Cirugía de fundoplicatura laparoscópica versus tratamiento médico para la enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico (ERGE) en adultos
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Randomised clinical trial | |
| Participants | Country: Canada. Number randomised: 104 Post‐randomisation drop‐outs: 21 (20.2%) Revised sample size: 83 Average age: 43 years Females: 49 (59%) Barretts oesophagus: not stated Hiatus hernia: not stated Body mass index: not stated Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
| |
| Interventions | Participants were randomly assigned to two groups. | |
| Outcomes | The outcomes reported were health‐related quality of life, GERD‐specific quality of life, and adverse events. | |
| Notes | Reasons for post‐randomisation drop‐outs: nine: surgical treatment (one did not follow received allocation; eight lost to follow‐up) and 12: medical treatment (two did not follow received allocation; 10 lost to follow‐up). | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The uniform random integers, 0 through 9, were generated in Minitab 12 (Minitab Inc, State College, PA) for each stratum….. The groups of 16 for blocks of 2 or 4 were generated at random, using single‐digit random numbers, odd being SC (surgery, control) and even being CS". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "To this extent the research assistants checking the eligibility were not exposed to the continuing randomization list". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "Consequently, this study did not have blinded implementation of the treatment arms". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Quote: "Consequently, this study did not have blinded implementation of the treatment arms". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Comment: There were post‐randomisation drop‐outs. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: Important outcomes were reported. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Quote: "Supported by grants from Canadian Institute of Health Research and Ontario Ministry of Health and Long‐term Care". |
| Methods | Randomised clinical trial | |
| Participants | Country: United Kingdom Number randomised: 357 Post‐randomisation drop‐outs: not stated Revised sample size: 357 Average age: 46 years Females: 121 (33.9%) Barretts oesophagus: not stated Hiatus hernia: not stated Body mass index: 29 Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
| |
| Interventions | Participants were randomly assigned to two groups. | |
| Outcomes | The outcomes reported were health‐related quality of life, GORD‐specific quality of life, proportion with heartburn, reflux, and dysphagia. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Random allocation was organised centrally by a secure system, using a computer‐generated sequence, stratified by clinical site, with balance in respect of age (18 ‐ 49 or ≥ 50), sex (men or women), and BMI (≤ 28 or > 29) secured by minimisation". |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Staff in the central trial office entered details of participants on the secure database, then notified participants and respective clinical sites of their allocation". |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Quote: "There was no subsequent blinding". |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Quote: "There was no subsequent blinding". |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: An intention‐to‐treat analysis was performed. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: Treatment‐related complications were not reported adequately. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Quote: "This study was funded by the NIHR Health Technology Assessment Programme (as part of project No 97/10/99)". |
| Methods | Randomised clinical trial | |
| Participants | Country: Europe Number randomised: 554 Post‐randomisation drop‐outs: not stated Revised sample size: 554 Average age: 45 years Females: 156 (28.2%) Barretts oesophagus: 60 (10.8%) Hiatus hernia: not stated Body mass index: not stated Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
| |
| Interventions | Participants were randomly assigned to two groups. | |
| Outcomes | The outcomes reported were GORD‐specific quality of life, proportion with heartburn, reflux, dysphagia and adverse events. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: This information was not available. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: This information was not available. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: Patients undergoing medical treatment did not have sham surgery. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Comment: This information was not available. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: An intention‐to‐treat analysis was performed. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Comment: Important outcomes were reported. |
| Other bias | High risk | Quote: "This study was funded by Astrazeneca, Mölndal, Sweden". |
| Methods | Randomised clinical trial | |
| Participants | Country: United Kingdom Number randomised: 217 Post‐randomisation drop‐outs: 51 (23.5%) Revised sample size: 166 Average age: 48 years Females: not stated Barretts oesophagus: not stated Hiatus hernia: not stated Body mass index: not stated Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
| |
| Interventions | Participants were randomly assigned to two groups. | |
| Outcomes | The outcomes reported were health‐related quality of life and gastrointestinal quality of life. | |
| Notes | Reasons for post‐randomisation drop‐outs: Lost‐to follow‐up. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: This information was not available. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: This information was not available. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Comment: Patients undergoing medical treatment did not have sham surgery. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Comment: This information was not available. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Comment: There were post‐randomisation drop‐outs. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Comment: Treatment‐related complications were not reported adequately. |
| Other bias | High risk | Quote: "This study was funded partly by Janssen Pharmaceuticals relating to physiology studies at the Norfolk Physiology Laboratory in conjunction with their GI Partnership Scheme. Yvette Sharpe performed most of these studies under the supervision of R.L. B.D., D.M. and B. K. were funded partly by Ethicon Endosurgery, UK". |
GERD or GORD = gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease
PPI = proton pump inhibitor
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Not a randomised controlled trial | |
| Open anti‐reflux surgery | |
| Open anti‐reflux surgery | |
| Open anti‐reflux surgery | |
| Not a randomised controlled trial | |
| Open anti‐reflux surgery | |
| Transoral anti‐reflux surgery | |
| Transoral anti‐reflux surgery | |
| Transoral anti‐reflux surgery |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Health‐related quality of life (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 3 | 605 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [‐0.02, 0.30] |
| Analysis 1.1 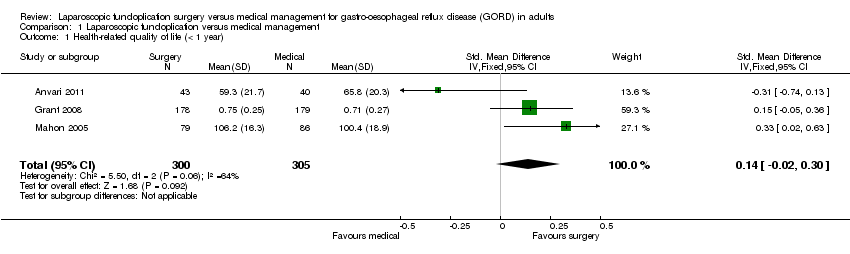 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 1 Health‐related quality of life (< 1 year). | ||||
| 2 Health‐related quality of life (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 2 | 323 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.19, 0.24] |
| Analysis 1.2 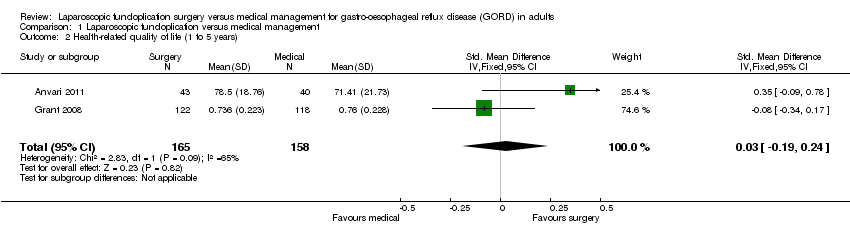 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 2 Health‐related quality of life (1 to 5 years). | ||||
| 3 GORD‐specific quality of life (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 4 | 1160 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.46, 0.70] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 3 GORD‐specific quality of life (< 1 year). | ||||
| 4 GORD‐specific quality of life (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 3 | 994 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.28 [‐0.27, 0.84] |
| Analysis 1.4 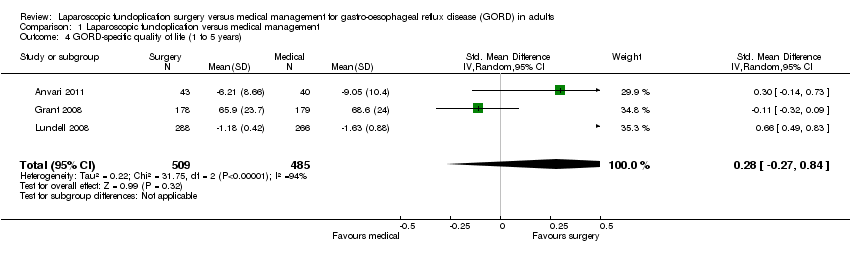 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 4 GORD‐specific quality of life (1 to 5 years). | ||||
| 5 Serious adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 637 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.46 [1.01, 2.11] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 5 Serious adverse events. | ||||
| 6 Adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 6 Adverse events. | ||||
| 7 Dysphagia (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 2 | 637 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.58 [1.91, 6.71] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 7 Dysphagia (< 1 year). | ||||
| 8 Dysphagia (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.8 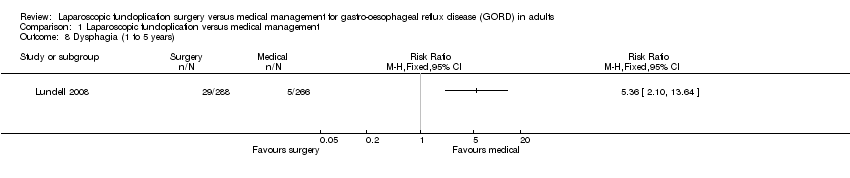 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 8 Dysphagia (1 to 5 years). | ||||
| 9 Dysphagia (5 years or more) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 9 Dysphagia (5 years or more). | ||||
| 10 Heartburn (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.10 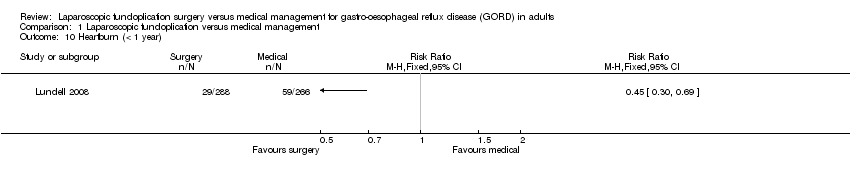 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 10 Heartburn (< 1 year). | ||||
| 11 Heartburn (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.11 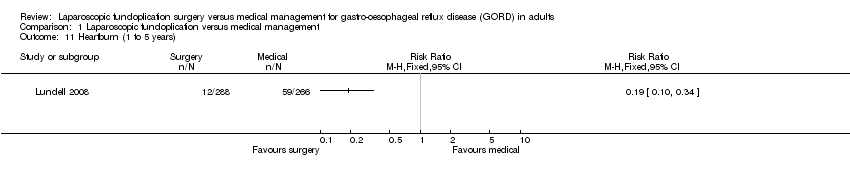 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 11 Heartburn (1 to 5 years). | ||||
| 12 Heartburn (5 years or more) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 12 Heartburn (5 years or more). | ||||
| 13 Reflux (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.13 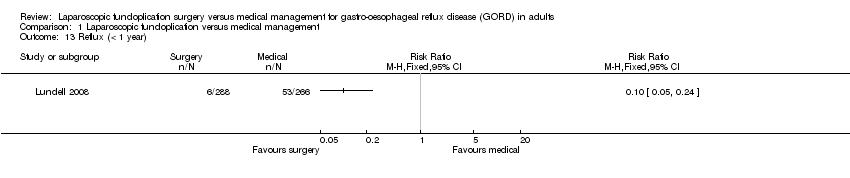 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 13 Reflux (< 1 year). | ||||
| 14 Reflux (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.14  Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 14 Reflux (1 to 5 years). | ||||
| 15 Reflux (5 years or more) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 1.15 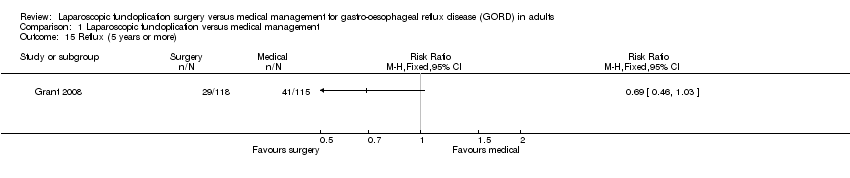 Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 15 Reflux (5 years or more). | ||||
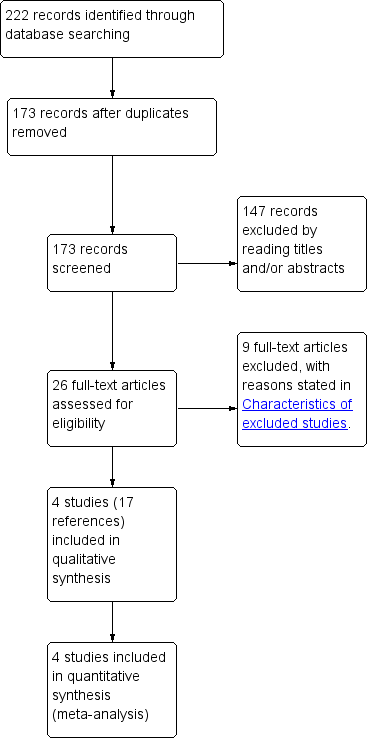
Study flow diagram.

Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 1 Health‐related quality of life (< 1 year).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 2 Health‐related quality of life (1 to 5 years).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 3 GORD‐specific quality of life (< 1 year).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 4 GORD‐specific quality of life (1 to 5 years).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 5 Serious adverse events.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 6 Adverse events.

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 7 Dysphagia (< 1 year).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 8 Dysphagia (1 to 5 years).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 9 Dysphagia (5 years or more).
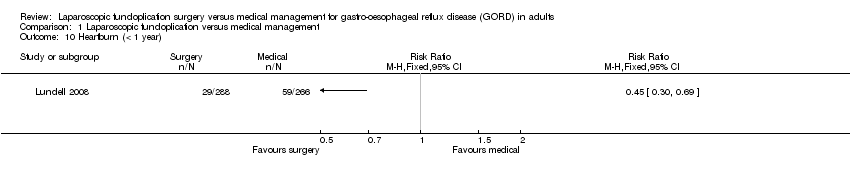
Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 10 Heartburn (< 1 year).
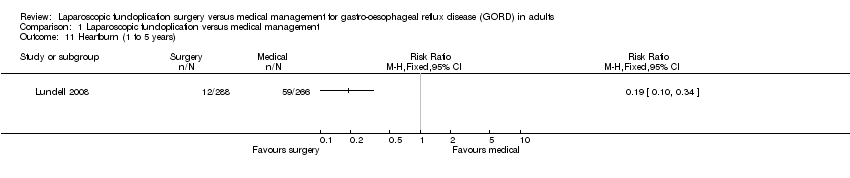
Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 11 Heartburn (1 to 5 years).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 12 Heartburn (5 years or more).
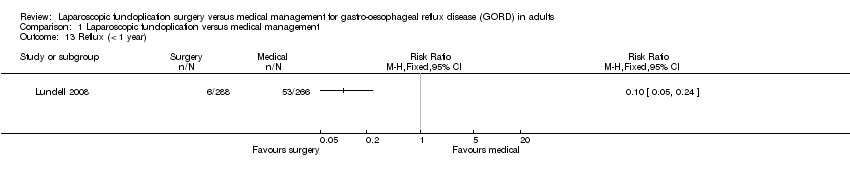
Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 13 Reflux (< 1 year).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 14 Reflux (1 to 5 years).

Comparison 1 Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management, Outcome 15 Reflux (5 years or more).
| Laparoscopic fundoplication versus medical management for gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) in adults | ||||||
| Patient or population: Patients with gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) in adults Control: Medical management | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Medical management | Laparoscopic fundoplication | |||||
| Health‐related quality of life | ||||||
| (< 1 year) | The mean health‐related quality of life (< 1 year) in the intervention groups was | 605 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | SMD 0.14 (‐0.02 to 0.3) | ||
| (1 to 5 years) | The mean health‐related quality of life (1 to 5 years) in the intervention groups was | 323 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | SMD 0.03 (‐0.19 to 0.24) | ||
| GORD‐specific quality of life | ||||||
| (< 1 year) | The mean GORD‐specific quality of life (< 1 year) in the intervention groups was | 1160 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | SMD 0.58 (0.46 to 0.7) | ||
| (1 to 5 years) | The mean GORD‐specific quality of life (1 to 5 years) in the intervention groups was | 994 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | SMD 0.28 (‐0.27 to 0.84) | ||
| Adverse events | ||||||
| Serious adverse events | 124 per 1000 | 181 per 1000 | RR 1.46 | 637 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Adverse events | 10 per 1000 | 140 per 1000 | RR 13.98 | 83 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Dysphagia | ||||||
| (< 1 year) | 36 per 1000 | 129 per 1000 | RR 3.58 | 637 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| (1 to 5 years) | 19 per 1000 | 101 per 1000 | RR 5.36 | 554 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| (5 years or more) | 255 per 1000 | 229 per 1000 | RR 0.9 | 228 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Heartburn | ||||||
| (< 1 year) | 222 per 1000 | 100 per 1000 | RR 0.45 | 554 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| (1 to 5 years) | 222 per 1000 | 42 per 1000 | RR 0.19 | 554 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| (5 years or more) | 736 per 1000 | 412 per 1000 | RR 0.56 | 217 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Reflux | ||||||
| (< 1 year) | 199 per 1000 | 20 per 1000 | RR 0.1 | 554 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| (1 to 5 years) | 139 per 1000 | 21 per 1000 | RR 0.15 | 554 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| (5 years or more) | 357 per 1000 | 246 per 1000 | RR 0.69 | 233 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | |
| Long‐term overall health‐related quality of life and long‐term GORD‐specific quality of life were not reported in any of the trials. | ||||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk was the mean control group risk across studies for all outcomes other than adverse events. For control group risk, 1% was used as the control group risk since there were no adverse events in the control group in the only trial that reported this outcome (Anvari 2011). The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 The trial(s) was/were at high risk of bias. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Health‐related quality of life (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 3 | 605 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [‐0.02, 0.30] |
| 2 Health‐related quality of life (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 2 | 323 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.19, 0.24] |
| 3 GORD‐specific quality of life (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 4 | 1160 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.46, 0.70] |
| 4 GORD‐specific quality of life (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 3 | 994 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.28 [‐0.27, 0.84] |
| 5 Serious adverse events Show forest plot | 2 | 637 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.46 [1.01, 2.11] |
| 6 Adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7 Dysphagia (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 2 | 637 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.58 [1.91, 6.71] |
| 8 Dysphagia (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 Dysphagia (5 years or more) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10 Heartburn (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11 Heartburn (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 12 Heartburn (5 years or more) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 13 Reflux (< 1 year) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 14 Reflux (1 to 5 years) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 15 Reflux (5 years or more) Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |

