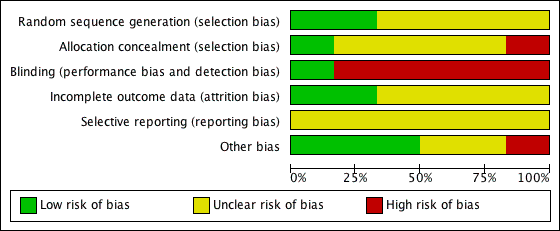
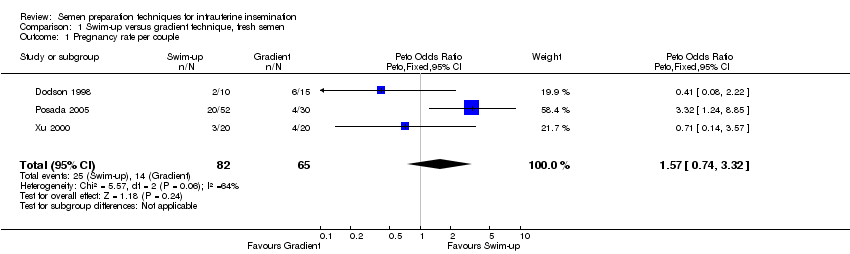
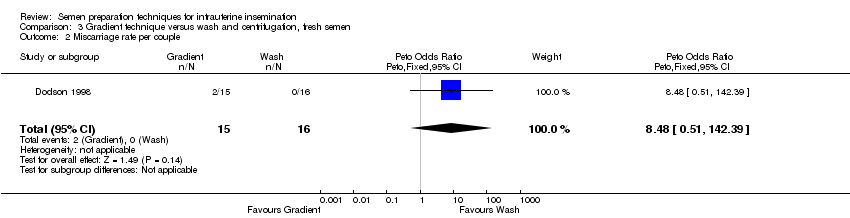
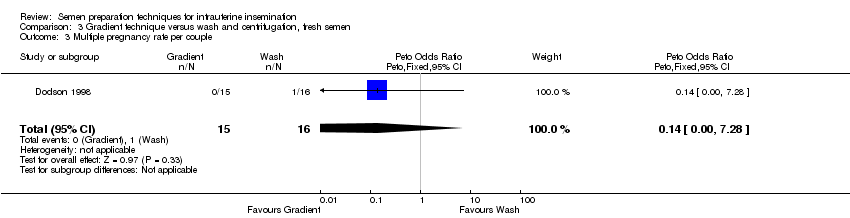
Contenido relacionado
Revisiones y protocolos relacionados
Carolien M. Boomsma, Ben J Cohlen, Cindy Farquhar | 15 octubre 2019
Astrid EP Cantineau, Ben J Cohlen, Maas Jan Heineman, Jane Marjoribanks, Cindy Farquhar | 30 octubre 2013
Petronella AL Kop, Monique H Mochtar, Paul A O'Brien, Fulco Van der Veen, Madelon van Wely | 25 enero 2018
Danielle M Teixeira, Andre H Miyague, Mariana AP Barbosa, Paula A Navarro, Nick Raine‐Fenning, Carolina O Nastri, Wellington P Martins | 21 febrero 2020
Reuben Olugbenga Ayeleke, Joyce Danielle Asseler, Ben J Cohlen, Susanne M Veltman‐Verhulst | 3 marzo 2020
Sam Lepine, Simon McDowell, Leigh M Searle, Ben Kroon, Demián Glujovsky, Anusch Yazdani | 30 julio 2019
Astrid EP Cantineau, Mirjam J Janssen, Ben J Cohlen, Thomas Allersma | 21 diciembre 2014
Lidija Rakic, Elena Kostova, Ben J Cohlen, Astrid EP Cantineau | 14 julio 2021
Zhongying Huang, Jun Li, Li Wang, Jing Yan, Yijiang Shi, Shangwei Li | 30 abril 2013
Fulvio Zullo, Roberta Venturella, Antonio Raffone, Gabriele Saccone | 6 mayo 2020