Nutrición enteral precoz (24 horas) versus inicio tardío de la alimentación para las complicaciones postoperatorias de la cirugía colorrectal
Referencias
Referencias de los estudios incluidos en esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en curso
Referencias adicionales
Referencias de otras versiones publicadas de esta revisión
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Randomised double blind prospective trial (no information on method) | |
| Participants | 30 patients in each group; nutrition versus placebo (water), mainly colorectal surgery (87%) | |
| Interventions | Nutridrink versus placebo in patients who received bowel resection. Route of feeding: Nasoduodenal | |
| Outcomes | Anastomotic leakage/dehiscence; acute myocardial infarction; pulmonary failure; wound infection; intraabdominal abscess/peritonitis; pneumonia; mortality in each group; | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method of randomisation not stated | |
| Participants | 32 patients in each group; nutrition gr. versus control gr., colorectal surgery (100%) | |
| Interventions | laparotomy with either a colonic or ileal resection, nutrition group received 'regular diet' within 24 hours from surgery. Route of feeding: Oral | |
| Outcomes | tube reinsertion; vomiting; length of hospital stay; various adverse effects reported | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Allocation of participants by the use of sealed envelopes | |
| Participants | 28 patients in each group undergoing elective gastrointestinal resection | |
| Interventions | Laparotomy, site of surgery not stated. Route of feeding: Nasojejunal tube | |
| Outcomes | Nausea; vomiting; distension; diarrhoea; bleeding duodenal ulcer; infection; length of hospital stay | |
| Notes | 30 eligible participants, two did not proceed to resection | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method not stated | |
| Participants | 58 participants (29 in each group) undergoing elective colorectal surgery | |
| Interventions | Colorectal surgery. Route of feeding: oral | |
| Outcomes | Nausea; vomiting; complications / infection; length of hospital stay | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, sealed envelope. | |
| Participants | 195 participants diagnosed with oesophageal (23), gastric (75), peripancreatic (86), or bile duct (11) cancer. | |
| Interventions | Resection of the tumour. Route of feeding: jejunostomy tube | |
| Outcomes | Anastomotic leakage/dehiscence; wound infection; intraabdominal abscess/peritonitis; pneumonia; mortality in each group; adverse effects reported | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
| Methods | A prospective randomised trial | |
| Participants | 51 consecutive patients undergoing elective open gastrointestinal surgery, primarily lower GI surgery. Laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery patients were excluded. | |
| Interventions | Resections, colectomies, proctectomies, and colostomy closures | |
| Outcomes | Lenght of Hospital stay, pneumonia, anastomotic leak | |
| Notes | The RCT also focused on tolerance of diet | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial, method not stated | |
| Participants | 73 patients undergoing colonic resection | |
| Interventions | Colonic resection | |
| Outcomes | GI adverse effects, length of hospital stay, incidence of infection, mortality | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method not stated | |
| Participants | 190 participants diagnosed with either neoplasm (165), inflammatory bowel disease (21) or diverticular disease (4) | |
| Interventions | Elective open colon or rectal surgery (resection, colectomy, hemicolectomy). Route of feeding: Oral | |
| Outcomes | Anastomotic leakage; wound infection; haemorrhage; pneumonia; venous thrombosis; urinary infection; abdominal abscess; intestinal obstruction; ileostomy necrosis | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method not stated | |
| Participants | 161 participants undergoing elective laparotomy | |
| Interventions | Bowel resection; proctocolectomy; stoma. Route of feeding: Oral | |
| Outcomes | Tube reinsertion; vomiting; length of hospital stay; various complications reported | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method not stated | |
| Participants | 30 participants undergoing major gastrointestinal surgery | |
| Interventions | Oesophago‐gastrectomy, gastrectomy, colectomy, anterior resection, abdominoperineal resection. Route of feeding: Nasojejunal tube | |
| Outcomes | Wound infection; anastomotic leakage; abdominal abscess; length of hospital stay; nitrogen balance | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method not stated | |
| Participants | 32 participants, 16 in each group, undergoing bowel resection | |
| Interventions | Bowel resection, ileoanal J pouch, or reanastomosis. Route of feeding: Nasojejunal tube | |
| Outcomes | Myocardial infarction; Atelectasis; Pneumonia; small bowel obstruction | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, using sealed envelopes | |
| Participants | 152 participants in four comparison groups, all undergoing elective colorectal surgery | |
| Interventions | Not stated, but all participants underwent 'moderate to major lower gastrointestinal surgery' | |
| Outcomes | Primarily weight changes, but complications are reported too. | |
| Notes | Exclusion criteria stated | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study, method not stated | |
| Participants | 80 participants undergoing elective intraperitoneal colorectal resections without stoma formation | |
| Interventions | Ileocolic resection (10); hemicolectomy (right or left) (35); subtotal colectomy (11); anterior resection (24). Route of feeding: Oral | |
| Outcomes | Tube reinsertion; vomiting; plus various complications reported | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
| Methods | Allocation of participants by the use of consecutive sealed envelopes | |
| Participants | 31 participants undergoing major elective abdominal or thoracic surgery | |
| Interventions | Esophagectomy; pancreatoduodenectomy. Route of feeding: Jejunostomy tube | |
| Outcomes | Anastomotic leakage; length of hospital stay; and 'vital capacity' measures | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Both comparisons groups start feeding more than 24 hours after surgery. | |
| Feeding did not start until a mean of 6,5 days after GI surgery, and the trial compared normal diet versus normal diet plus supplement | |
| An abstract. Results presented in the 1998 reference! | |
| Not randomised on early enteral feeding. The comparisons focus on post enteral nutrition for two surgical techniques, whether there is any difference between open and minimal invasive procedures with respect to the start of oral intake. | |
| Not a randomised trial | |
| This is a well performed RCT, but reported multiple variables not just diet. | |
| Both treatment groups were allowed liquid diet, therefore no control group to early enteral feeding | |
| Patients undergoing colonic and vascular surgery were randomly allocated to choose when they wanted to start an oral diet (patient controlled group) or a fixed feeding regime where diet was introduced on post‐operative day four | |
| It is not clear if some or all patients are common to the 2001 publication, but reason for exclusion the same: Patients undergoing colonic and vascular surgery were randomly allocated to choose when they wanted to start an oral diet (patient controlled group) or a fixed feeding regime where diet was introduced on post‐operative day four | |
| Patients receiving enteral nutrition is compared to a control group, receiving intravenous nutrition. Main outcome is cumulative 10 day nitrogen balance. | |
| Non‐traumatic GI perforation. 44% had DU’s, 39% ileal (TB or typhoid). Closure was direct, no resections and GI anastamosis formed. Feeding was started 24h after surgery. | |
| Not dealing with early enteral feeding, rather whether oral diet supplements have an effect or not. | |
| Both comparison groups receives early postoperative enteral nutrition. One with arginine‐omega‐3 fatty acids and ribonucleic acid‐supplemented diet versus placebo. | |
| Study on trauma patients, admitted in shock and stabilised in 6 hours. | |
| No control group was used, as the comparisons groups begin tube feedings at 4 h (group A) or at 24 h (group B) after intervention | |
| Review on multisystem trauma, a decade perspective. Will support the discussion of this review. | |
| Not able to determine if the study was randomised. | |
| This is a study examining the benefits of bowel confinement where the interventional group received clear liquids with high dose loperamide and codeine with the control group of patients started a regular dietary intake on the day of surgery | |
| All three groups undergoing elective partial colectomy received early feeding, randomized to receive either jejunal feeding of elemental diet (ED) or isotonic intravenous infusions of dextrose (IV). | |
| A comparison of laparoscopic or conventional resection of colorectal tumours. Major endpoints were the postoperative time to the first bowel movement and the time until oral feeding without parenteral alimentation was tolerated. | |
| No method stated. Individual protocol for commencement of postoperative feeding. | |
| Both groups received early postoperative feeding | |
| Patients in the early feeding group did not start receiving 'feed' until after 24h (before 24h they received saline/dextrose). Our study criteria is that patients receive enteral feed within 24h of surgery. | |
| Pseudo randomised on an intention to treat. Decision on treatment group was determined individually | |
| Comparison of three different methods of feeding administration | |
| Not a randomised study. | |
| Feeding started via NJ tube 12‐24h saline & 5% dextrose then 24‐48h 1L and half strength feed at 50ml/h. Thus patients were not fed within 24h of surgery | |
| Not a randomised study | |
| Comparison between enteral and parenteral nutrition. | |
| This study evaluates the feasibility of alpha‐ketoglutarate enrichment of enteral feeding and the effect on protein metabolism (nitrogen balance). | |
| Compares early versus late removal of naso‐gastric tubes after colorectal surgery |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
| Trial name or title | Relative benefits of preoperative and early postoperative oral nutrition supplements on postoperative insulin resistance |
| Methods | Prospective four‐arm double blind randomised controlled trial |
| Participants | 120 patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer undergoing colorectal surgery |
| Interventions | curative colorectal resection with primary anastomosis |
| Outcomes | glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance, muscle strength, lung function |
| Starting date | not stated |
| Contact information | Stephen Lewis |
| Notes | none |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 woundinfection Show forest plot | 9 | 879 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.48, 1.22] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 1 woundinfection. | ||||
| 2 intraabdominal abscess Show forest plot | 10 | 907 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.31, 2.42] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 2 intraabdominal abscess. | ||||
| 3 anastomotic leakage / dehiscence Show forest plot | 11 | 958 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.40, 1.39] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 3 anastomotic leakage / dehiscence. | ||||
| 4 mortality Show forest plot | 10 | 907 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.41 [0.18, 0.93] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 4 mortality. | ||||
| 5 pneumonia Show forest plot | 10 | 928 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.35, 1.46] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 5 pneumonia. | ||||
| 6 lenght of hospital stay Show forest plot | 14 | 1132 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.89 [‐1.58, ‐0.20] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 6 lenght of hospital stay. | ||||
| 7 Vomitting Show forest plot | 6 | 618 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [1.01, 1.61] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 7 Vomitting. | ||||

Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 1 woundinfection.
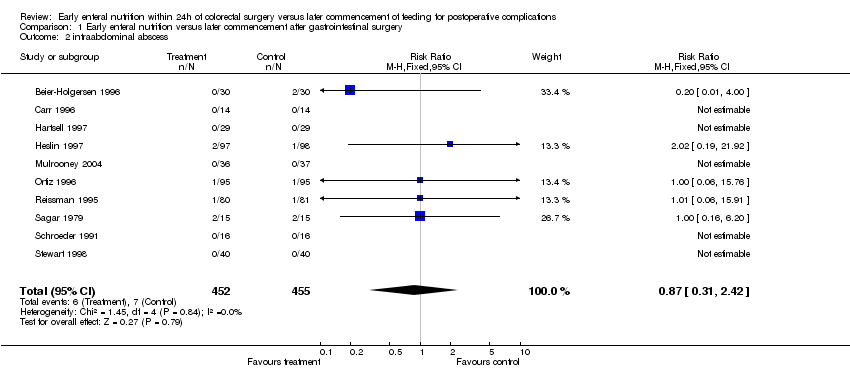
Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 2 intraabdominal abscess.

Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 3 anastomotic leakage / dehiscence.

Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 4 mortality.

Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 5 pneumonia.

Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 6 lenght of hospital stay.

Comparison 1 Early enteral nutrition versus later commencement after gastrointestinal surgery, Outcome 7 Vomitting.
| Study | Site of surgery | Feed type | Route of feeding | Pathology | Primary outcomes | Additional data |
| Beier Holgersen 1996 | Lower GI (87%), Upper GI (13%) | Standard | Nasoduodenal tube | 65% Malignant; 35% Benign | Wound infection; intraabdominal abscess, anastomotic leakage; mortality | yes |
| Binderow 1994 | Lower GI (100%) | Oral | Oral | Not reported | Lenght of hospital stay; adverse events | no |
| Carr 1996 | Not reported | Standard | Nasojejunal tube | Not reported | Wound infection; mortality; length of hospital stay | no |
| Hartsell 1997 | Lower GI (100%) | Standard | Oral | 64% Malignant, 36% Benign | Anastomotic leakage; mortality; adverse effects | no |
| Heslin 1997 | Upper GI (51%), Hepatobiliary (49%) | Immune enhancing type | Jejunostomy | 93% Malignant, 7% Benign | Wound infection; anastomotic leakage; intraabdominal abscess; mortality | yes |
| Mulrooney 2004 | Lower GI (100%) | Standard | Nasojejunal tube | 100% Malignant | Infection, mortality, length of hospital stay, GI adverse effects | yes |
| Ortiz 1996 | Lower GI (100%) | Oral | Oral | 87% Malignant, 13% Benign | Wound infection; anastomotic leakage; intraabdominal abscess; intestinal obstruction | yes |
| Reissman 1995 | Lower GI (100%) | Oral | Oral | Not reported | Lenght of hospital stay; various complications such as tube reinsertion | yes |
| Sagar 1979 | Lower GI (73%), Upper GI (23%) | Elemental | Nasojejunal tube | Not reported | Wound infection; anastomotic leakage; intraabdominal abscess; length of hospital stay | no |
| Schroeder 1991 | Lower GI (100%) | Standard | Nasojejunal tube | Not reported | Myocardial infarct; obstruction; various complications | no |
| Smedley 2004 | Lower GI (100%) | Oral | Oral | 62% Malignant, 38% Benign | Lenght of hospital stay; complications; costs | yes |
| Stewart 1998 | Lower GI (100%) | Standard | Nasogastric tube | Not reported | Complications such as tube reinsertion | yes |
| Watters 1997 | Lower GI (96%), Hepatobiliary (4%) | Standard | Jejunostomy | 93% Malignant, 7% Benign | Anastomotic leakage; length of hospital stay | no |
| Lucha 2005 | Lower GI (100%) | Standard | Nasogastric tube | Not reported | Lenght of hospital stay; complications; costs | yes |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 woundinfection Show forest plot | 9 | 879 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.48, 1.22] |
| 2 intraabdominal abscess Show forest plot | 10 | 907 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.31, 2.42] |
| 3 anastomotic leakage / dehiscence Show forest plot | 11 | 958 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.40, 1.39] |
| 4 mortality Show forest plot | 10 | 907 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.41 [0.18, 0.93] |
| 5 pneumonia Show forest plot | 10 | 928 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.35, 1.46] |
| 6 lenght of hospital stay Show forest plot | 14 | 1132 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.89 [‐1.58, ‐0.20] |
| 7 Vomitting Show forest plot | 6 | 618 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.27 [1.01, 1.61] |



