Acupuncture for neck disorders
Appendices
Appendix 1. Computerised search strategy
CENTRAL‐OVID
August 25, 2015
1. Neck Pain/
2. exp Brachial Plexus Neuropathies/
3. exp neck injuries/ or exp whiplash injuries/
4. cervical pain.mp.
5. neckache.mp.
6. whiplash.mp.
7. cervicodynia.mp.
8. cervicalgia.mp.
9. brachialgia.mp.
10. brachial neuritis.mp.
11. brachial neuralgia.mp.
12. neck pain.mp.
13. neck injur*.mp.
14. brachial plexus neuropath*.mp.
15. brachial plexus neuritis.mp.
16. thoracic outlet syndrome/ or cervical rib syndrome/
17. Torticollis/
18. exp brachial plexus neuropathies/ or exp brachial plexus neuritis/
19. cervico brachial neuralgia.ti,ab.
20. cervicobrachial neuralgia.ti,ab.
21. (monoradicul* or monoradicl*).tw.
22. or/1‐21
23. exp headache/ and cervic*.tw.
24. exp genital diseases, female/
25. genital disease*.mp.
26. or/24‐25
27. 23 not 26
28. 22 or 27
29. neck/
30. neck muscles/
31. exp cervical plexus/
32. exp cervical vertebrae/
33. atlanto‐axial joint/
34. atlanto‐occipital joint/
35. Cervical Atlas/
36. spinal nerve roots/
37. exp brachial plexus/
38. (odontoid* or cervical or occip* or atlant*).tw.
39. axis/ or odontoid process/
40. Thoracic Vertebrae/
41. cervical vertebrae.mp.
42. cervical plexus.mp.
43. cervical spine.mp.
44. (neck adj3 muscles).mp.
45. (brachial adj3 plexus).mp.
46. (thoracic adj3 vertebrae).mp.
47. neck.mp.
48. (thoracic adj3 spine).mp.
49. (thoracic adj3 outlet).mp.
50. trapezius.mp.
51. cervical.mp.
52. cervico*.mp.
53. 51 or 52
54. exp genital diseases, female/
55. genital disease*.mp.
56. exp *Uterus/
57. 54 or 55 or 56
58. 53 not 57
59. 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 58
60. exp pain/
61. exp injuries/
62. pain.mp.
63. ache.mp.
64. sore.mp.
65. stiff.mp.
66. discomfort.mp.
67. injur*.mp.
68. neuropath*.mp.
69. or/60‐68
70. 59 and 69
71. Radiculopathy/
72. exp temporomandibular joint disorders/ or exp temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome/
73. myofascial pain syndromes/
74. exp "Sprains and Strains"/
75. exp Spinal Osteophytosis/
76. exp Neuritis/
77. Polyradiculopathy/
78. exp Arthritis/
79. Fibromyalgia/
80. spondylitis/ or discitis/
81. spondylosis/ or spondylolysis/ or spondylolisthesis/
82. radiculopathy.mp.
83. radiculitis.mp.
84. temporomandibular.mp.
85. myofascial pain syndrome*.mp.
86. thoracic outlet syndrome*.mp.
87. spinal osteophytosis.mp.
88. neuritis.mp.
89. spondylosis.mp.
90. spondylitis.mp.
91. spondylolisthesis.mp.
92. or/71‐91
93. 59 and 92
94. exp neck/
95. exp cervical vertebrae/
96. Thoracic Vertebrae/
97. neck.mp.
98. (thoracic adj3 vertebrae).mp.
99. cervical.mp.
100. cervico*.mp.
101. 99 or 100
102. exp genital diseases, female/
103. genital disease*.mp.
104. exp *Uterus/
105. or/102‐104
106. 101 not 105
107. (thoracic adj3 spine).mp.
108. cervical spine.mp.
109. 94 or 95 or 96 or 97 or 98 or 106 or 107 or 108
110. Intervertebral Disk/
111. (disc or discs).mp.
112. (disk or disks).mp.
113. 110 or 111 or 112
114. 109 and 113
115. herniat*.mp.
116. slipped.mp.
117. prolapse*.mp.
118. displace*.mp.
119. degenerat*.mp.
120. (bulge or bulged or bulging).mp.
121. 115 or 116 or 117 or 118 or 119 or 120
122. 114 and 121
123. intervertebral disk degeneration/ or intervertebral disk displacement/
124. intervertebral disk displacement.mp.
125. intervertebral disc displacement.mp.
126. intervertebral disk degeneration.mp.
127. intervertebral disc degeneration.mp.
128. 123 or 124 or 125 or 126 or 127
129. 109 and 128
130. 28 or 70 or 93 or 122 or 129
131. animals/ not (animals/ and humans/)
132. 130 not 131
133. exp *neoplasms/
134. exp *wounds, penetrating/
135. 133 or 134
136. 132 not 135
137. Neck Pain/rh, th [Rehabilitation, Therapy]
138. exp Brachial Plexus Neuropathies/rh, th
139. exp neck injuries/rh, th or exp whiplash injuries/rh, th
140. thoracic outlet syndrome/rh, th or cervical rib syndrome/rh, th
141. Torticollis/rh, th
142. exp brachial plexus neuropathies/rh, th or exp brachial plexus neuritis/rh, th
143. or/137‐142
144. Radiculopathy/rh, th
145. exp temporomandibular joint disorders/rh, th or exp temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome/rh, th
146. myofascial pain syndromes/rh, th
147. exp "Sprains and Strains"/rh, th
148. exp Spinal Osteophytosis/rh, th
149. exp Neuritis/rh, th
150. Polyradiculopathy/rh, th
151. exp Arthritis/rh, th
152. Fibromyalgia/rh, th
153. spondylitis/rh, th or discitis/rh, th
154. spondylosis/rh, th or spondylolysis/rh, th or spondylolisthesis/rh, th
155. or/144‐154
156. 59 and 155
157. acupuncture/ or chiropractic/
158. exp Musculoskeletal Manipulations/
159. massage.tw.
160. mobili?ation.tw.
161. Acupuncture Therapy/
162. (acupuncture or acu‐puncture or needling or acupressure or mox?bustion).tw.
163. ((neck or spine or spinal or cervical or chiropractic* or musculoskeletal* or musculo‐skeletal*) adj3 (adjust* or manipulat* or mobiliz* or mobilis*)).tw.
164. (manual adj therap*).tw.
165. (manipulati* adj (therap* or medicine)).tw.
166. (massag* or reflexolog* or rolfing or zone therap*).tw.
167. Nimmo.mp.
168. exp Vibration/tu [Therapeutic Use]
169. (vibration adj5 (therap* or treatment*)).tw.
170. (Chih Ya or Shiatsu or Shiatzu or Zhi Ya).tw.
171. (flexion adj2 distraction*).tw.
172. (myofascial adj3 (release or therap*)).tw.
173. muscle energy technique*.tw.
174. trigger point.tw.
175. proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation*.tw.
176. cyriax friction.tw.
177. (lomilomi or lomi‐lomi or trager).tw.
178. aston patterning.tw.
179. (strain adj counterstrain).tw.
180. (craniosacral therap* or cranio‐sacral therap*).tw.
181. (amma or ammo or effleuurage or petrissage or hacking or tapotment).tw.
182. Complementary Therapies/
183. ((complement* or alternat* or osteopthic*) adj (therap* or medicine)).tw.
184. (Tui Na or Tuina).tw.
185. or/157‐184
186. 136 and 185
187. 143 or 156 or 186
188. animals/ not (animals/ and humans/)
189. 187 not 188
MEDLINE‐OVID
August 25, 2015
1. Neck Pain/
2. exp Brachial Plexus Neuropathies/
3. exp neck injuries/ or exp whiplash injuries/
4. cervical pain.mp.
5. neckache.mp.
6. whiplash.mp.
7. cervicodynia.mp.
8. cervicalgia.mp.
9. brachialgia.mp.
10. brachial neuritis.mp.
11. brachial neuralgia.mp.
12. neck pain.mp.
13. neck injur*.mp.
14. brachial plexus neuropath*.mp.
15. brachial plexus neuritis.mp.
16. thoracic outlet syndrome/ or cervical rib syndrome/
17. Torticollis/
18. exp brachial plexus neuropathies/ or exp brachial plexus neuritis/
19. cervico brachial neuralgia.ti,ab.
20. cervicobrachial neuralgia.ti,ab.
21. (monoradicul* or monoradicl*).tw.
22. or/1‐21
23. exp headache/ and cervic*.tw.
24. exp genital diseases, female/
25. genital disease*.mp.
26. or/24‐25
27. 23 not 26
28. 22 or 27
29. neck/
30. neck muscles/
31. exp cervical plexus/
32. exp cervical vertebrae/
33. atlanto‐axial joint/
34. atlanto‐occipital joint/
35. Cervical Atlas/
36. spinal nerve roots/
37. exp brachial plexus/
38. (odontoid* or cervical or occip* or atlant*).tw.
39. axis/ or odontoid process/
40. Thoracic Vertebrae/
41. cervical vertebrae.mp.
42. cervical plexus.mp.
43. cervical spine.mp.
44. (neck adj3 muscles).mp.
45. (brachial adj3 plexus).mp.
46. (thoracic adj3 vertebrae).mp.
47. neck.mp.
48. (thoracic adj3 spine).mp.
49. (thoracic adj3 outlet).mp.
50. trapezius.mp.
51. cervical.mp.
52. cervico*.mp.
53. 51 or 52
54. exp genital diseases, female/
55. genital disease*.mp.
56. exp *Uterus/
57. 54 or 55 or 56
58. 53 not 57
59. 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 58
60. exp pain/
61. exp injuries/
62. pain.mp.
63. ache.mp.
64. sore.mp.
65. stiff.mp.
66. discomfort.mp.
67. injur*.mp.
68. neuropath*.mp.
69. or/60‐68
70. 59 and 69
71. Radiculopathy/
72. exp temporomandibular joint disorders/ or exp temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome/
73. myofascial pain syndromes/
74. exp "Sprains and Strains"/
75. exp Spinal Osteophytosis/
76. exp Neuritis/
77. Polyradiculopathy/
78. exp Arthritis/
79. Fibromyalgia/
80. spondylitis/ or discitis/
81. spondylosis/ or spondylolysis/ or spondylolisthesis/
82. radiculopathy.mp.
83. radiculitis.mp.
84. temporomandibular.mp.
85. myofascial pain syndrome*.mp.
86. thoracic outlet syndrome*.mp.
87. spinal osteophytosis.mp.
88. neuritis.mp.
89. spondylosis.mp.
90. spondylitis.mp.
91. spondylolisthesis.mp.
92. or/71‐91
93. 59 and 92
94. exp neck/
95. exp cervical vertebrae/
96. Thoracic Vertebrae/
97. neck.mp.
98. (thoracic adj3 vertebrae).mp.
99. cervical.mp.
100. cervico*.mp.
101. 99 or 100
102. exp genital diseases, female/
103. genital disease*.mp.
104. exp *Uterus/
105. or/102‐104
106. 101 not 105
107. (thoracic adj3 spine).mp.
108. cervical spine.mp.
109. 94 or 95 or 96 or 97 or 98 or 106 or 107 or 108
110. Intervertebral Disk/
111. (disc or discs).mp.
112. (disk or disks).mp.
113. 110 or 111 or 112
114. 109 and 113
115. herniat*.mp.
116. slipped.mp.
117. prolapse*.mp.
118. displace*.mp.
119. degenerat*.mp.
120. (bulge or bulged or bulging).mp.
121. 115 or 116 or 117 or 118 or 119 or 120
122. 114 and 121
123. intervertebral disk degeneration/ or intervertebral disk displacement/
124. intervertebral disk displacement.mp.
125. intervertebral disc displacement.mp.
126. intervertebral disk degeneration.mp.
127. intervertebral disc degeneration.mp.
128. 123 or 124 or 125 or 126 or 127
129. 109 and 128
130. 28 or 70 or 93 or 122 or 129
131. animals/ not (animals/ and humans/)
132. 130 not 131
133. exp *neoplasms/
134. exp *wounds, penetrating/
135. 133 or 134
136. 132 not 135
137. Neck Pain/rh, th [Rehabilitation, Therapy]
138. exp Brachial Plexus Neuropathies/rh, th
139. exp neck injuries/rh, th or exp whiplash injuries/rh, th
140. thoracic outlet syndrome/rh, th or cervical rib syndrome/rh, th
141. Torticollis/rh, th
142. exp brachial plexus neuropathies/rh, th or exp brachial plexus neuritis/rh, th
143. or/137‐142
144. Radiculopathy/rh, th
145. exp temporomandibular joint disorders/rh, th or exp temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome/rh, th
146. myofascial pain syndromes/rh, th
147. exp "Sprains and Strains"/rh, th
148. exp Spinal Osteophytosis/rh, th
149. exp Neuritis/rh, th
150. Polyradiculopathy/rh, th
151. exp Arthritis/rh, th
152. Fibromyalgia/rh, th
153. spondylitis/rh, th or discitis/rh, th
154. spondylosis/rh, th or spondylolysis/rh, th or spondylolisthesis/rh, th
155. or/144‐154
156. 59 and 155
157. acupuncture/ or chiropractic/
158. exp Musculoskeletal Manipulations/
159. massage.tw.
160. mobili?ation.tw.
161. Acupuncture Therapy/
162. (acupuncture or acu‐puncture or needling or acupressure or mox?bustion).tw.
163. ((neck or spine or spinal or cervical or chiropractic* or musculoskeletal* or musculo‐skeletal*) adj3 (adjust* or manipulat* or mobiliz* or mobilis*)).tw.
164. (manual adj therap*).tw.
165. (manipulati* adj (therap* or medicine)).tw.
166. (massag* or reflexolog* or rolfing or zone therap*).tw.
167. Nimmo.mp.
168. exp Vibration/tu [Therapeutic Use]
169. (vibration adj5 (therap* or treatment*)).tw.
170. (Chih Ya or Shiatsu or Shiatzu or Zhi Ya).tw.
171. (flexion adj2 distraction*).tw.
172. (myofascial adj3 (release or therap*)).tw.
173. muscle energy technique*.tw.
174. trigger point.tw.
175. proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation*.tw.
176. cyriax friction.tw.
177. (lomilomi or lomi‐lomi or trager).tw.
178. aston patterning.tw.
179. (strain adj counterstrain).tw.
180. (craniosacral therap* or cranio‐sacral therap*).tw.
181. (amma or ammo or effleuurage or petrissage or hacking or tapotment).tw.
182. Complementary Therapies/
183. ((complement* or alternat* or osteopthic*) adj (therap* or medicine)).tw.
184. (Tui Na or Tuina).tw.
185. or/157‐184
186. 136 and 185
187. 143 or 156 or 186
188. animals/ not (animals/ and humans/)
189. 187 not 188
190. exp randomized controlled trials as topic/
191. randomized controlled trial.pt.
192. controlled clinical trial.pt.
193. (random* or sham or placebo*).tw.
194. placebos/
195. random allocation/
196. single blind method/
197. double blind method/
198. ((singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) adj25 (blind* or dumm* or mask*)).ti,ab.
199. (rct or rcts).tw.
200. (control* adj2 (study or studies or trial*)).tw.
201. or/190‐200
202. 189 and 201
EMBASE‐OVID
August 25, 2015
1. neck pain/
2. brachial plexus neuropathy/
3. neck injury/ or whiplash injury/
4. cervical pain.mp.
5. neckache.mp.
6. whiplash.mp.
7. cervicodynia.mp.
8. cervicalgia.mp.
9. brachialgia/
10. brachialgia.mp.
11. brachial neuritis.mp.
12. brachial neuralgia.mp.
13. neck pain.mp.
14. neck injur*.mp.
15. brachial plexus neuropath*.mp.
16. brachial plexus neuritis.mp.
17. thorax outlet syndrome/
18. torticollis/
19. cervico brachial neuralgia.ti,ab.
20. cervicobrachial neuralgia.ti,ab.
21. (monoradicul* or monoradicl*).tw.
22. or/1‐21
23. exp headache/ and cervic*.tw.
24. exp gynecologic disease/
25. genital disease*.mp.
26. exp *uterine cervix/
27. or/24‐26
28. 23 not 27
29. 22 or 28
30. neck/ or neck muscle/
31. cervical plexus/
32. cervical spine/
33. atlantoaxial joint/
34. atlantooccipital joint/
35. atlas/
36. "spinal root"/
37. brachial plexus/
38. (odontoid* or cervical or occip* or atlant*).tw.
39. odontoid process/
40. cervical vertebra.mp.
41. cervical vertebrae.mp.
42. cervical plexus.mp.
43. cervical spine.mp.
44. (neck adj3 muscles).mp.
45. (brachial adj3 plexus).mp.
46. (thoracic adj3 vertebra?).mp.
47. neck.mp.
48. (thoracic adj3 spine).mp.
49. (thoracic adj3 outlet).mp.
50. trapezius.mp.
51. cervical.mp.
52. cervico*.mp.
53. 51 or 52
54. exp gynecologic disease/
55. genital disease*.mp.
56. exp *uterine cervix/
57. 54 or 55 or 56
58. 53 not 57
59. 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 58
60. exp pain/
61. exp injury/
62. pain.mp.
63. ache.mp.
64. sore.mp.
65. stiff.mp.
66. discomfort.mp.
67. injur*.mp.
68. neuropath*.mp.
69. or/60‐68
70. radiculopathy/
71. temporomandibular joint disorder/
72. myofascial pain/
73. spondylosis/ or cervical spondylosis/
74. neuritis/
75. exp arthritis/
76. fibromyalgia/
77. exp spondylitis/
78. diskitis/
79. spondylolisthesis/
80. radiculopathy.mp.
81. radiculitis.mp.
82. temporomandibular.mp.
83. myofascial pain syndrome*.mp.
84. spinal osteophytosis.mp.
85. neuritis.mp.
86. spondylosis.mp.
87. spondylitis.mp.
88. spondylolisthesis.mp.
89. or/70‐88
90. 59 and 89
91. neck/
92. cervical spine/
93. neck.mp.
94. (thoracic adj3 vertebra?).mp.
95. cervical.mp.
96. cervico*.mp.
97. exp gynecologic disease/
98. genital disease*.mp.
99. exp *uterine cervix/
100. or/97‐99
101. 95 or 96
102. 101 not 100
103. (thoracic adj3 spine).mp.
104. cervical spine.mp.
105. 91 or 92 or 93 or 94 or 102 or 103 or 104
106. intervertebral disk/
107. (disc or discs).mp.
108. (disk or disks).mp.
109. 106 or 107 or 108
110. 105 and 109
111. herniat*.mp.
112. slipped.mp.
113. prolapse*.mp.
114. displace*.mp.
115. degenerat*.mp.
116. (bulge or bulged or bulging).mp.
117. 110 or 111 or 112 or 113 or 114 or 115 or 116
118. 110 and 117
119. intervertebral disk hernia/
120. intervertebral disk degeneration/
121. intervertebral disc degeneration.mp.
122. intervertebral disk degeneration.mp.
123. intervertebral disc displacement.mp.
124. intervertebral disk displacement.mp.
125. 119 or 120 or 121 or 122 or 123 or 124
126. 105 and 125
127. 59 and 69
128. 29 or 90 or 118 or 126 or 127
129. exp *neoplasm/
130. exp *penetrating trauma/
131. 129 or 130
132. 128 not 131
133. neck pain/rh, th
134. brachial plexus neuropathy/rh, th
135. neck injury/ or whiplash injury/rh, th
136. brachialgia/rh, th
137. thorax outlet syndrome/rh, th
138. Torticollis/rh, th
139. Radiculopathy/rh, th
140. temporomandibular joint disorder/rh, th
141. myofascial pain/rh, th
142. spondylosis/rh, th or cervical spondylosis/rh, th
143. neuritis/rh, th
144. exp arthritis/rh, th
145. Fibromyalgia/rh, th
146. exp spondylitis/rh, th
147. diskitis/rh, th
148. spondylolisthesis/rh, th
149. acupuncture/ or acupressure/ or acupuncture analgesia/
150. exp manipulative medicine/
151. massage.tw.
152. mobili?ation.tw.
153. (acupuncture or acu‐puncture or needling or acupressure or mox?bustion).tw.
154. ((neck or spine or spinal or cervical or chiropractic* or musculoskeletal* or musculo‐skeletal*) adj3 (adjust* or manipulat* or mobiliz* or mobilis*)).tw.
155. (manual adj therap*).tw.
156. (manipulati* adj (therap* or medicine)).tw.
157. (massag* or reflexolog* or rolfing or zone therap*).tw.
158. Nimmo.tw.
159. (vibration adj5 (therap* or treatment*)).tw.
160. (Chih Ya or Shiatsu or Shiatzu or Zhi Ya).tw.
161. (flexion adj2 distraction*).tw.
162. (myofascial adj3 (release or therap*)).tw.
163. muscle energy technique*.tw.
164. trigger point.tw.
165. proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation*.tw.
166. cyriax friction.tw.
167. (lomilomi or lomi‐lomi or trager).tw.
168. aston patterning.tw.
169. (strain adj counterstrain).tw.
170. (craniosacral therap* or cranio‐sacral therap*).tw.
171. (amma or ammo or effleuurage or petrissage or hacking or tapotment).tw.
172. alternative medicine/
173. ((complement* or alternat* or osteopthic*) adj (therap* or medicine)).tw.
174. (Tui Na or Tuina).tw.
175. (swedish massage or rolfing).tw.
176. therapeutic touch.mp.
177. massotherapy.tw.
178. effleurage.mp.
179. or/149‐178
180. 132 and 179
181. 133 or 134 or 135 or 136 or 137 or 138
182. or/139‐148
183. 59 and 182
184. 180 or 181 or 183
185. randomized controlled trial/
186. controlled clinical trial/
187. (random* or sham or placebo*).tw.
188. placebo/
189. randomization/
190. single blind procedure/
191. double blind procedure/
192. ((singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) adj5 (blind* or dumm*or mask*)).ti,ab.
193. (rct or rcts).tw.
194. (control* adj2 (study or studies or tiral*)).tw.
195. or/185‐194
196. human/
197. nonhuman/
198. animal/
199. animal experiment/
200. or/197‐199
201. 200 not (200 and 196)
202. 195 not 201
203. 184 and 202
MANTIS‐OVID
November 2013 (last available access)
1 neck pain.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
2 brachial plexus neuropathies.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
3 neck injuries.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
4 cervical pain.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
5 neckache.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
6 whiplash.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
7 cervicodynia.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
8 cervicalgia.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
9 brachialgia.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
10 brachial neuritis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
11 brachial neuralgia.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
12 brachial plexus neuropath*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
13 brachial plexus neuritis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
14 (thoracic outlet syndrome or cervical rib syndrome).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
15 torticollis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
16 cervico brachial neuralgia.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
17 (monoradicul* or monoradicl*).tw.
18 or/1‐17
19 headache.mp. and cervic*.tw. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
20 genital diseases, female.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
21 genital disease*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
22 or/20‐21
23 19 not 22
24 18 or 23
25 neck.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
26 neck muscles.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
27 cervical plexus.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
28 cervical vertebrae.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
29 atlanto‐axial joint.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
30 atlanto‐occipital joint.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
31 cervical atlas.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
32 spinal nerve roots.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
33 brachial plexus.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
34 (odontoid* or cervical or occip* or atlant*).tw.
35 (axis or odontoid process).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
36 thoracic vertebrae.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
37 cervical vertebrae.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
38 cervical plexus.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
39 cervical spine.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
40 (neck adj3 muscles).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
41 (brachial adj3 plexus).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
42 (thoracic adj3 vertebrae).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
43 (thoracic adj3 spine).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
44 (thoracic adj3 outlet).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
45 trapezius.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
46 cervical.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
47 cervico*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
48 46 or 47
49 genital diseases, female.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
50 genital disease*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
51 uterus.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
52 49 or 50 or 51
53 48 not 52
54 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 or 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36
or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 53
55 pain.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
56 injuries.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
57 ache.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
58 sore.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
59 stiff.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
60 discomfort.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
61 injur*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
62 neuropath*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
63 or/55‐62
64 54 and 63
65 radiculopathy.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
66 (temporomandibular joint disorders or temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
67 myofascial pain syndromes.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
68 "sprains and strains".mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
69 spinal osteophytosis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
70 neuritis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
71 polyradiculopathy.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
72 arthritis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
73 fibromyalgia.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
74 (spondylitis or discitis).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
75 (spondylosis or spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
76 radiculitis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
77 tempomandibular.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
78 myofascial pain syndrome*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
79 thoracic outlet syndrome*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
80 spinal osteophytosis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
81 neuritis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
82 spondylosis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
83 spondylitis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
84 spondylolisthesis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
85 or/65‐84
86 54 and 85
87 neck.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
88 cervical vertebrae.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
89 thoracic vertebrae.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
90 (thoracic adj3 vertebrae).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
91 cervical.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
92 cervico*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
93 91 or 92
94 genital diseases, female.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
95 genital disease*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
96 uterus.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
97 or/94‐96
98 93 not 97
99 (thoracic adj3 spine).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
100 cervical spine.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
101 87 or 88 or 89 or 90 or 98 or 99 or 100
102 intervertebral disk.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
103 (disc or discs).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
104 (disk or disks).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
105 102 or 103 or 104
106 101 and 105
107 herniat*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
108 slipped.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
109 prolapse*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
110 displace*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
111 degenerat*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
112 (bulge or bulged or bulging).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
113 107 or 108 or 109 or 110 or 111 or 112
114 106 and 113
115 intervertebral disk displacement.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
116 intervertebral disc displacement.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
117 intervertebral disk degeneration.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
118 intervertebral disc degeneration.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
119 115 or 116 or 117 or 118
120 101 and 119
121 24 or 64 or 86 or 106 or 114 or 120
122 (animals not (animals and humans)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
123 121 not 122
124 neoplasms.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
125 wounds, penetrating.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
126 124 or 125
127 123 not 126
128 rehabilitation.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
129 therapy.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
130 128 or 129
131 (neck pain or brachial plexus neuropathies or neck injuries or whiplash or thoracic outlet syndrome or cervical rib syndrome or torticollis or brachial plexus neuritis).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
132 (temporomandibular joint disorder or temporomandibular joint dysfunction syndrome).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
133 (myofascial pain syndromes or "sprains and strains").mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
134 (radiculopathy or osteophytosis or neuritis or polyradiculopathy or arthritis or fibromyalgia or spondylitis or spondylosis or spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
135 131 or 132 or 133 or 134
136 130 and 135
137 54 and 136
138 (acupuncture or chiropractic).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
139 musculoskeletal manipulation*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
140 massage.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
141 mobili?ation.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
142 acupuncture therapy.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
143 (acupuncture or acu‐puncture or needling or acupressure or mox?bustion).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
144 ((neck or spine or spinal or cervical or chiropractic* or musculoskeletal*) adj3 (adjust* or manipulat* or mobiliz* or mobilis*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
145 (manual adj therap*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
146 (manipulati* adj (therap* or medicine)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
147 (massag* or reflexolog* or rolfing or zone therap*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
148 Nimmo.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
149 vibration therapy.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
150 (vibration adj5 (therap* or treatment*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
151 (ChihYa or Shiatsu or Shiatzu or ZhiYa).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
152 (flexion adj2 distraction*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
153 (myofascial adj3 (release or therap*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
154 muscle energy technique*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
155 trigger point.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
156 proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
157 cyriax friction.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
158 (lomilomi or lomi‐lomi or trager).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
159 aston patterning.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
160 (strain adj counterstrain).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
161 (craniosacraltherap* or cranio‐sacral therap* or craniosacral therap*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
162 (amma or ammo or effleuurage or effleurage or petrissage or hacking or tapotment).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
163 complementary therapies.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
164 ((complement* or alternat* or osteopathic*) adj (therap* or medicine)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
165 (Tui Na or Tuina).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
166 or/138‐165
167 127 and 166
168 136 or 137 or 167
169 (animals not (animals and humans)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
170 168 not 169
171 randomized controlled trial*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
172 controlled clinical trial*.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
173 (random* or sham or placebo*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
174 placebos.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
175 random allocation.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
176 single blind method.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
177 double blind method.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
178 ((singl* or doubl* or trebl* or tripl*) adj25 (blind* or dumm*or mask*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
179 (rct or rcts).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
180 (control* adj2 (study or studies or trial*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
181 or/171‐180
182 170 and 181
183 (guideline* or practice guideline*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
184 (guideline* or guidance* or recommendation*).ti.
185 consensus.ti.
186 183 or 184 or 185
187 170 and 186
188 meta‐analysis.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
189 (metaanaly* or meta analy* or met analy* or metanaly*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
190 (collaborative research or collaborative review* or collaborative overview*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
191 (integrative research or integrative review* or integrative overview*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
192 (quantitative adj3 (research or review* or overview*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
193 (research integration or research overview*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
194 (systematic* adj3 (review* or overview*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
195 (methodologic* adj3 (review* or overview*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
196 technology assessment biomedical.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
197 (hta or thas or technology assessment*).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
198 ((hand adj2 search*) or (manual* adj search*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
199 ((electronic adj database*) or (bibliographic* adj database*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
200 ((data adj2 abstract*) or (data adj2 extract*)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
201 (analys* adj3 (pool or pooled or pooling)).mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
202 mantel haenszel.mp. [mp=title, abstract, descriptors]
203 (cochrane or pubmed or pub med or medline or embase or psycinfo or psyclit or psychinfo or psychlit or cinahl or science citation index).ab.
204 or/188‐203
205 170 and 204
206 182 or 187 or 205
207 limit 206 to yr="2006 ‐Current"
CINAHL‐EBSCO
August 2015
S151 S90 or S104 or S150
S150 S82 and S149
S149 S105 or S106 or S107 or S108 or S109 or S110 or S111 or S112 or S113 or S114 or S115 or S116 or S117 or S118 or S119 or S120 or S121 or S122 or S123 or S124 or S125 or S126 or S127 or S128 or S129 or S130 or S131 or S132 or S133 or S134 or S135 or S136 or S137 or S138 or S139 or S140 or S141 or S142 or S143 or S144 or S145 or S146 or S147 or S148
S148 TX faradic
S147 MH biofeedback
S146 TX Relaxation Therapy
S145 MH Relaxation Therapy
S144 TX alexander N3 technique OR TX alexander N3 method
S143 TX Feldenkrais
S142 TX postur* correction
S141 MH ice
S140 TX Cryoanesthesia
S139 MH Cryoanesthesia
S138 TX vapocoolant spray
S137 (MH "Hyperthermia, Induced")
S136 MH Hydrotherapy
S135 MH cryotherapy
S134 TX repetitive magnetic stimulation
S133 (MH "Physical Therapy+")
S132 (MH "Physical Therapy Modalities+")
S131 MH lasers
S130 (MH "Phototherapy+")
S129 MH Ultrasonic Therapy
S128 (MH "Rehabilitation+")
S127 TX Laser Therapy
S126 (MH "Laser Therapy")
S125 TX traction
S124 MH traction
S123 TX pillow* OR TX collar*
S122 "Occlusal Splints"
S121 TX oral splints
S120 (MH "Periodontal Splints")
S119 TX taping
S118 TX kinesiotaping
S117 (MH "Orthoses")
S116 (MH "Electric Stimulation")
S115 (MH "Magnet Therapy")
S114 MH electromagnetics
S113 (MH "Electromagnetic Fields")
S112 "pulsed electromagnetic field"
S111 TX pulsed electro magnetic field
S110 (MH "Electrical Stimulation, Functional") OR (MH "Electrical Stimulation, Neuromuscular")
S109 (MH "Therapeutic Exercise+")
S108 (MH "Exertion")
S107 (MH "Exercise+")
S106 (MH "Exercise+")
S105 (MH "Combined Modality Therapy+")
S104 S34 and S103
S103 S91 or S92 or S93 or S94 or S95 or S96 or S97 or S98 or S99 or S100 or S101 or S102
S102 (MH "Spondylolisthesis/RH")
S101 (MH "Spondylolysis/RH") OR (MH "Spondylosis/RH")
S100 (MH "Spondylitis, Ankylosing/RH")
S99 (MH "Fibromyalgia/RH")
S98 (MH "Arthritis+/RH")
S97 (MH "Polyradiculopathy/RH")
S96 (MH "Neuritis/RH")
S95 (MH "Spinal Osteophytosis/RH")
S94 (MH "Sprains and Strains/RH")
S93 (MH "Myofascial Pain Syndromes/RH")
S92 (MH "Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome/RH") OR (MH "Temporomandibular Joint Diseases/RH")
S91 (MH "Radiculopathy/RH")
S90 S83 or S84 or S85 or S86 or S87 or S88 or S89
S89 (MH "Brachial Plexus Neuritis/RH")
S88 (MH "Torticollis/RH")
S87 (MH "Thoracic Outlet Syndrome/RH")
S86 (MH "Whiplash Injuries/RH")
S85 (MH "Neck Injuries/RH")
S84 (MH "Brachial Plexus Neuropathies/RH")
S83 (MH "Neck Pain/RH")
S82 S78 NOT S81
S81 S79 or S80
S80 (MM "Pregnancy+")
S79 (MM "Abortion, Induced+")
S78 S74 NOT S77
S77 S75 or S76
S76 (MM "Wounds, Penetrating+")
S75 (MM "Neoplasms+")
S74 S16 or S41 or S56 or S69 or S73
S73 S63 and S72
S72 S70 or S71
S71 TX intervertebral disk displacement or TX intervertebral disc displacement or TX intervertebral disk degeneration or TX intervertebral disc degeneration
S70 (MH "Intervertebral Disk Displacement")
S69 S67 and S68
S68 TX herniat* or TX slipped or TX prolapse* or TX displace* or TX degenerat* or TX ( bulged OR bulge OR bulging )
S67 S63 and S66
S66 S64 or S65
S65 TX disc or TX discs or TX disk or TX disks
S64 (MH "Intervertebral Disk")
S63 S61 NOT S62
S62 (MM "Genital Diseases, Female+") or ( (MM "Cervix") or (MM "Cervix Diseases") )
S61 S57 or S58 or S59 or S60
S60 TX thoracic N3 spine or TX cervical spine or TX cervico*
S59 TX neck or TX thoracic N3 vertebr*
S58 (MH "Thoracic Vertebrae")
S57 (MH "Neck")
S56 S34 and S55
S55 S42 or S43 or S44 or S45 or S46 or S47 or S48 or S49 or S50 or S51 or S52 or S53 or S54
S54 TX neuritis or TX spondylosis or TX spondylitis or TX spondylolisthesis
S53 TX myofascial pain syndome* or TX thoracic outlet syndrome* or TX spinalosteophytosis
S52 TX radiculopathy or TX radiculitis or TX temporomandibular
S51 (MH "Spondylolysis") or (MH "Spondylolisthesis+")
S50 (MH "Fibromyalgia")
S49 (MH "Arthritis+")
S48 (MH "Polyradiculopathy")
S47 (MH "Neuritis+")
S46 (MH "Spinal Osteophytosis")
S45 (MH "Sprains and Strains+")
S44 (MH "Myofascial Pain Syndromes+")
S43 (MH "Temporomandibular Joint Diseases+") or (MH "Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome")
S42 (MH "Radiculopathy")
S41 S34 and S40
S40 S35 or S36 or S37 or S38 or S39
S39 (MH "Neuralgia")
S38 TX stiff or TX discomfort or TX injur* or TX neuropath*
S37 TX pain or TX ache* or TX sore
S36 (MH "Wounds and Injuries+")
S35 (MH "Pain+")
S34 S33 NOT S32
S33 S17 or S18 or S19 or S20 or S21 or S22 or S23 or S24 or S25 or S26 or S27 or S28 or S29 or S30 or S31
S32 (MM "Genital Diseases, Female+") or ( (MM "Cervix") or (MM "Cervix Diseases") )
S31 TX trapezius or TX cervico*
S30 TX thoracic N3 spine or TX thoracic N3 outlet
S29 TX neck
S28 TX thoracic N3 verteb*
S27 TX brachial N3 plexus
S26 TX neck n3 muscles
S25 (MH "Thoracic Vertebrae")
S24 TX ondontoid* or TX cervical or TX occip* or TX atlant*
S23 (MH "Brachial Plexus+")
S22 (MH "Spinal Nerve Roots+")
S21 (MH "Atlanto‐Axial Joint") or (MH "Atlanto‐Occipital Joint")
S20 (MH "Cervical Vertebrae+") or (MH "Cervical Atlas")
S19 (MH "Cervical Plexus+")
S18 (MH "Neck")
S17 (MH "Neck Muscles+")
S16 S10 or S15
S15 S11 NOT S14
S14 S12 or S13
S13 (MM "Cervix") or (MM "Cervix Diseases")
S12 (MM "Genital Diseases, Female+")
S11 (MH "Headache+") and TX cervic*
S10 S1 or S2 or S3 or S4 or S5 or S6 or S7 or S8 or S9
S9 (MH "Brachial Plexus Neuritis")
S8 TX cervical brachial neuralgia
S7 TX cervical rib sydrome* or TX cervico brachial neuralgia or TX cervicobrachial neuralgia or TX monoradicul* or TX monoradicl*
S6 (MH "Thoracic Outlet Syndrome") or (MH "Torticollis")
S5 TX brachial neuralgia or TX neck pain or TX neck injur* or TX brachial plexus neuropath* or TX brachial plexus neuralgia or TX brachial plexus neuritis
S4 TX cervicalgia or TX brachialgia or TX brachial neuritis
S3 TX cervical pain or TX neckache or TX neck ache or TX whiplash or TX cervicodynia
S2 (MH "Neck Injuries+")
S1 (MH "Neck Pain") or (MH "Brachial Plexus Neuropathies") or (MH "Brachial Plexus Neuritis")
ICL
August 2015
S1 Subject:"Neck Pain" OR Subject:"Brachial Plexus Neuritis" OR All Fields:"brachial plexus neuropathies"
S2 All Fields:brachial plexus neuropathy
S4 Subject:"Neck Injuries" OR Subject:"Whiplash Injuries" OR Subject:"Cervical Vertebrae / abnormalities"
S5 All Fields:"cervical pain" OR All Fields:neckache OR All Fields:whiplash
S6 All Fields:cervicodynia OR All Fields:cervicalgia OR All Fields:brachialgia
S7 All Fields:"brachial neuritis" OR All Fields:"brachial neuralgia" OR All Fields:"neck pain"
S8 Subject:"Thoracic Outlet Syndrome" OR Subject:"Torticollis" OR All Fields:cervical rib syndrom*
S11 All Fields:cerv* AND All Fields:headache*
S12 All Fields:monoradicul* OR All Fields:monoradicl*
S13 S1 OR S2 OR S4 OR S5 OR S6 OR S7 OR S8 OR S11 OR S12
S14 Subject:"Neck" OR Subject:"Neck Muscles" OR Subject:"Cervical Vertebrae"
S16 Subject:"Cervical Atlas" OR Subject:"Atlanto‐Axial Joint" OR Subject:"Atlanto‐Occipital Joint"
S17 Subject:"Atlas" OR Subject:"Spinal Nerve Roots" OR All Fields:"brachial plexus"
S18 All Fields:ondontoid* OR All Fields:occip* OR All Fields:atlant*
S20 Subject:"Odontoid Process" OR Subject:"Thoracic Vertebrae" OR All Fields:"cervical vertebrae"
S21 All Fields:"cervical spine" OR All Fields:trapezius OR All Fields:cervico*
S22 S14 OR S16 OR S17 OR S18 OR S20 OR S21
S23 Subject:"Pain" OR All Fields:sore OR All Fields:stiff
S24 All Fields:ache OR All Fields:pain OR All Fields:discomfort
S25 All Fields:injur* OR All Fields:neuropath*
S26 S23 OR S24 OR S25
S27 S22 AND S26
S28 Subject:"Radiculopathy" OR Subject:"Temporomandibular Joint Disorders" OR Subject:"Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction Syndrome"
S30 Subject:"Myofascial Pain Syndromes" OR Subject:"Sprains and Strains" OR Subject:"Spinal Osteophytosis"
S31 Subject:"Neuritis" OR Subject:"Polyradiculoneuritis" OR Subject:"Arthritis"
S32 Subject:"Fibromyalgia" OR Subject:"Discitis" OR Subject:"Spondylitis"
S33 Subject:"Spondylolisthesis" OR Subject:"Spondylolysis" OR Subject:"Spondylosis"
S34 S28 OR S30 OR S31 OR S32 OR S33
S35 S22 AND S34
S36 Subject:"Neck" OR Subject:"Cervical Vertebrae" OR Subject:"Thoracic Vertebrae"
S37 All Fields:"thoracic spine" OR All Fields:"cervical spine" OR All Fields:cervico*
S38 S36 OR S37
S39 All Fields:herniat* OR All Fields:slipped OR All Fields:prolapse*
S40 All Fields:displace* OR All Fields:degenerat*
S41 All Fields:bulge OR All Fields:bulged OR All Fields:bulging
S42 S39 OR S40 OR S41
S43 S38 AND S42
S44 Subject:"Intervertebral Disk Displacement" OR All Fields:"intervertebral disk degeneration" OR All Fields:"intervertebral disc degeneration"
S45 All Fields:"Intervertebral Disk Displacement" OR All Fields:"intervertebral disc displacement"
S46 S44 OR S45
S47 S38 AND S46
S48 S13 OR S27 OR S35 OR S43 OR S47
S49 Year: from 2014 to 2015
S50 S48 AND S49
S51 Subject:"Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic" OR Subject:"Controlled Clinical Trials" OR Subject:"Placebos"
S52 All Fields:random* OR All Fields:sham OR All Fields:placebo*
S53 All Fields:clinical trial* OR All Fields:"controlled study" OR All Fields:"controlled studies"
S54 All Fields:RCT OR All Fields:RCTs
S55 S51 OR S52 OR S53 OR S54
S56 S50 AND S55
Appendix 2. Criteria for assessing risk of bias for internal validity
Random sequence generation (selection bias)
Selection bias (biased allocation to interventions) due to inadequate generation of a randomised sequence
Risk of selection bias is low if investigators describe a random component in the sequence generation process such as referring to a random number table, using a computer random number generator, tossing a coin, shuffling cards or envelopes, throwing dice, drawing lots and minimising (minimisation may be implemented without a random element, and this is considered to be equivalent to being random).
Risk of selection bias is high if investigators describe a non‐random component in the sequence generation process such as sequence generated by odd or even date of birth, date (or day) of admission, hospital or clinic record number; or allocation by judgement of the clinician, preference of the participant, results of a laboratory test or series of tests, or availability of the intervention.
Allocation concealment (selection bias)
Selection bias (biased allocation to interventions) due to inadequate concealment of allocations before assignment
Risk of selection bias is low if participants and investigators enrolling participants could not foresee assignment because one of the following, or an equivalent method, was used to conceal allocation: central allocation (including telephone, web‐based and pharmacy‐controlled randomisation); sequentially numbered drug containers of identical appearance; or sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes.
Risk of bias is high if participants or investigators enrolling participants could possibly foresee assignments and thus introduce selection bias, such as allocation based on using an open random allocation schedule (e.g. list of random numbers); assignment envelopes were used without appropriate safeguards (e.g. if envelopes were unsealed or non‐opaque or not sequentially numbered); alternation or rotation; date of birth; case record number; or other explicitly unconcealed procedures.
Blinding of participants
Performance bias due to knowledge of allocated interventions by participants during the study
Risk of performance bias is low if blinding of participants was ensured and it was unlikely that blinding could have been broken; or if no blinding or incomplete blinding was provided but the review authors judged that the outcome is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding.
Blinding of personnel/care providers (performance bias)
Performance bias due to knowledge of allocated interventions by personnel/care providers during the study
Risk of performance bias is low if blinding of personnel was ensured and it was unlikely that blinding could have been broken; or if no blinding or incomplete blinding was provided but the review authors judged that the outcome is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding.
Blinding of outcome assessor (detection bias)
Detection bias due to knowledge of allocated interventions by outcome assessors
Risk of detection bias is low if blinding of the outcome assessment was ensured and it was unlikely that blinding could have been broken; or if no blinding or incomplete blinding was provided but the review authors judged that the outcome is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding, or:
-
for patient‐reported outcomes in which the participant was the outcome assessor (e.g. pain, disability): Risk of bias for outcome assessors is low if risk of bias for participant blinding is low (Boutron 2005);
-
for outcome criteria that are clinical or therapeutic events that will be determined by the interaction between participants and care providers (e.g. co‐interventions, length of hospitalisation, treatment failure), in which the care provider is the outcome assessor: Risk of bias for outcome assessors is low if risk of bias for care providers is low (Boutron 2005); and
-
for outcome criteria that are assessed from data from medical forms: Risk of bias is low if the treatment or adverse effects of the treatment could not be noticed in the extracted data (Boutron 2005).
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias)
Attrition bias due to amount, nature or handling of incomplete outcome data
Risk of attrition bias is low if no outcome data were missing; reasons for missing outcome data were unlikely to be related to the true outcome (for survival data, censoring is unlikely to be introducing bias); missing outcome data were balanced in numbers, with similar reasons for missing data across groups; for dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with the observed event risk was not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on the intervention effect estimate; for continuous outcome data, the plausible effect size (difference in means or standardised difference in means) among missing outcomes was not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on observed effect size, or missing data were imputed using appropriate methods (if drop‐outs were very large, imputation using even 'acceptable' methods may still suggest high risk of bias) (van Tulder 2003). The percentage of withdrawals and drop‐outs should not exceed 20% for short‐term follow‐up and 30% for long‐term follow‐up and should not lead to substantial bias (these percentages are commonly used but arbitrary and are not supported by the literature) (van Tulder 2003).
Selective reporting (reporting bias)
Reporting bias due to selective outcome reporting
Risk of reporting bias is low if the study protocol is available and all of the study's pre‐specified (primary and secondary) outcomes of interest in the review have been reported in the pre‐specified way, or if the study protocol is not available but it is clear that published reports include all expected outcomes, including those that were pre‐specified (convincing text of this nature may be uncommon).
Risk of reporting bias is high if not all of the study's pre‐specified primary outcomes have been reported; one or more primary outcomes were reported using measurements, analysis methods or subsets of the data (e.g. subscales) that were not pre‐specified; one or more reported primary outcomes were not pre‐specified (unless clear justification for their reporting is provided, such as an unexpected adverse effect); one or more outcomes of interest in the review were reported incompletely so that they cannot be entered into a meta‐analysis; or the study report fails to include results for a key outcome that would be expected to have been reported for such a study.
Group similarity at baseline (selection bias)
Bias due to dissimilarity at baseline for the most important prognostic indicators.
Risk of bias is low if groups were similar at baseline for demographic factors, value of main outcome measure(s) and important prognostic factors (examples in the field of back and neck pain are duration and severity of complaints, vocational status and percentage of participants with neurological symptoms) (van Tulder 2003).
Co‐interventions (performance bias)
Bias because co‐interventions were different across groups
Risk of bias is low if no co‐interventions were provided, or if they were similar between index and control groups (van Tulder 2003).
Compliance (performance bias)
Bias due to inappropriate compliance with interventions across groups
Risk of bias is low if compliance with the interventions was acceptable and was based on reported intensity/dosage, duration, number and frequency for both index and control intervention(s). For single‐session interventions (e.g. surgery), this item is irrelevant (van Tulder 2003).
Intention‐to‐treat analysis
Risk of bias is low if all randomised participants were reported/analysed in the group to which they were allocated by randomisation.
Timing of outcome assessments (detection bias)
Bias because important outcomes were not measured at the same time across groups
Risk of bias is low if all important outcome assessments for all intervention groups were measured at the same time (van Tulder 2003).
Other bias
Bias due to problems not covered elsewhere in the table
Risk of bias is low if the study appears to be free of other sources of bias not addressed elsewhere (e.g. study funding).
Appendix 3. Questions for clinical relevance
-
Are patients described in sufficient detail that you can decide whether they are comparable with those whom you see in your practice?
-
Are interventions and treatment settings described well enough that you can provide the same for your patients?
-
Were all clinically relevant outcomes measured and reported?
-
Is the size of the effect clinically important?
-
Are likely treatment benefits worth potential harms?
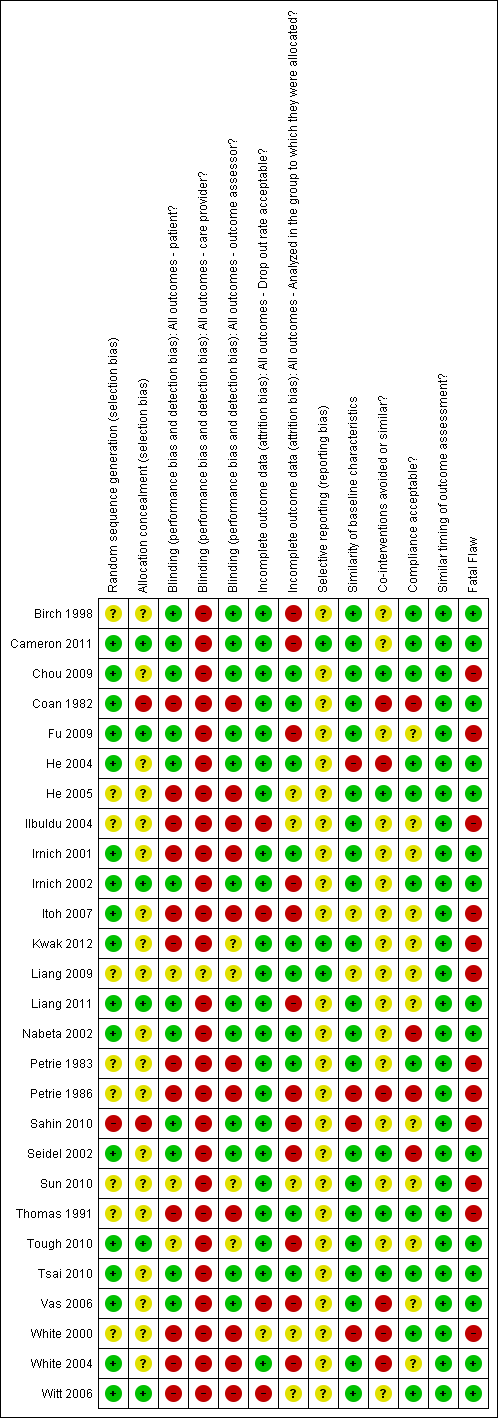
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 1 Pain intensity (VAS) immediate post treatment.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 2 Pain intensity (VAS) short term.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 3 Pain intensity (VAS) intermediate term.
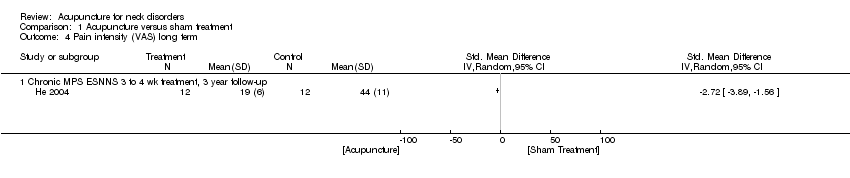
Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 4 Pain intensity (VAS) long term.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 5 Disability (NDI) immediate post treatment.
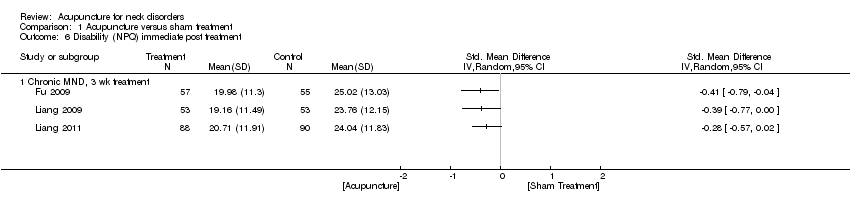
Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 6 Disability (NPQ) immediate post treatment.
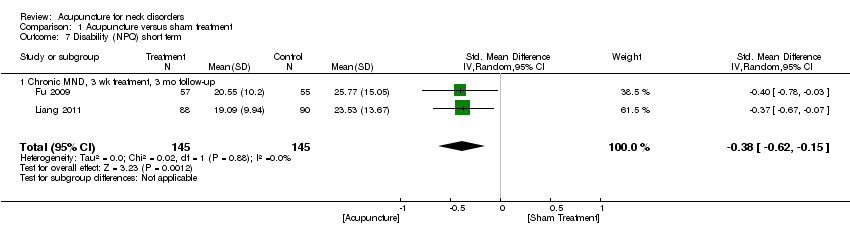
Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 7 Disability (NPQ) short term.
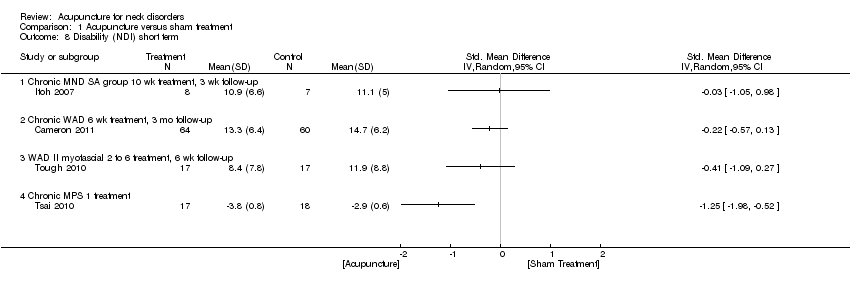
Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 8 Disability (NDI) short term.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 9 Disability (NDI) intermediate term.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 10 Quality of life (SF‐36) immediate post treatment.

Comparison 1 Acupuncture versus sham treatment, Outcome 11 Quality of life (SF‐36) short term.
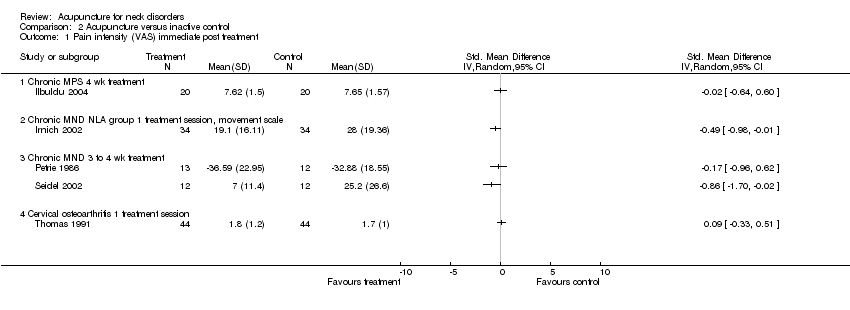
Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 1 Pain intensity (VAS) immediate post treatment.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 2 Pain intensity (VAS) short term.
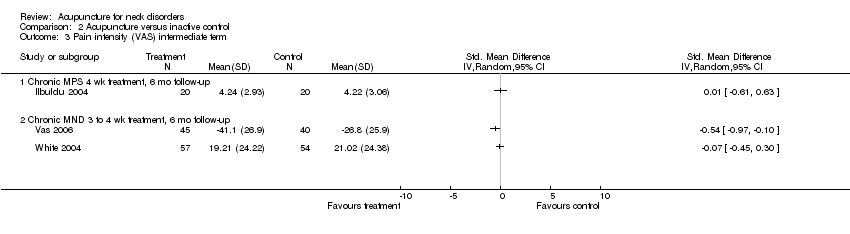
Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 3 Pain intensity (VAS) intermediate term.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 4 Pain intensity (VAS) long term.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 5 Pain pressure threshold immediate post treatment.
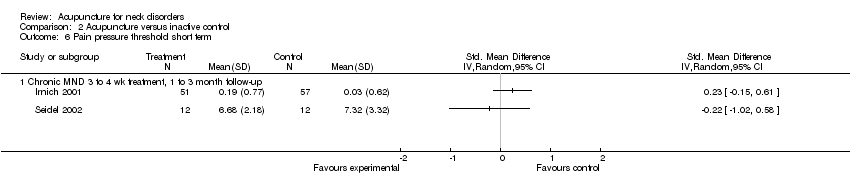
Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 6 Pain pressure threshold short term.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 7 Pain intensity (proportion pain relief) immediate post treatment.
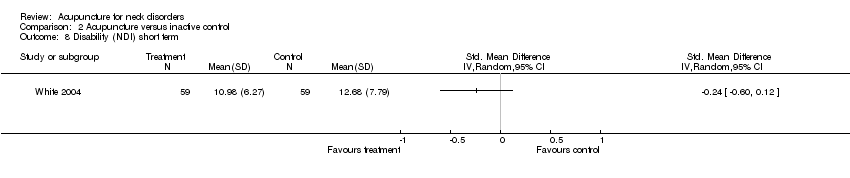
Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 8 Disability (NDI) short term.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 9 Disability (NDI) intermediate term.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 10 Disability (NDI) long term.
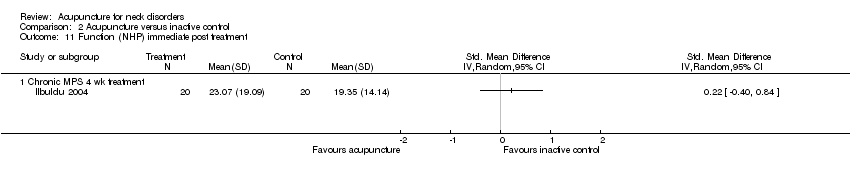
Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 11 Function (NHP) immediate post treatment.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 12 Function (NHP) intermediate term.

Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 13 Function (NPQ) short term.
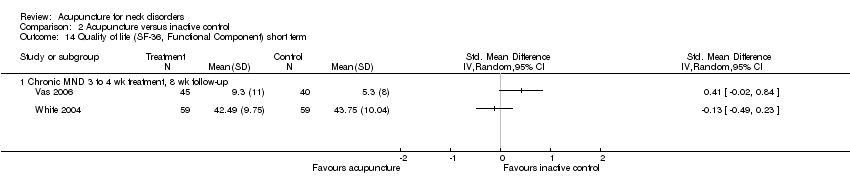
Comparison 2 Acupuncture versus inactive control, Outcome 14 Quality of life (SF‐36, Functional Component) short term.
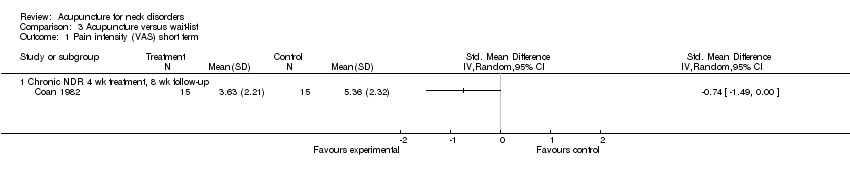
Comparison 3 Acupuncture versus wait‐list, Outcome 1 Pain intensity (VAS) short term.

Comparison 3 Acupuncture versus wait‐list, Outcome 2 Disability (neck and pain disability scale) short term.
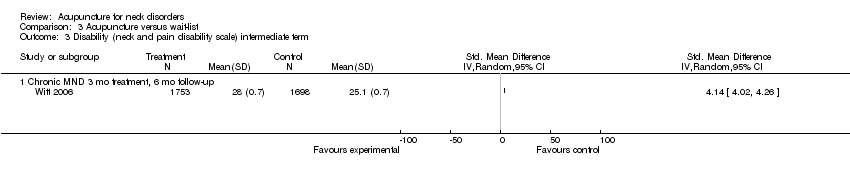
Comparison 3 Acupuncture versus wait‐list, Outcome 3 Disability (neck and pain disability scale) intermediate term.

Comparison 3 Acupuncture versus wait‐list, Outcome 4 Quality of life (SF‐36 mental score) short term.

Comparison 3 Acupuncture versus wait‐list, Outcome 5 Quality of life (SF‐36 mental score) intermediate term.

Comparison 3 Acupuncture versus wait‐list, Outcome 6 Quality of life (SF‐36 physical score) intermediate term.
| Acupuncture compared with sham for chronic neck pain | ||||||
| Patient or population: patients with chronic mechanical neck pain (pain for more than 90 days) Settings: varied, mostly at university or hospital clinics Intervention: acupuncture Comparison: sham | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Sham | Acupuncture | |||||
| Pain intensity (VAS) short term | Mean pain intensity ranged across sham groups from 3 points on a 0 to 10 scale to 47 points on a 0 to 100 scale | Mean pain intensity in intervention groups was 0.23 standard deviations lower (0.20 to 0.07 higher) | ‐0.23 (‐0.20 to ‐0.07) | 560 (8 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Limitations: ‐1 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: 0 Imprecision: 0 Other: 0 | Statistical pooling was appropriate in this instance because of statistical homogeneity. Results of the meta‐analysis favoured acupuncture |
| Disability (NPQ) short term | Mean disability ranged across control groups from 24 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 26 points on a 0 to 100 scale | Mean disability in intervention groups was | ‐0.38 (‐0.62 to ‐0.15) | 290 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Limitations: ‐1 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: 0 Imprecision: ‐1 Other: 0 | Two small trials were in favour of acupuncture. On the basis of the GRADE scale, quality level of evidence was downgraded to low because only 1 of the 2 studies (50%) was at low risk with small sample size |
| Disability (NDI) short term | Mean disability ranged across control groups from | Mean disability in intervention groups ranged from | ‐‐ | 173 | N/A | All 3 studies, 2 with low risk of bias, did not show a statistically significant result in favour of acupuncture |
| Quality of life (SF‐36) short term | Mean quality of life across control groups ranged from 86 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 86 points on a 0 to 100 scale | Mean quality of life in intervention groups ranged from 84 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 85 points on a 0 to 100 scale | ‐‐ | 178 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Limitations: 0 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: ‐1 Imprecision: ‐1 Other: 0 | One study with low risk of bias favoured acupuncture |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI) | ||||||
| Adverse effects were reported in 14 studies and included increased pain, bruising, fainting, worsening of symptoms, local swelling and dizziness. No life‐threatening adverse effects were noted by these studies. GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| Acupuncture compared with inactive treatments for chronic neck pain | ||||||
| Patient or population: patients with chronic neck pain (pain for more than 90 days) Settings: primary care, general practitioners' clinics to secondary care, outpatient pain clinics or speciality clinics Intervention: acupuncture Comparison: inactive treatments | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Inactive treatment | Acupuncture | |||||
| Pain intensity (VAS) short term | Mean pain intensity ranged across control groups from 17 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 31 points on a 0 to 100 scale | Mean pain intensity in intervention groups was 17 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 9 points on a 0 to 10 scale | ‐‐ | 404 (5 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Limitations: 0 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: 0 Imprecision: ‐1 Other: 0 | Five studies (n = 461) assessed participants with mechanical neck disorders. Four were at low risk of bias. Statistical pooling was inappropriate in this instance because of statistical heterogeneity. Four of these studies favoured acupuncture |
| Pain pressure threshold short term | Mean pain pressure threshold ranged across control groups from 0 points on a 0 to 10 scale to 7 points on a 0 to 10 scale | Mean pain pressure threshold in intervention groups ranged from 0.2 points on a 0 to 10 scale to 7 points on a 0 to 10 scale | ‐‐ | 132 (2 studies) | N/A | Two studies with low risk of bias did not favour acupuncture |
| Disability (NDI) short term Function (NPQ) short term | Mean disability ranged across control groups from 12 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 13 points on a 0 to 100 scale Mean function across control groups was 13 points on a 0 to 100 scale | Mean disability in intervention groups ranged from Mean function in intervention groups was 30 points on a 0 to 100 scale | ‐‐ | 118 (1 study) 123 (1 study) | N/A ⊕⊕⊝⊝ Limitations: 0 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: ‐1 Imprecision: ‐1 Other: 0 | One study with low risk of bias did not favour acupuncture One study with low risk of bias favoured acupuncture |
| Quality of life (SF‐36, Functional Component) short term | Mean function ranged across control groups from 0.7 points on a 0 to 10 scale to 5 points on a 0 to 10 scale | Mean function in intervention groups ranged from 41 points on a 0 to 100 scale to 9 points on a 0 to 10 scale | ‐‐ | 143 (2 studies) | N/A | Two studies with low risk of bias did not favour acupuncture |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI) | ||||||
| Adverse effects were reported in 14 studies and included increased pain, bruising, fainting, worsening of symptoms, local swelling and dizziness. No life‐threatening adverse effects were noted by these studies. GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| Acupuncture compared with wait‐list control for chronic neck pain | ||||||
| Patient or population: patients with chronic neck pain (pain for more than 90 days) Settings: primary care newspaper advertisement or recruited through participating physicians Intervention: acupuncture Comparison: wait‐list control | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect | Number of participants | Quality of the evidence | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Wait‐list control | Acupuncture | |||||
| Pain intensity (VAS) short term | Mean pain intensity across control groups was 5 points on a 0 to 10 scale | Mean pain intensity in intervention groups was | ‐‐ | 30 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Limitations: 0 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: ‐1 Imprecision: 0 Other: 0 | One trial with low risk of bias showed a small reduction in pain. Moderate evidence supporting acupuncture is helpful |
| Disability (neck and pain disability scale) short term | Mean disability across control groups was | Mean disability in intervention groups was 29 points on a 0 to 100 scale | ‐‐ | 3451 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Limitations: 0 Inconsistency: 0 Indirectness: ‐1 Imprecision: 0 Other: 0 | One large study with low risk of bias favoured acupuncture |
| Quality of life (SF‐36 mental score) short term | Mean quality of life score across control groups was | Mean quality of life score in intervention groups was 4 points on a 0 to 10 scale | ‐‐ | 3451 (1 study) | N/A | One large study showed no statistically significant findings in favour of acupuncture |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI) | ||||||
| Adverse effects were reported in 14 studies and included increased pain, bruising, fainting, worsening of symptoms, local swelling and dizziness. No life‐threatening adverse effects were noted by these studies Cost of care was calculated in 1 study, which found that acupuncture treatment was cost‐effective GRADE Working Group grades of evidence | ||||||
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain intensity (VAS) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 11 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Chronic MPS 1 treatment session | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment | 4 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 Chronic MPS 12 wk treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.4 Chronic MND SA group 10 wk treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.5 Cervical osteoarthritis 1 treatment session | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.6 Chronic MPS 3 wk treatment, pain with movement scale | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Pain intensity (VAS) short term Show forest plot | 8 | 560 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.23 [‐0.40, ‐0.07] |
| 2.1 Chronic MPS 3 wk treatment, 3 mo follow‐up, pain with movement scale | 1 | 34 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.67, 0.67] |
| 2.2 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 1 to 4 wk follow‐up | 1 | 34 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.15 [‐0.82, 0.52] |
| 2.3 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 3 | 319 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.18 [‐0.40, 0.04] |
| 2.4 Subacute/chronic WAD 6 wk treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 1 | 124 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.38 [‐0.73, ‐0.02] |
| 2.5 WAD myofascial 2 to 6 sessions, 6 wk follow‐up | 1 | 34 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.60 [‐1.29, 0.09] |
| 2.6 Chronic MND SA group 10 wk treatment, 3 wk follow‐up | 1 | 15 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.10 [‐1.11, 0.92] |
| 3 Pain intensity (VAS) intermediate term Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Chronic MPS ESNS 3 to 4 wk treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 Chronic WAD 6 wk treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Pain intensity (VAS) long term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Chronic MPS ESNNS 3 to 4 wk treatment, 3 year follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Disability (NDI) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 Chronic MND SA group 10 wk treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Disability (NPQ) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 3 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.1 Chronic MND, 3 wk treatment | 3 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7 Disability (NPQ) short term Show forest plot | 2 | 290 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.38 [‐0.62, ‐0.15] |
| 7.1 Chronic MND, 3 wk treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 2 | 290 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.38 [‐0.62, ‐0.15] |
| 8 Disability (NDI) short term Show forest plot | 4 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8.1 Chronic MND SA group 10 wk treatment, 3 wk follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8.2 Chronic WAD 6 wk treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8.3 WAD II myofascial 2 to 6 treatment, 6 wk follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8.4 Chronic MPS 1 treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 9 Disability (NDI) intermediate term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.1 Chronic WAD 6 wk treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 10 Quality of life (SF‐36) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.1 Chronic MND, 3 wk treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11 Quality of life (SF‐36) short term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11.1 Chronic MND, 3 wk treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain intensity (VAS) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 5 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Chronic MPS 4 wk treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.2 Chronic MND NLA group 1 treatment session, movement scale | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.3 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 1.4 Cervical osteoarthritis 1 treatment session | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Pain intensity (VAS) short term Show forest plot | 5 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 1 to 4 wk follow‐up | 5 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Pain intensity (VAS) intermediate term Show forest plot | 3 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Chronic MPS 4 wk treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3.2 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Pain intensity (VAS) long term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 12 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Pain pressure threshold immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Pain pressure threshold short term Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.1 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 1 to 3 month follow‐up | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 7 Pain intensity (proportion pain relief) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.1 Chronic MND 4 wk treatment | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 8 Disability (NDI) short term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9 Disability (NDI) intermediate term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.1 Chronic MND 4 wk treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 10 Disability (NDI) long term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.1 Chronic MND 4 wk treatment, 12 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 11 Function (NHP) immediate post treatment Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 11.1 Chronic MPS 4 wk treatment | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 12 Function (NHP) intermediate term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 12.1 Chronic MPS 4 wk treatment 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 13 Function (NPQ) short term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 13.1 Chronic MND 1 wk follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 14 Quality of life (SF‐36, Functional Component) short term Show forest plot | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 14.1 Chronic MND 3 to 4 wk treatment, 8 wk follow‐up | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
| 1 Pain intensity (VAS) short term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.1 Chronic NDR 4 wk treatment, 8 wk follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 2 Disability (neck and pain disability scale) short term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.1 Chronic MND 3 mo treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 3 Disability (neck and pain disability scale) intermediate term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.1 Chronic MND 3 mo treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 4 Quality of life (SF‐36 mental score) short term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.1 Chronic MND 3 mo treatment, 3 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 5 Quality of life (SF‐36 mental score) intermediate term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.1 Chronic MND 3 mo treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |
| 6 Quality of life (SF‐36 physical score) intermediate term Show forest plot | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.1 Chronic MND 3 mo treatment, 6 mo follow‐up | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] | |


