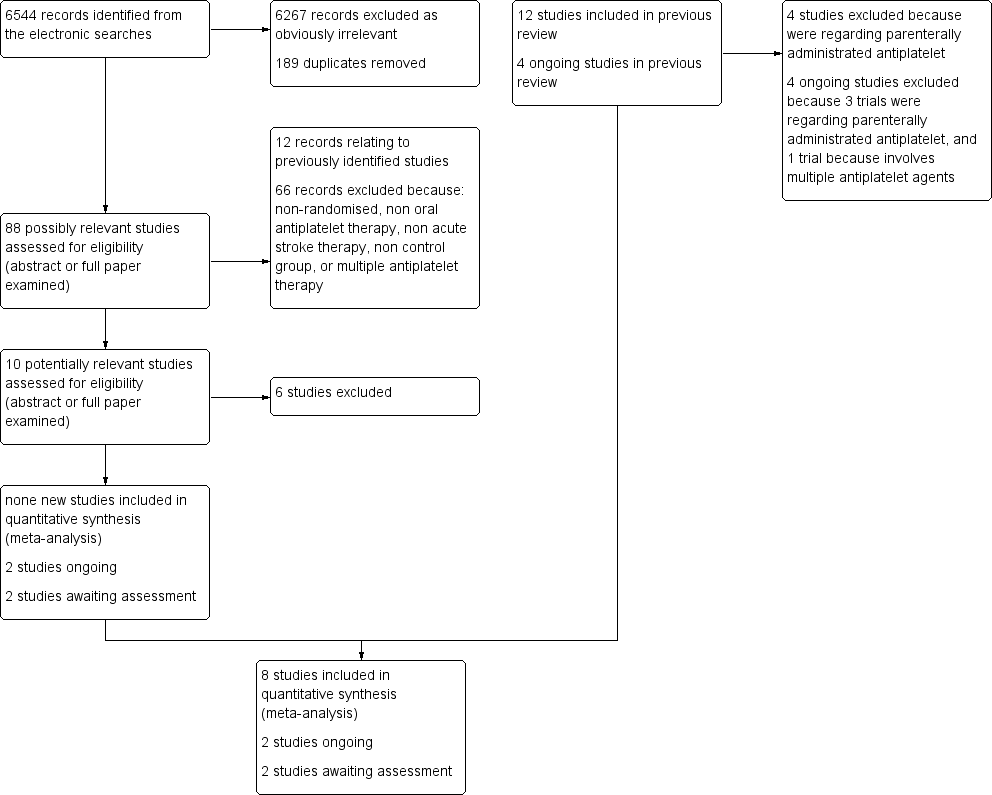
கடுமையான (acute) ஆக்சிஜன் குறைவினால்(இரத்த ஓட்ட தடை காரணமாக நிகழும்) ஏற்படும் பக்கவாதத்திற்கு வாய்வழி உட்கொள்ளும் எதிர் இரத்த வட்டு சிகிச்சை
Appendices
Appendix 1. CENTRAL search strategy
#1 [mh ^"cerebrovascular disorders"] or [mh ^"basal ganglia cerebrovascular disease"] or [mh ^"brain ischemia"] or [mh "brain infarction"] or [mh ^"hypoxia‐ischemia, brain"] or [mh ^"carotid artery diseases"] or [mh ^"carotid artery thrombosis"] or [mh ^"carotid artery, internal, dissection"] or [mh ^"intracranial arterial diseases"] or [mh ^"cerebral arterial diseases"] or [mh ^"infarction, anterior cerebral artery"] or [mh ^"infarction, middle cerebral artery"] or [mh ^"infarction, posterior cerebral artery"] or [mh "intracranial embolism and thrombosis"] or [mh stroke] or [mh ^"vertebral artery dissection"]
#2 isch*mi* near/6 (stroke* or apoplex* or cerebral next vasc* or cerebrovasc* or cva or attack*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#3 (brain or cerebr* or cerebell* or vertebrobasil* or hemispher* or intracran* or intracerebral or infratentorial or supratentorial or middle next cerebr* or mca* or "anterior circulation") near/5 (isch*mi* or infarct* or thrombo* or emboli* or occlus* or hypoxi*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#4 #1 or #2 or #3
#5 [mh "Platelet aggregation inhibitors"]
#6 [mh "Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors"] or [mh Thienopyridines] or [mh "Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors"] or [mh "Thromboxane A2"/AI] or [mh "Purinergic P2Y Receptor Antagonists"]
#7 [mh "Platelet activation"/DE]
#8 [mh "Blood platelets"/DE]
#9 antiplatelet* or anti‐platelet* or antithrombocytic or "anti‐thrombocytic":ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#10 (platelet* or thrombocyte*) near/5 (inhibit* or antagonist* or antiaggreg* or anti‐aggreg*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#11 cyclooxygenase next inhibitor* or thienopyridine* or phosphodiesterase next inhibitor*:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#12 "thromboxane A2" near/3 (inhib* or antag*):ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#13 aspirin* or "acetyl salicylic acid" or "acetylsalicylic acid":ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#14 ARC1779 or AZD6140 or alprostadil or asasantin or carnitine or cilostazol or clopidogrel or cloricromene or cv4151 or "cv‐4151" or defibrotide or dilazep or dipyridamol* or disintegrin* or ditazol or E5880 or E5510 or epoprostenol* or fluribrofen or "fut‐175" or iloprost* or indobufen or isbogrel or kbt3022 or "kbt‐3022" or ketanserin* or ketoprofen or ketorolac or levamisol* or ligustrazine* or tromethamine* or milrinone* or mopidamol* or naudicelle or nimesulide or ozagrel* or oky046 or "oky‐046" or "oky‐1581" or phthalzinol or picotamide or policosanol or prasugrel or procainamide or sarpogrelate or satigrel or sulphinpyrazone or sulfinpyrazone or suloctadil or terutroban or ticagrelor or ticlopidine or trapidil or triflusal or vorapaxar:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched)
#15 {or #5‐#14}
#16 #4 and #15
#17 cardiac or aneurysm* or angina or "atrial fibrillation" or cancer or athritis or diabetes or coronary or myocardial:ti (Word variations have been searched)
#18 #16 not #17
Appendix 2. MEDLINE search strategy
1. cerebrovascular disorders/ or basal ganglia cerebrovascular disease/ or brain ischemia/ or exp brain infarction/ or hypoxia‐ischemia, brain/ or carotid artery diseases/ or carotid artery thrombosis/ or carotid artery, internal, dissection/ or intracranial arterial diseases/ or cerebral arterial diseases/ or infarction, anterior cerebral artery/ or infarction, middle cerebral artery/ or infarction, posterior cerebral artery/ or exp "intracranial embolism and thrombosis"/ or exp stroke/ or vertebral artery dissection/
2. (isch?emi$ adj6 (stroke$ or apoplex$ or cerebral vasc$ or cerebrovasc$ or cva or attack$)).tw.
3. ((brain or cerebr$ or cerebell$ or vertebrobasil$ or hemispher$ or intracran$ or intracerebral or infratentorial or supratentorial or middle cerebr$ or mca$ or anterior circulation) adj5 (isch?emi$ or infarct$ or thrombo$ or emboli$ or occlus$ or hypoxi$)).tw.
4. 1 or 2 or 3
5. exp Platelet aggregation inhibitors/
6. exp Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors/ or exp Thienopyridines/ or exp Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors/ or Thromboxane A2/ai or exp Purinergic P2Y Receptor Antagonists/
7. exp Platelet activation/de
8. exp Blood platelets/de
9. (antiplatelet$ or anti‐platelet$ or antithrombocytic or anti‐thrombocytic).tw.
10. ((platelet$ or thrombocyte$) adj5 (inhibit$ or antagonist$ or antiaggreg$ or anti‐aggreg$)).tw.
11. (cyclooxygenase inhibitor$ or thienopyridine$ or phosphodiesterase inhibitor$).tw.
12. (thromboxane A2 adj3 (inhib$ or antag$)).tw.
13. (aspirin$ or acetyl salicylic acid$ or acetyl?salicylic acid$).tw,nm.
14. (ARC1779 or AZD6140 or alprostadil or asasantin or carnitine or cilostazol or clopidogrel or cloricromene or cv4151 or cv‐4151 or defibrotide or dilazep or dipyridamol$ or disintegrin$ or ditazol or E5880 or E5510 or epoprostenol$ or fluribrofen or fut‐175 or iloprost$ or indobufen or isbogrel or kbt3022 or kbt‐3022 or ketanserin$ or ketoprofen or ketorolac or levamisol$ or ligustrazine$ or tromethamine$ or milrinone$ or mopidamol$ or naudicelle or nimesulide or ozagrel$ or oky046 or oky‐046 or oky‐1581 or phthalzinol or picotamide or policosanol or prasugrel or procainamide or sarpogrelate or satigrel or sulphinpyrazone or sulfinpyrazone or suloctadil or terutroban or ticagrelor or ticlopidine or trapidil or triflusal or vorapaxar).tw,nm.
15. or/5‐14
16. Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic/
17. random allocation/
18. Controlled Clinical Trials as Topic/
19. control groups/
20. clinical trials as topic/ or clinical trials, phase i as topic/ or clinical trials, phase ii as topic/ or clinical trials, phase iii as topic/ or clinical trials, phase iv as topic/
21. double‐blind method/
22. single‐blind method/
23. Placebos/
24. placebo effect/
25. Therapies, Investigational/
26. Drug Evaluation/
27. Research Design/
28. randomized controlled trial.pt.
29. controlled clinical trial.pt.
30. (clinical trial or clinical trial phase i or clinical trial phase ii or clinical trial phase iii or clinical trial phase iv).pt.
31. (random$ or RCT or RCTs).tw.
32. (controlled adj5 (trial$ or stud$)).tw.
33. (clinical$ adj5 trial$).tw.
34. ((control or treatment or experiment$ or intervention) adj5 (group$ or subject$ or patient$)).tw.
35. (quasi‐random$ or quasi random$ or pseudo‐random$ or pseudo random$).tw.
36. ((control or experiment$ or conservative) adj5 (treatment or therapy or procedure or manage$)).tw.
37. ((singl$ or doubl$ or tripl$ or trebl$) adj5 (blind$ or mask$)).tw.
38. (placebo$ or sham).tw.
39. trial.ti.
40. (assign$ or allocate$).tw.
41. or/16‐40
42. 4 and 15 and 41
43. exp animals/ not humans.sh.
44. 42 not 43
Appendix 3. EMBASE search strategy
1. cerebrovascular disease/ or brain infarction/ or brain stem infarction/ or cerebellum infarction/ or exp brain ischemia/ or carotid artery disease/ or exp carotid artery obstruction/ or cerebral artery disease/ or exp cerebrovascular accident/ or exp occlusive cerebrovascular disease/ or stroke patient/
2. (isch?emi$ adj6 (stroke$ or apoplex$ or cerebral vasc$ or cerebrovasc$ or cva or attack$)).tw.
3. ((brain or cerebr$ or cerebell$ or vertebrobasil$ or hemispher$ or intracran$ or intracerebral or infratentorial or supratentorial or middle cerebr$ or mca$ or anterior circulation) adj5 (isch?emi$ or infarct$ or thrombo$ or emboli$ or occlus$ or hypoxi$)).tw.
4. 1 or 2 or 3
5. exp Antithrombocytic agent/
6. thienopyridine derivative/ or exp phosphodiesterase inhibitor/ or thromboxane A2 receptor blocking agent/ or exp purinergic receptor blocking agent/
7. (antiplatelet$ or anti‐platelet$ or antithrombocytic or anti‐thrombocytic).tw.
8. ((platelet$ or thrombocyte$) adj5 (inhibit$ or antagonist$ or antiaggreg$ or anti‐aggreg$)).tw.
9. (cyclooxygenase inhibitor$ or thienopyridine$ or phosphodiesterase inhibitor$).tw.
10. (thromboxane A2 adj3 (inhib$ or antag$)).tw.
11. (aspirin$ or acetyl salicylic acid$ or acetyl?salicylic acid$).tw.
12. (ARC1779 or AZD6140 or alprostadil or asasantin or carnitine or cilostazol or clopidogrel or cloricromene or cv4151 or cv‐4151 or defibrotide or dilazep or dipyridamol$ or disintegrin$ or ditazol or E5880 or E5510 or epoprostenol$ or fluribrofen or fut‐175 or iloprost$ or indobufen or isbogrel or kbt3022 or kbt‐3022 or ketanserin$ or ketoprofen or ketorolac or levamisol$ or ligustrazine$ or tromethamine$ or milrinone$ or mopidamol$ or naudicelle or nimesulide or ozagrel$ or oky046 or oky‐046 or oky‐1581 or phthalzinol or picotamide or policosanol or prasugrel or procainamide or sarpogrelate or satigrel or sulphinpyrazone or sulfinpyrazone or suloctadil or terutroban or ticagrelor or ticlopidine or trapidil or triflusal or vorapaxar).tw.
13. or/5‐12
14. Randomized Controlled Trial/
15. Randomization/
16. Controlled Study/
17. control group/
18. clinical trial/ or phase 1 clinical trial/ or phase 2 clinical trial/ or phase 3 clinical trial/ or phase 4 clinical trial/ or controlled clinical trial/
19. Double Blind Procedure/
20. Single Blind Procedure/ or triple blind procedure/
21. placebo/
22. drug comparison/ or drug dose comparison/
23. "types of study"/
24. random$.tw.
25. (controlled adj5 (trial$ or stud$)).tw.
26. (clinical$ adj5 trial$).tw.
27. ((control or treatment or experiment$ or intervention) adj5 (group$ or subject$ or patient$)).tw.
28. (quasi‐random$ or quasi random$ or pseudo‐random$ or pseudo random$).tw.
29. ((control or experiment$ or conservative) adj5 (treatment or therapy or procedure or manage$)).tw.
30. ((singl$ or doubl$ or tripl$ or trebl$) adj5 (blind$ or mask$)).tw.
31. (placebo$ or sham).tw.
32. trial.ti.
33. (assign$ or allocat$).tw.
34. (RCT or RCTs).tw.
35. or/14‐34
36. 4 and 13 and 35
37. exp animals/ or exp invertebrate/ or animal experiment/ or animal model/ or animal tissue/ or animal cell/ or nonhuman/
38. human/ or normal human/ or human cell/
39. 37 not 38
40. 36 not 39
41. (cardiac or aneurysm$ or angina or atrial fibrillation or cancer or athritis or diabetes or coronary or myocardial).ti.
42. 40 not 41
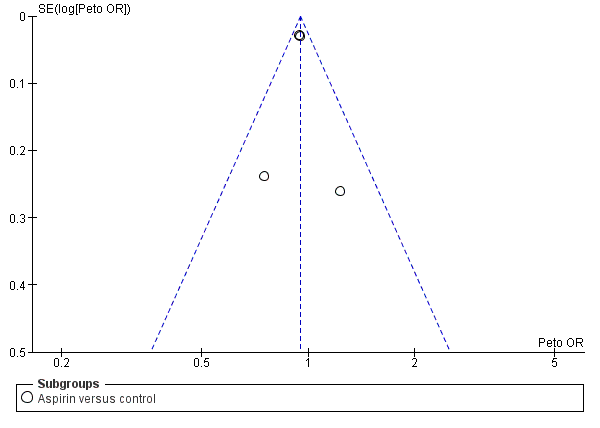
Funnel plot of comparison: 1 Antiplatelet agent versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, outcome: 1.1 Death or dependence at end of follow‐up.

Funnel plot of comparison: 1 Antiplatelet agent versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, outcome: 1.2 Deaths from all causes during treatment period.
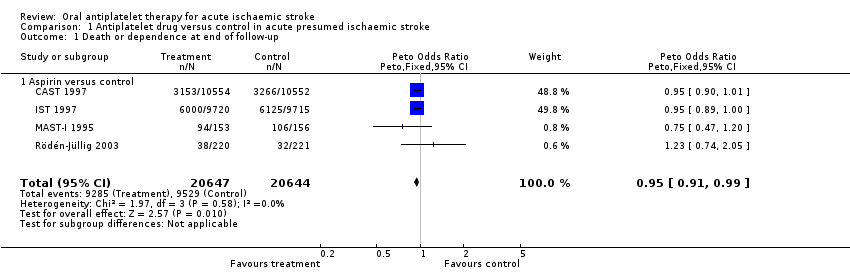
Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 1 Death or dependence at end of follow‐up.

Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 2 Deaths from all causes during treatment period.

Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 3 Deaths from all causes during follow‐up.

Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 4 Deep venous thrombosis during treatment period.
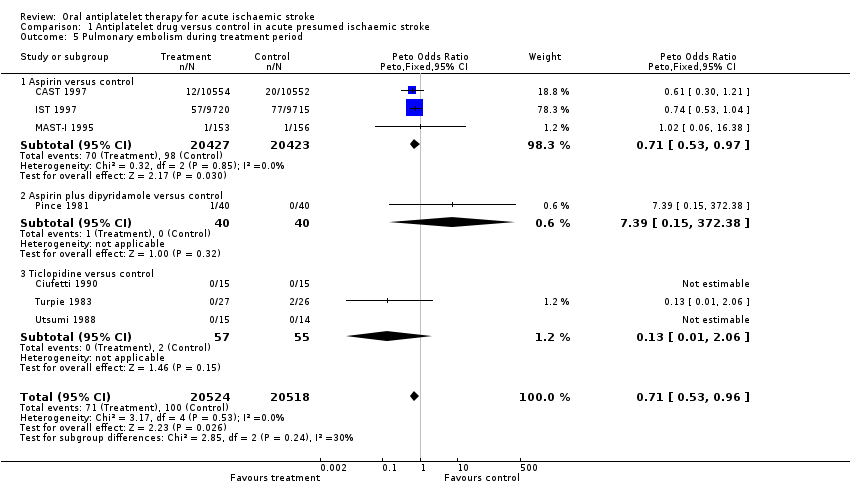
Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 5 Pulmonary embolism during treatment period.

Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 6 Recurrent ischaemic/unknown stroke during treatment period.
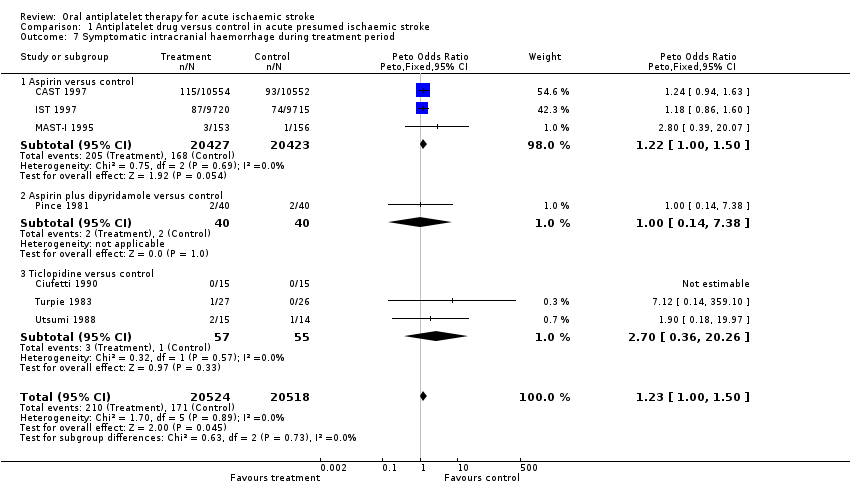
Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 7 Symptomatic intracranial haemorrhage during treatment period.

Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 8 Any recurrent stroke/intracranial haemorrhage during treatment period.

Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 9 Major extracranial haemorrhage during treatment period.
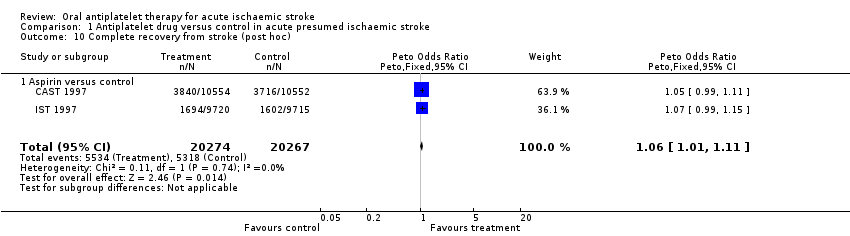
Comparison 1 Antiplatelet drug versus control in acute presumed ischaemic stroke, Outcome 10 Complete recovery from stroke (post hoc).
| Outcome | Control event rate | No of events avoided | NNTB or NNTH |
| Per 1000 people treated (95% CI) | Data are number needed to treat to benefit (NNTB) (95% CI) unless otherwise indicated. NNTH = number needed to treat to harm | ||
| Estimated from the average of the control event rate in the 2 largest trials (CAST 1997 and IST 1997) | Estimated by applying the odds ratio for the outcome for studies of aspirin. Calculator is available at: http://www.dcn.ed.ac.uk/csrg/entity/entity_NNT2.asp | Estimated by applying the odds ratio for the outcome for studies of aspirin. Calculator is available at: http://www.dcn.ed.ac.uk/csrg/entity/entity_NNT2.asp | |
| Death or dependence at end of follow‐up | 0.47 | 13 (3 to 23) | 79 (43 to 400) |
| Deaths from all causes during follow‐up | 0.13 | 9 (2 to 15) | 108 (66 to 436) |
| Pulmonary embolism during treatment period | 0.01 | 1 (0 to 2) | 693 (427 to 6700) |
| Recurrent ischaemic/unknown stroke during treatment period | 0.03 | 7 (4 to 10) | 140 (104 to 248) |
| Symptomatic intracranial haemorrhage during treatment period | 0.01 | ‐2 (i.e. 2 extra) (‐4 to 0) | NNTH 574 (254 to 126 010) |
| Any recurrent stroke/intracranial haemorrhage during treatment | 0.04 | 5 (1 to 8) | 200 (123 to 868) |
| Major extracranial haemorrhage during treatment period | 0.01 | ‐4 (i.e. 4 extra) (‐7 to ‐2) | NNTH 245 (153 to 481) |
| Complete recovery from stroke (post hoc) | 0.26 | 11 (2 to 21) | 89 (49 to 523) |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Death or dependence at end of follow‐up Show forest plot | 4 | 41291 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.91, 0.99] |
| 1.1 Aspirin versus control | 4 | 41291 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.91, 0.99] |
| 2 Deaths from all causes during treatment period Show forest plot | 8 | 41483 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.85, 1.00] |
| 2.1 Aspirin versus control | 4 | 41291 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.85, 1.00] |
| 2.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.47 [0.43, 4.99] |
| 2.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.12 [0.01, 1.20] |
| 3 Deaths from all causes during follow‐up Show forest plot | 8 | 41483 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.87, 0.98] |
| 3.1 Aspirin versus control | 4 | 41291 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.87, 0.98] |
| 3.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.47 [0.43, 4.99] |
| 3.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.12 [0.02, 0.88] |
| 4 Deep venous thrombosis during treatment period Show forest plot | 2 | 133 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.36, 1.67] |
| 4.1 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.13, 0.95] |
| 4.2 Ticlopidine versus control | 1 | 53 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.37 [0.72, 7.73] |
| 5 Pulmonary embolism during treatment period Show forest plot | 7 | 41042 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.71 [0.53, 0.96] |
| 5.1 Aspirin versus control | 3 | 40850 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.71 [0.53, 0.97] |
| 5.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.39 [0.15, 372.38] |
| 5.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.13 [0.01, 2.06] |
| 6 Recurrent ischaemic/unknown stroke during treatment period Show forest plot | 7 | 41042 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.69, 0.87] |
| 6.1 Aspirin versus control | 3 | 40850 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.69, 0.87] |
| 6.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 7 Symptomatic intracranial haemorrhage during treatment period Show forest plot | 7 | 41042 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.23 [1.00, 1.50] |
| 7.1 Aspirin versus control | 3 | 40850 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.22 [1.00, 1.50] |
| 7.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.14, 7.38] |
| 7.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.70 [0.36, 20.26] |
| 8 Any recurrent stroke/intracranial haemorrhage during treatment period Show forest plot | 7 | 41042 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.79, 0.97] |
| 8.1 Aspirin versus control | 3 | 40850 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.79, 0.97] |
| 8.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.14, 7.38] |
| 8.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.70 [0.36, 20.26] |
| 9 Major extracranial haemorrhage during treatment period Show forest plot | 7 | 41042 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.69 [1.35, 2.11] |
| 9.1 Aspirin versus control | 3 | 40850 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.69 [1.35, 2.11] |
| 9.2 Aspirin plus dipyridamole versus control | 1 | 80 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 9.3 Ticlopidine versus control | 3 | 112 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10 Complete recovery from stroke (post hoc) Show forest plot | 2 | 40541 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [1.01, 1.11] |
| 10.1 Aspirin versus control | 2 | 40541 | Peto Odds Ratio (Peto, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [1.01, 1.11] |