கர்ப்பக்காலத்தில் இடுப்பு மற்றும் முதுகு வலியைத் தடுப்பதற்கும், சிகிச்சையளிப்பதற்குமான சிகிச்சை தலையீடுகள்
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | 'following ethical approval and through a randomised controlled clinical trial, 120 pregnant women with LBP were recruited into experimental and control groups.' Conducted in Iran; no funding source stated. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Gestational age: 17 to 22 weeks. History of at least 12 weeks back pain during pregnancy.
Exclusion criteria: Contraindications of physical activity according to ACOG committee guidelines. History of exercise before pregnancy. History of spinal surgery, spinal tumours, hip fracture, vertebral malformations, osteoporosis, and multiple sclerosis. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: N = 60
Control group: N = 60 No intervention. | |
| Outcomes | Pain (VAS) and disability (Oswestry disability questionnaire) were measured in both groups. But in the results, only the baseline and the difference from baseline, with no report of SD, was reported in each study group. The comparison of all changes between 2 study groups were statistically significant with P < 0.0001. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Change score from immediately after treatment was subtracted from the baseline pain score for an 'immediately after treatment' VAS score; reported lost to follow‐up was assumed to have happened during treatment; RevMan calculator was used to calculate SD to allow results to be included in meta‐analysis for 'any exercise vs usual prenatal care', analysis 1.1 ‐ translated from Arabic by single Iranian researcher. Funding = no information provided. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Block randomisation with matching (stratification?) for age, gestational age, and BMI. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned in paper. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Patients were not blinded. Nothing mentioned about blinding of providers. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Nothing mentioned about blinding of outcome assessors. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 120 patients were enrolled (60 in each group). 3 patients in intervention group, 5 in control group missed. In all cases the researchers lost track of the patients due to the change in living location. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The outcomes were also measured at 6th month and 1 year after delivery. But only the results for immediately after treatment, and 3 months after delivery were reported. Pain (VAS) and disability (Oswestry disability questionnaire) were measured in both groups. But in the results, only the baseline and the difference from baseline, with no report of SD, was reported in each study group. The comparison of all changes between 2 study groups were statistically significant with P < 0.0001. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing noted in the paper. |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Pregnant women referred to the National Women’s Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand physical therapy outpatient department for treatment. Have pain (insidious onset) and tenderness on palpation in the symphysis pubis, with or without radiation to the groin. Have a positive ASLR test result. A positive test result required the participant to experience pain or difficulty with this movement. (See study’s Appendix 1 for more description). Exclusion criteria: Medical conditions preventing the use of pelvic support belts. For example, some types of placenta previa. Posterior (sacroiliac joint or lumbar spine) pain that was considered by the woman to be worse than the symphysis pubis pain. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: 1. Exercise plus non‐rigid support belt: N = 29.
2. Exercise plus rigid support belt: N = 28.
Control group: Exercise only: N = 30. Participants received an exercise booklet with 5 exercises aimed to increase the stability of the pelvic bones. A trained physical therapist demonstrated the exercises and checked that they were being performed correctly. Exercise needed to be completed 3 times daily for 1 week. Participants were given logbook to record the frequency they exercised. Participants also received verbal and written education about the anatomy and pathology of symphysis pubis dysfunction and self‐help management. (See study’s Appendix 2 and 3 for specific exercises and self‐help management techniques.) | |
| Outcomes | Average and worst pain in last week ‐ VAS (0‐100); days off work; modified Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire; Patient Specific Functional Scale; measured at baseline, after treatment. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | X | |
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | There were no significant differences between the groups in adherence to their exercise program or belt wearing. The adherence rate is acceptable (average for all participants: Exercises = 16.5/21 times, Number of hours belt worn/week = 44.2). Funding = Maurice and Phyllis Paykel Trust for a Research Scholarship. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: 'Randomization process involved the use of a table of 3 randomly permuted blocks'. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specifically mentioned: patients assigned to groups by independent person (not connected to study) but unclear how this was actually done. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Patients not blinded; therapists providing exercise therapy were unaware of the intervention groups to which participants were assigned. However, unclear as to who distributed the belts. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Authors did not specify who collected the outcomes (outcomes were self‐report measures). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No withdrawals in the control group. 1 woman in the non‐rigid support belt group delivered her baby before the post‐intervention assessment. 2 women in the rigid support belt group delivered their babies before their post‐intervention assessment. 1 woman refused to be in the study as she was 'not prepared to be in the exercise‐only group'. No exclusions mentioned. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes it said it would report in methods. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Groups similar at baseline; adherence similar between groups; outcomes taken at same time for each group, co‐interventions likely to be similar. |
| Methods | Observer‐blinded randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 257 women were randomised. Inclusion criteria: Healthy Norwegian speaking women between 18 to 40 years from 2 Maternity Care Units (within the Norwegian Public Health System). Exclusion criteria: 1. Pregnant women carrying twins. 2. Inflammatory rheumatic disorders. 3. Risk factors for miscarriage. | |
| Interventions | Intervention group (N = 129/106 analysed):
Control group (N = 128/107 analysed): Usual prenatal care. | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: The proportion of women experiencing pain in the pelvic girdle or lumbar spine. Secondary outcomes: 1. Functional status measured with the modified Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire (0‐24). 2. Low‐back and lumbo‐pelvic pain measured using the VAS scale (0‐10). 3. Health related quality of life measured with the SF‐8 Health Survey. All outcomes measured at 24, 28, 32, and 36 weeks' gestation. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Funding/sponsor: Norwegian Fund for Postgraduate Training in Physiotherapy (Norway) Lead author contacted to clarify the number analysed in intervention group; she confirmed that it should be 106, not 103 as stated in the Figure and tables. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | 'randomisation procedure was computer generated by the statistician not involved in data collection.' |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | 'group allocation was concealed in consecutively numbered, sealed, opaque envelopes.' |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Outcomes were self‐reported, therefore not blinded; however the midwives who distributed the questionnaires to the women were not aware of their group allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Treatment group lost 22/129 (17.8%) and the control group lost 21/128 (16.4%) by the end of follow‐up at 36 weeks' gestation. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Results provided for all the outcomes outlined in the trial registration (ISRCTN95014448). |
| Other bias | Low risk | Groups were similar at baseline except that the training group had significantly higher BMI; almost twice as many women in the training group had experienced moderate to severe PGP in a previous pregnancy but this was adjusted for in the outcome analyses; adherence to exercises did not seem to vary between groups, nor did consultation with healthcare providers. |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants | Inclusion: healthy pregnant women with low‐back and pelvic pain diagnosed using posterior pain provocation test. Exclusion: treatment with cortisone, anticoagulants or immunosuppressive drugs, heart disease, diabetes, pacemakers, epilepsy, hepatitis, HIV or AIDS, acute infection, psychiatric disease, haematological disorders, renal disease, premature contractions, needle phobia. | |
| Interventions | Both groups received the same treatment; 8 acupuncture treatments over a 6 week period (2 treatments per week in the first 2 weeks and once per week thereafter) with first treatment lasting 20 minutes and number of needles limited to 5, and remainder 30 minutes with maximum 10 needles. Group 1 (mean age 28.6 yrs) started treatment at 20 weeks' gestation and Group 2 (mean age 27.9 yrs) at 26 weeks' gestation. No control group ‐ acupuncture intervention was started either at 20 (group 1) or 26 weeks (group 2) gestation. | |
| Outcomes | Short Form Health survey questionnaire (SF‐36), Short Form Magill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Pain‐o‐meter, Foetal sound measured at baseline, at 4th and 8th treatment sessions, at same times for each group; qualitative data collected via telephone interviews 2‐3 months after delivery. Both groups had similar experience of acupuncture (from qualitative interviews). Small number of study participants acknowledged by authors. Non compliance in both groups reported. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Funding = Council of Research and Development (FoU‐centrum), Landstinget Kronoberg, Sweden. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information given about sequence generation; in the discussion it states that 'the women were chosen randomly'. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Telephone allocation. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | 'both groups had similar experience with acupuncture when asked at end of treatment'; unclear if acupuncturists were informed of gestation, or if they were able to determine by observation, however, the difference was only 20 to 26 weeks, therefore likely not a big issue. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information provided on who collected the self‐report outcomes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Both groups had 4 drop‐outs with reasons given ‐ did not appear to be related to intervention. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Qualitative data supports quantitative data ‐ however the telephone interviews were completed by the study author. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Co‐interventions and adherence similar across groups, timing of outcome assessment same across groups, mean pain intensity was significantly lower in group 1 than group 2 at baseline. |
| Methods | 386 women consecutively selected by doctors and midwives and randomised to 3 groups by distribution of pre‐sealed opaque envelopes, with group assignment by computer‐generated random table to determine the allocation sequence before the study. Intention to treat: those who finished the trial were analysed in the group to which they had been assigned. | |
| Participants | Location: East Hospital, Sahlgrenska Academy and 27 maternity care centres in the hospital's reference area in Gothenburg, Sweden; 2000‐2002. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group 1 ‐ acupuncture. Experiment group 2 ‐ stabilising exercises. Control group: standard treatment. | |
| Outcomes | Measured at 1 week post‐treatment: self‐report pain each a.m. ‐ 100 mm VAS; examiner assessment of recovery from symptoms ‐ positive pain drawing; examiner assessment of recovery from symptoms ‐ posterior pelvic pain provocation test; examiner assessment of recovery from symptoms ‐ pain when turning in bed. Adverse events: none reported for any of the 3 groups. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | X | |
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Funding = The Vardal Foundation, the Dagmar Foundation, the Trygg‐Hansa Insurance Company, the Sahlgrenska University Foundation. 14 March 2012 ‐ email & LinkedIn message sent to Dr Elden to clarify number of participants in Table 3; response received ‐ clarified that there were 130 in the standard group and 131 in the exercise group; other data are correct. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated random table to determine the allocation sequence before the study. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Pre‐sealed opaque envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and providers were not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | 'Results coded and entered by personnel from independent institution; Statistician blinded to group and treatment.' |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Standard treatment group; randomised = 130; analysed = 108 [83.0%] (lost to follow‐up: declined treatment N = 15, early delivery N = 3, declined visit N = 3, moved from area N = 1). Acupuncture group: randomised = 125; analysed = 110 [88%] (lost to follow‐up: declined treatment N = 10, declined visit N = 1, early delivery N = 5). Stabilising exercises: randomised = 131; analysed = 112 [85.5%] (lost to follow‐up: declined treatment N = 9, moved from area N = 1, early delivery N = 4, declined visit N = 5). ITT: analysed participants measured one week post‐treatment against those randomised. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Data presented for a priori determined outcomes. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Table 3 seems to have the number of women reversed between 'Standard' and 'Exercise' groups. Author clarified this to be so. |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Pregnant women. Exclusion criteria: Women with other pain conditions, history of orthopaedic disease or surgery in the spine or pelvic girdle, systemic disorders, coagulation disturbances or increased risk of infection. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: standard treatment + penetrating acupuncture Standard treatment: general information about condition and anatomy of back and pelvis and a pelvic belt, gave advice and home programme exercised designed to increase strength in the abdominal and gluteal muscles. Information was supplemented by a leaflet. Also instructed to avoid other treatments during intervention period. Penetrating acupuncture: see study methods for exact acupuncture points used. Sterilised disposable needles were used and inserted intramuscularly to depth of 15‐50mm. Needles were left in situ for 30 minutes and manually stimulated every 10 minutes. Control group: Standard treatment + non‐penetrating acupuncture Standard treatment: identical to experimental group Non‐penetrating acupuncture: used a validated sham acupuncture device (which looks like real acupuncture needles but the tip of needle is blunted). The shaft of the sham needle did not penetrate the skin, it collapsed into the handle and creates an illusion of insertion. Needles were left in situ for 30 minutes and manually stimulated every 10 minutes. | |
| Outcomes | EQ‐5d questionnaire and EQ‐5d VAS; VAS ‐ Pain (0‐100) in the morning & evening; Oswestry Disability Index (back specific function); frequency of sick leave; Disability Rating Index (DRI) measured at baseline, after treatment and 1 week follow‐up. Adverse events: transient, tingling, needle pain, slight bleeding, fainting, sleepiness. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | X | |
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Pain severity diagnosed with ASLR test and posterior pain provocation test. N = 165 women assessed for eligibility (N = 50 did not meet inclusion criteria). All women acupuncture naive & singleton fetus. No serious adverse events reported. Same contact time, manual contact during search and stimulation of needles, interaction between patient and therapist in both groups. Drop‐outs reported with reasons. Funding = grants from the Foundation of the Health and Medical care committee of the Region of Västra Götaland (Sweden), grants from the Swedish Medical Reserach Council and Swedish government grants to researchers in the public health service. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: 'Computer‐generated random table was used'. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Statistician who was not involved in the study administered pre‐coded numbered identical opaque envelopes to assign participants to the intervention groups. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Participants: low risk ‐ only LI4 (on hand) not blinded 'Women were blinded to whether they were receiving sham or active treatment.' Providers: high risk Not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Assessors: low risk Blinded to treatment allocation, doctors handling decisions about sick‐listing were also blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Dropouts: 2 in treatment and 5 in control dropped intervention because it 'violated protocol'. At follow‐up: 3 drop‐outs in treatment group due to early birth and declined visit, 2 in control group due to declined visit. Low drop‐out rate, and similar reasons between the groups. Low risk: attrition and drop‐outs reported and reasons, numbers at each stage add up, ITT ‐ last value carried forward. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes it said it would report in methods. All outcome data are found in tables. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Randomisation procedure successful (however more in control group on sick leave?). |
| Methods | 266 randomised: those who could not exercise were excluded from the exercise group, but it's unclear why 54 people dropped out of exercise group and none out of control. | |
| Participants | 280 women invited to participate from those registered at Hazrat Zaynab Hospital prenatal clinic in Tehran, Iran (no details about how they were selected from the 2358 who had registered at the clinic during the study period). Baseline characteristics. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group. Control group: no treatment. | |
| Outcomes | Adverse events: none reported. No scales/units given for outcomes measured, but 1 may assume they are reporting the group mean, measured on the KEBEK questionnaire (range 0 to 100, higher = worse pain); change scores do not appear to be included, the degree of lordosis and degree of flexibility of the spine. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | All numbers do not add up; there are contradictions in text; we tried unsuccessfully to clarify data with lead author during the 2007 update. Funding: not stated. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | ‘prospective randomised study’ but method of randomisation not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and providers were not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Report states that the outcome assessor was blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Difficult to assess since numbers do not add up; appears that 14 withdrew prior to randomisation; about 20% withdrew/dropped out after randomisation; it appears that 54 dropped out of the intervention group and none out of the control group. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Results are difficult to interpret and appear to be reversed. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing more to add. |
| Methods | Potential women were identified through obstetric records and approached, in person or by phone, to determine if they met the inclusion criteria. 41 women were invited to attend; 4 declined, 3 did not attend the first follow‐up. 34 women randomised to either Global Postural Re‐education (GPR) treatment or usual prenatal care. | |
| Participants | Women selected from those receiving prenatal care in 3 health centres and those who attended lectures in preparation for birth at a private hospital in Campinas, Brazil. Both groups of women were similar in most of the characteristics studied on admission to the study: in the GPR group 10 women came from a private hospital and 7 from a health (publish) centres, in the control group there were 6 women coming from the private hospital and 11 health (public) centres. Inclusion criteria: LBP, nulliparity, low‐risk singleton pregnancy, gestational age between 20 to 25 weeks, aged 18 to 40 years, absence of obstetric or medical illness, absence of pre‐existing spinal pathologies. Differentiation made between LBP and posterior pelvic pain at baseline physiotherapy assessment. | |
| Interventions | Global Postural Re‐education (GPR) treatment (n = 17) Weekly 40‐minute sessions for 8 weeks. Stretching of the muscles of the posterior chain ‐ angle closure coxo‐femoral and abduction of the upper limbs & closing angle coxo‐femoral with adduction of the upper limbs. Control group (n = 17) Regular prenatal care. | |
| Outcomes | GPR group Intensity of LBP, measured with VAS (0‐10) at baseline, before/after each treatment session. Back‐related function, measured with the RMDQ at baseline, before/after each session. Control group Intensity of LBP and back‐related function were measured at baseline, at 4 and 8 weeks of the study. Use of pain medication collected for both study groups. | |
| Low‐back pain | x | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Used Google Translate to translate from Portuguese; verified by single Portuguese researcher. Paper stated that there was no external funding. Data needed for the meta‐analyses appeared to be incorrectly reported in the paper and were re‐analysed. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | 'randomisation was performed by using a list of random numbers generated by computer.' |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No mention in translated version of allocation concealment. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | 'these professionals had lagged randomisation, so did not know to which group each woman was allocated' ... however, those who provided the exercise therapy and those who received it would have known to which group they were allocated. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | 'at the end of the participation on each woman in the study, they conducted a professional full re‐evaluation of LBP' ... however, the women were the ones who reported their symptoms via the VAS and RMDQ. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 3 participants are reported as lost to follow‐up; there is no real clarification of their initial group ‐ it could be control group, but the 17 in each group do not seem to take any losses into consideration. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Data provided for baseline and after intervention outcome measures for pain and disability. |
| Other bias | High risk | Not similar at baseline for education or age (intervention group was better educated and older), but similar in other prognostic factors; women in control group used more pain medication (87% versus 12% in intervention group); no information provided on compliance, co‐interventions or use of pain medication; the control group was only measured twice after baseline, the intervention group was measured 8 times, but all within the same time‐frame. |
| Methods | Prospective randomised controlled trial ‐ 169 pregnant women. Study tested the hypothesis the hypothesis that a multi‐modal approach of manual therapy, exercise and education for LBP/PP in pregnancy is superior to standard obstetric care for the reduction of pain, impairment and disability. Enrollment to the study between 24 and 28 weeks' gestation with follow‐up at 33 weeks' gestation and 3 months postpartum. | |
| Participants | Pregnant women with LBP/PP at enrolment (24 to 28 weeks' gestation). No other criteria provided. | |
| Interventions | Experimental group (n = 87): multi‐modal musculoskeletal and obstetric management (MOM) ‐ standard obstetric care PLUS a chiropractic specialist provided manual therapy, stabilisation exercises and patient education ‐ no details on number of treatments. Control group (n = 82): Standard Obstetric Care (STOB). | |
| Outcomes | Pain intensity (NRS), Disability (Quebec Disability Questionnaire ‐ QDQ), Personal Pain History (PPH), SLR, P4. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | This was a poster presentation at the 32nd Annual Meeting for the Society for Maternal‐Fetal Medicine with only the abstract published in a supplement of the journal, so further biases are difficult to assess; there was no reference to other publications on this trial and none were identified by a Google and MEDLINE search on 16 Aug 2012. August 27, 2012: email sent to Dr Gross requesting data, via Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Division of Maternal‐Fetal Medicine general email since unable to find individual email; as of November 2nd, 2012 there has been no response. Assume study conducted in US, since all PIs list American university affiliations Grant number: R18HP07640. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No information provided on method of generating allocation sequence apart from 'randomised' stated in the title and study design section. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Details not provided. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient detail provided ‐ Chiropractic specialist performing baseline evaluation and follow‐up exams 'single masked'. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient detail provided ‐ Chiropractic specialist performing baseline evaluation and follow‐up exams 'single masked'. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient detail provided ‐ only number in each arm of trial provided in results section. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Limited data provided; e.g. results section states that there was a significant reduction in NRS, QDQ, PPH and SLR scores in the experimental group at 33 weeks' gestation whilst the control group only showed an improvement in QDQ, however on both occasions only P values given (P < 0.05). |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Groups were demographically similar and baseline evaluation showed no differences in pain, disability or physical assessments between groups however no data provided pre versus post intervention. |
| Methods | N = 115 women randomised (N = 55 to Bellybra and N = 60 to Tubigrip). | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Women between 20 and 36 weeks pregnancy with lumbar back or posterior pelvic pain. Exclusion criteria: Women with high back pain or symphysiolysis but with no concomitant lumbar back or posterior pelvic pain. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: BellyBra A nylon/spandex undergarment worn like a vest, has a 1‐way stretch panel across the thoracolumbar back that is designed to provide support and assisted by the involvement of shoulder straps, to improve posture. A wide elastic band sits below the abdomen supporting the uterus and lifting weight off the pelvis. Control group: Tubigrip More generic form of support. Worn as a double layer and extends from the mid‐thoracic spine to the sacral spine and pelvis. | |
| Outcomes | VAS (0‐10 cm), physical activity including work, satisfaction with life survey (SWLS), use of analgesic medication, usefulness of garment at baseline, completion of 3‐week intervention, 'on a return visit to the antenatal clinic' ‐ ? timing. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Although the primary aim was to assess the severity of LBP and posterior pelvic pain, the pelvic pain was primarily due to pain in the sacroiliac joint. Australia Funding = no funding or support was provided for any of the authors; Furtile Mind Pty Ltd (retailers for maternity and postpartum clothes, supplies) provided the BellyBras used in the trial. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: 'Participants were randomised...by means of computer‐generated numbered, sealed, opaque envelopes'. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Opaque sealed envelopes used. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No blinding of participants, providers mentioned. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | No blinding of assessors mentioned. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 9 participants (16%) in intervention group were lost at follow‐up (2 delivered within study period, 7 failed to attend appointment and could not be contacted). 12 participants in control group (20%) were lost at follow‐up (3 delivered within study period, 9 failed to attend their follow‐up appointment and could not be contacted). No exclusions mentioned; 14% were lost to follow‐up with no reason. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes it said it would report in methods. |
| Other bias | High risk | 11 women (23.9%) in intervention group and 23 women (47.9%) in control group reported the use of other treatments for their back pain during the study period, including the use of analgesic medication, physiotherapy, acupuncture, massage, etc. (co‐interventions make it difficult to attribute change to the intervention). Most noticeably, 3 in the intervention and 14 in the control group used analgesic medication during the study period. 44 (95.7%) women in intervention group stated that they wore the garment at least once a week compared with 33 (68.8%) in the control group. High risk ‐ co‐interventions and compliance different. |
| Methods | 30 women 'randomly assigned' to study group (N = 15) or control group (N = 15). | |
| Participants | Inclusion: women between 20 and 30 years, back pain, nulliparous, 16 weeks' gestation, no regular exercise prior to entering study. Exclusion: pelvic pain, any systemic disorder or drug use, previous trauma, surgery, damage to spine or lower limbs, any pregnancy complications, ≥ 3 missed treatments. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group = 1 hour introduction session with 7 exercises and relaxation movements taught. Each exercise session lasted 30 minutes x 3 / week x 8 weeks. Exercise included warm up (4.5 minutes) walking, stretching (spine extensors, hamstrings, thigh adductors, lumbar paravertebral muscles), strengthening (thigh extensors and abdominal obliques) x 21 minutes, relaxation x 4.5 minutes. Control = routine prenatal care ‐ did not perform any of the study exercises. | |
| Outcomes | Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire; lumbar lordosis using flexible ruler and formula measured at baseline, after 1 and 2 months. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | This was part of the journal's 'brief communication' section only, so further biases are difficult to assess; there was no reference to other publications on this trial and none were identified during a Google search 13 March 2012. 14 March 2012 ‐ email & Linked‐In message sent to lead author, requesting more information => as of November 2nd, 2012, no response. Assume the study was carried out in Iran, since all authors were affiliated with Iranian universities. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'randomly assigned' ‐ details not provided. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Details not provided. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Details not provided. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Details not provided. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Details not provided, but number randomised are included in the results table. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Limited data provided; e.g. states that RMDQ was used, but no values given; pain outcome measure not identified, while pain results provided. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | This was part of the journal's 'brief communication' section only, so further biases are difficult to assess; there was no reference to other publications on this trial and none were identified during a Google search 13 March 2012. |
| Methods | Preventive randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | Women registering at 1 of 6 maternity clinics run by Falun County Health Care Board in Sweden and had their ultrasound between gestational age 15 to 18 weeks. Inclusion criteria Exclusion criteria Drop‐outs due to inability to participate in water gymnastics, recurrent UTIs, shift work, baby‐sitting problems, miscarriage, intrauterine death, lack of time, invited to participate after date of closure. | |
| Interventions | Intervention group: Control group: no treatment. | |
| Outcomes | Back pain ‐ VAS; number of days taken as sick leave because of back pain in pregnancy. Adverse effects: no excess risk for pregnancy associated with water gymnastics observed: no differences with gyn/UTI infections, maternal weight gain, gestational age at delivery, weight/height of neonate, delivery characteristics. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Funding: Dalarna Research Institute; Local Insurance Office. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'Preventive randomised controlled trial' randomised 'using sealed envelopes' ‐ actual method of randomisation not described, but it was conducted 'by a mid‐wife when the women had their ultrasound.' |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Adequate ‐ sealed envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and caregiver not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Assessor blinding unclear. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Participants who completed the study were analysed in the groups to which they were randomised; less than 5% reported as lost to follow‐up; numbers do not always add up ‐ query if N for outcomes are based on those who answered specific questions on follow‐up?. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Not enough data were given to allow use of the VAS; pain data provided in graphs from which one cannot extract exact values. Difficult to follow the path of recruitment, drop‐outs since numbers given in text do not add up. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing noted. |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial ‐ 50 women. | |
| Participants | South African women of 20 to 40 years between 16 and 24 weeks' gestation; LBP/PP (with or without radiation to the knee) that had started during current pregnancy (72% of sample had LBP). | |
| Interventions | Exercise group (N = 26/24 analysed): 1 formal exercise class lasting 30‐45 minutes with warm‐up and cool down periods incorporated. Handout illustrating and explaining the exercise program which consisted of postural, transversus abdominis and pelvic floor exercises to train correct isolation and isometric contraction. Exercises then individually progressed to increase level of difficulty and facilitate co‐contraction of transversus abdominis and pelvic floor muscles with gluteals, quadriceps and other muscle groups. Follow‐up class every second week for 10 weeks. Women also asked to complete a daily home exercise programme and record their goals in their training diary. Verbal information on basic back care and posture during pregnancy and an information pamphlet. Control group (N = 24/22 analysed): verbal information on basic back care and posture during pregnancy and an information pamphlet as for exercise group but no specific instructions given to participants regarding whether to perform any exercise. | |
| Outcomes | Pain intensity (NRS 0‐10); functional ability (Likert modified Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ). | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Neurological exam was completed at assessment along with erector spinae palpation, sacroiliac palpation, P4 test and passive SLR however, apart from erector spinae palpation eliciting LBP symptoms, the positive yield of these tests for subtyping of symptoms was low. Funding not reported. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated random numbers in balanced blocks of 20. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed numbered opaque envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Unblinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Unblinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis completed; less than 10% of sample lost to follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes reported as specified. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Groups similar at baseline regarding most important prognostic indicators; outcomes assessed at same time for both groups; compliance reported in detail. |
| Methods | 100 women, enrolled and randomised to 1 of 2 groups. The code for group allocation was obtained in advance by throwing dice in pairs of 10, and enclosed in advance in an envelope, marked with the order number of inclusion and opened consecutively by midwife on inclusion to the study. Study in Sweden. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: 3rd trimester of pregnancy, presented at the maternity ward centres in southern Sweden, complaining of pelvic girdle or LBP. Baseline. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group. Control group: no treatment. | |
| Outcomes | Pain increased, pain unchanged, pain decreased, no pain during last 3 weeks of pregnancy, pain on activity decreased, Visits to maternity centres, number of participants who used analgesics, number of participants who used TENS, number of participants who used sacroiliac belt, number of participants who used physiotherapy, baby's birthweight, baby's Apgar at 1/5/10 minutes. Adverse effects: reported by 38% of acupuncture group ‐ local pain (6); heat or sweating (5); local haematoma (2); tiredness (2); nausea (2); weakness (1). | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | No mention of funding. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | ‘code for group obtained in advance by throwing dice in pairs of 10.’ |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | 'Predetermined code enclosed in advance in envelop, marked with the order number of inclusion and opened consecutively by midwife on inclusion.' |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No explicit mention in the report, but it seems unlikely that either the women, midwives or acupuncturists were unaware of inclusion into the acupuncture or control group. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | 'two blinded investigators independently assessed the development of the patients' individual VAS scoring over time with a kappa coefficient of 0.68% (95% CI 0.54 to 0.83)'. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Over 20% lost to follow‐up in each group. 1 ward closed to recruitment after 12 months because women no longer wished to be included in the study => excluded 12 participants who had been enrolled by this clinic, leaving 44 in each group. Acupuncture group ‐ lost 3 because they delivered, 2 did not like acupuncture, 1 did not complete assessment correctly, 1 lost due to vacation of midwife (7) ‐ analysed 37/50. Control group ‐ lost 5 ‐ did not complete forms correctly, 3 insisted on acupuncture, 1 was admitted to hospital for pain management and rest (9) ‐ analysed 35/50. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data provided on outcomes listed in methods section but at times they are difficult to follow and not presented in a fashion that allow analyses. |
| Other bias | High risk | Variety of other treatments used by the women to relieve symptoms (analgesics, TENS, pelvic belt, physio); length of study unclear. |
| Methods | N = 146 randomised (group 1: N = 49; group 2: N = 48; group 3; N = 49). Participants stratified by age and gravida. | |
| Participants | Inclusion: obstetric patients with back pain up to 30 weeks' gestation; exclusion: intent to deliver outside study site, high‐risk pregnancy, including gestational diabetes, pre‐eclampsia, placenta previa, abruptio placenta. | |
| Interventions | Group 1: usual obstetric care plus osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT). Group 2: usual obstetric care plus sham ultrasound (Sham US). Group 3 (controls): usual obstetric care. 7 treatments each lasting 30 minutes at 30, 32, 34, 36, 37, 38, 39 weeks' gestation. OMT = included any of the following modalities: soft tissue, myofascial release, muscle energy, range of motion mobilisations used in a systematic manner by all providers*. Sham US = using a non‐functional ultrasound therapy unit that provided both visible and auditory cues provided by a normal ultrasound unit. Usual obstetric care during pregnancy ‐ no study treatments provided (7 visits in total: at 30, 32, 34, 36, 37, 38, 39 weeks' gestation). | |
| Outcomes | VAS (0‐10cm) ‐ average back pain experienced; Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire (back‐specific function) measured at baseline and after 7th (last) treatment session; at same times for each group. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | *Treatment providers met regularly to ensure consistency in duration, type, anatomic location and manner of OMT provided. OMT and Sham US provided by same physicians with same amount of attention given to both groups. 2 from each treatment group missed more than 50% of treatments. Compliance best in control group. Funding = grants from the Osteopathic Heritage Foundation and the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine at the National Institutes of Health. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Patients randomly assigned and stratified by age and gestation, but no other information given about the sequence generation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information given. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not possible to blind patients or care providers. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Outcome measures were by self‐report, but high risk because patients not blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | ITT analysis = 144 participants; last observation carried forward, attrition and exclusions reported (23 (16%) withdrew before visit 7; 60 (42%) withdrew due to delivery) ... but query the reliability of imputing over 1/2 of the data (actual data for 146 ‐ 83 = 63). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Several approaches used to decrease risk of bias from last observation carried forward method. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Similar compliance in treatment groups, baseline measurements similar, co‐interventions controlled, outcomes taken at same time points. |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Gestational age: 22 to 36 weeks. (i) In 1 of 3 tests: posterior pelvic pain provocation test (P4), standing on 1 leg, Patrick’s Fabere test; (ii) In palpating tissue over: the sacroiliac joints, the symphysis pubis, or mm. Gluteus maximus/medius. Exclusion criteria: Earlier experience of acupuncture treatment. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: Deep stimulation acupuncture (N = 25) 10 acupuncture treatments of 30 minutes each, given twice weekly for 5 weeks by a registered physiotherapist. See study for exact location of acupuncture points used. Control group: Superficial stimulation acupuncture (N = 22) 10 acupuncture treatments of 30 minutes each, given twice weekly for 5 weeks by a registered physiotherapist. See study for exact location of acupuncture points used. | |
| Outcomes | VAS pain (at rest and during 3 daily activities); Nottingham Health Profile measured 5 days prior to and 5 days after treatment; at same time for both groups. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | X | |
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Funding = research grants from Praktikertjänst AB and the National Security in Sweden. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'women ... were randomised ...' but randomisation procedure not described Unclear risk ‐ as above, randomisation procedure not explained. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: 'Sealed envelopes with labels for determination of treatment were used in randomisation provided by a statistician not involved in the study'. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Both groups given acupuncture so could not tell difference as patients were acupuncture naive; care providers knew whether they gave superficial or deep acupuncture but acted the same towards the patient regardless. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Self‐reported outcomes collected from patients who were unaware of their treatment group. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Dropout rate: 23 participants out of 70 (13 in Superficial group, 10 in Deep group) Reasons for drop‐outs listed; reasons similar for both groups. It does not seem that the grouping affected the drop‐out reasons, and although almost 1/3 dropped out from each group, the over‐riding reason was non‐compliance with completing pain diaries. No excluded data mentioned ‐ and it appears that analyses only done on complete data sets. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes it said it would report in methods. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other Women all acupuncture naive. Groups similar at baseline. |
| Methods | The physiotherapist conducting the research randomised the women into 2 groups by means of a 'raffle' or 'lottery'. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: women with lumbar or pelvic pain, gestational age greater than 12 weeks, live in city of Paulinia, Brazil. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: exercises in groups for 'global activity and stretching'. Control group: routine medical recommendations. | |
| Outcomes | Proportion of women with improvement, VAS after 8 weeks. Adverse events: not reported. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Funding: not reported translated from Portugese by single Portuguese researcher | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Used a 'Raffle' or 'lottery'. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Physiotherapist who was doing the research allocated to groups. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Description of blinding for participants, caregiver not provided. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Description of blinding for assessors not provided. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Outcome table appears to indicate no drop‐outs; report appears to indicate that there is no contamination between groups, but none of this is clearly described. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Results are incomplete (only intervention group's improvement reported, no data for control group). |
| Other bias | High risk | Other treatments not described; baseline data were not comparable: Exercise group = 48% greater than 5 on VAS 0‐10; Usual care group = 61% greater than 5 on VAS 0‐10. |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Nulliparous. Singleton live fetus at a routine ultrasound scan at 18 weeks of pregnancy. Exclusion criteria: Pregnancy complications. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: Exercise training group Training with a physical therapist in groups of 10 to 15 women for 60 minutes once per week for 12 weeks, where training focused on PFM and other exercises. Control group: Women received customary information given by their midwife or general practitioner. They were not discouraged from exercising on their own. | |
| Outcomes | Self‐reported pain in the low‐back area lasting for ≥ 1 week; pain drawing, off sick due to low‐back/pelvic pain (yes/no); Disability Rating index; pelvic floor muscle strength measured at baseline (20 weeks' gestation); 36 weeks' gestation, 3 months' postpartum. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Adherence to training protocol was registered based on the women’s personal training diary (must do 2 sets of 8 to 12 contractions of PFM per day) and reports from the physical therapists that led the group training (participation in ?6 group training sessions). Funding = Norwegian Fund for Postgraduate Training in Physiotherapy and the Norwegian Women's Public Health Association. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: 'Randomization was done in blocks of 32 with the use of opaque sealed envelopes', did not specify method used to select the blocks, but likely OK, given the fact that they used other safeguards. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Opaque sealed envelopes used. Quote: 'A secretary with no other involvement in the trial prepared the envelopes. Each woman opened 1 of the envelopes herself and was enrolled by the secretary in the secretary's office.' |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and care providers were aware of treatments (exercise vs usual care). |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: 'The principal investigator was not involved in the training of the women and was blinded to group allocation while making the assessments and plotting the data'. However, the outcomes were self‐report and the women were not blinded to their treatment; unclear if those who received usual care were aware of other options. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 7 participants in control and 5 in training group withdrew after the first assessment Reasons for withdrawal were diseases connected to pregnancy (n = 6) or personal reasons (n = 6). It does not seem that the grouping affected the drop‐out reasons. No excluded data mentioned. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes it said it would report in methods. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unclear risk: Influence of co‐interventions, adherence not reported in results. |
| Methods |
| |
| Participants |
| |
| Interventions | Intervention group: received 4 osteopathic treatments in weekly intervals. Waiting list comparison group, after 5 weeks on the waiting list they received osteopathic treatment that was reported as 'having no relevance for the study'. | |
| Outcomes | Pain, measured with VAS; interference with ADL, measured with Quebec Back Pain Disability Scale at baseline and end of first 5 weeks (end of treatment for intervention group). | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Information taken from an abstract of an unpublished thesis that is available in German, for a cost, from Akademie füf Osteopathie (AFO), Deutschland (funds not available to obtain full manuscript). Funding not reported. Abstract initially translated from German by single German‐speaking researcher, then English abstract found on‐line. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'Randomised controlled clinical trial' ‐ methodology not reported in abstract. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Waiting list comparison group, after 5 weeks waiting list they get a treatment that is reported as having no relevance for the study. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No mention of blinding in abstract. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No mention of blinding in abstract. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 3 patients in the control group dropped out; no information provided on exclusions or analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Data provided for pain and Quebec Back Pain Disability Scale. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Difficult to assess since we were unable to access the full thesis. |
| Methods | Pilot randomised controlled trial ‐ 57 participants randomised. All participants screened initially by phone and all treatments described prior to randomisation. No limit on what stage in pregnancy women could enter the trial. Before randomisation all participants identified their treatment preference. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: healthy pregnant women with singleton fetus and LBP of unknown origin that began during pregnancy and was reproduced by manual palpation. Exclusion criteria: women with health conditions that contra‐indicated exercise (including heart disease, hypertension, BMI > 40, diabetes, incompetent cervix, ruptured membranes, decreased fetal movement) or manipulation (including unrelenting night pain, loss of bladder or bowel control, progressive neurological deficit, cancer, spinal fracture, unexplained weight loss, unrelenting fever). Women who smoked, consumed alcohol, were taking anti‐depressants or had Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire score above 20 or below 4. Women planning to move during pregnancy, not willing to comply with study procedures and unable to read and write English. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group (control; N = 22): exercise booklet provided with specific exercises and recommendations for postural and movement patterns to alleviate LBP, and advice on when to stop exercising. Individualised stretching and strengthening exercises were prescribed, demonstrated and practiced at each study visit. Exercisies took approximately 15 minutes to perform and participants were asked to exercise 5 x/week. Spinal manipulative therapy (N = 15): high velocity, low amplitude thrust applied to isolated joint to move it just past physiological end range in side‐lying position. Direction, velocity and amplitude determined by the clinician from palpation findings. Neuro emotional technique (NET; N = 20): Chiropractic mind‐body technique using relaxed breathing and visualisation techniques with elements of traditional Chinese medicine (such as association of emotions with certain organs or meridians) and chiropractic medicine (adjustment of spinal levels innervating specific organs. The NET standard protocol was followed (Pablis et al., 2008). Maximum number of treatments per participant = 8 with very few in any group reaching this amount. Co‐interventions controlled. | |
| Outcomes | Pain intensity (NRS 0‐10), RMDQ (back‐specific function), sick leave due to pregnancy related LBP (assessed but not listed as 1 of the outcomes). | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | 138 participants screened; sick leave not listed in methods as 1 of the outcomes but reported in Table 2; higher drop‐out from exercise group however adherence to exercise did not affect outcomes. Funding provided by The One Foundation, the research division of the NeuroEmotional Technique; 'The One Foundation did not contribute to the study in any other way'. Conducted at Oregon Health & Science University, USA. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | The method used to generate the allocation sequence was not described ‐ 'before being randomised, participants identified their treatment preference ... she would open the consecutive envelope in her preference strata in the presence of the researcher ... women were randomly allocated into 1 of three treatment groups'. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | 'the randomisation schedule was completed prior to initiating the study and was concealed from all study staff by using consecutively numbered, sealed, opaque envelopes for each strata of preference group.' |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and practitioners were not blinded to treatment group after randomisation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Participants were outcome assessors. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | ITT analysis performed. Missing data ‐ last observation carried forward. Minor inaccuracies noted in number excluded prior to randomisation, and between text and Figure 1 in drop‐outs from exercise group (N = 1). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Last observation carried forward may limit data but carried out to replicate methods used in an earlier trial by Licciardone and colleagues (2010). Sensitivity analysis completed providing similar results to primary outcome analysis. |
| Other bias | High risk | Participants randomised according to their treatment preference, entered the study at different gestational points, groups were not similar at baseline for all prognostic factors, and were paid to participate (USD$20 per visit). |
| Methods | 100 women invited and divided into 2 groups; 10 withdrawn from exercise group prior to intervention => 90 analysed. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Pregnant women in the second half of pregnancy referred to prenatal clinics of Qom province, Iran. Exclusion criteria: Inability to perform exercises; excluded after missing 3 sessions. | |
| Interventions | Experiment group: Exercise program = 40 Program consisted of 15 minute warm up and cool down plus 30 minute cycling in the range of 55% to 65% of the maximal heart rate with respect to the age. Exercises were prescribed by a physical training specialist. The exercise sessions were 3 times a week for 8 weeks. Control group: = 50 The study did not specify what the control group was. | |
| Outcomes | Pain, measured with Quebec questionnaire, measured at baseline and 8 weeks after start of program; demographic data collected at baseline; P value < 0.05 considered to be statistically significant. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Email to the corresponding author for clarification failed to elicit a response. Funding = grant from Sports Medicine Research Center and Vice Chancellor for Research at Tehran University of Medical Sciences. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No description of sequence generation were described except 'the total numbers of 100 invited were divided into two exercise and control groups'. 'Randomised' was only mentioned in the abstract. Unclear risk: randomisation procedure not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not mentioned, but assume not. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Quote: 'every woman missing three session of exercise was excluded from the study' ‐ but unclear how many this affected. Drop‐outs/withdrawals from study not mentioned, however, 10 women who were randomised did not proceed to the intervention because they were unable to participate in the exercises. Did not specify how they dealt with the missing/excluded data. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes it said it would report in methods. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unclear risk: compliance not reported, nor co‐interventions. |
| Methods | 2‐armed, 2 centre randomised controlled trial ‐ 855 women randomised. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: aged 18 years or more, singleton live fetus and within 30 minute drive of hospital and able to attend weekly training. Exclusion criteria: high‐risk pregnancy or diseases that could interfere with participation in exercise. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group (N = 429/396 analysed): 60‐minute exercise sessions 1x/week for 12 weeks between 20 to 36 weeks' gestation led by a physiotherapist in groups of 8 to 15 participants. Each session consisted of moderate intensity (13‐14 on Borg scale) aerobic activity, strength training and balance exercises. 45 minute home exercise session 2 x/week consisting of 30 minutes of aerobic activity and 15 minutes of strengthening and balance exercises. Adherence monitored throughout. Control group (N = 426/365 analysed): standard antenatal care; not discouraged from exercising Both groups given written information on pelvic floor exercises, diet and pregnancy related lumbo‐pelvic pain. | |
| Outcomes | Lumbopelvic pain ‐ VAS (0‐100) ‐ morning and evening, sick leave due to lumbo‐pelvic pain, Disability Rating Index (DRI), Fear avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Additional outcomes related to a related study: gestational diabetes, glucose metabolism. Approximately 60% of women who enrolled reported lumbo‐pelvic pain at time of inclusion. Funding sources: Norwegian University of Sciences and Technology, Norweigian Fund for Postgraduate Training in Physiotherapy, Liason Committee for Central Norway Regional Health Authority. 30 October 2012 ‐ email sent to lead author to clarify correct number analysed in the intervention group ‐ 396 or 397; author confirmed that there were 396 women in the intervention group | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computerised randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | 'concealed randomisation' by a web‐based computerised procedure; ... personnel had no influence over randomisation.' |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | While personnel had no influence over the process of randomisation, the physiotherapists who delivered the programmes were aware of the end results ... i.e. they were providing the participants with the intervention. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Outcomes were self‐reported symptoms, therefore the women were the outcome assessors and they knew whether they were receiving exercise therapy or not. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Exercise group = 8% drop‐out/loss to follow‐up; control group = 14% drop‐out/loss to follow‐up with a large proportion of these giving no reason and not included in the analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All outcomes reported as specified in methods. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Groups similar at baseline even when not including those lost to follow‐up. Co‐interventions avoided or similar between groups and compliance with exercise assessed against specified level of 3 x/week. Timing of outcome assessment same for both groups. |
| Methods | 74 women were allocated to experimental or control groups by using a 'random sampling technique' (no description). | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: primigravida, healthy ‐ no underlying disease, 20 to 35 years old, 26 to 30 weeks' gestation, at least 140 cm tall, BMI before becoming pregnant less than 25 kg/m2, non‐smoker, no previous severe back and pelvic pain, no contraindication for exercise during pregnancy, did not exercise regularly (< 1/week), attending prenatal clinic and intend to deliver at King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, fluent in Thai, willing to participate in study regimen. Exclusion criteria: Women were similar at baseline for all factors except job activities: exercise group sat more often at work (N/S); control group stood more often at work and income: exercise group were in higher paid jobs than the control (P = 0.008). | |
| Interventions | Experiment group. Control group: no treatment (nothing noted in article). | |
| Outcomes | Pain improved, pain worsened, pain measured with VAS, gestational age at birth, baby's Apgar score at 1 minute, baby's Apgar score at 5 minutes. Adverse events: 'no negative effects on mother or fetus; no preterm labour; no premature rupture of membranes'. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | Numbers are not consistently reported throughout the article; total number of participants seems to range from 73 to 84, with most mention of 74 randomised, which is the number we used. Data needed for the meta‐analyses appeared to be incorrectly reported in the paper and were re‐analysed. Funding: not mentioned. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | ‘random sampling technique’ but not described; in discussion section, the authors state 'the inclusion and exclusion criteria were used to match these two groups as closely as possible and scrutinize the variables that may contribute to the impact of physical conditioning or pregnancy outcomes'... which doesn't sound like 'randomisation'... |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear ‐ 'allocated to experimental or control groups'. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No blinding of participants or providers. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear about outcome assessors. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 17% loss of participants from control group; 24% loss of participants from intervention group; details for withdrawals not clearly described. Analysis on 67 completers only. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Reported on LBP for mothers, 1‐minute and 5‐minute Apgar scores and birthweight of babies. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Exercise diary kept and checked by exercise instructor; co‐interventions not described. |
| Methods | Cross‐over trial: order of use of pillows being 'randomly assigned' ‐‐ further details on randomisation not given. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria. Drop‐outs related to delivery, failure to present to clinic for assignment of 2nd pillow, failure to return completed questionnaires. | |
| Interventions | Provision of 2 different types of pillow to support the pregnant abdomen when lying in a lateral position. The pillows were taken home and used for 1 week each, consecutively. The Ozzlo pillow was a locally designed, curved, sloping, soft cushion conforming to the shape of the abdomen; the control pillow was a standard hospital pillow. | |
| Outcomes | Numbers of women reporting moderate improvement in backache or better. Numbers of women reporting relief of insomnia. No adverse effected noted. | |
| Low‐back pain | X | |
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | ||
| Notes | There was no comparison with no treatment. We contacted the authors in 1999 and the Ozzlo pillow seems no longer to be made. Funding source not noted. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Cross‐over trial: order of use of pillows being 'randomly assigned' ‐‐ further details on randomisation not given. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and personnel did not seem to be blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | Outcome assessors did not appear to be blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 84% of women completed study; women acted as their own control but there was no 'wash‐out period' provided between pillows. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data were measured for all women when they used 1 pillow and all women when they used the second one, rather than providing data at the end of the first phase of the trials, before the cross‐over. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Daily worksheets describing sleep patterns, pain, etc handed in end of each week; co‐interventions not mentioned. |
| Methods |
159R/152A | |
| Participants | Inclusion: pregnant women between 25‐38 weeks' gestation) with LBP and/or posterior PP. Exclusion: associated nerve root syndrome, neurologic deficit, fever, abdominal pain, other systematic manifestations, active uterine contractions. N = 159 randomised. AA = 58; Sham AA = 54; WL = 47. All patients acupuncture naive. Drop‐outs and exclusions reported with reasons. | |
| Interventions | Group 1: auricular (ear) acupuncture x 7 days plus self‐care (AA). N = 58. Used specific acupuncture points (kidney, analgesia, shenmen). Group 2: sham auricular (ear) acupuncture x 7 days plus self‐care (Sham AA). N = 54. used non‐specific points (shoulder, wrist, extra auricular point). Group 3: self‐care only waiting list control (WL). N = 47. Self care only. No acupuncture treatment received. Women just given advice. NB: All women given advice to rest if desired, take 650 mg acetaminophen every 6 hours if needed, use hot/cold compress as desired. | |
| Outcomes | VAS ‐ Pain (0‐100 mm); Disability Rating Index (DRI) ‐ functional status; State Trait Anxiety Index (STAI), measured at baseline, after 7 days of continuous AA or Sham AA and at 1 week post treatment (for both groups). Days off work not included in outcomes. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | Funding = national Center for the Complementary and Alternative Medicine Grant. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | 'randomly assigned to one of the three treatment groups based on a computer generated randomisation sheet.' |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No information provided on allocation concealment. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Women had no previous experience with acupuncture and were asked to complete a credibility questionnaire after the removal of the needles. While not blinded, acupuncturist was skilled and trained and followed a strict script during treatment to avoid any nuances being picked up by the participants. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Assessors and statisticians were blinded; women who gave self‐reports were also blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Attrition and exclusions reported, numbers add up in the analysis, authors indicate how they managed missing values in their analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study reported all outcomes as indicated in the methods section. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Similar co‐interventions; groups similar at baseline, timing of outcome assessment same across groups and compliance acceptable across groups. |
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial ‐ 60 women. | |
| Participants | Swedish women with pelvic or back pain arising before 32 weeks' gestation. | |
| Interventions | Acupuncture. Physiotherapy. | |
| Outcomes | VAS (pain), disability rating indices and rating of overall effect all assessed by the women in the trial. Adverse effects: no serious adverse effects reported, but 2 women reported small subcutaneous hematomas in the ear from acupuncture. | |
| Low‐back pain | ||
| Pelvic pain | ||
| Low‐back pain and pelvic pain | X | |
| Notes | There was no comparison with no treatment. The pain and disability scales were not used in this review because of insufficient data. Study funded by the Council of Research and Development of Vrinnevi Hospital, Norrkoping, Sweden. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 60 women who accepted invitation to join study 'drew a closed envelope from a box to randomise to either the acupuncture or physiotherapy group', but method of randomisation not described. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | 'drew a closed envelope from a box.' |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Participants and caregiver not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Aassessor blinding unclear. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Analysed those who completed the intervention in the group to which they had been randomised. 2 of 30 women were not analysed in the acupuncture group since they had both inadvertently received both acupuncture and physiotherapy. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data for pain and disability outcomes not provided with sufficient detail to include in analyses. |
| Other bias | High risk | Statistically significant difference in the distribution of type of pain at baseline, women pursued different co‐treatments to relieve symptoms. |
ACOG: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
ASLR: active straight leg raise
ADL: activities of daily living
BMI: body mass index
CI: confidence interval
gyn: gynaecological
ITT: intention‐to‐treat
kg/m2: kilogram/meters squared
LBP: low‐back pain
NRS: numerical rating scale
N/S: not significant
P4: Posterior Pelvic Pain Provocation Test
PGP: pelvic girdle pain
PP: pelvic pain
PFM: pelvic floor muscles
RMDQ: Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire
SD: standard deviation
SLR: straight leg raise test
UTI: urinary tract infection
VAS: visual analogue scale
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| CCT ‐ participants not randomised. | |
| QRCT ‐ participants not randomised. Translated from Polish by one Polish‐speaking researcher. | |
| QRCT ‐ pilot study of 8 women assigned to groups based on ability to attend classes. | |
| QRCT ‐ women assigned to groups based on the day they attended the prenatal clinic ‐ Tuesday and Thursday were assigned to study group; Monday and Wednesday were assigned to control group. | |
| Not a clinical trial; publication reports on an audit/evaluation of a Midwifery Acupuncture Service. | |
| Trial studied the effect of massage on stress reduction in pregnancy; back pain was measured, but only as a stressor that was managed with massage, not as an outcome of real interest. Attempts to contact 1st author for clarification were unsuccessful. | |
| Intervention designed to study the effect of yoga or massage compared to standard prenatal care on depressed pregnant women; back and leg pain was measured but not an outcome of real interest and not listed as 1 of the outcomes in methods section. | |
| Participants not randomised. Secondary analysis of intervention to prevent gestational diabetes. | |
| QRCT ‐ Randomisation was by date of birth. | |
| Intervention was started during pregnancy, but goal and outcomes measured 6 and 12 weeks postpartum. | |
| CCT ‐ sequence generation not described '...140 women were included in the study...80 patients were enrolled into the treatment group ... Pregnant women with the same pregnancy‐related pains were observed without Pycnogenol® treatment as a control group'. | |
| QRCT ‐ described as a 'Prospective controlled trial', with no details given for allocation. Report of conference proceedings, but unable to locate trial register (http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/Default.aspx; accessed 15 August 2012). | |
| Cross‐sectional study to determine the sensitivity and specificity of specific tests for LBP/PP. No intervention involved. | |
| CCT ‐ sequence generation not described ‐ attempts to contact the author for clarification unsuccessful. Translated from Japanese by one Japanese‐speaking researcher and a native Japanese non‐researcher. | |
| QRCT ‐ women stratified by previous pregnancies, then assigned to 1 of 3 treatment groups in sequence (1st primigravida to group 1, 2nd primigravida to group 2, 3rd primigravida to group 3, etc). | |
| QRCT ‐ 3 groups divided by whether date of birth was 1st to10th day in the month, 11th to 20th or 21st to 31st. | |
| Not a trial but an overview of the benefits of exercise in pregnancy. | |
| Article is described as a 'Single center, prospective, randomised ,experimental study', but there are no details of allocation, the control group(s), or comparison of outcomes between groups. Results are provided for 15 participants who appear to be the only ones entered into the study. | |
| Longitudinal cohort study that assessed peak oxygen uptake and incidence of back pain during and after pregnancy. | |
| Women were not pregnant at the time of intervention, just at the inception of the LBP. | |
| Not a RCT ‐ recruited pregnant women were allocated into study groups using block technique (AABB); acronym (AABB) implies that the block allocation was not probably random. Translated from Farsi by one Farsi‐speaking researcher. |
CCT: controlled clinical trial
LBP: low‐back pain
PP: pelvic pain
RCT: randomised controlled trial
QRCT: quasi‐randomised controlled trial
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
| Trial name or title | Comparison between 2 types of treatment for pelvic girdle pain in pregnancy: Abdomino lumbo pelvic belt and exercise therapy. |
| Methods | Participants will be allocated to 3 groups, including 2 interventions and 1 control, through randomisation. |
| Participants | 132 healthy pregnant women with pelvic girdle pain and pregnancy date 20 ‐ 32 weeks will be recruited. Other eligibility criteria: 1‐ Mono fetus. 2‐ Pelvic girdle pain had been diagnosed with history, physical examination and specific tests. Exclusion criteria: contraindications of exercise in pregnancy, Systemic diseases such as: restrictive lung diseases, heart disease; if participants do not come back after 3 and 6 weeks of intervention; If participants do not use belt or exercise regularly. |
| Interventions | Participants will be prescribed exercise plus educational pamphlet, abdominal lumbo pelvic belt with educational pamphlet and educational pamphlet alone (control) for 6 weeks. |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome of this study is improvement in back pain during pregnancy. Data collected at baseline, 3 and 6 weeks after interventions.
|
| Starting date | 2009‐10‐23 to 2010‐10‐23: recruitment is complete. |
| Contact information | Maryam Abolhasani; email: [email protected] |
| Notes | Irct registration number : IRCT138812113470N1. |
| Trial name or title | Randomised controlled trial for the treatment of pelvic girdle pain in pregnancy. |
| Methods | Open‐label randomised controlled single‐centre trial. |
| Participants | 226 pregnant women (primigravida and multigravida; no age limits) from 20 to 35 weeks of gestation attending Cork University Maternity Hospital (CUMH) low‐risk antenatal clinics who are referred to the physiotherapy department by their health care provider or following self‐referral with back pain or pelvic pain will be assessed for inclusion in the trial. Women referred to the physiotherapy department with symptoms of pelvic girdle pain (PGP) will be assessed on presentation by a 1 of 6 departmental physiotherapists specializing in women's health. |
| Interventions | Following initial assessment participants will be randomly allocated to 1 of 2 treatment groups (randomisation ratio 1:1). Patients will be asked to keep a pain score diary where they will record their pain score using a visual analogue scoring system. Patients will be asked to record a score every morning and every evening during the treatment course. The first treatment in both treatment arms will be 1 week following initial assessment. |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: a reduction in the current intensity of PGP related to motion on a 100‐point VAS in the morning and in the evening recorded in the patient's diaries (0 represented no pain and 100 represented worst conceivable pain). |
| Starting date | 01/04/2009 ‐ estimated end = 31/03/2010 ‐ trial completed. |
| Contact information | Prof Richard A Greene, Cork University Maternity Hospital ([email protected])
|
| Notes | Sponsor: Cork University Maternity Hospital (Ireland); March 8, 2012 ‐ recruiting not yet started. |
| Trial name or title | Osteopathic manipulative medicine in pregnancy: physiologic and clinical effects. |
| Methods | Allocation: randomised. Endpoint classification: efficacy study. Intervention model: single group assignment. Masking: double blind (participant, caregiver). Primary Purpose: treatment. |
| Participants | Inclusion Criteria: |
| Interventions | Other: Osteopathic manipulative treatment. |
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes Roland‐Morris Low Back Pain and Disability Questionnaire at each visit. 5 years No Secondary outcome CLINICAL STUDY 5 years No |
| Starting date | April 2006 |
| Contact information | Mayra Rodriguez, BS |
| Notes | Kendi Hensel, D.O., Principal Investigator, University of North Texas Health Science Center ‐ Osteopathic Research Center. March 8, 2012 ‐ currently recruiting |
| Trial name or title | Exercise training in pregnancy for obese women (ETIP). |
| Methods | Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. |
| Participants | 150 previously sedentary, pregnant women with a pre‐pregnancy BMI at or above 30 kg/m2; randomised into intervention and control groups. |
| Interventions | Intervention group: organised exercise training 3 x/week starting in gestation week 14 (range 12‐16) Control group: standard antenatal care. |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: weight gain from baseline to delivery. Secondary outcomes: changes in exercise capacity, physical activity level, endothelial function, body composition, incontinence, lumbo‐pelvic pain and cardiac function from baseline to gestation week 37 (range 36‐38). Offspring outcome measures include anthropometric variables at birth, Apgar score. |
| Starting date | September 2010. |
| Contact information | Principal Investigator:Trine T Moholdt, PhD. |
| Notes | Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01243554. Sponsor: Norwegian University of Science and Technology. |
ECG: electrocardiogram
EMG: electromyography
VAS: visual analogue scale
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain intensity Show forest plot | 6 | 543 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.80 [‐1.07, ‐0.53] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Pain intensity. | ||||
| 2 Disability Show forest plot | 2 | 146 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.56 [‐0.89, ‐0.23] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 2 Disability. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women taking sick leave because of back pain after 32 weeks' gestation Show forest plot | 1 | 241 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.17, 0.92] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Low‐back pain: water gymnastics + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Number of women taking sick leave because of back pain after 32 weeks' gestation. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Low‐back pain, measured with VAS; 0 to 10; 0 = no pain Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 Low‐back pain: support belts, Outcome 1 Low‐back pain, measured with VAS; 0 to 10; 0 = no pain. | ||||
| 1.1 Low‐back Pain | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.20 [‐1.19, 0.79] |
| 1.2 ADL | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.90 [‐1.81, 0.01] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Evening pain Show forest plot | 1 | 47 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.73, 1.54] |
| Analysis 4.1 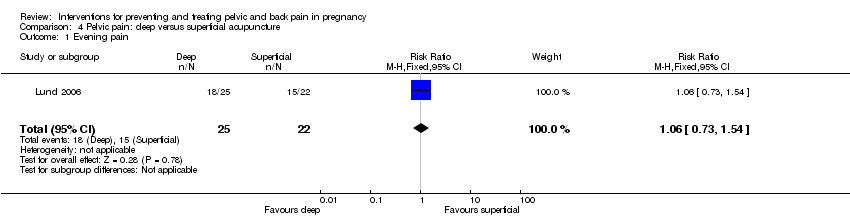 Comparison 4 Pelvic pain: deep versus superficial acupuncture, Outcome 1 Evening pain. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Women who reported pain on Visual Analogue Scale Show forest plot | 4 | 1344 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.73, 1.00] |
| Analysis 5.1 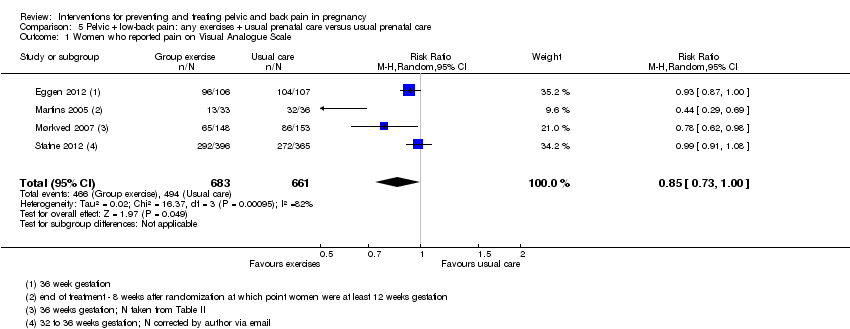 Comparison 5 Pelvic + low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Women who reported pain on Visual Analogue Scale. | ||||
| 2 Women who reported LBP/PGP‐related sick leave Show forest plot | 2 | 1062 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.62, 0.94] |
| Analysis 5.2  Comparison 5 Pelvic + low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 2 Women who reported LBP/PGP‐related sick leave. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women who reported decreased pain Show forest plot | 1 | 72 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.16 [1.77, 9.78] |
| Analysis 6.1 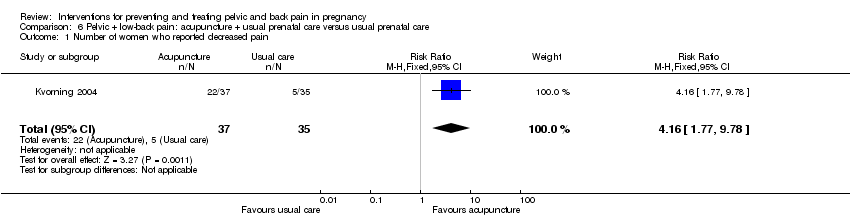 Comparison 6 Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Number of women who reported decreased pain. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Numbers of women rating treatment as good or excellent Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.24 [0.96, 1.60] |
| Analysis 7.1  Comparison 7 Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus individualised physio + usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Numbers of women rating treatment as good or excellent. | ||||

'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
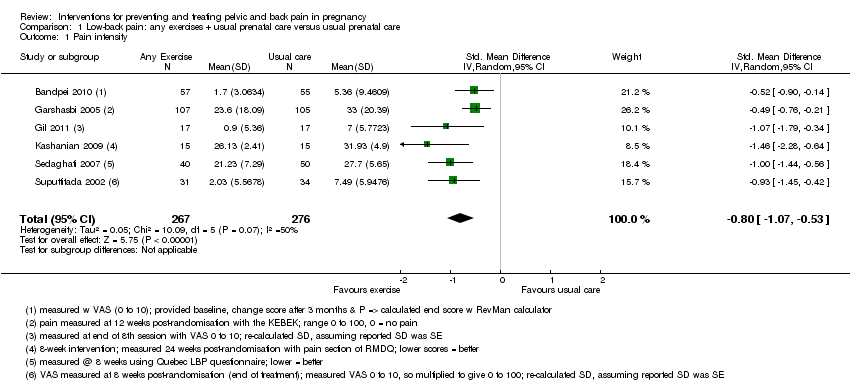
Comparison 1 Low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Pain intensity.

Comparison 1 Low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 2 Disability.

Comparison 2 Low‐back pain: water gymnastics + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Number of women taking sick leave because of back pain after 32 weeks' gestation.

Comparison 3 Low‐back pain: support belts, Outcome 1 Low‐back pain, measured with VAS; 0 to 10; 0 = no pain.
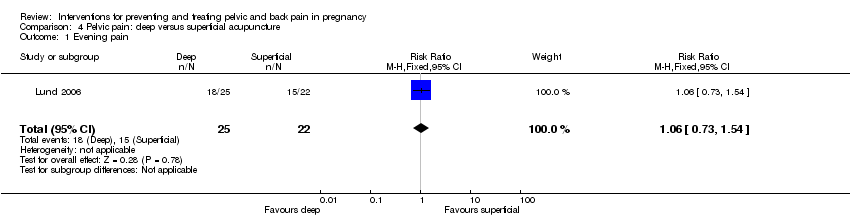
Comparison 4 Pelvic pain: deep versus superficial acupuncture, Outcome 1 Evening pain.

Comparison 5 Pelvic + low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Women who reported pain on Visual Analogue Scale.
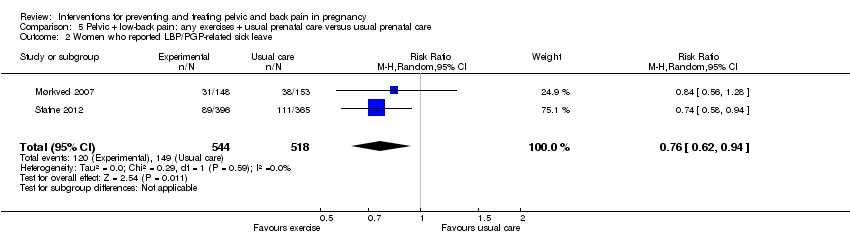
Comparison 5 Pelvic + low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 2 Women who reported LBP/PGP‐related sick leave.

Comparison 6 Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Number of women who reported decreased pain.
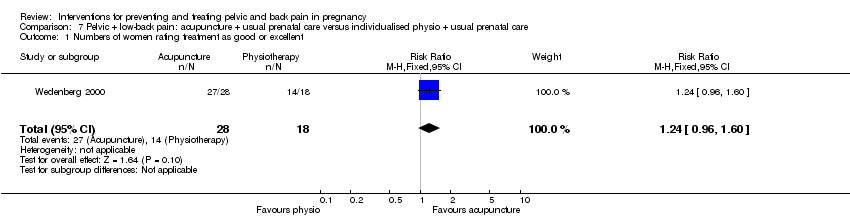
Comparison 7 Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus individualised physio + usual prenatal care, Outcome 1 Numbers of women rating treatment as good or excellent.
| Low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care for treating back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with back pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care | |||||
| Pain intensity measured by a number of different measurements; lower score = better | The mean pain intensity in the control groups was18.75 | The mean pain intensity in the intervention groups was | SMD ‐0.80 (‐1.07, ‐0.53) | 543 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| Disability measured by Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire and Oswestry Disability Index | The mean disability in the control groups was 26.6 | The mean disability in the intervention groups was | SMD ‐0.56 (‐0.89 to ‐0.23) | 146 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 poor or no description of randomisation process, allocation concealment, blinding of research personnel | ||||||
| Low‐back pain: water gymnastics + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care for treating back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with back pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control (usual care) | water gymnastics | |||||
| Number of women taking sick leave because of back pain after 32 weeks' gestation | Study population | RR 0.4 | 241 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 144 per 1000 | 58 per 1000 | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 unclear methods of randomisation; research personnel not blinded | ||||||
| Low‐back pain: support belts for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with back pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Low‐back pain: support belts | |||||
| BellyBra versus Tubigrip ‐ Low‐back Pain | The mean Bellybra versus Tubigrip back pain in the control group was 4.7, measured on VAS 0 to 10 | The mean Bellybra versus Tubigrip ‐ back pain in the intervention group was 0.2 lower (1.19 lower to 0.79 higher) | MD ‐0.20 (95% CI ‐1.19 to 0.79) | 94 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| BellyBra versus Tubigrip ‐ ADL | The mean Bellybra versus Tubigrip ability to perform activities of daily living in the control group was 5.6, measured as a total of several activities | The mean Bellybra versus Tubigrip ability to perform activities of daily living in the intervention group was 0.9 lower | MD ‐0.90 (95% CI ‐1.81 to 0.01) | 94 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 no blinding of research personnel described; no explanation provided for lost‐to‐follow‐up data; different co‐interventions and compliance between groups | ||||||
| Pelvic pain: deep versus superficial acupuncture for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with pelvic pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control (superficial) | Intervention (deep) | |||||
| evening pain, reported as better, based on women's report on Visual Analogue Scale | Study population | RR 1.06 | 47 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 682 per 1000 | 723 per 1000 | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 randomisation process and attrition rate/explanations not described | ||||||
| Pelvic + low‐back pain: any exercises + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with, or at risk of developing, pelvic and back pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control (usual prenatal care) | Any exercises + usual prenatal care | |||||
| Number of women who reported pain on Visual Analogue Scale | Study population | RR 0.85 | 1344 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 747 per 1000 | 635 per 1000 | |||||
| Number of women who reported LBP/PGP‐related sick leave | Study population | RR 0.76 | 1062 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 288 per 1000 | 219 per 1000 | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 there was a mix of potential biases among the four studies: no allocation concealment (1); no blinding of research personnel (all); poor/no description of drop‐outs, co‐interventions and baseline inequality (mixed) | ||||||
| Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with, or at risk of developing, pelvic and back pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus usual prenatal care | |||||
| Number of women who reported decreased pain | Study population | RR 4.16 | 72 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 143 per 1000 | 594 per 1000 | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 no blinding of research personnel, over 20% attrition, different co‐interventions | ||||||
| Pelvic + low‐back pain: acupuncture + usual prenatal care versus individualised physio + usual prenatal care for preventing and treating pelvic and back pain in pregnancy | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with, or at risk of developing, pelvic and back pain | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control (individualised physio + usual prenatal care) | acupuncture + usual prenatal care | |||||
| Numbers of women rating treatment as good or excellent | Study population | RR 1.24 | 46 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 778 per 1000 | 964 per 1000 | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 no description of randomisation process, no blinding of research personnel described, uneven attrition (12 dropped out of physio group, while none dropped out of the acupuncture group) and co‐interventions between groups | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain intensity Show forest plot | 6 | 543 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.80 [‐1.07, ‐0.53] |
| 2 Disability Show forest plot | 2 | 146 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.56 [‐0.89, ‐0.23] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women taking sick leave because of back pain after 32 weeks' gestation Show forest plot | 1 | 241 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.40 [0.17, 0.92] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Low‐back pain, measured with VAS; 0 to 10; 0 = no pain Show forest plot | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Low‐back Pain | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.20 [‐1.19, 0.79] |
| 1.2 ADL | 1 | 94 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.90 [‐1.81, 0.01] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Evening pain Show forest plot | 1 | 47 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.73, 1.54] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Women who reported pain on Visual Analogue Scale Show forest plot | 4 | 1344 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.73, 1.00] |
| 2 Women who reported LBP/PGP‐related sick leave Show forest plot | 2 | 1062 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.62, 0.94] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Number of women who reported decreased pain Show forest plot | 1 | 72 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.16 [1.77, 9.78] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Numbers of women rating treatment as good or excellent Show forest plot | 1 | 46 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.24 [0.96, 1.60] |

