiac disease.mp or heart failure.mp or ventricular dysfunction.mp or shortening fraction.mp or ejection fraction.mp or (MUGA or LVEF or LVSF).mp or echocardiography.mp or exp echocardiography/ or radionuclide angiography.mp or radionuclide ventriculography.mp or exp radioisotope ventriculography/ or gated blood‐pool imaging.mp or endomyocardial biopsy.mp or exp heart muscle biopsy/ or angiocardiography.mp or exp angiocardiography/ or blood pool scintigraphy.mp or (cardiotox$ or cardiomyop$ or echocardiogr$ or ventriculogr$ or scintigr$).mp
For randomised controlled trials the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review; based on the highly sensitive search strategy for identifying reports of randomised controlled trials as described in the Cochrane Handbook (Higgins 2005)):
Randomized controlled trial/ or clinical trial/ or exp clinical trial/ or exp randomization/ or exp controlled study/ or double blind procedure/ or single blind procedure/ or exp placebo/ or exp comparative study/ or exp prospective study/
For the updates we used the following strategy (based on the highly sensitive search strategy for identifying reports of randomised controlled trials as described in the Cochrane Handbook (Higgins 2008)): (randomized controlled trial/ or controlled clinical trial/ or randomized.ti,ab or placebo.ti,ab or randomly.ti,ab or trial.ti,ab or groups.ti,ab or drug therapy.sh) and human/
The above described searches for anthracycline chemotherapy, dosage schedules, heart damage and randomised trials were combined.
[mp = title, abstract, subject headings, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer name]; [ti,ab = title, abstract]; [sh = subject heading]
Appendix 2. Search strategy for the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)
For anthracycline chemotherapy the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
Anthracyclines or adriamycin or epirubicin or daunorubicin or idarubicin or doxorubicin or anthracyclin* or doxorubic* or idarubic* or epirubic* or daunorubic* or epiadriamycin or adriamyc* or rubidomyc* or doxil or daunoxome or antibiotics anthracycline or (anthracycline next antibiotic)
For the updates we added the following to the search: or anthracycline antibiotics or farmorubicin* or rubidomycin or cerubidin* or caelyx or myocet
For the different dosage schedules the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
Drug administration schedule or infusions intravenous or dosage or (peak next dose) or (drug next administration next schedule)
For the updates we added the following to the search: or (administration and dosage) or drug administration schedules or cumulative or peak or infusion duration
For heart damage the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
Heart or heart diseases or ventricular dysfunction or (heart next diseases) or heart* or (heart next disease*) or (cardiac next disease*) or cardiomyopathy or cardiotoxicity or (heart next failure) or (cardiac next failure) or (congestive next heart next failure)
For the updates we added the following to the search: or cardiotox* or cardiomyopathies or cardiomyop* or shortening fraction or ejection fraction or LVSF or LVEF or echocardiography or echocardiogr* or radionuclide angiography or radionuclide ventriculography or ventriculogr* or MUGA or gated blood‐pool imaging or angiocardiography or endomyocardial biopsy or first pass ventriculography
The above described searches for anthracycline chemotherapy, dosage schedules and heart damage were combined.
Appendix 3. Search strategy for MEDLINE/PubMed
For anthracycline chemotherapy the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
anthracyclines OR anthracyclin* OR anthracycline antibiotics OR antibiotics, anthracycline OR 4‐demethoxydaunorubicin OR 4 demethoxydaunorubicin OR 4‐desmethoxydaunorubicin OR 4 desmethoxydaunorubicin OR IMI 30 OR IMI30 OR IMI‐30 OR idarubicin hydrochloride OR hydrochloride, idarubicin OR NSC 256439 OR NSC‐256439 OR NSC256439 OR idarubicin OR idarubic* OR 4'‐epiadriamycin OR 4' epiadriamycin OR 4'‐epidoxorubicin OR 4' epidoxorubicin OR 4'‐epi‐doxorubicin OR 4' epi doxorubicin OR 4'‐epi‐adriamycin OR 4' epi adriamycin OR 4'‐epi‐DXR OR 4' epi DXR OR epirubicin hydrochloride OR hydrochloride, epirubicin OR farmorubicin OR IMI‐28 OR IMI 28 OR IMI28 OR NSC 256942 OR NSC‐256942 OR NSC256942 OR epirubicin OR epirubic* OR adriablastine OR adriblastin OR adriablastin OR adriamycin OR DOX‐SL OR DOX SL OR DOXSL OR doxorubicin hydrochloride OR hydrochloride, doxorubicin OR doxorubic* OR adriamyc* OR dauno‐rubidomycine OR dauno rubidomycin OR rubidomycin OR rubomycin OR daunomycin OR cerubidine OR daunoblastin OR daunoblastine OR daunorubicin hydrochloride OR hydrochloride, daunorubicin OR daunorubic* OR rubidomyc* OR NSC‐82151 OR NSC 82151 OR NSC82151 OR daunoxome OR daunosom* OR doxil OR caelyx OR liposomal doxorubicin OR doxorubicin, liposomal.
For the updates we changed farmorubicin into farmorubicin*, adriblastin into adriblastin* and dauno rubidomycin into dauno rubidomycine; we added myocet, daunorubicin and doxorubicin (using OR) to the search.
For the different dosage schedules the following subject headings and text words were used (in both the original version of the review and the updates):
administration and dosage OR administration schedule, drug OR administration schedules, drug OR drug administration schedules OR schedule, drug administration OR schedules, drug administration OR drug administration schedule OR cumulative OR peak OR infusion duration OR dosage.
For heart damage the following subject headings and text words were used (in the original version of the review):
heart OR heart diseases OR heart disease OR disease, heart OR diseases, heart OR cardiac diseases OR cardiac disease OR diseases, cardiac OR disease, cardiac OR cardiotoxicity OR cardiomyopathy OR heart failure, congestive OR heart failure OR cardiomyopathy, congestive OR ventricular dysfunction OR ventricular dysfunction, left OR ventricular dysfunction, right.
For the updates we added the following to the search: OR shortening fraction OR ejection fraction OR echocardiography OR radionuclide angiography OR radionuclide ventriculography OR ventriculography, radionuclide OR gated blood‐pool imaging OR blood pool scintigraphy OR gated radionuclide ventriculography OR ventriculography, first pass OR cardiotox* OR cardiomyop* OR echocardiogr* OR ventriculogr* OR scintigr* OR MUGA OR LVEF OR LVSF OR endomyocardial biopsy OR angiocardiography OR cardiomyopathies.
The above described searches for anthracycline chemotherapy, dosage schedules and heart damage were combined.
Finally, the results of this search were combined with the highly sensitive search strategy for identifying reports of randomised controlled trials as described in the Cochrane Handbook (for the original review: Higgins 2005 (all phases); for the updates: Higgins 2008 (sensitivity‐maximizing version)).
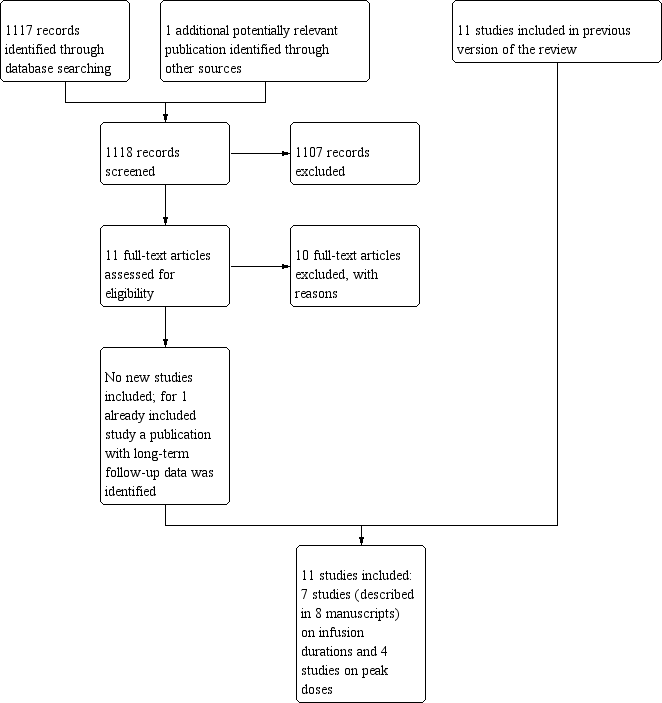
Study flow diagram.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1: Infusion duration less than 6 hours versus infusion duration 6 hours or more, Outcome 1: Clinical heart failure

Comparison 1: Infusion duration less than 6 hours versus infusion duration 6 hours or more, Outcome 2: (Sub)clinical heart failure combined

Comparison 1: Infusion duration less than 6 hours versus infusion duration 6 hours or more, Outcome 3: Response rate

Comparison 1: Infusion duration less than 6 hours versus infusion duration 6 hours or more, Outcome 4: Overall survival

Comparison 2: Doxorubicin peak dose less than 60 mg/m2 versus 60 mg/m2 or more, Outcome 1: Clinical heart failure

Comparison 2: Doxorubicin peak dose less than 60 mg/m2 versus 60 mg/m2 or more, Outcome 2: Overall survival

Comparison 2: Doxorubicin peak dose less than 60 mg/m2 versus 60 mg/m2 or more, Outcome 3: Adverse effects other than cardiac damage

Comparison 3: Liposomal doxorubicin (Caelyx) peak dose 25 mg/m2 versus 50 mg/m2, Outcome 1: Response rate (defined as objective palliative tumour response (i.e. decrease in PSA levels of >= 50%))

Comparison 3: Liposomal doxorubicin (Caelyx) peak dose 25 mg/m2 versus 50 mg/m2, Outcome 2: Adverse effects other than cardiac damage

Comparison 4: Epirubicin peak dose 110 mg/m2 versus 83 mg/m2, Outcome 1: Clinical heart failure

Comparison 4: Epirubicin peak dose 110 mg/m2 versus 83 mg/m2, Outcome 2: Adverse effects other than cardiac damage
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1.1 Clinical heart failure Show forest plot | 5 | 557 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.27 [0.09, 0.81] |
| 1.2 (Sub)clinical heart failure combined Show forest plot | 4 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.2.1 (Sub)clinical heart failure combined (subclinical defined as >=10% decrease in LVEF) | 1 | 82 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.46, 1.26] |
| 1.2.2 (Sub)clinical heart failure combined (subclinical defined as >=15% decrease in LVEF) | 1 | 52 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.03, 2.78] |
| 1.2.3 (Sub)clinical heart failure combined (subclinical defined as a fall in LVEF of > 20%) | 1 | 62 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.04 [0.00, 0.60] |
| 1.2.4 (Sub)clinical heart failure combined (subclinical defined as a decrease in LVEF) | 1 | 240 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.36 [0.15, 0.90] |
| 1.3 Response rate Show forest plot | 3 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.3.1 Response rate (defined as complete or partial remission) | 2 | 292 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.20 [0.65, 2.22] |
| 1.3.2 Response rate (defined as good response) | 1 | 178 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.23 [0.91, 1.66] |
| 1.4 Overall survival Show forest plot | 2 | 322 | Hazard Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.42 [0.61, 3.30] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 2.1 Clinical heart failure Show forest plot | 2 | 4146 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.23, 1.88] |
| 2.2 Overall survival Show forest plot | 2 | 4146 | Hazard Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.93, 1.22] |
| 2.3 Adverse effects other than cardiac damage Show forest plot | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.3.1 Treatment‐related death | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.19 [0.01, 3.99] |
| 2.3.2 Death attributable to chemotherapy | 1 | 1032 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.34 [0.01, 8.26] |
| 2.3.3 Leukopenia grade 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.53, 0.64] |
| 2.3.4 Leukopenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1032 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.26 [0.21, 0.31] |
| 2.3.5 Granulocytopenia grade 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.67 [0.61, 0.73] |
| 2.3.6 Thrombocytopenia grade 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.45 [0.34, 0.59] |
| 2.3.7 Diarrhoea grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.34 [0.19, 0.60] |
| 2.3.8 Dyspnoea grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.51 [0.28, 0.93] |
| 2.3.9 Infection grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.42, 0.86] |
| 2.3.10 Malaise/fatigue/lethargy grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.66 [0.49, 0.91] |
| 2.3.11 Nausea grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.19 [0.98, 1.44] |
| 2.3.12 Stomatitis grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.27, 0.61] |
| 2.3.13 Vomiting grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 3114 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.31 [1.07, 1.59] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 3.1 Response rate (defined as objective palliative tumour response (i.e. decrease in PSA levels of >= 50%)) Show forest plot | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.00, 1.13] |
| 3.2 Adverse effects other than cardiac damage Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.2.1 Gastrointestinal toxicity grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.17 [0.01, 3.08] |
| 3.2.2 Tachycardia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.00, 1.00] |
| 3.2.3 Arrhythmia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.04, 3.52] |
| 3.2.4 Dyspnoea grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.47 [0.10, 2.20] |
| 3.2.5 Palmar‐plantar erythrodysesthesia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 5.91 [1.45, 24.16] |
| 3.2.6 Hepatic toxicity grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.20 [0.05, 0.79] |
| 3.2.7 Leukopenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.03, 1.87] |
| 3.2.8 Thrombocytopenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.02, 9.15] |
| 3.2.9 Haemoglobin‐related toxicity grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.00, 1.13] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 4.1 Clinical heart failure Show forest plot | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.06, 15.48] |
| 4.2 Adverse effects other than cardiac damage Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.2.1 Anaemia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.91 [0.79, 10.70] |
| 4.2.2 Leukopenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.75, 1.49] |
| 4.2.3 Neutropenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.84, 1.31] |
| 4.2.4 Febrile neutropenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.47, 1.31] |
| 4.2.5 Thrombocytopenia grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 12.62 [0.71, 223.52] |
| 4.2.6 Nausea/vomiting grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.45, 1.82] |
| 4.2.7 Fatigue grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.07, 1.60] |
| 4.2.8 Infection grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.79 [0.48, 1.31] |
| 4.2.9 Central nervous system grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.91 [0.12, 71.35] |
| 4.2.10 Pulmonary grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.91 [0.12, 71.35] |
| 4.2.11 Peripheral neuropathy grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.50 [2.37, 8.54] |
| 4.2.12 Hepatotoxicity grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.70 [0.50, 5.77] |
| 4.2.13 Hypersensitivity reactions grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.88 [1.71, 8.82] |
| 4.2.14 Mucositis grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.48, 2.28] |
| 4.2.15 Pain grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.01, 7.93] |
| 4.2.16 Arthralgias/myalgias grade 3 or 4 | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.88 [1.31, 11.54] |
| 4.2.17 Treatment‐related death | 1 | 1086 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.91 [0.12, 71.35] |

