Routine intraoperative ureteric stenting for kidney transplant recipients
Información
- DOI:
- https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004925.pub3Copiar DOI
- Base de datos:
-
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- Versión publicada:
-
- 17 junio 2013see what's new
- Tipo:
-
- Intervention
- Etapa:
-
- Review
- Grupo Editorial Cochrane:
-
Grupo Cochrane de Riñón y trasplante
- Copyright:
-
- Copyright © 2013 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cifras del artículo
Altmetric:
Citado por:
Autores
Contributions of authors
Writing of review ‐ CHW, AAB, DMM
Screening of titles and abstracts ‐ CHW, AAB
Quality assessment ‐ CHW, AAB, DAR
Data extraction ‐ CHW, AAB
Data analysis ‐ CHW, AAB, DMM
Resolution of discrepancies/disagreements ‐ DMM, DAR
Declarations of interest
None known
Acknowledgements
This review has been co‐published with Transplantation Oct 2005 (Wilson 2005)
We would also like to thank Dr Nicholas Brooks, Dr David Cranston, Dr Francis Keeley and Dr Petra Macaskill for their editorial advice during the preparation of this review.
Version history
| Published | Title | Stage | Authors | Version |
| 2013 Jun 17 | Routine intraoperative ureteric stenting for kidney transplant recipients | Review | Colin H Wilson, David A Rix, Derek M Manas | |
| 2005 Oct 19 | Routine intraoperative ureteric stenting for kidney transplant recipients | Review | Colin H Wilson, Aftab B Bhatti, David A Rix, Derek M Manas | |
| 2004 Jul 19 | Routine intraoperative ureteric stenting for kidney transplant recipients | Protocol | Colin Wilson, Aftab B Bhatti, Derek M Manas | |
Keywords
MeSH
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Keywords
- Anastomosis, Surgical;
- Hematuria [etiology];
- Kidney Transplantation [*adverse effects];
- Postoperative Complications [*prevention & control];
- Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic;
- Stents [*adverse effects];
- Ureter [surgery];
- Ureteral Obstruction [etiology, prevention & control];
- Urinary Tract Infections [etiology];
Medical Subject Headings Check Words
Humans;

Comparison 1 Stent versus no stent, Outcome 1 Urine leak and obstruction.

Comparison 1 Stent versus no stent, Outcome 2 Surgeon number MUC subgroup analysis.
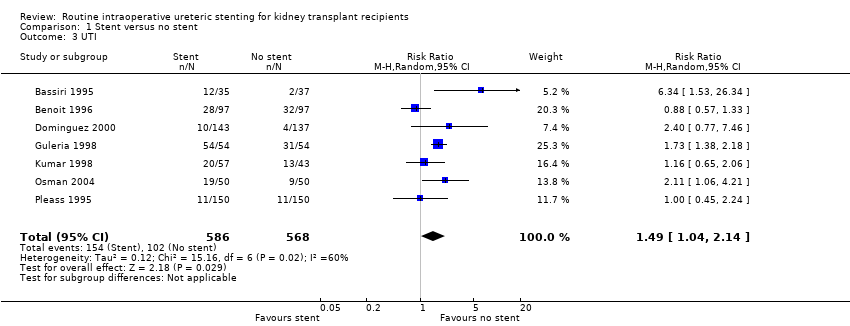
Comparison 1 Stent versus no stent, Outcome 3 UTI.
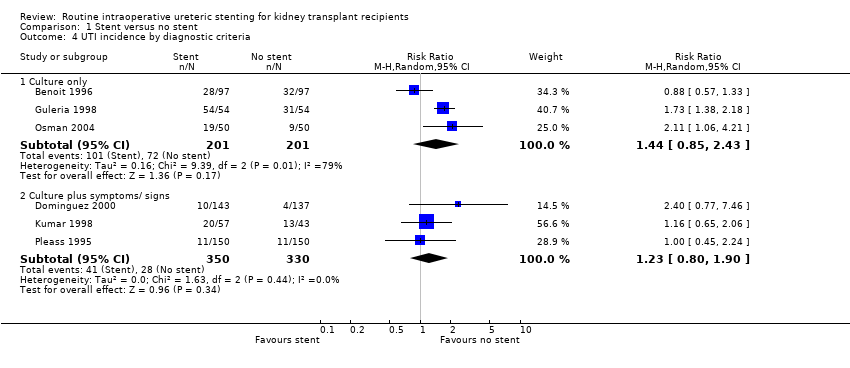
Comparison 1 Stent versus no stent, Outcome 4 UTI incidence by diagnostic criteria.

Comparison 1 Stent versus no stent, Outcome 5 UTI incidence by antibiotic regime.
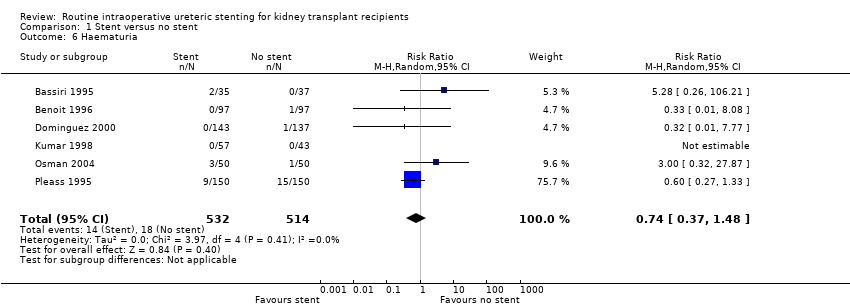
Comparison 1 Stent versus no stent, Outcome 6 Haematuria.
| Study | Events (stent) | Patients (stent) | Incidence (stent) | Events (no stent) | Patients (no stent) | Incidence (no stent) |
| 0 | 35 | 0% | 3 | 37 | 8.1% | |
| 1 | 97 | 1.0% | 10 | 97 | 10.3% | |
| 5 | 143 | 3.5% | 9 | 137 | 6.6% | |
| 1 | 54 | 1.9% | 3 | 54 | 5.6% | |
| 0 | 57 | 0% | 3 | 43 | 7.0% | |
| 2 | 50 | 4% | 0 | 50 | 0% | |
| 0 | 150 | 0% | 26 | 150 | 17.3% | |
| Total | 9 | 586 | median 1.0 (0 ‐ 4.0) | 54 | 568 | median 7.0 (0 ‐ 17.3) |
| Comparison/ Study | Events (stent) | Patients (stent) | Incidence (stent) | Events (no stent) | Patients (no stent) | Incidence (no stent) |
| 0 | 35 | 0% | 3 | 37 | 8.1% | |
| 1 | 54 | 1.9% | 3 | 54 | 5.6% | |
| 0 | 57 | 0% | 3 | 43 | 7.0% | |
| 2 | 50 | 4% | 0 | 50 | 0% | |
| Same surgeon (4 studies, 380 patients) | 3 | 196 | median 0.95 (0 ‐ 4.0) | 9 | 184 | median 6.3 (0 ‐ 8.1) |
| 1 | 97 | 1.0% | 10 | 97 | 10.3% | |
| 5 | 143 | 3.5% | 9 | 137 | 6.6% | |
| 0 | 150 | 0% | 26 | 150 | 17.3% | |
| Many surgeons (3 studies, 774 patients) | 6 | 390 | median 1.0 (0 ‐ 3.5) | 45 | 384 | median 10.3 (6.6 ‐ 17.3) |
| Study | Follow‐up | Stent related loss | Stent related deaths | Overall mortality | Overall graft loss |
| 2‐10 months | 0 | 0 | 5 patients total either lost their graft or died (6.5%) | ‐ | |
| Up to 3 years | 2 | 0 | 7.8% | NR | |
| 3 months | 0 | 0 | NR | NR | |
| 6 months | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.9% | |
| 16‐32 months | 0 | 0 | 93% 1 year survival | 89% 1 year survival | |
| 7‐16 months | 0 | 0 | 0.8% | 0.8% | |
| 3 months | 0 | 0 | NR | NR | |
| NR ‐ not reported | |||||
| Study | Stent | No Stent |
| 5.7% | 0% | |
| NR | 1 ureter clot retention (1.0%) | |
| NR | 1 ureter clot retention (0.7%) | |
| NR | NR | |
| 0% | 0% | |
| 6.0% | 2.0% | |
| 6.0% | 10.0% | |
| NR ‐ not reported | ||
| Study | Irritative symptoms | Breakage | Migration/malpositioning | Encrustation | Forgotten | Expulsion |
| NR | NR | NR | 5.7% | NR | 0 | |
| NR | 2.1% | 1.0% | 2.1% | NR | 1.0% | |
| 0% | 0 % | 0 % | 0 % | NR | 0% | |
| 5.6% | 0 % | 7.4% | 0 % | NR | 7.4% | |
| 5.3% | 0 % | 0 % | 0 % | 7.0 % | 0 | |
| NR | 0 % | 4.0% | 0 % | 0 | 0 | |
| NR | 0 % | "+" | "++" | NR | > 1 patient | |
| NR ‐ not reported | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Urine leak and obstruction Show forest plot | 7 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Combined ‐ urine leak and obstruction | 7 | 1154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.07, 0.77] |
| 1.2 Urine leak | 7 | 1154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.12, 0.74] |
| 1.3 Ureteric obstruction | 7 | 1154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.27 [0.09, 0.81] |
| 2 Surgeon number MUC subgroup analysis Show forest plot | 7 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Same surgeon | 4 | 380 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.39 [0.08, 1.86] |
| 2.2 Many surgeons | 3 | 774 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.13 [0.01, 1.16] |
| 3 UTI Show forest plot | 7 | 1154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.49 [1.04, 2.14] |
| 4 UTI incidence by diagnostic criteria Show forest plot | 6 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 4.1 Culture only | 3 | 402 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.44 [0.85, 2.43] |
| 4.2 Culture plus symptoms/ signs | 3 | 680 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.23 [0.80, 1.90] |
| 5 UTI incidence by antibiotic regime Show forest plot | 6 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5.1 Co‐trimoxazole 480mg od (960 mg alt. days) | 3 | 594 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.71, 1.33] |
| 5.2 Other regime | 3 | 488 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.78 [1.44, 2.21] |
| 6 Haematuria Show forest plot | 6 | 1046 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.37, 1.48] |

