Ejercicio para embarazadas con diabetes gestacional para mejorar los resultados maternos y fetales
References
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to studies awaiting assessment
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 79 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: pregnant women diagnosed with GDM. Exclusion criteria: not described. Setting: Montreal, Canada. Timing: no details. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group ‐ individualised follow‐up by kinesiologist (n = 40) versus control group ‐ general counselling about physical activity (n = 39). | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome was the use of insulin. Secondary outcomes included excessive gestational weight gain according to the IOM guidelines, evaluation of medical intervention (non stress test and induction) and a composite outcome of maternal and fetal complications (hypertension, pre‐eclampsia, caesarean section, assisted delivery, macrosomia, prematurity, neonatal unit admission). | |
| Notes | There was also a third “control” group. However, these women were not randomly assigned to receive 'no advice' about physical activity, they were matched for age, BMI at term, and GDM diagnosis to women in the trial. Data for this group have not been included in this review. Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: statement that there are no conflicts of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "randomly assigned" no other information. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No details as to whether all participants completed the trial. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The study was assessed from a brief conference abstract, without access to the study protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | The report states that “characteristics were similar at baseline”. There is no power calculation, but the authors comment that the study could be under‐powered to show differences. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 33 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: physician or certified nurse‐midwife diagnosis of GDM, 34 weeks’ gestation or less, no other important medical or obstetric complications, ability to read and write English, age 18‐40 years, no current regular exercise regimen for continuous 30‐minute periods more than twice per week. Exclusion criteria: no details, although “19 women were ineligible for medical reasons” and “three subjects in the control group were withdrawn for medical reasons” (p12). 3 women were excluded because exercise was recommended to them by the care provider. Setting: USA, large mid‐western health maintenance organisation. Timing: no details. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group ‐ exercise for 30 minutes 3 to 4 times weekly for the remainder of the pregnancy. 5 minutes warm up, 5 minutes cool down, 20 minutes cycle ergometer or walking at 70% of estimated maximal heart rate. 2 exercise sessions were in the presence of the investigator, with maternal and fetal monitoring. Once or twice a week, the women exercised unsupervised (n = 16). versus control group ‐ continued dietary therapy and usual physical activity level. They were asked not to change their current amount of activity. They were telephoned weekly by the investigator to monitor progress in the study and were asked to record any exercise (n = 17). | |
| Outcomes | Daily fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels, HbA1C, incidence of exogenous insulin therapy, incidence of newborn hypoglycaemia. | |
| Notes | Funding: National Institute of Nursing Research, National Institute of Health NR06568‐01A1; the American Diabetes Association, MN Affiliate; the March of Dimes, Greater Twin Cities Chapter; Boehringer Manheim Corporation; the Clinical Research and Education Fund, Group Health Foundation. Funding source: National Institute of Nursing Research, National Institutes of Health, American Diabetes Association, March of Dimes, Greater Twin Cities Chapter, Boerhinger Manheim Corporation, Clinial Research and Education Fund. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | “Group assignment was determined using a random‐numbers table by the block randomisation procedure”. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | “subjects were not blinded as to the nature of the study intervention”. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | The number of eligible women was 144, however 19 were ineligible for medical reasons, 21 were beyond 34 weeks’ gestation, 68 declined, and exercise was recommended to 3 by the care provider. Withdrawals ‐ exercise group n = 16 (1 woman subsequently dropped out); control group n = 17 (3 women were subsequently withdrawn for medical reasons). “several subjects gave birth before the follow‐up exercise test”, however the number of women included in the measures at the end is unclear. Home blood glucose levels are reported for 10/15 women in the exercise group, and 12/14 women in the control group. It is unclear why the other women's results are missing. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | This study was assessed from a published report, without a protocol available. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Baseline characteristics were mostly similar, however parity was higher in the exercise group. The trial authors are aware that the trial is underpowered to detect differences in blood glucose values or HbA1C. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised 3‐arm trial. | |
| Participants | 17 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: pregnant women with GDM, 27 to 37 weeks' gestation. Exclusion criteria: not described. Setting: Sao Paulo, Brazil. Timing: no details. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group 1: aerobic activity: 30 minutes brisk walking (n = 6). Exercise group 2: resistance exercises: 30 minutes circuit workout with elastic‐band exercises (n = 5) versus control group: remained seated for 30 minutes listening to explanations about Shantala exercises for the baby (n = 6). | |
| Outcomes | Capillary blood glucose before, at the end of session and 1 hour after. | |
| Notes | Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "randomized" no other details. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not described. Assessed from a brief abstract, without the trial protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Very little detail of methodology reported. |
| Methods | 2 x 2 factorial randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 200 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: pregnant women, age 18‐50, 24‐26th weeks of gestation, GDM diagnosis based on a 75 g OGTT, singleton pregnancy. Exclusion criteria: BMI > 40 kg/m2, any known diseases, medications or obstetrical absolute/relative contraindications to exercise. Setting: Sant’Anna Hospital, Torino, Italy. Timing: July 2009‐February 2012. | |
| Interventions | All women were given an individually‐prescribed diet (carbohydrates 48% to 50%, proteins 18% to 20%, fats 30% to 35%, fibre 20 g to 25 g/day, no alcohol). In addition: Group E: advised to briskly walk at least 20 minutes/day. N = 51. Group B: individually oral/written recommendations for helping with healthy dietary choices (i.e. lowering carbohydrate intake, strategies for out‐of‐home eating, healthy cooking and food shopping and related behavioural suggestions) and debunking false myths about diet in pregnancy. N = 49. Group BE brisk walk and dietary advice n = 50. Group D (control group): individually‐prescribed dietary recommendations only n = 50. All women were monitored by weekly phone calls and visited every 2 weeks to monitor adverse events and protocol adherence. Participants self‐monitored capillary blood glucose concentrations 4‐6 times per day with a glucometer. | |
| Outcomes | Fasting glucose values, high‐density lipoprotein (HDL)‐cholesterol, triglycerides, insulin, Homeostasis‐Model‐Assessment‐Insulin Resistance (HOMA‐IR), high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein (CRP), glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), postprandial glucose, maternal/neonatal complications. | |
| Notes | Funding source: Regione Piemonte 2009. Declarations of interest: the authors report no conflicts of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | “Randomization was stratified by baseline body mass index (BMI) and METs, and was implemented through a website (www.epiclin.it)”. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details provided on method used to conceal allocation. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | It was not feasible to blind women to the intervention. However, “The dieticians, the obstetricians who reported maternal/neonatal complications, and the laboratory personnel were blinded to the group assignment”. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | “It is possible that women in the exercise group could have over‐reported exercise or declared healthier nutritional habit. However, all the outcomes, which were blindly measured, were consistent with the declared lifestyle changes”. Outcome assessment was done by dieticians, obstetricians and laboratory personnel who were blinded to group allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | The authors state that “All participants completed the study”. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The protocol was available for this trial. All prespecified outcomes except infant birthweight were reported. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Baseline characteristics appear to be similar across groups. The sample size was calculated to have 95% statistical power to detect at least a 10% reduction in fasting glucose by exercise. The authors acknowledge that the study is underpowered to find small differences in the incidence of adverse maternal/neonatal outcomes. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | Possibly 38 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: otherwise healthy pregnant women with GDM, between age 20 and 40 years, gestational age between 26 and 32 weeks', BMI below 40 kg/m2, nonsmokers, who were not involved in a regular exercise program. Exclusion criteria: no details. Setting: Alberta, Canada. Diabetic Outpatient Clinics at the Royal Alexandra and Grey Nuns Hospitals in Edmonton. Timing: not stated. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group: progressive physical conditioning program. 3 supervised introductory sessions, and weekly contact with supervisor. Instructed to perform resistance training circuit‐type exercises 3 times per week. Women were instructed to exercise at a level that felt “somewhat hard”, and were taught to monitor their heart rate to ensure that it did not rise above 140 beats/min during exercise. All exercise sessions were recorded in a log book (n = 16) versus control group: diet alone. Standard diabetic diet advice: 40% carbohydrate, 20% protein, 40% fat, calculated at 24 to 30 kcal/kg per day on the basis of the woman’s ideal pre‐pregnant body weight. Women were asked not to begin a structured exercise program for the remainder of the pregnancy (n = 16). | |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: requirement for insulin. Secondary outcomes: latency to insulin treatment, amount of insulin required, gestational age at birth, birthweight. | |
| Notes | Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random numbers table used. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequentially numbered opaque envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 38 women randomised. However physicians advised against the program for 3 women because of pregnancy‐induced hypertension, and 2 women who were randomised to exercise did not enter the program. 1 woman dropped out of the study due to time constraints: it does not say which group she was randomised to, but exercise would demand more time commitment so probably this group). “four women in each group did not record their blood glucose measurements adequately” so these data are missing from blood glucose levels. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The protocol was not available for this trial, so it was assessed from only the published report. Several outcomes are reported in the text as “no significant differences” but without providing the number of women/infants (gestational age at delivery, rate of caesarean deliveries, birthweight). |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | The report states that the analyses were done by intention to treat, however 6 women who were probably randomised to the exercise group were not included in the analyses. The groups had similar baseline physical characteristics, although the diet‐alone group had a significantly higher mean pre‐pregnant body mass (weight) than the diet plus exercise group. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 41 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: pathological results in a OGTT and persisting fasting blood glucose values > 105, but < 130 mg/dl after a failed 1 week ADA diet trial (24 to 30 kcal/kg/day); following the clinical protocol these women would then require Insulin therapy. No contraindications to exercise, before 33 weeks' pregnancy (to allow at least 4 weeks of exercise). Exclusion criteria: other medical or obstetrical complications of pregnancy; women at risk for premature labour. Setting: high risk obstetrical clinic of Los Angeles County/University of Southern California Women’s Hospital. Timing: May – November 1990. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group ‐ exercise and diet. Instructed to conduct a non‐sedentary lifestyle, and attend the exercise laboratory 3 times a week to exercise under medical supervision. 45 minutes with 2 x 5‐minute breaks, on a recumbent bicycle, at 50% of their last determined maximum aerobic capacity (classed as moderate exercise) (n = 21) versus Control group ‐ insulin therapy and diet (n = 20). | |
| Outcomes | Heart rate and uterine activity. Clinical data, pregnancy complications, maternal and neonatal outcome variables. | |
| Notes | Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Double‐stratified randomisation, but no information on sequence generation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | 17/21 women in the exercise group completed the study. 4 women were excluded for: pPROM, non‐compliance with exercises, moving away, and withdrew. 17/20 women in the control group completed the study. 3 women did not return to the clinic and were lost to follow‐up. Some of this attrition may be related to the intervention, but these women were not included in the analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Assessed from published reports without access to the protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | There were small discrepancies between reports, for example birthweight and number of babies with Apgar < 7 at 5 minutes. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 64 women Inclusion criteria: pregnant women with a diagnosis of GDM, sedentary according to the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ), nonsmokers, age 18‐45 years, no physical factor or disease limiting exercise, singleton pregnancy, absence of fetal malformation upon ultrasound, gestational age 24‐34 weeks', no risk factors for preterm delivery. Exclusion criteria: clinical or obstetric complications contraindicating exercise during pregnancy and loss to follow‐up. Setting: Obstetric clinic of the University Hospital, University of Sao Paulo School of Medicine, Brazil. Timing: October 2006‐November 2008. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group ‐ resistance exercise program with an elastic band. Women exercised 3 times a week, for 30‐40 minutes, on non‐consecutive days, twice a week at home and once in the clinic under supervision. Women were instructed to maintain an exercise intensity of 5 or 6 on an exertion scale, which is “somewhat heavy” exercise perception. Exercises were adapted by the researcher at the weekly clinic to maintain this intensity. Women started the program about 90 minutes after eating and after measuring capillary glycaemia. If capillary glucose levels were between 100 mg/dL and 250 mg/dL, women did the program, otherwise they waited until the next day (n = 32) versus control group ‐ no change to prenatal routine care, weekly outpatient visits. Occasional questions about whether they had started any physical activity. Instructed not to start any new type of physical activity after randomisation (n = 32). | |
| Outcomes | Requirement for insulin, amount of insulin required, latency to insulin requirement (weeks), mean glucose levels, percentage of weeks spent within the target glucose range, maternal BMI at birth, pregnancy weight gain, gestational age at delivery, birthweight. | |
| Notes | Sample size was calculated as 30 women in each group to show reduction in insulin requirement. Funding source: Coodenacao de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nivel Superior. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | “Women admitted to the study were randomized using a computer‐generated random series produced by a person not related to the protocol” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequential sealed opaque envelopes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Women were not blinded, and the main researcher knew their allocation. “The obstetricians responsible for clinical and prenatal care and data recording was unaware to which group the patients belonged, and only the main researcher questioned the patients with respect to the exercise practice” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | The obstetricians recording data were blinded to group allocation. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | After randomisation, 1 woman withdrew because of lack of time to perform the exercise program, and another started using metformin for glycaemic control. These women were included in the analyses. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | This trial was assessed from a published report, without access to the protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence of other bias. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 40 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: pregnant women, within 1 week of GDM diagnosis, singleton pregnancy, between 26 and 30 weeks' gestation, normal 18 week anatomy scan, BMI ≤ 45 kg/m2, non‐exercise program, medically cleared for exercise participation. Exclusion criteria: less than 18 years of age, unable to understand the implications of participation, on any medications at the time of recruitment, low‐lying placenta, pre‐existing diabetes (type 1 or 2), or cardiac disease. Setting: King Edward Memorial Hospital, Perth, Western Australia, Australia. Timing: no details. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group: experimental intervention: home‐based exercise program involving 5 sessions per week continued until week 34 of gestation. 3 sessions per week were supervised, 2 were unsupervised, using an upright stationary cycle ergometer. Sessions were 25‐30 minutes in week 1, increasing to 40‐45 minutes by week 4 (n = 20). versus control group: continued with their usual physical activity regimen for the duration of the intervention. Both groups: assessment of glycaemic control and counselling by a diabetes educator and dietician. Daily fasting and 120 minutes postprandial glucose levels after breakfast, lunch and dinner. Food and drink diary. | |
| Outcomes | Aerobic fitness, maternal weight gain, obstetric and neonatal outcomes. | |
| Notes | Funding source: University of Western Australia, Women's and Infants Research Foundation, National Health and Medical Research Council. Declarations of interest: publication states there were no personal or financial conflicts of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | “randomized”, no description of sequence generation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | “Concealed, sequentially numbered opaque envelopes selected by each participant”. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No attrition is described, however the mode of delivery for control group adds up to 19, not 20. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | This study was assessed from published reports, without access to a protocol. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Sample size was calculated to detect differences in blood glucose based on previous study and pilot data. |
| Methods | Parallel randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 39 women randomised. Inclusion criteria: pregnant women with gestational diabetes diagnosed according to standard protocol. The study appears to have started at 28 weeks' gestation. Exclusion criteria: maternal morbidity (1 woman with placenta praevia was excluded from the study). Setting: USA. Timing: not stated. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group: supervised arm ergometer training, 20 minutes, 3 times a week for 6 weeks, plus diet (24 to 30 kcal/kg/24 hours; 20% protein, 40% carbohydrate, 40% fat). Target heart rate: (220‐age in years) x 70% unless > 140 bpm, then target was 140 bpm (n = 20) versus control group: diet alone (24 to 30 kcal/kg/24 hours; 20% protein, 40% carbohydrate, 40% fat), divided into 3 meals and 3 snacks. Women did not participate in any structured exercise program (n = 19). | |
| Outcomes | Blood glucose, glycosylated Hb. | |
| Notes | Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | “women were randomized into two groups by drawing a number”. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No details. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | “one woman was dropped from the study because she was found to have placenta previa”, the woman appears to have been excluded before randomisation, and otherwise all women are accounted for. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | This study was assessed from a published report without access to the protocol. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | There is incomplete reporting of methodology, possibly due to publication in 1989. The diet group had lower peak 1 hour plasma glucose on 100 g glucose tolerance test at the start of the study. |
| Methods | Parallel‐arm, randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 6 women randomised (interim report from an ongoing trial) Inclusion: pregnant women with gestational diabetes, over 20 years old, gestational age 20‐27 weeks, singleton pregnancy, no orthopaedic limitations, non‐smoker, medical clearance for exercise. Exclusion: pre‐eclampsia, fetal malformations, intrauterine fetal death. Setting: prenatal clinics, Hospital de Clinicas de Porto Alegre, Brazil. Timing: not stated. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group: low‐intensity aerobic training in cycle‐ergometer for 50 minutes per session, 3 times a week, for 10 weeks (n = 2) versus control group: relaxation and stretching for 50 minutes per session, once a week for 10 weeks (n = 4). | |
| Outcomes | (from protocol on clinicaltrials.gov NCT01885234) Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), homeostasis model assessment (HOMA), first ventilatory threshold, type of delivery, weight and length of newborn. | |
| Notes | Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: publication lists no conflicts of interest. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | States "randomised" however, no details provided of method used to generate the random sequence. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No description of method used to conceal allocation. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Not described, but unlikely due to the nature of the intervention. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol states single blind (investigator), but no further details provided. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Study is ongoing. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Assessed from protocol and very brief interim abstract; not all prespecified outcomes were reported at this stage. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information at this stage. |
| Methods | Parallel‐arm, randomised controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 180 women. Inclusion: pregnant women diagnosed with GDM A1, 24‐30 weeks gestational age, fasting blood glucose concentration less than 105 mg/dL, postprandial blood glucose concentration less than 120 mg/dL, not receiving insulin therapy for glycaemic control, no serious complications such as gestational hypertension, pre‐eclampsia, preterm labour or other serious health problems. Exclusion: blood glucose concentration higher than 120 mg/L and therefore receiving insulin therapy for glycaemic control. Setting: tertiary hospital in southern Thailand, which is the referral centre for diabetes care. Timing: not stated. | |
| Interventions | Exercise group: trained to perform mindfulness eating and yoga exercise in 2 50 minute sessions. Then encouraged to continue mindfulness eating and yoga exercise at home for 15 to 20 minutes, 5 times a week for 8 weeks. Encouraged and monitored by the research team every week by phone and at face to face appointments (n = 90) versus control group: standard diabetes care (n = 90). | |
| Outcomes | Fasting and postprandial blood glucose concentrations, glysated haemoglobin (HbA1c). | |
| Notes | Funding source: no details. Declarations of interest: no details. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No information provided on method used to generate random sequence. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Opaque envelopes used. No information provided on numbering sequence. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Unclear risk | Not described as blinded. Unlikely due to nature of intervention. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Unclear risk | No mention of blinding of outcome assessors. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 90 women were randomised to each group. 5 women from each group did not complete the study or were lost to follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | This study was assessed from a published report without access to the protocol, however outcomes specified in the publication were reported on. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unclear |
BMI: body mass index
bpm: beats per minute
GDM: gestational diabetes mellitus
Hb: haemoglobin
OGTT: oral glucose tolerance test
pPROM: preterm premature rupture of membranes
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Ineligible population: examines the effect of exercise on the prevention of GDM. | |
| Ineligible intervention: the exercise component of the intervention commences at 6 weeks postpartum. | |
| Ineligible population: the participants have an abnormal oral glucose challenge test, but are not diagnosed with GDM. | |
| Ineligible population: participants are women with "high risk pregnancy" including women with diabetes at the time of trial entry. | |
| Ineligible trial design: prospective cohort study ‐ not randomised. | |
| Ineligible population: participants were healthy women without GDM. | |
| Ineligible trial design: not randomised. | |
| Ineligible trial design: cross‐over trial. | |
| Ineligible population: healthy participants. | |
| Ineligible trial design: cross‐over trial. | |
| Ineligible population: examines the effect of exercise in prevention of GDM. | |
| Ineligible population: participants do not have a diagnosis of GDM. | |
| Ineligible trial/population: systematic review on effect of physical activity on prevention of GDM. |
GDM: gestational diabetes mellitus
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
| Methods | Interventional treatment trial. |
| Participants | Women, 18 years and older, newly diagnosed with GDM. Women with pre‐existing diabetes are excluded. |
| Interventions | Intervention group: instructed on moderate‐to‐vigorous intensity exercise. Control group: routine diet and exercise counselling. |
| Outcomes | Need for medication for diabetes Birthweight HbA1c at delivery Mode of delivery |
| Notes | ClinicalTrials.gov stated this trial has been terminated due to recruitment issues. Attempts will be made to contact the responsible party for further information. |
GDM: gestational diabetes mellitus
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
| Trial name or title | Effects of an aquatic physical exercise program on glycaemic control and perinatal outcomes of gestational diabetes. |
| Methods | Parallel‐arm randomised controlled trial. |
| Participants | Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira (IMIP, Recife, Brazil. Pregnant women recently diagnosed with GDM by OGTT between 24 and 28 weeks' gestation using IADPSG criteria. |
| Interventions | Comparison group ‐ usual care consisting of standard dietary and exercise advice. Intervention group ‐ in addition to standard dietary and exercise advice, participants in the intervention group will take part in aquatic exercises such as walking, walking backwards, swimming laps, jogging, step climbing and strength exercises in a temperature maintained swimming pool for 45 minutes, 3 times a week, conducted from GDM diagnosis until the end of the third trimester. |
| Outcomes | Primary ‐ glucose control. Secondary ‐ weight gain in pregnancy, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pre‐eclampsia, urinary tract infections, vaginal infections, intrauterine growth restriction, preterm birth, caesarean section, birth injury, macrosomia, maternal or neonatal intensive care admission. |
| Starting date | Recruitment between August 2013 to March 2014. |
| Contact information | |
| Notes | Reference for protocol: da Silva 2013b Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01940003. |
| Trial name or title | Structured aerobic and resistance exercise and gestational diabetes. |
| Methods | Parallel‐arm randomised controlled trial. |
| Participants | Association for Functional Rehabiliations, Recreation and Applied Kinesiology Impulse, Zagreb, Croatia. Pregnant women between the ages of 20 and 40, with established diagnosis of GDM. |
| Interventions | Comparison group ‐ standard antenatal care. Intervention group ‐ participation in a 50‐minute structured exercise program twice a week consisting of aerobic, resistance and stretching and relaxation exercises, conducted from GDM diagnosis until the end of pregnancy. |
| Outcomes | Primary ‐ number of women with complications during pregnancy, labour and delivery, blood glucose levels, need for insulin and oral hypoglycaemic drugs, caesarean section and other operative delivery methods, other adverse occurrences during pregnancy. Secondary ‐ macrosomia, weight gain in pregnancy, body mass and fat percentage, lower back pain, physical activity in pregnancy (questionnaire). |
| Starting date | Janurary 2014 ‐ December 2014. |
| Contact information | Iva Sklempe Kokic. |
| Notes | Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02196571. |
| Trial name or title | Strength training in gestational diabetes mellitus. |
| Methods | Parallel‐arm randomised controlled trial. |
| Participants | International Diabetes Insitute, Melbourne, Australia. Pregnant women between the ages of 18 and 40 years, diagnosed with GDM. |
| Interventions | Comparison group ‐ usual care. Intervention group ‐ supervised 45‐minute strength training program twice a week from diagnosis of GDM to birth. |
| Outcomes | Primary ‐ changes in fasting glucose concentrations. Secondary ‐ changes in HbA1c, use of insulin, time until use of insulin, insulin resistance, blood pressure, muscle strength. |
| Starting date | Retrospectively registered ‐ start date March 2005. |
| Contact information | |
| Notes | ANZCTR identifier: ACTRN12605000378628. |
GDM: gestational diabetes mellitus
OGTT: oral glucose tolerance test
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (pre‐eclampsia) Show forest plot | 2 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.01, 7.09] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 1 Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (pre‐eclampsia). | ||||
| 2 Caesarean section Show forest plot | 5 | 316 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.63, 1.16] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 2 Caesarean section. | ||||
| 3 Perinatal mortality (stillbirth and neonatal mortality) Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 3 Perinatal mortality (stillbirth and neonatal mortality). | ||||
| 4 Mortality and morbidity composite (variously defined by trials, e.g. perinatal or infant death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture or nerve palsy) Show forest plot | 2 | 169 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.12, 2.61] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 4 Mortality and morbidity composite (variously defined by trials, e.g. perinatal or infant death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture or nerve palsy). | ||||
| 5 Use of additional pharmacotherapy Show forest plot | 7 | 413 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.54, 1.08] |
| Analysis 1.5 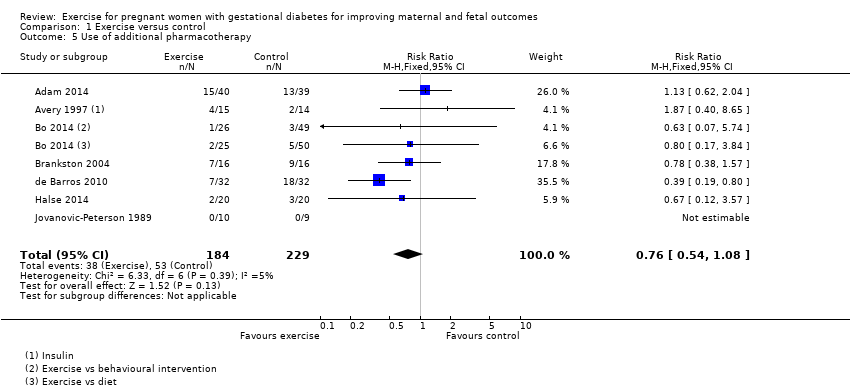 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 5 Use of additional pharmacotherapy. | ||||
| 6 Maternal hypoglycaemia Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 6 Maternal hypoglycaemia. | ||||
| 7 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Mean) Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.28 [0.04, 0.52] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 7 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Mean). | ||||
| 8 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Fasting blood glucose concentration) Show forest plot | 4 | 363 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.59 [‐1.07, ‐0.11] |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 8 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Fasting blood glucose concentration). | ||||
| 9 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Postprandial blood glucose concentration) Show forest plot | 3 | 344 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.85 [‐1.15, ‐0.55] |
| Analysis 1.9 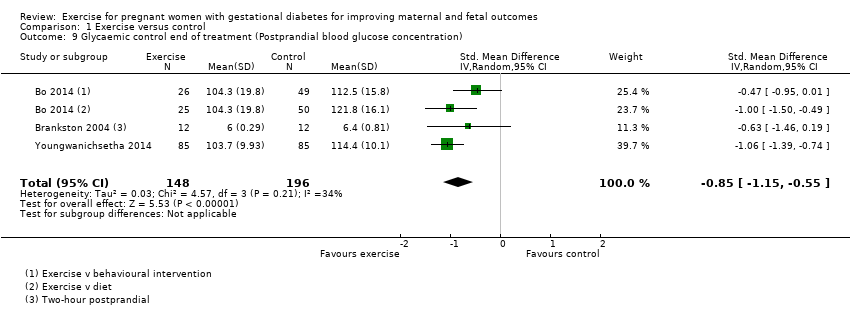 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 9 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Postprandial blood glucose concentration). | ||||
| 10 Glycaemic control end of treatment (HbA1c) Show forest plot | 2 | 320 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.43 [‐0.51, ‐0.35] |
| Analysis 1.10  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 10 Glycaemic control end of treatment (HbA1c). | ||||
| 11 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Glucose tolerance test) Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐81.6 [‐96.03, ‐67.17] |
| Analysis 1.11 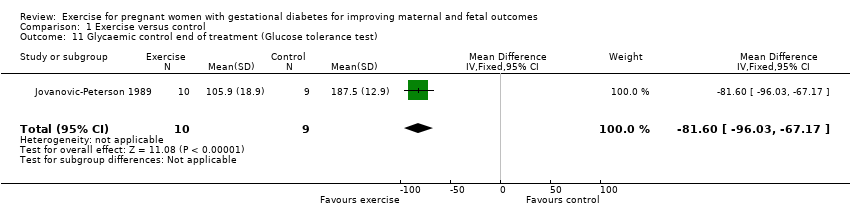 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 11 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Glucose tolerance test). | ||||
| 12 Weight gain in pregnancy Show forest plot | 2 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.34 [‐1.25, 0.58] |
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 12 Weight gain in pregnancy. | ||||
| 13 Weight gain in pregnancy (Excessive) Show forest plot | 1 | 79 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.9 [0.47, 1.72] |
| Analysis 1.13 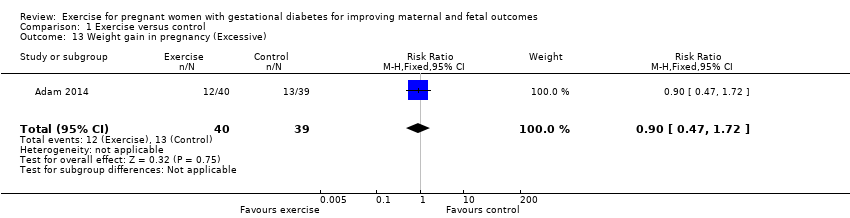 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 13 Weight gain in pregnancy (Excessive). | ||||
| 14 Adherence to the intervention Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.83, 1.21] |
| Analysis 1.14 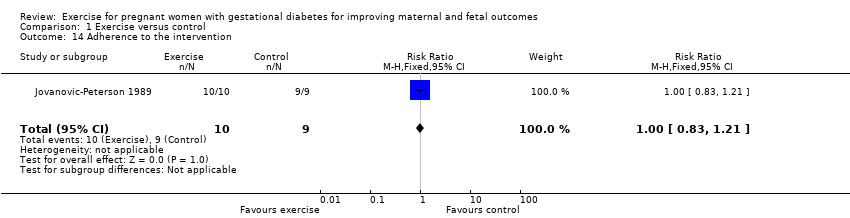 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 14 Adherence to the intervention. | ||||
| 15 Induction of labour Show forest plot | 1 | 40 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.38 [0.71, 2.68] |
| Analysis 1.15  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 15 Induction of labour. | ||||
| 16 Maternal mortality Show forest plot | 2 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.16 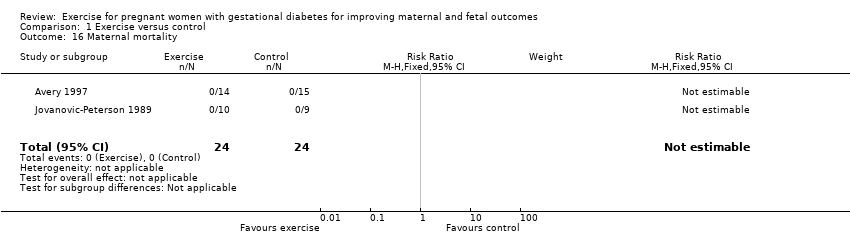 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 16 Maternal mortality. | ||||
| 17 Views of the intervention (favourable) Show forest plot | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.17 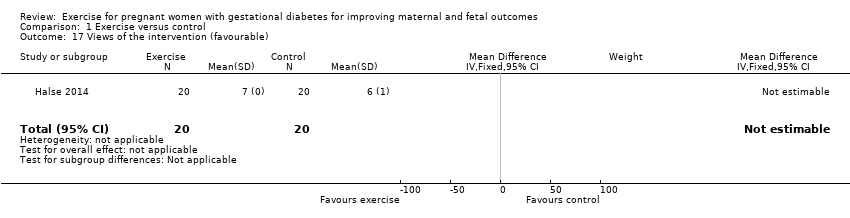 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 17 Views of the intervention (favourable). | ||||
| 18 Postnatal weight retention or return to pre‐pregnancy weight Show forest plot | 3 | 254 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐1.04, 1.26] |
| Analysis 1.18 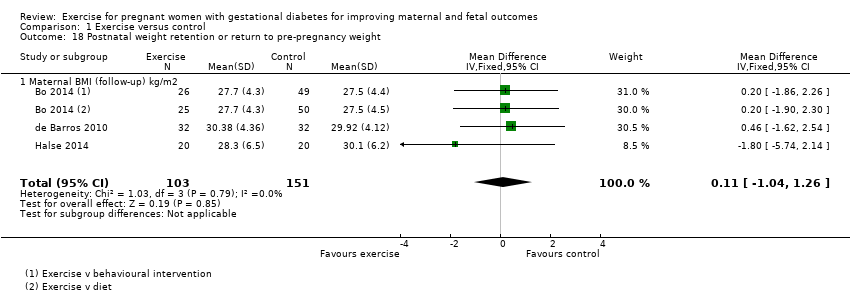 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 18 Postnatal weight retention or return to pre‐pregnancy weight. | ||||
| 18.1 Maternal BMI (follow‐up) kg/m2 | 3 | 254 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐1.04, 1.26] |
| 19 Stillbirth Show forest plot | 1 | 29 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.19 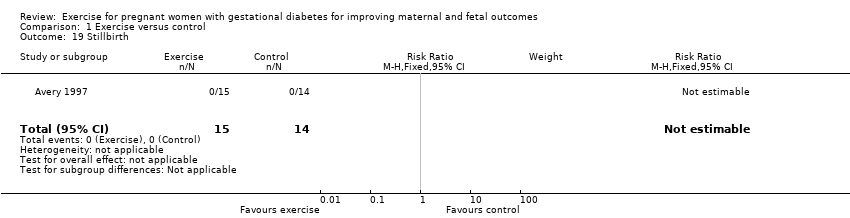 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 19 Stillbirth. | ||||
| 20 Macrosomia Show forest plot | 5 | 296 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.35, 1.35] |
| Analysis 1.20 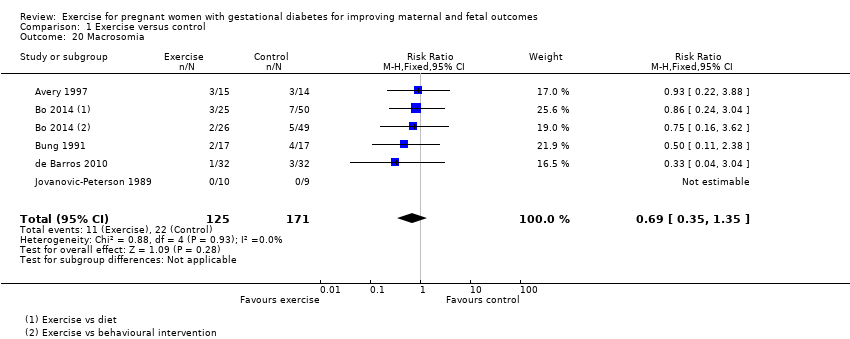 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 20 Macrosomia. | ||||
| 21 Gestational age at birth Show forest plot | 4 | 167 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.40, 0.38] |
| Analysis 1.21  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 21 Gestational age at birth. | ||||
| 22 Preterm birth Show forest plot | 5 | 302 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.39, 2.36] |
| Analysis 1.22  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 22 Preterm birth. | ||||
| 23 Five‐minute Apgar < seven Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.65] |
| Analysis 1.23  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 23 Five‐minute Apgar < seven. | ||||
| 24 Birthweight Show forest plot | 6 | 192 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐61.50 [‐195.21, 72.20] |
| Analysis 1.24  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 24 Birthweight. | ||||
| 25 Length (cm) (at birth) Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.70 [‐3.41, 0.01] |
| Analysis 1.25  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 25 Length (cm) (at birth). | ||||
| 26 Neonatal hypoglycaemia Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.20, 20.04] |
| Analysis 1.26 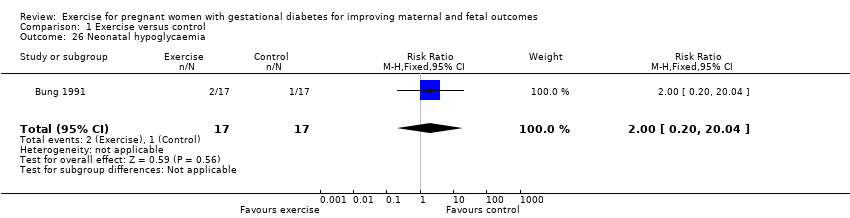 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 26 Neonatal hypoglycaemia. | ||||
| 27 Respiratory distress syndrome Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.27  Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 27 Respiratory distress syndrome. | ||||
| 28 Neonatal jaundice (hyperbilirubinaemia) Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.65] |
| Analysis 1.28 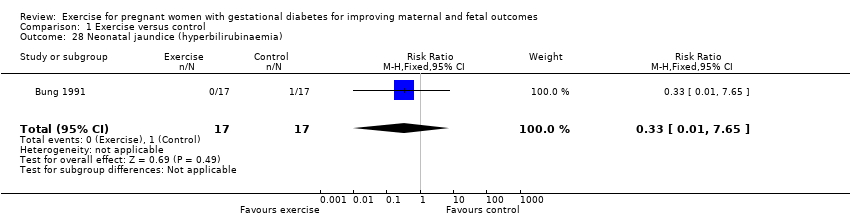 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 28 Neonatal jaundice (hyperbilirubinaemia). | ||||
| 29 Hypocalcaemia Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| Analysis 1.29 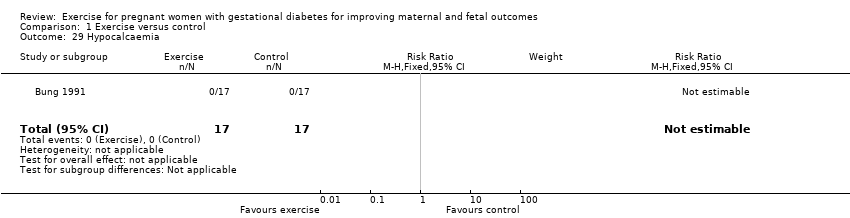 Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 29 Hypocalcaemia. | ||||
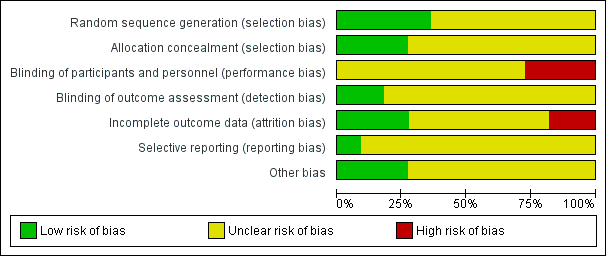
'Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 1 Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (pre‐eclampsia).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 2 Caesarean section.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 3 Perinatal mortality (stillbirth and neonatal mortality).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 4 Mortality and morbidity composite (variously defined by trials, e.g. perinatal or infant death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture or nerve palsy).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 5 Use of additional pharmacotherapy.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 6 Maternal hypoglycaemia.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 7 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Mean).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 8 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Fasting blood glucose concentration).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 9 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Postprandial blood glucose concentration).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 10 Glycaemic control end of treatment (HbA1c).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 11 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Glucose tolerance test).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 12 Weight gain in pregnancy.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 13 Weight gain in pregnancy (Excessive).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 14 Adherence to the intervention.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 15 Induction of labour.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 16 Maternal mortality.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 17 Views of the intervention (favourable).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 18 Postnatal weight retention or return to pre‐pregnancy weight.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 19 Stillbirth.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 20 Macrosomia.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 21 Gestational age at birth.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 22 Preterm birth.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 23 Five‐minute Apgar < seven.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 24 Birthweight.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 25 Length (cm) (at birth).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 26 Neonatal hypoglycaemia.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 27 Respiratory distress syndrome.

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 28 Neonatal jaundice (hyperbilirubinaemia).

Comparison 1 Exercise versus control, Outcome 29 Hypocalcaemia.
| Exercise compared to control for pregnant women with gestational diabetes for improving maternal outcomes | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with gestational diabetes | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with control | Risk with exercise | |||||
| Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (pre‐eclampsia) | 43 per 1000 | 13 per 1000 | RR 0.31 | 48 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Event rates were very low with 0/25 in the exercise group and 1/23 in the control group. No data were reported for pregnancy‐induced hypertension or eclampsia. |
| Caesarean section | 319 per 1000 | 274 per 1000 | RR 0.86 | 316 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | |
| Development of type 2 diabetes ‐ not measured | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | This outcome was not measured in any of the included studies in this review. |
| Perineal trauma/tearing ‐ not measured | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | This outcome was not measured in any of the included studies in this review. |
| Postnatal weight retention or return to pre‐pregnancy weight (maternal BMI (follow‐up) kg/m2) | The mean maternal BMI (follow‐up) kg/m2 was 0 | MD 0.11 higher | ‐ | 254 | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ | |
| Postnatal depression ‐ not measured | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | This outcome was not measured in any of the included studies in this review. |
| Induction of labour | 400 per 1000 | 552 per 1000 | RR 1.38 | 40 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Event rates and sample size were low 11/20 in exercise group and 8/20 in control group. |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 Lack of clarity for most items related to risk of bias ‐ downgraded one level. 2 Wide confidence intervals crossing the line of no effect and low event rates with a small sample size are suggestive of imprecision ‐ downgraded one level. 3 Imprecision ‐ low event rates and small sample size ‐ downgraded one level. | ||||||
| Exercise compared to control for pregnant women with gestational diabetes for improving maternal and fetal outcomes | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women with gestational diabetes Setting: USA, Italy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with control | Risk with exercise | |||||
| Large‐for‐gestational age ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | None of the included studies in this review reported data for this outcome. |
| Perinatal mortality (stillbirth and neonatal mortality) | 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 | not estimable | 19 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There were no events in either the exercise or the control group and the sample size in only 19 infants. |
| Mortality and morbidity composite (variously defined by trials, e.g. perinatal or infant death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture or nerve palsy) | 65 per 1000 | 36 per 1000 | RR 0.56 | 169 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | Event rates and sample size were low with 2/61 in the exercise group and 7/108 in the control group. |
| Neonatal hypoglycaemia | 59 per 1000 | 118 per 1000 | RR 2.00 | 34 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Event rates and sample size were low with 2/17 in the exercise group and 1/17 in the control group. |
| Adiposity ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | None of the included studies in this review reported data for this outcome at any life stage. |
| Diabetes (type 1, type 2) ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | None of the included studies in this review reported data for this outcome at any life stage. |
| Neurosensory disability | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | None of the included studies in this review reported data for this outcome. |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1 There is a lack of clarity for most items associated with risk of bias ‐ downgraded one level. 2 Imprecision ‐ There are no events in either group and the sample size is only 19 infants ‐ downgraded one level. 3 Imprecision ‐ wide confidence intervals and low event rates ‐ downgraded one level. | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (pre‐eclampsia) Show forest plot | 2 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.31 [0.01, 7.09] |
| 2 Caesarean section Show forest plot | 5 | 316 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.63, 1.16] |
| 3 Perinatal mortality (stillbirth and neonatal mortality) Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Mortality and morbidity composite (variously defined by trials, e.g. perinatal or infant death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture or nerve palsy) Show forest plot | 2 | 169 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.56 [0.12, 2.61] |
| 5 Use of additional pharmacotherapy Show forest plot | 7 | 413 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.54, 1.08] |
| 6 Maternal hypoglycaemia Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 7 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Mean) Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.28 [0.04, 0.52] |
| 8 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Fasting blood glucose concentration) Show forest plot | 4 | 363 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.59 [‐1.07, ‐0.11] |
| 9 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Postprandial blood glucose concentration) Show forest plot | 3 | 344 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.85 [‐1.15, ‐0.55] |
| 10 Glycaemic control end of treatment (HbA1c) Show forest plot | 2 | 320 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.43 [‐0.51, ‐0.35] |
| 11 Glycaemic control end of treatment (Glucose tolerance test) Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐81.6 [‐96.03, ‐67.17] |
| 12 Weight gain in pregnancy Show forest plot | 2 | 104 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.34 [‐1.25, 0.58] |
| 13 Weight gain in pregnancy (Excessive) Show forest plot | 1 | 79 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.9 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 14 Adherence to the intervention Show forest plot | 1 | 19 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.83, 1.21] |
| 15 Induction of labour Show forest plot | 1 | 40 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.38 [0.71, 2.68] |
| 16 Maternal mortality Show forest plot | 2 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 17 Views of the intervention (favourable) Show forest plot | 1 | 40 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 18 Postnatal weight retention or return to pre‐pregnancy weight Show forest plot | 3 | 254 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐1.04, 1.26] |
| 18.1 Maternal BMI (follow‐up) kg/m2 | 3 | 254 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [‐1.04, 1.26] |
| 19 Stillbirth Show forest plot | 1 | 29 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 20 Macrosomia Show forest plot | 5 | 296 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.35, 1.35] |
| 21 Gestational age at birth Show forest plot | 4 | 167 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.40, 0.38] |
| 22 Preterm birth Show forest plot | 5 | 302 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.39, 2.36] |
| 23 Five‐minute Apgar < seven Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.65] |
| 24 Birthweight Show forest plot | 6 | 192 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐61.50 [‐195.21, 72.20] |
| 25 Length (cm) (at birth) Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.70 [‐3.41, 0.01] |
| 26 Neonatal hypoglycaemia Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.20, 20.04] |
| 27 Respiratory distress syndrome Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 28 Neonatal jaundice (hyperbilirubinaemia) Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.65] |
| 29 Hypocalcaemia Show forest plot | 1 | 34 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |


