بررسی حوادث جانبی مرتبط با مصرف میانمدت و طولانیمدت اوپیوئیدها برای درد مزمن غیر‐سرطانی: بررسی اجمالی مرورهای کاکرین
References
منابع مرورهای واردشده
Jump to:
منابع مرورهای خارجشده
Jump to:
منابع اضافی
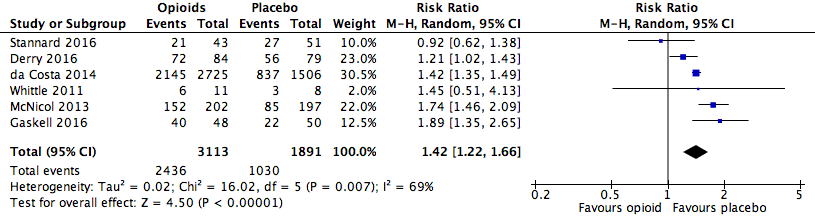
Analysis 1.1: Opioids versus placebo, any adverse event.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)
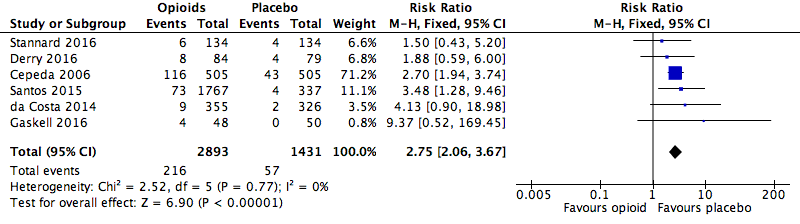
Analysis 1.2: Opioids versus placebo, any serious adverse event.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 1.3: Opioids versus placebo, withdrawals due to adverse events.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)
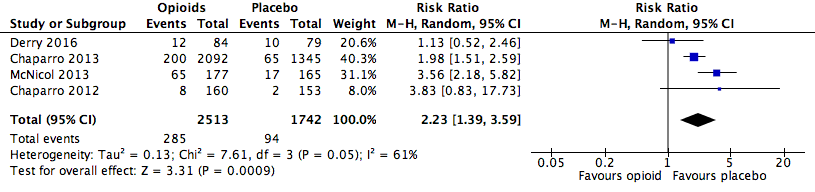
Analysis 2.1: Opioids versus placebo, constipation.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 2.6: Opioids versus placebo, dizziness.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 2.7: Opioids versus placebo, drowsiness.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)
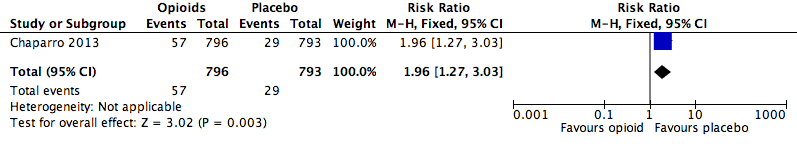
Analysis 2.8: Opioids versus placebo, fatigue.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)
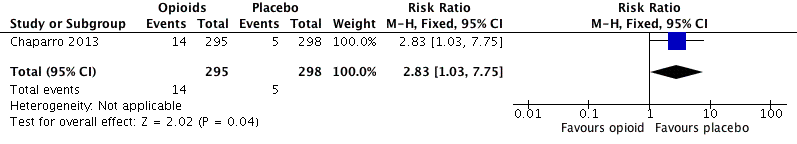
Analysis 2.10: Opioids versus placebo, hot flushes.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 2.11: Opioids versus placebo, increased sweating.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 2.12: Opioids versus placebo, nausea.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 2.13: opioids versus placebo, pruritus.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 2.15: Opioids versus placebo, vomiting.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 3.1: Opioids versus active pharmacological comparator, any adverse event.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 3.2: Opioids versus active pharmacological comparator, any serious adverse event.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 3.3: Opioids versus active pharmacological comparator, withdrawals due to adverse events.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)

Analysis 4.1: Opioids versus active non‐pharmacological comparator, any adverse event.
CI: confidence interval
df: degrees of freedom
M‐H: Mantel‐Haenszel method of meta‐analysis
P: probability
Z: Z score (standard score)
| Review | Reason for exclusion |
| Trials either included cancer pain, did not use opioids, or were not at least 2 weeks in duration. | |
| Did not exclude cancer pain | |
| Review update published as Gaskell 2016. | |
| No opioids studied. | |
| No opioids studied. | |
| Trials with opioids were less than 2 weeks in duration. | |
| No opioids studied. | |
| Trials with opioids were for acute pain. |
| Review | Total number of trials | Number of eligible trials | Number of trials also in other reviews | Number of de‐duplicated trials |
| 11 | 8 | 0 | 8 | |
| 21 | 5 | 4 | 5 | |
| 15 | 10 | 2 | 9 | |
| 22 | 19 | 2 | 18 | |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 13 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 31 | 13 | 10 | 6 | |
| 26 | 6 | 1 | 6 | |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 11 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Totals | 173 | 79 | 29 | 63 |
| Events reported | Totals | ||||||||||||
| Any adverse event | X | X | X | X | X | X | 6 | ||||||
| Any serious adverse event | X | X | X | X | X | X | 6 | ||||||
| Withdrawals due to adverse events | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 10 | ||
| Deaths | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 9 | |||
| Anorexia | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Constipation | X | X | X | X | 4 | ||||||||
| Diarrhoea | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Dizziness | X | X | X | X | X | 5 | |||||||
| Drowsiness or somnolence | X | X | X | X | 4 | ||||||||
| Fatigue | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Gastrointestinal (unspecified) | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Headache | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Hot flushes | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Increased sweating | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Infection | X | X | 2 | ||||||||||
| Nausea | X | X | X | X | 4 | ||||||||
| Nervous system (unspecified) | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Pruritus | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Sinusitis | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| Vomiting | X | X | X | 3 | |||||||||
| Xerostomia | X | 1 | |||||||||||
| An "X" indicates that the outcome was reported (whether or not any participants experienced it). In Cepeda 2006, "serious adverse events" were defined as adverse events that resulted in withdrawals. These data are therefore included in both categories for the review in question. | |||||||||||||
| Events reported | Totals | ||||||
| Any adverse event | X | X | 2 | ||||
| Any serious adverse event | X | 1 | |||||
| Withdrawals due to adverse events | X | X | X | X | 4 | ||
| Constipation | X | X | 2 | ||||
| Dizziness | X | 1 | |||||
| Drowsiness or somnolence | X | 1 | |||||
| Nausea | X | 1 | |||||
| Vomiting | X | 1 | |||||
| An "X" indicates that the outcome was reported (whether or not any participants experienced it). | |||||||
| Review | Date assessed as up‐to‐date | Condition(s) studied | Participant characteristics | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Duration of treatment in eligible studies |
| Oct‐11 | Phantom limb pain | Participants of any age with established phantom limb pain | Pharmacologic agents given singly or in combination | Stump/residual limb pain alone, or postamputation pain that was not phantom pain, or phantom pain mixed with other neuropathic pains; pharmacologic interventions aimed at preventing phantom limb pain | 10 weeks (no quantitative data reported on outcomes of interest) | |
| May‐06 | Osteoarthritis | Adults with primary or secondary osteoarthritis of the hip or knee | Tramadol or tramadol plus paracetamol used | Other types of arthritis; non‐osteoarthritic joint pain or back pain | 14 to 91 days | |
| Apr‐12 | Neuropathic pain | Adults with neuropathic pain | Compared combinations of 2 or more drugs against placebo or another comparator | Studies with a neuraxial approach or that included injection therapies, transcutaneous electrical stimulation, or vitamins | 5 to 36 weeks (includes a cross‐over trial of 9 weeks with 4 conditions) | |
| Apr‐13 | CLBP | Adults with persistent pain in the low back for at least 12 weeks | Any opioid prescribed in an outpatient setting for 1 month or longer | Participants with cancer, infections, inflammatory arthritic conditions, compression fractures, or studies where less than 50% of participants had CLBP | 4 to 15 weeks | |
| Aug‐12 | Osteoarthritis | Adults with osteoarthritis of the knee or hip | Any type of opioid except tramadol | Trials with inflammatory arthritis exclusively or with less than 75% of participants having osteoarthritis of the knee or hip | 2 to 30 weeks | |
| Jan‐15 | Neuropathic pain | Adults with a chronic neuropathic pain condition | Nortriptyline at any dose, by any route, compared to placebo or any active comparator | Nortriptyline given in combination with other drugs, without separate reporting | 28 weeks (no unique data was reported) | |
| Jun‐16 | Neuropathic pain | Adults with postherpetic neuralgia, complex regional pain syndrome, or chronic postoperative pain | Fentanyl at any dose, by any route | Treatment of < 2 weeks | 94 to 113 days | |
| Jun‐15 | CLBP | Adults with non‐specific CLBP for at least 12 weeks | 1 or more types of NSAIDs used | Trials of NSAIDs no longer available on the market; participants with sciatica or with specific low back pain caused by pathological entities, e.g. infection, neoplasm, metastases, osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, or fractures | 6 weeks | |
| Dec‐15 | Chronic neuropathic pain | Adults with painful diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia | Any dose or formulation of oxycodone | Fewer than 10 participants per treatment arm, or less than 2 weeks of treatment | 12 weeks | |
| Apr‐12 | CNCP | Adults having any type of CNCP | Methadone by any route in randomised or quasi‐randomised studies | Studies with fewer than 10 participants | 40 to 119 days | |
| Aug‐13 | Neuropathic pain | Adults with central or peripheral neuropathic pain of any aetiology | Opioid agonists used in an RCT | Partial opioid agonists or agonist‐antagonists used | 6 to 16 weeks (includes a 6‐ and 8‐week cross‐over trial with 2 conditions) | |
| May‐09 | CNCP | Adults with chronic pain for at least 3 months | Treament for at least 6 months | Fewer than 10 participants | 2 weeks to 13 months | |
| Dec‐09 | CLBP | Adults with CLBP, with or without radiating pain | Mean duration of CLBP > 12 weeks | Single‐treatment studies; studies examining specific pathologies (e.g. sciatica) | 6 weeks | |
| Mar‐14 | CNCP | Adults with osteoarthritis of the knee or hip, CLBP | Tapentadol ER in doses of 100 to 500 mg/day | Pain for less than 3 months or that was not moderate to severe | 15 to 52 weeks | |
| Nov‐15 | Neuropathic pain | Adults with 1 or more chronic neuropathic pain conditions | Hydromorphone at any dose, by any route | Treatment of < 2 weeks | 14 to 16 weeks | |
| May‐10 | Rheumatoid arthritis pain | Adults with rheumatoid arthritis | Opioids of any formulation at any dose, by any route | Studies of opioid therapy for rheumatoid arthritis in the immediate postoperative setting | 6 to 10 weeks | |
| CLBP: chronic low back pain | ||||||
| Drug | Formulations | Dosing Schedule | Dose (lowest) | Dose (highest) | MEq (lowest) | MEq (highest) | ||||||||||||||
| Buprenorphine | Transdermal patch (µg/h) | ‐ | 5 µg/h | 40 µg/h | 12 | 96 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Codeine | Contin | Twice a day, 3 times a day | 32 | 200 | 4.8 | 30 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Dextropropoxyphene | ‐ | 3 times a day | 300 | ‐ | 30 | ‐ | X | |||||||||||||
| Dihydrocodeine | LA | Every 12 hours | 30 | 240 | 3 | 24 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Fentanyl | Transdermal patch (µg/h) | ‐ | 12.5 µg/h | 250 µg/h | 45 | 944 | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Hydromorphone | ER, OROS | Once a day | 4 | 64 | 16 | 256 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Levorphanol | ‐ | 3 times a day | 0.45 | 15.75 | 4.95 | 173.5 | X | |||||||||||||
| Methadone | ‐ | Twice a day | 5 | 80 | 15 | 240 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Morphine | Avinza, Contin, CR, ER, LA, SR | Twice a day, once a day, every 12 hours, as needed | 15 | 300 | 15 | 300 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Oxycodone | CR, ER, LA, MR, PR, immediate‐release, liquid | Twice a day, 3 times a day to 6 times a day | 10 | 160 | 15 | 240 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Oxycodone and naloxone | PR | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | X | |||||||||||||
| Oxycodone and naltrexone | ‐ | 4 times a day | 10 | 40 | 15 | 60 | X | |||||||||||||
| Oxymorphone | ER | Twice a day, every 12 hours | 10 | 140 | 30 | 420 | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Tapentadol | ER, immediate‐release | Twice a day, 3 times a day to 6 times a day | 100 | 500 | 40 | 200 | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Tilidine and naloxone | ‐ | ‐ | 4 | 12 | 10 | 30 | X | |||||||||||||
| Tramadol | ER, LP, Retard | Twice a day, as needed, 3 times a day, 4 times a day, once a day, every 12 hours | 37.5 | 400 | 3.75 | 40 | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Dose is given in milligrams, except for transdermal opioids, which are given in micrograms. CR: controlled‐release PR: Prolonged release | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Opioid | Source | Equivalent dose of oral morphine, in mg, per 1 mg of the converted opioid |
| Buprenorphine (transdermal) | 100 | |
| Codeine | 0.15 | |
| Dextropropoxyphene | 0.1 | |
| Dihydrocodeine | 0.1 | |
| Fentanyl (transdermal) | 158* | |
| Hydromorphone | 4 | |
| Levorphanol | 7.5 | |
| Methadone | 3 | |
| Oxycodone | 1.5 | |
| Oxymorphone | 3 | |
| Tapentadol | 0.4 | |
| Tilidine | 0.2 | |
| Tramadol | 0.1 | |
| Transdermally delivered opioid doses (buprenorphine and fentanyl) are usually expressed as an hourly rate of delivery, but were converted to the dose per 24 hours before being converted into morphine equivalents. *Calculated as the mean conversion factor from data in Fentanyl monograph 2017. | ||
| Review | Events | Total | Event rate (%) | |
| Average | 95% CI | |||
| 481 | 1613 | 29.8 | 27.6 to 32.1 | |
| 2145 | 2725 | 78.7 | 77.2 to 80.3 | |
| 454 | 785 | 57.8 | 54.4 to 61.3 | |
| 40 | 48 | 83.3 | 72.8 to 93.9 | |
| 1 | 17 | 5.9 | ‐5.3 to 17.1 | |
| 766 | 894 | 85.7 | 83.4 to 88 | |
| 21 | 43 | 48.8 | 33.9 to 63.8 | |
| Total events | 3908 | 6622 | 59.0 | 57.8 to 60.2 |
| CI: confidence interval | ||||
| Review | Events | Total | Event rate (%) | |
| Average | 95% CI | |||
| 196 | 899 | 21.8 | 19.1 to 24.5 | |
| 9 | 355 | 2.5 | 0.9 to 4.2 | |
| 4 | 48 | 8.3 | 0.5 to 16.2 | |
| 73 | 1767 | 4.1 | 3.2 to 5.1 | |
| 6 | 134 | 4.5 | 1 to 8 | |
| Total events | 288 | 3203 | 9.0 | 8 to 10 |
| CI: confidence interval | ||||
| Review | Events | Total | Event rate (%) | |
| Average | 95% CI | |||
| 196 | 899 | 21.8 | 19.1 to 24.5 | |
| 63 | 526 | 12.0 | 9.2 to 14.8 | |
| 1169 | 4398 | 26.6 | 25.3 to 27.9 | |
| 132 | 785 | 16.8 | 14.2 to 19.5 | |
| 3 | 48 | 6.3 | 0 to 13.1 | |
| 11 | 90 | 12.2 | 5.5 to 19 | |
| 19 | 177 | 10.7 | 6.2 to 15.3 | |
| 620 | 1830 | 33.9 | 31.7 to 36.1 | |
| 480 | 1770 | 27.1 | 24.9 to 29.3 | |
| 3 | 43 | 7.0 | 7 to 7 | |
| 3 | 11 | 27.3 | 27.3 to 27.3 | |
| Total events | 2699 | 10,577 | 25.5 | 25.5 to 25.5 |
| AMSTAR criteria | ||||||||||||||||
| 1. A priori design | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2. Duplicate selection and extraction | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3. Comprehensive literature search | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4. Published and unpublished, no language restrictions | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5. List of studies provided | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6. Characteristics of studies provided | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7. Scientific quality assessed | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8. Scientific quality used in formulating conclusions | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 9. Methods used to combine appropriate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 10. Conflict of interest stated | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total score/10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| AMSTAR: Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews | ||||||||||||||||
| Participants (reviews) | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Overall quality of evidence | |
| Any adverse event | 1583 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | +++◯ |
| Any serious adverse event | 108 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | +++◯ MODERATE |
| Withdrawals due to adverse events | 2375 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | +++◯ |
| Participants (reviews) | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Overall quality of evidence | |
| Constipation | 4255 (4 reviews) | Serious | Not serious | Serious | Not serious | Strong association | +++◯ |
| Dizziness | 4130 (4 reviews) | Serious | Not serious | Serious | Not serious | Strong association | +++◯ |
| Drowsiness or somnolence | 3856 (3 reviews) | Serious | Not serious | Serious | Not serious | Strong association | +++◯ |
| Fatigue | 1589 (1 review) | Serious | Not serious | Very serious | Not serious | None | +◯◯◯ |
| Hot flushes | 593 (1 review) | Serious | Not serious | Very serious | Not serious | None | +◯◯◯ |
| Increased sweating | 1350 (1 review) | Serious | Not serious | Very serious | Not serious | Very strong association | +++◯ |
| Nausea | 4346 (3 reviews) | Serious | Not serious | Serious | Not serious | Strong association | +++◯ |
| Pruritus | 2865 (1 review) | Serious | Not serious | Very serious | Not serious | None | +◯◯◯ |
| Vomiting | 3368 (2 reviews) | Serious | Not serious | Very serious | Not serious | Strong association | ++◯◯ |
| Participants (reviews) | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Overall quality of evidence | |
| Any adverse event | 1583 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | +++◯ |
| Any serious adverse event | 108 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Very serious | None | +◯◯◯ |
| Withdrawals due to adverse events | 2375 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | +++◯ |
| Participants (reviews) | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other considerations | Overall quality of evidence | |
| Any adverse event | 32 (1 review) | Very serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | +◯◯◯ |
| Adverse event | Studies | Participants | Statistical method | Risk ratio | NNTH |
| Any adverse event | 6 | 5004 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.42 (1.22, 1.66) | 4.20 (3.78, 4.74) |
| Any serious adverse event | 6 | 4324 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.75 (2.06, 3.67) | 28.71 (20.50, 47.88) |
| Withdrawals due to adverse events | 10 | 11,510 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.40 (3.02, 3.82) | 5.55 (5.19, 5.97) |
| CI: confidence interval | |||||
| Opioid | Placebo | ||||||||
| Number of participants | Event rate (%) | Number of participants | Event rate (%) | ||||||
| Analysis | Adverse event | With AE | Total | Average | 95% CI | With AE | Total | Average | 95% CI |
| 1.1 | Any adverse event | 2436 | 3113 | 78.3 | 76.8 to 79.7 | 1030 | 1891 | 54.5 | 52.2 to 56.7 |
| 1.2 | Any serious adverse event | 216 | 2893 | 7.5 | 6.5 to 8.4 | 57 | 1431 | 4.0 | 3 to 5 |
| 1.3 | Withdrawals due to adverse events | 1836 | 7316 | 25.1 | 24.1 to 26.1 | 297 | 4194 | 7.1 | 6.3 to 7.9 |
| 2.1 | Constipation | 285 | 2513 | 11.3 | 10.1 to 12.6 | 94 | 1742 | 5.4 | 4.3 to 6.5 |
| 2.6 | Dizziness | 284 | 2448 | 11.6 | 10.3 to 12.9 | 71 | 1682 | 4.2 | 3.3 to 5.2 |
| 2.7 | Drowsiness or somnolence | 237 | 2313 | 10.3 | 9 to 11.5 | 57 | 1543 | 3.7 | 2.8 to 4.6 |
| 2.8 | Fatigue | 57 | 796 | 7.2 | 5.4 to 8.9 | 29 | 793 | 3.7 | 2.4 to 5 |
| 2.10 | Hot flushes | 14 | 295 | 4.8 | 2.3 to 7.2 | 5 | 298 | 1.7 | 0.2 to 3.1 |
| 2.11 | Increased sweating | 32 | 674 | 4.7 | 3.1 to 6.3 | 2 | 676 | 0.3 | 0.0 to 0.7 |
| 2.12 | Nausea | 535 | 2556 | 20.9 | 20.9 to 20.9 | 151 | 1790 | 8.4 | 8.4 to 8.4 |
| 2.13 | Pruritus | 155 | 1809 | 8.6 | 8.6 to 8.6 | 52 | 1056 | 4.9 | 4.9 to 4.9 |
| 2.15 | Vomiting | 184 | 2058 | 8.9 | 8.9 to 8.9 | 28 | 1310 | 2.1 | 2.1 to 2.1 |
| AE: adverse event | |||||||||
| Adverse event | Studies | Participants | Statistical method | Risk ratio | NNTH |
| Anorexia | 1 | 330 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 13.64 (0.77, 240.21) | ‐ |
| Constipation | 4 | 4255 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.23 (1.39, 3.59) | 16.82 (13.20, 23.19) |
| Diarrhoea | 1 | 313 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.55 (0.69, 9.43) | ‐ |
| Dizziness | 4 | 4130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.76 (2.15, 3.55) | 13.55 (11.15, 17.28) |
| Drowsiness, sleepiness, somnolence, or anergia | 3 | 3856 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.89 (2.19, 3.83) | 15.26 (12.34, 20.00) |
| Fatigue | 1 | 1589 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.96 (1.27, 3.03) | 28.54 (17.48, 77.71) |
| Gastrointestinal (unspecified) | 1 | 98 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.77 (0.90, 3.47) | ‐ |
| Headache | 1 | 313 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 (0.33, 1.84) | ‐ |
| Hot flushes | 1 | 593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.83 (1.03, 7.75) | 32.60 (16.95, 421.76) |
| Increased sweating | 1 | 1350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 16.05 (3.86, 66.69) | 22.46 (16.37, 35.78) |
| Infection | 2 | 631 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.87 (0.47, 1.61) | ‐ |
| Nausea | 3 | 4346 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 (2.08, 2.92) | 8.00 (6.88, 9.56) |
| Nervous system disorders (unspecified) | 1 | 98 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.50 (0.95, 6.56) | ‐ |
| Pruritus | 1 | 2865 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.74 (1.28, 2.36) | 27.44 (18.25, 55.27) |
| Sinusitis | 1 | 318 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.56 (0.52, 4.67) | ‐ |
| Vomiting | 2 | 3368 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.29 (2.90, 6.34) | 14.70 (12.10, 18.72) |
| Xerostomia | 1 | 1668 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 (0.47, 2.57) | ‐ |
| CI: confidence interval | |||||
| Drug | Total dose per day | Dosing schedule | ||||
| Celecoxib | 400 mg | ‐ | X | |||
| Desipramine | 10 to 160 mg | ‐ | X | |||
| Diclofenac | 25 to 150 mg | Up to 3 times a day | X | |||
| Gabapentin | 1200 to 3600 mg | 3 times a day | X | |||
| Lorazepam | 0.7 to 1.6 mg | Twice a day and 3 times a day | X | |||
| Naproxen | 250 to 1000 mg | ‐ | X | |||
| Nortriptyline | 10 to 160 mg | Twice a day | X | X | ||
| An "X" indicates that the drug was used as an active comparator to opioids in the review. Rubinstein 2011 used a non‐pharmacological comparator (spinal manipulative therapy). | ||||||
| Opioid | Active comparator | ||||||||
| Number of participants | Event rate (%) | Number of participants | Event rate (%) | ||||||
| Analysis | Adverse event | With AE | Total | Average | 95% CI | With AE | Total | Average | 95% CI |
| 1.1 | Any adverse event | 454 | 785 | 57.8 | 54.4 to 61.3 | 381 | 798 | 47.7 | 44.3 to 51.2 |
| 1.2 | Any serious adverse event | 5 | 54 | 9.3 | 1.5 to 17 | 1 | 54 | 1.9 | 0 to 5.4 |
| 1.3 | Withdrawals due to adverse events | 185 | 1201 | 15.4 | 13.4 to 17.4 | 56 | 1174 | 4.8 | 3.6 to 6 |
| AE: adverse event | |||||||||
| Adverse event | Studies | Participants | Statistical method | Risk ratio | NNTH |
| Any adverse event | 1 | 1583 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 (1.10, 1.33) | 9.91 (6.67, 19.24) |
| Any serious adverse event | 1 | 108 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.00 (0.60, 41.39) | ‐ |
| Withdrawals due to adverse events | 4 | 2375 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.23 (2.42, 4.30) | 9.40 (7.69, 12.11) |
| CI: confidence interval | |||||
| Opioid | Active comparator | ||||||||
| Number of participants | Event rate (%) | Number of participants | Event rate (%) | ||||||
| Analysis | Adverse event | With AE | Total | Average | 95% CI | With AE | Total | Average | 95% CI |
| 1.1 | Any adverse event | 1 | 17 | 5.8 | 0 to 17.1 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 to 0 |
| AE: adverse event | |||||||||


