Strategien zur Spülung von langfristig liegenden Blasenkathetern bei Erwachsenen
Información
- DOI:
- https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004012.pub5Copiar DOI
- Base de datos:
-
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- Versión publicada:
-
- 06 marzo 2017see what's new
- Tipo:
-
- Intervention
- Etapa:
-
- Review
- Grupo Editorial Cochrane:
-
Grupo Cochrane de Incontinencia
- Copyright:
-
- Copyright © 2017 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Cifras del artículo
Altmetric:
Citado por:
Autores
Contributions of authors
AS and SH independently assessed all titles and abstracts identified by the search strategy. AS, SH and WM completed the data extraction and quality assessment of all included trials. AS contacted authors of papers, and gathered additional data. SH was responsible for data entry, analysis and interpretation. WM provided clinical perspective and further interpretation. SH was the review guarantor.
Sources of support
Internal sources
-
No sources of support supplied
External sources
-
National Institute for Health Research, UK.
This project was supported by the National Institute for Health Research, via Cochrane Infrastructure, Cochrane Programme Grant or Cochrane Incentive funding to the Incontinence Group. The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Systematic Reviews Programme, NIHR, NHS or the Department of Health.
Declarations of interest
Ashley Shepherd: None known.
Suzanne Hagen: None known.
William McKay: None known.
Acknowledgements
The review authors would like to thank Sheila Wallace of the Cochrane Incontinence Group for her assistance with searching and developing the search strategy. The authors would wish to thank both Lesley Sinclair and Stephen Cross who were co‐authors of the original review (Hagen 2010).
Version history
| Published | Title | Stage | Authors | Version |
| 2017 Mar 06 | Washout policies in long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation in adults | Review | Ashley J Shepherd, William G Mackay, Suzanne Hagen | |
| 2010 Mar 17 | Washout policies in long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation in adults | Review | Suzanne Hagen, Lesley Sinclair, Stephen Cross | |
| 2006 Jan 25 | Washout policies for the management of long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation in adults | Protocol | Lesley Sinclair, Stephen Cross, Suzanne Hagen, Barbara S Niël‐Weise | |
| 2004 Jul 19 | Washout policies for management of long‐term voiding problems in catheterised adults | Protocol | Lesley Sinclair, Stephen Cross, Suzanne Hagen, Barbara S Niël‐Weise | |
| 2002 Oct 21 | Washout policies for management of long‐term voiding problems in catheterised adults | Protocol | J Mooney, S Hagen, B Niel‐Weise | |
Differences between protocol and review
For the 2017 update of the review there was no additional searching of databases other than the Cochrane Incontinence Specialised Register as this now includes relevant searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, MEDLINE In‐Process, MEDLINE Epub Ahead of Print, CINAHL, ClinicalTrials.gov, WHO ICTRP, and UK Clinical Research Network Portfolio. Cochrane now organises centralised searches of Embase (including conference abstracts) that are included in CENTRAL so no additional Embase searches were performed. We continued to search the reference lists of relevant articles. The order of primary outcomes presented in the review has changed from the 2010 version following editors' advice.
Keywords
MeSH
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Keywords
- *Catheters, Indwelling [statistics & numerical data];
- Device Removal;
- Equipment Failure;
- Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic;
- Solutions [*administration & dosage, chemistry];
- Therapeutic Irrigation [adverse effects, *methods];
- Time Factors;
- Urinary Bladder Neck Obstruction [therapy];
- Urinary Catheterization [*instrumentation];
- Urinary Incontinence [therapy];
Medical Subject Headings Check Words
Adult; Aged; Aged, 80 and over; Female; Humans; Male; Middle Aged;
PICO
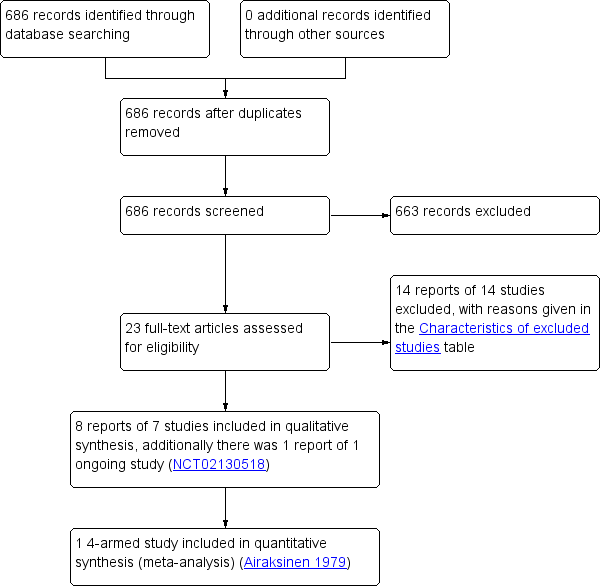
Study flow diagram
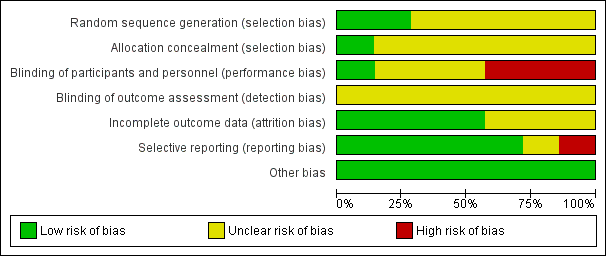
Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies
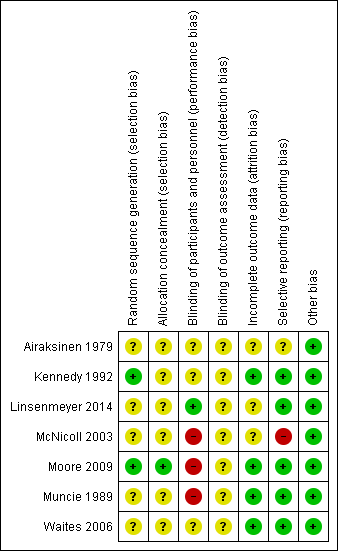
Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study
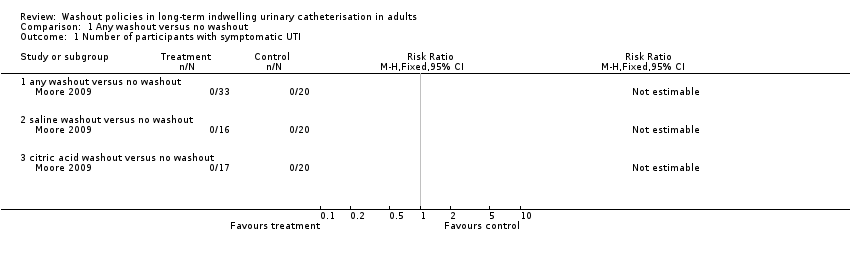
Comparison 1 Any washout versus no washout, Outcome 1 Number of participants with symptomatic UTI.
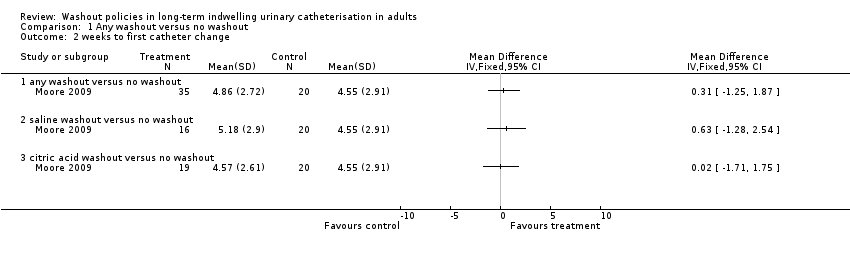
Comparison 1 Any washout versus no washout, Outcome 2 weeks to first catheter change.
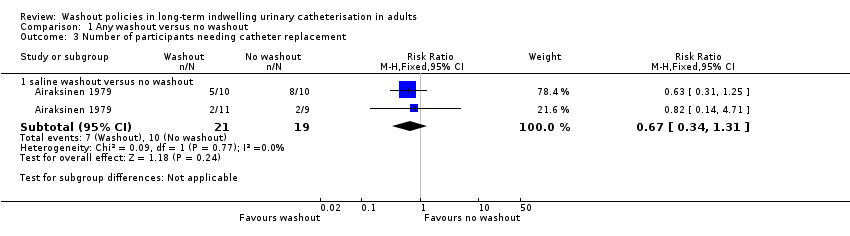
Comparison 1 Any washout versus no washout, Outcome 3 Number of participants needing catheter replacement.
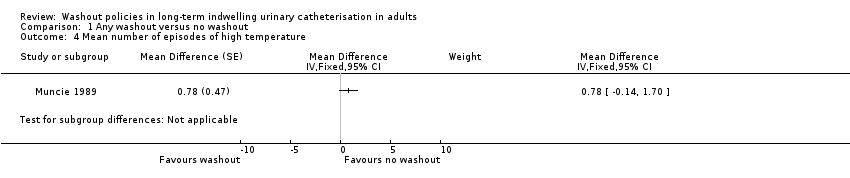
Comparison 1 Any washout versus no washout, Outcome 4 Mean number of episodes of high temperature.
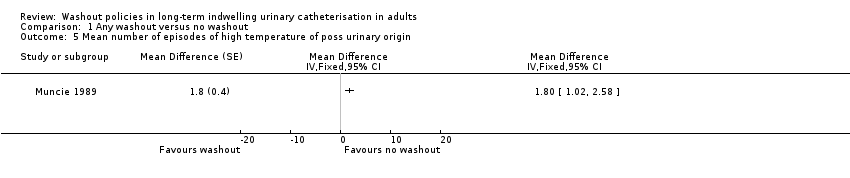
Comparison 1 Any washout versus no washout, Outcome 5 Mean number of episodes of high temperature of poss urinary origin.
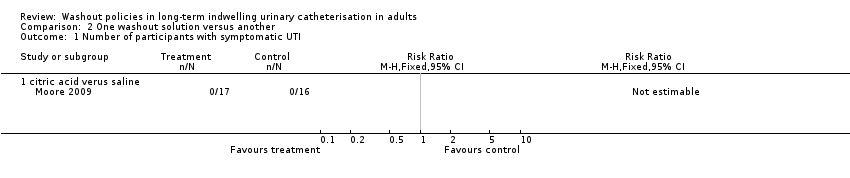
Comparison 2 One washout solution versus another, Outcome 1 Number of participants with symptomatic UTI.
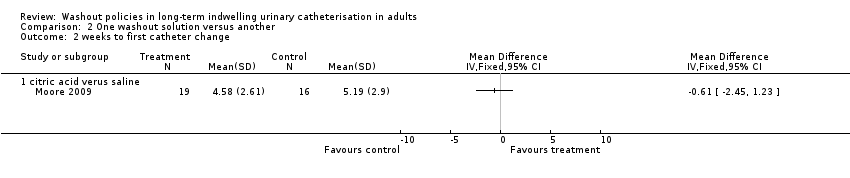
Comparison 2 One washout solution versus another, Outcome 2 weeks to first catheter change.
| Any washout compared to no washout for participants with long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation | ||||||
| Patient or population: Long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation in adults | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| No washout | Any washout | |||||
| Symptomatic UTI (Number of participants with symptomatic UTI, citric acid or saline washout versus no washout) | 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 (0 to 0) | Not estimable | 53 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | No participants met the study criteria for symptomatic UTI |
| Symtomatic UTI Mean number of episodes of high temperature (saline washout versus no washout) | ‐ | The mean number of episodes of high temperature (saline washout versus no washout) in the intervention groups was: 0.78 (‐0.14 to 1.70) | Not estimable | 23 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Symptomatic UTI Mean number of episodes of high temperature due to possible urinary origin (saline washout versus no washout) | ‐ | The mean number of episodes of high temperature of possible urinary origin (saline washout versus no washout) in the intervention groups was: 1.80 (1.02 to 2.58) | Not estimable | 23 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Number of catheters used (Number of participants needing catheter replacement, saline washout versus no washout) | 526 per 1000 | 353 per 1000 (179 to 689) | RR 0.67 | 40 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Length of time each catheter was in situ | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Catheter removal rates due to blockage/infection | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Rates of asymptomatic bacteriuria | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded two levels: The sample size was small (N = 53). Personnel not blinded to allocation of treatment. Blinding of outcome assessment not clear. | ||||||
| One washout solution versus another for participants with long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation | ||||||
| Patient or population: Long‐term indwelling urinary catheterisation in adults | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | One washout solution versus another | |||||
| Symptomatic UTI Number of participants with symptomatic UTI (citric acid versus saline) | 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 (0 to 0) | Not estimable | 33 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | No participants met the study criteria for symptomatic UTI |
| Symtomatic UTI Mean number of episodes of high temperature | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Symptomatic UTI Mean number of episodes of high temperature due to possible urinary origin | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Number of catheters used Number of participants needing catheter replacement | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Length of time each catheter was in situ | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Catheter removal rates due to blockage/infection | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| Rates of asymptomatic bacteriuria | Not estimable | Not reported | No data available | |||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Downgraded two levels: The sample size was small (N = 33). Personnel not blinded to allocation of treatment. Blinding of outcome assessment not clear. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of participants with symptomatic UTI Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 any washout versus no washout | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 saline washout versus no washout | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 citric acid washout versus no washout | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 weeks to first catheter change Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 any washout versus no washout | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.2 saline washout versus no washout | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2.3 citric acid washout versus no washout | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Number of participants needing catheter replacement Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 saline washout versus no washout | 1 | 40 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.67 [0.34, 1.31] |
| 4 Mean number of episodes of high temperature Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 5 Mean number of episodes of high temperature of poss urinary origin Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of participants with symptomatic UTI Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 citric acid verus saline | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 weeks to first catheter change Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 citric acid verus saline | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |

