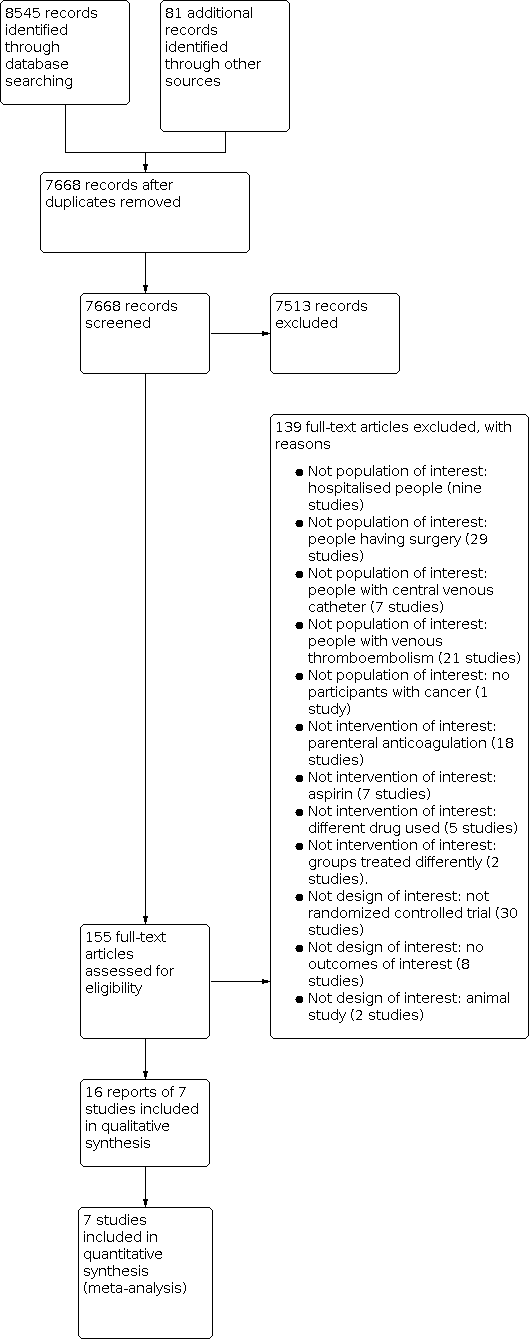
Anticoagulación por vía oral en personas con cáncer en quienes no hay indicación terapéutica o profiláctica de anticoagulantes
References
Referencias de los estudios incluidos en esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios excluidos de esta revisión
Referencias de los estudios en curso
Referencias adicionales
Referencias de otras versiones publicadas de esta revisión
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 189 participants with small cell lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy (CALBG 0‐3). Mean age 60 years, 70% male. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: warfarin (PT 1.5‐2). Control: no intervention. Cointervention: both arms received chemotherapy. Discontinued treatment: none. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: not reported.
Screening test for DVT/PE: none. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No placebo used. Comment: not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may have led to differential behaviors across intervention groups (e.g. differential dropout, differential cross‐over to an alternative intervention or differential administration of co interventions. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | No placebo used. Comment: probably not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may not have impacted on the assessment of the physiological outcomes (mortality, DVT, PE, bleeding, etc.) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: judgment based on comparison between MPD rate (mortality 5/189 (2.6%), major bleeding 8/294 (2.7%)) and event rate (mortality 61/186 (32.8%), major bleeding 7/186 (3.7%)). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study not registered. No published protocol. All outcomes listed in the methods section were reported on. Probably free of selective reporting. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Study not stopped early. |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 91 participants with lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: warfarin starting day 1 of chemotherapy at a dose of 5 mg daily to achieve a target INR of 1.5‐2.5. Control: no warfarin. Cointervention: both arms received chemotherapy. Discontinued treatment: not reported. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: 6 months.
Diagnostic test for DVT/PE: not reported. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "patients with lung cancer were randomly assigned." Comment: yes. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | Not reported. No placebo used. Comment: not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may have led to differential behaviors across intervention groups (e.g. differential dropout, differential cross‐over to an alternative intervention, or differential administration of co interventions. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Not reported. Comment: probably not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may not have impacted on the assessment of the physiological outcomes (mortality, DVT, PE, bleeding, etc.) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 315 participants with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy; minimum life expectancy 3 months; good performance status (ECOG < 3). | |
| Interventions | Intervention: very‐low‐dose warfarin 1 mg daily for 6 weeks (INR 1.3‐1.9) started within 4 weeks of chemotherapy until 1 week after termination of chemotherapy. Control: placebo. Cointervention: both arms received chemotherapy. 2 participants in the warfarin group and 2 in the control group did not receive chemotherapy and they were not considered in the analysis. No surveillance tests used. Discontinued treatment: 27 participants in each arm discontinued treatment. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: not reported.
Diagnostic test for DVT: venography, impedance plethysmography or Doppler. Diagnostic test for PE: ventilation/perfusion scan or angiography. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients were assigned warfarin or placebo according to a computer‐generated random arrangement." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Neither patients nor doctors were aware of treatment allocation." Comment: definitely blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The manager relayed the INR (actual value for patients on active drug, sham value for patients on placebo) to the study nurse and investigator." Comment: Definitely blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may not have impacted on impact the assessment of the physiological outcomes (mortality, DVT, PE, bleeding, etc.) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: Jjudgment based on comparison between MPD rate in study population (4/315= (1.3%)) and event rate (mortality at 1 year 186/311= (60%), DVT 6/311= (1.9%)). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study not registered. No published protocol. All outcomes listed in the methods section were reported on. Probably free of selective reporting. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Study not stopped early for benefit. |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized, phase II, double blind trial. | |
| Participants | 125 participants with advanced or metastatic lung, breast, gastrointestinal, bladder, ovarian or prostate cancers; cancer of unknown origin; myeloma; or selected lymphomas from 6 sites in Canada and 8 in the USA. Mean age 60 years, 50% male, ECOG 0 50%, with central venous catheter (VTE risk factor) 30%. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: apixaban 5 mg, 10 mg or 20 mg once daily for 12 weeks beginning within 4 weeks of the date on which the first‐line or second‐line chemotherapy was begun. Control: placebo. Cointervention: either first‐line or second‐line chemotherapy (expected course ≥ 90 days). Discontinued treatment: none. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: 30 days after completion of the 12‐week treatment period (114‐121 days) or premature discontinuation of study medication or of the study.
Diagnostic tests for bleeding: "In the absence of visible bleeding, confirmatory imaging techniques that can detect the presence of bleeding (e.g. ultrasound [US], computed tomography [CT], and magnetic resonance imaging) could be used." Diagnostic tests for DVT: compression ultrasound or venography. Diagnostic tests for PE: spiral computed tomography or ventilation/perfusion lung scan. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Randomization was performed centrally by contacting a computerized telephone voice response system provided by Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS)." "Treatment assignments were implemented with a randomization schedule with blocks of size four; blocks were stratified by the presence (or not) of metastatic liver disease and clinical center." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Subjects received blister packs containing a combination of apixaban (2.5‐mg or 10‐mg tablets) and matching placebo tablets supplied by BMS. All subjects took four tablets orally once daily; these consisted of a combination of apixaban and matching placebo tablets for the apixaban treatment groups, or all placebo tablets for the placebo treatment group, such that the study supplies for subjects in all treatment groups were identical in appearance." Comment: blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "All bleeding and VTE events were adjudicated by a committee unaware of treatment allocation." Comment: blinded. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Complete follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study not registered. No published protocol. All outcomes listed in the methods section were reported on. Quote: "Study protocol approved by Institutional Review Board of each participating center." Comment: probably free of selective reporting. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No other bias suspected. |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized controlled study. | |
| Participants | 369 participants aged > 18 years with small cell lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy and radiotherapy from 27 CALBG main member institutions and their affiliates. Mean age 48 years, 65% male, 55% performance status 0, minimum life expectancy 2 months; CALGB < 3. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: warfarin (PT 1.4‐1.6) started with chemotherapy at 10 mg daily for 3 days and continued for 3 weeks after last cycle of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Control: no warfarin. Cointervention: both arms received 3 cycles of chemotherapy. 3 participants were randomized but excluded pretreatment because they did not receive protocol treatment (unclear in which group). Discontinued treatment: not reported. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: not reported.
Diagnostic tests for PE: not reported. Diagnostic tests for DVT: not reported. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients were randomized to receive warfarin or no warfarin." Communication with author: "allocation by central office." Comment: probably yes given this was done by a central office. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Communication with author: "allocation by central office." Comment: yes. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No placebo used. Comment: not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may have led to differential behaviors across intervention groups (e.g. differential dropout, differential cross‐over to an alternative intervention or differential administration of co interventions. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | No placebo used Comment: probably not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may not have impacted on the assessment of the physiological outcomes (mortality, DVT, PE, bleeding, etc.) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Unclear risk | Follow‐up rate: not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study not registered. No published protocol. All outcomes listed in the methods section were reported on. Probably free of selective reporting. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Study not stopped early for benefit. |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 24 participants with a small cell carcinoma (at least stage T3 disease) of the bronchus receiving chemotherapy. 75% male, 79% extrathoracic metastases. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: 48 hours before each induction course of cytotoxic drugs, a loading dose of heparin 5000 IU and then heparin 20,000 IU daily for 6 days. During the first 24 hours of anticoagulants, participants also received 1 L of dextran (Rheomacrodex). A loading dose of warfarin 25 mg was given on the 4th day of heparin treatment. On the day of the intravenous maintenance chemotherapy, each patient of the anticoagulant group also received heparin 5000 IU contained in 500 mL of dextran over 4 hours. Control: no anticoagulant. Cointervention: "Both groups received two induction courses of chemotherapy at three weekly intervals followed by maintenance drugs given three times weekly." Discontinued treatment: none. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: 16 months.
Diagnostic tests for PE: not reported. Diagnostic tests for DVT: not reported. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "They were assigned to either the anticoagulant or control treatment groups according to a table of random numbers." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No placebo used. Comment: not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may have led to differential behaviors across intervention groups (e.g. differential dropout, differential cross‐over to an alternative intervention or differential administration of co interventions. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | No placebo used Comment: probably not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may not have impacted on the assessment of the physiological outcomes (mortality, DVT, PE, bleeding, etc.). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Complete follow‐up. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Study not registered. No published protocol. No listing of outcomes in the methods section. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Study not reported as stopped early for benefit. No other bias suspected. |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial. | |
| Participants | 431 participants with different types of cancer undergoing chemotherapy; minimum life expectancy of 2 months from 13 different Veterans Affairs Medical Centers over a 4‐year period and were followed for an additional 12 months. | |
| Interventions | Intervention: warfarin (therapeutic range). Control: no intervention. Cointervention: not reported. 13 randomized participants were excluded from survival analyses (unclear in which group). Discontinued treatment: 0 participants. | |
| Outcomes | Duration of follow‐up: 4 years followed for an additional 12 months.
Diagnostic tests for PE: not reported. Diagnostic tests for DVT: not reported. | |
| Notes |
| |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Patients admitted to the study were subjected to computer randomization by hospital, performance status and tumour category to receive standard therapy either with or without warfarin anticoagulation." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) | High risk | No placebo used. Comment: not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may have led to differential behaviors across intervention groups (e.g. differential dropout, differential cross‐over to an alternative intervention or differential administration of co‐interventions. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) | Low risk | No placebo used. Comment: probably not blinded; knowledge of the assigned intervention may not have impacted on the assessment of the physiological outcomes (mortality, DVT, PE, bleeding, etc.). |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) | Low risk | Comment: judgment based on comparison between MPD rate (13/431 (3%)) and event rate (mortality in warfarin group 136/215 (63.3%) in warfarin group; mortality in control group 138/216 (63.9%) in control group). |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study not registered. No published protocol. All outcomes listed in the methods section were not reported. Probably free of selective reporting. |
| Other bias | Low risk | Study not stopped early for benefit. |
CALBG: Cancer and Leukemia Group B; DVT: deep vein thrombosis; ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; INR: international normalized ratio; IU: international unit; MPD: missing patient data; PE: pulmonary embolism; PT: prothrombin time; VKA: vitamin K antagonist; VTE: venous thromboembolism.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE); included 2 reports. | |
| Different drug/agent studied. | |
| No control group. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure); included 2 reports. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Observational study. | |
| No control group. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (hospitalized). | |
| Not population of interest (hospitalized people with cancer); included 3 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with CVC without VTE); included 3 reports. | |
| Groups treated differently. | |
| Groups treated differently. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| No reporting outcome of interest. | |
| No reporting outcome of interest. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (hospitalized people with cancer); included 3 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (hospitalized people with cancer); included 2 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| No control group. | |
| No control group. | |
| Animal study. | |
| No reporting outcome of interest. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| No control group. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer who had a surgical procedure); included 2 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| No reporting outcome of interest. | |
| Not comparison of interest (parenteral anticoagulant); included 2 reports. | |
| Different drug/agent studied. | |
| Different drug/agent studied. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not comparison of interest (LMWH vs aspirin). | |
| Different drug/agent studied. | |
| Review. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE); included 9 reports. | |
| Not population of interest, no people with cancer. | |
| Observational study: retrospective. | |
| Not comparison of interest (parenteral anticoagulant); included 4 reports. | |
| No control group. | |
| No control group. | |
| No control group. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Animal study. | |
| No control group. | |
| No control group. | |
| No control group. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not comparison of interest (aspirin versus warfarin); included 6 reports. | |
| Not comparison of interest (parenteral anticoagulant); included 10 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE); included 2 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE); included 3 reports. | |
| Different drug/agent studied. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with VTE). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE). | |
| Review. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| No reporting outcome of interest. | |
| Controlled clinical trial, inadequate randomization. | |
| Controlled clinical trial, inadequate randomization. | |
| Controlled clinical trial, inadequate randomization (each alternate person with the same histology was given warfarin). | |
| No control group. | |
| No relevant outcomes reported. | |
| No relevant outcomes reported. | |
| No relevant outcomes reported. | |
| No control group. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer who had a surgical procedure); included 5 reports. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with CVC without VTE); included 4 reports. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer with VTE); included 2 reports. | |
| Protocol. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| Review. | |
| Letter to editor. | |
| Not population of interest (people with cancer without VTE undergoing a surgical procedure). | |
| Not comparison of interest (parenteral anticoagulant); included 2 reports. |
CVC: central venous catheter; LMWH: low‐molecular‐weight heparin; VTE: venous thromboembolism.
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Jump to:
| Study name | A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Rivaroxaban Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis in Ambulatory Cancer Participants. |
| Methods | Randomized, parallel assignment, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. |
| Participants | People aged ≥ 18 years with histologically confirmed solid malignancy, and a plan to initiate systemic cancer therapy within ± 1 week of receiving first dose of study drug. |
| Interventions | Rivaroxaban: 10 mg tablet orally once daily for 180 days. Placebo: tablet orally once daily for 180 days. |
| Outcomes |
|
| Starting date | 11 September 2015. |
| Contact information | Janssen Research & Development, LLC. [email protected]. |
| Notes | NCT02555878 Status as of November 2017: currently recruiting participants. |
| Study name | Rationale and Design of AESOP: APIXABAN for Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia or Lymphoma Treated with L‐Asparaginase |
| Methods | Phase III trial, randomized, open‐label, control: no anticoagulation. |
| Participants | Children and adolescents aged 1 to < 18 years with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia or lymphoma and a central venous catheter in place. |
| Interventions | Apixaban. |
| Outcomes | DVT prevention in children and adolescents during induction chemotherapy including l‐asparaginase. |
| Starting date | March 2015. |
| Contact information | Vilmarie Rodriguez, MD, Mayo Clinic. |
| Notes | NCT02369653 Status as of November 2017: currently recruiting participants |
DVT: deep vein thrombosis; PE: pulmonary embolism.
Data and analyses
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1.1 Mortality at 6 months: main analysis Show forest plot | 3 | 946 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.77, 1.13] |
| Analysis 1.1  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 1: Mortality at 6 months: main analysis | ||||
| 1.2 Mortality at 6 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 3 | 946 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.77, 1.14] |
| Analysis 1.2  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 2: Mortality at 6 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) | ||||
| 1.2.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 3 | 813 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.72, 1.06] |
| 1.2.2 Non‐lung cancer | 1 | 133 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.22 [0.82, 1.82] |
| 1.3 Mortality at 12 months: main analysis Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.87, 1.03] |
| Analysis 1.3  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 3: Mortality at 12 months: main analysis | ||||
| 1.4 Mortality at 12 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.87, 1.03] |
| Analysis 1.4  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 4: Mortality at 12 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) | ||||
| 1.4.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 4 | 837 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.85, 1.05] |
| 1.4.2 Non‐lung cancer | 2 | 444 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.81, 1.10] |
| 1.5 Mortality at 2 years Show forest plot | 2 | 528 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.70, 1.30] |
| Analysis 1.5  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 5: Mortality at 2 years | ||||
| 1.6 Mortality at 5 years Show forest plot | 1 | 344 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.83, 1.03] |
| Analysis 1.6  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 6: Mortality at 5 years | ||||
| 1.7 Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis Show forest plot | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.08 [0.00, 1.42] |
| Analysis 1.7  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 7: Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis | ||||
| 1.8 Pulmonary embolism Show forest plot | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.07, 16.58] |
| Analysis 1.8  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 8: Pulmonary embolism | ||||
| 1.9 Major bleeding: main analysis Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.93 [1.86, 4.62] |
| Analysis 1.9  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 9: Major bleeding: main analysis | ||||
| 1.10 Major bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.85 [1.76, 4.62] |
| Analysis 1.10  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 10: Major bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) | ||||
| 1.10.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 4 | 837 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.95 [2.38, 6.55] |
| 1.10.2 Non‐lung cancer | 2 | 444 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.63, 4.89] |
| 1.11 Minor bleeding: main analysis Show forest plot | 4 | 863 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.14 [1.85, 5.32] |
| Analysis 1.11  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 11: Minor bleeding: main analysis | ||||
| 1.12 Minor bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 4 | 865 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.19 [1.83, 5.55] |
| Analysis 1.12  Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 12: Minor bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) | ||||
| 1.12.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 3 | 554 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.79 [1.55, 9.24] |
| 1.12.2 Non‐lung cancer | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.44 [0.64, 9.27] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 2.1 Mortality at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.02, 2.56] |
| Analysis 2.1  Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 1: Mortality at 3 months | ||||
| 2.2 Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.00, 1.32] |
| Analysis 2.2  Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 2: Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis | ||||
| 2.3 Pulmonary embolism Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.01, 3.91] |
| Analysis 2.3  Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 3: Pulmonary embolism | ||||
| 2.4 Major bleeding Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.01, 3.91] |
| Analysis 2.4  Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 4: Major bleeding | ||||
| 2.5 Minor bleeding Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.43 [0.25, 79.68] |
| Analysis 2.5  Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 5: Minor bleeding | ||||

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgments about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 1: Mortality at 6 months: main analysis

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 2: Mortality at 6 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer)

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 3: Mortality at 12 months: main analysis

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 4: Mortality at 12 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer)

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 5: Mortality at 2 years

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 6: Mortality at 5 years

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 7: Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 8: Pulmonary embolism

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 9: Major bleeding: main analysis

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 10: Major bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer)

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 11: Minor bleeding: main analysis

Comparison 1: Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) versus no VKA, Outcome 12: Minor bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer)

Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 1: Mortality at 3 months

Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 2: Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis

Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 3: Pulmonary embolism

Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 4: Major bleeding

Comparison 2: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) versus no DOAC, Outcome 5: Minor bleeding
| VKA prophylaxis compared to No prophylaxis in ambulatory patients with cancer without VTE receiving systemic therapy | |||||
| Patient or population: ambulatory people with cancer without VTE receiving systemic therapy Setting: outpatient Intervention: VKA prophylaxis Control: no prophylaxis | |||||
| Outcomes | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Relative effect | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk with No prophylaxis | Risk difference with VKA prophylaxis | ||||
| Mortality | 1281 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | RR 0.95 | Study population | |
| 574 per 1,000 | 29 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| PE | 311 | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ | RR 1.05 | Study population | |
| 6 per 1,000 | 0 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| Symptomatic DVT | 311 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.08 | Study population | |
| 38 per 1,000 | 35 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| Major bleeding | 1281 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | RR 2.93 | Study population | |
| 55 per 1,000 | 107 more per 1,000 | ||||
| Minor bleeding | 863 | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ | RR 3.14 | Study population | |
| 78 per 1,000 | 167 more per 1,000 | ||||
| HRQoL ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| 1 Downgraded by one level due to concern about both risk of bias (lack of blinding in patients and personnel and unclear allocation concealment in 4 out of 5 studies) and imprecision (95% CI is consistent with the possibility for important benefit (75 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (17 per 1000 absolute increase), large event rate) 2 Downgraded by one level due to indirectness. Levine 1994 used fixed dose of VKA instead of adjusted dose which is not representative of the current practice. This study was the only trial that reported on PE and symptomatic DVT. 3 Downgraded by two levels due to very serious imprecision. 95% CI is consistent with the possibility for important benefit (6 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (98 per 1000 absolute increase), including only 2 events. 4Levine 1994 used fixed dose of VKA instead of adjusted dose which is not representative of the current practice. This study was the only trial that reported on PE and symptomatic DVT. We do not think that this indirectness has underestimated the effect on symptomatic DVT (RR 0.08) 5 Downgraded by two levels due to very serious imprecision. Only 6 events among 311 participants. 6 Downgraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in patients and personnel and unclear allocation concealment in 4 out of 5 studies) 7 Downgraded by one level due to concern about risk of bias (lack of blinding in patients and personnel and unclear allocation concealment in 3 out of 4 studies) | |||||
| DOAC prophylaxis compared to No prophylaxis in ambulatory patients with cancer without VTE receiving systemic therapy | |||||
| Patient or population: ambulatory people with cancer without VTE receiving systemic therapy Setting: outpatient Intervention: DOAC prophylaxis Control: no prophylaxis | |||||
| Outcomes | № of participants | Certainty of the evidence | Relative effect | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk with No prophylaxis | Risk difference with DOAC prophylaxis | ||||
| Mortality | 92 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.24 | Study population | |
| 67 per 1,000 | 51 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| PE | 92 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.16 | Study population | |
| 33 per 1,000 | 28 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| Symptomatic DVT | 92 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.07 | Study population | |
| 100 per 1,000 | 93 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| Major bleeding | 92 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 0.16 | Study population | |
| 33 per 1,000 | 28 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| Minor bleeding | 92 | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ | RR 4.43 | Low | |
| 0 per 1,000 | 0 fewer per 1,000 | ||||
| HRQoL ‐ not reported | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | |||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | |||||
| 1 Concern due to unclear allocation concealment 2 Downgraded by two levels due to very serious imprecision: 95% CI is consistent with the possibility for important benefit (65 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (104 per 1000 absolute increase), including only 3 events among 92 participants. 3 Downgraded by two levels due to very serious imprecision: 95% CI is consistent with the possibility for important benefit (33 per 1000 absolute reduction) and the possibility of important harm (97 per 1000 absolute increase), including only 1 events among 92 participants. 4 Downgraded by two levels due to very serious imprecision: Including only 3 events among 92 participants. 5 Downgraded by two levels due to very serious imprecision: Including only 4 events among 92 participants. | |||||
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Adjuvant therapy | Assisting in the amelioration or cure of disease. |
| Anticoagulation | Process of hindering the clotting of blood especially by treatment with an anticoagulant. |
| Antithrombotic | Used against or tending to prevent thrombosis (clotting). |
| Apixaban | Oral direct factor Xa inhibitor used for anticoagulation. |
| Coagulation | Clotting. |
| Direct factor Xa inhibitor | Anticoagulant medications used for anticoagulation. Apixaban is an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor. |
| Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) | Condition marked by the formation of a thrombus within a deep vein (e.g. leg or pelvis) that may be asymptomatic or symptomatic (as swelling and pain) and that is potentially life‐threatening if dislodgment of the thrombus results in pulmonary embolism. |
| Fibrin | White insoluble fibrous protein formed from fibrinogen by the action of thrombin especially in the clotting of blood. |
| Fondaparinux | An anticoagulant medication. |
| Hemostatic system | The system that shortens the clotting time of blood and stops bleeding. |
| Heparin | Enzyme occurring especially in the liver and lungs that prolongs the clotting time of blood by preventing the formation of fibrin. 2 forms of heparin that are used as anticoagulant medications are: unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low‐molecular‐weight heparins (LMWH). |
| Major bleeding | Bleeding that is intracranial or retroperitoneal, if it leads directly to death, or if results in hospitalization or transfusion. |
| Metastasis | Spread of a cancer cells from the initial or primary site of disease to another part of the body. |
| Minor bleeding | Any bleeding not classified as major bleeding. |
| Oncogene | Gene having the potential to cause a normal cell to become cancerous. |
| Osteoporosis | Condition that affects mainly older women and is characterized by decrease in bone mass with decreased density and enlargement of bone spaces producing porosity and brittleness. |
| Pulmonary embolism (PE) | Embolism of a pulmonary artery or 1 of its branches that is produced by foreign matter and most often a blood clot originating in a vein of the leg or pelvis and that is marked by labored breathing, chest pain, fainting, rapid heart rate, cyanosis, shock and sometimes death. |
| Stroma | The supporting framework of an organ typically consisting of connective tissue. |
| Thrombin | Proteolytic enzyme formed from prothrombin that facilitates the clotting of blood by catalyzing conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. |
| Thrombocytopenia | Persistent decrease in the number of blood platelets that is often associated with hemorrhagic conditions. |
| Vitamin K antagonist (VKA) | Anticoagulant medications. Warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist. |
| Warfarin | Anticoagulant medication that is a vitamin K antagonist. |
| Ximelagatran | Anticoagulant medication. |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1.1 Mortality at 6 months: main analysis Show forest plot | 3 | 946 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.77, 1.13] |
| 1.2 Mortality at 6 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 3 | 946 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.77, 1.14] |
| 1.2.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 3 | 813 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.72, 1.06] |
| 1.2.2 Non‐lung cancer | 1 | 133 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.22 [0.82, 1.82] |
| 1.3 Mortality at 12 months: main analysis Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.87, 1.03] |
| 1.4 Mortality at 12 months: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.87, 1.03] |
| 1.4.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 4 | 837 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.85, 1.05] |
| 1.4.2 Non‐lung cancer | 2 | 444 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.81, 1.10] |
| 1.5 Mortality at 2 years Show forest plot | 2 | 528 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.70, 1.30] |
| 1.6 Mortality at 5 years Show forest plot | 1 | 344 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.83, 1.03] |
| 1.7 Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis Show forest plot | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.08 [0.00, 1.42] |
| 1.8 Pulmonary embolism Show forest plot | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.07, 16.58] |
| 1.9 Major bleeding: main analysis Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.93 [1.86, 4.62] |
| 1.10 Major bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 5 | 1281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.85 [1.76, 4.62] |
| 1.10.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 4 | 837 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.95 [2.38, 6.55] |
| 1.10.2 Non‐lung cancer | 2 | 444 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.63, 4.89] |
| 1.11 Minor bleeding: main analysis Show forest plot | 4 | 863 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.14 [1.85, 5.32] |
| 1.12 Minor bleeding: subgroup analysis (lung cancer) Show forest plot | 4 | 865 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.19 [1.83, 5.55] |
| 1.12.1 Lung cancer (small cell and non‐small cell) | 3 | 554 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.79 [1.55, 9.24] |
| 1.12.2 Non‐lung cancer | 1 | 311 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.44 [0.64, 9.27] |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 2.1 Mortality at 3 months Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [0.02, 2.56] |
| 2.2 Symptomatic deep vein thrombosis Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.00, 1.32] |
| 2.3 Pulmonary embolism Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.01, 3.91] |
| 2.4 Major bleeding Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.01, 3.91] |
| 2.5 Minor bleeding Show forest plot | 1 | 92 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.43 [0.25, 79.68] |