Alivio del dolor para la histeroscopia ambulatoria
References
References to studies included in this review
References to studies excluded from this review
References to ongoing studies
Additional references
References to other published versions of this review
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Methods | Randomised, single‐blind study. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, Canada. 42 women in intervention group and 42 women in placebo group | |
| Participants | Women undergoing hysteroscopy. Study included 84 women. Mean age of women was 36 years in intervention group and 35 in the placebo group. 1 woman dropped out of the study. | |
| Interventions | Local intracervical anaesthesia compared to combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia. 0.5% bupivacaine hydrochloride into anterior wall of cervix compared to 0.5% bupivacaine hydrochloride into anterior wall of cervix plus bupivacaine into lateral vaginal fornix at 3 and 9 o’clock at 10 mm depth. Both interventions were performed 5 min before the procedure. | |
| Outcomes | Mean pain score during the procedure, 10, 30 and 60 min after the procedure. 10‐point VAS used | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation was done using a computer generated random table." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | Single‐blinded ‐ outcome assessor blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 1 woman dropped out of the study but included in the final analysis (ITT). "A patient could not tolerate speculum examination and the procedure was aborted." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Co‐administration of 10 mg lorazepam 30 min prior to procedure |
| Methods | Randomised, non‐blinded, controlled study. Single‐centre trial at the Obstetrics and Gynaecology Service, Health Consortium of Terrassa, Barcelona, Spain | |
| Participants | 102 consecutive women scheduled for diagnostic or operative hysteroscopy were invited; 10 declined. Following randomisation there was 1 loss from the EMLA (intervention) group due to "deviation from protocol". No mean ages stated, no exclusions | |
| Interventions | "Either 3 mL EMLA cream 5% or 3 mL ultrasound gel was applied in the endocervical canal 10 min before surgery, with a 5‐mL needleless syringe. A subsequent application of either gel was made with a swab at ectocervix level." | |
| Outcomes | 10 cm VAS. Pain score within 30 min of procedure. Women who completed the hysteroscopy were asked if they would recommend the procedure to other women, if they had wished to abandon the hysteroscopy and whether they would repeat the procedure if needed. | |
| Notes | This study was added to this review in 2014. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Women were randomized to the EMLA or control group using computer‐generated random numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomization was conducted with sealed envelopes containing computer‐generated randomization numbers." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | Study is described as non‐blinded in the title, however in the discussion comments that "the main limitation of our study was that it was not double‐blinded, as we were unable to prepare a placebo with identical appearance and texture to the EMLA gel in our laboratory." This suggests that the operator would not be blinded, the participant may have been. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | "One of the women in the EMLA group was excluded for protocol violation". Nature of violation not specified |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No pre‐published protocol seen, however all planned outcomes from methods are reported, together with adverse outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | All women were given 600 mg ibuprofen (if allergic 1 g paracetamol) and 5 mg diazepam 2 h before procedure and misoprostol was administered only to postmenopausal women |
| Methods | Randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at The Minimally Invasive Therapy Unit, University Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, The Royal Free Hospital, London, UK. 50 women in the placebo group and 50 women in the intervention group | |
| Participants | 100 consecutive women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy for abnormal uterine bleeding consented to be included in the study. The median age of the women was 43 years. 3 exclusions | |
| Interventions | Intracervical injection of either 10 mL of lignocaine 1% with 1:200 000 adrenaline or normal saline was injected into the cervix at 1, 5, 7, and 11 o’clock | |
| Outcomes | 10 cm VAS. Pain score before, during, after and 60 min after the procedure. Data grouped into dichotomous outcomes | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Each patient was randomly allocated to receive either lignocaine 1 % or normal |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Each patient was randomly allocated to receive either lignocaine 1 % or normal saline intracervically. Randomization was performed using a predetermined randomization code in a double blind fashion." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomization was performed using a predetermined randomization code in a double blind fashion." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "Hysteroscopy was unsuccessful in three women: two (one from each group) found the procedure too painful, and one patient fainted after the intracervical injection of saline. These women were excluded from further analysis." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data converted into a dichotomous manner. 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. No P values stated, which may indicate an element of under reporting |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at University of Bari, Italy. 40 women in intervention group and 40 women in placebo group | |
| Participants | Postmenopausal women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy. Mean age of women was 59 years in both the intervention and placebo group. No dropouts or exclusions | |
| Interventions | 2 mL of 2% mepivacaine or 2 mL of 0.9% saline injected transcervically (inserted up the cervical canal to the internal os) 5 min before the procedure | |
| Outcomes | Mean pain score before the procedure, during the procedure, at endometrial biopsy and 15 min after the procedure. 20 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation was done by opening sealed envelopes containing computer generated block‐randomisation numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomisation was done by opening sealed envelopes containing computer generated block‐randomisation numbers." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "Women were randomly and double blindly assigned." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No dropouts or exclusions. "Hysteroscopy performed in all patients." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (20 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes. Insufficient evidence of under reporting |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blinded, placebo controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at University of Bari, Italy. 36 women in intervention group and 36 women in placebo group | |
| Participants | Postmenopausal women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy. Mean age of women was 55 years in the intervention group and 56 in the placebo group. No dropouts or exclusions | |
| Interventions | 10 mL of 1.5% mepivacaine or saline injected into junction of cervix and vagina (4 and 8 o'clock positions) 10 min before procedure | |
| Outcomes | Mean pain score before the procedure, during the procedure, at endometrial biopsy and 15 min after the procedure. 20 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation was done by opening sealed envelopes containing computer generated block‐randomisation numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomisation was done by opening sealed envelopes containing computer generated block‐randomisation numbers." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "Women were randomly and double blindly assigned." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No dropouts or exclusions. "Hysteroscopy performed in all patients." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (20 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes. Insufficient evidence of under reporting |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at Day Unit, Queen Charlotte's and Chelsea Hospital, London. 44 women in the intervention arm, 44 women in the placebo arm and 35 women in the control arm | |
| Participants | Women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy. Mean age of women 44.5 years in intervention group ad 44.6 and 43.4 in the placebo and control group respectively. 14 exclusions | |
| Interventions | Lignocaine gel, placebo gel or no gel administered. Some women received intracervical lignocaine block if determined to need cervical dilatation | |
| Outcomes | Mean pain score across the whole procedure, at gel administration, at lignocaine injection, cervical dilatation, hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy. 4‐point descriptive scale used | |
| Notes | Co‐administration in some women of intracervical block. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "A total of 88 consecutive women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy were allocated in a double‐blind manner to one of two groups using a pre determined randomization code." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "A total of 88 consecutive women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy were allocated in a double‐blind manner to one of two groups using a pre determined randomization code." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | "Gel was given prior to the investigation by a different operator from those who carried out hysteroscopy, and the patient, hysteroscopist and other staff were unaware of which gel had been used." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Failed procedure in 14 women. No reasons given |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Data grouped into two outcomes. 1 measuring instrument used (4‐point descriptive scale). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline |
| Other bias | High risk | Co‐administration of intracervical block in some women |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at Royal Hospital for Women, Sydney, Australia. 50 women in intervention group and 50 women in placebo group | |
| Participants | Women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy with or without endometrial biopsy. Mean age of women was 46 years in the intervention group and 47 in the placebo group. 1 exclusion as no cervical os could be identified | |
| Interventions | 5 mL of 2% lignocaine or 5 mL of 0.9% saline injected into cervical canal and uterine cavity via hysteroscope 2 min before hysteroscope was manoeuvred | |
| Outcomes | Mean pain score during the procedure. 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Pre determined randomization code administered by the hospital pharmacy." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Pre determined randomization code administered by the hospital pharmacy." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | "The physicians performing the procedure and the patients were blinded to treatment assignment." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "One patient was unable to undergo hysteroscopy as there was no identifiable cervical os." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | High risk | All women were instructed to take 2 naproxen tablets 275 mg prior to procedure. As women had received naproxen already, the study was more or less on the pain level of manoeuvring the scope, not introduction of the scope, as the pain medication was infused though the scope which was already in the uterine cavity. This may have introduced bias too. In 2 women, hysteroscopy was abandoned due to pain. In both cases, the randomisation code was broken. In both cases normal saline had been used: following the administration of 5 mL 2% lignocaine the procedure was completed |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. 34 women in intervention group and 28 women in placebo group. Single‐centre trial in day hospital, Bahia, Brazil | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. Age of women ranged between 20 and 71 years, with the mean age of 45 years in both groups. 3 dropouts due to stenosis of the internal uterine cavity | |
| Interventions | Intracervical application at 1, 5, 7 and 11 o'clock positions of 4 x 2 mL ampoules of 2% lidocaine hydrochloride ampoules or saline | |
| Outcomes | Pain score during hysteroscopy, during the biopsy, at the end of the procedure and 30 min after the procedure. 10‐point Huskinssion VAS used | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | “Patients were randomly allocated into two groups.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated in study |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double‐blinded, “neither the patient nor the attendant physician were aware of the content of the ampoules.” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | 65 women initially enrolled into study with two exclusions. 1 woman not accounted for in results |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unequal numbers in 2 groups ‐ could happen by chance |
| Methods | Prospective randomised study. No loss to follow‐up. 60 women in both intervention groups Single‐centre trial at Flinders Medical Centre, Adelaide, Australia | |
| Participants | Women undergoing hysteroscopy referred from GPs and other gynaecologists. Mean ages not stated. No exclusions | |
| Interventions | 20 mL of 1% lignocaine paracervical block or 2% uterosacral block | |
| Outcomes | Pain during hysteroscopy. 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "The patients were randomised according to an odd or even unit record number." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "The patients were randomised according to an odd or even unit record number." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | No exclusions |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data grouped into 3 dichotomous outcomes. 1 measurement scale used. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, unblinded study. No loss to follow‐up. 3‐arm study; 5 mm diagnostic sheath, 5 mm diagnostic sheath with paracervical block and 3.5 mm sheath. 119 women in group 1 and 121 women in groups 2 and 3. Results for groups 1 and 2 only were included within the meta‐analysis. Single‐centre trial in Centro di Fiferimento Oncologico in Aviano, Italy | |
| Participants | Postmenopausal women referred for outpatient diagnostic hysteroscopy. The mean ages of women were 60 years in group 1 and 61 years in group 2. 22 women were excluded. | |
| Interventions | 20 mL of 1% mepivacaine injected para cervically at 3, 5, 7 and 9 o'clock position of the junction of cervix and vagina at least 5 min before the procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score after the procedure. 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Procedures were randomly assigned through a computer randomization list." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | Not blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Excluded 22 women and 38 women not randomised (previous hysteroscopy, severe previous vagal reaction, allergy to local anaesthesia, vaginal stenosis, cervical stenosis, gas leakage, bubble formation, large polyps) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported; data were further subgrouped into those receiving hormonal treatment. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes but data presented as percentages in the abstract. SE stated rather than SDs |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other source of potential bias identified |
| Methods | Prospective, double‐blind RCT on 210 women between 20‐45 years old undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. No losses to follow‐up. 70 women allocated to the tramadol group; 70 to the celecoxib group and the remaining 70 to the placebo group Cairo University Hopsitals, Egypt. May 2014‐November 2014 | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. Study included 210 after 23 women declined to participate and 12 women were excluded. Mean age of women in tramadol group 29.25 ± 6.39; mean age of women in Clecoxib group 29.52 ± 6.44; mean age of women in placebo group 30.8 (6%). None of the procedures had to be stopped in the tramadol and celecoxib groups however, 1 procedure had to be stopped in the placebo group due to severe, intolerable pain (VAS 0‐10 cm) | |
| Interventions | Women were assigned into 1 of three groups to receive either 100 mg of oral tramadol (Tramaw, Global Napi, Giza, Egypt) or 200 mg of Celecoxib (Celebrexw 200, Pfizer, USA) or placebo in the control group. All women received the medication 1 h before the intervention. The procedure was performed in the lithotomy position. A 30º angle was used to introduce a 2.9 mm rigid hysteroscope with 3.8 mm diagnostic sheath (Karl Storzw, Germany). The vaginoscopic approach was used for insertion of the hysteroscope in all cases (no use of speculum or tenaculum). The hysteroscope was gently introduced into the uterine cavity after visualisation of the cervix and identification of the external os. Saline was used as the distension medium and the maximum pressure was set at 100 mmHg. | |
| Outcomes | Before surgery, women were educated about the VAS, in which 0 indicated no pain and 10 the worst pain imaginable. Women’s perception of pain was assessed for each group during, immediately after and 30 min after the procedure with the use of the score on VAS. Time until no pain was estimated by asking women to report the time when they thought pain had completely gone. All women stayed in the clinic for at least 30 min and for up to 2 h until the time no pain was reported, and all women were pain free before leaving the clinic. Women were also asked to report side effects. | |
| Notes | With regard to Hassan 2016a and Hassan 2016b, the corresponding author confirmed by email (20 September 2017) "that the 2 papers represent 2 different studies with independent data" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "An independent person generated the allocation sequence using computer generated random numbers in a 3 block table" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Drugs were enclosed in sequentially numbered, sealed envelopes and were kept with the attending nurse." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double blinding. "Neither the patient nor the physician were aware of the drug used." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No loss to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument was used (10 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
| Methods | Prospective, double‐blind RCT on 140 women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy of reproductive age (12‐49 years). 70 women allocated to the tramadol group; 70 allocated to the placebo group Cairo University Hopsitals, Egypt, from May 2014‐March 2015 | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. Study included 140 after 46 women declined to participate and 26 women were excluded. Mean age of women in tramadol group 31.5 (+/‐ 7.4); mean age of women in placebo group 32.3 (+/‐ 8.1). None of the procedures had to be stopped in the tramadol group; 1 procedure had to be stopped in the placebo group due to severe, intolerable pain (VAS 0‐10 cm) | |
| Interventions | Women were assigned to 1 of two groups to receive either 50 mg of oral tramadol (Tramaw, Global Napi, Gisa, Egypt) or placebo in the control group. All women received the medication 1 h before the intervention. The procedure was performed in the lithotomy position. A 30º angle was used to introduce a 2.9 mm rigid hysteroscope with 3.8 mm diagnostic sheath (Karl Storzw, Germany). The vaginoscopic approach was used for insertion of the hysteroscope in all cases (no use of speculum or tenaculum). The hysteroscope was gently introduced into the uterine cavity after visualisation of the cervix and identification of the external os. Saline was used as the distension medium and the maximum pressure was set at 100 mmHg. All procedures done by the same operator with same technique | |
| Outcomes | Women’s perception of pain was assessed for each group during, immediately after and 30 min after the procedure with the use of the score on a VAS. Women were also asked to report side effects. | |
| Notes | With regard to Hassan 2016a and Hassan 2016b, the corresponding author confirmed by email (20 September 2017) "that the 2 papers represent 2 different studies with independent data" | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "An independent person generated the allocation sequence using computer generated random numbers" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Drugs were enclosed in sequentially numbered, sealed envelopes and were kept with the attending nurse." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double blinding. "The nurse, the patient and the physician were not aware of the drug used." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No loss to follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | 1 measuring instrument was used (10 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes. Pain outcomes reported as median scores and not means. |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
| Methods | A prospective, randomised trial. No loss to follow‐up. 36 women in local cervical group and 42 women in combined local cervical and intrauterine anaesthesia group. Single‐centre trial at Academic Teaching Centre, McGill University, Montreal, Canada | |
| Participants | Infertile women undergoing hysteroscopy. Mean age of 37 years in local cervical group and 38 in combined local cervical and intrauterine anaesthesia group. 4 exclusions | |
| Interventions | 2 mL of 1% lidocaine into anterior wall. Distension medium of either saline only or 18 mL of lidocaine in 250 mL of saline | |
| Outcomes | Pain score during hysteroscopy and 10, 30 and 60 min after hysteroscopy. 10‐point VAS | |
| Notes | Co‐administration of lorazepam 10 mg orally 30 min before the procedure | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation was done using a computer generated random number table." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomisation was done using a computer generated random number table." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | Single blinded. "The patients were blinded but the operators were aware of the content of the solution." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "Three withdrew consent and one could not tolerate speculum examination." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Data presented as medians. 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Co‐administration of lorazepam 10 mg orally |
| Methods | Prospective RCT on 200 women undergoing hysteroscopy for abnormal uterine bleeding. No losses to follow‐up. 100 women received local anaesthesia while 100 women did not receive any local anaesthesia Department of Gynaecology of Zekai Tahir Burak Woman's Health Research and Education Hospitals, Ankara, Turkey, May 2013‐September 2013 | |
| Participants | Study included 200 women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. Mean age of women in Group 1 (received local anaesthesia) 41.94 ± 9.01; mean age of women in Group 2 (no local anaesthesia) 42.03 ± 8.30 None of the procedures had to be stopped in Group 1 or 2 | |
| Interventions | All women were examined between the 5 LH and 10 LH cycle days. A disposable speculum was used to visualise the cervix and the cervix was cleaned with a water solution of octenidine hydrochloride 0.1% and 2‐phenoxyethanol 2%. Intracervical local anaesthesia (10 mL of 1% prilocaine) was applied at the 4 and 8 o’clock positions on the posterior lip of the cervix in divided doses and then the speculum was removed. A rigid, 3‐mm outer diameter Storz® hysteroscope was used for the procedure. Hysteroscopy was performed without the use of a tenaculum and without cervical dilatation by the same physician who knew the group to which the women belonged. Uterine distension was maintained by a steady stream of 1.5% Glycine solution | |
| Outcomes | Before surgery, women were educated about the VAS in which 0 indicated no pain and 10 the worst pain imaginable. Women were observed for 60 min and they were asked to complete a standardised pain evaluation form to evaluate the worst pain experienced during the procedure after 30 min and 60 min of the procedure by a clinician who did not know who did not know the group to which the women belonged. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | All the 200 women were randomised using a computer |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | Physician performing the procedure were not blinded to the allocation. However, physicians evaluating the pain score using VAS were blinded to the procedure. Unclear as to whether the women were blinded to the procedure. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No exclusions reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other potential bias detected |
| Methods | Double‐blinded, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. 49 women in intervention group, 50 in placebo group. Single‐centre trial at The Chinese University of Hong Kong | |
| Participants | Women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy for abnormal uterine bleeding. Mean age of 49 years in intervention and placebo group | |
| Interventions | Paracervical block at 3, 5, 7 and 9 o'clock positions of 10 mL of 2% lignocaine or saline, 5 min prior to procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score before the procedure, at grasping the cervix, after injection, at insertion of hysteroscope, distension of uterus, after endometrial biopsy and 30 min after the procedure. 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "They were randomized into two groups using a computer generated block number and put inside a sealed envelope." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "They were randomized into two groups using a computer generated block number and put inside a sealed envelope." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | "The attending doctor, nursing staff and the women were all blinded to the identity of the medication used." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 1 exclusion reported. "Hysteroscopy failed in one woman because of cervical stenosis" |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Double‐blinded, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. 45 women in intervention group, 44 in placebo group. Single‐centre study at Prince Wales Hospital, Hong Kong | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. Mean age 48 years in intervention group and 44 in placebo group. 1 exclusion | |
| Interventions | Transcervical intrauterine instillation of 5 mL of 2% lignocaine or normal saline into the uterine cavity 5 min before procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score before the procedure, at grasping of the cervix, after instillation, at insertion of hysteroscope, during hysteroscopy, at endometrial sampling and 30 min after the procedure. 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "The woman was randomized into one of the two groups using random numbers generated by a computer." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "The allocations placed into opaque sealed envelopes." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double blinded. “Both the woman and the attending medical staff were unaware of the medication used.” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 1 exclusion. "One woman in the placebo group who experienced intolerable pain." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, placebo‐controlled study. No loss to follow‐up. 80 women in intervention group. 84 in placebo group. Single‐centre trial at Wu Ho‐Su Memorial Hospital, Taiwan | |
| Participants | Women undergoing office hysteroscopy. 15 exclusions. Mean age of 41 years in intervention group and 40 in placebo group | |
| Interventions | 0.2 mg of buprenorphine or placebo given under tongue 40 min prior to procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score during the procedure. 10 cm VAS used | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "The patients were randomized by computer generated numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "The procedure failed in 15 patients because of cervical stenosis." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes. The P values were described as not significant but were not actually reported, which may suggest an element of under reporting |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, comparative treatment trial conducted by 5 private obstetrics and gynaecology practices in the USA with 1 investigator per site. 3 women lost to follow‐up. 40 premenopausal women randomised to combined para/intracervical anaesthetic block protocol of 37 cc local anaesthetic administered at 6 different injection sites in association with application of topical 1% lidocaine gel or intracervical only anaesthetic block protocol of 22 cc administered at 3 different injection sites without topical anaesthesia | |
| Participants | Women undergoing hysteroscopy for removal of intrauterine polyps and myomas using the MyoSure device. Study included 40 women. 19 randomised to the para/intracervical group and 21 to the intracervical group. Mean age of women was 44.2 ± 7.7 in the combined para/intracervical block group and 41.8 ± 7.5 n the intracervical group. All randomised subjects underwent the procedure | |
| Interventions | The para/intracervical block group received a total of 37 cc of anaesthetic at 6 different sites. Topical 1 % lidocaine was applied to the cervix, with a set time of 2‐3 min before the injection of anaesthetic, for para/intracervical group only. The intracervical group received a total of 22 cc of anaesthetic administered at 3 different sites | |
| Outcomes | The main outcome measure was composite score for procedure‐related pain, which incorporated individual pain scores during: 1) the cervical block injection; 2) cervical dilatation; 3) uterine distension; 4) the tissue resection | |
| Notes | This study used the Wong Baker scale, a 0‐10 cm measure | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Women were randomised on the day to combined para/intracervical block or an intracervical block group in a 1:1 ratio, using a computer‐generated randomisation scheme |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | The randomisation sequence was provided to sites, using sealed, sequentially labelled opaque envelopes |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | Single‐blinded ‐ women were blinded to the assignment because they were not told how many injections each group would be receiving |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | All randomised women underwent the procedure however, 2 women failed to meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria and 1 woman had a major protocol deviation. As a result the final analysis included 17 women in the para/intracervical block and 20 in the intracervical block. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument, the Wong‐baker face rating scale was used. This scale provides a scale ranging from 0‐10 cm, with 0 indicating no pain with 10 indicating maximum pain. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Women were told to take 800 mg of ibuprofen the night before the procedure. 1 h before the procedure the women received 10 mg of diazepam and 10 mg of hydrocodone/acetaminophen, followed by an intramuscular injection of 30 mg ketorolac and 0.4% of atropine |
| Methods | A randomised, placebo‐controlled study. No loss to follow‐up. 200 women were prospectively randomised into two groups, the study group (n = 100) and the control group (n = 100). Single‐centre trial at the hysteroscopy unit of the First Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the University of Athens | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy, with or without endometrial biopsy. Mean age of 35.4 years in the intervention group and 36.1 in the placebo group | |
| Interventions | 1 mL to 3 mL (30 to 90 mg) of mepivacaine 3% or saline administered intracervically 3 min prior to procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score during the procedure, 30 min after the procedure and 60 min after the procedure. 11‐point scale used | |
| Notes | Varying dose of mepivacaine given | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "200 patients were prospectively randomised into two groups." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "200 patients were prospectively randomised into two groups." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | "No patient from either group needed to be hospitalised. All patients left the hospital within 90 min after the end of the procedure." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | 1 measuring instrument used (11‐point scale). Data were reported in a graphical form as well as numerical form. However, these data could not be accurately included within the review as the P values and SDs were described as not significant but were not actually reported, which may indicate an element of under reporting. All time points stated to have data collected were reported in the graph, but could not be interpreted accurately. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Varying dose of mepivacaine administered |
| Methods | A randomised prospective study. No loss to follow‐up. A total of 148 women received dexketoprofen tablets and 150 women received local anaesthetic drug. Single‐centre trial at Menopause Clinic, University ‘Federico II’ of Naples, Via Pansini 5, Naples, Italy | |
| Participants | 305 consecutive postmenopausal women were referred to outpatient Menopause Clinic for hysteroscopy because of uterine bleeding. Mean ages not stated. Postmenopausal women | |
| Interventions | The women were randomly allocated to receive either local infiltration of the cervix by injecting of 5 mL mepivacaine 2% intracervically up to the level of the internal os or 1 tablet of dexketoprofen given 1 h before the procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain experienced during hysteroscopy and at 30, 60 and 120 min after the procedure | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation was achieved with sealed envelopes containing computer generated block randomisation numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomisation was achieved with sealed envelopes containing computer generated block randomisation numbers." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "Seven women were excluded from the study. Five of these thought to be too anxious to tolerate hysteroscopy under local anaesthesia or pharmacological sedation, two because previous conisation." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data presented in a graphical form only with no numerical values. 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Double‐blind RCT. 70 nulliparous women with primary infertility undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. 18 lost to follow‐up. 44 women in lidocaine group (9 lost to follow‐up in this group so final analysis of 35 women) and 44 (9 lost to follow‐up so final analysis of 35 women) women in diclofenac group. Center of Reproductive Medicine, Dr. Shariati Hospital, July 2012‐April 2013 | |
| Participants | Women undergoing hysteroscopy. Study included 70 women after excluding 24 due to not meeting inclusion criteria or being lost to follow‐up. Mean age of women in lidocaine group 29.3 ± 4.4; mean age of women in diclofenac group 30.8 ± 4.4. 9 women in the lidocaine group needed sedation with propofol. 5 women in the diclofenac group needed sedation and 4 women needed an invasive procedure in the diclofenac group | |
| Interventions | Women were assigned into 1 of two groups to receive either 100 mg of rectal diclofenac or 5 mL of 2% intrauterine lidocaine. In the gynaecologic ward, 30 min before transferring to the operating room, the staff gave 100 mg rectal diclofenac to women in the diclofenac group. The study drugs (lidocaine or saline) were prepared by the anaesthesia staff who gave it to the surgeon who was blinded to allocation. Then 5 mL of 2% lidocaine or the same volume of saline was instilled through the endocervix into the uterine cavity with an 18‐gauge angiocatheter. The angiocatheter was left in place for 3 min before it was withdrawn while women were in the Trendelenburg position to limit backflow and to allow the anaesthetic to take effect | |
| Outcomes | Before surgery, women were educated about the NRS, 0 indicated no pain and 10 the worst pain imaginable. Pain scoring was performed during insertion of the hysteroscope, during visualisation of the intrauterine cavity, and during extrusion of the hysteroscope | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation was performed using computer‐generated codes. Sealed envelopes containing the information of the randomisation code were kept by the staff not involved in the study. The envelope was transferred to a specific member of the gynaecologic staff |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Sealed envelopes containing the information of the randomisation code, generated by a computer were given to a member of the gynaecology staff |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double blinded ‐ outcome assessor and the women were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Of the 88 women randomised, 18 were lost to follow‐up (9 needed propofol in the lidocaine group); 5 needed sedation with propofol and 4 needed an invasive procedure in the diclofenac group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument was used (NRS 0–10) and the data were reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. 49 women were randomised to the active drug, and 46 to placebo. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at Minimally Invasive Therapy Unit and Endoscopy Training Centre, University Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, The Royal Free Hospital, London, UK | |
| Participants | The mean age of the women was 43 to 49 years. Women attending for diagnostic hysteroscopy | |
| Interventions | Active mefenamic acid 500 mg or placebo tablets 1 h before the procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain scores during, immediately after (0 min), 30 min and 60 min after outpatient hysteroscopy. 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Active (mefenamic acid 500 mg) and placebo tablets, which were identical in appearance, were packaged in coded bottles, randomisation being provided by the manufacturer." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Active (mefenamic acid 500 mg) and placebo tablets, which were identical in appearance, were packaged in coded bottles, randomisation being provided by the manufacturer." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "Active (mefenamic acid 500 mg) and placebo tablets, which were identical in appearance, were packaged in coded bottles, randomisation being provided by the manufacturer." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Hysteroscopy was unsuccessful in 4 women (2 in each group): 2 refused because they were too anxious and 2 procedures had to be abandoned because of pain |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data presented graphically with no numerical values. 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Odds ratio of experiencing pain calculated |
| Other bias | High risk | Some women given local anaesthesia as well as intervention |
| Methods | Double‐blind RCT. 206 women suspected of having endometrial polyp, abnormal uterine bleeding or diagnosis of myoma and infertility. No losses to follow‐up. The total 206 women comprised 68 (33%) in the placebo group, 76 (36.89%) in the lidocaine group and 62 (30.09%) in the indomethacin group Bakirköy Dr. Sadi Konuk Training and Research Hospital. July 2014‐March 2015 | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy. Study included 206 women. Mean age of women in placebo group 45.62 ± 9.04; mean age of women in lidocaine group 45.54 ± 11.73; mean age of women in indomethacin group 44.71 ± 9.97 | |
| Interventions | The control group was administered with a 1000 mL distention medium containing 18 mL serum physiologic per 250 mL and a rectal placebo. The second group was administered with a 1000 mL distention medium containing 18 mL lidocaine per 250 mL (Jetokain ampoule 20 mg 2% Adeka, Samsun, Turkey) and rectal placebo. The third group was administered with rectal | |
| Outcomes | Before the procedure, women were educated about the NRS in which 0 indicated no pain and 10 the worst pain imaginable. Pain scoring was performed during insertion of the hysteroscope, during visualisation of the intrauterine cavity and 10 min after the procedure | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Women were selected using random‐number tables |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | The hysteroscopist and woman were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | There was no loss to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | 1 measuring instrument was used (NRS 0–10) and the data were reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes. Pain score outcomes were reported as medians |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other potential risk identified |
| Methods | Randomised trial. No loss to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at outpatient gynaecology department of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India. 40 women in each intervention group with a total of 120 women | |
| Participants | A total of 120 women with a medical indication for hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy (infertility, abnormal uterine bleeding) were recruited. The mean ages were 36.28 years in group 1, 37.75 in group 2 and 36.82 years in group 3 | |
| Interventions | Group 1 women received fixed‐dose oral tablet containing drotaverine (80 mg) with mefenamic acid (250 mg) 1 h prior to the procedure. Group 2 women received paracervical block with 10 mL of 1% lignocaine solution injected at 3 and 9‐o'clock position at the junction of the cervix and vagina in divided doses 5 min prior to the procedure. Group 3 women received intravenous sedation with diazepam (0.2 mg/kg body weight) and pentazocine (0.6 mg/kg body weight) 10 min prior to the procedure. This group was not included in the review | |
| Outcomes | The worst pain experienced during the procedure and the degree of their discomfort after 30 min and 60 min of the procedure using a 10 cm VAS | |
| Notes | Only 2 of the 3 comparison groups were eligible for this review | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "This study was an open‐label randomised trial where all the 120 patients were randomised using a predetermined computer‐generated randomisation code into 3 groups." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details reported |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | "This study was an open‐label randomised trial." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | "Of the 120 patients recruited, procedure was performed successfully in all, and at no point anyone was excluded from the study." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Double‐blinded RCT. 62 in intervention group, 56 in placebo group. None lost to follow‐up. Single‐centre trial at Hopital Hotel‐Dieu de Paris, Paris, France | |
| Participants | Women undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy for abnormal uterine bleeding or infertility. Mean age of 41 years in intervention group and 40 in placebo group | |
| Interventions | 30 mg (3 metered doses) of lignocaine or placebo sprayed onto surface of cervix and cervical canal through 360° 5 min prior to procedure. 3 exclusions | |
| Outcomes | Pain score during the procedure. 10 cm VAS (pain) | |
| Notes | Unequal number in groups. No re‐inclusion of exclusions into analysis | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Women were assigned to receive either lidocaine spray or placebo according to a computer generated randomisation code." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Lidocaine and placebo were packaged in identical bottles and could not be differentiated." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double‐blinded. "Lidocaine and placebo were packaged in identical bottles and could not be differentiated." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 3 women excluded. "Two women did not fill out the questionnaire properly"; "one woman the diagnostic hysteroscopy was not done due to cervical stenosis." |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unequal numbers in intervention and placebo groups ‐ could happen by chance |
| Methods | Randomised, prospective study. No loss to follow‐up. 88 women in prilocaine cream group and 92 women in lignocaine spray group. Study refers to 165 in control group, but these women not part of RCT. Single‐centre trial at Castrovillari Hospital, Naples, Italy. | |
| Participants | Women attending for diagnostic hysteroscopy. No mean ages given | |
| Interventions | 1 cm3 of 5% prilocaine cream onto esocervix and 2 cm3 inserted 3 cm into cervical canal 10 min before procedure or 20 mg of lidocaine spray directed onto esocervix and 20 mg 3 cm into cervical canal immediately before procedure or no intervention | |
| Outcomes | 4‐point pain scale. Placement of tenaculum, progression through cervical canal and evaluation of uterine cavity | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "180 patients were included in the study and randomly allocated to group A or B" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "180 patients were included in the study and randomly allocated to group A or B." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "180 patients were included in the study and randomly allocated to group A or B." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear if any women excluded |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | 1 measuring instrument used (4‐point descriptive scale) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Data converted into two dichotomous groups |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. 92 in intervention group and 89 in placebo group. Single‐centre study at Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong | |
| Participants | Women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy. 2 women excluded and 19 women had procedure cancelled. Mean age of women was 50 years in intervention group and 48 in placebo group | |
| Interventions | 50 mg of oral diclofenac sodium or placebo tablet given 1‐2 h prior to procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score before the procedure, at grasping of the cervix, at insertion of the hysteroscope, during hysteroscopy, at endometrial sampling and 30 min after the procedure. VAS used | |
| Notes | Re‐inclusion of two exclusions into analysis but not of cancelled procedures | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Randomisation was performed by using a computer generated random numbers in blocks of 2." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Tablets individually placed into plastic bags according to group number and delivered to the woman by the research nurse |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Low risk | Double‐blinded. "Participants, attending medical staff and research nurses were blinded to the treatment used." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 22 cases not included. "Cancelled in 19"; "failure in inserting the hysteroscope in one case"; "intolerable pain in another" |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes. Insufficient evidence of under reporting |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Prospective, randomised trial comprising women referred to the Hysteroscopy Unit of the “Sanitas La Moraleja” Hospital in Madrid between November 2011 and May 2012. No losses to follow‐up. 200 women randomised to 2 groups: 100 women received 1000 mg paracetamol and 600 mg ibuprofen 1 h before the procedure and 100 did not receive any medication | |
| Participants | 200 women undergoing office hysteroscopy from November 2011‐May 2012. 100 women were randomised to a pre‐medication group (receiving 1 g of paracetamol and 600 mg of ibuprofen 1 h prior to hysteroscopy) and 100 women received no medication. Mean age of women was 45.9 ± 10.7 in the premedication group and 42.9 ± 11.9 in the no pre medication group | |
| Interventions | 1 g paracetamol and 600 mg ibuprofen were administered orally to the group receiving medication 1 h prior to hysteroscopy | |
| Outcomes | Pain was evaluated during the test at the time of cervical dilatation, as well as 5 and 30 min after completion of the test, by means of a VAS (5 faces on a scale of 0–10) | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | 200 women were randomised 1:1 (by means of a computer‐generated randomisation list, with same number of women in each group |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not available |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | High risk | The investigators assessing outcomes and statistician were blinded to the treatment assignment. Placebo was not used, so women and clinician who performed the intervention knew pre‐medicated women |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | No one was lost to follow‐up or not analyzed after randomisation |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument, VAS was used. This scale provides a scale ranging from 0‐10 cm, with 0 indicating no pain with 10 indicating maximum pain. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other source of bias detected |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blinded, controlled study. Single‐centre study at the Department of Gynaecology of the University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium | |
| Participants | 142 consecutive women presenting at the department's "One‐Stop Bleeding Clinic". Study does not mention if any women declined to participate prior to randomisation. From the population of 142 women who underwent gel installation sonohysterography (GIS), 132 went on to undergo hysteroscopy. Of these 132; mean age 50.6 years, premenopausal 78 (59.1%), perimenopausal 3 (2.3%), postmenopausal 51 (38.6%), nulliparity 21 (15.9%), median endometrial thickness on ultrasound 7.5 mm | |
| Interventions | Intervention group (n = 79 of 142) gel used for installation contained lidocaine (Instillagel) versus control group (n = 63 of 142) gel used for installation did not contain lidocaine (Endosgel) | |
| Outcomes | 100 mm VAS asking for perception of pain during the hysteroscopy, the questionnaire was completed shortly following the procedure | |
| Notes | This study was added to this review in 2014. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "...randomised into on of two groups using numbers generated randomly by a computer" further detail of the nature of the generation given |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "...placed in opaque‐sealed, numbered envelopes" |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "The patients as well as the medical staff performing the hysteroscopy were unaware which gel had been used." However the examiner performing the gel‐instillation sonography (GIS) was aware of which gel had been used. Although the relevant intervention was blinded there is a high risk that the blinding could be broken, although the likely impact of this on the results is unclear. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | High risk | Not all women who were randomised went on to have hysteroscopy, as some had GIS only. It is not specified if this was planned in advance or due to drop outs. In addition the number of responders was poor. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Although the outcome described in the method is reported, adverse events and reasons for non‐completion are not documented. Data was reported with interquartile ranges instead of SD. Study author failed to respond to attempts to make contact |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Open‐label, randomised trial. No loss to follow‐up. 87 in intervention group and 90 in no intervention group. Single‐centre study at University of Milan, Milan, Italy | |
| Participants | Women attending for diagnostic hysteroscopy. 4 women excluded. Mean age of 40 years in intervention group and 42 in no intervention group | |
| Interventions | Paracervical block at 3, 5, 7 and 9 o'clock positions of 10 mL 1% mepivacaine 5 min before procedure or no intervention given | |
| Outcomes | Pain score at hysteroscopy and endometrial biopsy. 10 cm VAS used | |
| Notes | Exclusions were not re‐included into final analysis | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "A randomisation list was used." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Patients were aware of which group they had been assigned to." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Women were aware of group |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 4 women excluded |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | 1 measuring instrument used (10 cm VAS) and data reported in 1 standard manner. All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | Randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. No loss to follow‐up. 250 women in intervention and placebo group. Single‐centre trial at Kwong Wah Hospital, Hong Kong | |
| Participants | Women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy. Mean age of 49 years in intervention and placebo group. No exclusions or dropouts | |
| Interventions | 4 mL of 2% lignocaine or placebo gel applied onto cervix before procedure | |
| Outcomes | Pain score at insertion of speculum, sounding of uterus, cervical dilatation, insertion of hysteroscope, inspection of uterine cavity and aspiration of tissue. 6‐point present pain intensity scale used | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomized into two groups with the use of a pre determined randomisation chart." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not stated |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | Double‐blind, "Neither the patient nor the gynaecologist were aware of the gel being applied” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | 3 cases excluded, "Severe pain or technical difficulty" |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | 1 measuring instrument used (6‐point present pain intensity scale). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline. Did not convert to dichotomous outcomes.Total area under curve also presented |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
| Methods | A randomised, double‐blind trial. No loss to follow‐up. Included 18 women | |
| Participants | Women undergoing hysteroscopy for infertility or abnormal uterine bleeding. Mean age not stated | |
| Interventions | 5 mL of 2% mepivacaine or 5 mL of saline intrauterine via 3 mm catheter | |
| Outcomes | 20 cm VAS. Pain score during the procedure, 15, 30, 60 and 120 min after the procedure | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "The women were randomised prospectively double blind into two groups." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "The women were randomised prospectively double blind into two groups." |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) | Unclear risk | "The women were randomised prospectively double blind into two groups." |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear if any exclusions |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Data presented graphically and without opportunity to calculate mean pain scores and SD. 1 measuring instrument used (20 cm VAS). All time points stated to have data collected were reported. Did not record change from baseline |
| Other bias | Low risk | Nothing detected |
GP: general practitioner; ITT: intention‐to‐treat; LH: luteinizing hormone; NRS: numeric rating scale; RCT: randomised controlled trial; SD: standard deviation; SE: standard error; VAS: visual analogue scale
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Hysteroscopy ‐ the study was not randomised | |
| Hysteroscopy ‐ intervention was TENs. Not pharmacological | |
| Hysteroscopy ‐ used general anaesthetic as an intervention | |
| Use of IV sedation | |
| Hysteroscopy ‐ use of IV remifentanil | |
| Hysteroscopy ‐ used IV propofol | |
| Hysteroscopy ‐ conscious sedation used as an intervention | |
| Microwave endometrial ablation ‐ use of general anaesthetic as an intervention |
IV: intravenous; TENs: transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Trial name or title | A comparison between lidocaine‐prilocaine cream (EMLA) application and wound infiltration with lidocaine for post caesarean section pain relief : a randomized controlled trial |
| Methods | Allocation: randomised Intervention model: parallel assignment Masking: single blind (investigator) Primary purpose: treatment |
| Participants | Women aged 18‐40 years |
| Interventions | Drug: EMLA cream 5 mg Drug: lidocaine 1 % |
| Outcomes | Primary outcome measures: time to the first dose of rescue analgesic in the first 6 h (time frame: 6 h) |
| Starting date | October 2014 |
| Contact information | Contact: Hany A Ibrahim MBBCH Contact: Ahmed M Mamdouh, MD |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Oral hyoscine butyl bromide versus diclofenac potassium before office hysteroscopy |
| Methods | Allocation: randomised Intervention model: parallel assignment Masking: single blind (participant) Primary purpose: prevention |
| Participants | Women ≥ 20 years |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Mean pain score during hysteroscopy (time frame: intraoperative) |
| Starting date | April 2016 |
| Contact information | Sponsored by: Assiut University |
| Notes |
| Trial name or title | Oral tramadol versus diclofenac for pain relief before outpatient hysteroscopy: (OPH) |
| Methods | Prospective, double‐blind, randomised, clinical trial. This will be conducted at Ain Shams University Maternity Hospital ‐ Early Cancer Detection Unite (ECDU) |
| Participants | Women aged 18‐35 years |
| Interventions | Women fulfilling inclusion and exclusion criteria will be divided into three groups. Group I (study group): 34 women who will receive tramadol 100 mg orally 1 h before the procedure Group II (study group): 34 women who will receive diclofenac 100 mg orally 1 h before the procedure Group III (control group) 34 women who will receive a placebo Pain will be evaluated on 2 separate occasions: immediately after the procedure and 15 min after procedure using a 100 mm line VAS |
| Outcomes |
|
| Starting date | May 2016 |
| Contact information | |
| Notes |
VAS: visual analogue scale
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 12 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 10 | 1496 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.29 [‐0.39, ‐0.19] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 5 | 545 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.50 [‐0.67, ‐0.33] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 4 | 450 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.11 [‐0.30, 0.07] |
| 2 Failure to complete procedure Show forest plot | 7 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 2 Failure to complete procedure. | ||||
| 2.1 Cervical stenosis | 6 | 805 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.23 [0.62, 2.43] |
| 2.2 Pain | 2 | 330 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.12, 0.69] |
| 3 Adverse events Show forest plot | 8 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 3 Adverse events. | ||||
| 3.1 Vasovagal reaction | 8 | 1309 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.43, 1.13] |
| 3.2 Non‐pelvic pain | 1 | 99 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.76 [0.53, 5.80] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 3 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2 Oral NSAID versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 3 | 521 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.18 [‐0.35, ‐0.00] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 2 | 340 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.25 [‐0.46, ‐0.04] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 2 | 321 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.27 [‐0.49, ‐0.05] |
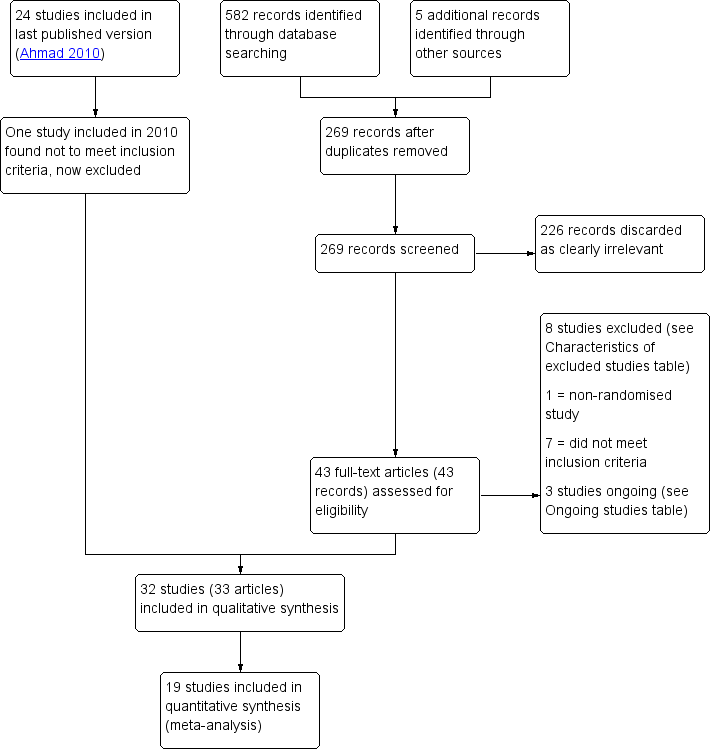
| 2 Adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 2.2 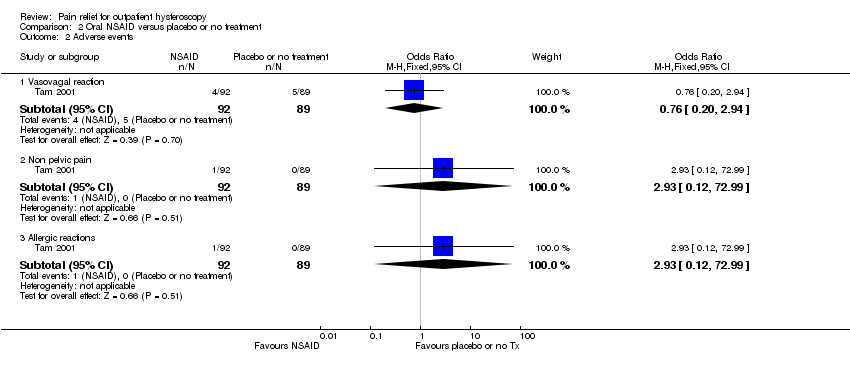 Comparison 2 Oral NSAID versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 2 Adverse events. | ||||
| 2.1 Vasovagal reaction | 1 | 181 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.20, 2.94] |
| 2.2 Non pelvic pain | 1 | 181 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.93 [0.12, 72.99] |
| 2.3 Allergic reactions | 1 | 181 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.93 [0.12, 72.99] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| Analysis 3.1  Comparison 3 Opioid versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Failure to complete procedure (due to pain) Show forest plot | 1 | 140 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.21] |
| Analysis 3.2  Comparison 3 Opioid versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 2 Failure to complete procedure (due to pain). | ||||
| 3 Adverse effects Show forest plot | 1 | 164 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 107.55 [6.44, 1796.46] |
| Analysis 3.3 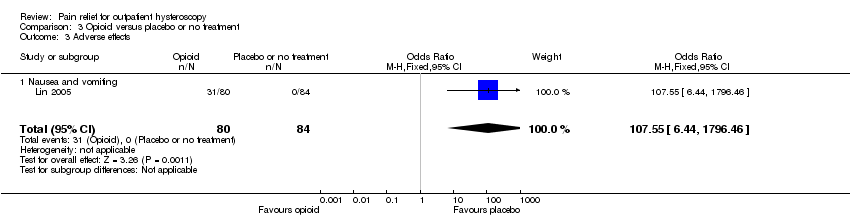 Comparison 3 Opioid versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 3 Adverse effects. | ||||
| 3.1 Nausea and vomiting | 1 | 164 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 107.55 [6.44, 1796.46] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 4.1  Comparison 4 Local intracervical anaesthesia versus combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 84 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.27 [3.49, 5.06] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 1 | 84 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.55 [1.06, 2.05] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | 84 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.47 [2.78, 4.15] |
| 2 Failure to complete procedure Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 4.2  Comparison 4 Local intracervical anaesthesia versus combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia, Outcome 2 Failure to complete procedure. | ||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 5.1  Comparison 5 Local intracervical anaesthesia versus combined intracervical, paracervical and topical anaesthesia, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 37 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.54 [‐1.20, 0.12] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 6.1  Comparison 6 Antispasmodic + NSAID versus local paracervical anaesthesia, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 80 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.40 [‐1.90, ‐0.91] |
| 1.2 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | 80 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.87 [‐1.33, ‐0.41] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Analysis 7.1  Comparison 7 Opioid versus NSAID, Outcome 1 Pain score. | ||||
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.15 [‐0.48, 0.18] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 1 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.25 [‐0.58, 0.08] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.17 [‐0.51, 0.16] |
| 2 Adverse effects Show forest plot | 1 | 140 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 9.54 [0.50, 180.64] |
| Analysis 7.2  Comparison 7 Opioid versus NSAID, Outcome 2 Adverse effects. | ||||
| 2.1 Nausea and vomiting | 1 | 140 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 9.54 [0.50, 180.64] |
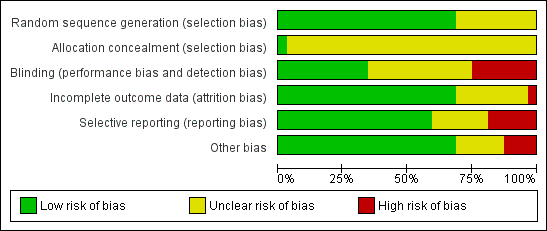
Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies
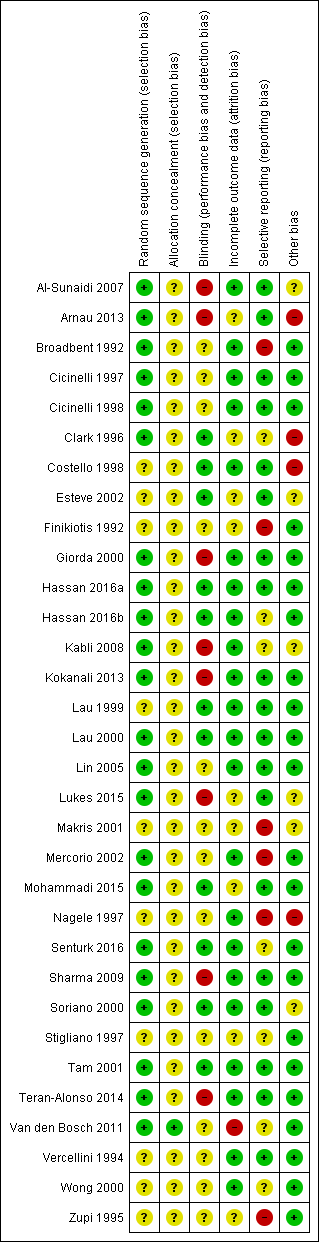
Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study
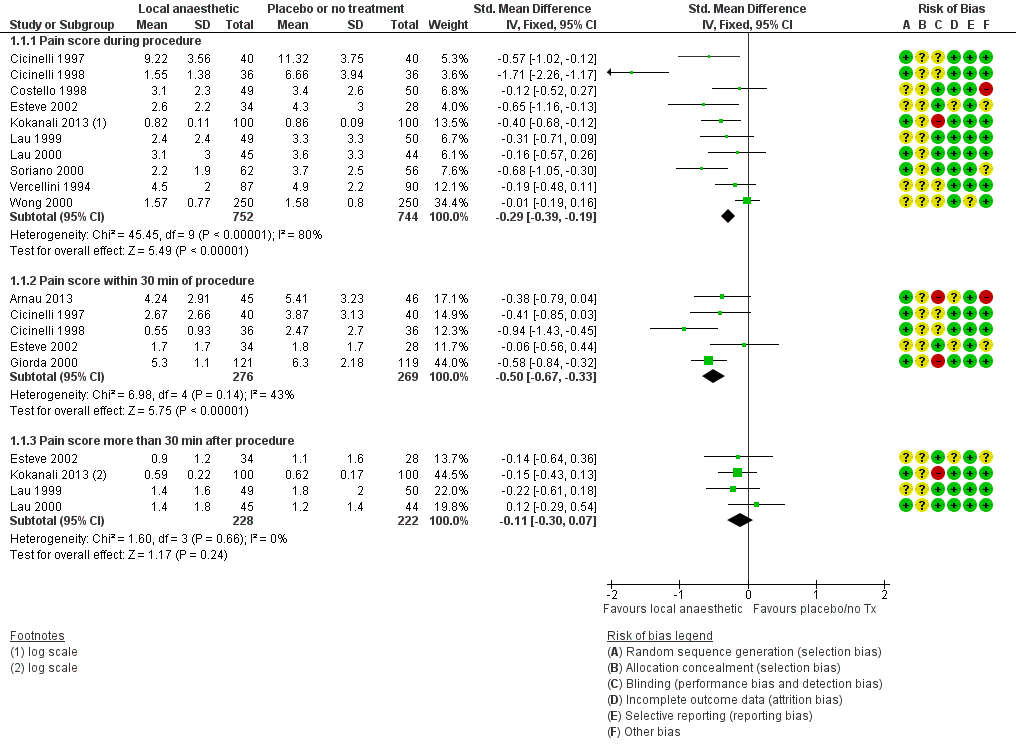
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, outcome: 1.1 Pain score.
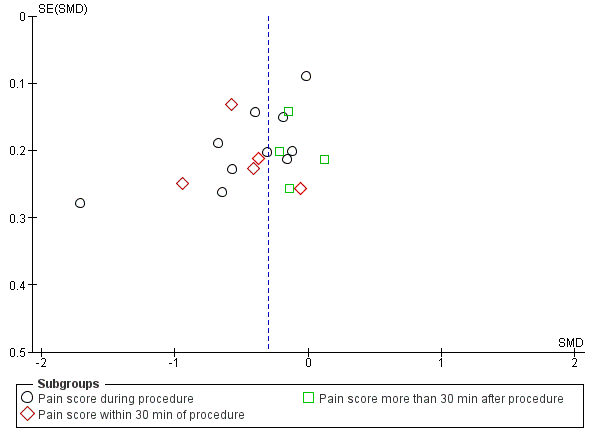
Funnel plot of comparison local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, outcome: pain score

Comparison 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 2 Failure to complete procedure.

Comparison 1 Local anaesthetic versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 3 Adverse events.

Comparison 2 Oral NSAID versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 2 Oral NSAID versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 2 Adverse events.

Comparison 3 Opioid versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 3 Opioid versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 2 Failure to complete procedure (due to pain).

Comparison 3 Opioid versus placebo or no treatment, Outcome 3 Adverse effects.

Comparison 4 Local intracervical anaesthesia versus combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 4 Local intracervical anaesthesia versus combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia, Outcome 2 Failure to complete procedure.

Comparison 5 Local intracervical anaesthesia versus combined intracervical, paracervical and topical anaesthesia, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 6 Antispasmodic + NSAID versus local paracervical anaesthesia, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 7 Opioid versus NSAID, Outcome 1 Pain score.

Comparison 7 Opioid versus NSAID, Outcome 2 Adverse effects.
| Local anaesthetic compared to placebo or no treatment for outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Population: women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with placebo or no treatment | Risk with local anaesthetic | |||||
| Pain score during procedure | The mean pain score ranged from 0.86 to 4.3 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.29 SD lower | ‐ | 1496 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | This suggests a marginally lower pain score in the intervention group, equating to up to 7 mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant |
| Pain score within 30 min of procedure | The mean pain score ranged from 1.8 to 6.3 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.5 SD lower | ‐ | 545 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | This suggests a marginally lower pain score in the intervention group, equating to up to 13 mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant |
| Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | The mean pain score ranged from 0.62 to 1.8 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.11 SD lower | ‐ | 450 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There was no clear evidence of a difference between the groups. |
| Vasovagal reaction | 63 per 1000 | 45 per 1000 | OR 0.70 | 1309 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | There was no clear evidence of a difference between the groups |
| Non‐pelvic pain | 100 per 1000 | 164 per 1000 | OR 1.76 | 99 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | There was insufficient evidence to determine whether there is a difference between the groups |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the mean risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded two levels for serious risk of bias: none of the studies adequately described methods of allocation concealment and methods of blinding were unclear or inadequate in many studies. | ||||||
| Oral NSAID compared to placebo or no treatment for outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Population: women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with placebo or no treatment | Risk with oral NSAID | |||||
| Pain score during procedure | The mean pain score ranged from 2.1 to 5.92 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.18 lower (0.35 lower to 0.00) | ‐ | 521 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | There was no clear evidence of a difference between the groups |
| Pain score within 30 min of procedure | The mean pain score ranged from 0.65 to 2.02 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.25 SD lower | ‐ | 340 participants | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | The evidence suggests a benefit in the NSAID group, equivalent to up to 2 mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant |
| Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | The mean pain score ranged from 1.2 to 1.55 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.27 lower | ‐ | 321 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | The evidence suggests a benefit in the NSAID group, equivalent to up to 7mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant |
| Vasovagal reaction | 56 per 1,000 | 43 per 1,000 | OR 0.76 | 181 participants | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Only 9 events There was insufficient evidence to determine whether there is a difference between the groups |
| Non pelvic pain | Not calculable: no events in one group | OR 2.93 | 181 participants | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Only 1 event There was insufficient evidence to determine whether there is a difference between the groups | |
| Allergic reaction | Not calculable: no events in one group | OR 2.93 | 181 participants | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | Only 1 event There was insufficient evidence to determine whether there is a difference between the groups | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the mean risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded one level due to serious risk of bias: none of the studies adequately described methods of allocation concealment. | ||||||
| Opioid compared to placebo or no treatment for outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Population: women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | № of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with placebo or no treatment | Risk with opioid | |||||
| Pain score during procedure: oral opioid | The mean pain score was 5.92 mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS | Oral opioid: SMD was 0.76 lower (95% CI 1.10 lower to 0.42 lower) | ‐ | 140 (1 study) | low1,2 | Data from the two studies were unsuitable for pooling due to extreme heterogeneity (I2 = 92%) with conflicting directions of effect. There is a suggestion of benefit from oral opioid, equating to a difference of up to 22 mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS. This may possibly be clinically significant |
| Pain score during procedure: sublingual opioid | The mean pain score was from 3.2 mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS | Sublingual opioid: SMD was 0.08 higher (95% CI 0.22 lower to 0.39 higher) | 164 (1 study) | low1,2 | ||
| Pain score within 30 min of procedure oral opioid | The mean pain score was 3.27 mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD ‐0.57 lower | ‐ | 140 | low1,2 | There is a suggestion of benefit from oral opioid, equating to a difference of up to 17 mm on a 0‐10 cm VAS. This may possibly be clinically significant |
| Pain score more than 30 min after procedure oral opioid | The mean pain score was 0.77 on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.17 lower | ‐ | 140 | very low1,2,3 | |
| Nausea and vomiting sublingual opioid | Not calculable as all 31 events were in the opioid group and none in the placebo group | OR 107.55 (6.44 to 1796.46) | 164 | low1 | There were 4 events in the intervention group of the oral opioid study, but events in the placebo group were not reported | |
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the mean risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded one level for serious risk of bias: method of allocation concealment or blinding, or both, not described. | ||||||
| Intracervical versus combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia | ||||||
| Population: women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Risk with combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia | Risk with local intracervical anaesthesia | |||||
| Pain score during procedure | The mean pain score was 2.1 (SD 0.2) on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 4.27 SD higher (3.49 higher to 5.06 higher) | ‐ | 84 participants | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | This suggests a significant benefit from combined anaesthesia, equating to up to 12 mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This is unlikely to be be clinically significant |
| Pain score within 30 minutes of the procedure | The mean pain score was 1.5 (SD 0.3) on a 0‐10 cm VAS | (SMD 1.55, 95% CI 1.06 higher to 2.05 higher) | ‐ | 84 participants (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | This suggests a significant benefit from combined anaesthesia, equating to up to 5 mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant |
| Pain score more than 30 minutes of the procedure | The mean pain score was 1 (SD 0.2) on a 0‐10 cm VAS | (SMD 3.47, 95% CI 2.78 higher to 4.15 higher) | ‐ | 84 participants (1 study) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | This suggests a significant benefit from combined anaesthesia, equating to up to 8 mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant |
| Adverse effects | No data available | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the mean risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; SMD: standardised mean difference; SD: standard deviation; VAS: visual analogue scale | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded two levels for very serious risk of bias: allocation concealment not described, participants not blinded. | ||||||
| Antispasmodic plus NSAID versus paracervical anaesthesia | ||||||
| Population: women undergoing outpatient hysteroscopy | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | No of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Paracervical anaesthesia | Antispasmodic plus NSAID | |||||
| Pain score during procedure | The mean pain score was 5.93 (SD ‐1.26) on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 1.40 SD lower (1.90 lower to 0.91 lower) | ‐ | 80 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | This suggests a beneficial effect in the drotaverine hydrochloride and mefenamic acid group, equating to up to 23 mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This may possibly be clinically significant |
| Pain score within 30 minutes of the procedure | This outcome was not reported | |||||
| Pain score more than 30 minutes after the procedure | The mean pain score was 2.53 (SD ‐0.81) on a 0‐10 cm VAS | SMD 0.87 SD lower | ‐ | 80 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | This suggests a beneficial effect in the drotaverine hydrochloride and mefenamic acid group, equating toup to11mm on a 0‐10 cm point VAS. This is unlikely to be clinically significant. |
| Adverse effects | This outcome was not reported | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the mean risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; SMD: standardised mean difference; SD: standard deviation; VAS: visual analogue scale | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| 1Downgraded two levels for very serious risk of bias: methods of allocation concealment not described, not blinded. | ||||||
| Study | Route | Dose |
| Intracervical versus intra and paracervical | Local intracervical anaesthesia compared to combined intracervical and paracervical anaesthesia. 0.5% bupivacaine hydrochloride into anterior wall of cervix compared to 0.5% bupivacaine hydrochloride into anterior wall of cervix plus bupivacaine into lateral vaginal fornix at 3 and 9 o’clock at 10 mm depth | |
| Endocervical topical cream | 3 mL of EMLA cream 5% or 3 mL ultrasound gel applied in the endocervical canal 10 min before surgery with 5 mL needleless syringe via speculum. A subsequent application of either gel was made with a swab at ectocervix level during vaginoscopic approach | |
| Intracervical | Intracervical injection of 10 mL of lignocaine 1% with 1:200 000 adrenaline or normal saline was injected into the cervix at 1, 5, 7, and 11 o’clock | |
| Transcervical | 2 mL of 2% mepivacaine or 2 mL of 0.9% saline injected trans cervically (inserted up the cervical canal to the internal os) | |
| Paracervical | 10 mL of 1.5% mepivacaine or saline injected into junction of cervix and vagina (4 and 8 o'clock positions) | |
| Topical spray | 10 mL of 2% lignocaine gel, placebo gel or no gel administered into cervical canal. Some women received intracervical lignocaine block if determined to need cervical dilatation | |
| Intrauterine | 5 mL of 2% lignocaine or 5 mL or 0.9% saline injected into cervical canal and uterine cavity via hysteroscope | |
| Intracervical | Intracervical application at 1, 5, 7 and 11 o'clock positions of 4 x 2 mL ampoules of 2% lidocaine hydrochloride ampoules or saline | |
| Paracervical versus uterosacral | 20 mL of 1% lignocaine paracervical block or 2 mL of 2% lignocaine uterosacral block | |
| Paracervical | 20 mL of 1% mepivacaine injected paracervically at 3, 5, 7 and 9 o'clock position of the junction of cervix and vagina at least 5 min before the procedure | |
| Intracervical versus intracervical and intrauterine | 2 mL of 1% lidocaine into anterior wall. Distension medium of either saline only or 18 mL of lidocaine in 250 mL of saline | |
| Intracervical | Intracervical local anaesthesia (10 mL of 1% prilocaine) was applied at the 4 and | |
| Paracervical | Paracervical block at 3, 5, 7 and 9 o'clock positions of 10 mL of 2% lignocaine or saline, 5 min prior to procedure | |
| Transcervical | Transcervical intrauterine instillation of 5 mL of 2% lignocaine or normal saline into the uterine cavity 5 min before procedure | |
| Para/intracervical versus intracervical only anaesthetic block | The para/intracervical group received a total of 37 cc of anaesthesia injected at 6 different sites. 2‐3 min prior to the injection, topical 1% lidocaine was applied to the cervix in this group. The intracervical group received a total of 22 cc of anaesthetic given at 3 different injection sites | |
| Intracervical | 1 mL to 3 mL (30 to 90 mg) of mepivacaine 3% or saline administered intracervically 3 min prior to procedure | |
| Intracervical versus NSAID | 5 mL mepivacaine 2% intracervically up to the level of the internal os or one tablet of dexketoprofen given 1 h before the procedure | |
| Transcervical intrauterine lidocaine instillation versus rectal diclofenac | 5 mL of 2% lidocaine or the same volume of saline was instilled through the endocervix into the uterine cavity with an 18‐gauge angiocatheter 3 min prior to the procedure | |
| Intracervical | The second group was administered with a 1000 mL distention medium containing 18 mL lidocaine per 250 mL (Jetokain ampoule 20 mg 2% Adeka, Samsun, Turkey) | |
| Topical spray | 30 mg (3 metered doses) of lignocaine or placebo sprayed onto surface of cervix and cervical canal through 360° 5 min prior to procedure | |
| Topical cream versus topical spray | 1 cm3 of 5% prilocaine cream onto esocervix and 2 cm3 inserted 3 cm into cervical canal 10 min before procedure or 20 mg of lidocaine spray directed onto esocervix and 20 mg 3 cm into cervical canal immediately before procedure or no intervention | |
| Intrauterine | Unspecified volume of Instillagel (contains 2% lidocaine) or Endosgel (does not contain local anaesthetic) warmed to 37°C and instilled via a 2 mm neonatal suction catheter as part of sonography procedure 30 min prior to hysteroscopy | |
| Paracervical | Paracervical block at 3, 5, 7 and 9 o'clock positions of 10 mL 1% mepivacaine 5 min before procedure or no intervention given | |
| Topical gel | 4 mL of 2% lignocaine or placebo gel applied onto cervix before procedure | |
| Intrauterine | 5 mL of 2% mepivacaine or 5 mL of saline intrauterine via 3 mm catheter | |
| NSAID: nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drug | ||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 12 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 10 | 1496 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.29 [‐0.39, ‐0.19] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 5 | 545 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.50 [‐0.67, ‐0.33] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 4 | 450 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.11 [‐0.30, 0.07] |
| 2 Failure to complete procedure Show forest plot | 7 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Cervical stenosis | 6 | 805 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.23 [0.62, 2.43] |
| 2.2 Pain | 2 | 330 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.12, 0.69] |
| 3 Adverse events Show forest plot | 8 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 3.1 Vasovagal reaction | 8 | 1309 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.70 [0.43, 1.13] |
| 3.2 Non‐pelvic pain | 1 | 99 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.76 [0.53, 5.80] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 3 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 3 | 521 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.18 [‐0.35, ‐0.00] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 2 | 340 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.25 [‐0.46, ‐0.04] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 2 | 321 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.27 [‐0.49, ‐0.05] |
| 2 Adverse events Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 2.1 Vasovagal reaction | 1 | 181 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.20, 2.94] |
| 2.2 Non pelvic pain | 1 | 181 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.93 [0.12, 72.99] |
| 2.3 Allergic reactions | 1 | 181 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.93 [0.12, 72.99] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Failure to complete procedure (due to pain) Show forest plot | 1 | 140 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 8.21] |
| 3 Adverse effects Show forest plot | 1 | 164 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 107.55 [6.44, 1796.46] |
| 3.1 Nausea and vomiting | 1 | 164 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 107.55 [6.44, 1796.46] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 84 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.27 [3.49, 5.06] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 1 | 84 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.55 [1.06, 2.05] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | 84 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.47 [2.78, 4.15] |
| 2 Failure to complete procedure Show forest plot | 1 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 37 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.54 [‐1.20, 0.12] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 80 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.40 [‐1.90, ‐0.91] |
| 1.2 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | 80 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.87 [‐1.33, ‐0.41] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain score Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.1 Pain score during procedure | 1 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.15 [‐0.48, 0.18] |
| 1.2 Pain score within 30 min of procedure | 1 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.25 [‐0.58, 0.08] |
| 1.3 Pain score more than 30 min after procedure | 1 | 140 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.17 [‐0.51, 0.16] |
| 2 Adverse effects Show forest plot | 1 | 140 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 9.54 [0.50, 180.64] |
| 2.1 Nausea and vomiting | 1 | 140 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 9.54 [0.50, 180.64] |