Thermothérapie par micro‐ondes dans les cas d'hyperplasie bénigne de la prostate
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Multicenter | |
| Participants | French men, mean age 65, with symptomatic BPH, peak urinary flow < 15 mL/s with voided volume > 150 mL; prostate volume 30 to 80 cc; post‐void residual < 300 cc. | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 66) | |
| Outcomes | Adverse events | |
| Notes | No evaluable symptom or urinary flow data provided | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Permutation tables |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not documented |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 57/200 subjects unavailable for follow‐up, investigators classified outcomes "to maximize bias." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | British men, mean age 69 (range 56 to 88); urodynamically obstructive BPH; AUA symptom score > 12; peak urinary flow < 15 mL/s. | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 30) | |
| Outcomes | AUA symptom score, peak urinary flow, voiding pressure, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Patients failing to complete treatment or return for follow‐up were "substituted." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Describes only "sealed envelope" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Due to "substitution" noted above, number not provided. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus TURP |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Multicenter Randomized Subjects and outcome assessor blinded | |
| Participants | US men, mean age 65 (range 50 to 80); AUA symptom score > 13; peak urinary flow < 12 ml/s Lost to follow‐up: 0 | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 125) TherMatrx TMx‐2000 2. Sham (n = 65) Study duration: 3 months | |
| Outcomes | AUA symptom score; peak urinary flow; adverse events; bother score; quality of life | |
| Notes | Study unblinded with cross‐over at 3 months and follow‐up to 1 year. Instruments used to measure bother and quality of life not reported. Mean PUF not reported at follow‐up. No standard deviation reported with mean AUA score | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | British men, mean age 63, symptomatic BPH eligible for surgery. AUA symptom score > 10, peak urinary flow < 15 mL/s, prostate length < 40 mm; post‐void residual < 200 mL | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 22) | |
| Outcomes | AUA symptom score, modified World Health Organization symptom score, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, residual volume, adverse events | |
| Notes | Study unblinded with cross‐over at 3 months and follow‐up to 1 year | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Describes only "sealed envelope" |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | American men, mean age 67, symptomatic BPH. Madsen symptom score > 8; PFR < 10 mL/s with voided volume > 150 mL; post‐void residual 100 to 200 mL; prostate length 35 to 50 mm. | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 78) | |
| Outcomes | Madsen‐Iversen symptom score, AUA symptom score, global assessment of improvement, peak urinary flow, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | Study unblinded with cross‐over at 3 months with follow‐up to 1 year | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelopes identified only by a unique patient number |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | Dutch men, mean age 69 (range 54 to 89), symptomatic BPH eligible for TURP. Madsen symptom score > 7, peak urinary flow ≤ 15 mL/s with voided volume > 100 mL; prostate length 25 to 50 mm, prostate volume 30 to 100 cc, post‐void residual < 350 mL | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 31) | |
| Outcomes | Madsen‐Iversen symptom score, IPSS symptom score, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, hospital length of stay, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus TURP |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | Swedish men, mean age 68, symptomatic BPH eligible for TURP. Madsen > 7; peak urinary flow < 15 mL/s with voided volume > 150 mL; prostate length 35 to 50 mm; prostate volume 25‐100 cc. | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 37) | |
| Outcomes | Madsen‐Iversen symptom score, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, hospital length of stay, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus TURP |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Multicenter | |
| Participants | Dutch and British men, mean age 65, symptomatic BPH. Madsen symptom score > 8; peak urinary flow < 15 mL/s. Post‐void residual < 300 mL | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 47) | |
| Outcomes | Madsen‐Iversen symptom score, quality of life, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, residual volume, adverse events | |
| Notes | Study unblinded with cross‐over at 3 months with follow‐up to 1 year | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | Austrian men, mean age 65 (range 45 to 85), symptomatic BPH. IPSS symptom score > 8; peak urinary flow < 12 mL/s with voided volume ≥ 150 mL; prostatic urethra length 30 to 50 mm; post‐void residual ≤ 250 mL; prostate size < 100 cc | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 51) | |
| Outcomes | IPSS symptom score, quality of life, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Alternating group assignments of consecutive patients one by one |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Alternating group assignments of consecutive patients one by one |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Higher proportion (> 10%) of dropouts among alpha blocker group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus oral medication |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | Dutch men, mean age 67, symptomatic BPH. Madsen symptom score > 7, peak urinary flow ≤ 15 mL/s; prostate length ≥ 25 mm; prostate volume ≥ 30 cc | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 78) | |
| Outcomes | Madsen‐Iversen symptom score, IPSS symptom score, quality of life, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, alpha blocker/anticholinergic treatment, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus TURP |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Multicenter | |
| Participants | American men, mean age 66, symptomatic BPH. AUA symptom score > 8; peak urinary flow ≤ 12 mL/s with voided volume ≥ 125 mL; prostatic urethra length 30 to 50 mm | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 125) | |
| Outcomes | AUA symptom score, peak urinary flow, quality of life, rehospitalization/retreatment, hospital length of stay, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Single center | |
| Participants | British men, median age 70 (range 56 to 80), symptomatic BPH eligible for TURP; peak urinary flow < 15 mL/s with voided volume ≥ 150 mL.; prostate urethra < 30 mm; post‐void residual < 350 mL | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 38) | |
| Outcomes | AUA symptom score, peak urinary flow, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Randomized by selecting one of three differently numbered but otherwise identical balls from a sealed bag |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Two centers | |
| Participants | Danish men, mean age 67, symptomatic BPH. IPSS symptom score > 6; peak urinary flow < 12 mL/s; prostatic urethra ≥ 25 mm; post‐void residual ≤ 350 mL | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 46) | |
| Outcomes | IPSS symptom score, quality of life, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, hospital length of stay, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition documented |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus laser versus TURP/TUIP |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Methods | Multicenter | |
| Participants | American and Canadian men, mean age 66, symptomatic BPH. AUA symptom score > 13; peak urinary flow < 13 mL/s with voided volume > 125 mL; prostate volume 25‐100 cc; prostatic urethra ≤ 30 mm | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 147) | |
| Outcomes | AUA symptom score, quality of life, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Higher proportion (> 10%) lost to follow‐up in TUMT group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Methods | Multicenter | |
| Participants | Scandinavian and American men, mean age 68, symptomatic BPH. IPSS symptom score > 12; peak urinary flow < 13 mL/s; prostate volume 30 to 100 cc | |
| Interventions | 1. TUMT (n = 100) | |
| Outcomes | IPSS symptom score, quality of life, peak urinary flow, rehospitalization/retreatment, residual volume, prostate size, adverse events | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 21/154 did not complete the study, similar proportions in each arm |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
| Other bias | Low risk | Adequate |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | TUMT versus TURP |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Adequate |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Variant technique: periurethral; cross‐over at 3 months with no interpretable outcome data | |
| Hyperthermia | |
| Superseded by Bdesha 1994 | |
| Four‐month follow‐up, outcome data not interpretable; ICS symptom index, no complication data | |
| Superseded by D'Ancona 1998 | |
| Superseded by D'Ancona 1998 | |
| Superseded by Dahlstrand 1995 | |
| Superseded by Dahlstrand 1995 | |
| Superseded by De Wildt 1996, (combined UK Netherlands) versus Netherlands | |
| Economic data only | |
| TUMT ± neoadjuvant alpha‐blocker | |
| 18‐month f/u, large loss to follow‐up. 6‐month data (Journal of Urology 1999) used in analyses | |
| Superseded by De Wildt 1996 (combined UK, Netherlands) versus UK | |
| Duplicates Floratos 2001 | |
| Economic data only | |
| 5‐year outcome data from Wagrell 2002, 34% loss to follow‐up | |
| Economic data only | |
| Superseded by De Wildt 1996 | |
| Men with persistent urinary retention | |
| Compared two similar energy TUMT systems that differed only by an adjunct balloon dilator | |
| Long‐term follow‐up of the sham crossed‐over group, no longer randomized. Very small sample size | |
| Duplicates Roehrborn 1998 | |
| Pooled observational with previously extracted RCT data | |
| 3‐month cross‐over, outcome data un interpretable, no complication data | |
| Long‐term follow‐up of Wagrell 2002. Substantial loss to follow‐up (31/99 in TUMT; 11/46 in TURP) | |
| Economic data only | |
| Hyperthermia | |
| Hyperthermia |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up Show forest plot | 4 | 306 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [‐2.03, 0.03] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up. | ||||
| 1.1 ProstaLund Feedback Treatment | 1 | 136 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐2.44, 2.24] |
| 1.2 Prostatron (high‐energy Prostasoft 2.5) | 2 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.95 [‐2.40, 0.51] |
| 1.3 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0 and 2.5) | 1 | 66 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.7 [‐5.87, 0.47] |
| 2 Madsen‐Iversen Symptom Score (range 0 to 27): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up Show forest plot | 2 | 108 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.59 [0.69, 2.48] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 2 Madsen‐Iversen Symptom Score (range 0 to 27): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up. | ||||
| 2.1 Prostatron (high‐energy Prostasoft 2.5) | 1 | 44 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.5 [‐1.07, 4.07] |
| 2.2 Prostatron (low‐energy Prostasoft 2.0) | 1 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.6 [0.64, 2.56] |
| 3 50% Improvement in AUA Symptom Score: # subjects Show forest plot | 2 | 121 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.50, 1.09] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 3 50% Improvement in AUA Symptom Score: # subjects. | ||||
| 4 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up Show forest plot | 5 | 338 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.08 [3.88, 6.28] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 4 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up. | ||||
| 4.1 ProstaLund Feedback Treatment | 1 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.17, 4.97] |
| 4.2 Prostatron (high‐energy Prostasoft 2.5) | 2 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.26 [3.67, 6.85] |
| 4.3 Prostatron (low‐energy Prostasoft 2.0) | 1 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.30 [3.80, 8.80] |
| 4.4 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0 and 2.5) | 1 | 66 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.40 [1.68, 13.12] |
| 5 Hematuria (requiring additional treatment/judged to be serious) Show forest plot | 3 | 258 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.15, 0.05] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 5 Hematuria (requiring additional treatment/judged to be serious). | ||||
| 6 Urinary retention Show forest plot | 4 | 343 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.94 [1.52, 5.70] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 6 Urinary retention. | ||||
| 7 Dysuria/Urgency Show forest plot | 3 | 277 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.22 [1.28, 3.86] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 7 Dysuria/Urgency. | ||||
| 8 Urinary tract infections/epididymitis/orchitis Show forest plot | 5 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.70, 1.86] |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 8 Urinary tract infections/epididymitis/orchitis. | ||||
| 9 Retrograde ejaculation (sexually active men only) Show forest plot | 2 | 78 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.34 [‐0.55, ‐0.13] |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 9 Retrograde ejaculation (sexually active men only). | ||||
| 10 Erectile dysfunction Show forest plot | 3 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.41 [0.16, 1.05] |
| Analysis 1.10  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 10 Erectile dysfunction. | ||||
| 11 Repeat treatments/Reoperations up to 1 year Show forest plot | 4 | 335 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.76 [0.54, 5.70] |
| Analysis 1.11  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 11 Repeat treatments/Reoperations up to 1 year. | ||||
| 12 Urethral/bladder neck strictures Show forest plot | 3 | 197 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.13 [0.02, 0.71] |
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 12 Urethral/bladder neck strictures. | ||||
| 13 Transfusions Show forest plot | 2 | 128 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.11 [‐0.21, ‐0.02] |
| Analysis 1.13  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 13 Transfusions. | ||||
| 14 Clot retention Show forest plot | 3 | 283 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.27 [0.06, 1.31] |
| Analysis 1.14  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 14 Clot retention. | ||||
| 15 TURP Syndrome Show forest plot | 3 | 274 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.11, ‐0.00] |
| Analysis 1.15  Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 15 TURP Syndrome. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) Show forest plot | 4 | 482 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.15 [‐6.04, ‐4.26] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS). | ||||
| 1.1 LEO Microthermer: 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐9.1 [‐15.64, ‐2.56] |
| 1.2 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0): 3/6 months follow‐up | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.0 [‐8.09, ‐1.91] |
| 1.3 Dornier Urowave: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 193 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.30 [‐6.32, ‐4.28] |
| 1.4 Urologix Targis system: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 155 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.80 [‐6.26, ‐1.34] |
| 2 Madsen Symptom Score Show forest plot | 2 | 196 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.10 [‐6.42, ‐3.79] |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 2 Madsen Symptom Score. | ||||
| 2.1 Prostatron (Prostasoft): 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 108 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐4.50 [‐6.37, ‐2.63] |
| 2.2 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0): 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 88 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.7 [‐7.56, ‐3.84] |
| 3 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax) Show forest plot | 6 | 643 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.01 [0.85, 3.16] |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 3 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax). | ||||
| 3.1 LEO Microthermer: 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 4.80 [1.98, 7.62] |
| 3.2 Prostatron (Prostasoft): 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 108 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.10 [0.56, 3.64] |
| 3.3 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0): 3/6 months follow‐up | 2 | 168 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.94 [‐1.29, 5.16] |
| 3.4 Dornier Urowave: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 195 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.90 [‐0.45, 2.25] |
| 3.5 Urologix Targis system: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 132 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.14, 3.86] |
| 4 Hematuria (post‐procedure) Show forest plot | 4 | 684 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.01, 0.13] |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 4 Hematuria (post‐procedure). | ||||
| 5 Urinary retention Show forest plot | 7 | 812 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.04 [2.51, 14.52] |
| Analysis 2.5  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 5 Urinary retention. | ||||
| 6 Dysuria (self‐limited) Show forest plot | 2 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.06 [1.03, 4.13] |
| Analysis 2.6  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 6 Dysuria (self‐limited). | ||||
| 7 UTI/epididymitis Show forest plot | 3 | 486 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.70, 2.39] |
| Analysis 2.7  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 7 UTI/epididymitis. | ||||
| 8 Ejaculatory disorders Show forest plot | 2 | 389 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.10 [0.83, 45.08] |
| Analysis 2.8  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 8 Ejaculatory disorders. | ||||
| 9 Retreatment Show forest plot | 2 | 209 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.12 [0.03, 0.48] |
| Analysis 2.9  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 9 Retreatment. | ||||
| 10 Quality of Life Show forest plot | 2 | 347 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.95 [‐1.14, ‐0.77] |
| Analysis 2.10  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 10 Quality of Life. | ||||
| 11 Bladder spasm Show forest plot | 3 | 443 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.71, 1.47] |
| Analysis 2.11  Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 11 Bladder spasm. | ||||

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
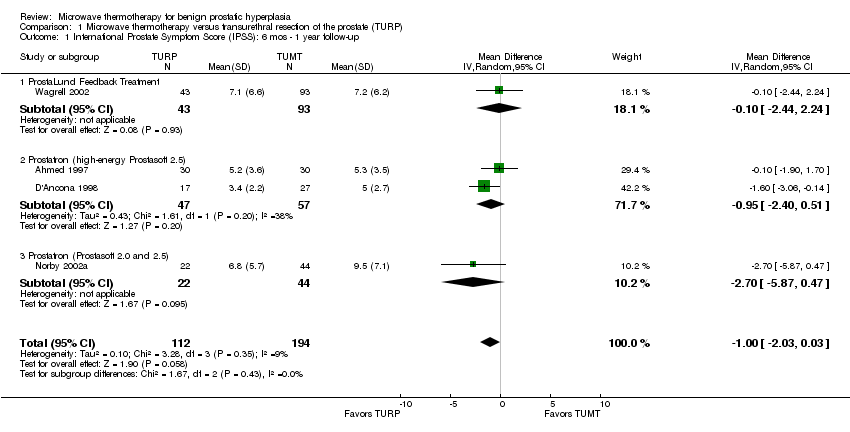
Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 2 Madsen‐Iversen Symptom Score (range 0 to 27): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 3 50% Improvement in AUA Symptom Score: # subjects.
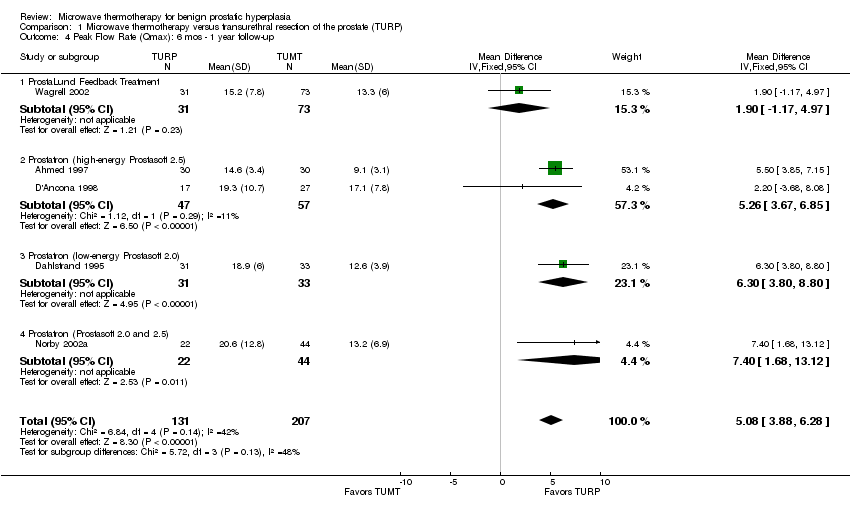
Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 4 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 5 Hematuria (requiring additional treatment/judged to be serious).

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 6 Urinary retention.
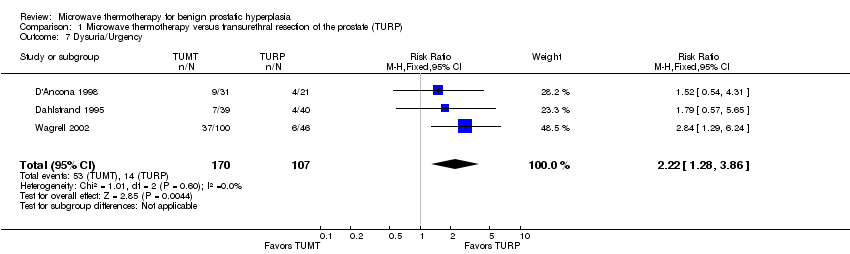
Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 7 Dysuria/Urgency.
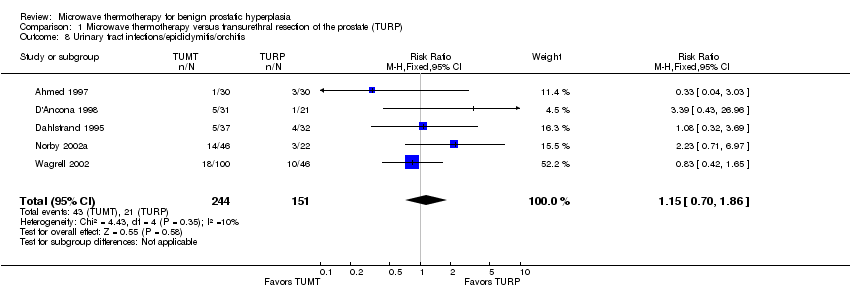
Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 8 Urinary tract infections/epididymitis/orchitis.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 9 Retrograde ejaculation (sexually active men only).

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 10 Erectile dysfunction.
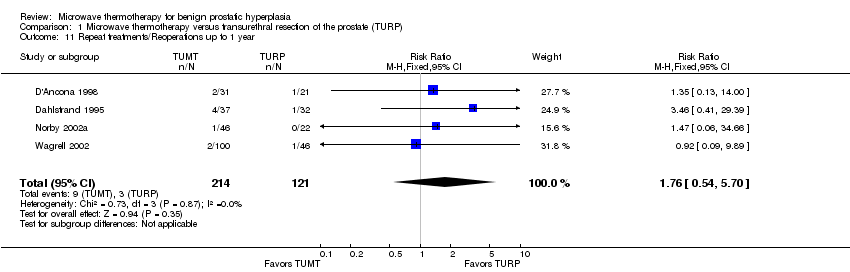
Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 11 Repeat treatments/Reoperations up to 1 year.
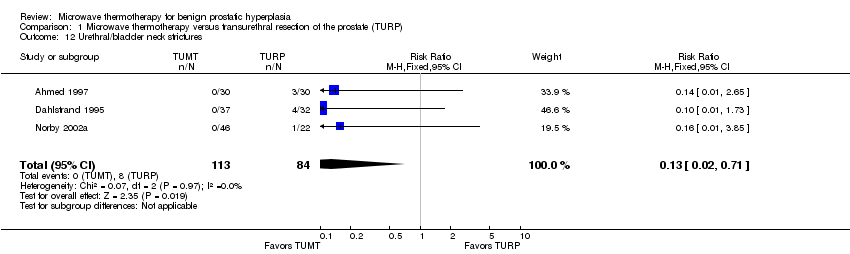
Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 12 Urethral/bladder neck strictures.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 13 Transfusions.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 14 Clot retention.

Comparison 1 Microwave thermotherapy versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), Outcome 15 TURP Syndrome.

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS).
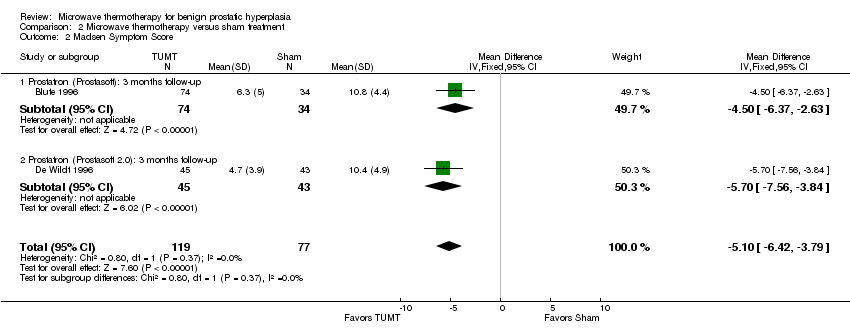
Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 2 Madsen Symptom Score.
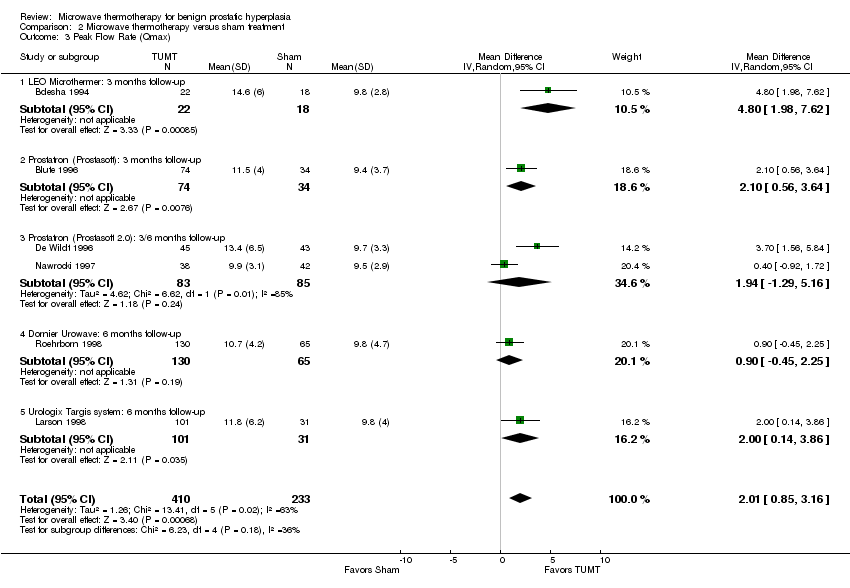
Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 3 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax).

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 4 Hematuria (post‐procedure).

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 5 Urinary retention.

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 6 Dysuria (self‐limited).

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 7 UTI/epididymitis.

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 8 Ejaculatory disorders.

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 9 Retreatment.

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 10 Quality of Life.

Comparison 2 Microwave thermotherapy versus sham treatment, Outcome 11 Bladder spasm.
| Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) compared with transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) for symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia | ||||
| Patient or population: men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia Settings: office (TUMT) or hospital (TURP) Intervention: Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) Comparison: Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) | ||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||
| TURP | TUMT | |||
| International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS). Range: 0 to 35 points. Follow‐up: 6 mos ‐ 1 year | The mean IPSS scores ranged across control groups from 3.4 to 7.1 points | The mean IPSS in the intervention group was 1 point higher (95% CI, 0.03 lower to 2.03 higher) | 306 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Madsen‐Iversen Symptom Score Range 0 to 27 points Follow‐up: 6 mos ‐ 1 year | The mean Madsen‐Iversen Symptom scores ranged across control groups from 0.62 to 2.7 points | The mean Madsen‐Iversen Symptom score in the intervention group was 1.59 points higher (95% CI, 0.69 lower to 2.48 higher) | 338 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| Peak Flow Rate (Qmax): Measurement: mL per second Follow‐up: 6 mos ‐ 1 year | The mean Peak Flow Rate ranged across control groups from 14.6 to 20.6 mL/s | The mean urinary peak flow rate in the intervention group was 5.08 mL/s lower (95% CI, 3.88 to 6.28 lower) | 108 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||
| 1 <400 subjects evaluated for this outcome which is a non‐optimal information size | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up Show forest plot | 4 | 306 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [‐2.03, 0.03] |
| 1.1 ProstaLund Feedback Treatment | 1 | 136 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐2.44, 2.24] |
| 1.2 Prostatron (high‐energy Prostasoft 2.5) | 2 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.95 [‐2.40, 0.51] |
| 1.3 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0 and 2.5) | 1 | 66 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐2.7 [‐5.87, 0.47] |
| 2 Madsen‐Iversen Symptom Score (range 0 to 27): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up Show forest plot | 2 | 108 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.59 [0.69, 2.48] |
| 2.1 Prostatron (high‐energy Prostasoft 2.5) | 1 | 44 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.5 [‐1.07, 4.07] |
| 2.2 Prostatron (low‐energy Prostasoft 2.0) | 1 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.6 [0.64, 2.56] |
| 3 50% Improvement in AUA Symptom Score: # subjects Show forest plot | 2 | 121 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.50, 1.09] |
| 4 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax): 6 mos ‐ 1 year follow‐up Show forest plot | 5 | 338 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.08 [3.88, 6.28] |
| 4.1 ProstaLund Feedback Treatment | 1 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.90 [‐1.17, 4.97] |
| 4.2 Prostatron (high‐energy Prostasoft 2.5) | 2 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.26 [3.67, 6.85] |
| 4.3 Prostatron (low‐energy Prostasoft 2.0) | 1 | 64 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.30 [3.80, 8.80] |
| 4.4 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0 and 2.5) | 1 | 66 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.40 [1.68, 13.12] |
| 5 Hematuria (requiring additional treatment/judged to be serious) Show forest plot | 3 | 258 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.15, 0.05] |
| 6 Urinary retention Show forest plot | 4 | 343 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.94 [1.52, 5.70] |
| 7 Dysuria/Urgency Show forest plot | 3 | 277 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.22 [1.28, 3.86] |
| 8 Urinary tract infections/epididymitis/orchitis Show forest plot | 5 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.15 [0.70, 1.86] |
| 9 Retrograde ejaculation (sexually active men only) Show forest plot | 2 | 78 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.34 [‐0.55, ‐0.13] |
| 10 Erectile dysfunction Show forest plot | 3 | 212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.41 [0.16, 1.05] |
| 11 Repeat treatments/Reoperations up to 1 year Show forest plot | 4 | 335 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.76 [0.54, 5.70] |
| 12 Urethral/bladder neck strictures Show forest plot | 3 | 197 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.13 [0.02, 0.71] |
| 13 Transfusions Show forest plot | 2 | 128 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.11 [‐0.21, ‐0.02] |
| 14 Clot retention Show forest plot | 3 | 283 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.27 [0.06, 1.31] |
| 15 TURP Syndrome Show forest plot | 3 | 274 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.11, ‐0.00] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) Show forest plot | 4 | 482 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.15 [‐6.04, ‐4.26] |
| 1.1 LEO Microthermer: 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐9.1 [‐15.64, ‐2.56] |
| 1.2 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0): 3/6 months follow‐up | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.0 [‐8.09, ‐1.91] |
| 1.3 Dornier Urowave: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 193 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.30 [‐6.32, ‐4.28] |
| 1.4 Urologix Targis system: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 155 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.80 [‐6.26, ‐1.34] |
| 2 Madsen Symptom Score Show forest plot | 2 | 196 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.10 [‐6.42, ‐3.79] |
| 2.1 Prostatron (Prostasoft): 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 108 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐4.50 [‐6.37, ‐2.63] |
| 2.2 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0): 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 88 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐5.7 [‐7.56, ‐3.84] |
| 3 Peak Flow Rate (Qmax) Show forest plot | 6 | 643 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.01 [0.85, 3.16] |
| 3.1 LEO Microthermer: 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 4.80 [1.98, 7.62] |
| 3.2 Prostatron (Prostasoft): 3 months follow‐up | 1 | 108 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.10 [0.56, 3.64] |
| 3.3 Prostatron (Prostasoft 2.0): 3/6 months follow‐up | 2 | 168 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 1.94 [‐1.29, 5.16] |
| 3.4 Dornier Urowave: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 195 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.90 [‐0.45, 2.25] |
| 3.5 Urologix Targis system: 6 months follow‐up | 1 | 132 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.14, 3.86] |
| 4 Hematuria (post‐procedure) Show forest plot | 4 | 684 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.01, 0.13] |
| 5 Urinary retention Show forest plot | 7 | 812 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.04 [2.51, 14.52] |
| 6 Dysuria (self‐limited) Show forest plot | 2 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.06 [1.03, 4.13] |
| 7 UTI/epididymitis Show forest plot | 3 | 486 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.70, 2.39] |
| 8 Ejaculatory disorders Show forest plot | 2 | 389 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.10 [0.83, 45.08] |
| 9 Retreatment Show forest plot | 2 | 209 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.12 [0.03, 0.48] |
| 10 Quality of Life Show forest plot | 2 | 347 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.95 [‐1.14, ‐0.77] |
| 11 Bladder spasm Show forest plot | 3 | 443 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.71, 1.47] |

