Eritromicina para la prevención de la enfermedad pulmonar crónica en recién nacidos prematuros intubados con riesgo de Ureaplasma urealyticum o ya colonizados o infectados por este microorganismo
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to studies awaiting assessment
Additional references
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Quasi ‐ randomized (alternate assignment). Concealed randomization‐ No. Masked intervention‐No (placebo not used). Complete follow‐up‐Yes. Masked outcome‐No. | |
| Participants | 28 intubated preterm infants <30 weeks gestation culture positive for U. urealyticum. 14 treated, 14 control | |
| Interventions | Treated every other colonized infant with a 10 day course of erythromycin, 40 mg/kg/day, orally (n=10) or intravenously (n=4). Average age at treatment 7 days. Controls received no treatment. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: Oxygen dependency at 36 weeks PMA. Secondary outcome: Side effects of erythromycin treatment (GI, hepatic, cardiovascular) | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | High risk | C ‐ Inadequate |
| Methods | Randomized trial | |
| Participants | 75 intubated infants equal to or less than 30 weeks gestation. Of the 75 randomized infants, 9 infants proved to be positive for U. urealyticum by culture and/or PCR. | |
| Interventions | Erythromycin (45 mg/kg/day TID, IV for 7 days) treatment versus no treatment before culture/PCR results were known. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: Inflammatory cytokine response after birth in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| No control group. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| No control group. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| Treatment was not randomized. | |
| No treatment with erythromycin was involved. | |
| No treatment with erythromycin was involved. | |
| No treatment with erythromycin was involved. |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Not known |
| Participants | Not known |
| Interventions | Not known |
| Outcomes | Not known |
| Notes |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 CLD Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.72, 2.70] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 1 CLD. | ||||
| 1.1 Culture/PCR positive | 1 | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 22.06] |
| 1.2 Culture/PCR negative | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.68, 2.69] |
| 2 Death Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.22, 1.83] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 2 Death. | ||||
| 2.1 Culture/PCR positive | 1 | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.03, 11.21] |
| 2.2 Culture/PCR negative | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.21, 2.00] |
| 3 CLD or death Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.66, 1.69] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 3 CLD or death. | ||||
| 3.1 Culture/PCR positive | 1 | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.14, 7.10] |
| 3.2 Culture/PCR negative | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.66, 1.72] |
| 4 Side effects of erythromycin Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 4 Side effects of erythromycin. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 CLD Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.9 [0.54, 1.50] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 1 CLD. | ||||
| 2 Death Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 2 Death. | ||||
| 3 CLD or death Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.9 [0.54, 1.50] |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 3 CLD or death. | ||||
| 4 Side effects of erythromycin Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 4 Side effects of erythromycin. | ||||

Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 1 CLD.

Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 2 Death.

Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 3 CLD or death.
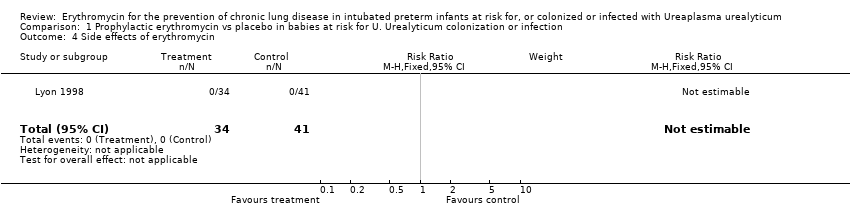
Comparison 1 Prophylactic erythromycin vs placebo in babies at risk for U. Urealyticum colonization or infection, Outcome 4 Side effects of erythromycin.

Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 1 CLD.

Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 2 Death.
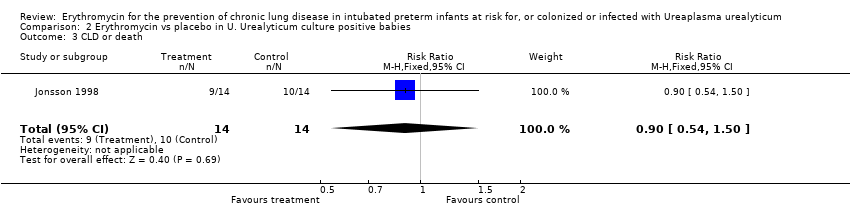
Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 3 CLD or death.

Comparison 2 Erythromycin vs placebo in U. Urealyticum culture positive babies, Outcome 4 Side effects of erythromycin.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 CLD Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.40 [0.72, 2.70] |
| 1.1 Culture/PCR positive | 1 | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 22.06] |
| 1.2 Culture/PCR negative | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.35 [0.68, 2.69] |
| 2 Death Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.64 [0.22, 1.83] |
| 2.1 Culture/PCR positive | 1 | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.03, 11.21] |
| 2.2 Culture/PCR negative | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.21, 2.00] |
| 3 CLD or death Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.66, 1.69] |
| 3.1 Culture/PCR positive | 1 | 9 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.14, 7.10] |
| 3.2 Culture/PCR negative | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.66, 1.72] |
| 4 Side effects of erythromycin Show forest plot | 1 | 75 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 CLD Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.9 [0.54, 1.50] |
| 2 Death Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 CLD or death Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.9 [0.54, 1.50] |
| 4 Side effects of erythromycin Show forest plot | 1 | 28 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |

