Tests to assist in the staging of cutaneous melanoma: a generic protocol
Appendices
Appendix 1. Current content and structure of the Programme Grant
| LIST OF REVIEWS | Estimated number of studies | |
| Diagnosis of melanoma | ||
| 1 | Visual inspection | 50 |
| 2 | Dermoscopy | 88 |
| 3 | Teledermatology | 15 |
| 4 | Mobile phone applications | 2 |
| 5a | Computer‐aided diagnosis – dermoscopy‐based techniques | 37 |
| 5b | Computer‐aided diagnosis – spectroscopy‐based techniques | This review will be amalgamated into 5a |
| 6 | Reflectance confocal microscopy | 19 |
| 7 | High frequency ultrasound | 5 |
| 8 | Overview: Comparing the accuracy of tests for which sufficient evidence is identified either alone or in combination | Number not estimable |
| Diagnosis of keratinocyte skin cancer (BCC and cSCC) | ||
| 9 | Visual inspection +/‐ Dermoscopy | 22 |
| 10a | Computer‐aided diagnosis – dermoscopy‐based techniques | 3 |
| 10b | Computer‐aided diagnosis – spectroscopy‐based techniques | This review will be amalgamated into 10a |
| 11 | Optical coherence tomography | 5 |
| 12 | Reflectance confocal microscopy | 9 |
| 13 | Exfoliative cytology | 9 |
| 14 | Overview: Comparing the accuracy of tests for which sufficient evidence is identified either alone or in combination | Number not estimable |
| Staging of melanoma | ||
| 15 | Ultrasound | 25 ‐ 30 |
| 16 | CT | 5 ‐ 10 |
| 17 | PET or PET‐CT | 20 ‐ 25 |
| 18 | MRI | 5 |
| 19 | Sentinel lymph node biopsy +/‐ high frequency ultrasound | 70 |
| 20 | Overview: Comparing the accuracy of tests for which sufficient evidence is identified either alone or in combination | Number not estimable |
| Staging of cSCC | ||
| 21 | Imaging tests review | 10 ‐ 15 |
| 22 | Sentinel lymph node biopsy +/‐ high frequency ultrasound | 15 ‐ 20 |
Appendix 2. MEDLINE (OVID) search strategy
Database: Ovid MEDLINE(R) <1946 to August 2016 (as run on 28 August 2016) FINAL
Amended Search Strategy:
1 exp melanoma/
2 exp skin cancer/
3 exp basal cell carcinoma/
4 exp Neoplasms, basal cell/
5 basalioma$1.ti,ab.
6 ((basal cell or skin) adj2 (cancer$ or carcinoma$1 or mass or masses or tumour$ or tumor$ or neoplasm$1 or adenoma$1 or epithelioma$1 or lesion$1 or malignan$ or nodule$1)).ti,ab.
7 (pigmented adj2 (lesion$1 or mole$ or nevus or nevi or naevus or naevi or skin)).ti,ab.
8 (melanom$ or nonmelanoma$ or non‐melanoma$ or melanocyt$ or non‐melanocyt$ or nonmelanocyt$ or keratinocyt$).ti,ab.
9 nmsc.ti,ab.
10 rodent ulcer$.ti,ab.
11 (squamous cell adj2 (cancer$ or carcinoma$1 or mass or masses or tumor$1 or tumour$1 or neoplasm$1 or adenoma$1 or epithelioma$1 or epithelial or lesion$1 or malignan$ or nodule$1) adj2 (skin or epiderm$ or cutaneous)).ti,ab.
12 (BCC or CSCC or NMSC).ti,ab.
13 keratinocy$.ti,ab.
14 Keratinocytes/
15 or/1‐14 (253324)
16 dermoscop$.ti,ab.
17 dermatoscop$.ti,ab.
18 photomicrograph$.ti,ab.
19 exp epiluminescence microscopy/
20 Microscopy, Confocal/
21 (epiluminescence adj2 microscop$).ti,ab.
22 (confocal adj2 microscop$).ti,ab.
23 Tomography, Optical Coherence/
24 Dielectric Spectroscopy/
25 Cytodiagnosis/
26 (incident light adj2 microscop$).ti,ab.
27 (surface adj2 microscop$).ti,ab.
28 (visual adj (inspect$ or examin$)).ti,ab.
29 ((clinical or physical) adj examin$).ti,ab.
30 3 point.ti,ab.
31 three point.ti,ab.
32 pattern analys$.ti,ab.
33 ABCD$.ti,ab.
34 menzies.ti,ab.
35 7 point.ti,ab.
36 seven point.ti,ab.
37 (digital adj2 (dermoscop$ or dermatoscop$)).ti,ab.
38 artificial intelligence.ti,ab.
39 AI.ti,ab.
40 computer assisted.ti,ab.
41 computer aided.ti,ab.
42 neural network$.ti,ab
43 exp diagnosis, computer‐assisted/
44 MoleMax.ti,ab.
45 image process$.ti,ab.
46 automatic classif$.ti,ab.
47 image analysis.ti,ab.
48 SIAscop$.ti,ab.
49 Aura.ti,ab.
50 (optical adj2 scan$).ti,ab.
51 MelaFind.ti,ab.
52 SIMSYS.ti,ab.
53 MoleMate.ti,ab.
54 SolarScan.ti,ab.
55 VivaScope.ti,ab.
56 (high adj3 ultraso$).ti,ab.
57 (canine adj2 detect$).ti,ab.
58 ((mobile or cell or cellular or smart) adj ((phone$1 adj2 app$1) or application$1)).ti,ab.
59 smartphone$.ti,ab.
60 (DermoScan or SkinVision or DermLink or SpotCheck).ti,ab.
61 Mole Detective.ti,ab.
62 Spot Check.ti,ab.
63 (mole$1 adj2 map$).ti,ab.
64 (total adj2 body).ti,ab.
65 exfoliative cytolog$.ti,ab.
66 digital analys$.ti,ab.
67 (imag$ adj3 software).ti,ab.
68 (teledermatolog$ or tele‐dermatolog$ or telederm or tele‐derm or teledermoscop$ or tele‐dermoscop$ or teledermatoscop$ or tele‐dermatoscop$).ti,ab.
69 (optical coherence adj (technolog$ or tomog$)).ti,ab.
70 OCT.ti,ab.
71 (computer adj2 diagnos$).ti,ab.
72 exp sentinel lymph node biopsy/)
73 (sentinel adj2 node).ti,ab.
74 nevisense.mp. or HFUS.ti,ab.
75 electrical impedance spectroscopy.ti,ab.
76 history taking.ti,ab
77 patient history.ti,ab.
78 (naked eye adj (exam$ or assess$)).ti,ab.
79 (skin adj exam$).ti,ab.
80 physical examination/
81 ugly duckling.mp. or UD.ti,ab.
82 ((physician$ or clinical or physical) adj (exam$ or triage or recog$)).ti,ab.
83 ABCDE.mp. or VOC.ti,ab.
84 clinical accuracy.ti,ab.
85 Family Practice/ or Physicians, Family/ or clinical competence/
86 (confocal adj2 microscop$).ti,ab.
87 diagnostic algorithm$1.ti,ab.
88 checklist$.ti,ab.
89 virtual imag$.ti,ab.
90 volatile organic compound$1.ti,ab.
91 dog$1.ti,ab.
92 gene expression analy$.ti,ab.
93 reflex transmission imag$.ti,ab
94 thermal imaging.ti,ab.
95 elastography.ti,ab.
96 or/16‐95 (849678)
97 (CT or PET).ti,ab.
98 PET‐CT.ti,ab.
99 (FDG or F18 or Fluorodeoxyglucose or radiopharmaceutical$).ti,ab.
100 exp Deoxyglucose/
101 deoxy‐glucose.ti,ab.
102 deoxyglucose.ti,ab.
103 CATSCAN.ti,ab. 104 exp Tomography, Emission‐Computed/
105 exp Tomography, X‐ray computed/
106 positron emission tomograph$.ti,ab.
107 exp magnetic resonance imaging/
108 (MRI or fMRI or NMRI or scintigraph$).ti,ab.
109 exp echography/
110 Doppler echography.ti,ab.
111 sonograph$.ti,ab.
112 ultraso$.ti,ab.
113 doppler.ti,ab)
114 magnetic resonance imag$.ti,ab.
115 or/97‐114 (1337432)
116 (stage$ or staging or metasta$ or recurr$ or advanced or sensitivity or specificity or false negative$ or thickness$).ti,ab.
117 "Sensitivity and Specificity"/
118 exp cancer staging/
119 or/116‐118 (2164365)
120 115 and 119
121 96 or 120
122 15 and 121 (18542)
Appendix 3. Full‐text exclusion criteria
| The study: | Response (enter X if any of the exclusion criteria are met) |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
cSCC: cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
SLNB: sentinel lymph node biopsy.
US: ultrasound.
CT: computed tomography.
PET: positron emission tomography.
PET‐CT: positron emission tomography‐computed tomography.
MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.
Appendix 4. QUADAS interpretation
| Item | Response (delete as required) |
| PARTICIPANT SELECTION (1) ‐ RISK OF BIAS | |
| 1) Was a consecutive or random sample of participants or images enrolled? | Yes ‐ if paper states consecutive or random No – if paper describes other method of sampling Unclear – if participant sampling not described |
| 2) Was a case‐control design avoided? | Yes ‐ if consecutive or random or case‐control design clearly not used No – if study described as case‐control or describes sampling specific numbers of participants with particular diagnoses Unclear – if not described |
| 3) Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions, e.g. needs examples of inappropriate exclusions in this context – for both melanoma and for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) staging? | Yes ‐ if inappropriate exclusions were avoided No – if lesions were excluded that might affect test accuracy, e.g. indeterminate results or where disagreement between evaluators was observed Unclear – if not clearly reported |
| 4) For between‐person comparative (BPC) studies only (i.e. allocating different tests to different study participants such as randomised controlled trials (RCTs)): | |
|
| Yes ‐ if same selection criteria were used for each index test No – if different selection criteria were used for each index test Unclear – if selection criteria per test were not described N/A – if only one index test was evaluated or all participants received all tests |
|
| Yes ‐ if adequate randomisation procedures are described No – if inadequate randomisation procedures are described Unclear – if the method of allocation to groups is not described (a description of ‘random’ or ‘randomised’ is insufficient) N/A – if only one index test was evaluated or all participants received all tests |
|
| Yes ‐ if appropriate methods of allocation concealment are described No – if appropriate methods of allocation concealment are not described Unclear – if the method of allocation concealment is not described (sufficient detail to allow a definite judgement is required) N/A – if only one index test was evaluated |
| Could the selection of participants have introduced bias? | |
| v FOR NON‐COMPARATIVE (NC) STUDIES | |
| If answers to all of questions 1) and 2) and 3) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk Unclear |
| v FOR BETWEEN‐PERSON COMPARATIVE STUDIES | |
| If answers to all of questions 1) and 2) and 3) and 4) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) or 4) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) or 4) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk Unclear |
| PARTICIPANT SELECTION (1) ‐ CONCERNS REGARDING APPLICABILITY | |
| For sentinel lymph node biopsy and imaging tests: | |
| 1) Does the study report results for participants unselected by stage of disease or site of primary lesion, i.e. the study does not focus solely on those with a particular stage of disease such as AJCC I or melanoma <=1 mm in thickness? | Yes ‐ if an unrestricted group of participants have been included No ‐ if a selected group of study participants have been included, e.g. those with clinical stage I disease or only those with thin melanoma Unclear – if insufficient details are provided to determine the spectrum of included participants |
| 2) Did the study report data on a per‐patient rather than per‐lesion basis? | Yes – if a per‐patient analysis was reported No – if a per‐lesion analysis only was reported Unclear – if it is not possible to assess whether data are presented on a per‐patient or per‐lesion basis |
| For imaging tests only: | |
| 3) Does the study focus primarily on participants undergoing primary staging or those undergoing staging for disease recurrence? | Yes ‐ if at least 80% of study participants are undergoing primary staging following diagnosis of a primary cutaneous melanoma or staging of recurrence No ‐ if less than 80% of study participants are undergoing primary staging following diagnosis of a cutaneous melanoma or staging of recurrence Unclear – if insufficient details are provided to determine the proportion of patients undergoing primary staging versus those undergoing staging of recurrence |
| Is there concern that the included participants do not match the review question? | |
| If the answer to question 1) or 2) (and 3)) was ‘Yes’: | Concern is Low |
| If the answer to question 1) or 2) (and 3)) was ‘No’: | Concern is High |
| If the answer to question 1) or 2) (and 3)) was ‘Unclear’: | Concern is Unclear |
| INDEX TEST (2) ‐ RISK OF BIAS (to be completed per test evaluated) | |
| 1) Was the index test or testing strategy result interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | Yes ‐ if index test described as interpreted without knowledge of reference standard result, or for prospective studies, if index test is always conducted and interpreted prior to the reference standard No – if index test described as interpreted in knowledge of reference standard result Unclear – if index test blinding is not described |
| 2) Was the diagnostic threshold at which the test was considered positive prespecified? | Yes ‐ if threshold was prespecified (i.e. prior to analysing study results) No ‐ if threshold was not prespecified Unclear ‐ if not possible to tell whether or not diagnostic threshold was prespecified |
| For imaging tests only: | |
| 3) For studies reporting the accuracy of multiple diagnostic thresholds (tumour characteristic or parameter) for the same index test, was each threshold interpreted without knowledge of the results of the others? | Yes ‐ if thresholds were selected prospectively and each was interpreted by a different reader, or if study implements a retrospective (or no) cutoff No ‐ if study uses prospective threshold and report states reported by same reader Unclear ‐ if no mention of number of readers for each threshold or if pre‐specification of threshold not reported N/A ‐ multiple diagnostic thresholds not reported for the same index test |
| 4) For within‐person comparisons (WPC) of index tests or testing strategies (i.e. > 1 index test applied per participant), was each index test result interpreted without knowledge of the results of other index tests or testing strategies? | Yes ‐ if all index tests were described as interpreted without knowledge of the results of the others No ‐ if the index tests were described as interpreted in the knowledge of the results of the others Unclear – if it is not possible to tell whether knowledge of other index tests could have influenced test interpretation N/A – if only one index test was evaluated |
| Could the conduct or interpretation of the index test have introduced bias? | |
| v FOR NC and BPC STUDIES item 3) / 4) to be added | |
| If answers to questions 1) and 2) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to either questions 1) or 2) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to either questions 1) or 2) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk is Unclear |
| v FOR WPC STUDIES | |
| If answers to all questions 1), 2) for any index test and 3) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) for any index test or 3) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) for any index test or 3) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk is Unclear |
| INDEX TEST (2) ‐ CONCERN ABOUT APPLICABILITY | |
| 1) Were thresholds or criteria for diagnosis reported in sufficient detail to allow replication? This item applies equally to studies using objective and more subjective approaches to test interpretation. For SLNB studies, this requires description of the tracer threshold for identification of the SLN and the histological assessment. | Yes – if the criteria for diagnosis of the target disorder were reported in sufficient detail to allow replication No – if the criteria for diagnosis of the target disorder were not reported in sufficient detail to allow replication Unclear – if some but not sufficient information on criteria for diagnosis to allow replication were provided |
| 2) Was the test interpretation carried out by an experienced examiner? | Yes – if the test was interpreted by an experienced examiner as defined in the review protocol No – if the test was not interpreted by an experienced examiner (see above) Unclear – if the experience of the examiner(s) was not reported in sufficient detail to judge or if examiners described as 'Expert' with no further detail given |
| Is there concern that the index test, its conduct, or interpretation differ from the review question? | |
| If answers to questions 1) and 2) was ‘Yes’: | Concern is Low |
| If answers to questions 1) or 2) was ‘No’: | Concern is High |
| If answers to questions 1) or 2) was ‘Unclear’: | Concern is Unclear |
| REFERENCE STANDARD (3) ‐ RISK OF BIAS | |
| 1) Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | |
| a) DISEASE POSITIVE ‐ One or more of: ‐ Histological confirmation of metastases following lymph node dissection (or SLNB or core biopsy for imaging studies) ‐ Clinical/radiological follow up to identify clinically detectable disease in a mapped nodal basin (SLNB studies) ‐ Clinical/radiological follow up to identify any metastases (imaging studies) subsequently confirmed on histology | Yes – if all disease positive participants underwent one of the listed reference standards No – if a final diagnosis for any disease positive participant was reached without histopathology Unclear – if the method of final diagnosis was not reported for any disease positive participant |
| b) DISEASE NEGATIVE ‐ One or more of: ‐ Histological confirmation of absence of disease in a mapped nodal basin following lymph node dissection (or following SLNB for imaging studies) ‐ Clinical/radiological follow up of test negative participants | Yes – if at least 90% of disease negative participants underwent one of the listed reference standards No – if more than 10% of benign diagnoses were reached by concurrent imaging test Unclear – if the method of final diagnosis was not reported for any participant with benign or disease negative diagnosis |
| 2) Were the histology‐based reference standard results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes – if the histopathologist was described as blinded to the index test result No – if the histopathologist was described as having knowledge of the index test result Unclear – if blinded histology interpretation was not clearly reported |
| 3) Were the reference standard results based on patient follow‐up interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test? | Yes – if the clinician or radiologist was described as blinded to the index test result No – if the clinician or radiologist was described as having knowledge of the index test result Unclear – if blinded interpretation was not clearly reported |
| Could the reference standard, its conduct, or its interpretation have introduced bias? | |
| If answers to questions 1) and 2) and 3) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk is Unclear |
| REFERENCE STANDARD (3) ‐ CONCERN ABOUT APPLICABILITY | |
| 1) Does the study use the same definition of disease positive as the primary review question or is it possible to fully disaggregate data such that data matching the review question can be extracted? | Yes – same definition of disease positive used, or patients can be disaggregated and regrouped according to review definition No – some patients cannot be disaggregated For SLNB review – disease positive includes participants with any nodal recurrence (not restricted to clinical recurrence in same nodal basin) For imaging reviews – participants with nodal versus distant recurrences cannot be disaggregated Unclear – definition of disease positive not clearly reported |
| For studies of imaging tests: | |
| 2) The result of another imaging test (without patient follow‐up to determine later emergence of disease) was not used as a reference standard | Yes – if imaging‐based diagnosis was not used as a reference standard for any participant No – if imaging‐based diagnosis was used as a reference standard for any participant Unclear – if not clearly reported |
| 3) Item on observer experience could be included? Is there concern that the target condition as defined by the reference standard does not match the review question? | |
| If answers to all questions 1), 2) and 3) was ‘Yes’: | Concern is Low |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘No’: | Concern is High |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘Unclear’: | Concern is Unclear |
| ***For teledermatology studies only: | |
| If answers to questions 1) and 3) was ‘Yes’: | Concern is Low |
| If answers to questions 1) or 3) was ‘No’: | Concern is High |
| If answers to questions 1) or 3) was ‘Unclear’: | Concern is Unclear |
| FLOW AND TIMING (4): RISK OF BIAS | |
| 1) Was there an appropriate interval between index test and reference standard? | |
|
| Yes – if study reports <= 1 month between index and histological reference standard No – if study reports > 1 month between index and histological reference standard Unclear – if study does not report interval between index and histological reference standard |
|
| Yes – if study reports a follow‐up visit within 6 months of application of the index test No – if study reports the first follow‐up visit beyond 6 months of the index test Unclear – if study does not report timing of follow‐up visits |
| 2) Did all participants receive the same reference standard? | Yes – if all participants underwent the same reference standard No – if more than one reference standard was used Unclear – if not clearly reported |
| 3) Were all participants included in the analysis? | Yes – if all participants were included in the analysis No – if some participants were excluded from the analysis Unclear – if not clearly reported |
| 4) For WITHIN‐PERSON COMPARISONS (WPC) of index tests: Was the interval between application of index tests <= 1 month? Could the participant flow have introduced bias? | Yes – if study reports <= 1 month between index tests No – if study reports > 1 month between index tests Unclear – if study does not report interval between index tests |
| v FOR NON‐COMPARATIVE and BPC STUDIES | |
| If answers to questions 1) and 2) and 3) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to any one of questions 1) or 2) or 3) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk is Unclear |
| v FOR WITHIN‐PERSON COMPARATIVE STUDIES (WPC) | |
| If answers to all questions 1), 2), 3), and 4) was ‘Yes’: | Risk is Low |
| If answers to any one of questions 1), 2), 3), or 4) was ‘No’: | Risk is High |
| If answers to any one of questions 1), 2), 3), or 4) was ‘Unclear’: | Risk is Unclear |
Appendix 5. Calculation of diagnostic accuracy statistics
i) Contingency table (2x2 table)
Reference standard
| +ve Diseased | ‐ve Nondiseased | ||
| Index test result + ve | True positives a | b False positives | Total test positive |
| ‐ ve | False negatives c | d True negatives | Total test negative |
| Total diseased | Total nondiseased |
ii) Diagnostic accuracy indices
| Sensitivity | Proportion of diseased who have positive test results | True positives / total diseased a / (a + c) |
| Specificity | Proportion of nondiseased who have negative test results | True negatives / total nondiseased d / (b + d) |
| Positive predictive value (PPV) | Proportion with positive test result who actually have the disease | True positives / total test positive a / (a + b) |
| Negative predictive value (NPV) | Proportion with negative test result who really do not have the disease | True negatives / total test negative d / (c + d) |
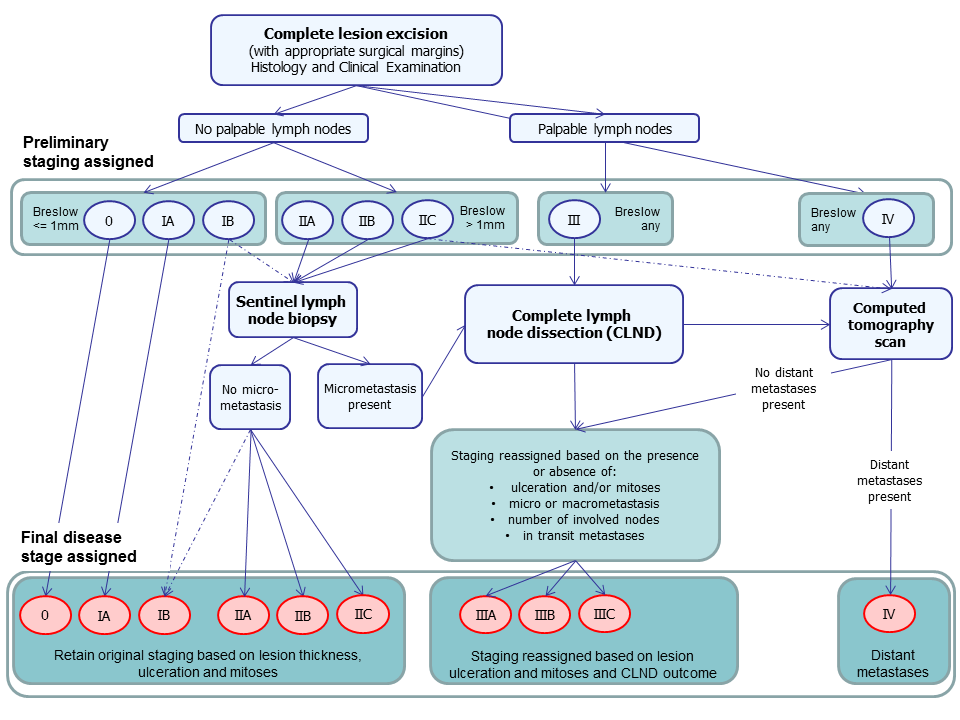
Summary of NICE guideline recommendations for the management of cutaneous melanoma following primary diagnosis (NICE guidance 2015)
| Term | Definition |
| Adjuvant therapy or treatment | A treatment given after the main treatment for cancer to reduce the risk of recurrence. |
| Adverse event | Detrimental change in health occurring in a person receiving the treatment whether or not it has been caused by the treatment. |
| Axillary | In the armpit. |
| Biopsy | Removal of a sample of tissue from the body to assist in diagnosis or inform the choice of treatment of a disease. |
| BRAF V600 mutation | BRAF is a human gene that makes a protein called B‐Raf which is involved in the control of cell growth. BRAF mutations (damaged DNA) occur in around 40% of melanomas, which can then be treated with particular drugs. |
| BRAF inhibitors | Therapeutic agents which inhibit the serine‐threonine protein kinase BRAF mutated metastatic melanoma. |
| Breslow thickness | A scale for measuring the thickness of melanomas by the pathologist using a microscope, measured in mm from the top layer of skin to the bottom of the tumour. |
| Cervical (lymph nodes) | Lymph nodes found in the neck area of the body. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | Imaging technique in which the person lies on a table within an x‐ray gantry. The images are acquired using a spiral (helical) path and banks of detectors, allowing presentation of the internal organs and blood vessels in different projections including 3‐D views. |
| Coronal | Frontal plane dividing the body into front and back. |
| False negative | An individual who is truly positive for a disease, but whom a diagnostic test classifies them as disease‐free. |
| False positive | An individual who is truly disease‐free, but whom a diagnostic test classifies them as having the disease. |
| Histopathology | The study of tissue, usually obtained by biopsy or excision, for example under a microscope. |
| Incidence | The number of new cases of a disease in a given time period. |
| Inguinal | Lymph nodes in or just above or just below the groin. |
| Isolated limb perfusion | A medical procedure that directly delivers a drug through the bloodstream in a limb to the site affected by melanoma. |
| Local recurrence | Regrowth of a tumour in the area from which it was originally removed. |
| Locoregional recurrence | Regrowth of a tumour in the area from which it was originally removed or in the regional lymph nodes (usually nearest to the original tumour site). |
| Lymph node | Lymph nodes filter the lymphatic fluid (clear fluid containing white blood cells) that travels around the body to help fight disease; they are located throughout the body often in clusters (nodal basins). |
| Lymph node dissection | Surgical removal or one or more lymph nodes in the absence of proven involvement with melanoma. |
| Lymphadenectomy | Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is a surgical operation to remove one or more groups of lymph nodes. |
| Lymphoscintigraphy | An imaging technique used to identify the lymph drainage basin, determine the number of sentinel nodes, differentiate sentinel nodes from subsequent nodes, locate the sentinel node in an unexpected location, and mark the sentinel node over the skin for biopsy. It requires the injection of a radioisotope into the skin around the biopsy scar and a scan some hours later to determine to which lymph nodes the tracer has travelled. |
| Lymphovascular invasion | Tumour cells which have spread to involve the blood vessels and lymphatic vessels within the skin. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | A type of scan which uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce images of sections of the body. |
| Mediastinal and hilar adenopathy | Enlargement of the pulmonary lymph nodes. |
| MEK inhibitors | Drugs that inhibit the mitogen‐activated protein kinase enzymes which are often upregulated in melanoma. |
| Meta‐analysis | A form of statistical analysis used to synthesise results from a collection of individual studies. |
| Metastases/metastatic disease | Spread of cancer away from the primary site to somewhere else through the bloodstream or the lymphatic system. |
| Micrometastases | Micrometastases are metastases so small that they can only be seen under a microscope. |
| Mitotic rate | Microscopic evaluation of number of cells actively dividing in a tumour. |
| Morbidity | Detrimental effects on health. |
| Mortality | Either (1) the condition of being subject to death; or (2) the death rate, which reflects the number of deaths per unit of population in relation to any specific region, age group, disease, treatment or other classification, usually expressed as deaths per 100, 1000, 10,000 or 100,000 people. |
| Multidisciplinary team | A team with members from different healthcare professions and specialties (e.g. urology, oncology, pathology, radiology, and nursing). Cancer care in the National Health Service (NHS) uses this system to ensure that all relevant health professionals are engaged to discuss the best possible care for that patient. |
| Nodal basin | Cluster of lymph nodes which filter lymphatic fluid as it travels around the body; clusters are located under the arm (axilla), in the groin, neck, chest and abdomen. |
| Oncology | The study of cancers. This term also refers to the medical specialty of cancer care, with particular reference to the use of radiotherapy or drugs to treat cancer. The medical specialty is often split into clinical oncology (doctors who use radiotherapy and drug treatment) and medical oncology (doctors who use drug treatment). |
| Palpation | Feeling with the fingers or hands as part of a clinical examination of the body. |
| Positron emission tomography (PET) | A nuclear medicine imaging technique whereby a radioactive glucose (usually 18FDG) is administered intravenously before a scan is conducted to create an image using colours to show where the FDG (or other radioactive tracer) has been taken up in the body. |
| Prevalence | The proportion of a population found to have a condition. |
| Prognostic factors/indicators | Specific characteristics of a cancer or the person who has it which might affect the patient’s prognosis. |
| Radiotherapy | The use of radiation, usually high energy x‐rays to control the growth of cancer cells. |
| RAS‐RAF‐MEK‐ERK signalling pathway | A chain of proteins which allow signals from a receptor on the surface of a cell to be sent to the DNA in the cell nucleus; a mutation in one of the proteins in the pathway is associated with the development of many cancers. |
| Recurrence | Recurrence is when new cancer cells are detected following treatment. This can occur either at the site of the original tumour or at other sites in the body. |
| Relapse | Where cancer starts to grow again after treatment. |
| Sagittal | Median plane dividing the body into left and right. |
| Sensitivity | In this context the term is used to mean the proportion of individuals with a disease who have that disease correctly identified by the study test. |
| Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) | A radioactive tracer and blue dye are injected into the skin surrounding the primary lesion and the 'sentinel' lymph nodes to which the tracer drains are located by imaging (usually lymphoscintigraphy) and then removed and examined for nodal metastatic spread that cannot be detected clinically or on imaging. |
| Signal transduction | Occurs when extracellular signalling molecules activate a specific receptor which then triggers cellular pathways. |
| Staging | Clinical description of the size and spread of a patient’s tumour, fitting into internationally agreed categories. |
| Stereotactic radiotherapy | A technique for delivering high dose radiotherapy very accurately to small areas inside the body which reduces the damage done by the radiotherapy to adjacent healthy tissues. |
| Subclinical (disease) | Disease that is usually asymptomatic and not easily observable, e.g. by clinical or physical examination. |
| Systemic treatment | Treatment, usually given by mouth or by injection, that reaches and affects cancer cells throughout the body rather than targeting one specific area. |
| Ultrasound | A type of scan in which high‐frequency sound waves are used to outline a part of the body. |
| Some of the definitions above have been obtained from the NICE Guideline for the management of melanoma (NICE 2015a). | |
| a. TNM staging categories for cutaneous melanoma | |||||||||
| Classification | |||||||||
| T | Thickness (mm) | Ulceration status/mitoses | |||||||
| Tis | NA | NA | |||||||
| T1 | <= 1.00 | a: Without ulceration and mitosis 1/mm2 | |||||||
| b: With ulceration or mitoses 1/mm2 | |||||||||
| T2 | 1.01 to 2.00 | a: Without ulceration | |||||||
| b: With ulceration | |||||||||
| T3 | 2.01 to 4.00 | a: Without ulceration | |||||||
| b: With ulceration | |||||||||
| T4 | > 4.00 | a: Without ulceration | |||||||
| b: With ulceration | |||||||||
| N | Number of metastatic nodes | Nodal metastatic burden | |||||||
| N0 | 0 | NA | |||||||
| N1 | 1 | a: Micrometastasis* | |||||||
| b: Macrometastasis† | |||||||||
| N2 | 2 to 3 | a: Micrometastasis* | |||||||
| b: Macrometastasis† | |||||||||
| c: In transit metastases/satellites without metastatic nodes | |||||||||
| N3 | 4 metastatic nodes, or matted nodes, or in transit metastases/satellites with metastatic nodes | ||||||||
| M | Site | Serum LDH | |||||||
| M0 | No distant metastases | NA | |||||||
| M1a | Distant skin, subcutaneous, or nodal metastases | Normal | |||||||
| M1b | Lung metastases | Normal | |||||||
| M1c | All other visceral metastases | Normal | |||||||
| Any distant metastasis | Elevated | ||||||||
| b. Anatomical stage groupings | |||||||||
| Clinical stage‡ | T | N | M | Pathological stage δ | T | N | M | ||
| 0 | Tis | N0 | M0 | 0 | Tis | N0 | M0 | ||
| IA | T1a | N0 | M0 | IA | T1a | N0 | M0 | ||
| IB | T1b | N0 | M0 | IB | T1b | N0 | M0 | ||
| T2a | N0 | M0 | T2a | N0 | M0 | ||||
| IIA | T2b | N0 | M0 | IIA | T2b | N0 | M0 | ||
| T3a | N0 | M0 | T3a | N0 | M0 | ||||
| IIB | T3b | N0 | M0 | IIB | T3b | N0 | M0 | ||
| T4a | N0 | M0 | T4a | N0 | M0 | ||||
| IIC | T4b | N0 | M0 | IIC | T4b | N0 | M0 | ||
| III | Any T | N > N0 | M0 | IIIA | T1‐ T4a | N1a | M0 | ||
| T1‐ T4a | N2a | M0 | |||||||
| IIIB | T1‐ T4b | N1a | M0 | ||||||
| T1‐ T4b | N2a | M0 | |||||||
| T1‐ T4a | N1b | M0 | |||||||
| T1‐ T4a | N2b | M0 | |||||||
| T1‐ T4a | N2c | M0 | |||||||
| IIIC | T1‐ T4b | N1b | M0 | ||||||
| T1‐ T4b | N2b | M0 | |||||||
| T1‐ T4b | N2c | M0 | |||||||
| Any T | N3 | M0 | |||||||
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | ||
| LDH ‐ lactate dehydrogenase; M ‐ metastasis; N ‐ nodes; NA ‐ not applicable; T ‐ tumour; Tis ‐ melanoma in situ. *Micrometastases are diagnosed after sentinel lymph node biopsy. †Macrometastases are defined as clinically detectable nodal metastases confirmed pathologically. ‡Clinical staging is based on histology of the primary lesion and clinical (or radiological) examination. δPathological staging is assigned based on histology of the primary lesion and of the regional lymph nodes (either sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) or complete lymph node dissection (CLND), where indicated. | |||||||||

