Geplanter Kaiserschnitt bei Beckenendlage am Geburtstermin
Referencias
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Methods | Allocation by "random selection". Method not specified. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: singleton frank breech presentation; 36 weeks or more gestation; estimated fetal weight between 2500 and 3800 g; cervical dilation 7 cm or less. Exclusion criteria: hyperextension of the fetal head or evidence of fetal skeletal anomalies on abdominal x‐ray; elderly primigravidae; obstetric indication for caesarean section; class B‐F diabetes mellitus; floating station; involuntary infertility; pelvic contracture by previous x‐ray pelvimetry; history of previous difficult or traumatic delivery. 208 women randomised to vaginal delivery group (115 women) and caesarean section group (93 women). | |
| Interventions | Planned delivery by caesarean section compared with a policy of vaginal breech delivery; x‐ray pelvimetry was performed and if 1 or more pelvic inlet or mid‐cavity measurements were reduced, caesarean section performed; oxytocin induction was permitted only for premature rupture of membranes with the fetus engaged in the maternal pelvis; oxytocin augmentation of labour was used for prolonged latent phase and protracted active phase dilation; fetal heart rate and uterine contractions were monitored throughout labour. Delivery by or supervised by a senior obstetric resident. | |
| Outcomes | Actual use of caesarean section; brachial plexus injury; Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes; short‐term neonatal morbidity; perinatal mortality; maternal morbidity. | |
| Notes | Los Angeles, California, USA. Data presented for 4 groups according to protocol selection and actual method of delivery. For this review, analysed according to protocol selection only (i.e. according to 'intention‐to‐treat'). A large discrepancy in numbers between groups (93 versus 115, and 37 versus 57 multiparous women) is not accounted for. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Allocation by "random selection". Method not specified. Reason for large discrepancy in group sizes not given. High risk of selection bias. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Inadequate. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not possible due to the nature of the intervention. No attempt at partial blinding described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | No blinding described. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No incomplete data. Difference in group sizes not explained. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient evidence to assess whether all prespecified outcomes were reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insuficient detail in reporting to be sure whether additional risk exists. |
| Methods | 2‐arm trial. "Randomisation" in a ratio of 1 caesarean section to 2 trials of labour, to allow for exclusions from trial of labour. Method of randomisation not specified. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: singleton pregnancy; non‐frank breech presentation on abdominal x‐ray; in labour; estimated gestational age 36‐42 weeks; estimated fetal weight 2000 to 4000 g; cervix < 7 cm dilated; non‐extended normal appearing fetal skull on x‐ray; no contraindication to labour. Of 105 enrolled, 35 allocated to caesarean section and 70 to trial of labour. | |
| Interventions | Planned elective caesarean section compared with planned trial of labour: x‐ray pelvimetry performed and trial of labour allowed if measurements were at least 11 cm at anteroposterior diameter of the inlet, 12 cm at widest transverse diameter of the inlet and 10 cm between ischial spines at the midpelvis; continuous electronic fetal monitoring; oxytocin infusion on an optional basis for poor progress of labour; intravenous analgesia and assisted breech delivery with application of Piper forceps to aftercoming head. Delivery supervised by chief resident and/or obstetric staff. | |
| Outcomes | Actual use of caesarean section; brachial plexus injury; Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes; perinatal mortality; maternal morbidity. | |
| Notes | Los Angeles. California, USA. Results reported in the study in 4 groups according to allocated and actual method of delivery. For this review analysed according to allocated method of delivery ('intention‐to‐treat') only. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified, stated only as "randomisation" done. High risk of selection bias. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not possible due to the nature of the intervention. No attempt at partial blinding described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | High risk | No blinding described. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 3 women appear to have been excluded shortly after randomisation: 2 progressed so rapidly to emergency caesarean section that x‐rays could not be obtained, and the third had inadequate pelvic dimensions so elected caesarean section. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient evidence to assess whether all prespecified outcomes were reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Report not detailed enough to be sure of other bias |
| Methods | Centrally controlled computerised randomisation, stratified by parity (0 or > 0) and block sizes of 2. | |
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: singleton live fetus; frank or complete breech presentation; 37 or more weeks' gestation. | |
| Interventions | Planned caesarean section: if not in labour, scheduled for 38 or more weeks' gestation if known, or following maturity testing or onset of labour. If no longer breech presentation, method of delivery reviewed. | |
| Outcomes | Primary: perinatal or neonatal mortality up to 28 days of age (excluding lethal congenital abnormalities) or specified serious neonatal morbidity. | |
| Notes | Multicentre trial. Countries classified as having low (20/1000 or less) or high perinatal mortality rates. Follow‐up at 3 months excluding centres unable to accomplish 80% follow‐up. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Centrally controlled computerised randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Adequate, random allocation accessed by means of a touch‐tone telephone. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not possible due to the nature of the intervention. No attempt at partial blinding described. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Blinding was not possible for most outcomes. Group allocation was masked for the assessment of a few outcomes (e.g. diagnosis of severe morbidity was made by the steering committee masked to the group allocation (Hannah 2000 p1377) and diagnosis of neonatal outcomes such as lethal congenital abnormality and Down syndrome were also masked to group allocation (Whyte 2004 p865)). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No unbalanced loss to follow‐up ‐ only 2 + 3 lost to follow‐up from 2088 women. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All outcomes measured appear to have been reported |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Baseline characteristics similar. Analysis by intention‐to‐treat. Study was stopped early because of significant differences in perinatal or neonatal mortality at less than 28 days of age (excluding lethal congenial anomalies). Some protocol violations may have biased the results towards favouring caesarean section (e.g. including the recruitment of babies who may already have been dead, twin pregnancies, not having an experienced clinician at vaginal breech deliveries, and including babies with footling or "uncertain" breech presentation). 58 out of 646 women who had vaginal deliveries violated the protocol (Lawson 2012). |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Ir a:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Excluded because not a randomised trial. Breech delivery outcomes were compared retrospectively for alternate‐day obstetric units. Unit 'B' used a conservative approach towards vaginal breech delivery and performed more caesarean sections (105/277, 38% versus 69/266, 26%). Unit 'A' made more use of x‐ray pelvimetry, early rupture of membranes and oxytocin augmentation of labour. There were no statistically significant differences in duration of labour, Apgar scores or neonatal morbidity. There were 2 (0.7%) neonatal deaths in unit 'B' and 7 (2.6%) in unit 'A'. | |
| Not a randomised trial, but a comparison of the results of 2 clinics with differing protocols for management of breech birth. |
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Perinatal/neonatal death or severe neonatal morbidity Show forest plot | 1 | 2078 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.23 [0.02, 2.44] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 1 Perinatal/neonatal death or severe neonatal morbidity. | ||||
| 1.1 Low national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1025 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.29] |
| 1.2 High national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1053 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.66 [0.35, 1.24] |
| 2 Death or neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 920 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.52, 2.30] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 2 Death or neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years. | ||||
| 3 Perinatal/neonatal mortality (excluding fatal malformations) Show forest plot | 3 | 2388 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.10, 0.86] |
| Analysis 1.3 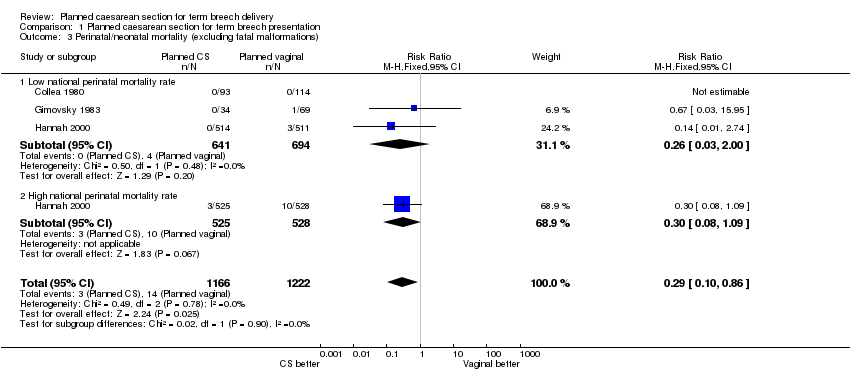 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 3 Perinatal/neonatal mortality (excluding fatal malformations). | ||||
| 3.1 Low national perinatal mortality rate | 3 | 1335 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.26 [0.03, 2.00] |
| 3.2 High national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1053 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.30 [0.08, 1.09] |
| 4 5 minute Apgar < 7 Show forest plot | 3 | 2375 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.12, 1.47] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 4 5 minute Apgar < 7. | ||||
| 5 5 minute Apgar < 4 Show forest plot | 1 | 2062 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.01, 0.87] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 5 5 minute Apgar < 4. | ||||
| 6 Cord blood pH < 7.0 Show forest plot | 1 | 1013 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.03, 0.67] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 6 Cord blood pH < 7.0. | ||||
| 7 Cord blood base deficit =/> 15 Show forest plot | 1 | 899 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.30 [0.10, 0.92] |
| Analysis 1.7 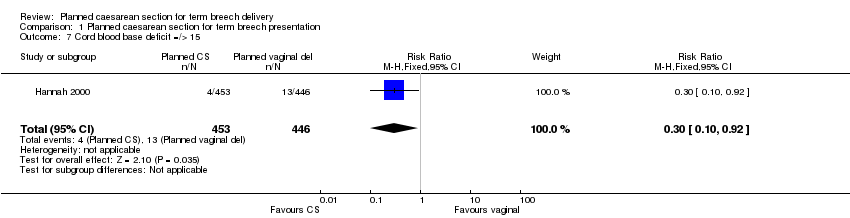 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 7 Cord blood base deficit =/> 15. | ||||
| 8 Birth trauma, as defined by trial authors Show forest plot | 1 | 2062 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.10] |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 8 Birth trauma, as defined by trial authors. | ||||
| 9 Brachial plexus injury Show forest plot | 3 | 2375 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.08, 1.47] |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 9 Brachial plexus injury. | ||||
| 10 Infant medical problems at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 843 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.41 [1.05, 1.89] |
| Analysis 1.10  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 10 Infant medical problems at 2 years. | ||||
| 11 Neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 920 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.74 [0.69, 4.37] |
| Analysis 1.11 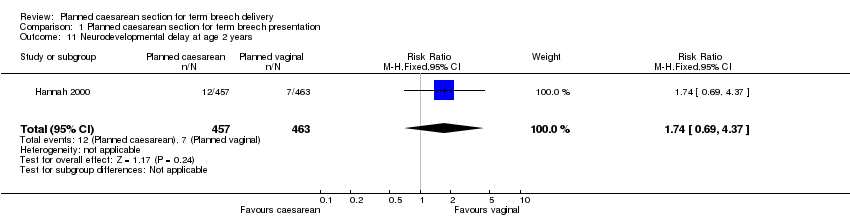 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 11 Neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years. | ||||
| 12 Caesarean section Show forest plot | 3 | 2396 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.88 [1.60, 2.20] |
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 12 Caesarean section. | ||||
| 13 Short‐term maternal morbidity Show forest plot | 3 | 2396 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [1.03, 1.61] |
| Analysis 1.13  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 13 Short‐term maternal morbidity. | ||||
| 14 Woman not satisfied Show forest plot | 1 | 1596 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.64, 1.56] |
| Analysis 1.14  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 14 Woman not satisfied. | ||||
| 15 Postnatal depression at 3 months, as defined by trial authors Show forest plot | 1 | 1586 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.70, 1.24] |
| Analysis 1.15  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 15 Postnatal depression at 3 months, as defined by trial authors. | ||||
| 16 Not breastfeeding at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1557 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.90, 1.21] |
| Analysis 1.16 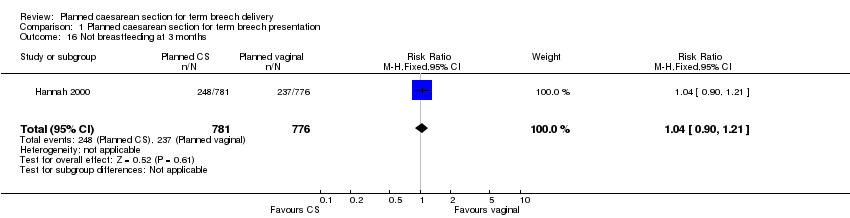 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 16 Not breastfeeding at 3 months. | ||||
| 17 Perineal pain at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.18, 0.58] |
| Analysis 1.17 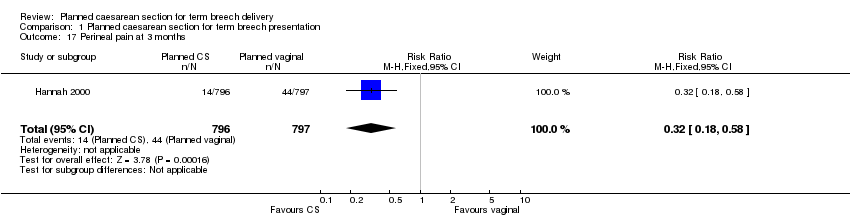 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 17 Perineal pain at 3 months. | ||||
| 18 Abdominal pain at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.89 [1.29, 2.79] |
| Analysis 1.18 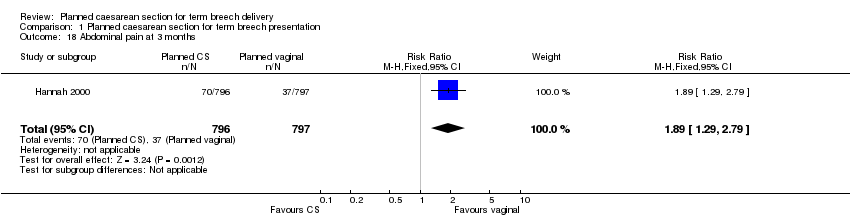 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 18 Abdominal pain at 3 months. | ||||
| 19 Backache after at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.71, 1.22] |
| Analysis 1.19  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 19 Backache after at 3 months. | ||||
| 20 Any pain after at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.93, 1.29] |
| Analysis 1.20  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 20 Any pain after at 3 months. | ||||
| 21 Dyspareunia at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1329 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.72, 1.14] |
| Analysis 1.21  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 21 Dyspareunia at 3 months. | ||||
| 22 Urinary incontinence at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1595 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.41, 0.93] |
| Analysis 1.22 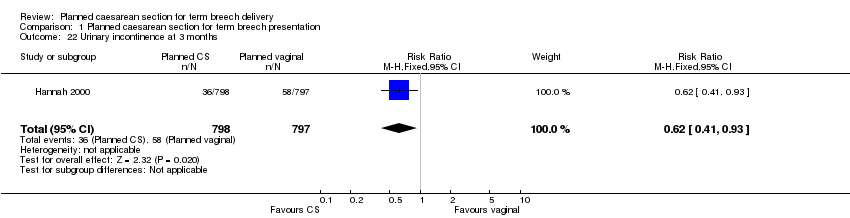 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 22 Urinary incontinence at 3 months. | ||||
| 23 Flatus incontinence at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1222 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.79, 1.53] |
| Analysis 1.23  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 23 Flatus incontinence at 3 months. | ||||
| 24 Faecal incontinence at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1226 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.54 [0.18, 1.62] |
| Analysis 1.24 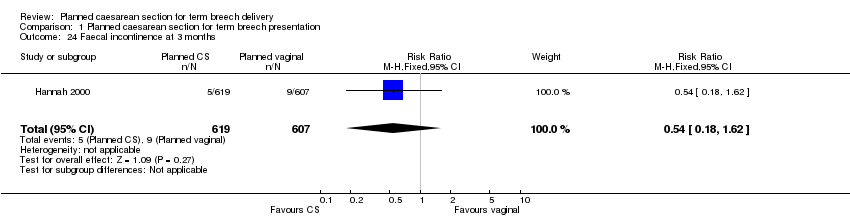 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 24 Faecal incontinence at 3 months. | ||||
| 25 Headache at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.88, 1.25] |
| Analysis 1.25 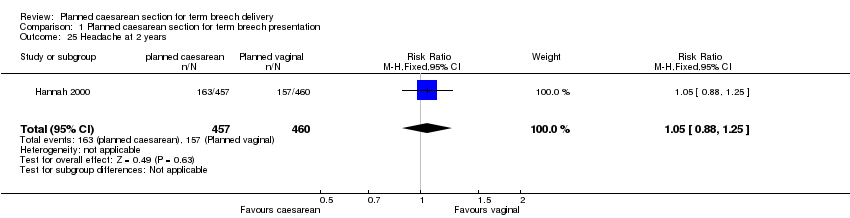 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 25 Headache at 2 years. | ||||
| 26 Perineal pain at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.36, 1.15] |
| Analysis 1.26  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 26 Perineal pain at 2 years. | ||||
| 27 Back pain at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.88, 1.20] |
| Analysis 1.27 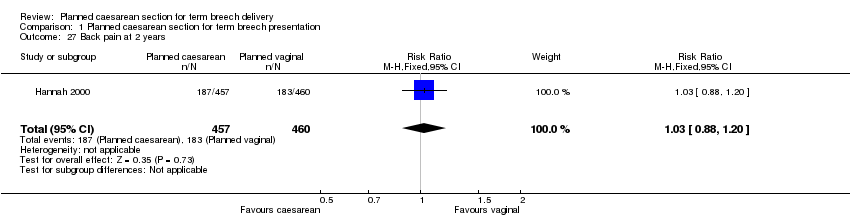 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 27 Back pain at 2 years. | ||||
| 28 Sexual problems at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.62, 1.48] |
| Analysis 1.28  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 28 Sexual problems at 2 years. | ||||
| 29 Painful intercourse at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 830 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [0.53, 4.12] |
| Analysis 1.29  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 29 Painful intercourse at 2 years. | ||||
| 30 Urinary incontinence at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.63, 1.06] |
| Analysis 1.30  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 30 Urinary incontinence at 2 years. | ||||
| 31 Flatus incontinence at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.81, 1.61] |
| Analysis 1.31 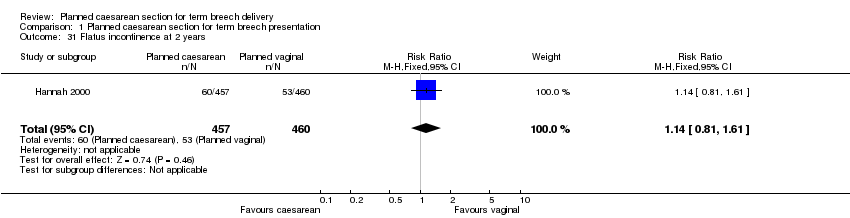 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 31 Flatus incontinence at 2 years. | ||||
| 32 Faecal incontinence at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.47, 2.58] |
| Analysis 1.32  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 32 Faecal incontinence at 2 years. | ||||
| 33 Constipation at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.34 [1.06, 1.70] |
| Analysis 1.33  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 33 Constipation at 2 years. | ||||
| 34 Haemorrhoids at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.85, 1.43] |
| Analysis 1.34  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 34 Haemorrhoids at 2 years. | ||||
| 35 Subsequent birth or pregnant at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.71, 1.24] |
| Analysis 1.35  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 35 Subsequent birth or pregnant at 2 years. | ||||
| 36 Subsequent caesarean section at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.24 [0.60, 2.55] |
| Analysis 1.36  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 36 Subsequent caesarean section at 2 years. | ||||
| 37 Painful menstrual periods at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.71, 1.15] |
| Analysis 1.37  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 37 Painful menstrual periods at 2 years. | ||||
| 38 Heavy menstrual periods at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.78, 1.52] |
| Analysis 1.38 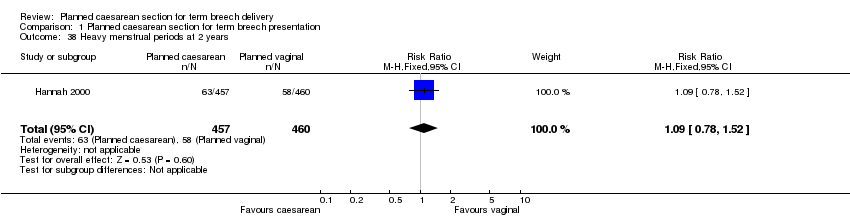 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 38 Heavy menstrual periods at 2 years. | ||||
| 39 Depression at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.62, 1.29] |
| Analysis 1.39  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 39 Depression at 2 years. | ||||
| 40 Difficulty caring for child at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 873 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.72, 1.29] |
| Analysis 1.40  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 40 Difficulty caring for child at 2 years. | ||||
| 41 Relationship with partner unhappy at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 856 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.63, 1.66] |
| Analysis 1.41 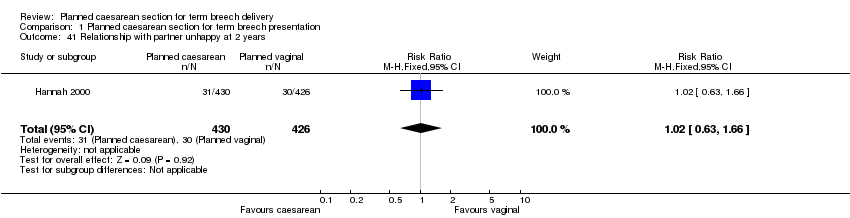 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 41 Relationship with partner unhappy at 2 years. | ||||
| 42 Unhappy with sexual relations at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 702 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.51, 1.50] |
| Analysis 1.42 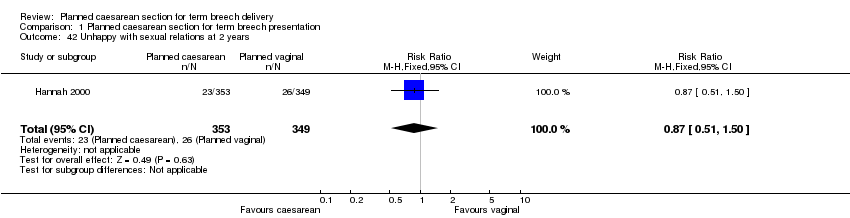 Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 42 Unhappy with sexual relations at 2 years. | ||||
| 43 Estimated cost of intervention (in Canadian dollars) Show forest plot | 1 | 1027 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐877.0 [‐894.89, ‐859.11] |
| Analysis 1.43  Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 43 Estimated cost of intervention (in Canadian dollars). | ||||
| 43.1 Low national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1027 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐877.0 [‐894.89, ‐859.11] |
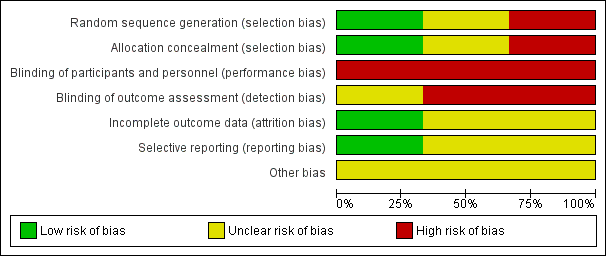
'Risk of bias. graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

.Risk of bias. summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
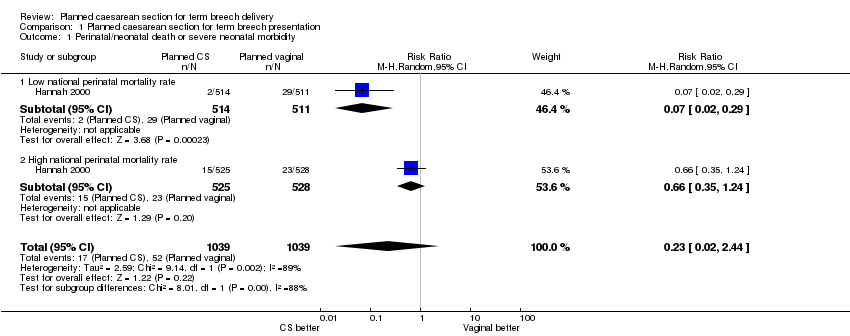
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 1 Perinatal/neonatal death or severe neonatal morbidity.
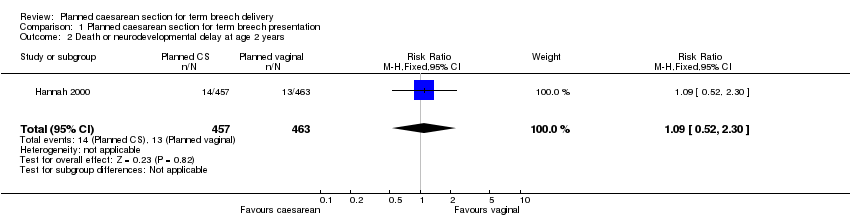
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 2 Death or neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 3 Perinatal/neonatal mortality (excluding fatal malformations).

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 4 5 minute Apgar < 7.
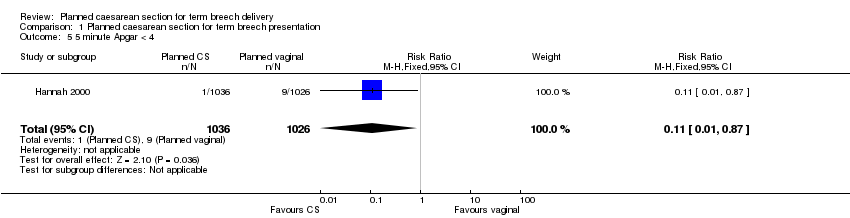
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 5 5 minute Apgar < 4.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 6 Cord blood pH < 7.0.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 7 Cord blood base deficit =/> 15.
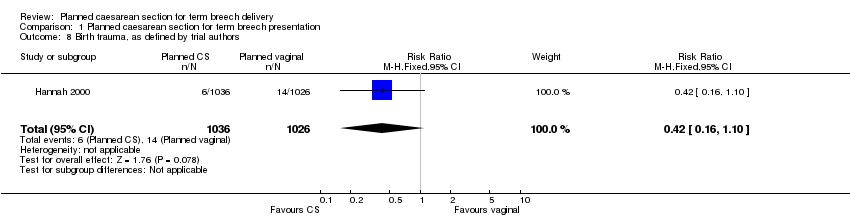
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 8 Birth trauma, as defined by trial authors.
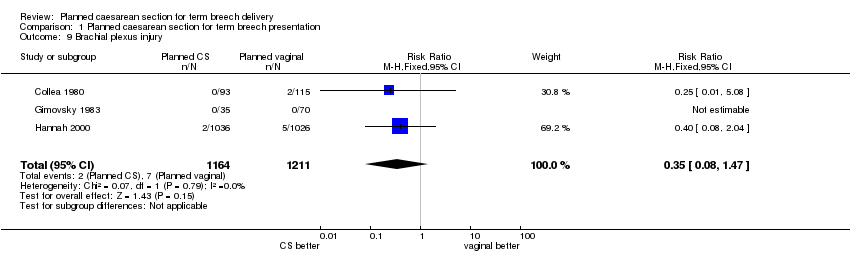
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 9 Brachial plexus injury.
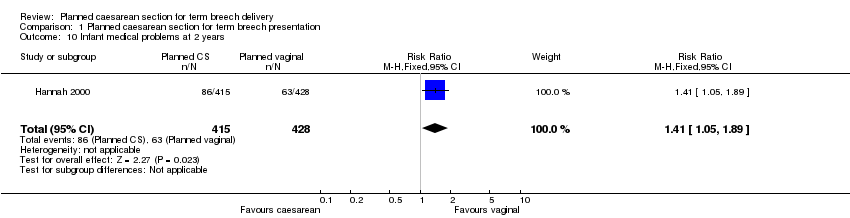
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 10 Infant medical problems at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 11 Neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years.
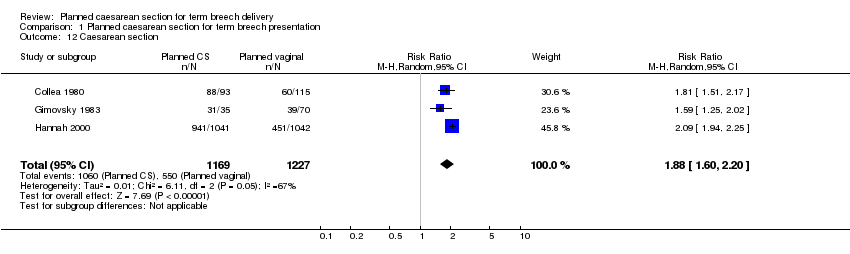
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 12 Caesarean section.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 13 Short‐term maternal morbidity.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 14 Woman not satisfied.
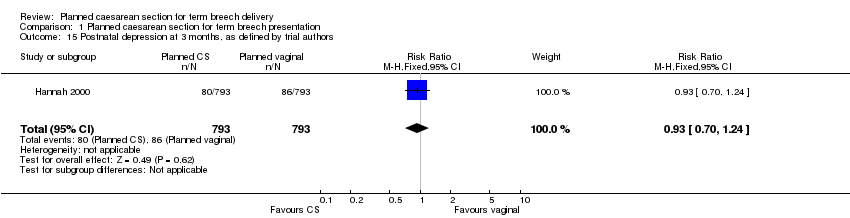
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 15 Postnatal depression at 3 months, as defined by trial authors.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 16 Not breastfeeding at 3 months.
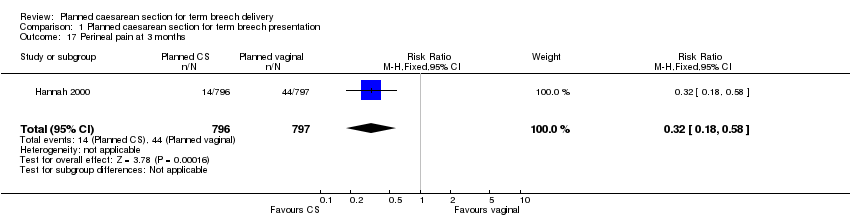
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 17 Perineal pain at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 18 Abdominal pain at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 19 Backache after at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 20 Any pain after at 3 months.
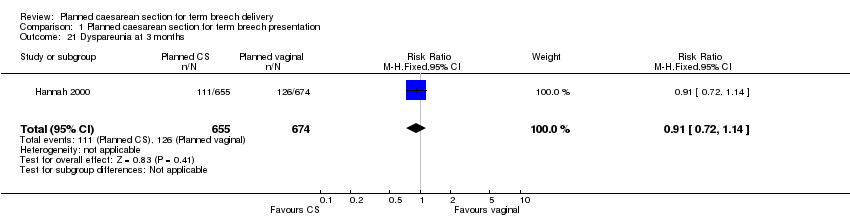
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 21 Dyspareunia at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 22 Urinary incontinence at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 23 Flatus incontinence at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 24 Faecal incontinence at 3 months.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 25 Headache at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 26 Perineal pain at 2 years.
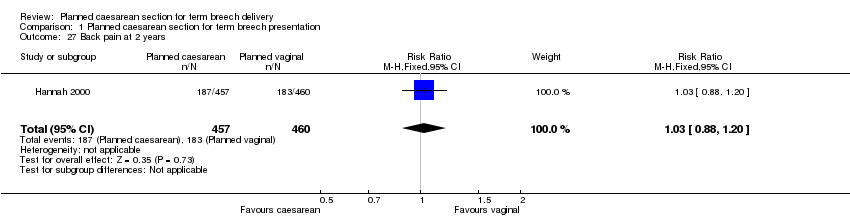
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 27 Back pain at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 28 Sexual problems at 2 years.
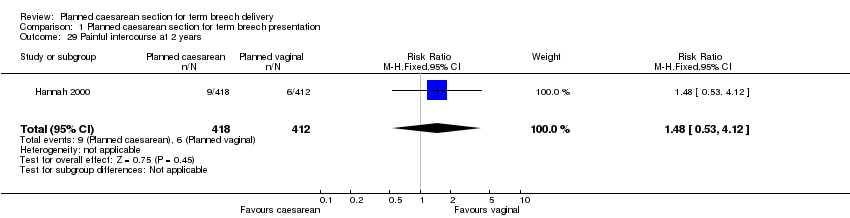
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 29 Painful intercourse at 2 years.
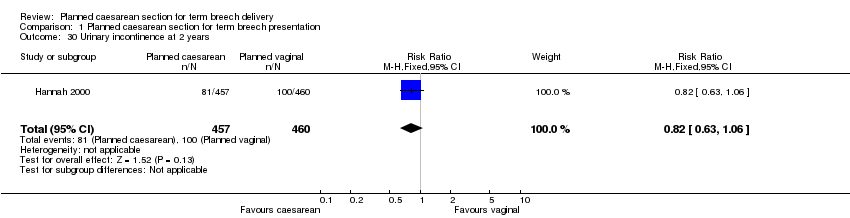
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 30 Urinary incontinence at 2 years.
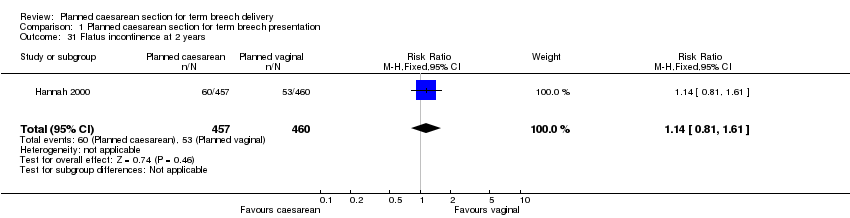
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 31 Flatus incontinence at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 32 Faecal incontinence at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 33 Constipation at 2 years.
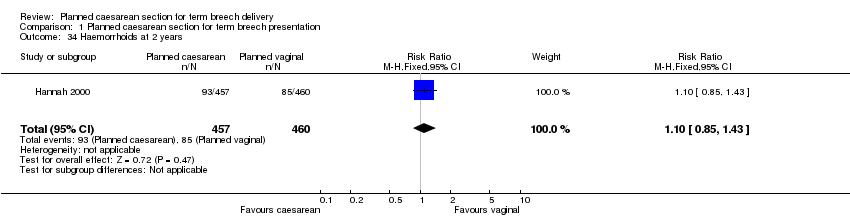
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 34 Haemorrhoids at 2 years.
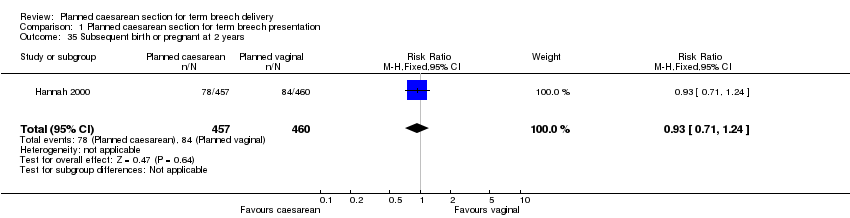
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 35 Subsequent birth or pregnant at 2 years.
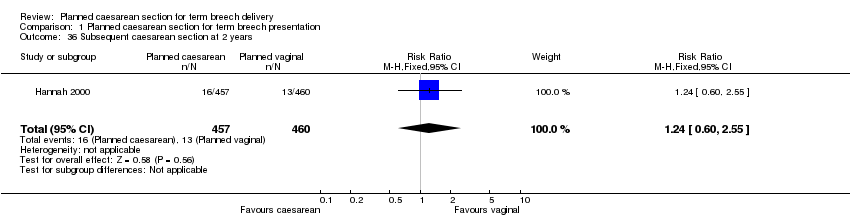
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 36 Subsequent caesarean section at 2 years.
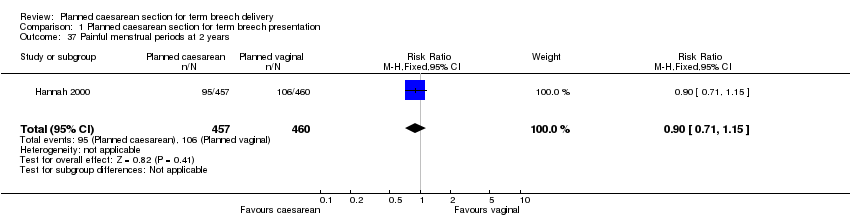
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 37 Painful menstrual periods at 2 years.
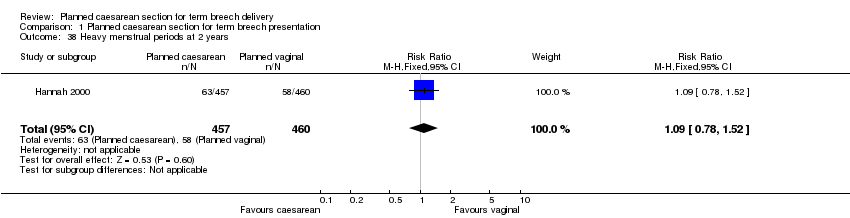
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 38 Heavy menstrual periods at 2 years.
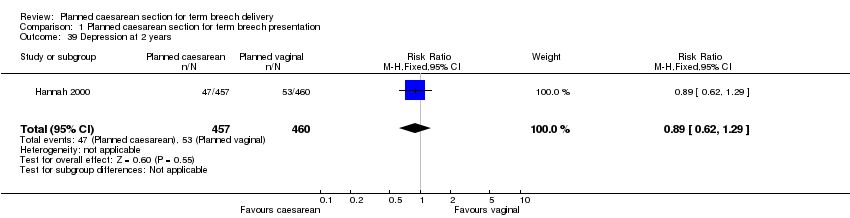
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 39 Depression at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 40 Difficulty caring for child at 2 years.
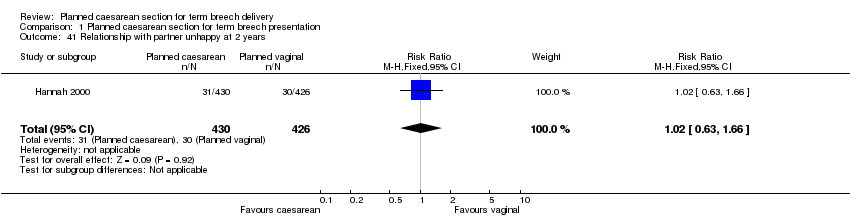
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 41 Relationship with partner unhappy at 2 years.
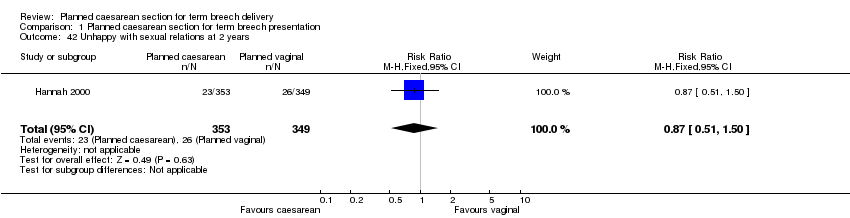
Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 42 Unhappy with sexual relations at 2 years.

Comparison 1 Planned caesarean section for term breech presentation, Outcome 43 Estimated cost of intervention (in Canadian dollars).
| Planned caesarean section for term breech delivery | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with term breech delivery | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of Participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Planned caesarean section | |||||
| Perinatal/neonatal death or severe neonatal morbidity ‐ Low national perinatal mortality rate | Study population | RR 0.07 | 1025 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | ||
| 57 per 1000 | 4 per 1000 | |||||
| Perinatal/neonatal death or severe neonatal morbidity ‐ High national perinatal mortality rate | Study population | RR 0.66 | 1053 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 44 per 1000 | 29 per 1000 | |||||
| Birth trauma, as defined by trial authors | Study population | RR 0.42 | 2062 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 14 per 1000 | 6 per 1000 | |||||
| Death or neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years | Study population | RR 1.09 | 920 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 28 per 1000 | 31 per 1000 | |||||
| Caesarean section | Study population | RR 2.04 | 2396 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 448 per 1000 | 843 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 522 per 1000 | 981 per 1000 (835 to 1000) | |||||
| Short‐term maternal morbidity | Study population | RR 1.29 | 2396 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 86 per 1000 | 111 per 1000 | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 391 per 1000 | 504 per 1000 | |||||
| Any pain after at 3 months | Study population | RR 1.09 | 1593 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | ||
| 250 per 1000 | 272 per 1000 | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: Confidence interval; RR: Risk ratio; | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 One study with design limitations. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Perinatal/neonatal death or severe neonatal morbidity Show forest plot | 1 | 2078 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.23 [0.02, 2.44] |
| 1.1 Low national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1025 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.02, 0.29] |
| 1.2 High national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1053 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.66 [0.35, 1.24] |
| 2 Death or neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 920 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.52, 2.30] |
| 3 Perinatal/neonatal mortality (excluding fatal malformations) Show forest plot | 3 | 2388 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.10, 0.86] |
| 3.1 Low national perinatal mortality rate | 3 | 1335 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.26 [0.03, 2.00] |
| 3.2 High national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1053 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.30 [0.08, 1.09] |
| 4 5 minute Apgar < 7 Show forest plot | 3 | 2375 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.43 [0.12, 1.47] |
| 5 5 minute Apgar < 4 Show forest plot | 1 | 2062 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.01, 0.87] |
| 6 Cord blood pH < 7.0 Show forest plot | 1 | 1013 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.15 [0.03, 0.67] |
| 7 Cord blood base deficit =/> 15 Show forest plot | 1 | 899 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.30 [0.10, 0.92] |
| 8 Birth trauma, as defined by trial authors Show forest plot | 1 | 2062 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.10] |
| 9 Brachial plexus injury Show forest plot | 3 | 2375 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.08, 1.47] |
| 10 Infant medical problems at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 843 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.41 [1.05, 1.89] |
| 11 Neurodevelopmental delay at age 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 920 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.74 [0.69, 4.37] |
| 12 Caesarean section Show forest plot | 3 | 2396 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.88 [1.60, 2.20] |
| 13 Short‐term maternal morbidity Show forest plot | 3 | 2396 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [1.03, 1.61] |
| 14 Woman not satisfied Show forest plot | 1 | 1596 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.64, 1.56] |
| 15 Postnatal depression at 3 months, as defined by trial authors Show forest plot | 1 | 1586 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.70, 1.24] |
| 16 Not breastfeeding at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1557 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.90, 1.21] |
| 17 Perineal pain at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.32 [0.18, 0.58] |
| 18 Abdominal pain at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.89 [1.29, 2.79] |
| 19 Backache after at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.71, 1.22] |
| 20 Any pain after at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.93, 1.29] |
| 21 Dyspareunia at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1329 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.72, 1.14] |
| 22 Urinary incontinence at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1595 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.41, 0.93] |
| 23 Flatus incontinence at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1222 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.79, 1.53] |
| 24 Faecal incontinence at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 1226 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.54 [0.18, 1.62] |
| 25 Headache at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.88, 1.25] |
| 26 Perineal pain at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.65 [0.36, 1.15] |
| 27 Back pain at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.03 [0.88, 1.20] |
| 28 Sexual problems at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.62, 1.48] |
| 29 Painful intercourse at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 830 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.48 [0.53, 4.12] |
| 30 Urinary incontinence at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.63, 1.06] |
| 31 Flatus incontinence at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.81, 1.61] |
| 32 Faecal incontinence at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.47, 2.58] |
| 33 Constipation at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.34 [1.06, 1.70] |
| 34 Haemorrhoids at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.85, 1.43] |
| 35 Subsequent birth or pregnant at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.71, 1.24] |
| 36 Subsequent caesarean section at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.24 [0.60, 2.55] |
| 37 Painful menstrual periods at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.71, 1.15] |
| 38 Heavy menstrual periods at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.78, 1.52] |
| 39 Depression at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 917 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.62, 1.29] |
| 40 Difficulty caring for child at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 873 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.72, 1.29] |
| 41 Relationship with partner unhappy at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 856 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.63, 1.66] |
| 42 Unhappy with sexual relations at 2 years Show forest plot | 1 | 702 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.51, 1.50] |
| 43 Estimated cost of intervention (in Canadian dollars) Show forest plot | 1 | 1027 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐877.0 [‐894.89, ‐859.11] |
| 43.1 Low national perinatal mortality rate | 1 | 1027 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐877.0 [‐894.89, ‐859.11] |

